Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Chitosan for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Determination of Acrylation Degree of CS Functionalized with GMA
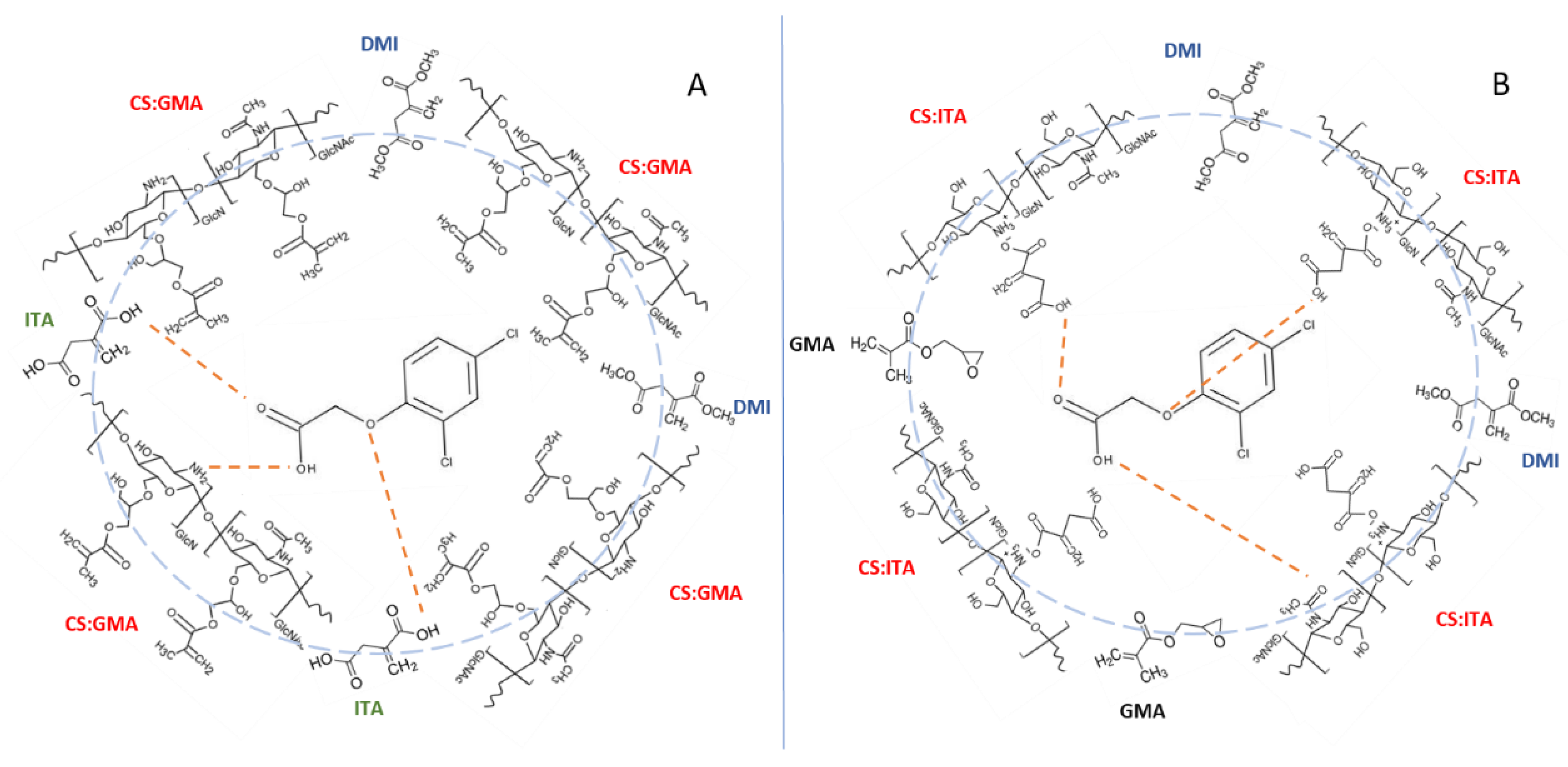
2.2. Characterization of the Prepared CS_GMA and CS_ITA MIPs and NIPs
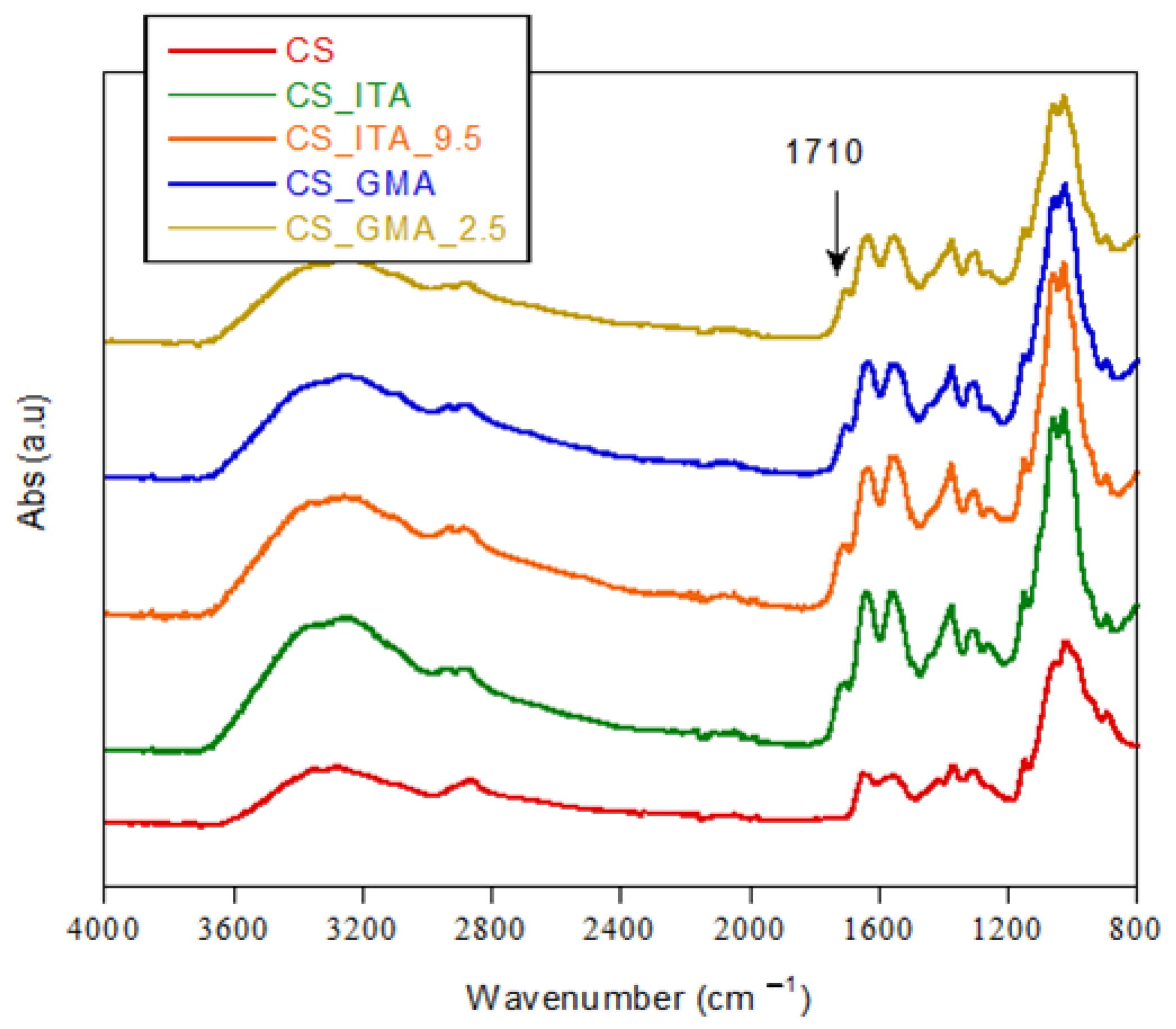
2.2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
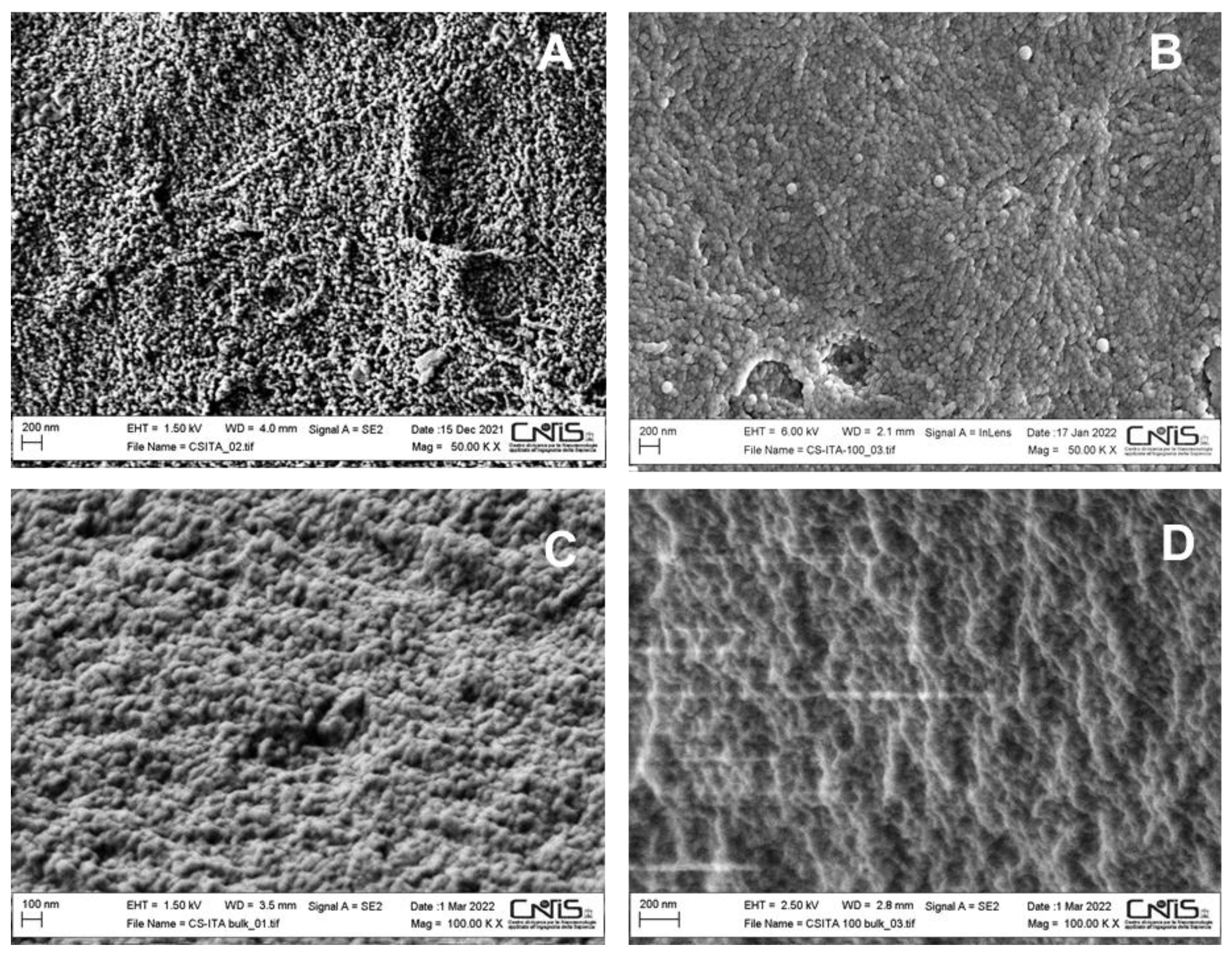
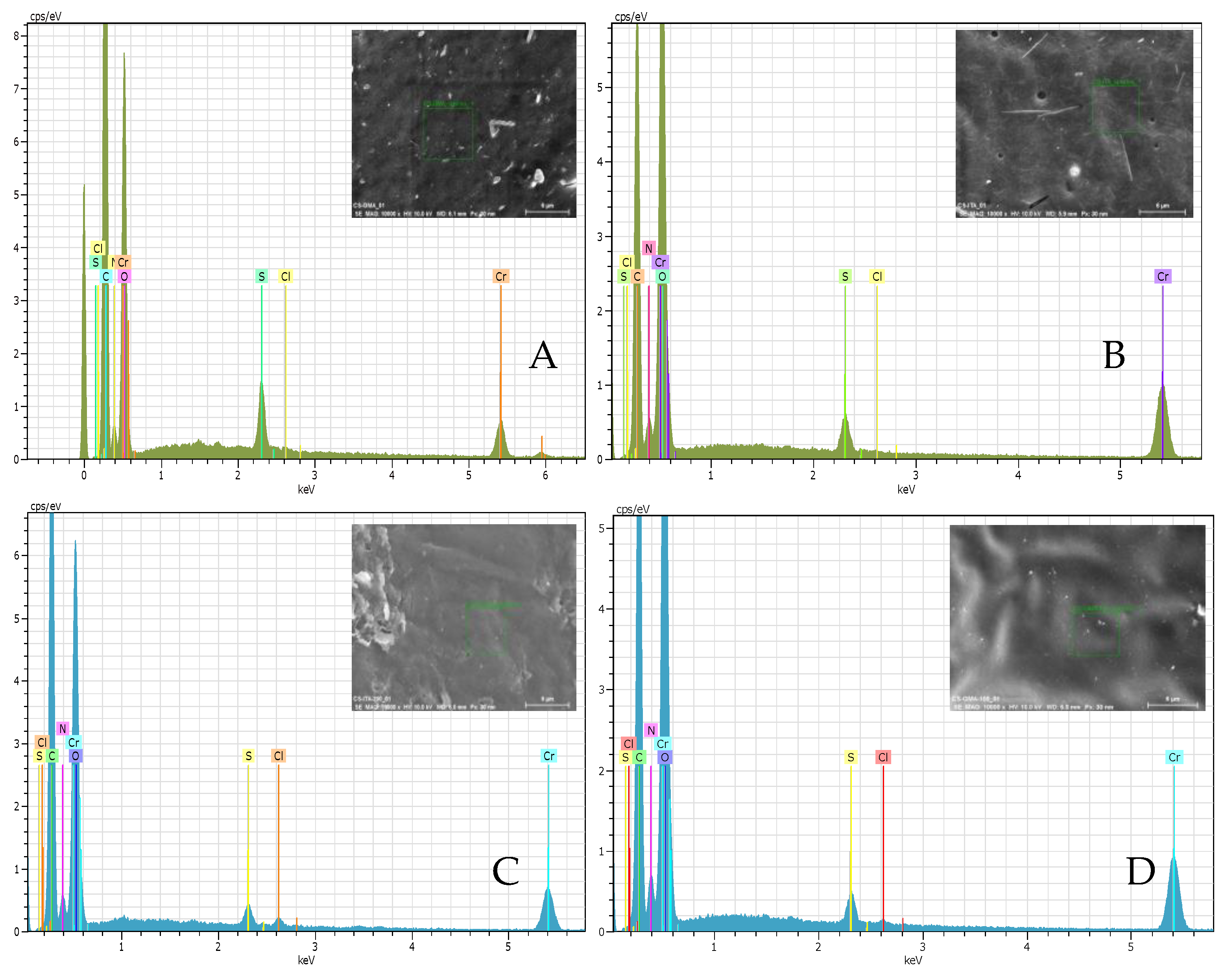
2.2.2. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) Analysis
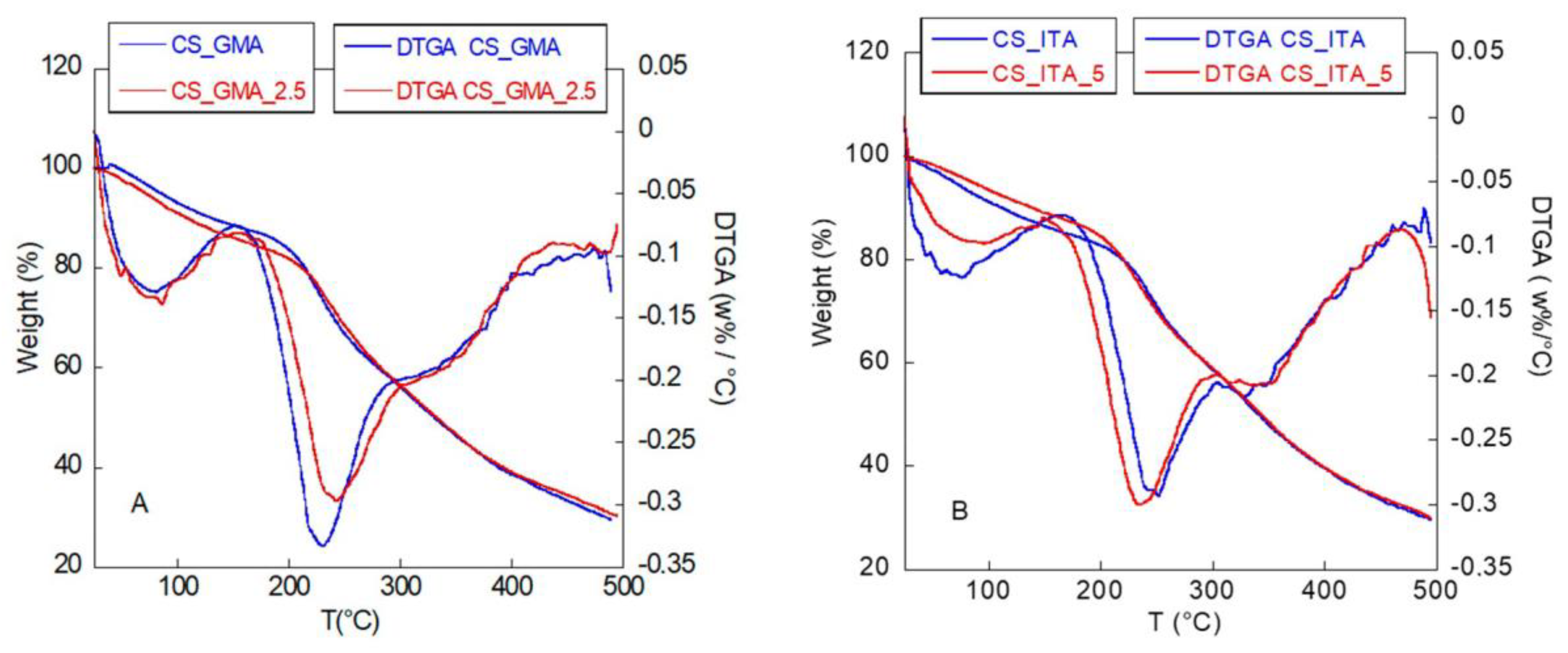
2.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
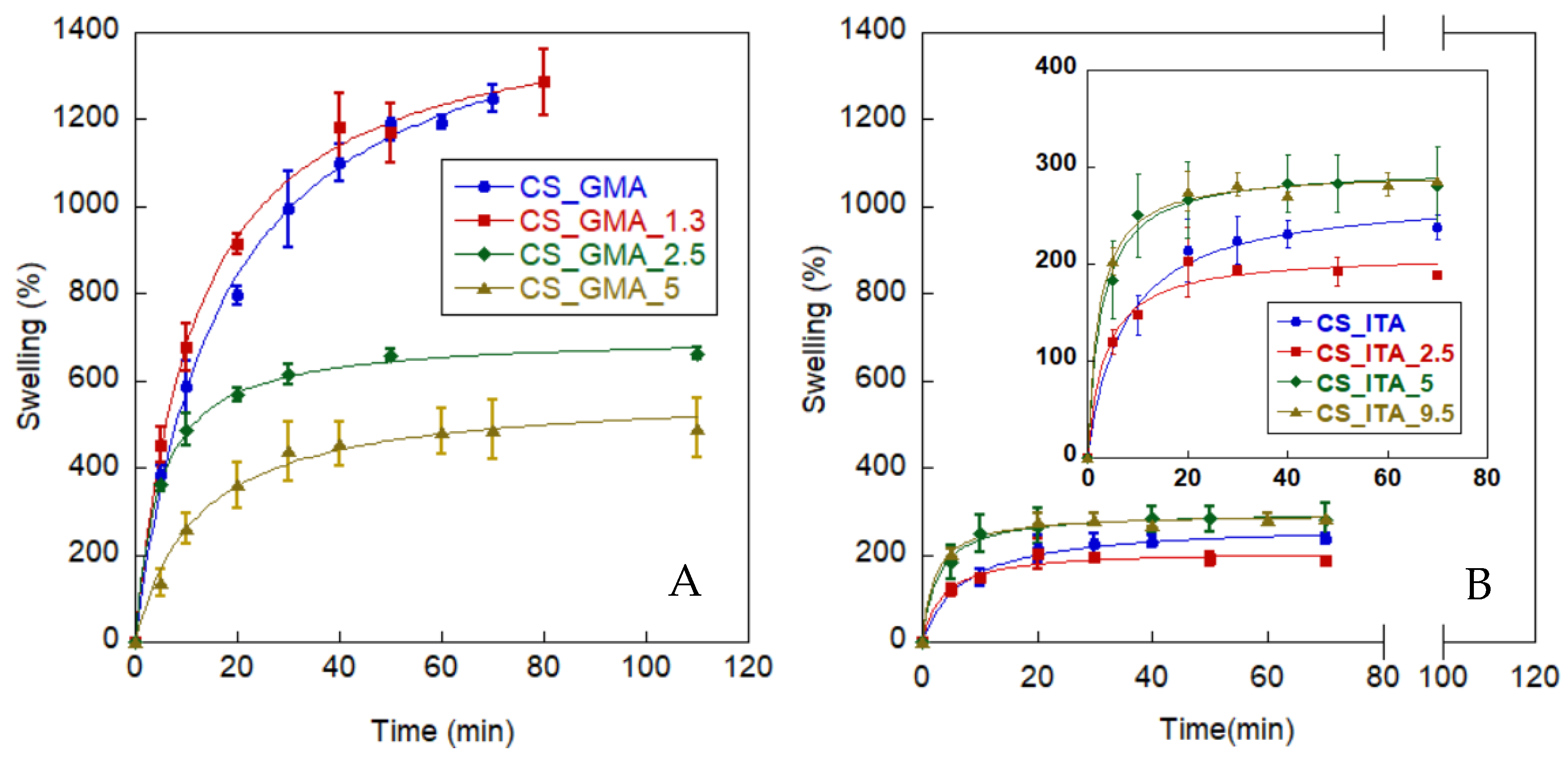
2.2.4. Water Uptake
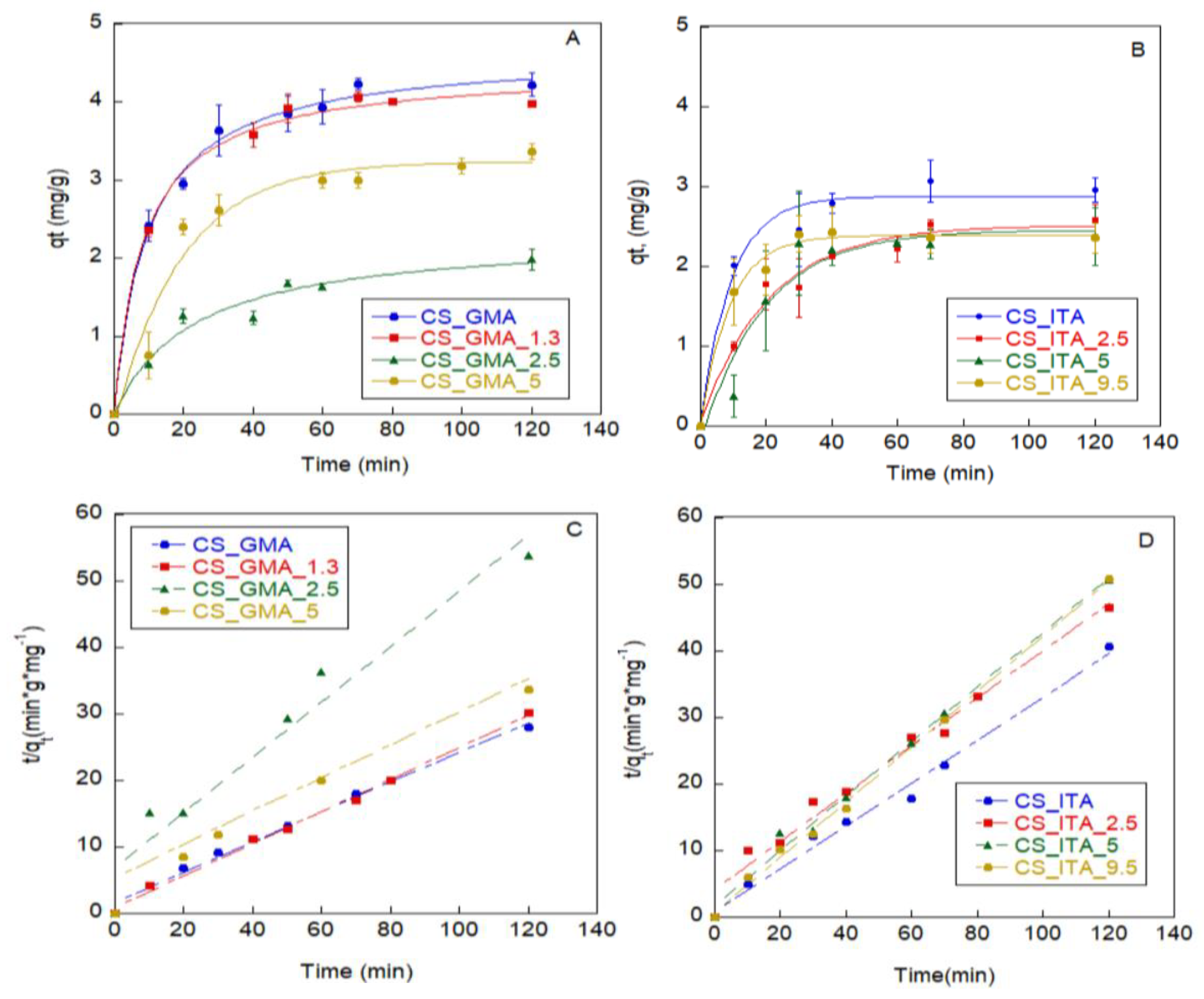
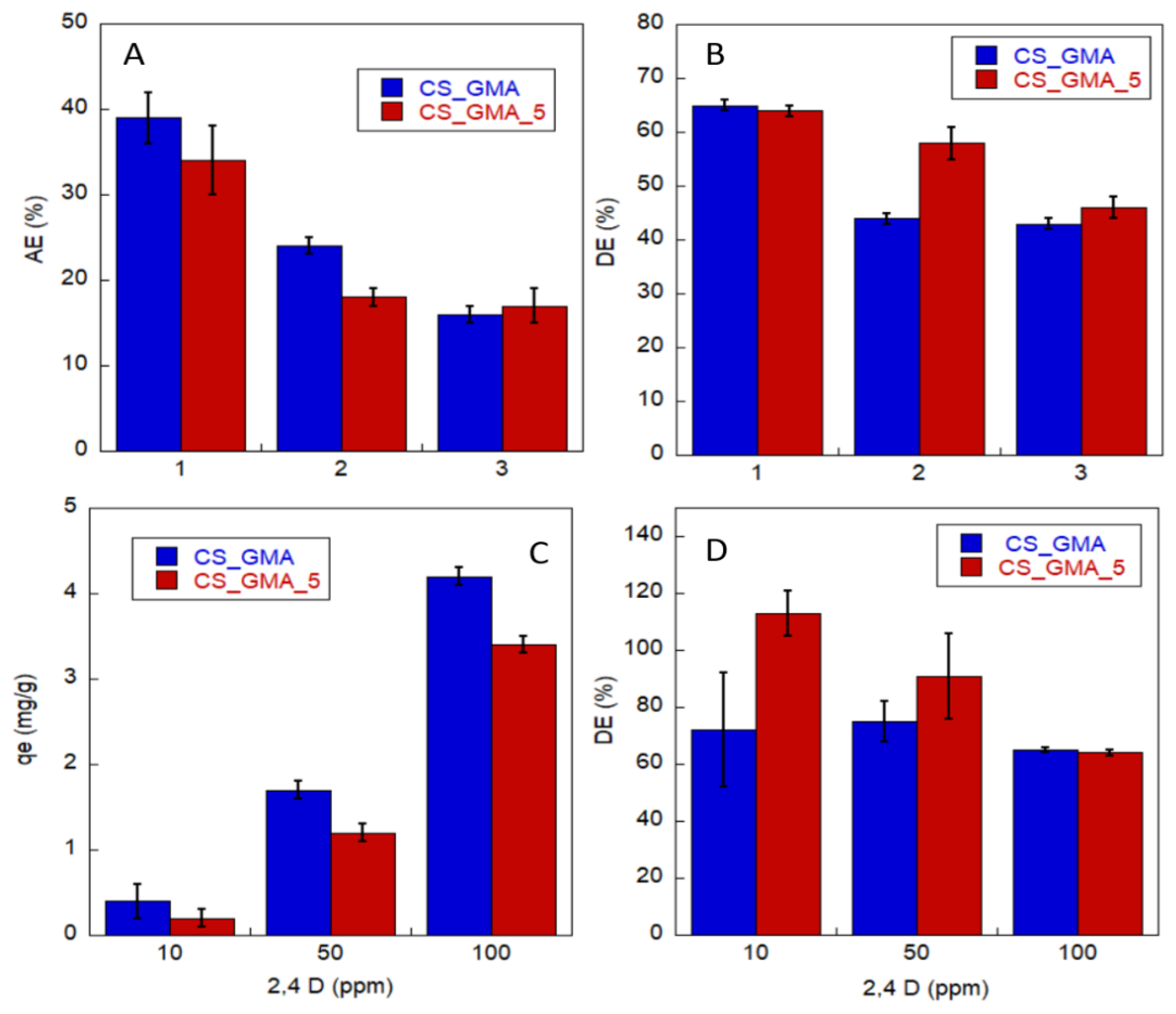
2.3. Pesticide Adsorption Kinetics and Desorption Test
3. Materials end Methods
3.1. Functionalization of Chitosan (CS) with Glycidyl Methacrylate (GMA) and Itaconic Acid (ITA)
3.2. Preparation of MIPs and NIPs Hydrogels with Modified Chitosan
Determination of Acrylation Degree of CS Functionalized with GMA
3.3. Characterization of the Prepared MIPs and NIP Systems
3.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.3.2. Scanning Electron Spectroscopy
3.3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3.4. Water Uptake
3.4. Study of Pesticide Adsorption
3.5. Reusability of Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muszyński, P.; Brodowska, M.S.; Paszko, T. Occurrence and transformation of phenoxy acids in aquatic environment and photochemical methods of their removal: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1276–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, R.; Etter, M.L.; Buehler, K.; Starks, K.; Yowin, Y. Phenoxyacid Herbicides in Stormwater Retention Ponds: Urban Inputs. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 02, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- González, A.F.E.; Zúñiga-Benítez, H.; Peñuela, G.A. Removal of herbicide 2,4-D using constructed wetlands at pilot scale. Emerg. Contam. 