Abstract
Pharmacological agents limiting secondary tissue loss and improving functional outcomes after stroke are still limited. Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive component of Cannabis sativa, has been proposed as a neuroprotective agent against experimental cerebral ischemia. The effects of CBD mostly relate to the modulation of neuroinflammation, including glial activation. To investigate the effects of CBD on glial cells after focal ischemia in vivo, we performed time-lapse imaging of microglia and astroglial Ca2+ signaling in the somatosensory cortex in the subacute phase of stroke by in vivo two-photon laser-scanning microscopy using transgenic mice with microglial EGFP expression and astrocyte-specific expression of the genetically encoded Ca2+ sensor GCaMP3. CBD (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) prevented ischemia-induced neurological impairment, reducing the neurological deficit score from 2.0 ± 1.2 to 0.8 ± 0.8, and protected against neurodegeneration, as shown by the reduction (more than 70%) in Fluoro-Jade C staining (18.8 ± 7.5 to 5.3 ± 0.3). CBD reduced ischemia-induced microglial activation assessed by changes in soma area and total branch length, and exerted a balancing effect on astroglial Ca2+ signals. Our findings indicate that the neuroprotective effects of CBD may occur in the subacute phase of ischemia, and reinforce its strong anti-inflammatory property. Nevertheless, its mechanism of action on glial cells still requires further studies.
1. Introduction
Stroke is one of the most important causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Globally, from 1990 to 2019, the number of incident strokes and related deaths increased by 70% and 43%, respectively [1]. Stroke survivors are particularly vulnerable to secondary consequences, including sensory, motor, and cognitive impairments, as well as mood dysfunction [2]. Current pharmacological treatment of acute stroke essentially focuses on the reperfusion of salvageable, non-infarcted ischemic brain tissue, employing intravenous administration of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA). However, only a small number of patients are suitable to receive effective thrombolytic therapy within its narrow therapeutic window (4–6 h) after stroke onset [3]. Therefore, the identification of new therapeutic strategies capable of counteracting neurodegenerative processes and functional deficits occurring after an ischemic insult is one of the major challenges in this field. Stroke triggers a robust inflammatory response, and resident microglia are the first cells sensing and responding to the damage [4]. Within minutes following injury, microglia become activated and secrete pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist [5]. Concomitantly, astrocytes undergo significant changes in their internal Ca2+ concentration, which in turn mediate the reactive phenotype, namely reactive astrogliosis, one of the classic pathological hallmarks of ischemic stroke [6,7,8]. The astroglial and microglial reactive phenotypes and the subsequent inflammatory response after stroke encompass both beneficial and harmful effects, and their real contribution to the progression of stroke still remains unclear [9,10,11]. Breakdown of the blood–brain barrier takes place after an episode of cerebral ischemia, which facilitates the infiltration of peripheral leukocytes to the ischemic brain. Leukocytes further increase the inflammatory response by enhancing excitotoxicity and oxidative stress, accompanied by cell death [4]. These pathological events propagate microvascular dysfunction, edema expansion, and poor clinical outcome [12]. The complex pathophysiology of ischemic stroke may be the reason for the ineffectiveness of treatments that act only on some mechanisms of the ischemic cascade. Thus, therapies acting on multiple pathophysiological processes might offer promising results in the treatment of stroke. Cannabidiol (CBD), one of over 100 phytocannabinoids identified in Cannabis sativa, has received substantial research attention in the last few years due to its multimodal pharmacological profile and remarkable safety [13,14,15]. In humans, CBD is approved for treating spasticity in multiple sclerosis [16] and seizures associated with Lennox–Gastaut or Dravet syndromes in children [17]. In preclinical settings, several studies point towards neuroprotective actions for CBD in different pathology models such as Parkinson’s disease [18,19], Alzheimer’s diseases [20,21], epilepsy [22,23], multiple sclerosis [24,25,26], schizophrenia [27,28], cerebral ischemia [29,30], as well as spinal cord injury [31,32]. The neuroprotective effects of CBD in cerebral ischemic conditions have been associated with the capacity of this compound to restrain inflammatory responses mediated by inflamed microglial cells and activated astrocytes [9,33]. For example, reductions in microglia and astroglial reactivity were observed in mice treated with CBD after bilateral common carotid artery occlusion [33,34], a model of transient global cerebral ischemia. Improvements in neurological deficits and cerebral blood flow were accompanied by a reduced infarct size and microglial activation in mice treated with CBD after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) [35,36,37,38]. Only few studies examined the modulatory effects of CBD on glial cells in experimental models of ischemic stroke [9,35,38]. Although several studies have demonstrated a beneficial effect of CBD in focal cerebral ischemia, administration of CBD was performed before the MCAO [30,37,38,39]. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to explore the effect of CBD when administered acutely and after the onset of ischemia in adult mice. Furthermore, we investigated the effect of CBD on glial cells using an in vivo approach. For this purpose, we took advantage of transgenic mice with microglial expression of the enhanced green fluorescent protein EGFP [40] and the astrocyte-specific expression of the genetically encoded Ca2+ indicator GCaMP3 [41,42] to test the impact of CBD on microglial activation and astroglial Ca2+ activity over time, in vivo, using two-photon laser-scanning microscopy (2P-LSM).
2. Results
2.1. Ischemia-Induced Neurodegeneration and Neurological Deficit Are Reduced after Cannabidiol Treatment
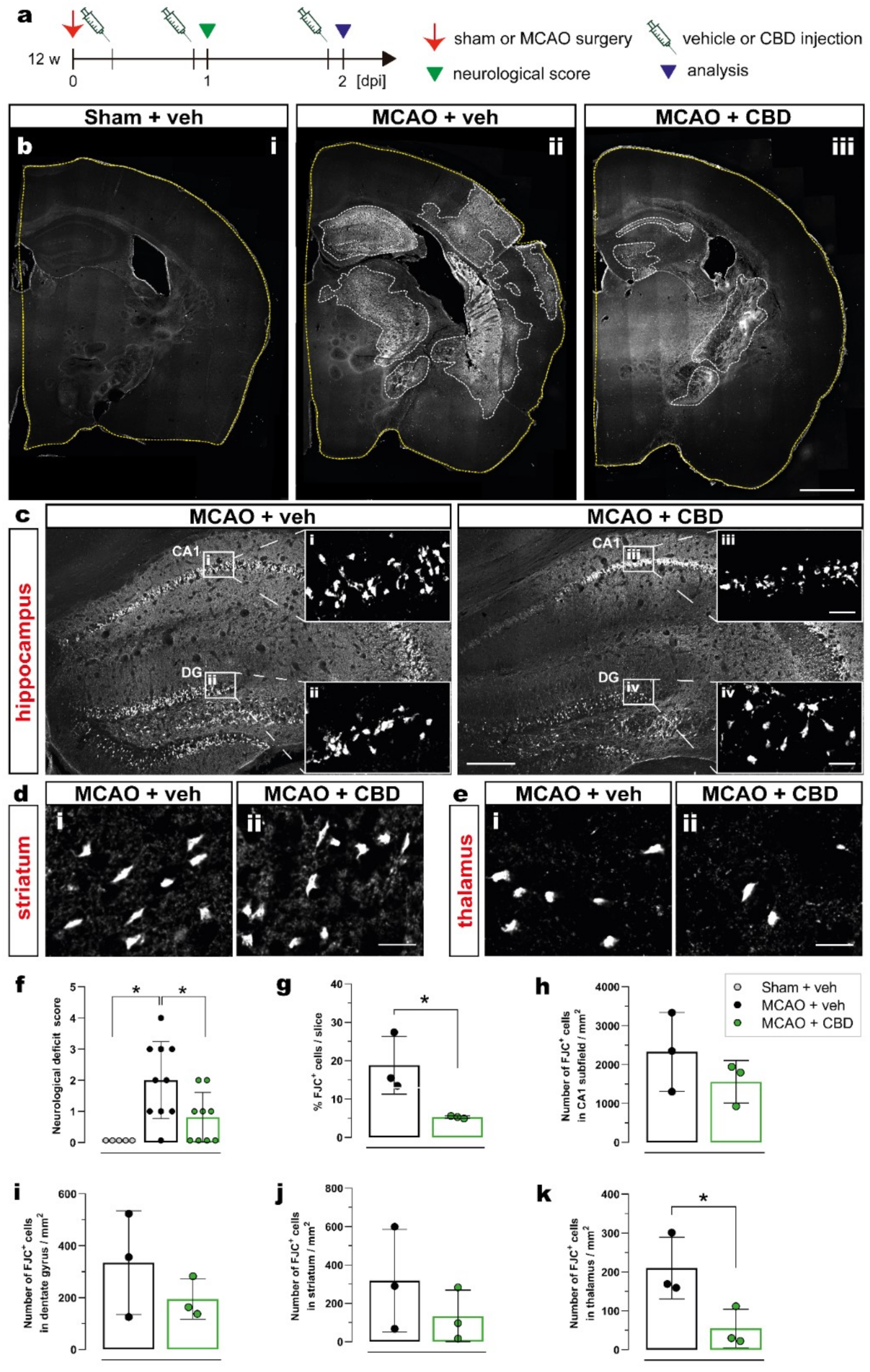
To evaluate the effect of cannabidiol (CBD) on ischemia-induced neurological deficits and neurodegeneration, 12-week-old C57BL/6N wt mice were submitted to 15 min middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and treated with intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of vehicle or CBD (10 mg/kg) at 30 min, 24 h, and 48 h after reperfusion. The effects of ischemia and CBD on neurological function were evaluated 24 h after reperfusion using the neurological deficit score (Figure 1a). To assess neurodegeneration, the number of dying neurons was quantified by Fluoro-Jade C (FJC) staining 2 days after sham or MCAO surgery in the hippocampal CA1 subfield, dentate gyrus (DG), thalamus, and striatum in both ipsi- and contralateral hemispheres (Figure 1b–e). Ischemic mice treated with vehicle presented a mean deficit score of 2 (moderate impairment), while sham-operated mice displayed normal behavior. Treating mice submitted to MCAO with CBD resulted in a significant reduction in the deficit score to about 1 (mild impairment) (Figure 1f). An increased percentage of FJC+ cells per slice was found in the brains of ischemic animals treated with vehicle compared to the brains of ischemic animals treated with CBD, reflecting the beneficial effect of CBD on MCAO-induced neurodegeneration (Figure 1g). While in the hippocampus (CA1, DG) and striatum, the numbers of degenerating neurons (FJC+ cells) showed only a beneficial trend between mice treated with vehicle and CBD (Figure 1h–j, respectively), administering CBD led to a significantly reduced number of dying neurons in the thalamus (Figure 1k).
