RNADSN: Transfer-Learning 5-Methyluridine (m5U) Modification on mRNAs from Common Features of tRNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
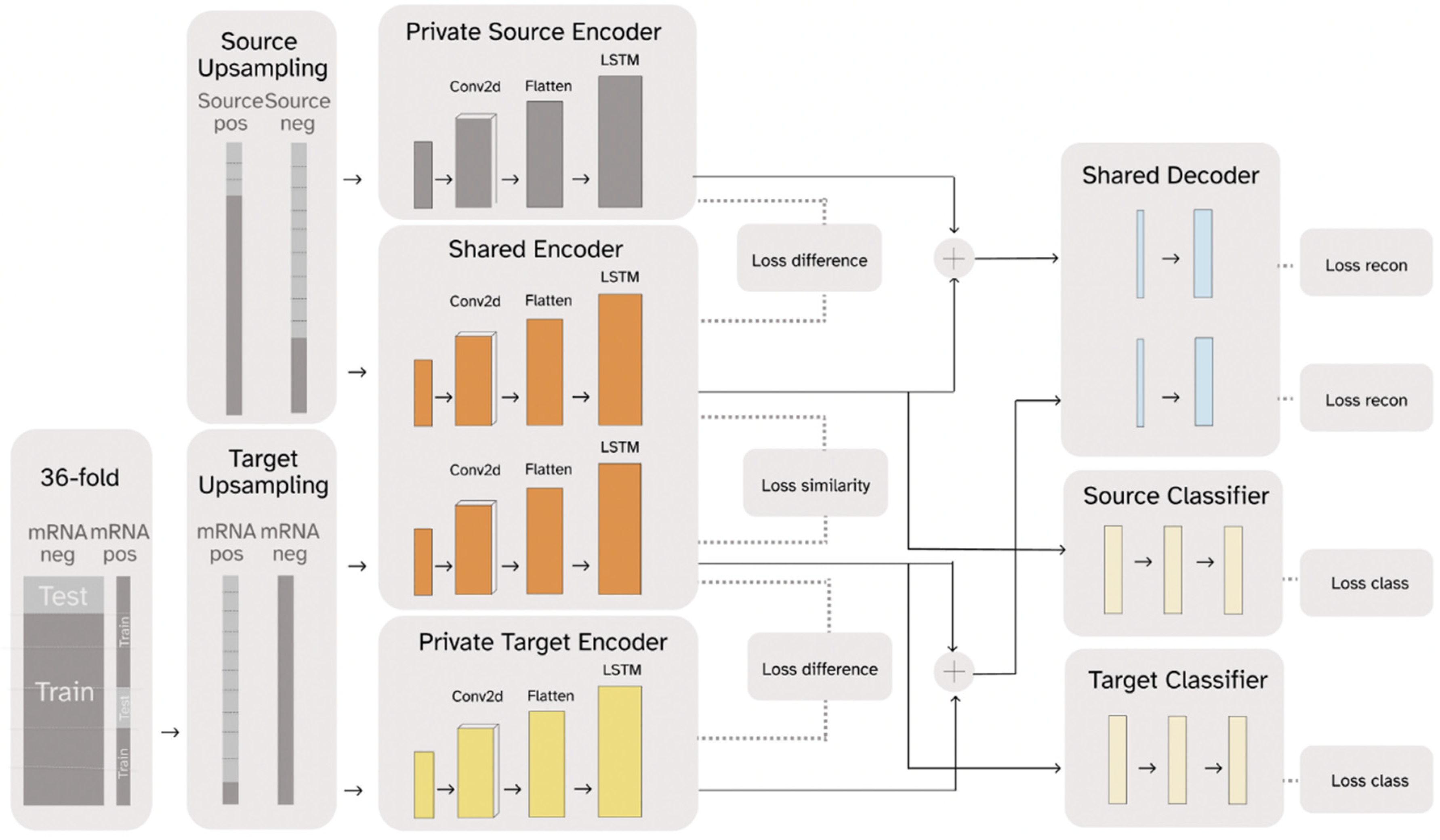
2.1. RNADSN Allows Transfer Learning from tRNA m5U to mRNA m5U
2.2. RNADSN Outperforms Baseline Models
| 41-nt | 51-nt | 61-nt | 71-nt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naive Bayes | 0.7808 | 0.7766 | 0.7873 | 0.7846 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.6157 | 0.6210 | 0.6254 | 0.6216 |
| KNN | 0.4466 | 0.4177 | 0.3871 | 0.3728 |
| m5UPred (SVM) | 0.8438 | 0.8401 | 0.8440 | 0.8313 |
| Random Forest | 0.9355 | 0.9334 | 0.9326 | 0.9310 |
| XGBoost | 0.8816 | 0.8796 | 0.8759 | 0.8783 |
| Training Data | Model | Acc | Spe | F1 | AUC | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source only | NB | 0.7808 | 0.7930 | 0.6107 | 0.8070 | 0.3471 |
| LR | 0.6157 | 0.6212 | 0.4778 | 0.6378 | 0.1323 | |
| KNN | 0.4466 | 0.4070 | 0.3945 | 0.6878 | 0.1577 | |
| m5UPred | 0.8438 | 0.8602 | 0.6756 | 0.8603 | 0.4675 | |
| RF | 0.9355 | 0.9814 | 0.7694 | 0.8983 | 0.6526 | |
| XGBoost | 0.8816 | 0.8945 | 0.7342 | 0.9131 | 0.6473 | |
| mRNA only | NB | 0.8325 | 0.8434 | 0.6707 | 0.8558 | 0.4266 |
| LR | 0.7141 | 0.7342 | 0.5348 | 0.6692 | 0.1679 | |
| KNN | 0.4964 | 0.4842 | 0.4093 | 0.6256 | 0.1476 | |
| m5UPred | 0.9091 | 0.9579 | 0.7038 | 0.8323 | 0.4105 | |
| RF | 0.9163 | 0.9987 | 0.5613 | 0.8663 | 0.5771 | |
| XGBoost | 0.9258 | 0.9724 | 0.7450 | 0.8767 | 0.5959 | |
| Source + mRNA negative | RNADSN | 0.9392 | 0.9639 | 0.6748 | 0.9394 | 0.7670 |
| Source + mRNA | RNADSN | 0.9527 | 0.9862 | 0.7019 | 0.9422 | 0.7855 |
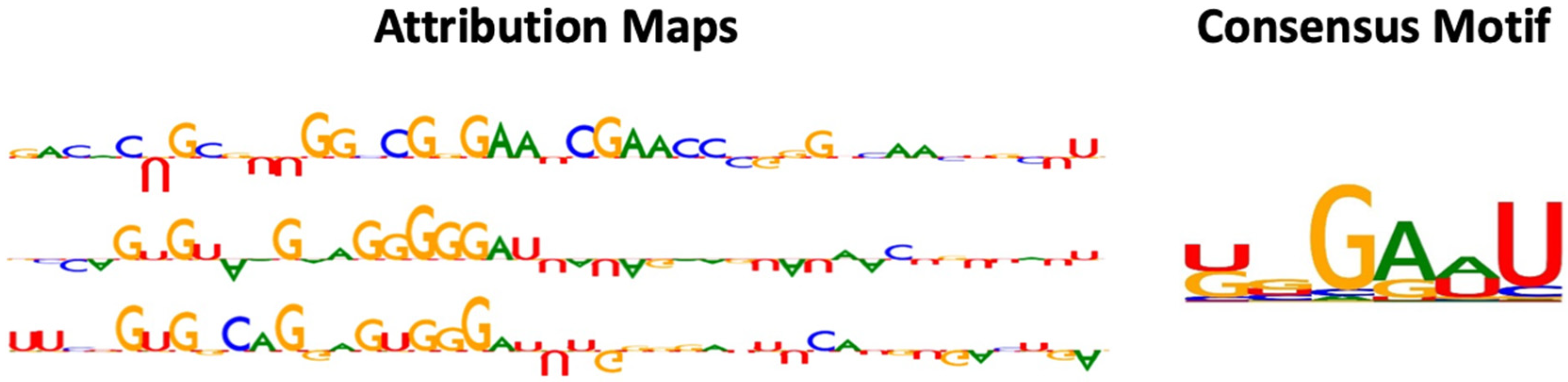
2.3. Interpretation of RNADSN Allows Motif Mining
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Benchmark Dataset
3.2. Data Processing
3.3. Model-Architecture Design
3.4. Model Training
3.5. Model Interpretation
3.6. Evaluation Metrics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boccaletto, P.; Stefaniak, F.; Ray, A.; Cappannini, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Purta, E.; Kurkowska, M.; Shirvanizadeh, N.; Destefanis, E.; Groza, P.; et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways. 2021 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D231–D235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, X.; Li, Z. Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Stem Cell Fate Decisions and Early Embryonic Development in Mammals. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaunay, S.; Frye, M. RNA modifications regulating cell fate in cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Lin, Z.; Du, C.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, Q. mRNA modification orchestrates cancer stem cell fate decisions. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathoux, J.; Henshall, D.C.; Brennan, G.P. Regulatory Mechanisms of the RNA Modification m6A and Significance in Brain Function in Health and Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 671932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livneh, I.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G.; Dominissini, D. The m6A epitranscriptome: Transcriptome plasticity in brain development and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 21, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tang, H.; Ye, J.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.C. iRNA-PseU: Identifying RNA pseudouridine sites. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e332. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Feng, P.; Ding, H.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.C. iRNA-Methyl: Identifying N(6)-methyladenosine sites using pseudo nucleotide composition. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 490, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Song, X.; Lv, H.; Lin, H. iRNA-m2G: Identifying N(2)-methylguanosine Sites Based on Sequence-Derived Information. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Su, R.; Chen, W.; Wei, L. iRNA5hmC: The First Predictor to Identify RNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Modifications Using Machine Learning. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, P.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Q. SRAMP: Prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based on sequence-derived features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Chen, H.; Su, R. M6APred-EL: A Sequence-Based Predictor for Identifying N6-methyladenosine Sites Using Ensemble Learning. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Smith, A.I.; I Webb, G.; Akutsu, T.; Baggag, A.; Bensmail, H.; Song, J. Comprehensive review and assessment of computational methods for predicting RNA post-transcriptional modification sites from RNA sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 21, 1676–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Rong, R.; Lu, Z.; Su, J.; de Magalhães, J.P.; Rigden, D.J.; Meng, J. Whistle: A high-accuracy map of the human N6-methyladenosine (m6A) epitranscriptome predicted using a machine learning approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Xing, P.; Wei, L.; Liu, B. Gene2vec: Gene subsequence embedding for prediction of mammalian N (6)-methyladenosine sites from mRNA. RNA 2019, 25, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhou, Y. NmSEER V2.0: A prediction tool for 2′-O-methylation sites based on random forest and multi-encoding combination. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20 (Suppl. S25), 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Feng, P.; Cui, L.; Su, R.; Chen, W.; Wei, L. Iterative feature representation algorithm to improve the predictive performance of N7-methylguanosine sites. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ding, H.; Zou, Q. RF-PseU: A Random Forest Predictor for RNA Pseudouridine Sites. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Huang, D.; Song, B.; Chen, K.; Song, Y.; Liu, G.; Su, J.; Magalhães, J.P.; Rigden, D.J.; Meng, J. Attention-based multi-label neural networks for integrated prediction and interpretation of twelve widely occurring RNA modifications. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ju, Y.; Zou, Q.; Lin, C. DeepAc4C: A convolutional neural network model with hybrid features composed of physicochemical patterns and distributed representation information for identification of N4-acetylcytidine in mRNA. Bioinformatics 2021, 38, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Chen, H.; Ye, X.; Su, R.; Wei, L. M6AMRFS: Robust Prediction of N6-Methyladenosine Sites With Sequence-Based Features in Multiple Species. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; He, N.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L. BERMP: A cross-species classifier for predicting m(6)A sites by integrating a deep learning algorithm and a random forest approach. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, C.; Zou, Q.; Yu, L. NmRF: Identification of multispecies RNA 2′-O-methylation modification sites from RNA sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, D.; Tian, T.; Hong, L.; Jiang, T.; Zeng, J. Modeling multi-species RNA modification through multi-task curriculum learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3719–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Tayara, H.; Zou, Q.; Chong, K.T. TS-m6A-DL: Tissue-specific identification of N6-methyladenosine sites using a universal deep learning model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4619–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L. Deep analysis of RNA N(6)-adenosine methylation (m(6)A) patterns in human cells. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2020, 2, lqaa007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, F.Y.; Lv, H.; Yang, Y.H.; Zulfiqar, H.; Gao, H.; Lin, H. Computational identification of N6-methyladenosine sites in multiple tissues of mammals. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Song, B.; Wei, J.; Su, J.; Coenen, F.; Meng, J. Weakly supervised learning of RNA modifications from low-resolution epitranscriptome data. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, i222–i230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Du, P.F. i5hmCVec: Identifying 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Sites of Drosophila RNA Using Sequence Feature Embeddings. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 896925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, Y.; Ren, J.; Zuo, Z. RMVar: An updated database of functional variants involved in RNA modifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D1405–D1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, K.; Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Lin, D.; Zuo, Z.; Zheng, J. M6A2Target: A comprehensive database for targets of m6A writers, erasers and readers. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-H.; Zhang, G.; Cui, Q. PPUS: A web server to predict PUS-specific pseudouridine sites: Table 1. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3362–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Chen, W. iMRM: A platform for simultaneously identifying multiple kinds of RNA modifications. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3336–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Xiang, D.; Chen, Y.Z.; Akutsu, T.; Daly, R.J.; Webb, G.I.; Zhao, Q.; et al. iLearnPlus: A comprehensive and automated machine-learning platform for nucleic acid and protein sequence analysis, prediction and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, P.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Akutsu, T.; Bain, C.; Gasser, R.B.; Li, J.; et al. iFeatureOmega: an integrative platform for engineering, visualization and analysis of features from molecular sequences, structural and ligand data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W434–W447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Song, J.; Cheng, Q.; Tang, Y.; Ma, C. PEA: An integrated R toolkit for plant epitranscriptome analysis. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3747–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhou, Y. m6Acorr: An online tool for the correction and comparison of m(6)A methylation profiles. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontiveros, R.J.; Shen, H.; Stoute, J.; Yanas, A.