A Schematic Approach to Defining the Prevalence of COL VI Variants in Five Years of Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allamand, V.; Briñas, L.; Richard, P.; Stojkovic, T.; Quijano-Roy, S.; Bonne, G. ColVI myopathies: Where do we stand, where do we go? Skelet. Muscle 2011, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graziano, A.; Bianco, F.; D’Amico, A.; Moroni, I.; Messina, S.; Bruno, C.; Pegoraro, E.; Mora, M.; Astrea, G.; Magri, F.; et al. Prevalence of congenital muscular dystrophy in Italy: A population study. Neurology 2015, 84, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Jin, S.-Q.; Yi, J.-F.; Liu, X.-J.; Lyn, H.; Wang, Z.-X.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, J.-X.; Yuan, Y. ‘Target’ and ‘sandwich’ signs in thigh muscles have high diagnostic values for collagen VI-related myopathies. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Lampe, A.; Allsop, J.; Knight, R.; Pane, M.; Kinali, M.; Bonnemann, C.; Flanigan, K.; Lapini, I.; Bushby, K.; et al. Muscle MRI in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2005, 15, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Clements, E.; Offiah, A.; Pichiecchio, A.; Vasco, G.; Bianco, F.; Berardinelli, A.; Manzur, A.; Pane, M.; Messina, S.; et al. Muscle magnetic resonance imaging involvement in muscular dystrophies with rigidity of the spine. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguti, S.; Bolduc, V.; Ala, P.; Turmaine, M.; Bönnemann, C.G.; Muntoni, F.; Zhou, H. Exon-Skipping Oligonucleotides Restore Functional Collagen VI by Correcting a Common COL6A1 Mutation in Ullrich CMD. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, V.; Foley, A.R.; Solomon-Degefa, H.; Sarathy, A.; Donkervoort, S.; Hu, Y.; Chen, G.S.; Sizov, K.; Nalls, M.; Zhou, H.; et al. A recurrent COL6A1 pseudoexon insertion causes muscular dystrophy and is effectively targeted by splice-correction therapies. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e124403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briñas, L.; Richard, P.; Quijano-Roy, S.; Bs, C.G.; Bs, C.L.; Bs, E.L.; Makri, S.; Ferreiro, A.; Bs, S.M.; Topaloglu, H.; et al. Early onset collagen VI myopathies: Genetic and clinical correlations. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eymard, B.; Ferreiro, A.; Yaou, R.B.; Stojkovic, T. Muscle diseases with prominent joint contractures: Main entities and diagnostic strategy. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 69, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, D.; Lampe, A.K.; Barresi, R.; Charlton, R.; Fiorillo, C.; Bonnemann, C.G.; Hudson, J.; Sutton, R.; Lochmuller, H.; Straub, V.; et al. A refined diagnostic algorithm for Bethlem myopathy. Neurology 2008, 70, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.A.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, A.; Jang, S.S.; Lim, B.C.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, J.-I.; et al. Collagen VI-related myopathy: Expanding the clinical and genetic spectrum. Muscle and Nerve 2018, 58, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, B.; Lozano-Arango, A.; Araneda, D.; Cortes, F.; Hervias, C.; Calcagno, G.; Ortega, X.; Castiglioni, C. Collagen VI related myopathies. When to suspect, how to identify. the contribution of muscle magnetic resonance. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2018, 89, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deconinck, N.; Dion, E.; Ben Yaou, R.; Ferreiro, A.; Eymard, B.; Briñas, L.; Payan, C.; Voit, T.; Guicheney, P.; Richard, P.; et al. Differentiating Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and collagen VI-related myopathies using a specific CT scanner pattern. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2010, 20, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deconinck, N.; Richard, P.; Allamand, V.; Behin, A.; Laforet, P.; Ferreiro, A.; de Becdelievre, A.; Ledeuil, C.; Gartioux, C.; Nelson, I.; et al. Bethlem myopathy: Long-term follow-up identifies COL6 mutations predicting severe clinical evolution. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, A.; Wei, C.; Yang, H.; Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Bonnemann, C.; Wu, Q.; Wu, X.; et al. Genetic and clinical findings in a Chinese cohort of patients with collagen VI-related myopathies. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano-Roy, S.; Khirani, S.; Colella, M.; Ramirez, A.; Aloui, S.; Wehbi, S.; de Becdelievre, A.; Carlier, R.; Allamand, V.; Richard, P.; et al. Diaphragmatic dysfunction in Collagen VI myopathies. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2014, 24, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlíková, K.; Skálová, D.; Zídková, J.; Haberlová, J.; Voháňka, S.; Mazanec, R.; Mrázová, L.; Vondráček, P.; Ošlejšková, H.; Zámečník, J.; et al. Muscular dystrophies and myopathies: The spectrum of mutated genes in the Czech Republic. Clin. Genet. 2017, 91, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Quereda, L.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Diaz-Manera, J.; Alonso-Perez, J.; Gallardo, E.; Nascimento, A.; Ortez, C.; Benito, D.N.-D.; Olive, M.; Gonzalez-Mera, L.; et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing in a large cohort of genetically undiagnosed patients with neuromuscular disorders in Spain. Genes 2020, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallamilli, B.R.R.; Chakravorty, S.; Kesari, A.; Tanner, A.; Ankala, A.; Schneider, T.; da Silva, C.; Beadling, R.; Alexander, J.J.; Askree, S.H.; et al. Genetic landscape and novel disease mechanisms from a large LGMD cohort of 4656 patients. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoteli, E.; Soares, P.S.; da Silva, A.M.S.; Camelo, C.G.; Fonseca, A.T.Q.S.M.; Albuquerque, M.A.V.; Moreno, C.A.M.; Neto, O.L.A.; Filho, G.M.N.; Kulikowski, L.D.; et al. Clinical features of collagen VI-related dystrophies: A large Brazilian cohort. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 192, 105734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, W.; Davis, M.R. Facial weakness and eyelid ptosis: Expanding the clinical heterogeneity of Bethlem myopathy from a novel gene mutation. Muscle Nerve. 2017, 55, E2–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todd, J.J.; Sagar, V.; Lawal, T.A.; Allen, C.; Razaqyar, M.S.; Shelton, M.S.; Chrismer, I.C.; Zhang, X.; Cosgrove, M.M.; Kuo, A.; et al. Correlation of phenotype with genotype and protein structure in RYR1-related disorders. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2506–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubegni, A.; Malandrini, A.; Dosi, C.; Astrea, G.; Baldacci, J.; Battisti, C.; Bertocci, G.; Donati, M.A.; Dotti, M.T.; Federico, A.; et al. Next-generation sequencing approach to hyperCKemia: A 2-year cohort study. Neurol. Genet. 2019, 5, e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Aguilera, M.A.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

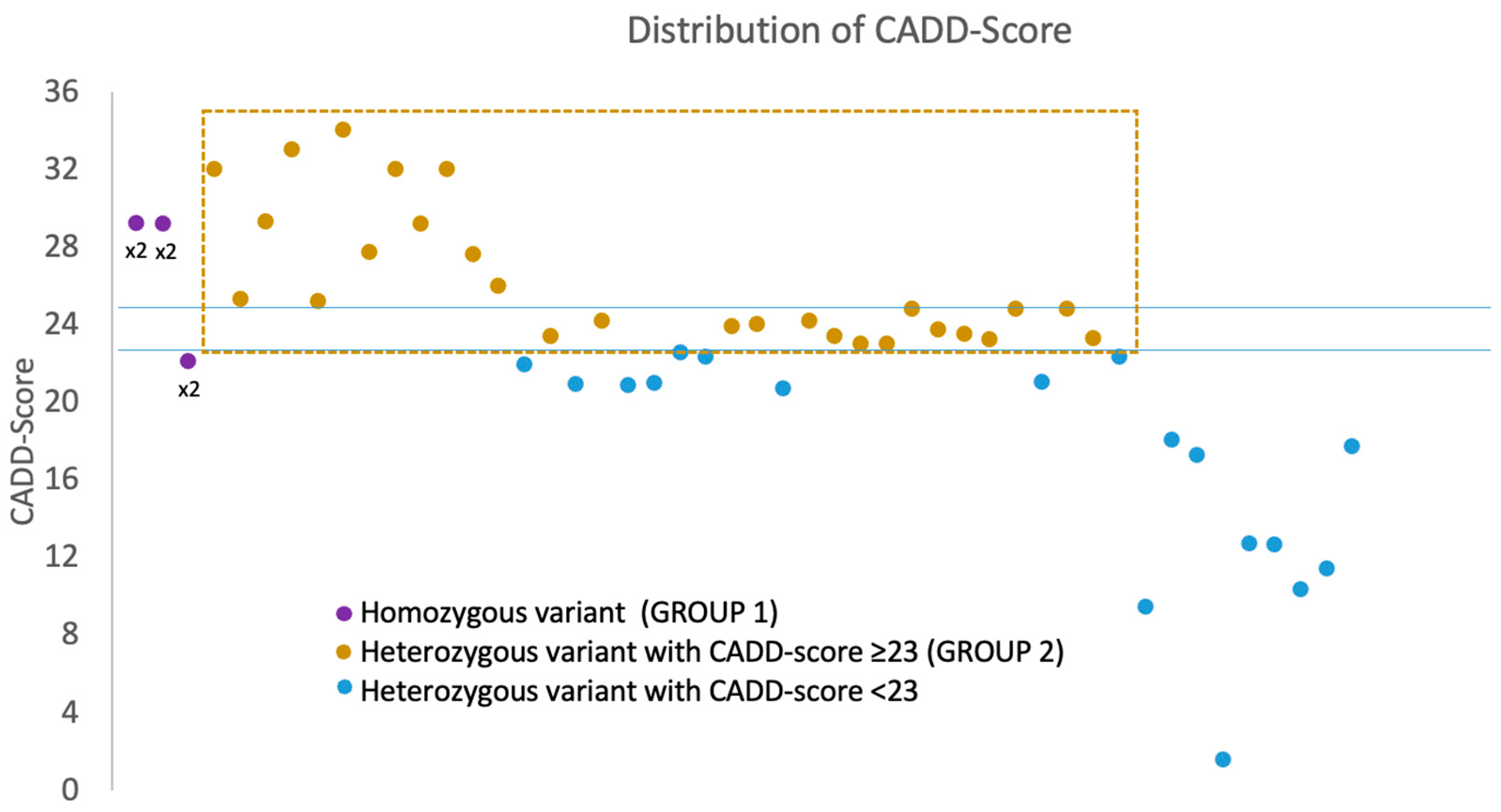