2019, 5, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Z.; Gong, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Lyu, P.; Li, L.; Xia, L. Metal–Organic Frameworks Meet Metallic Oxide on Carbon Fiber: Synergistic Effect for Enhanced Photodegradation of Antibiotic Pollutant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, M.F.; Sapawe, N. A review on the current techniques and technologies of organic pollutants removal from water/wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, A158–A165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.U.; Saeed, M.; Usman, M.; Muneer, M.; Adeel, S.; Abbas, S.; Iqbal, A. Removal of butachlor from aqueous solution using cantaloupe seed shell powder: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6029–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, W. Environment-friendly Juncus effusus-based adsorbent with a three-dimensional network structure for highly efficient removal of dyes from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J.; Chen, J. Enhanced adsorption removal of antibiotics from aqueous solutions by modified al-ginate/graphene double network porous hydrogel. J. Colloid Interface Scii. 2017, 507, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, T.; Pasquini, D.; Lima, A.D.F.; Rosa, E.V.; Sousa, M.H.; Cerqueira, D.A.; de Morais, L.C. Efficient removal of lead ions from water by magnetic nanosorbents based on manganese ferrite nanoparticles capped with thin layers of modified biopolymers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, H.; Moradi, S.; Hudson, S.M.; Tonelli, A.E.; King, M.W. Chitosan based bioadhesives for biomedical applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 282, 119100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucitti, V.C.; Migneco, L.M.; Piozzi, A.; Taresco, V.; Garnett, M.; Argent, R.H.; Francolini, I. Intermolecular interaction and solid state characterization of abietic acid/chitosan solid dispersions possessing antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 125, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, N.; Mano, J. Chitosan derivatives obtained by chemical modifications for biomedical and environmental applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestro, I.; Francolini, I.; Di Lisio, V.; Martinelli, A.; Pietrelli, L.; D’Abusco, A.S.; Scoppio, A.; Piozzi, A. Preparation and Characterization of TPP-Chitosan Crosslinked Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Materials 2020, 13, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestro, I.; Sergi, R.; D’Abusco, A.S.; Mariano, A.; Martinelli, A.; Piozzi, A.; Francolini, I. Chitosan scaffolds with enhanced mechanical strength and elastic response by combination of freeze gelation, photo-crosslinking and freeze-drying. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, I.; Ciarlantini, C.; Francolini, I.; Tomai, P.; Gentili, A.; Bosco, C.D.; Piozzi, A. Chitosan–Graphene Oxide Composite Membranes for Solid-Phase Extraction of Pesticides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.; Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; Soto, D.; Pérez, D.; Rangel, M.; Colina, M.; Fernández-García, M. Removal of anionic and cationic dyes with bioadsorbent oxidized chitosans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apriceno, A.; Silvestro, I.; Girelli, A.; Francolini, I.; Pietrelli, L.; Piozzi, A. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan-Coated Manganese-Ferrite Nanoparticles Conjugated with Laccase for Environmental Bioremediation. Polymers 2021, 13, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, R.; Mujtaba, M.; Rahman, M.U.; Shalmani, A.; Ahmad, H.; Anwar, T.; Tianchan, D.; Wang, X. The Multifunctional Role of Chitosan in Horticultural Crops; A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Acosta, N.; Civera, C.; Elorza, B.; Mingo, J.; Castro, C.; de Los Llanos Gandía, M.; Caballero, A.H. Cosmetics and Cosmeceutical Applications of Chitin, Chitosan and Their Derivatives. Polymers 2018, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Removal of various pollutants from water and wastewater by modified chitosan adsorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 2331–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrelli, L.; Francolini, I.; Piozzi, A. Dyes Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions by Chitosan. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 50, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrelli, L.; Francolini, I.; Piozzi, A.; Sighicelli, M.; Silvestro, I.; Vocciante, M. Chromium(III) Removal from Wastewater by Chitosan Flakes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, P.M.; Peighambardoust, S.J. Review on recent progress in chitosan-based hydrogels for wastewater treatment application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Huang, Y.