SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (RBD) Subunit Adsorption at Abiotic Surfaces and Corona Formation at Polymer Particles
Abstract
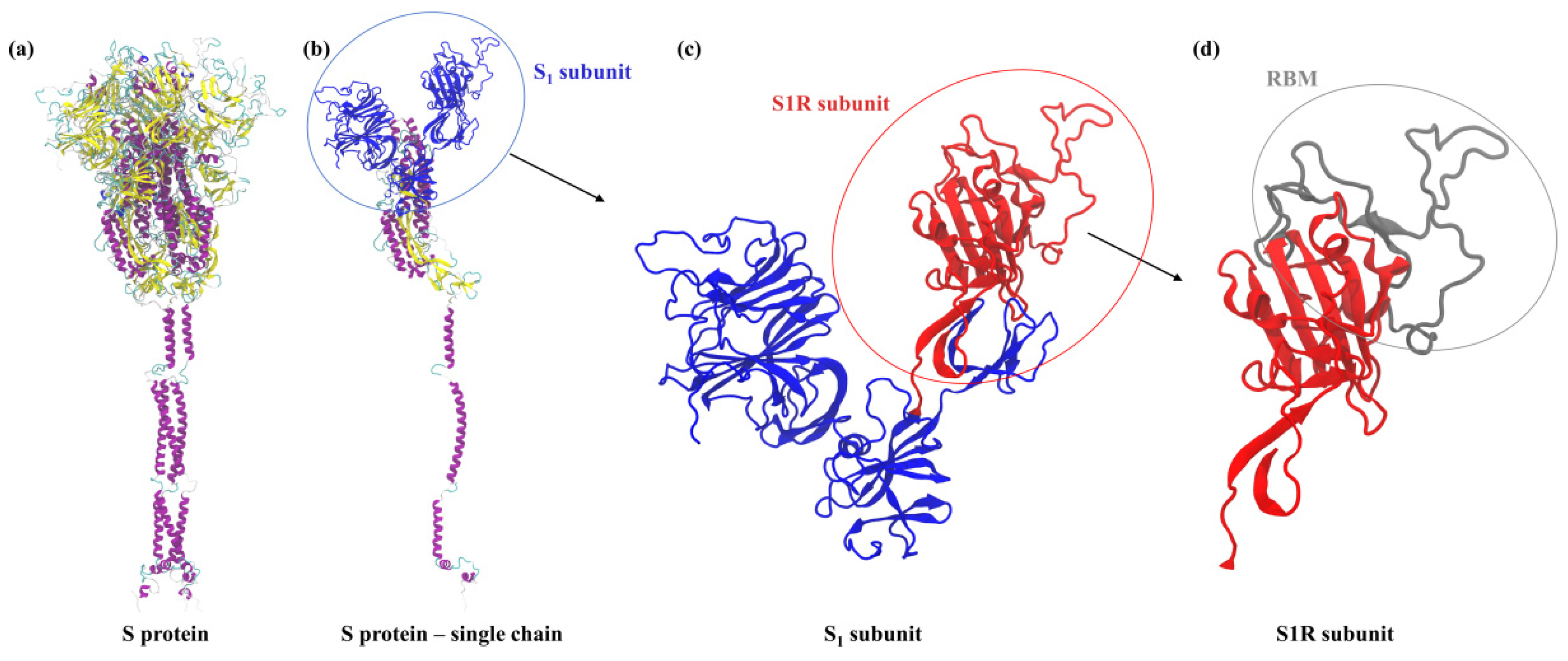
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
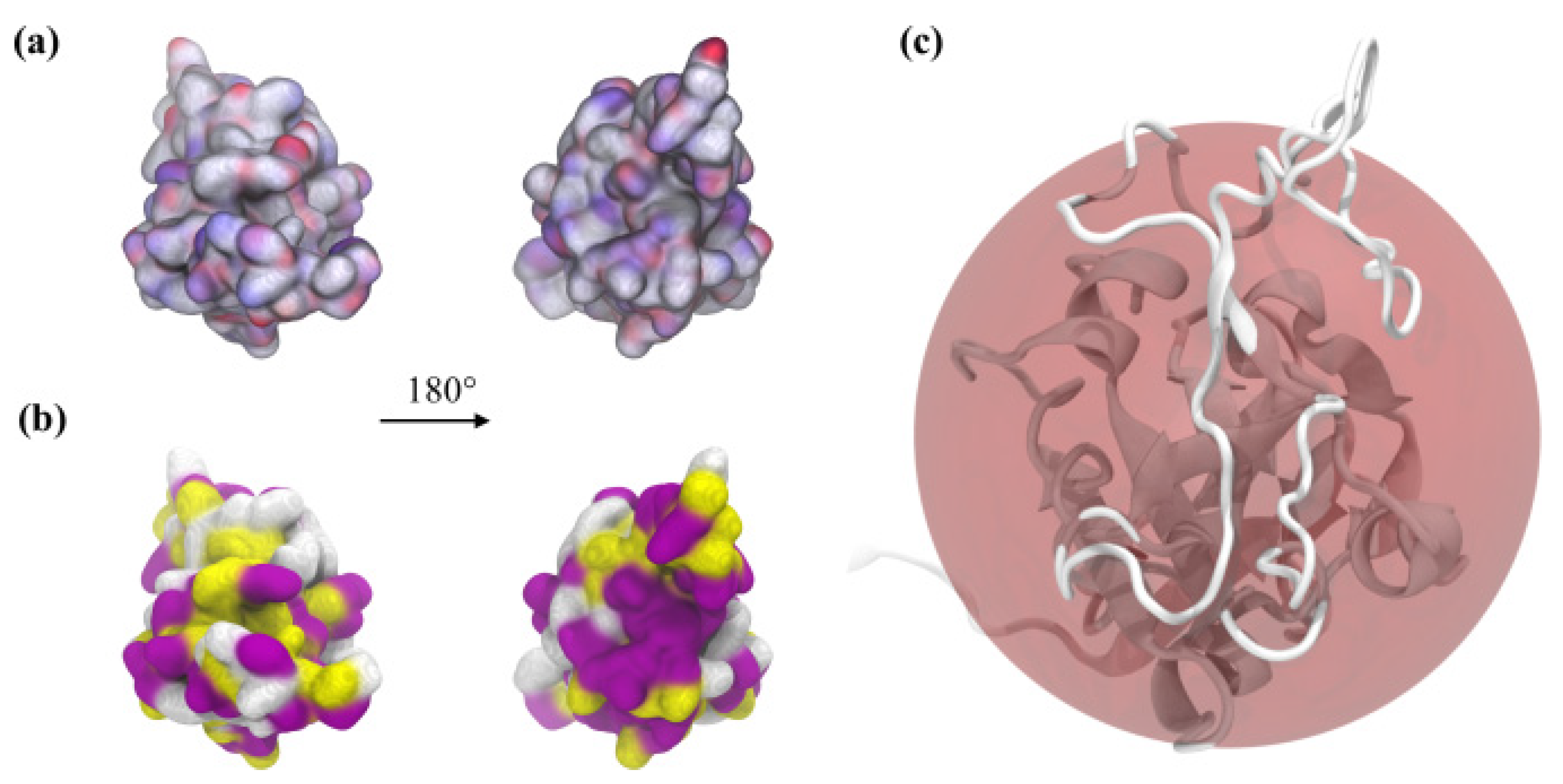
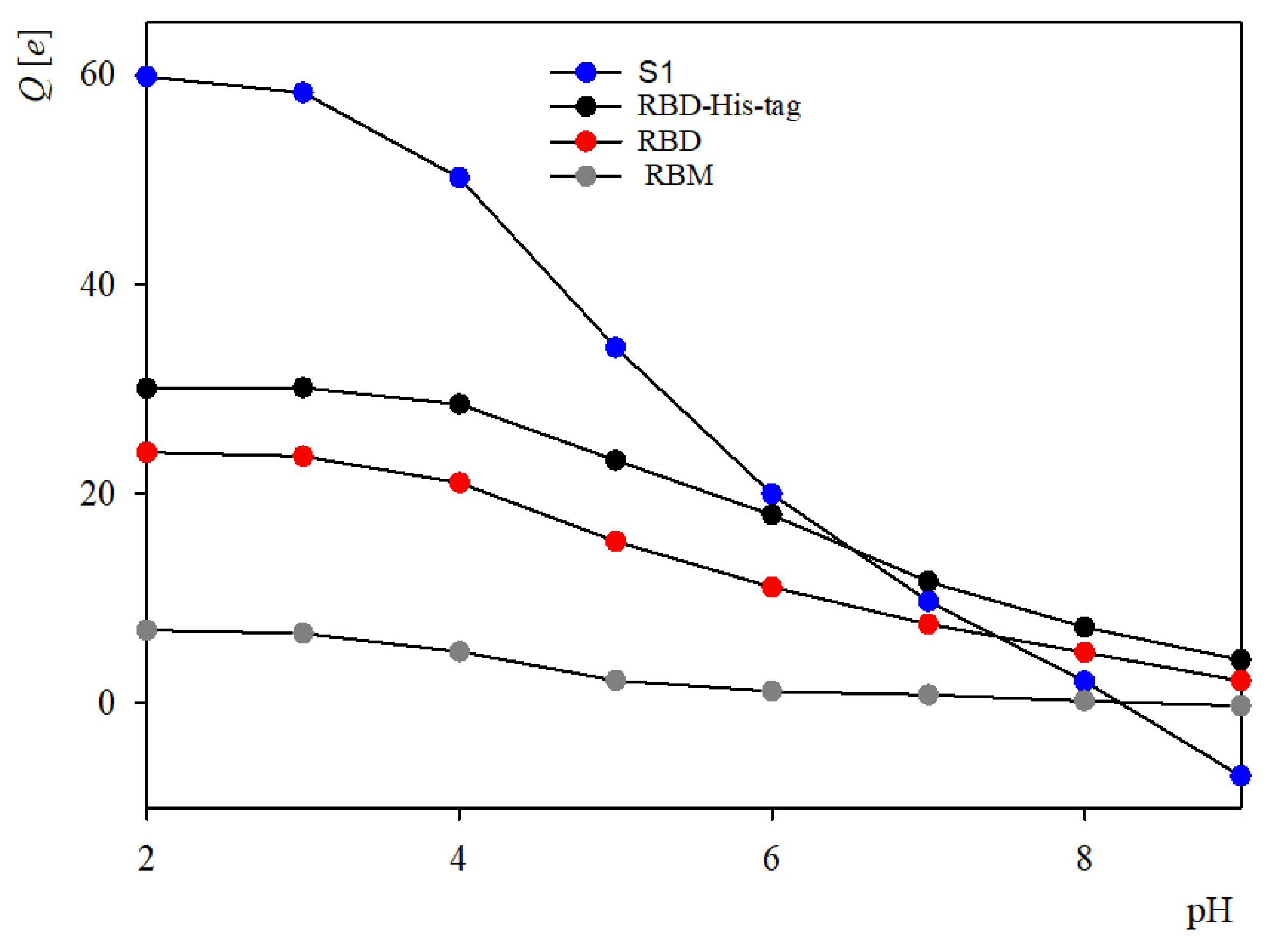
2.1. Theoretical Charge Distribution and Hydrophobicity of the S1R Subunit
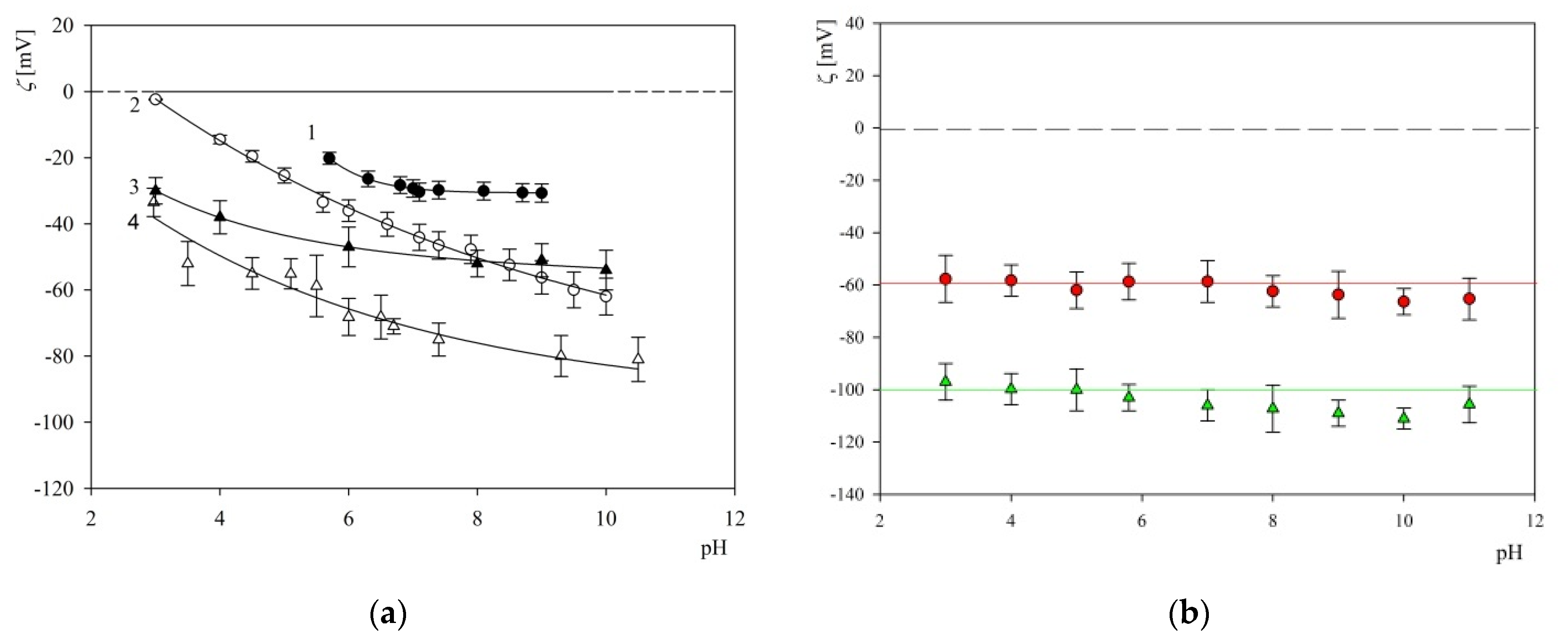
2.2. Characteristics of Substrates Used in Adsorption Experiments
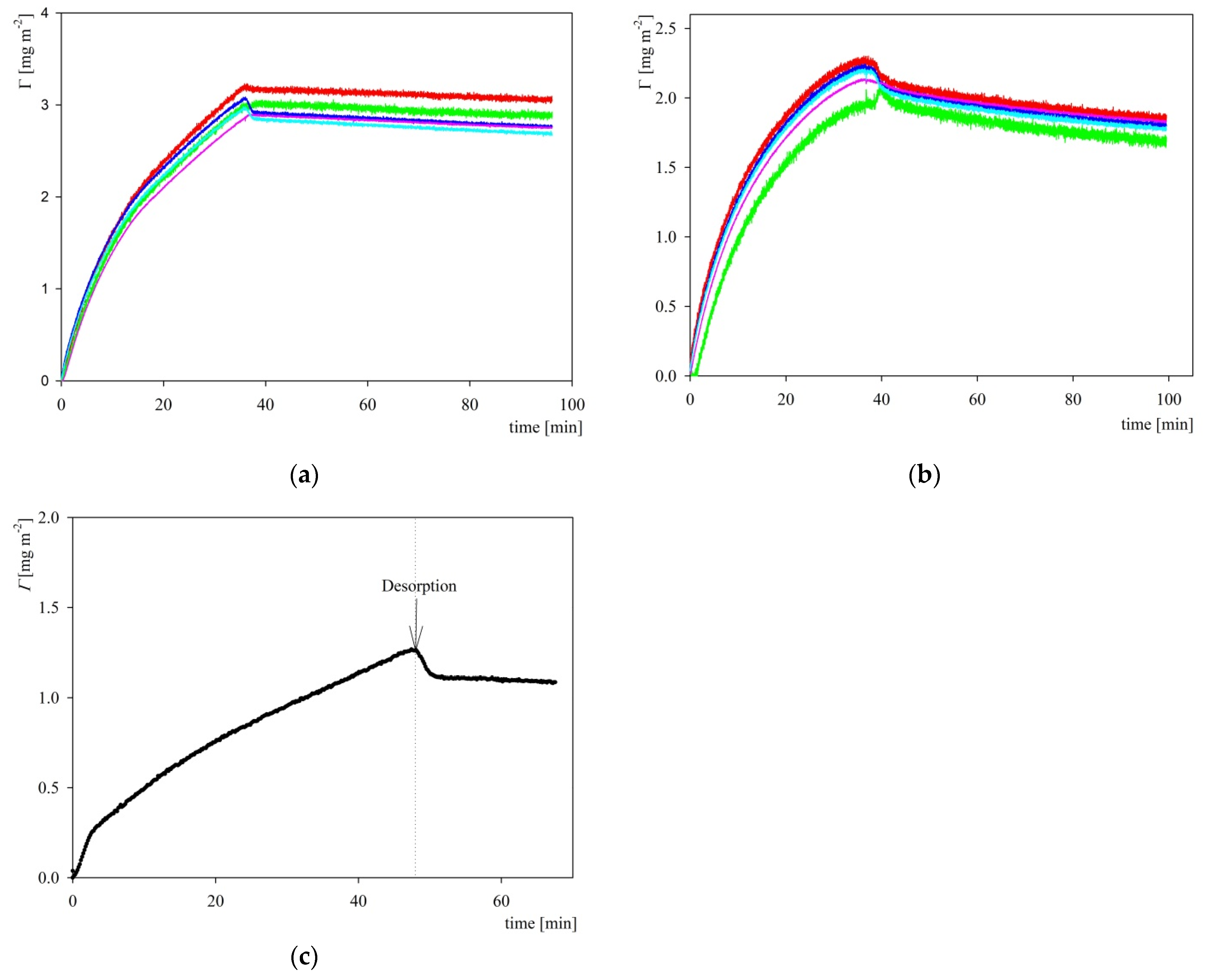
2.3. S1R Adsorption: AFM, QCM and OWLS Measurements
| Aggregate/Parameter | dH dAFM [nm] | Sg‖ [nm2] | Sg┴ [nm2] | Γ∞‖ [mg m−2] | Γ∞┴ [mg m−2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monomer, na = 1 M1 = 22 kDa  | 3.84 | ||||
| 3.84 | 12 | 12 | 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| Dimer, na = 2 M2 = 44 kDa  | 5.4 5.8 | 24 | 12 | 1.6 | 3.2 |
| Tetramer, na = 4 M4 = 88 kDa  | |||||
| 7.6 9.2 | 52 | 24 | 1.5 | 3.6 | |
| Dodekamer (micelle), na = 12 M12 = 264 kDa  | 12 12 | 87 | 87 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| Micelle, na = 20 M20 = 440 kDa  | |||||
| 14 14 | 100 | 100 | 3.4 | 3.4 |
2.4. S1R Protein Corona Formation on Polymer Particles
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Celik, U.; Celik, K.; Celik, S.; Abayli, H.; Sahna, K.C.; Tonbak, S.; Toraman, Z.A.; Oral, A. Interpretation of SARS-CoV-2 behaviour on different substrates and denaturation of virions using ethanol: An atomic force microscopy study. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 44079–44086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, genetic recombination, and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Weng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Molecular architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Cell 2020, 183, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterization and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, A.R. Immunological challenges of the “new” infections: Corona viruses in A new history of vaccines for infectious diseases. New Hist. Vaccines Infect. Dis. 2022, 395–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turoňová, B.; Sikora, M.; Schürmann, C.; Hagen, W.J.H.; Welsch, S.; Blanc, F.E.C.; Von Bülow, S.; Gecht, M.; Bagola, K.; Hörner, C.; et al. In situ structural analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike reveals flexibility mediated by three hinges. Science 2020, 370, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, L.; Gaieb, Z.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hjorth, C.K.; Dommer, A.C.; Harbison, A.M.; Fogarty, C.A.; Barros, E.P.; Taylor, B.C.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. Beyond Shielding: The Roles of Glycans in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, S. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Structural and functional basis of SARS-CoV-2 entry by using human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 recemtor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Zhao, R.; Gao, L.J.; Gao, X.F.; Wang, D.P.; Cao, J.M. SARS-CoV-2: Structure, Biology, and Structure-Based Therapeutics Development. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 587269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.G.; Morano, N.C.; Celikgil, A.; Georgiev, G.I.; Malonis, R.J.; Lee, J.H.; Tong, K.; Vergnolle, O.; Massimi, A.B.; Yen, L.Y.; et al. Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein: Biophysical, biochemical, structural, and antigenic analysis. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, C.; Peng, W.; Li, D.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Bi, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A noncompeting pair of human neutralizing antibodies block COVID-19 virus binding to its receptor ACE2. Science 2020, 368, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-H.; Tao, X.; Agrawal, A.S.; Algaissi, A.; Peng, B.-H.; Pollet, J.; Strych, U.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Hotez, P.J.; Lustigman, S.; et al. Yeast-expressed SARS-CoV recombinant receptor-binding domain (RBD219-N1) formulated with aluminum hydroxide induces protective immunity and reduces immune enhancement. Vaccine 2020, 38, 7533–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkuleva, I.A.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Borgoyakova, M.B.; Shanshin, D.V.; Rudometov, A.P.; Karpenko, L.I.; Belenkaya, S.V.; Isaeva, A.A.; Nesmeyanova, V.S.; Kazachinskaia, E.I.; et al. Comparative Immunogenicity of the Recombinant Receptor-Binding Domain of Protein S SARS-CoV-2 Obtained in Prokaryotic and Mammalian Expression Systems. Vaccines 2022, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Grundmeier, G.; Keller, A. Adsorption of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 at Oxide Surfaces Studied by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy. Adv. Nanobiomed Res. 2021, 1, 2000024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, M.; Adamczyk, Z.; Pomorska, A.; Nattich-Rak, M.; Sadowska, M. Human Serum Albumin Adsorption Kinetics on Silica: Influence of Protein Solution Stability. Langmuir 2019, 35, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrynin, D.; Polishchuk, I.; Portal, L.; Zlotver, I.; Sosnik, A.; Pokroy, B. Adsorption of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins on various functionalized surfaces correlates with the high transmissibility of Delta and Omicron variants. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 14, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; SØndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical pKa predictions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, C.R.; Olsson, M.H.M.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. Improved treatment of ligands and coupling effects in empirical calculation and rationalization of pKa values. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 2284–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Robertson, A.D.; Jensen, J.H. Very fast empirical prediction and rationalization of protein pKa values. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 61, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batys, P.; Nattich-Rak, M.; Adamczyk, Z. Myoglobin molecule charging in electrolyte solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 26764–26775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Polikarpov, I.; Craievich, A.F. Average protein density is a molecular-weight-dependent function. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 2825–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Batys, P.; Barbasz, J. SARS-CoV-2 virion physicochemical characteristics pertinent to abiotic substrate attachment. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 55, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morga, M.; Adamczyk, Z.; Godrich, S.; Oćwieja, M.; Papastavrou, G. Monolayers of poly-L-lysine on mica–Electrokinetic characteristics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 456, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska, M.; Adamczyk, Z. Fibrinogen adsorption on mica studied by AFM and in situ streaming potential measurements. Langmuir 2011, 27, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, M.; Żeliszewska, P.; Pogoda, K.; Deptuła, P.; Bucki, R.; Adamczyk, Z. Human vimentin layers on solid substrates: Adsorption kinetics and corona formation investigations. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 3308–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, Z. Particles at Interfaces. Interactions, Deposition, Structure, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kubiak, K.; Adamczyk, Z.; Wasilewska, M. Mechanisms of fibrinogen adsorption at the silica substrate determined by QCM-D measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 457, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratek-Skicki, A.; Żeliszewska, P.; Adamczyk, A.; Cieśla, M. Human fibrinogen monolayers on latex particles: Role of ionic strength. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3700–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Morga, M.; Nattich-Rak, M.; Sadowska, M. Nanoparticle and bioparticle deposition kinetics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 302, 102630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, K.; Susumu, K.; Chen, J.; Xu, M.; Pradhan, M.; Zhu, W. Quantum dot-conjugated SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudo-virions enable tracking of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 binding and endocytosis. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12234–12247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Ichiki, A. Nano-size dependence in the adsorption by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein over gold colloid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 615, 126275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Sadlej, K.; Wajnryb, E.; Nattich, M.; Ekiel-Jeżewska, M.L.; Bławzdziewicz, J. Streaming potential studies of colloid, polyelectrolyte and protein deposition. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 153, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofińska, K.; Adamczyk, Z.; Kujda, M.; Nattich-Rak, M. Recombinant albumin monolayers on latex particles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, J.; Hearn, J.; Ho, C.C.; Otewill, R.H. Studies on the preparation and characterisation of monodisperse polystyrene laticee. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1974, 252, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reviakine, I.; Johannsmann, D.; Richter, R.P. Hearing what you cannot see and visualizing what you hear: Interpreting quartz crystal microbalance data from solvated interfaces. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8838–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saftics, A.; Kurunczi, S.; Peter, B.; Szekacs, I.; Ramsden, J.J.; Horvath, R. Data evaluation for surface-sensitive label-free methods to obtain real-time kinetic and structural information of thin films: A practical review with related software packages. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property, Symbol Unit | Value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Molar mass, monomer, M1 kg mol−1 [kDa] | ||
| 25.0 | Calculated from the sequence | |
| 25.8 (His-tagged) | ||
Density, ρp kg m−3 | 1.4 × 103 | assumed Ref. [26] |