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.F. Coordination of mRNA and tRNA methylations by TRMT10A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7782–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, O.; Arava, Y.S. RNA modifications as a common denominator between tRNA and mRNA. Curr. Genet. 2021, 67, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchardt, E.K.; Martinez, N.M.; Gilbert, W.V. Regulation and Function of RNA Pseudouridylation in Human Cells. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 309–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safra, M.; Nir, R.; Farouq, D.; Vainberg Slutskin, I.; Schwartz, S. TRUB1 is the predominant pseudouridine synthase acting on mammalian mRNA via a predictable and conserved code. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Chen, W. iRNA-m5U: A sequence based predictor for identifying 5-methyluridine modification sites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods 2022, 203, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Song, B.; Tang, Y.; Chen, K.; Wei, Z.; Meng, J. m5UPred: A Web Server for the Prediction of RNA 5-Methyluridine Sites from Sequences. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousmalis, K.; Trigeorgis, G.; Silberman, N.; Krishnan, D.; Erhan, D. Domain Separation Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 343–351. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararajan, M.; Taly, A.; Yan, Q. Axiomatic Attribution for Deep Networks. Proccedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 11 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shrikumar, A.; Tian, K.; Avsec, v.; Shcherbina, A.; Banerjee, A.; Sharmin, M.; Nair, S.; Kundaje, A. Technical Note on Transcription Factor Motif Discovery from Importance Scores (TF-MoDISco) version 0.5.6.5. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.00416. [Google Scholar]
| Training | Testing | Acc | Spe | F1 | AUC | AP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNADSN | FICC-seq | miCLIP | 0.9282 | 0.9732 | 0.5476 | 0.8731 | 0.5853 |
| miCLIP | FICC-seq | 0.8909 | 0.9174 | 0.5105 | 0.8845 | 0.5724 | |
| HEK293 | HAP1 | 0.9408 | 0.9632 | 0.6873 | 0.9342 | 0.7369 | |
| HAP1 | HEK293 | 0.9262 | 0.9722 | 0.5343 | 0.8765 | 0.5679 | |
| m5UPred | FICC-seq | miCLIP | 0.9011 | 0.9668 | 0.6282 | 0.791 | 0.3142 |
| miCLIP | FICC-seq | 0.7991 | 0.8231 | 0.6088 | 0.7654 | 0.2569 | |
| HEK293 | HAP1 | 0.8592 | 0.9019 | 0.6396 | 0.7983 | 0.3127 | |
| HAP1 | HEK293 | 0.9031 | 0.9763 | 0.596 | 0.73 | 0.2498 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Mao, J.; Huang, D.; Song, B.; Meng, J. RNADSN: Transfer-Learning 5-Methyluridine (m5U) Modification on mRNAs from Common Features of tRNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113493
Li Z, Mao J, Huang D, Song B, Meng J. RNADSN: Transfer-Learning 5-Methyluridine (m5U) Modification on mRNAs from Common Features of tRNA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113493
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhirou, Jinge Mao, Daiyun Huang, Bowen Song, and Jia Meng. 2022. "RNADSN: Transfer-Learning 5-Methyluridine (m5U) Modification on mRNAs from Common Features of tRNA" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113493
APA StyleLi, Z., Mao, J., Huang, D., Song, B., & Meng, J. (2022). RNADSN: Transfer-Learning 5-Methyluridine (m5U) Modification on mRNAs from Common Features of tRNA. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113493