-A.; Zhu, Q.-J.; Ye, C. Chitosan in Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers: Current and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18328–18347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Row, K.H. Characteristic and Synthetic Approach of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2006, 7, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Andersson, H.; Andersson, L.I.; Ansell, R.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A.; O’Mahony, J.; Whitcombe, M.J. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years up to and including 2003. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 106–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, N.; Chen, C.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-Based Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres for Sustained Release of Sinomenine Hydrochloride in Aqueous Media. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 185, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lian, Z.; Song, C.; Ge, C. Release of florfenicol in seawater using chitosan-based molecularly imprinted microspheres as drug carriers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, E.; Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Y. Synthesis of chitosan molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction of methandrostenolone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L. Preparation of chitosan-based molecularly imprinted material for enantioseparation of racemic mandelic acid in aqueous medium by solid phase extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 3544–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Abdelbar, N.M.; Mohamed, A.A. Molecular imprinted chitosan-TiO2 nanocomposite for the selective removal of Rose Bengal from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Zakaria, E.; Khalil, M.; El-Tantawy, A.; El-Saied, F. Synthesis of ion-imprinted polymers based on chitosan for high selectivity of La(III), Ce(III) and Sm(III) via solid phase extraction. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 356, 119058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymer for 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid prepared by a sol-gel method. J. Chem. Sci. 2014, 126, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, F.; Behbahani, M.; Abandansari, H.S.; Sedighi, A.; Shahtaheri, S.J. Application of molecular imprinted polymer nanoparticles as a selective solid phase extraction for preconcentration and trace determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in the human urine and different water samples. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limaee, N.Y.; Rouhani, S.; Olya, M.E.; Najafi, F. Selective 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid optosensor employing a polyethersulfone nanofiber-coated fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer. Polymer 2019, 177, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Harmoudi, H.; El Gaini, L.; Daoudi, E.; Rhazi, M.; Boughaleb, Y.; El Mhammedi, M.A.; Migalska-Zalas, A.; Bakasse, M. Removal of 2,4-D from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using two biopolymers: Chitin and chitosan and their optical properties. Opt. Mater. 2014, 36, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.; Becegato, V.A.; Paulino, A.T. Equilibrium Isotherms, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics of the Adsorption of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid to Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, K.; He, L.L.; Tang, H.; Gao, J.Q.; Zhu, S.F.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.N. Use of Chitosan-modified Bentonite for Removal of Cu2+, Cl− and 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid (2,4-D) from Aqueous Solution. Kem. u Ind. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 63, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.R.; Araújo, K.R.O.; Moura, A.O. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyactic acid herbicide removal from water using chitosan. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 45, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhu, S.; Song, F.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.; Xu, W. Synthesis and Characterization of Sensitive Molecular Imprinting Electrochemical Sensor Based on Chitosan Modified HPSNS-NH2@Au for Detection of 2,4-D. SSRN Electron. J. 2021, 181, 107593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadmehr, F.; Zarei, K. An imprinted polymeric matrix containing DNA for electrochemical sensing of 2,4–dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, T.; Friebel, S. Itaconic acid—A versatile building block for renewable polyesters with enhanced functionality. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2922–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleky, B.-E.; Vodnar, D.C. Recent Advances in Biotechnological Itaconic Acid Production, and Application for a Sustainable Approach. Polymers 2021, 13, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Ji, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R. Novel organic glass with superior optical properties based on dimethyl itaconate and diethyl itaconate. Polym. Test. 2021, 103, 107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.; Muniz, E.C.; Hsieh, Y.-L. 1H NMR and 1H–13C HSQC surface characterization of chitosan–chitin sheath-core nanowhiskers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.V.; Fajardo, A.R.; Schuquel, I.T.A.; Guilherme, M.R.; Vidotti, G.J.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Reaction of Glycidyl Methacrylate at the Hydroxyl and Carboxylic Groups of Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Poly(acrylic acid): Is This Reaction Mechanism Still Unclear? J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 3750–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, A.R.; Fávaro, S.L.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Dual-network hydrogels based on chemically and physically crosslinked chitosan/chondroitin sulfate. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, M.R.; Reis, A.V.; Alves, B.R.; Kunita, M.H.; Rubira, A.F.; Tambourgi, E.B. Smart hollow microspheres of chondroitin sulfate conjugates and magnetite nanoparticles for magnetic vector. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 352, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudiyanselage, T.K.; Neckers, D.C. Highly absorbing superabsorbent polymer. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Kurdtabar, M.; Mahdavinia, G.R.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Synthesis and super-swelling behavior of a novel protein-based superabsorbent hydrogel. Polym. Bull. 2006, 57, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Deng, S.; Yu, G. Selective removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from aqueous solution using chitosan-based molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3089–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Li, C.; Zhou, S.