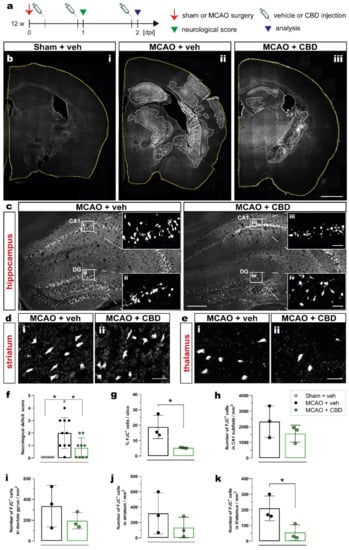
Figure 1.
Reduction in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration and neurological deficits after CBD treatment. (a) Experimental design: C57BL/6N WT mice were submitted to sham or MCAO surgery and were injected with vehicle or CBD. One day after reperfusion the neurological score was determined and the brain tissue was analyzed at 2 dpi for FJC staining. (b) Overview of coronal brain sections among the experimental groups (i) Sham + veh, (ii) MCAO + veh, (iii) MCAO + CBD). (c) Overview of the hippocampus showing the FJC+ neurons; magnified view from white box in (c) in the CA1 area (i, iii) and DG (ii, iv). (d,e) Micrographs showing FJC+ cells in the striatum (d) and thalamus (e) of mice treated with vehicle (i) or CBD (ii). (f) Neurological deficit score of mice among the groups. (g) Quantification of ischemic area represented as percentage (%) of FJC+ cells per coronal brain slice. (h–k) Quantification of FJC+ cells represented as number of FJC+ cells in the CA1 subfield (h), DG (i), striatum (j), or thalamus (k). Data are shown as individual values (closed circles) and the means ± SD (columns and bars) of the experimental groups (n = 5–10/group (f), n = 3/group (g–k)). Non-parametric data were analyzed using the Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (f). Parametric data were analyzed using a Shapiro–Wilk normality test and were compared using Student’s unpaired t-test (g–k). * p ≤ 0.05. Scale bars: 1.000 µm, (b) overviews; 200 µm, (c) overviews; and 20 µm, (d,e) magnified views of (c). CBD, cannabidiol; DG, dentate gyrus; FJC, Fluoro-Jade C; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion.
2.2. Less Activated Microglia Cells in the Ischemic Brain after Cannabidiol Treatment
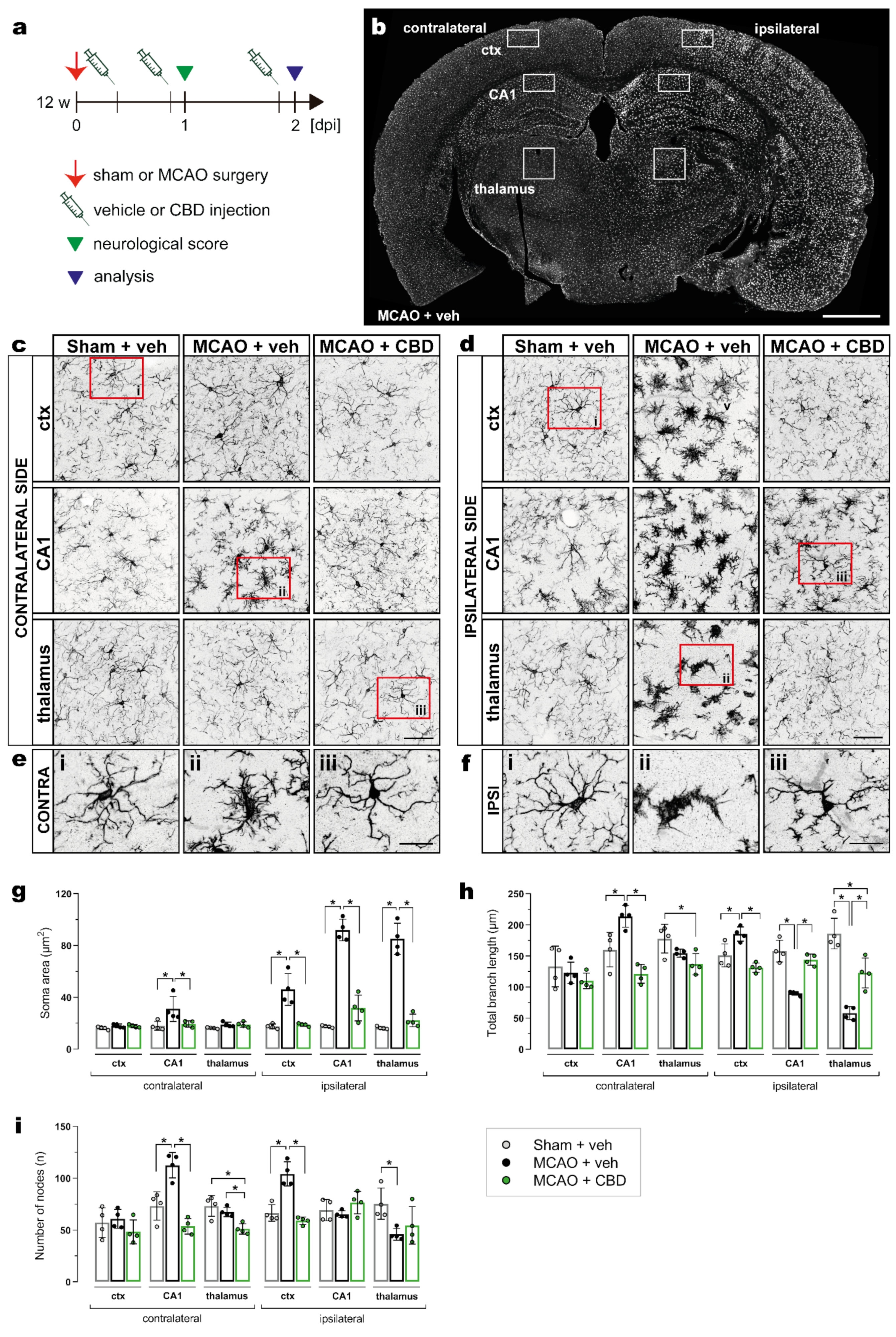
MCAO-induced microglial activation was assessed using the same experimental design as described above (Figure 2a) and by immunohistochemistry of Iba1 in the cortex, hippocampal CA1 subfield, and thalamus on the contra- and ipsilateral sides of the brain (Figure 2b). Microglial morphology was analyzed by semiautomatic extraction of morphological parameters using MIA software (see section “Materials and Methods” for details). In general, a strong activation of microglia was observed at the ipsilateral side of the MCAO when compared to sham surgery or to the contralateral side, and this activation was significantly reduced by the CBD treatment (Figure 2b–f). The soma area is most sensitive to the ischemic insult (Figure 2g). As expected, it appears to directly correlate with microglia hypertrophy. The total branch length as well as the number of process nodes are more variable in respect to the brain regions (Figure 2h,i).

Figure 2.
Reduction in ischemia-induced microglial activation by CBD treatment. (a) Experimental design: C57BL/6N WT mice were submitted to sham or MCAO surgery, and were injected with vehicle or CBD. Brain tissue was analyzed at 2 dpi for Iba-1 immunoreactivity. (b) Overview of coronal brain section showing the ctx, CA1 subfield, and thalamus, where the analysis for microglial morphology was performed. (c,d) Micrographs showing the heterogeneity in the morphology of Iba-1+ cells on the contralateral (c) and ipsilateral sides (d) of the brain among the groups. (e,f) Magnified views from the areas indicated by red boxes in (c) and (d) of the ctx (i), CA1 (ii), and thalamus (iii) on the contra- (e) and ipsilateral sides (f). (g–i) Soma area, total branch length, and number of nodes in the ctx, CA1, and thalamus on the contra- and ipsilateral sides of the brain. Data are shown as individual values (closed circles) and the means ± SD (columns and bars) of the experimental groups (n = 4/group). Data were analyzed using a Shapiro–Wilk normality test and were compared using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. * p ≤ 0.05. Scale bars: 1000 µm, (b) overview; 50 µm, (c,d); and 20 µm, (e,f) magnified views. CBD, cannabidiol; ctx, cortex; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion.
In ischemic mice treated with CBD, the microglial soma area, total branch length, and number of nodes in CA1 from the contralateral brain side were not different from sham-operated animals (Figure 2g–i). Treatment with CBD was also able to reverse the ischemia-induced alterations of total branch length, i.e., the increase in the cortex as well as the decrease in the hippocampus and thalamus on the ipsilateral side (Figure 2h). In addition, ischemic mice treated with CBD exhibited a number of nodes in the cortex that did not differ from sham-operated mice (Figure 2i).
