Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF-2) and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP-7) Are Upregulated after Atypical Antipsychotics in Spanish Schizophrenia Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Data
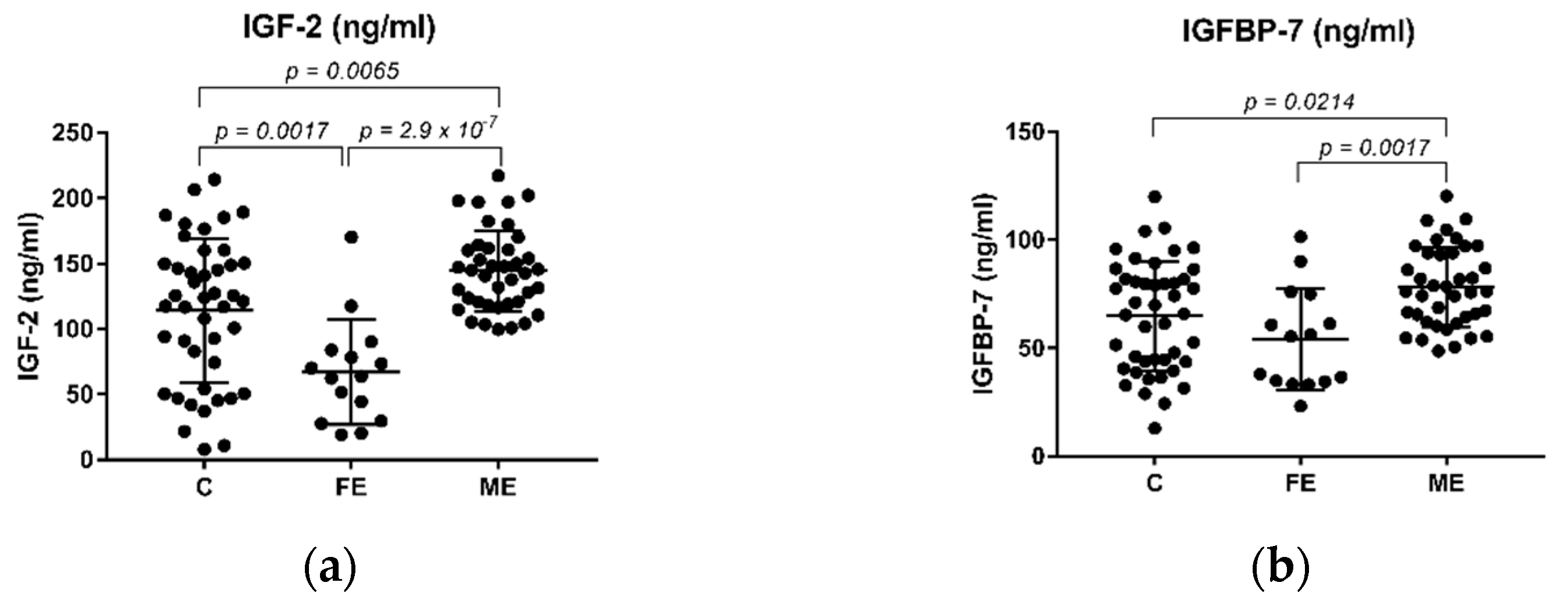
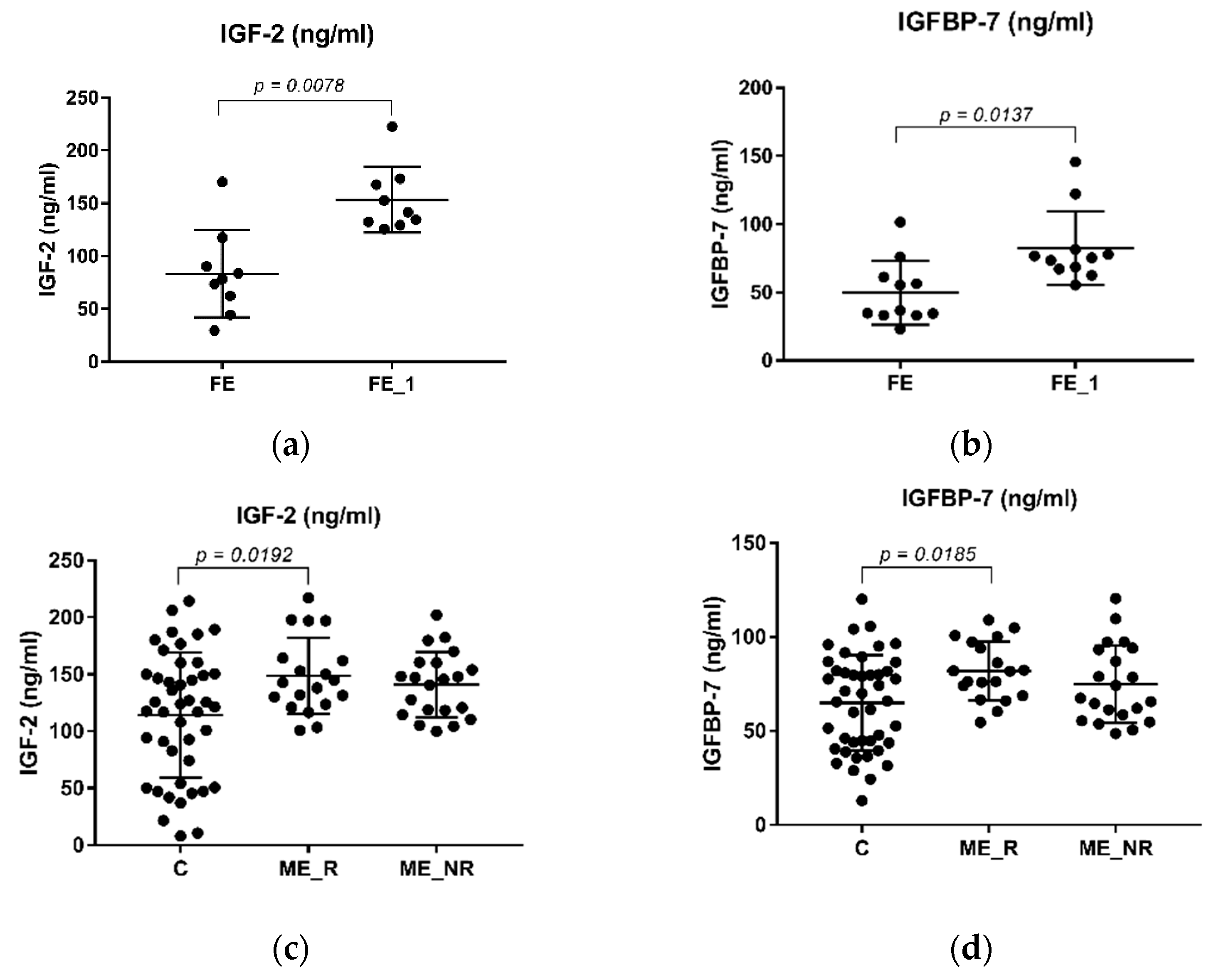
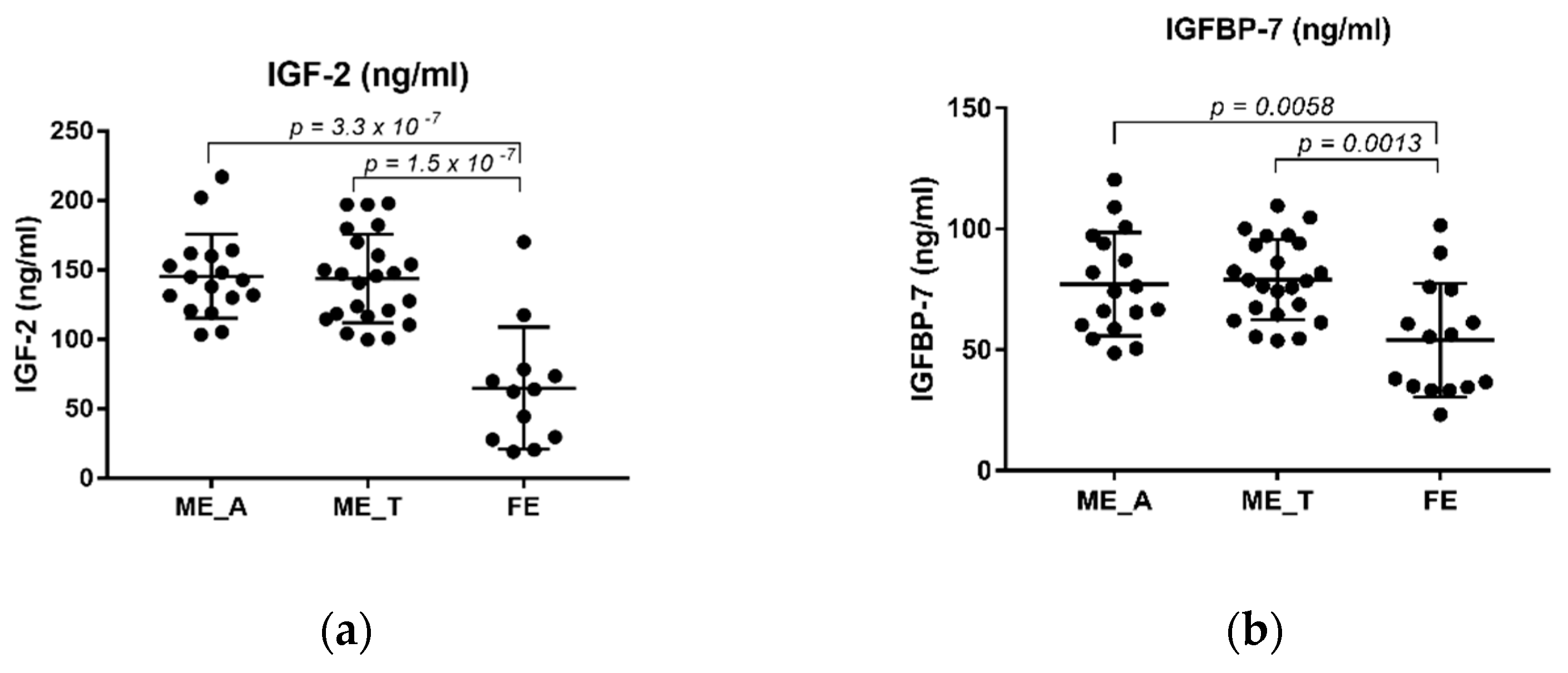
2.2. The Levels of IGF-2 and IGFBP-7 in Schizophrenia Patients and Healthy Controls
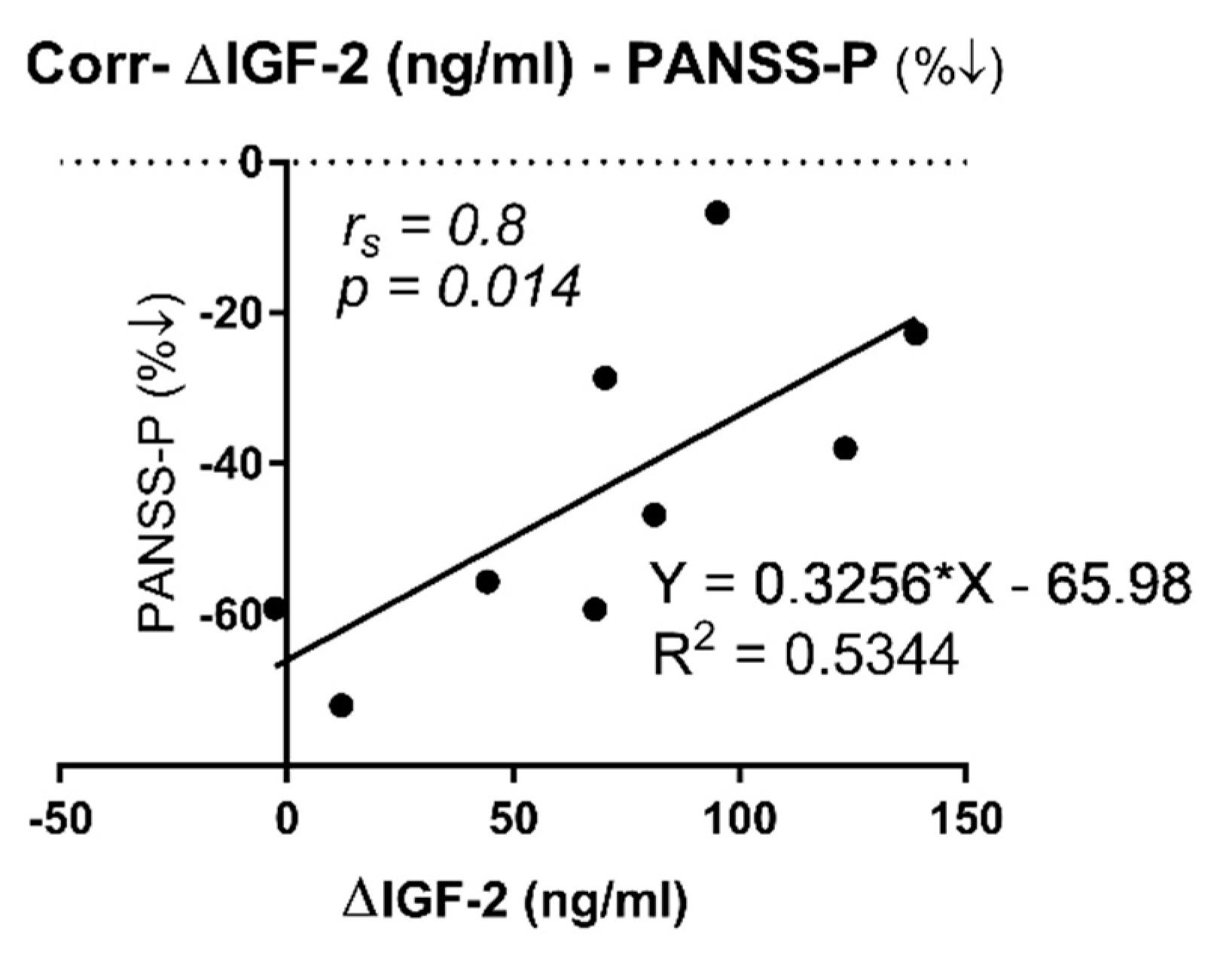
2.3. Correlation between IGF-2 and IGFBP-7 Plasma Protein Levels with PANSS and SAAS Scales
2.4. Correlation between IGF-2 and IGFBP-7 Plasma Protein Levels and Metabolic Parameters
3. Discussion
Limitations and Future Perspectives
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Blood Collection
4.3. Measurement of Psychopathological Symptoms (PANSS) and Anhedonia (SAAS)
4.4. Metabolic Parameters Measurement
4.5. Measurement of IGF-2 and IGFBP-7 Plasma Proteins
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mueser, K.T.; McGurk, S.R. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2004, 363, 2063–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penedo, M.A.; Rivera-Baltanás, T.; Pérez-Rodríguez, D.; Allen, J.; Borrajo, A.; Alonso-Crespo, D.; Fernández-Pereira, C.; Nieto-Araujo, M.; Ramos-García, S.; Barreiro-Villar, C.; et al. The role of dopamine receptors in lymphocytes and their changes in schizophrenia. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 12, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stilo, S.A.; Murray, R.M. Non-Genetic Factors in Schizophrenia. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritsner, M.S.; Mar, M.; Arbitman, M.; Grinshpoon, A. Symptom severity scale of the DSM5 for schizophrenia, and other psychotic disorders: Diagnostic validity and clinical feasibility. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 208, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Amorim, D.; Rivera-Baltanás, T.; López, M.; Spuch, C.; Olivares, J.M.; Agís-Balboa, R.C. Schizophrenia: A review of potential biomarkers. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 93, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, L.; Gan, R.; Wu, G.; Tang, X.; Wei, Y.; Cui, H.; Hui, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. A potential objective marker in first-episode schizophrenia based on abnormal niacin response. Schizophr. Res. 2022, 243, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J.A.; Small, S.A.; Girgis, R.R. Early Detection and Preventive Intervention in Schizophrenia: From Fantasy to Reality. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 794–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riecher-Rössler, A.; Gschwandtner, U.; Aston, J.; Borgwardt, S.; Drewe, M.; Fuhr, P.; Pflüger, M.; Radü, W.; Schindler, C.H.; Stieglitz, R.D. The Basel early-detection-of-psychosis (FEPSY)-study—Design and preliminary results. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2007, 115, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Y.; Scarr, E.; Udawela, M.; Everall, I.; Chen, W.J.; Dean, B. Biomarkers in schizophrenia: A focus on blood-based diagnostics and theranostics. World J. Psychiatry 2016, 22, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Os, J.; Kapur, S. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2009, 374, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D. World leaders describe the latest in IGF research. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, E1–E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E. Insulin-like growth factors in the brain and their potential clinical implications. Neurology 2012, 79, 2148–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kusky, J.; Ye, P. Neurodevelopmental effects of insulin-like growth factor signaling. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 33, 230–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y. IGFBPs and neoplastic models: New concepts for roles of IGFBPs in regulation of cancer cell growth. Endocrine 1997, 7, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, B.E.; Blyth, A.J.; Wit, J.M. Disorders of IGFs and IGF-1R signaling pathways. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 111035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denduluri, S.K.; Idowu, O.; Wang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Yan, Z.; Mohammed, M.K.; Ye, J.; Wei, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling in tumorigenesis and the development of cancer drug resistance. Genes Dis. 2015, 2, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, L.A. IGF-binding proteins. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T11–T28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranke, M.B. Insulin-like growth factor binding-protein-3 (IGFBP-3). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Nagalla, S.R.; Yamanaka, Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Wilson, E.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein (IGFBP)-7. