Software Tool for Visualization and Validation of Protein Turnover Rates Using Heavy Water Metabolic Labeling and LC-MS
Abstract
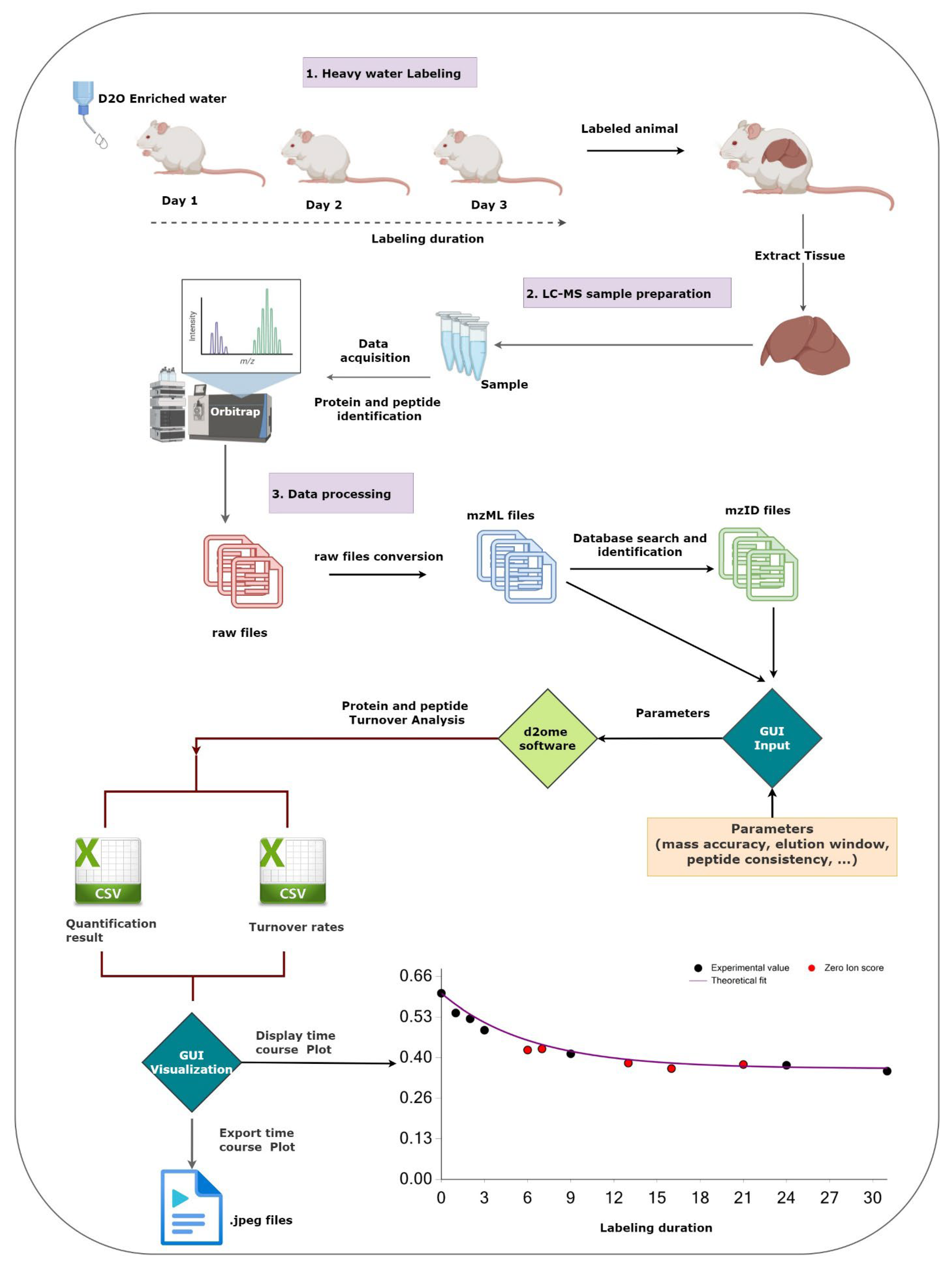
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
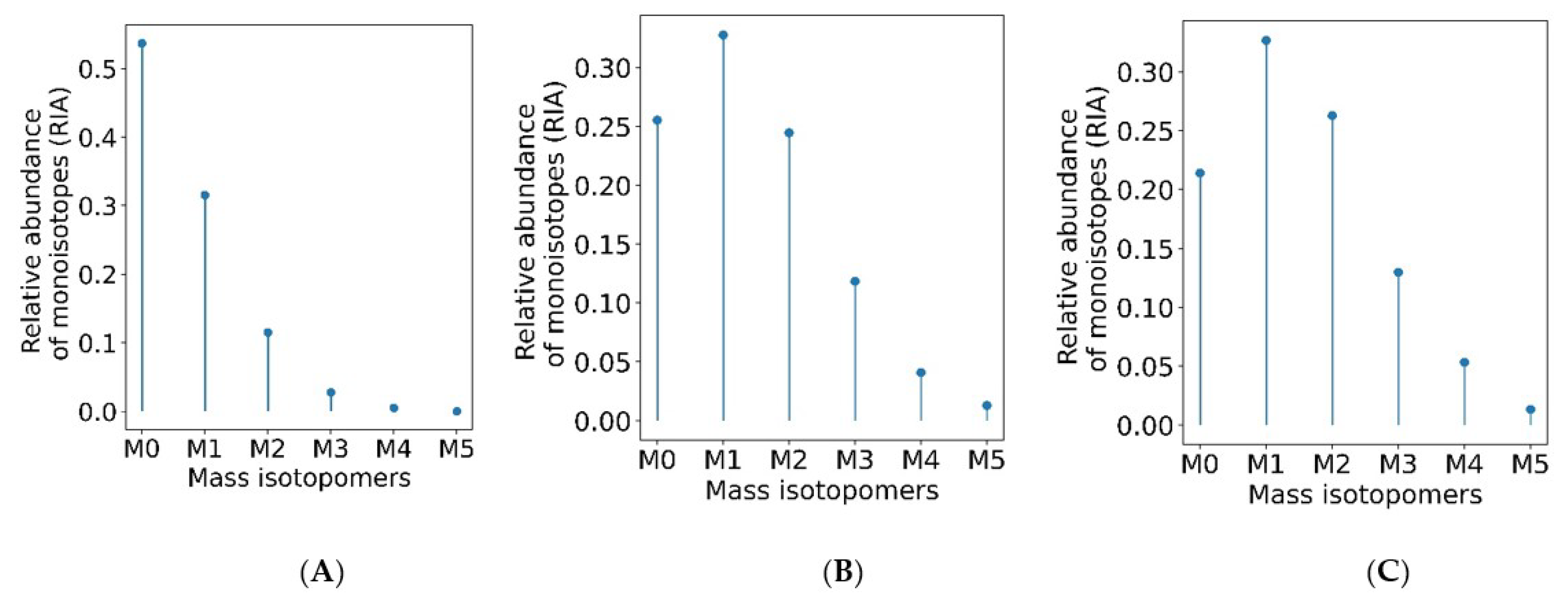
2.1. Data Input and Data Processing Parameters
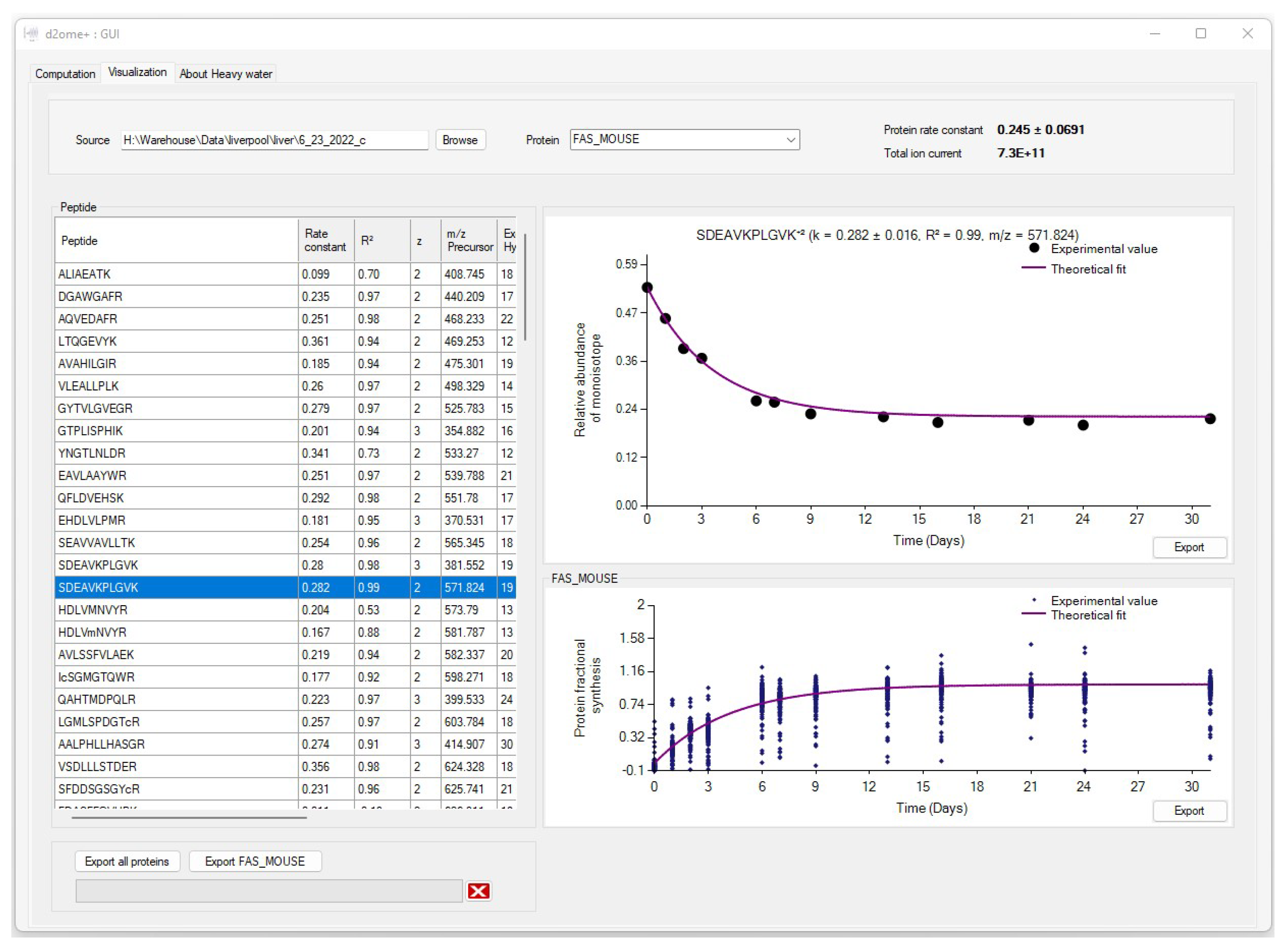
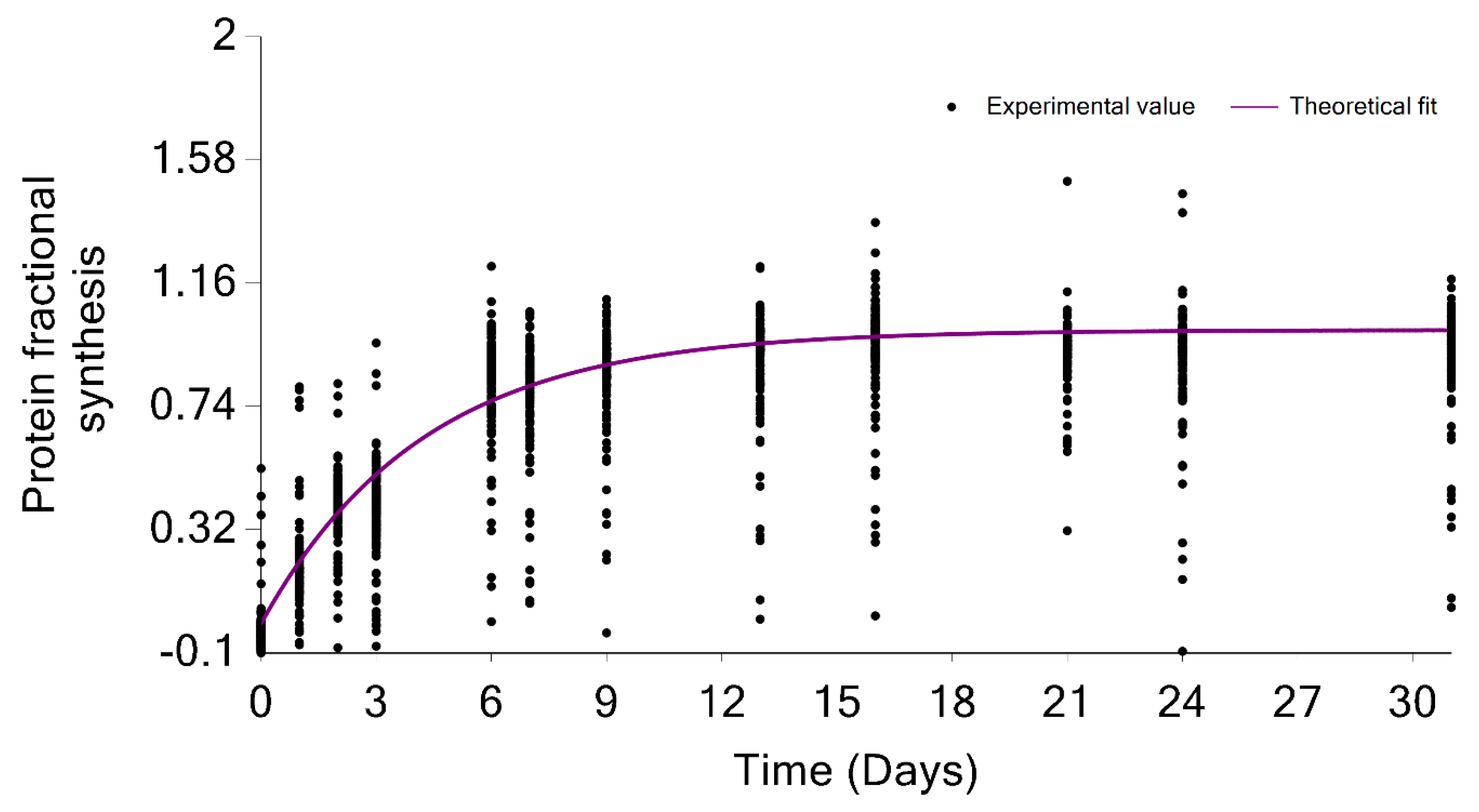
2.2. The Output of Data Processing
2.3. Visualization of the Results
2.4. Future Plans
3. Methods
Data Used in This Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fornasiero, E.F.; Savas, J.N. Determining and interpreting protein lifetimes in mammalian tissues. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadygov, R.G. Protein turnover models for LC-MS data of heavy water metabolic labeling. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, W.E.; Angel, T.E.; Li, K.W.; Hellerstein, M.K. Dynamic Proteomics: In Vivo Proteome-Wide Measurement of Protein Kinetics Using Metabolic Labeling. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 561, 219–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Busch, R.; Kim, Y.K.; Neese, R.A.; Schade-Serin, V.; Collins, M.; Awada, M.; Gardner, J.L.; Beysen, C.; Marino, M.E.; Misell, L.M.; et al. Measurement of protein turnover rates by heavy water labeling of