2.3. In Vivo 2P-LSM Revealed a Reduced Number of Microglia Cells with Smaller Somata in the Somatosensory Cortex of Ischemic Animals after Cannabidiol Treatment
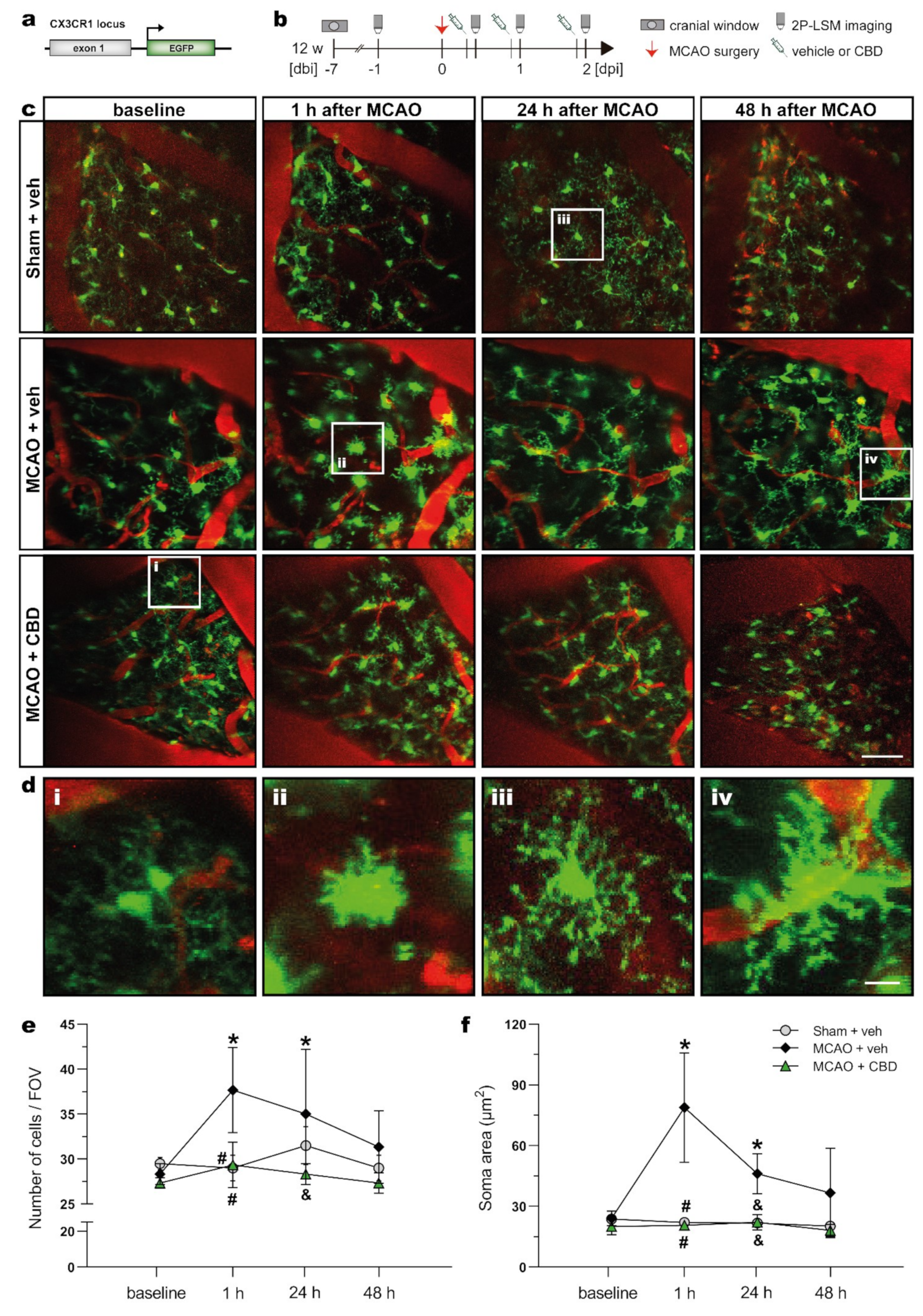
In order to evaluate the progression of the MCAO insult and the concomitant CBD treatment on microglial activation in vivo, heterozygous mice with microglia-specific EGFP expression (TgH(CX3CR1-EGFP)) were submitted to MCAO 1 week after recovery from a cortical craniotomy and imaging window implantation. The ischemic mice were i.p. injected with vehicle or CBD at 30 min, 24 h, and 48 h after reperfusion. In vivo two-photon laser-scanning microscopy (2P-LSM) imaging was performed at different time points (Figure 3a,b), and the number of EGFP+ cells per field of view (FOV) and the microglial soma area were analyzed 2 days after reperfusion (Figure 3c–f). At baseline conditions, no differences in the number of cells and soma area could be detected between groups, indicating no microglial activation before the MCAO insult for all experimental groups. This also indicates that the implantation of the cranial window itself did not elicit an apparent microglia activation. One hour after the onset of ischemia, a larger number of microglia with increased soma area were found in the somatosensory cortex of ischemic mice treated with vehicle. Longitudinal analysis of the time-dependent morphological changes indicates that ischemia-induced microglial activation was strongly prevented by CBD treatment (Figure 3e,f). Similar outcomes were observed for cell density and soma size at 24 h after MCAO. The number of microglia cells and soma area did not differ between the sham-operated and CBD-treated ischemic mice at any recorded time point. Taken together, in vivo microglial imaging displayed a beneficial effect of CBD on microglia activation evoked by an ischemic insult.

Figure 3.
In vivo 2P-LSM demonstrated reduced microglial activation in the cortex of ischemic mice treated with CBD. (a) Transgene structure of mouse line used for in vivo 2P-LSM imaging. (b) Experimental design: CX3CR1EGFP mice underwent cortical craniotomy and, after 1 week recovery, were submitted to MCAO. The ischemic mice were injected with vehicle or CBD, and 2P-LSM imaging was performed before MCAO (baseline) and 30 min after the injections. (c), Maximum-intensity projections of the EGFP signal for representative FOV among the experimental groups. Cerebral blood vessels were labeled with Texas Red dextran. (d) Magnified views indicated by white boxes in (c) at baseline conditions (i) and 1 h (ii), 24 h (iii), and 48 h (iv) after MCAO among the groups. (e) Number of EGFP+ cells found per FOV over the recorded time points. (f) Soma area of EGFP+ cells recorded with 2P-LSM. The bars represent the means ± SD of the experimental groups (n = 3/group). Data were analyzed using a Shapiro–Wilk normality test and were compared using a two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Group was the between-subject factor and time (test day) was the within-subject factor. * p ≤ 0.05 compared to MCAO + veh group at baseline, # p ≤ 0.05 compared to MCAO + veh group at 1 h, and & p ≤ 0.05 compared to MCAO + veh group at 24 h. Scale bars: 50 µm (c) and 10 µm (d) magnified views. 2P-LSM, two-photon laser scanning microscopy; CBD, cannabidiol; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; FOV, field of view; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion.
2.4. Cannabidiol Balances Ischemia-Induced Alterations of Astroglial Ca2+ Signaling after MCAO In Vivo
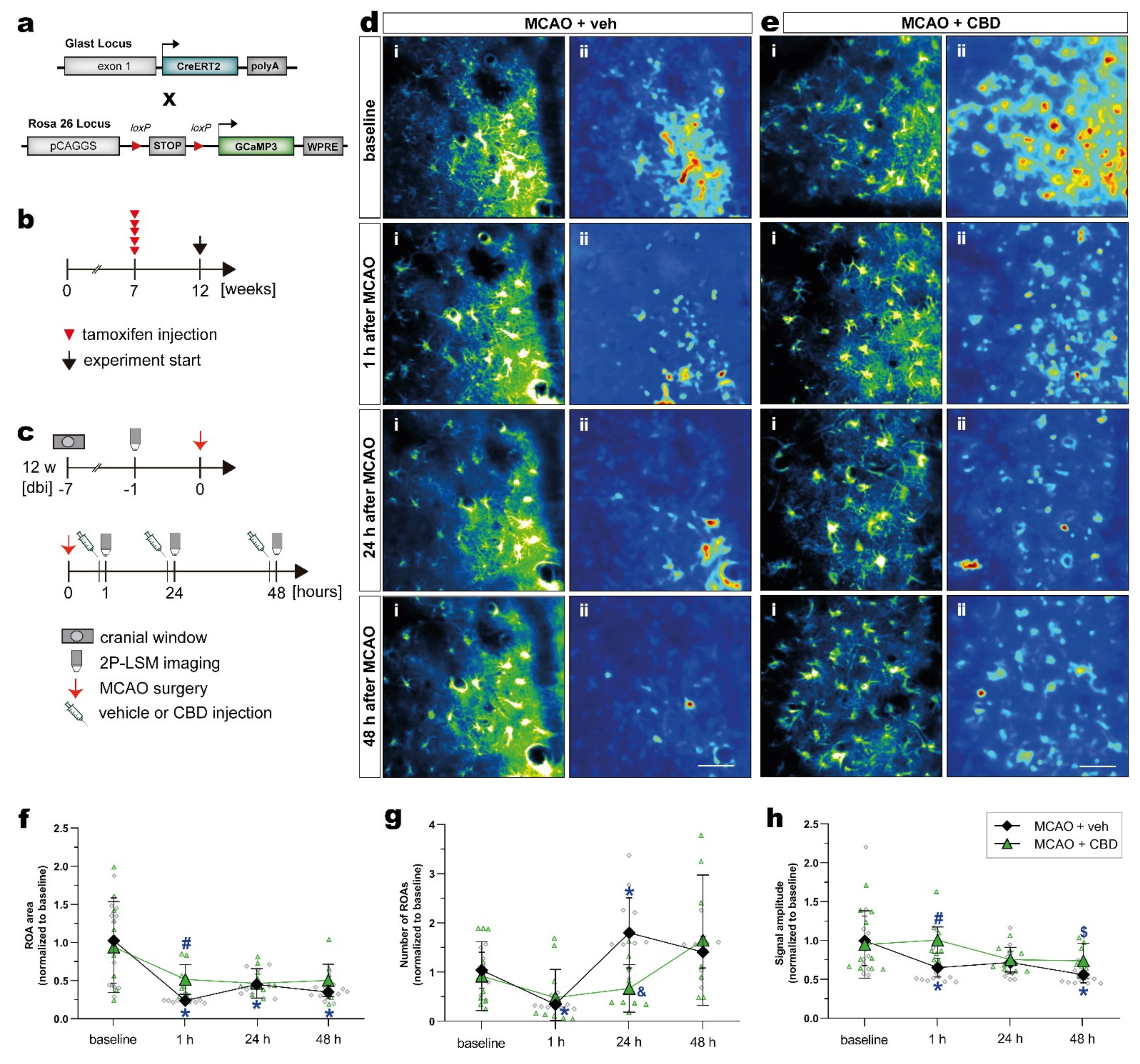
Next, we investigated in vivo astroglial Ca2+ changes in the subacute phase of stroke in the somatosensory cortex of mice, and tested whether the treatment with CBD could modulate astroglial Ca2+ signaling. In order to record astroglial Ca2+, we took advantage of GLAST-CreERT2 knock-in mice to achieve cell-specific and time-controlled expression of the genetically encoded Ca2+ indicator GCaMP3 in astrocytes [41,42]. To induce reporter expression in astroglia, 7-week-old mice with a C57BL/6N background were treated with tamoxifen (100 mg/kg body weight, i.p., five times, once per day), and MCAO was performed 5 weeks later (Figure 4a,b). The mice were submitted to the same surgeries, treatment, and 2P-LSM protocol as described before (Figure 4c). The astroglial Ca2+ changes were recorded in the somatosensory cortex. Data processing and analysis was performed using a custom-made MATLAB-based toolbox (Figure 4d,e; see section “Materials and Methods” for details).