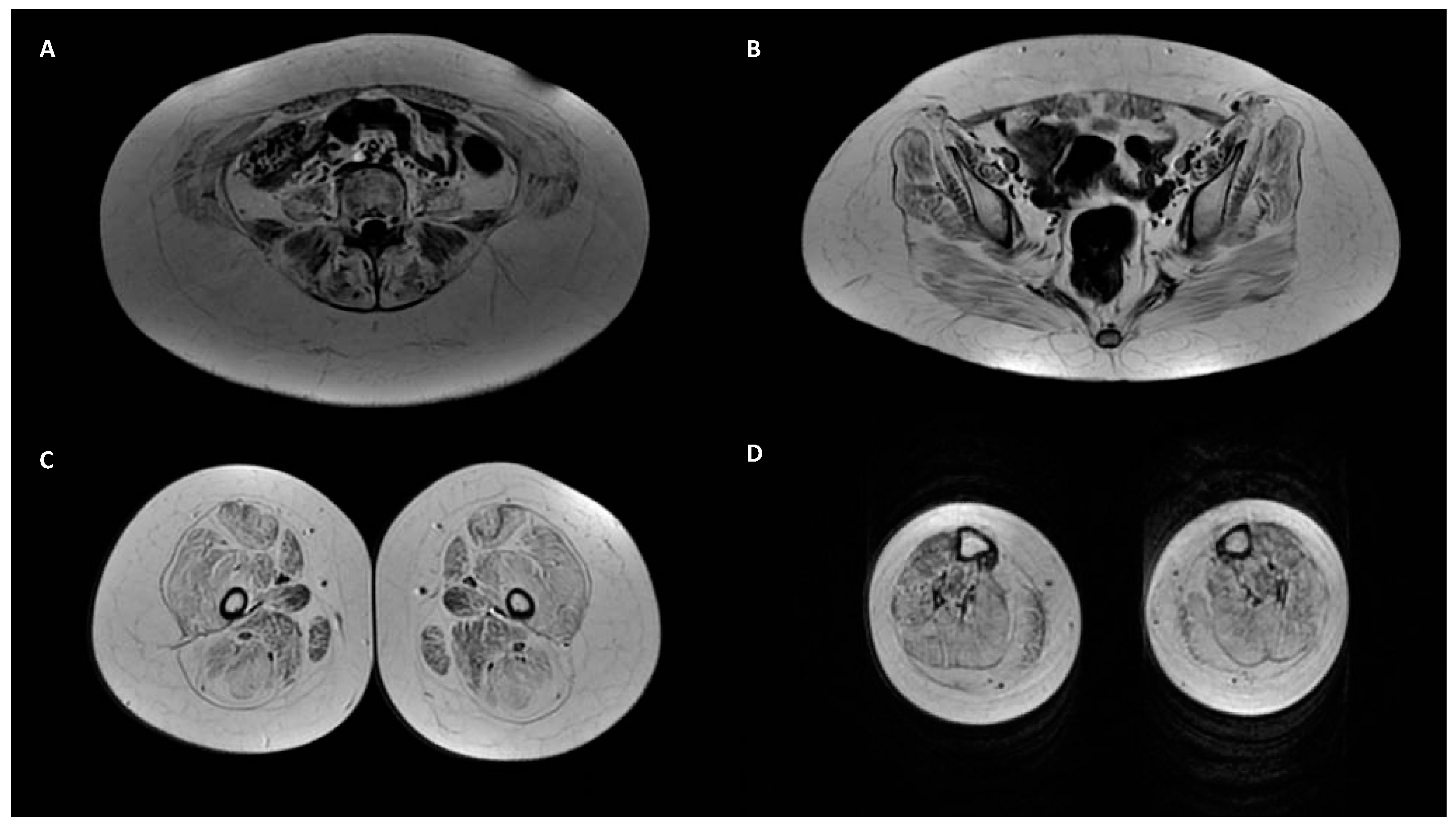
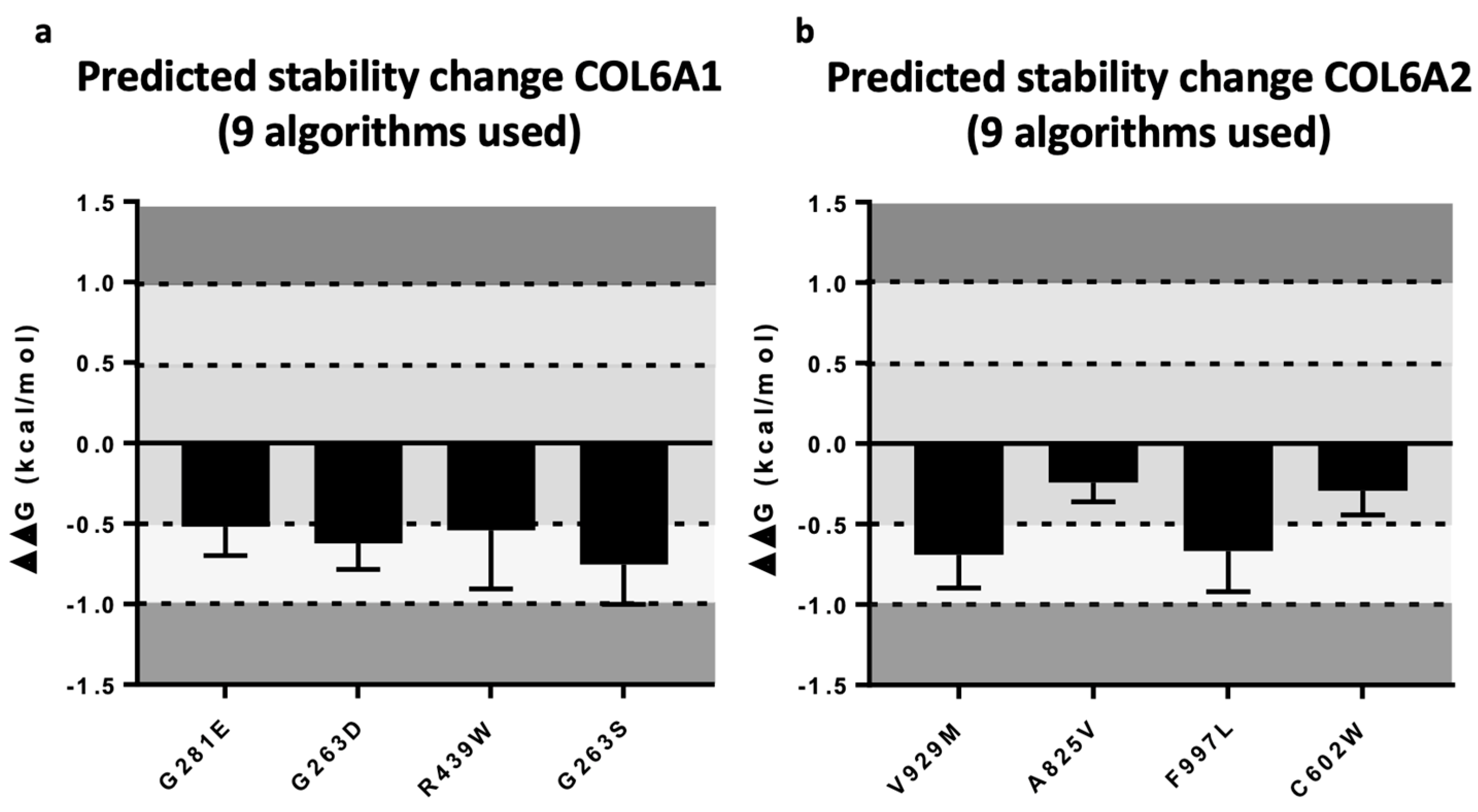
| ID | Age Onset | Gender | Gene | Mutation | CADD-Score | Varsome | Muscle Weakness | Joint Laxity | Contracture or Retraction of Achilleus Tendon | Rigid Spine Scoliosis Hip Alt. | Skin Sign | Lung Alt. | CK Elevation | Muscle Biopsy and COLVI Expression | Skin Biopsy and COLVI Expression | Muscle Magnetic Resonance | Segregation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Congenital | F | COL6A3 | c.7176delG: p.G2392fs* homo | 29.2 | Pathogenic | Global (>shoulder and pelvic girdle) | x | x | x | mild | Myopathic sign; COLVI reduction | Reduction | Typical | Father and mother het | ||
| 2 | Congenital | M | COL6A3 | c.7176delG: p.G2392fs* homo | 29.2 | Pathogenic | Global (>shoulder and pelvic girdle) | x | x | x | x | mild | N/A | N/A | N/A | Father and mother het | |
| 3 | 14 | M | COL6A2 | c.1970-9G>A homo | 22.1 | Likely pathogenic | Pelvic girdle | x | x | x | Normal | N/A | N/A | Typical | Father and mother het | ||
| 4 | 58 | M | COL6A1 | c.3013C>T: p.R1005C | 32 | Uncertain significance | Distal muscles of leg | Normal | Myopathic sign | N/A | Normal | N/A | |||||
| 5 | 60 | M | COL6A2 | c.2474C>T: p.A825V | 25.3 | Uncertain significance | Global | Normal | Myopathic sign; COLVI normal | N/A | Normal | N/A | |||||
| 6 | N/A | F | COL6A2 | c.791G>A: p.R264H | 29.3 | Likely Pathogenic | Myalgia, generalized asthenia | x | Normal | N/A | N/A | Atypical | N/A | ||||
| 7 | 44 | M | COL6A2 | c.2461+1G>A | 33 | Pathogenic | Shoulder and pelvic girdle (>pelvic) | N/A | Dystrophic signs | N/A | Typical | N/A | |||||
| 8 | 65 | F | COL6A1 | c.3006C>A: p.H1002Q | 25.2 | Uncertain significance | Distal muscles of arm and leg | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 9 | Congenital | F | COL6A3 | c.6210+1G>A | 34 | Pathogenetic | Global (>shoulder and pelvic girdle) | x | mild | Myopathic sign; COLVI reduction | Normal | N/A | N/A | ||||
| 10 | Congenital | M | COL6A1 | c.842G>A: p.G281E | 27.7 | Likely pathogenic | Global (>shoulder and pelvic girdle) | x | x | x | mild | Myopathic sign; COLVI normal | Intracellular distribution | N/A | N/A | ||
| 11 | 40 | M | COL6A3 | c.2029C>T: p.R677C | 32 | Uncertain significance | Trunk, shoulder and pelvic girdle | severe | Atypical sign | N/A | Atypical | N/A | |||||