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W. Utilization of Waste Leather Powders for Highly Effective Removal of Dyes from Water. Polymers 2019, 11, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.-H.; Han, H.-S.; Baik, S.; Helms, V.; Kim, Y. Detection of Acidic Pharmaceutical Compounds Using Virus-Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupai, J.; Razali, M.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Szekely, G. Long-term stability and reusability of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polym. Chem. 2016, 8, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zong, Y. Removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol by chitosan-immobilized laccase from Coriolus versicolor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 45, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.L.; Cao, P.A.; Popa, M.; Xuan, H.N. Hybrid Composite Based on Magnetite/Chitosan for 2,4-D and Chrysoidine Removal. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 56, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type of Modified CS | Imprinting | Template Amount wt (%) | Acronyms |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS:GMA | no | - | CS_GMA |
| yes | 1.3 | CS_GMA_1.3 | |
| yes | 2.5 | CS_GMA_2.5 | |
| yes | 5 | CS_GMA_5 | |
| CS:ITA | no | - | CS_ITA |
| yes | 2.5 | CS_ITA_2.5 | |
| yes | 5 | CS_ITA_5 | |
| yes | 9.5 | CS_ITA_9.5 |
| Sample | Physical Characterization | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl at.%/Cat.% (%) Surface | Cl at.%/Cat.% (%) Bulk | Td (°C) | W (%) | |
| CS_GMA | - | - | 222 ± 3 | 1250 ± 30 |
| CS_GMA_1.3 | - | - | 227 ± 2 | 1290 ± 70 |
| CS_GMA_2.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | - | 228 ± 2 | 660 ± 20 |
| CS_GMA_5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | - | 230 ± 3 | 490 ± 70 |
| CS_ITA | - | - | 243 ± 1 | 238 ± 12 |
| CS_ITA_2.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.50 ± 0.05 | 229 ± 4 | 188 ± 10 |
| CS_ITA_5 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | - | 230 ± 1 | 280 ± 40 |
| CS_ITA_9.5 | 0.60 ± 0.04 | 0.70 ± 0.04 | 227 ± 2 | 286 ± 10 |