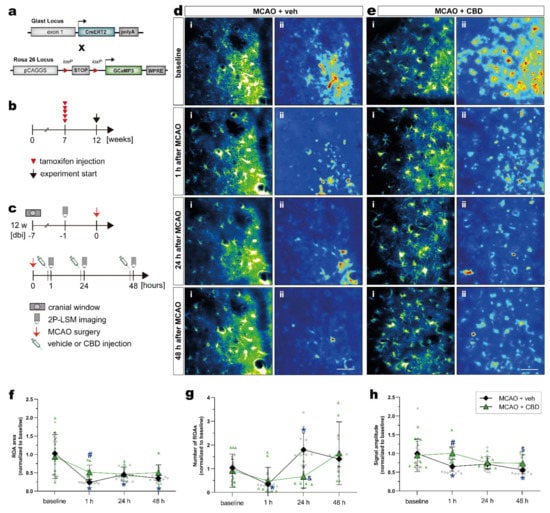
Figure 4.
Activity-based in vivo astrocytic Ca2+ signals showed higher signal amplitude and ROA area in the cortex of ischemic mice treated with CBD. (a) Scheme of transgenic constructs carrying CreERT2 and GCaMP3. (b,c) Experimental design: GCaMP3 induction was achieved in 7-week-old mice injected with tamoxifen (b). GLASTGCAMP3 mice underwent cortical craniotomy and, after 1 week recovery, were submitted to the MCAO. The ischemic mice were injected with vehicle or CBD, and in vivo 2P-LSM imaging was performed before MCAO (baseline) and 30 min after the injections (c). (d,e) Automated Ca2+ signaling analysis for ischemic mice treated with vehicle (d) or CBD (e) using a custom-made MATLAB-based software toolbox. Maximum-intensity projections of GCaMP3 signals for representative FOV (i) over the entire recording time (up to 5 min) and relative fluorescence change projection (ii). (f) ROA area. (g) Number of ROAs. (h) Signal amplitude. Single datasets were analyzed using a Shapiro–Wilk normality test, and data were compared using a two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. Group was the between-subject factor and time (test day) was the within-subject factor. Student’s unpaired t-test was used to compare the time points between experimental groups. * p ≤ 0.05 compared to MCAO + veh group at baseline, # p ≤ 0.05 compared to MCAO + veh group at 1 h, & p ≤ 0.05 compared to MCAO + veh group at 24 h, and $ p ≤ 0.05 compared to MCAO + veh group at 48 h. Scale bars: 50 µm (d,e). 2P-LSM, two-photon laser scanning microscopy; CBD, cannabidiol; FOV, field of view; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; ROA, region of activity.
Within 48 h after ischemic insult, astrocytes displayed a strongly reduced area compared to baseline conditions. When mice were treated with CBD, the area of these regions of activity (ROAs) was much less affected (Figure 4f). Such a balancing effect of CBD was also observed, when the number of ROAs in the ischemic forebrain was quantified (Figure 4g). While ischemic mice displayed variable numbers of ROAs within 2 days after injury, CBD dampened this variability, and the Ca2+ signals were comparable to the baseline. A similar observation was made when the signal amplitude was quantified (Figure 4h), though the time course of post-injury changes were different when the number of ROAs or the respective signal amplitudes were investigated. However, the in vivo analysis of spontaneous Ca2+ signals revealed substantial variability, as indicated by the scatter of data points (Figure 4f–h); simultaneous treatment with CBD reduces such variations and shifts the respective physiological parameters of Ca2+ signals towards baseline conditions.
In summary, CBD is a potent drug that can reduce the consequences of ischemic insults evoked by MCAO and observed as motor impairment, neuronal cell death, microglia activation, and changes in astroglial Ca2+ signaling.
3. Discussion
Despite some recent advances in the treatment of ischemic stroke caused by large-vessel occlusions, such as mechanical thrombectomy, a neuroprotective pharmacological agent that reduces the consequences of stroke is still needed in the clinical treatment of patients [43]. In this study, cannabidiol (CBD (10 mg/kg, i.p. 30 min, 24, and 48 h after ischemia)) prevented neurological deficits induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in mice. CBD also reduced ischemia-induced neurodegeneration and microglial activation, and influenced astroglial Ca2+ signaling. The results of this study agree with previous findings, showing the neuroprotective action of CBD treatment in different in vitro and in vivo models of neurodegeneration [18,21,26]. For example, CBD prevented learning deficit and cytokine expression induced by intraventricular administration of β-amyloid, an in vivo model of Alzheimer’s disease [20]. In vitro, pretreatment with CBD rescued the β-amyloid peptide-mediated long-term potentiation deficit in the CA1 area of hippocampal slices [44]. Moreover, in an animal model of multiple sclerosis, CBD treatment reduced the clinical signs and disease progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. These effects of CBD were accompanied by decreased axonal damage, microglial activation, and T-cell proliferation [24]. Therefore, CBD is a promising candidate for the treatment of neuronal degeneration in humans. Indeed, CBD is very well tolerated, and produces adverse effects only at low incidence [45,46]. In clinical trials, the most common adverse effects reported after CBD administration included somnolence, sedation, fatigue, diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea [47,48]. It is worth mentioning that serious adverse effects following CBD treatment were observed in clinical trials with epilepsy, including severe somnolence, lethargy, increased hepatic transaminases, rash, and pneumonia. Nevertheless, these effects were related to the concomitant use of CBD with other antiepileptic drugs, including clobazam and valproate [49,50,51,52,53]. The impairment of sensorimotor and cognitive performance is a common outcome in rodents with MCAO [54,55,56]. Here, we observed neurological impairment in mice during the subacute phase after injury, i.e., 1 day after MCAO. CBD attenuated the effects of MCAO, reflected by a decrease in the neurological score, indicating an overall positive effect on functional outcomes after the injury. Consistent with our results, CBD led to an improvement in motor and neurological deficits in mice with MCAO and treated immediately before and 3 h after the occlusion. These effects of CBD were accompanied by a reduction in infarct size and an increase in cerebral blood flow [30,37,57]. In addition, CBD (5 mg/kg, i.p.) given once, 15 min after reperfusion, led to functional and sensorimotor recovery in neonatal rats submitted to MCAO [35]. Similar beneficial effects of CBD were also observed in MCAO rats treated with CBD by intracerebroventricular injection for 5 days before surgery [36]. However, mice submitted to MCAO and treated with CBD (3 mg/kg) from day 5 did not show any improvement in neurological score or motor coordination on day 14 after reperfusion. Taken together, it seems that the neuroprotective effects of CBD in cerebral ischemic insults are time-dependent, and might occur in the complex early phase of the injury. MCAO is known to cause a robust reduction in cerebral blood flow and consequent massive neuronal death. Neurodegeneration (detected by Fluoro-Jade C staining) was seen in the hippocampus, striatum, and thalamus of MCAO animals, 2 days after the insult. CBD treatment reduced the extension of neuronal loss induced by MCAO in the thalamus. Protective effects of CBD on neuronal death have been detected in the striatum and hippocampus of MCAO mice treated immediately before and 3 h after the occlusion [38], and gerbils submitted to global brain ischemia treated 5 min after reperfusion [58]. In addition, a reduction in necrotic neurons in the cortex was reported in newborn pigs submitted to hypoxic ischemic brain injury and treated with CBD (1 mg/kg, intravenous) 30 min after the insult [59]. In one study, CBD (10 mg/kg, i.p. 30 min before and 3, 24, and 48 h after ischemia) decreased neurodegeneration and normalized caspase-9 protein levels 21 days after global cerebral ischemia in mice [34]. Neuroinflammation is a critical aspect of stroke, which includes the early activation of microglia and production of cytokines and chemokines [60,61,62]. Depending on injury severity, microglia may present distinct functional and spatiotemporal profiles, which may protect or contribute to the ischemic injury evolution [63,64,65]. We observed an extensive microglial activation up to 2 days after MCAO, which extended from the ipsilateral side of the brain, including large areas in the cortex, hippocampus, striatum, and thalamus, to the contralateral hippocampus (Figure 2g–i). In line with our results, early microglial activation was also observed in regions outside of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory, such as the contralateral cortex and hippocampus [66]. In this sense, microglial reactivity not only indicates imminent ischemic neuronal damage, but possibly reflects subtle changes in neuronal activity outside the MCA territory. Selective neuronal loss, which refers to the death of single neurons with a preserved extracellular matrix, i.e., in the ischemic penumbra zone, is consistently associated with microglial activation in the first few days after injury [63,67,68,69]. Our results also show that microglia morphology varies across brain regions within the ipsilateral hemisphere. Microglia with robust de-ramification and amoeboid-like morphology were prominent in brain regions with intense neurodegeneration, i.e., hippocampus and thalamus, while hyper-ramified microglia with increased soma area were observed in the cortex. Our results support the idea that microglia morphology after stroke is an indicator of cerebral injury severity, involving initial increases in microglial ramification and cell body size, followed by de-ramification and ameboid-like morphology according to the progression of neurodegeneration. Cannabidiol-mediated neuroprotection after experimental cerebral ischemia has generally been related to the modulation of inflammation, including the control of microglia activation, and the toxicity exerted by these cells by producing proinflammatory mediators [34,59,70]. For