A Potent Antagonist of Smoothened in Hedgehog Signaling for Epilepsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
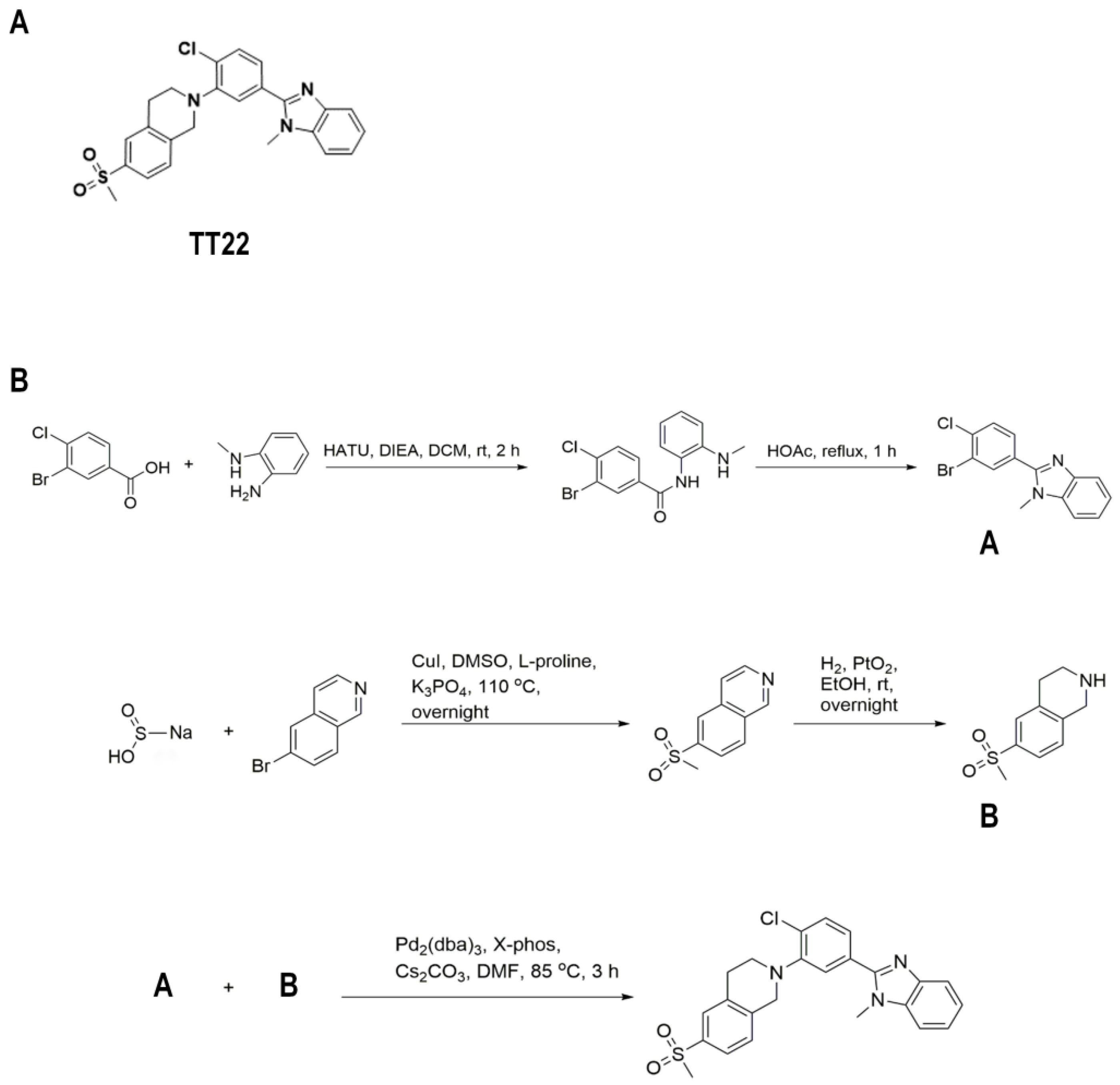
2.1. Identification of the Compound TT22 as a Smo Inhibitor
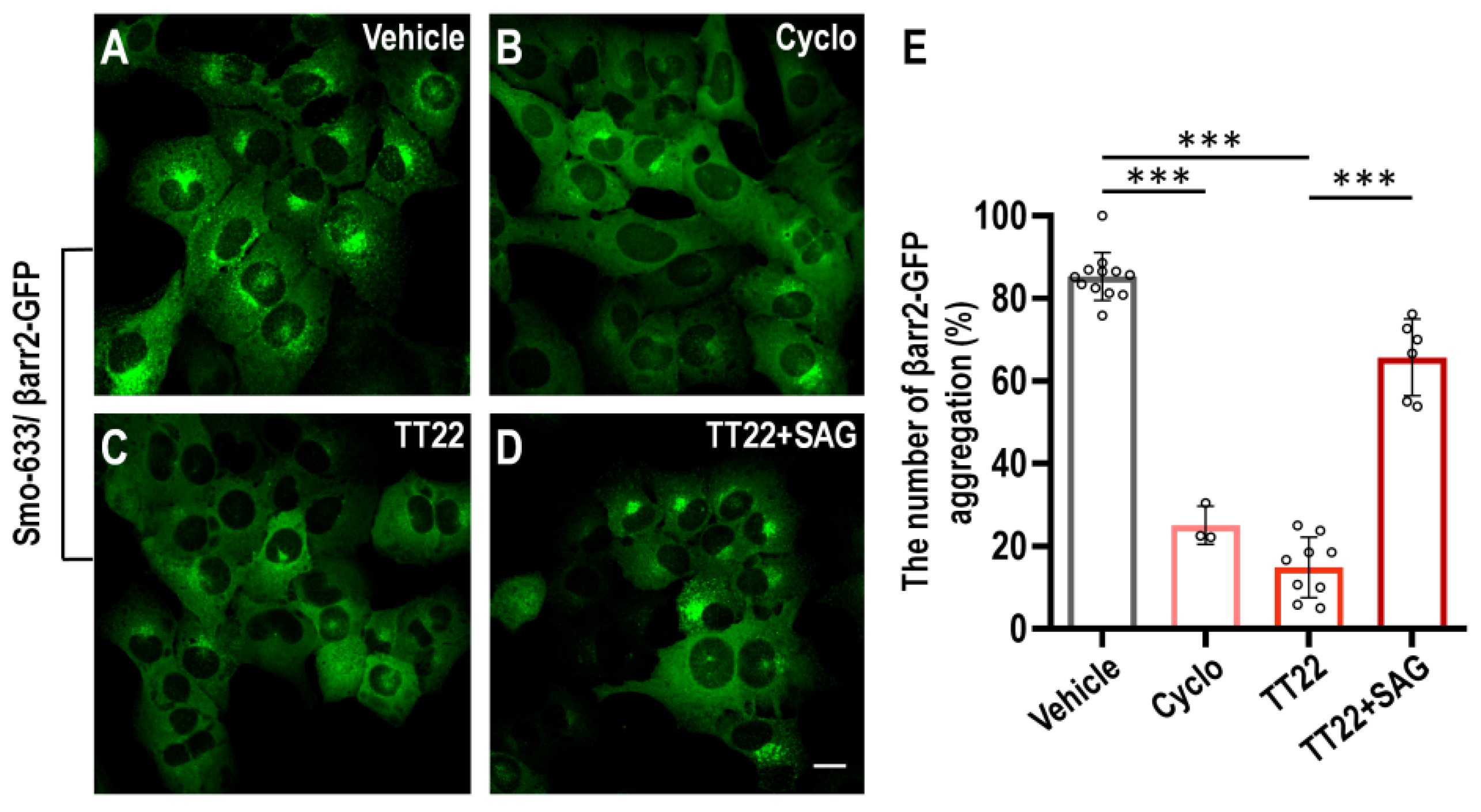
2.2. TT22 Is a Competitive Antagonist of Smo
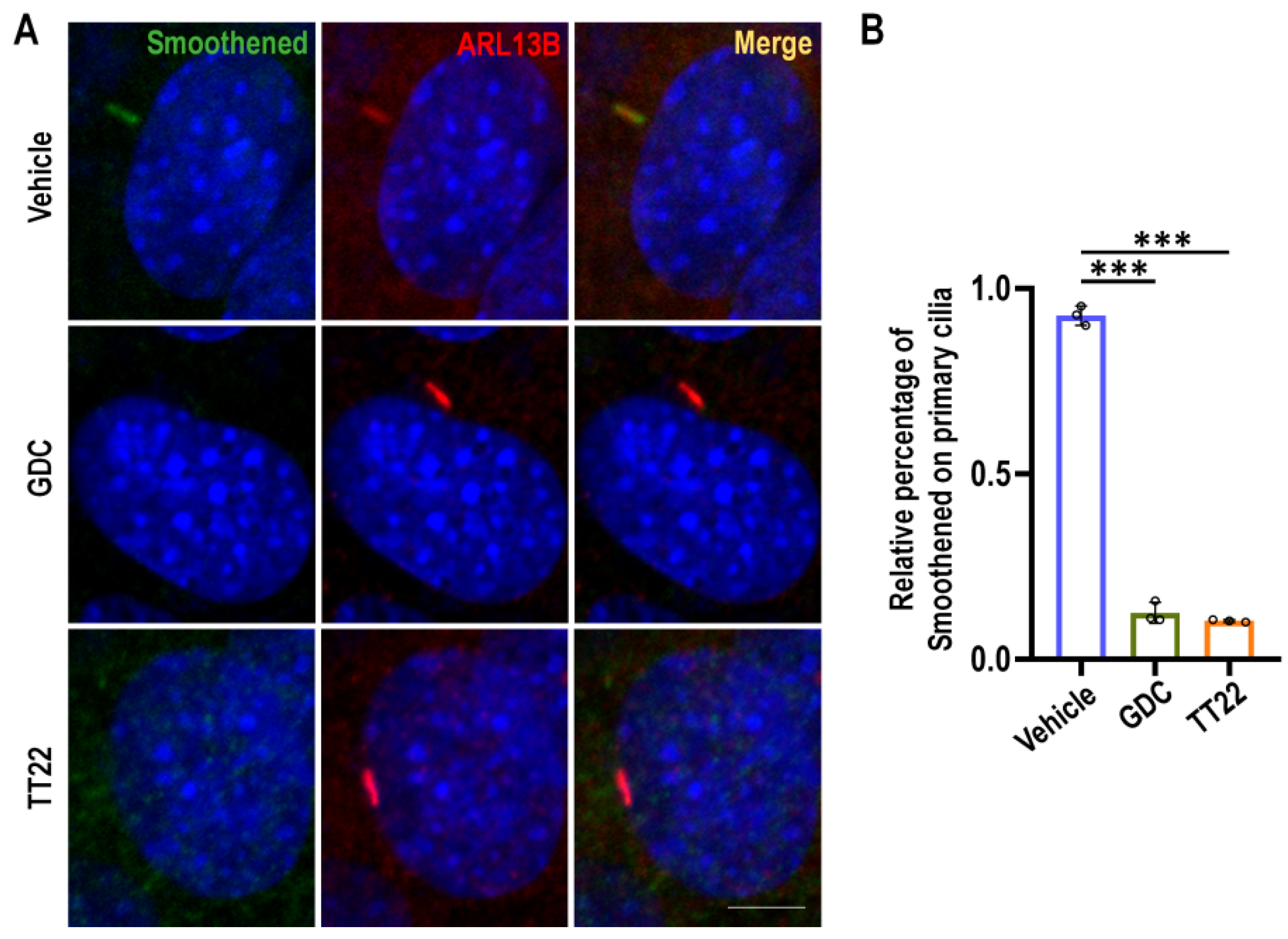
2.3. TT22 Blocks the Aggregation of Smo on the Primary Cilia
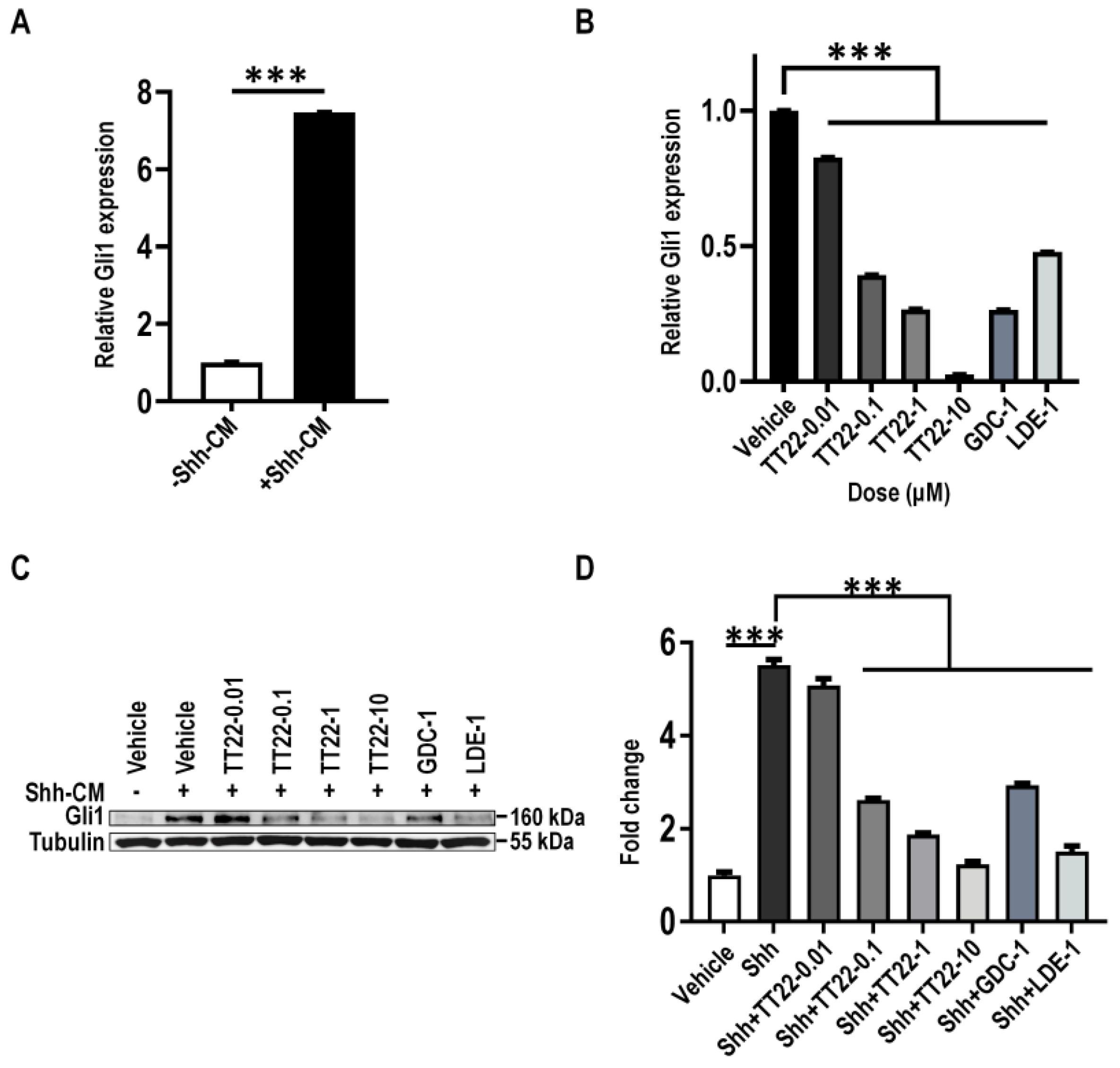
2.4. TT22 Inhibits Shh Signaling
2.5. TT22 Inhibits the Abnormal Seizure-like Activity in Cultured Neurons
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. N-Shh Conditioned Medium
4.3. Cell Culture, Plasmids, and Western Blotting
4.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.5. Primary Rat Hippocampal Neuron Culture
4.6. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time PCR
4.7. Bodipy-Cyclopamine Binding Assay
4.8. Hippocampal Neuron Culture Electrophysiology
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorojankina, T. Hedgehog signaling pathway: A novel model and molecular mechanisms of signal transduction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1317–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ren, X.R.; Nelson, C.D.; Barak, L.S.; Chen, J.K.; Beachy, P.A.; de Sauvage, F.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Activity-dependent internalization of smoothened mediated by beta-arrestin 2 and GRK2. Science 2004, 306, 2257–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, D.J.; Fei, D.L.; Riobo, N.A. The Hedgehog signal transduction network. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, re6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arensdorf, A.M.; Marada, S.; Ogden, S.K. Smoothened Regulation: A Tale of Two Signals. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Xie, G.; Fan, Q.; Xie, J. Activation of the hedgehog-signaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical implications. Oncogene 2010, 29, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Wu, H.; Teng, Z.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y. Prostaglandin E1 Inhibits GLI2 Amplification-Associated Activation of the Hedgehog Pathway and Drug Refractory Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2818–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.W.; Orr, B.A.; Wu, G.; Gururangan, S.; Lin, T.; Qaddoumi, I.; Packer, R.J.; Goldman, S.; Prados, M.D.; Desjardins, A.; et al. Vismodegib Exerts Targeted Efficacy against Recurrent Sonic Hedgehog-Subgroup Medulloblastoma: Results from Phase II Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Studies PBTC-025B and PBTC-032. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Wu, X.; Jiang, J.; Gao, W.; Wan, Y.; Cheng, D.; Han, D.; Liu, J.; Englund, N.P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a Potent and Selective Smoothened Antagonist. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Song, Q.; Day, B.W. Phase I and phase II sonidegib and vismodegib clinical trials for the treatment of paediatric and adult MB patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Bond, M.C.; Chen, M.; Ren, X.R.; Lyerly, H.K.; Barak, L.S.; Chen, W. Identification of select glucocorticoids as Smoothened agonists: Potential utility for regenerative medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9323–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mook, R.A., Jr.; Lu, J.; Gooden, D.M.; Ribeiro, A.; Guo, A.; Barak, L.S.; Lyerly, H.K.; Chen, W. Identification of a novel Smoothened antagonist that potently suppresses Hedgehog signaling. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6751–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Li, H.; Kuang, L.; Zhao, Z.; He, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, W. Identification of a potent antagonist of smoothened in hedgehog signaling. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; et al. ILAE official report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thijs, R.D.; Surges, R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Sander, J.W. Epilepsy in adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucca, P.; Gilliam, F.G. Adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorenzo, R.J.; Sun, D.A.; Deshpande, L.S. Cellular mechanisms underlying acquired epilepsy: The calcium hypothesis of the induction and maintainance of epilepsy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 105, 229–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brodie, M.J.; Dichter, M.A. Antiepileptic drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J., Jr.; McDermott, M.P.; Wiebe, S.; Langfitt, J.T.; Stern, J.M.; Dewar, S.; Sperling, M.R.; Gardiner, I.; Erba, G.; Fried, I.; et al. Early surgical therapy for drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy: A randomized trial. JAMA 2012, 307, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Perdigues, S.; Bailles, E.; Mane, A.; Carreno, M.; Donaire, A.; Rumia, J.; Bargallo, N.; Boget, T.; Setoain, X.; Valdes, M.; et al. Psychiatric Symptoms in Refractory Epilepsy during the First Year After Surgery. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, G.J.; Shen, L.; Pan, Y.M.; Wang, X.F. Increased expression of sonic hedgehog in temporal lobe epileptic foci in humans and experimental rats. Neuroscience 2011, 182, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.S.; Tomar, S.; Sharma, D.; Mahindroo, N.; Udayabanu, M. Targeting sonic hedgehog signaling in neurological disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Lin, J. The role of Shh signalling pathway in central nervous system development and related diseases. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2021, 39, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, N.; Zou, N.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Cowell, J.K.; Shen, Y. Essential roles of leucine-rich glioma inactivated 1 in the development of embryonic and postnatal cerebellum. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Ma, S.; Jia, C.; Su, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, K.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, D.; Fan, L.; et al. Sonic hedgehog is a regulator of extracellular glutamate levels and epilepsy. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.K.; Taipale, J.; Young, K.E.; Maiti, T.; Beachy, P.A. Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14071–14076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Walsh, C.T.; McMahon, A.P. Selective translocation of intracellular Smoothened to the primary cilium in response to Hedgehog pathway modulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Arvanites, A.C.; Davidow, L.; Blanchard, J.; Lam, K.; Yoo, J.W.; Coy, S.; Rubin, L.L.; McMahon, A.P. Selective identification of hedgehog pathway antagonists by direct analysis of smoothened ciliary translocation. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, V.M.; Chen, S.C.; Arkin, M.R.; Reiter, J.F. Small molecule inhibitors of Smoothened ciliary localization and ciliogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13644–13649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osterlund, T.; Kogerman, P. Hedgehog signalling: How to get from Smo to Ci and Gli. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshe, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Schachter, S.C. Drug treatment of epilepsy in adults. BMJ 2014, 348, g254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Loscher, W.; Rho, J.M. Mechanisms of Action of Antiseizure Drugs and the Ketogenic Diet. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a022780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, M.C.; Fuller, C.; Hogg, T.L.; Dalton, J.; Finkelstein, D.; Lau, C.C.; Chintagumpala, M.; Adesina, A.; Ashley, D.M.; Kellie, S.J.; et al. Genomics identifies medulloblastoma subgroups that are enriched for specific genetic alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; Jones, D.T.; Jager, N.; Northcott, P.A.; Pugh, T.J.; Hovestadt, V.; Piro, R.M.; Esparza, L.A.; Markant, S.L.; Remke, M.; et al. Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belgacem, Y.H.; Borodinsky, L.N. Sonic hedgehog signaling is decoded by calcium spike activity in the developing spinal cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4482–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belgacem, Y.H.; Borodinsky, L.N. Inversion of Sonic hedgehog action on its canonical pathway by electrical activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4140–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delmotte, Q.; Diabira, D.; Belaidouni, Y.; Hamze, M.; Kochmann, M.; Montheil, A.; Gaiarsa, J.L.; Porcher, C.; Belgacem, Y.H. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Agonist (SAG) Triggers BDNF Secretion and Promotes the Maturation of GABAergic Networks in the Postnatal Rat Hippocampus. Front Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmotte, Q.; Hamze, M.; Medina, I. Smoothened receptor signaling regulates the developmental shift of GABA polarity in rat somatosensory cortex. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs247700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Estrogen suppresses epileptiform activity by enhancing Kv4.2-mediated transient outward potassium currents in primary hippocampal neurons. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanton, P.K.; Jones, R.S.; Mody, I.; Heinemann, U. Epileptiform activity induced by lowering extracellular [Mg2+] in combined hippocampal-entorhinal cortex slices: Modulation by receptors for norepinephrine and N-methyl-D-aspartate. Epilepsy Res. 1987, 1, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solger, J.; Heinemann, U.; Behr, J. Electrical and chemical long-term depression do not attenuate low-Mg2+-induced epileptiform activity in the entorhinal cortex. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, H.; He, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W. A Potent Antagonist of Smoothened in Hedgehog Signaling for Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314505
Fan J, Zhao Z, Liu R, Li H, He W, Wu J, Wang Y, Chen W. A Potent Antagonist of Smoothened in Hedgehog Signaling for Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314505
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Junwan, Zichen Zhao, Ru Liu, Haowen Li, Wenyan He, Jianping Wu, Yongjun Wang, and Wei Chen. 2022. "A Potent Antagonist of Smoothened in Hedgehog Signaling for Epilepsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314505
APA StyleFan, J., Zhao, Z., Liu, R., Li, H., He, W., Wu, J., Wang, Y., & Chen, W. (2022). A Potent Antagonist of Smoothened in Hedgehog Signaling for Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314505