| Specific volume, monomer, v1, nm3 | ||
| 29.7 30.6 (His-tagged) | Calculated as: | |
| Equivalent sphere (hydrodynamic) diameter, d1, nm | 3.84 3.88 (His-tagged) | Calculated as: |
| Geometrical cross-section area, of equivalent sphere, Sg1, nm2 | 11.6 11.8 (His-tagged) | Calculated as: |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Żeliszewska, P.; Wasilewska, M.; Batys, P.; Pogoda, K.; Deptuła, P.; Bucki, R.; Adamczyk, Z. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (RBD) Subunit Adsorption at Abiotic Surfaces and Corona Formation at Polymer Particles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012374
Żeliszewska P, Wasilewska M, Batys P, Pogoda K, Deptuła P, Bucki R, Adamczyk Z. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (RBD) Subunit Adsorption at Abiotic Surfaces and Corona Formation at Polymer Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(20):12374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012374
Chicago/Turabian StyleŻeliszewska, Paulina, Monika Wasilewska, Piotr Batys, Katarzyna Pogoda, Piotr Deptuła, Robert Bucki, and Zbigniew Adamczyk. 2022. "SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (RBD) Subunit Adsorption at Abiotic Surfaces and Corona Formation at Polymer Particles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 20: 12374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012374
APA StyleŻeliszewska, P., Wasilewska, M., Batys, P., Pogoda, K., Deptuła, P., Bucki, R., & Adamczyk, Z. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (RBD) Subunit Adsorption at Abiotic Surfaces and Corona Formation at Polymer Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(20), 12374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012374