nonessential amino acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.J.; Narayan, V.; Wong, Y.; Seitzer, P.; Sandoval, C.M.; Haste, N.; Smith, M.; Rad, R.; Gaun, A.; Baker, A.; et al. Precise Estimation of In Vivo Protein Turnover Rates. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadygov, R.G. Partial Isotope Profiles Are Sufficient for Protein Turnover Analysis Using Closed-Form Equations of Mass Isotopomer Dynamics. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14747–14753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D.E.; Simpson, D.M.; Franco, C.; Wright Muelas, M.; Waters, J.; Ludwig, R.W.; Prescott, M.C.; Hurst, J.L.; Beynon, R.J.; Lau, E. Harmonizing Labeling and Analytical Strategies to Obtain Protein Turnover Rates in Intact Adult Animals. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2022, 21, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepyala, S.R.; Liu, X.; Yang, K.; Wu, Z.; Breuer, A.M.; Cho, J.H.; Li, Y.; Mancieri, A.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. JUMPt: Comprehensive Protein Turnover Modeling of In Vivo Pulse SILAC Data by Ordinary Differential Equations. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13495–13504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, B.C.; Porter, M.T.; Wilson, E.; Herring, A.; Lofthouse, S.; Hannemann, A.; Piccolo, S.R.; Rockwood, A.L.; Price, J.C. DeuteRater: A tool for quantifying peptide isotope precision and kinetic proteomics. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadygov, R.G.; Avva, J.; Rahman, M.; Lee, K.; Ilchenko, S.; Kasumov, T.; Borzou, A. d2ome, Software for in Vivo Protein Turnover Analysis Using Heavy Water Labeling and LC-MS, Reveals Alterations of Hepatic Proteome Dynamics in a Mouse Model of NAFLD. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3740–3748, Correction in J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rolfs, Z.; Frey, B.L.; Shi, X.; Kawai, Y.; Smith, L.M.; Welham, N.V. An atlas of protein turnover rates in mouse tissues. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basisty, N.; Shulman, N.; Wehrfritz, C.; Marsh, A.N.; Shah, S.; Rose, J.; Ebert, S.; Miller, M.; Dai, D.F.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; et al. TurnoveR: A Skyline External Tool for Analysis of Protein Turnover in Metabolic Labeling Studies. J. Proteome Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, B.; Tomazela, D.M.; Shulman, N.; Chambers, M.; Finney, G.L.; Frewen, B.; Kern, R.; Tabb, D.L.; Liebler, D.C.; MacCoss, M.J. Skyline: An open source document editor for creating and analyzing targeted proteomics experiments. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martens, L.; Chambers, M.; Sturm, M.; Kessner, D.; Levander, F.; Shofstahl, J.; Tang, W.H.; Rompp, A.; Neumann, S.; Pizarro, A.D.; et al. mzML—A community standard for mass spectrometry data. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2011, 10, R110000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.R.; Eisenacher, M.; Mayer, G.; Kohlbacher, O.; Siepen, J.; Hubbard, S.J.; Selley, J.N.; Searle, B.C.; Shofstahl, J.; Seymour, S.L.; et al. The mzIdentML data standard for mass spectrometry-based proteomics results. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11, M111-014381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perkins, D.N.; Pappin, D.J.; Creasy, D.M.; Cottrell, J.S. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadygov, R.G.; Maroto, F.M.; Huhmer, A.F. ChromAlign: A two-step algorithmic procedure for time alignment of three-dimensional LC-MS chromatographic surfaces. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8207–8217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar]
- Sadygov, V.R.; Zhang, W.; Sadygov, R.G. Timepoint Selection Strategy for In Vivo Proteome Dynamics from Heavy Water Metabolic Labeling and LC-MS. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Paulo, J.A.; Gygi, S.P. Evaluating False Transfer Rates from the Match-between-Runs Algorithm with a Two-Proteome Model. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 4020–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilski, M.J.; Sadygov, R.G. Comparison of Programmatic Approaches for Efficient Accessing to mzML Files. J. Data Min. Genom. Proteom. 2011, 2, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deberneh, H.M.; Sadygov, R.G. Software Tool for Visualization and Validation of Protein Turnover Rates Using Heavy Water Metabolic Labeling and LC-MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314620
Deberneh HM, Sadygov RG. Software Tool for Visualization and Validation of Protein Turnover Rates Using Heavy Water Metabolic Labeling and LC-MS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314620
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeberneh, Henock M., and Rovshan G. Sadygov. 2022. "Software Tool for Visualization and Validation of Protein Turnover Rates Using Heavy Water Metabolic Labeling and LC-MS" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314620
APA StyleDeberneh, H. M., & Sadygov, R. G. (2022). Software Tool for Visualization and Validation of Protein Turnover Rates Using Heavy Water Metabolic Labeling and LC-MS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314620