example, in microglial cells challenged with lipopolysaccharide, CBD inhibited the release of proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β) and also of glutamate, a non-cytokine mediator of inflammation closely related to excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration processes [71,72]. In mice submitted to 4 h of MCAO, repeated CBD treatment from day 1 after ischemia reduced the number of Iba1-positive cells expressing the pleiotropic HMGB1 protein (high-mobility group box 1) with proinflammatory function, which is released in high concentrations during the acute phase of ischemic processes [9]. A reduction in the number of Iba1-positive cells was also reported in neonatal rats submitted to a model of ischemic stroke and treated once with CBD (5 mg/kg, i.p.) 15 min after the injury [35]. Here, we also demonstrate the strong microglial activation 2 days after the onset of ischemia, and the effect of CBD thereon (Figure 2g–i). In our study, CBD treatment was able to revert ischemia-induced alterations in microglial morphological parameters in the cortex, CA1 area, and thalamus. To test the effects of CBD on microglia in vivo, we performed time-lapse imaging of microglial activity using two-photon laser-scanning microscopy (2P-LSM). Immediately after reperfusion, we observed that microglia became activated and increased their number in the ischemic penumbra. Supporting our findings, in vivo imaging of mice submitted to a cortical microhemorrhage has shown a coordinated pattern of microglia migration, where microglia within 200 µm of the injury migrated toward the lesion, leading to an increased microglia local density [73]. Moreover, in mice submitted to MCAO, it was demonstrated that many round-shaped microglia migrated to the peri-infarct area 24 h after the insult [74]. In vivo, microglia in the penumbra were found associated with blood vessels within 24 h post reperfusion. These perivascular microglia started to phagocytose endothelial cells, leading to the activation of the local endothelium, and contributing to the degradation of blood vessels, with an eventual breakdown of the blood–brain barrier [75]. Considering these findings, the inhibition of microglial activation within the first day after stroke could stabilize blood vessels in the penumbra, improving the outcomes after ischemia through an increase in blood flow. Our results show that CBD treatment decreased microglia activation after MCAO, consistent with other findings, and reinforces the strong anti-inflammatory profile of CBD in ischemic conditions. Additional to microglia, astrocytes also play an active role in the neuroinflammation process, producing complex and not yet completely understood responses to cerebral ischemia [76]. We tested whether focal ischemia would impact astroglial Ca2+ signaling, a characteristic form of excitability and reactivity in this cell type [77], and whether CBD treatment could modulate these signals. In our study, in vivo 2P-LSM imaging revealed that cortical astroglial Ca2+ signals in ischemic mice displayed a smaller area and amplitude up to 2 days after MCAO. In contrast to our findings, in vivo imaging of mice submitted to photothrombotic-induced focal cerebral ischemia (FCI) for 20 min showed an increase in frequency and amplitude of transient Ca2+ signals in astrocytes located in the penumbra area [78]. Moreover, permanent MCAO led to increased astroglial Ca2+ activity in the penumbra of aged mice, while a moderate reduction in Ca2+ activity at regions of interest was observed in adult mice [79]. A strong increase in intracellular Ca2+ in astrocytes associated with detrimental peri-infarct depolarizations was reported by Rakers and Petzold [80] in mice after permanent MCAO. It is known that astrocytes display enhanced intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in response to neuronal death and alarmin release, thus suggesting that the alterations in astrocytic Ca2+ dynamics detected in these studies may be specific to the peri-infarct zone as well as the penumbra zone. On the contrary, the somatosensory cortex (which we assessed via 2P-LSM) is not directly affected by local neuronal loss, but from the loss of ascending projections from the infarct and peri-infarct area, thus possibly explaining the reduction in cortical astroglial Ca2+ dynamics. If this is true, the dampening effect of CBD on astroglial Ca2+ alterations would therefore probably be a secondary effect mediated by CBD as a protective effect against neuronal loss. It is also important to consider methodological differences when using a permanent model of FCI or photothrombotic-induced FCI, most importantly for preventing cerebral reperfusion. To our knowledge, no study has been conducted to investigate the impact of CBD on astroglial Ca2+ signals after stroke. Here, the treatment with CBD balanced ischemia-induced alterations in astroglial Ca2+ signaling after MCAO. The effect of CBD was observed by an increase in ROA area and signal amplitude in ischemic animals in vivo (Figure 4f,h). Other studies have demonstrated an overall positive effect of CBD on astroglial activation. For example, in newborn piglets submitted to hypoxic ischemic brain injury, treatment with CBD attenuated the loss of cortical GFAP-positive cells and decreased the levels of S100B in the cerebrospinal fluid [81]. In mice submitted to global cerebral ischemia, CBD (10 mg/kg, i.p.) decreased the hippocampal reactivity of astrocytes (GFAP-positive) and total levels of GFAP 21 days after the insult [34]. In cultured astrocytes, CBD treatment decreased the ß-amyloid-induced release of proinflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β. In the same study, CBD treatment (10 mg/kg, i.p.) for 15 days diminished the proinflammatory response and gliosis triggered by intrahippocampal injection of ß-amyloid [82]. It is important to mention, that these studies evaluated astroglial activation after brain insults at periods later than 2 days after the injury. CBD mitigates ischemia-induced neurological impairments and neurodegeneration. Importantly, we show a reduction in microglial activation in different brain regions after CBD treatment, and confirm these findings in vivo. Furthermore, we point out a possible effect of CBD on modulating astroglial Ca2+ signals in ischemic brains.
4. Conclusions
Overall, the present findings suggest that the functional and structural protective effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are closely associated with anti-inflammatory activity in the subacute phase of ischemia. Even though the mechanisms of action of CBD are not yet fully understood, our data have heuristic value to inspire further studies investigating the effect of CBD using different treatment schedules, for example, when administered for longer periods or later after the onset of ischemia. In conclusion, our data highlight the potential of CBD as a neuroprotective compound in stroke.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Ethics Statement
All animal procedures were carried out at the University of Saarland in strict accordance with the recommendations to European and German guidelines for the welfare of experimental animals and approved by the Saarland state’s “Landesamt für Gesundheit und Verbraucherschutz” in Saarbrücken/Germany (animal license number: 65/2013 and 36/2016).
5.2. Animals
Mice were housed at the animal facility of the Center for Integrative Physiology and Molecular Medicine (CIPMM) in Homburg under controlled temperature (22 ± 1 °C) and 12 h light–dark cycle, with food and autoclaved tap water ad libitum (standard autoclaved rodent diet, Ssniff Spezialdiäten, Soest, Germany). Experiments were conducted with 12- to 15-week-old male and female C57BL/6N wildtype (WT) and transgenic mice with C57BL/6N background. To image microglia in vivo, heterozygous knock-in mice (TgH(CX3CR1-EGFP)) were used (Cx3cr1tm1Litt, MGI: 2670351). To visualize astrocytic Ca2+ signals, the inducible CreERT2 DNA recombinase knock-in mouse line TgH(GLAST-CreERT2) (Slc1a3tm1(cre/ERT2)Mgoe, MGI:3830051) was crossed to the floxed reporter mouse line TgH(Rosa26-CAG-flstopfl-GCaMP3-WPRE) (Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(CAG-GCaMP3)Dbe, MGI:5659933). For simplification, hereafter, the mouse lines are termed CX3CR1EGFP and GLASTGCAMP3, respectively [40,41,42].
5.3. Tamoxifen Induced Recombination
To induce GCaMP3 expression, 7-week-old mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with tamoxifen for 5 consecutive days (once per day, 100 mg/kg body weight) [83] (Figure 4b).
5.4. Cannabidiol Treatment
Cannabidiol (CBD (THC Pharma, cat. no. DWO161.207-2, Frankfurt, Germany)) was diluted with 1% Tween 80 in sterile isotonic saline (vehicle). The animals were randomly assigned to receive injections (i.p.) of CBD 10 mg/kg or vehicle 30 min, 24 h, and 48 h after surgery (Figure 1a, Figure 2a, Figure 3b and Figure 4c). The 10 mg/kg dose of CBD and the administration route were based on previous studies that reported a neuroprotective effect of CBD against cerebral ischemia in rodents [34,36]. To date, no adverse effects related to the use of this dose in mice have been reported in the literature [45]. It is important to mention that CBD is highly lipophilic and quickly crosses the blood–brain barrier, as previously demonstrated in mice and rats [84]. The number of mice used in the experimental groups are listed below (Table 1).

Table 1.
Sample size according to experimental groups and analyses.