| Sample | qe,exp (mg/g) | AE (%) | DE (%) | K2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | qe,cal (mg/g) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS_GMA | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 39 ± 3 | 65 ± 1 | 0.03422 | 4.4 | 0.9921 |
| CS_GMA_1.3 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 41 ± 1 | 45 ± 2 | 0.06972 | 4.1 | 0.9953 |
| CS_GMA_2.5 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 21 ± 1 | 95 ± 5 | 0.02139 | 2.4 | 0.9177 |
| CS_GMA_5 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 34 ± 4 | 64 ± 1 | 0.01205 | 3.8 | 0.9349 |
| CS_ITA | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 30 ± 1 | 66 ± 4 | 0.11756 | 3.1 | 0.9892 |
| CS_ITA_2.5 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | 29 ± 1 | 54 ± 4 | 0.03117 | 2.8 | 0.9785 |
| CS_ITA_5 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 24 ± 2 | 72 ± 5 | 0.09963 | 2.4 | 0.9924 |
| CS_ITA_9.5 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 23 ± 1 | 66 ± 3 | 0.23976 | 2.4 | 0.9975 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silvestro, I.; Fernández-García, M.; Ciarlantini, C.; Francolini, I.; Girelli, A.; Piozzi, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Chitosan for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Removal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113192
Silvestro I, Fernández-García M, Ciarlantini C, Francolini I, Girelli A, Piozzi A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Chitosan for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Removal. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113192
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilvestro, Ilaria, Marta Fernández-García, Clarissa Ciarlantini, Iolanda Francolini, Annamaria Girelli, and Antonella Piozzi. 2022. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Chitosan for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Removal" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113192
APA StyleSilvestro, I., Fernández-García, M., Ciarlantini, C., Francolini, I., Girelli, A., & Piozzi, A. (2022). Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Chitosan for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Removal. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113192