| 12 | 13 | F | COL6A2 | c.1358G>A: p.R453H | 29.2 | Likely Pathogenic | Normal | Episodic | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 13 | N/A | M | COL6A2 | c.1395+2T>C | 32 | Pathogenic | Normal | severe | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 14 | Congenital | F | COL6A2 | c.1806C>G: p.C602T | 27.6 | Uncertain Significance | Global | x | x | x | normal | Myopathic sign; COLVI reduction | Reduction | Typical | Father het | ||
| 15 | 42 | F | COL6A3 | c.4121A>T: p.D1374V | 26 | Uncertain significance | Distal muscles of leg | low | Myopathic sign | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 16 | 17 | M | COL6A2 | c.2785G>A: p.V929M | 23.4 | Uncertain Significance | Normal | moderate | Myopathic sign; COLVI reduction | Reduction | Typical | N/A | |||||
| 17 | 75 | M | COL6A3 | c.6224C>T: p.P2075L | 24.2 | Uncertain Significance | Right shoulder girdle and orbicular muscles | severe | Atypical sign | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 18 | Congenital | F | COL6A1 | c.788G>A: p.G263D | 23.9 | Likely pathogenic | Global (>shoulder and pelvic girdle) | x | mild | Dystrophic signs | Reduction | Typical | Parents wt | ||||
| 19 | 6 | M | COL6A1 | c.787G>A: p.G263S | 24 | Likely pathogenic | Myalgia | x | x | severe | Normal | N/A | Normal | N/A | |||
| 20 | 4 | F | COL6A3 | c.2845G>A: p.A949T | 24.2 | Uncertain Significance | Normal | moderate | Myopathic sign | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 21 | Congenital | F | COL6A3 | c.8359G>A: p.A2787T | 23.4 | Uncertain Significance | Shoulder and pelvic girdle | x | x | x | normal | Myopathic sign | N/A | Normal | N/A | ||
| 22 | 4 | F | COL6A3 | c.8009C>T: p.A2670V | 23 | Likely pathogenetic | Orbicular muscles | normal | Atypical sign | N/A | Normal | N/A | |||||
| 23 | 60 | F | COL6A1 | c.2635A>G: p.S879G | 23 | Uncertain Significance | Trunk, shoulder girdle and facial muscles | moderate | Myopathic sign | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||
| 24 | 40 | F | COL6A2 | c.2182G>A: p.V728M | 24.8 | Uncertain Significance | Myalgia | severe | Atypical sign | N/A | Normal | N/A | |||||
| 25 | Congenital | F | COL6A1 | c.1315C>T: p.R439W | 23.7 | Likely pathogenic | Trunk, shoulder and pelvic girdle | x | x | x | Normal | Normal | Reduction | Normal | Mother het | ||