5.5. Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was realized in animals under inhalational anesthesia (1.5–2% isoflurane, 66% O2, and 33% N2O) and executed as described previously [85]. Briefly, the left common carotid artery (CCA) and the external carotid artery were permanently ligated with silk sutures. A silicone-coated filament (Doccol Corp, cat. No. 602156PK10Re, Sharon, MA, USA) was introduced through an arteriotomy and advanced into the right internal carotid artery until mild resistance was felt, indicating the filament reached the origin of the MCA to occlude the blood flow. After 15 min occlusion, the filament was gently withdrawn, and a suture was made around the CCA to prevent backflow through the arteriotomy [86]. After recovery from anesthesia, the mice were kept in their cages with free access to food and water and received appropriate pain treatment (analgesic and antiphlogistic agents for at least three consecutive days). In addition, the mice received 10% glucose (0.5 mL/30 g body weight, subcutaneously) as a fluid replacement after the surgeries.
5.6. Cortical Craniotomy
For in vivo two-photon laser-scanning microscopy (2P-LSM), a cranial window was prepared over the somatosensory cortex (3.4 mm posterior to bregma and mediolateral 1.5 mm, 3–4 mm diameter) using an engraving driller as previously described [87]. After bone removal, a coverslip was placed on the exposed brain and the edge was sealed with dental cement (RelyX®, 3M ESPE, Saint Paul, MN, USA). Finally, a custom-made metal holder (5 mm diameter) was placed over the coverslip and glued with dental cement onto the bone.
5.7. Neurological Score
Mice were evaluated for neurological deficits and motor impairment at 24 h after MCAO using the modified Bederson score system [88,89]. Mice were first held by the tail 1 m above the floor and observed for forelimb flexion. Thereafter, they were placed on plastic-coated paper and lateral pressure behind the shoulder was applied repeatedly in each direction with the tail held by hand, registering sliding behavior. Finally, mice were allowed to move around freely and observed for circling behavior. Mice were staged as listed below (Table 2; Figure 1a). Two mice presenting a score of 5 were euthanized and excluded from the experiment.

Table 2.
Bederson neurological score (0–5).
5.8. Immunohistochemistry
Mice were perfused (4% paraformaldehyde), and post-fixed coronal tissue sections (40 µm) at the hippocampal level (bregma −1.34 mm to −2.70 mm, Franklin and Paxinos, 1997) were collected with a Leica VT1000S vibratome (Leica Biosystems, Wetzlar, Germany) and used for immunohistochemistry of free-floating tissue sections as published previously [85]. Briefly, sections were incubated in blocking solution (0.3% Triton X-100, 5% horse serum in PBS, 1 h, room temperature (RT)) following incubation with polyclonal rabbit anti-Iba1 antibody (1:1000, overnight, 4 °C, Wako Chemicals USA, cat. no. 019-19741, Richmond, VA, USA) and incubation (2 h, RT) with anti-rabbit secondary antibody (1:1000, Alexa, Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 710369, Waltham, MA, USA) and 4′,6-diamidin-2-phenylindol (DAPI, f.c. 0.025 µg/mL, AppliChem, Darmstadt, Germany). Finally, the sections were mounted with Immu-Mount®TM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Walthan, MA, USA).
5.9. Fluoro-Jade C Staining
To monitor MCAO-induced cell death, degenerating neurons were stained with Fluoro-Jade C (FJC) [90]. Vibratome sections, were mounted on gelatin-coated slides and dried at 50 °C for 30 min. The slides were immersed in 1% sodium hydroxide in 80% ethanol for 5 min, rinsed for 2 min in 70% EtOH, then for 2 min in distilled water, and incubated in 0.06% potassium permanganate solution for 15 min. Following a 1 min water rinse, the slides were transferred for 20 min into a 0.0001% solution of FJC (Sigma, cat. no. AG325, St. Louis, MO, USA) dissolved in 0.1% acetic acid vehicle in the dark. Thereafter, slides were washed in distilled water, air dried, and mounted with DPX (Sigma, cat. no. 44581 St. Louis, MO, USA).
5.10. Microscopic Analysis and Quantification on Fixed Brain Slices
Three brain sections per mouse, and at least three mice per group, were analyzed. The sections were the cortex, hippocampus, and thalamus in both brain hemispheres. Epifluorescent micrographs (FJC) were recorded using an automated slide scanner (AxioScan.Z1 equipped with the Colibri 7 LED Light Source and appropriate filters, and analyzed with ZEN1 software (Blue Edition, all Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). Confocal z-stacks were obtained using a laser-scanning microscope (LSM-710, Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) as previously described [85], processed with Fiji/ImageJ software [91], and displayed as maximum intensity projections for analyses with the semiautomatic morphological parameter extractor MIA software (provided by Prof. Bart Eggen, University of Groningen, The Netherlands).
5.11. Two-Photon Laser-Scanning Microscopy
Live in vivo imaging was performed using a custom-made 2P-LSM equipped with a mode-locked Ti:Sapphire laser (Vision II, Coherent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Scanning and image acquisition were controlled by ScanImage software [92]. The setup was equipped with XY-galvanometer-based scanning mirrors (Cambridge Technology). The excitation wavelength of the laser was set at 890 nm and a 20×/1.0 water-immersion objective (W Plan-Apochromat, Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) was used. To minimize photodamage, the average excitation laser intensity was kept at a minimum for a sufficient signal-to-noise ratio, ranging from 30 to 50 mW depending on depth. The emitted light was detected by photomultiplier tubes (H10770PB-40, Hamamatsu Photonics, Hamamatsu, Japan). The imaging settings were selected every time equally (512 × 512 pixel, zoom 2 (256 × 256 µm2), frame rate 1.9 Hz).
For imaging, isoflurane anesthesia was used as described for MCAO. After sedation, the animals were fixed with a metal holder on a custom-made head restrainer under the objective. Before the imaging session was started, animals were administered 50 µL Texas Red dextran (50 mg/mL, 70 kDa; Invitrogen, lot. no. 1915861, Waltham, MA, USA) via tail vein injection for visualization of brain blood vessels. Time-lapse imaging of cortical microglia was performed by the repeated acquisition of fluorescence image stacks (15 focal planes with 2 µm axial spacing) recorded 50–70 µm below the dura mater. Subsequent image stacks were recorded every 60 s, a total of 20 stacks were acquired from a single field of view (FOV). Astroglial GCaMP3 signals were recorded on a single focal plane located in the somatosensory cortex at a depth of 50–70 µm below the dura mater. Three to four regions of interest were recorded for each mouse. Astroglial images and videos were further processed using the custom-made software. The mice were imaged before (baseline), 1 h, 24 h, and 48 h after MCAO, respectively.
5.12. Analyses of Ca2+ Imaging Data
Ca2+ event analysis was performed using a custom-made analysis software developed in MATLAB [93] as previously described [94]. The algorithm detects fluorescence fluctuations with respect to basal per-pixel fluorescence levels (F0), computed by fitting a polynomial curve along the temporal axis of each pixel. Event detection and analysis were based on the range projection of the normalized and detrended image stack (∆F⁄F0). Fluorescence events were detected as temporally correlated, local fluorescence peaks, and segmented into individual regions of activity (ROAs).
Before analysis, Ca2+ imaging data were run through a preprocessing pipeline performing de-noising using the PURE-LET algorithm [95], image registration, as well as a temporal median filter of size 3.
5.13. Statistical Analysis
Prism 8 software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for the statistical analysis. Data were examined for assumptions of a normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk normality test. In case of normal distribution, data were analyzed using Student’s t-test and one- or two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) as appropriate, followed by the Tukey’s or Sidak’s multiple comparison post hoc test. In the two-way repeated measures ANOVA, group was the between-subject factor and time (test day) was the within-subject factor. Non-parametric data were analyzed using the Kruskal–Wallis analysis of variance followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post hoc test. The data are expressed as mean ± SD. Values of p ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Author Contributions
E.M., F.K. and R.M.W.d.O. conceived and designed the experiments; E.M. performed MCAO and craniotomy surgeries; E.M. and P.R. carried out 2-PLSM imaging; D.G. performed behavioral test and data analysis; E.M. carried out slice preparation, immunohistochemistry, confocal imaging and data analysis; G.C. helped with microglia analysis; A.S. performed the AxioScan imaging and data analysis; F.K. and R.M.W.d.O. supervised the project; E.M. wrote the manuscript with the input from the other authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the following grants: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—PDSE Edital nº41/2018 and by the CAPES/DAAD/PROBRAL grants #57447150: Neuron-glia interaction in chronic degenerative pathologies of the CNS (AS) and #57143447: Differentiation and regeneration potential of glial cells in acute and chronic central nervous system pathologies (FK); Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft: DFG FOR 2289 (AS), DFG SFB 894 (FK) and DFG SFB 1158 (FK); European Commission H2020-MSCA ITN EU-GliaPhD #722053 (FK).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations to European and German guidelines for the welfare of experimental animals and approved by the Saarland state’s “Landesamt für Gesundheit und Verbraucherschutz” in Saarbrücken/Germany (animal license number: 65/2013 and 36/2016).