| 26 | Congenital | F | COL6A3 | c.787G>A: p.D263N | 23.5 | Uncertain Significance | Pelvic girdle | x | x | x | Normal | N/A | Reduction | Normal | Father het | ||
| 27 | Congenital | M | COL6A2 | c.2950G>A: p.V984M | 23.2 | Uncertain Significance | Pelvic girdle | x | Normal | N/A | Normal | Atypical | Father het | ||||
| 28 | 11 | M | COL6A2 | c.2991C>G: p.F997L | 24.8 | Uncertain Significance | Pelvic girdle (ptosis) | Mild | Myopathic sign; COLVI normal | Reduction | Normal | Parents wt | |||||
| 29 | 30 | M | COL6A3 | c.2212A>T: p.R738W | 24.8 | Uncertain Significance | Global (ptosis) | x | Mild | Inflammatory signs | N/A | Atypical | N/A | ||||
| 30 | 40 | M | COL6A3 | c.7258C>T: p.R2420W | 23.3 | Uncertain Significance | Shoulder and pelvic girdle | x | x | Severe | Dystrophic signs | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marinella, G.; Astrea, G.; Buchignani, B.; Cassandrini, D.; Doccini, S.; Filosto, M.; Galatolo, D.; Gallone, S.; Giannini, F.; Lopergolo, D.; et al. A Schematic Approach to Defining the Prevalence of COL VI Variants in Five Years of Next-Generation Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314567
Marinella G, Astrea G, Buchignani B, Cassandrini D, Doccini S, Filosto M, Galatolo D, Gallone S, Giannini F, Lopergolo D, et al. A Schematic Approach to Defining the Prevalence of COL VI Variants in Five Years of Next-Generation Sequencing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314567
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarinella, Gemma, Guja Astrea, Bianca Buchignani, Denise Cassandrini, Stefano Doccini, Massimiliano Filosto, Daniele Galatolo, Salvatore Gallone, Fabio Giannini, Diego Lopergolo, and et al. 2022. "A Schematic Approach to Defining the Prevalence of COL VI Variants in Five Years of Next-Generation Sequencing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314567
APA StyleMarinella, G., Astrea, G., Buchignani, B., Cassandrini, D., Doccini, S., Filosto, M., Galatolo, D., Gallone, S., Giannini, F., Lopergolo, D., Maioli, M. A., Magri, F., Malandrini, A., Mandich, P., Mari, F., Massa, R., Mata, S., Melani, F., Moggio, M., ... Battini, R. (2022). A Schematic Approach to Defining the Prevalence of COL VI Variants in Five Years of Next-Generation Sequencing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314567