Data Availability Statement
Experimental data will be provided upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Daniel Schauenburg and Frank Rhode for their excellent animal husbandry and technical assistance support. We thank Elaine Del Bel (University of São Paulo, Brazil) for continuous support as the Brazilian coordinator of the CAPES/DAAD/PROBRAL exchange program. We thank Bart Eggen for providing MIA Software for microglia analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Selim, M.H.; Caplan, L.R. Medical complications after stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 335, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Tian, D.-C.; Li, Z.-G.; Ducruet, A.F.; Lawton, M.T.; Shi, F.-D. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertsen, K.L.; Finsen, B.; Clausen, B.H. Post-stroke inflammation—Target or tool for therapy? Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A. Glial calcium signaling in physiology and pathophysiology. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Orkand, R.K.; Kettenmann, H. Glial Calcium: Homeostasis and Signaling Function. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 99–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, G.R.; Ding, S. Reactive astrocytes and therapeutic potential in focal ischemic stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 85, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Irie, K.; Sano, K.; Watanabe, T.; Higuchi, S.; Enoki, M.; Nakano, T.; Harada, K.; Ishikane, S.; Ikeda, T.; et al. Therapeutic Time Window of Cannabidiol Treatment on Delayed Ischemic Damage via High-Mobility Group Box1-Inhibiting Mechanism. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.-Q.; Ma, X.-T.; Hu, Z.-W.; Yang, S.; Chen, M.; Bosco, D.B.; Wu, L.-J.; Tian, D.-S. Dual Functions of Microglia in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.-Y.; Gao, Z.-K.; Han, Y.; Yuan, M.; Guo, Y.-S.; Bi, X. Activation and Role of Astrocytes in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 755955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Denorme, F.; Langhauser, F.; Geuss, E.; Fluri, F.; Kleinschnitz, C. Thromboinflammation in Stroke Brain Damage. Stroke 2016, 47, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippa, J.A.; Guimarães, F.S.; Campos, A.C.; Zuardi, A.W. Translational Investigation of the Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol (CBD): Toward a New Age. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laux, L.C.; Bebin, E.M.; Checketts, D.; Chez, M.; Flamini, R.; Marsh, E.D.; Miller, I.; Nichol, K.; Park, Y.; Segal, E.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of cannabidiol in children and adults with treatment resistant Lennox-Gastaut syndrome or Dravet syndrome: Expanded access program results. Epilepsy Res. 2019, 154, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.D.; Mazurkiewicz-Bełdzińska, M.; Chin, R.F.; Gil-Nagel, A.; Gunning, B.; Halford, J.J.; Mitchell, W.; Perry, M.S.; Thiele, E.A.; Weinstock, A.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of add-on cannabidiol in patients with Lennox–Gastaut syndrome: Results of a long-term open-label extension trial. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 2228–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y.; McKeage, K.; Scott, L.J. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol/Cannabidiol (Sativex®): A Review of Its Use in Patients with Moderate to Severe Spasticity Due to Multiple Sclerosis. Drugs 2014, 74, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Patel, A.D.; Cross, J.H.; Villanueva, V.; Wirrell, E.C.; Privitera, M.; Greenwood, S.M.; Roberts, C.; Checketts, D.; VanLandingham, K.E.; et al. Effect of Cannabidiol on Drop Seizures in the Lennox–Gastaut Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos-Santos-Pereira, M.; Da-Silva, C.A.; Guimarães, F.S.; Del-Bel, E. Co-administration of cannabidiol and capsazepine reduces L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in mice: Possible mechanism of action. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 94, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, N.C.F.; dos-Santos-Pereira, M.; Guimarães, F.S.; Del Bel, E. Cannabidiol and Cannabinoid Compounds as Potential Strategies for Treating Parkinson’s Disease and l-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Moreno, A.M.; Reigada, D.; Ramírez, B.G.; Mechoulam, R.; Innamorato, N.; Cuadrado, A.; de Ceballos, M.L. Cannabidiol and Other Cannabinoids Reduce Microglial Activation In Vitro and In Vivo: Relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Spiro, A.S.; Jenner, A.M.; Garner, B.; Karl, T. Long-Term Cannabidiol Treatment Prevents the Development of Social Recognition Memory Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mice. J. Alzheimer Dis. 2014, 42, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, E.; Cunha, J.M. Hypnotic and Antiepileptic Effects of Cannabidiol. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 21, 417S–427S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, P.H.; Barker-Haliski, M.; White, H.S.; Whalley, B.J.; Glyn, S.; Sandhu, H.; Jones, N.; Bazelot, M.; Williams, C.M.; McNeish, A.J. Cannabidiol reduces seizures and associated behavioral comorbidities in a range of animal seizure and epilepsy models. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Lev, N.; Kaushansky, N.; Eilam, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Ben-Nun, A.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z. Cannabidiol inhibits pathogenic T cells, decreases spinal microglial activation and ameliorates multiple sclerosis-like disease in C57BL/6 mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecha, M.; Feliú, A.; Iñigo, P.; Mestre, L.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.; Guaza, C. Cannabidiol provides long-lasting protection against the deleterious effects of inflammation in a viral model of multiple sclerosis: A role for A2A receptors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoppo, S.; Rajan, T.S.; Galuppo, M.; Pollastro, F.; Grassi, G.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Purified Cannabidiol, the main non-psychotropic component of Cannabis sativa, alone, counteracts neuronal apoptosis in experimental multiple sclerosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 4906–4919. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, N.R.; Gomes, F.V.; Sonego, A.B.; da Silva, N.R.; Guimarães, F.S. Cannabidiol attenuates behavioral changes in a rodent model of schizophrenia through 5-HT1A, but not CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzi, J.F.; Sales, A.J.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R.; Crippa, J.A.; Del Bel, E. Cannabidiol prevents disruptions in sensorimotor gating induced by psychotomimetic drugs that last for 24-h with probable involvement of epigenetic changes in the ventral striatum. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.; Bonato, J.M.; Mori, M.A.; Mattos, B.A.; Guimarães, F.S.; Milani, H.; de Campos, A.C.; de Oliveira, R.M.W. Cannabidiol Confers Neuroprotection in Rats in a Model of Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia: Impact of Hippocampal Synaptic Neuroplasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 5338–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, K.; Hayakawa, K.; Abe, K.; Ikeda, T.; Egashira, N.; Iwasaki, K.; Fujiwara, M. Cannabidiol Prevents Cerebral Infarction Via a Serotonergic 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1A Receptor–Dependent Mechanism. Stroke 2005, 36, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkoski, M.; Guimarães, F.S.; Del-Bel, E. Cannabidiol-treated Rats Exhibited Higher Motor Score After Cryogenic Spinal Cord Injury. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Lin, Z.; Meng, Q.; Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Yan, H. Cannabidiol administration reduces sublesional cancellous bone loss in rats with severe spinal cord injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 809, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavon, A.P.; Soares, L.M.; Bonato, J.M.; Milani, H.; Guimarães, F.S.; De Oliveira, R.M.W. Protective Effects of Cannabidiol Against Hippocampal Cell Death and Cognitive Impairment Induced by Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion in Mice. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 26, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.A.; Meyer, E.; Soares, L.M.; Milani, H.; Guimarães, F.S.; de Oliveira, R.M.W. Cannabidiol reduces neuroinflammation and promotes neuroplasticity and functional recovery after brain ischemia. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceprián, M.; Jiménez-Sánchez, L.; Vargas, C.; Barata, L.; Hind, W.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Cannabidiol reduces brain damage and improves functional recovery in a neonatal rat model of arterial ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar, S.; Bigdeli, M.R. Anti-excitotoxic effects of cannabidiol are partly mediated by enhancement of NCX2 and NCX3 expression in animal model of cerebral ischemia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 794, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Mishima, K.; Nozako, M.; Hazekawa, M.; Irie, K.; Fujioka, M.; Orito, K.; Abe, K.; Hasebe, N.; Egashira, N.; et al. Delayed treatment with cannabidiol has a cerebroprotective action via a cannabinoid receptor-independent myeloperoxidase-inhibiting mechanism. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Mishima, K.; Irie, K.; Hazekawa, M.; Mishima, S.; Fujioka, M.; Orito, K.; Egashira, N.; Katsurabayashi, S.; Takasaki, K.; et al. Cannabidiol prevents a post-ischemic injury progressively induced by cerebral ischemia via a high-mobility group box1-inhibiting mechanism. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar, S.; Bigdeli, M.R. Intra-cerebral cannabidiol infusion-induced neuroprotection is partly associated with the TNF-α/TNFR1/NF-κB pathway in transient focal cerebral ischaemia. Brain Inj. 2017, 31, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Aliberti, J.; Graemmel, P.; Sunshine, M.J.; Kreutzberg, G.W.; Sher, A.; Littman, D.R. Analysis of Fractalkine Receptor CX 3 CR1 Function by Targeted Deletion and Green Fluorescent Protein Reporter Gene Insertion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 4106–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Tanaka, K.; Buffo, A.; Wurst, W.; Kühn, R.; Götz, M. Inducible gene deletion in astroglia and radial glia-A valuable tool for functional and lineage analysis. Glia 2006, 54, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paukert, M.; Agarwal, A.; Cha, J.; Doze, V.A.; Kang, J.U.; Bergles, D.E. Norepinephrine Controls Astroglial Responsiveness to Local Circuit Activity. Neuron 2014, 82, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, D.; Xiao, Z. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Stroke: Present Status and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, B.; Herron, C.E. Cannabidiol Reverses Deficits in Hippocampal LTP in a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huestis, M.A.; Solimini, R.; Pichini, S.; Pacifici, R.; Carlier, J.; Busardò, F.P. Cannabidiol Adverse Effects and Toxicity. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.G.; Guimarães, F.S.; Crippa, J.A.S.; Hallak, J.E.C.; Rossi, G.; Rocha, J.M.; Zuardi, A.W. Serious adverse effects of cannabidiol (CBD): A review of randomized controlled trials. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, P.; Robson, P.; Cubała, W.; Vasile, D.; Morrison, P.D.; Barron, R.; Taylor, A.; Wright, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) as an Adjunctive Therapy in Schizophrenia: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masataka, N. Anxiolytic Effects of Repeated Cannabidiol Treatment in Teenagers With Social Anxiety Disorders. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffrey, A.L.; Pollack, S.F.; Bruno, P.L.; Thiele, E.A. Drug-drug interaction between clobazam and cannabidiol in children with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Patel, A.D.; Thiele, E.A.; Wong, M.H.; Appleton, R.; Harden, C.L.; Greenwood, S.; Morrison, G.; Sommerville, K. On behalf of the GWPCARE1 Part A Study Group Randomized, dose-ranging safety trial of cannabidiol in Dravet syndrome. Neurology 2018, 90, e1204–e1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Fang, F. Trial of Cannabidiol for Drug-Resistant Seizures in the Dravet Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaston, T.E.; Bebin, E.M.; Cutter, G.R.; Liu, Y.; Szaflarski, J.P.; The Uab Cbd Program. Interactions between cannabidiol and commonly used antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, E.; Marsh, E.D.; French, J.; Mazurkiewicz-Beldzinska, M.; Benbadis, S.R.; Joshi, C.; Lyons, P.D.; Taylor, A.; Roberts, C.; Sommerville, K.; et al. Cannabidiol in patients with seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (GWPCARE4): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Lee, H.; Hurn, P.D.; Crain, B.J.; Traystman, R.J.; Devries, A.C. Cognitive Deficits After Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. Stroke 2000, 31, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, D.T.; Venna, V.R.; McCullough, L.D.; Fitch, R.H. Deficits in auditory, cognitive, and motor processing following reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 238, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, J.; Fassotte, L.; Tirelli, E.; Plumier, J.-C.; Ferrara, A. Assessment of behavioral flexibility after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 258, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Mishima, K.; Abe, K.; Hasebe, N.; Takamatsu, F.; Yasuda, H.; Ikeda, T.; Inui, K.; Egashira, N.; Iwasaki, K.; et al. Cannabidiol prevents infarction via the non-CB1 cannabinoid receptor mechanism. NeuroReport 2004, 15, 2381–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, D.; Pegorini, S.; Arcidiacono, M.V.; Consalez, G.G.; Croci, L.; Sala, M. Post-ischemic treatment with cannabidiol prevents electroencephalographic flattening, hyperlocomotion and neuronal injury in gerbils. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 346, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, M.R.; Mohammed, N.; Lafuente, H.; Santos, M.; Martínez-Pinilla, E.; Moreno, E.; Valdizan, E.; Romero, J.; Pazos, A.; Franco, R.; et al. Mechanisms of cannabidiol neuroprotection in hypoxic–ischemic newborn pigs: Role of 5HT1A and CB2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.; Chang, J.Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.-H.K.A.J.E. Inflammation after Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Leukocytes and Glial Cells. Exp. Neurobiol. 2016, 25, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, Y.; Shimoda, T.; Uno, K.; Tateishi, N.; Furuya, S.; Tsuchihashi, Y.; Kawai, Y.; Naruse, S.; Fujita, S. Temporal and sequential changes of glial cells and cytokine expression during neuronal degeneration after transient global ischemia in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benakis, C.; Garcia-Bonilla, L.; Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The role of microglia and myeloid immune cells in acute cerebral ischemia. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, S.; Perego, C.; Pischiutta, F.; Zanier, E.; de Simoni, M.G. The Ischemic Environment Drives Microglia and Macrophage Function. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, T.; Kalehua, A.N.; Streit, W.J. Characterization of microglial reaction after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993, 327, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, J.-C.; Yamauchi, H.; Fujioka, M.; Endres, M. Selective Neuronal Loss in Ischemic Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmrich, J.V.; Ejaz, S.; Neher, J.J.; Williamson, D.J.; Baron, J.-C. Regional Distribution of Selective Neuronal Loss and Microglial Activation across the MCA Territory after Transient Focal Ischemia: Quantitative versus Semiquantitative Systematic Immunohistochemical Assessment. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, T.-K.; Lee, J.-C.; Na Shin, B.; Hong, S.; Jeon, Y.H.; Kim, Y.-M.; et al. Neuronal loss and gliosis in the rat striatum subjected to 15 and 30 minutes of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.; Ceprian, M.; Jiménez-Sánchez, L.; Pazos, M.R.; Martinez-Orgado, J. Neuroprotective Effects of Cannabidiol in Hypoxic Ischemic Insult. The Therapeutic Window in Newborn Mice. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos-Santos-Pereira, M.; Guimarães, F.S.; Del-Bel, E.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Michel, P.P. Cannabidiol prevents LPS-induced microglial inflammation by inhibiting ROS/NF-κB-dependent signaling and glucose consumption. Glia 2020, 68, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, N.; Liu, Y.; Godlewski, G.; Kaplan, H.J.; Shrader, S.H.; Song, Z.-H.; Shao, H. Studies of involvement of G-protein coupled receptor-3 in cannabidiol effects on inflammatory responses of mouse primary astrocytes and microglia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.J.; Anrather, J.; Nishimura, N.; Schaffer, C.B. Diverse Inflammatory Response After Cerebral Microbleeds Includes Coordinated Microglial Migration and Proliferation. Stroke 2018, 49, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Komine-Kobayashi, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Yamada, M.; Furuya, T.; Migita, M.; Shimada, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Urabe, T. Migration of enhanced green fluorescent protein expressing bone marrow-derived microglia/macrophage into the mouse brain following permanent focal ischemia. Neuroscience 2003, 117, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivel, V.; Bicker, F.; Binamé, F.; Ploen, R.; Keller, S.; Gollan, R.; Jurek, B.; Birkenstock, J.; Poisa-Beiro, L.; Bruttger, J.; et al. Perivascular microglia promote blood vessel disintegration in the ischemic penumbra. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chopp, M. Astrocytes, therapeutic targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 144, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudal, L.C.; Gobbo, D.; Scheller, A.; Kirchhoff, F. The Paradox of Astroglial Ca2 + Signals at the Interface of Excitation and Inhibition. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 609947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Wang, T.; Cui, W.; Haydon, P.G. Photothrombosis ischemia stimulates a sustained astrocytic Ca2+ signaling in vivo. Glia 2009, 57, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordsmann, J.C.; Murmu, R.P.; Cai, C.; Brazhe, A.; Thomsen, K.J.; Zambach, S.A.; Lønstrup, M.; Lind, B.L.; Lauritzen, M. Spontaneous astrocytic Ca2+ activity abounds in electrically suppressed ischemic penumbra of aged mice. Glia 2019, 67, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakers, C.; Petzold, G.C. Astrocytic calcium release mediates peri-infarct depolarizations in a rodent stroke model. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, H.; Alvarez, F.J.; Pazos, M.R.; Alvarez, A.; Rey-Santano, M.C.; Mielgo, V.; Murgia-Esteve, X.; Hilario, E.; Martinez-Orgado, J. Cannabidiol Reduces Brain Damage and Improves Functional Recovery After Acute Hypoxia-Ischemia in Newborn Pigs. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Scuderi, C.; Valenza, M.; Togna, G.I.; Latina, V.; De Filippis, D.; Cipriano, M.; Carratù, M.R.; Iuvone, T.; Steardo, L. Cannabidiol Reduces Aβ-Induced Neuroinflammation and Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis through PPARγ Involvement. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, H.M.; Kasakow, C.V.; Helfer, A.; Michely, J.; Verkhratsky, A.; Maurer, H.H.; Scheller, A.; Kirchhoff, F. Refined protocols of tamoxifen injection for inducible DNA recombination in mouse astroglia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiana, S.; Watanabe, A.; Yamasaki, Y.; Amada, N.; Arthur, M.; Fleming, S.; Woodcock, H.; Dorward, P.; Pigliacampo, B.; Close, S.; et al. Plasma and brain pharmacokinetic profile of cannabidiol (CBD), cannabidivarine (CBDV), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) and cannabigerol (CBG) in rats and mice following oral and intraperitoneal administration and CBD action on obsessive–compulsive behaviour. Psychopharmacology 2012, 219, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Bai, X.; Meyer, E.; Scheller, A. Acute brain injuries trigger microglia as an additional source of the proteoglycan NG. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, J.-I.; Yoshida, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Ooneda, G. Experimental studies of ischemic brain edema. Jpn. J. Stroke 1986, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupido, A.; Catalin, B.; Steffens, H.; Kirchhoff, F. Surgical Procedures to Study Microglial Motility in the Brain and in the Spinal Cord by In Vivo Two-Photon Laser-Scanning Microcopy. In Confocal and Multiphoton Laser-Scanning Microscopy of Neuronal Tissue: Applications and Quantitative Image Analysis; Bakota, L., Brandt, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bieber, M.; Gronewold, J.; Scharf, A.-C.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Langhauser, F.; Hopp, S.; Mencl, S.; Geuss, E.; Leinweber, J.; Guthmann, J.; et al. Validity and Reliability of Neurological Scores in Mice Exposed to Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Stroke 2019, 50, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bederson, J.B.; Pitts, L.H.; Tsuji, M.; Nishimura, M.C.; Davis, R.L.; Bartkowski, H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: Evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 1986, 17, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmued, L.C.; Hopkins, K.J. Fluoro-Jade: Novel Fluorochromes for Detecting Toxicant-Induced Neuronal Degeneration. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pologruto, T.; Sabatini, B.L.; Svoboda, K. ScanImage: Flexible software for operating laser scanning microscopes. Biomed. Eng. Online 2003, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopper, L.C.; Caudal, P.; Rieder, D.; Gobbo, L.; Felix, K.; Everaerts, X.; Bai, L.; Stopper, C.R.; Scheller, A.R.; Kirchhoff, F. Novel algorithms for improved detection and analysis of fluorescent signal fluctuations. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, P.; Gobbo, D.; Stopper, G.; Welle, A.; Damo, E.; Kirchhoff, F.; Scheller, A. Astrocytes and Microglia Exhibit Cell-Specific Ca2+ Signaling Dynamics in the Murine Spinal Cord. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 840948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luisier, F.; Blu, T.; Unser, M. Image Denoising in Mixed Poisson–Gaussian Noise. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).