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30322–30325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, M.; Ling, J.; Cai, L.; Zhang, D.; Gu, H.F.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lai, M. Serum IGFBP7 levels associate with insulin resistance and the risk of metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.F.; Gu, T.; Hilding, A.; Zhu, Y.; Kärvestedt, L.; Ostenson, C.-G.; Lai, M.; Kutsukake, M.; Frystyk, J.; Tamura, K.; et al. Evaluation of IGFBP-7 DNA methylation changes and serum protein variation in Swedish subjects with and without type 2 diabetes. Clin. Epigenet. 2013, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamakou, M.; Thanopoulou, A.; Gonidakis, F.; Tentolouris, N.; Kontaxakis, V. Schizophrenia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Psychiatriki 2018, 29, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.; Johnston, M.; Campbell, R.; De Sousa, A.; Shah, N. Serum cholesterol and Suicide in first episode psychosis: A preliminary study. Indian J. Psychiatry 2017, 59, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.D.; Barr, A.M.; Fredrikson, D.H.; Honer, W.G.; Procyshyn, R.M. Association between Serum Lipids and Antipsychotic Response in Schizophrenia. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, M.; Kuloglu, M.; Tezcan, E.; Ustundag, B. Serum leptin and cholesterol levels in schizophrenic patients with and without suicide attempts. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2003, 108, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrikis, P.; Boumba, V.A.; Tzallas, A.T.; Voulgari, P.V.; Archimandriti, D.T.; Skapinakis, P.; Mavreas, V. Elevated levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in drug-naïve patients with psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 246, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Song, J.; Lin, C.; Yu, J. Effect of risperidone treatment on insulin-like growth factor-1 and interleukin-17 in drug naïve first-episode schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 297, 113717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasubramanian, G.; Chittiprol, S.; Neelakantachar, N. Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Abnormalities in Antipsychotic-Naive Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 5, 1557–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, A.; González-Pinto, A.; Martinez-Cengotitabengoa, M.; Ruiz de Azua, S.; Alberich, S.; Mosquera, F.; Matute, C. Relationship between negative symptoms and plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 in first-episode schizophrenia and bipolar disorder patients. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 44, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanji, A.O.; Ohaeri, J.U.; Al-Shammri, S.A.; Fatania, H.R. Associations of blood levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-II and IGF binding protein (IGFBP)-3 in schizophrenic Arab subjects. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okamoto, N.; Yoshino, K.; Kitagawa, S.; Fujii, R.; Hamada, S.; Ikenouchi, A.; Konishi, Y.; Ueda, N.; Eto, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y.; et al. Association Between Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Levels and the Clinical Symptoms of Chronic Schizophrenia: Preliminary Findings. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 653802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, O.D.; Gaughran, F.P.; Amiel, S.; Murray, R.M.; Pilowsky, L.S. The effect of clozapine on factors controlling glucose homeostasis. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2004, 65, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, A.; Demirel, O.F.; Emül, M.; Duran, A.; Uğur, M. Relationships between IGF-1, schizophrenia, and treatment of metabolic syndrome. Compr. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, X.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, J.; Zhan, J.; Yan, K.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L. The association between serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and cognitive impairments in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 285, 112731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilkaya, U.H.; Gica, S.; Ilnem, M.C.; Sen, M.; Ipekcioglu, D. Evaluation of IGF-1 as a novel theranostic biomarker for schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 140, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Luo, T.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, S.Z.; Xiong, J.W.; Zhan, J.Q.; Yu, B.; Yan, K.; Wei, B. Altered insulin-like growth factor-2 signaling is associated with psychopathology and cognitive deficits in patients with schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, J.; Zhan, J.; Wei, B.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y. Changes of Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-2 Response to Negative Symptom Improvements in Schizophrenia Patients Treated with Atypical Antipsychotics. Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromer, M.; Roussos, P.; Sieberts, S.K.; Johnson, J.S.; Kavanagh, D.H.; Perumal, T.M.; Ruderfer, D.M.; Oh, E.C.; Topol, A.; Shah, H.R.; et al. Gene expression elucidates functional impact of polygenic risk for schizophrenia. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, A.; Kasprzak, A. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) System in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, M.M.; Cohen, C.I. Late-life psychosis: Diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolin, M.-A.; Demers, M.-F.; Rauzier, C.; Bouchard, R.-H.; Cadrin, C.; Després, J.-P.; Roy, M.-A.; Alméras, N.; Picard, F. Circulating IGFBP-2 levels reveal atherogenic metabolic risk in schizophrenic patients using atypical antipsychotics. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 22, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.; Kim, J.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-I.; Seo, J.-S.; Webster, M.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, S. Gene expression profiling by mRNA sequencing reveals increased expression of immune/inflammation-related genes in the hippocampus of individuals with schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, R.; Gaebel, W.; Barch, D.M.; Bustillo, J.; Gur, R.E.; Heckers, S.; Malaspina, D.; Owen, M.J.; Schultz, S.; Tsuang, M.; et al. Definition and description of schizophrenia in the DSM-5. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 150, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, J.M.; Berrios, G.E.; Bousoño, M. Self-Assessment Anhedonia Scale (SAAS). Neurol. Psychiatry Brain Res. 2005, 12, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- del Carmen Vallejo-Curto, M.; Rodrigues-Amorim, D.; Jardón-Golmar, L.; Blanco-Formoso, M.; Rivera-Baltanás, T.; Rodriguez-Jamardo, C.; Fernández-Palleiro, P.; Álvarez-Ariza, M.; López-García, M.; García-Caballero, A.; et al. Proteomic and metabolic profiling of chronic patients with schizophrenia induced by a physical activity program: Pilot study. Rev. Psiquiatr. Y Salud Ment. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 14, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Baltanas, T.; Agis-Balboa, R.C.; Romay-Tallon, R.; Kalynchuk, L.E.; Olivares, J.M.; Caruncho, H.J. Serotonin transporter clustering in blood lymphocytes predicts the outcome on anhedonia scores in naïve depressive patients treated with antidepressant medication. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2015, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agis-Balboa, R.C.; Arcos-Diaz, D.; Wittnam, J.; Govindarajan, N.; Blom, K.; Burkhardt, S.; Haladyniak, U.; Agbemenyah, H.Y.; Zovoilis, A.; Salinas-Riester, G.; et al. A hippocampal insulin-growth factor 2 pathway regulates the extinction of fear memories. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4071–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agis-Balboa, R.C.; Fischer, A. Generating new neurons to circumvent your fears: The role of IGF signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2014, 71, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbemenyah, H.Y.; Agis-Balboa, R.C.; Burkhardt, S.; Delalle, I.; Fischer, A. Insulin growth factor binding protein 7 is a novel target to treat dementia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 62, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, K.D.; Lehmann, E.D.; Jones, R.L.; Holly, J.M.P.; Cwyfan-Hughes, S.C.; Turay, R.C.; Teale, J.D.; Gosling, R.G. Ethnicity affects IGFBP-3 and IGF-II in normal healthy young adult subjects. Clin. Endocrinol. 1996, 45, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; Cheng, Y.; Sitbon, Y.H.; Lowell, J.A.; Grieco, S.F.; Worthen, R.J.; Desse, S.; Barreda-Diaz, A. Insulin growth factor 2 (IGF2) as an emergent target in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Review. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 149, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, A.; Nordberg, A.; Grissom, F.E.; Carlsson-Skwirut, C.; Viitanen, M.; Sara, V.R. Insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type. J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 1993, 5, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åberg, D.; Johansson, P.; Isgaard, J.; Wallin, A.; Johansson, J.-O.; Andreasson, U.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Åberg, N.D.; Svensson, J. Increased Cerebrospinal Fluid Level of Insulin-like Growth Factor-II in Male Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 48, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, J.; Lucassen, P.J. Depression as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, steroids, cytokines and neurogenesis—What do we need to know? Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2016, 41, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.V.; Forlenza, O.V.; Gattaz, W.F. Lithium and risk for Alzheimer’s disease in elderly patients with bipolar disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry J. Ment. Sci. 2007, 190, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agís-Balboa, R.C.; Pinheiro, P.S.; Rebola, N.; Kerimoglu, C.; Benito, E.; Gertig, M.; Bahari-Javan, S.; Jain, G.; Burkhardt, S.; Delalle, I.; et al. Formin 2 links neuropsychiatric phenotypes at young age to an increased risk for dementia. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2815–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuring, J.K.; Mathias, J.L.; Ward, L. Risk of Dementia in persons who have previously experienced clinically-significant Depression, Anxiety, or PTSD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 274, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępnicki, P.; Kondej, M.; Kaczor, A.A. Current Concepts and Treatments of Schizophrenia. Molecules 2018, 23, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Rashidi, E.; Amooeian, V.G. Brain, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and serum biomarkers in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 265, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Control (n = 45) | FE (n = 15) | ME (n = 40) | ME_R (n = 19) | ME_NR (n = 21) | ME_A (n = 16) | ME_T (n = 23) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FE_1 (n = 11) | |||||||
| Sex (F/M) | 20/25 | 4/11 | 13/27 | 5/14 | 8/13 | 4/12 | 9/14 |
| 3/8 | |||||||
| Age (years) | 41.22 ± 10.58 | 31.73 ± 15.53 | 39.85 ± 11.26 | 40.00 ± 12.15 | 39.71 ± 10.69 | 37.69 ± 9.12 | 41.39 ± 12.73 |
| 32.36 ± 16.24 | |||||||
| IGF-2 (ng/mL) | 114.24 ± 55.00 | 66.93 ± 39.99 | 144.06 ± 30.84 | 148.64 ± 33.41 | 140.95 ± 28.64 | 144.68 ± 30.99 | 143.87 ± 31.93 |
| 153.45 ± 30.98 | |||||||
| IGFBP-7 (ng/mL) | 64.9174 ± 25.36 | 54.04 ± 23.49 | 78.28 ± 18.55 | 81.98 ± 15.61 | 74.93 ± 20.67 | 76.57 ± 21.90 | 79.09 ± 16.65 |
| 82.47 ± 27.04 | |||||||
| PANSS-P | - | 21.27 ± 5.02 | 22.92 ± 8.12 | 22.21 ± 8.16 | 23.57 ± 8.22 | 22.25 ± 9.73 | 22.91 ± 6.81 |
| 11.33 ± 4.06 | |||||||
| PANSS-N | - | 24.93 ± 8.92 | 27.42 ± 8.65 | 26.79 ± 7.44 | 28.00 ± 9.76 | 24.81 ± 6.92 | 29.04 ± 9.55 |
| 16.78 ± 7.33 | |||||||
| PANSS-G | - | 35.93 ± 9.38 | 38.15 ± 8.13 | 38.37 ± 7.65 | 37.95 ± 8.73 | 37.69 ± 9.16 | 38.30 ± 7.69 |
| 23.22 ± 5.99 | |||||||
| PANSS-T | - | 82.13 ± 19.37 | 88.5 ± 21.45 | 87.37 ± 19.20 | 89.52 ± 23.73 | 84. 75 ± 23.38 | 90.26 ± 20.31 |
| 51.33 ± 15.66 | |||||||
| SAAS | 108.17 ± 59.32 | 155.33 ± 60.54 | 198.55 ± 89.67 | 172.86 ± 94.93 | 181.50 ± 88.51 | 205.21 ± 85.42 | 196.48 ± 95.32 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | - | 87.14 ± 22.68 | 85.57 ± 14.17 | 84.62 ± 14.14 | 86.64 ± 14.65 | 82.54 ± 7.98 | 88.56 ± 17.74 |
| TC 1 (mg/dL) | - | 142.75 ± 24.82 | 185.41 ± 54.35 | 170.93 ± 56.67 | 201.00 ± 49.13 | 184.31 ± 51.06 | 191.23 ± 58.67 |
| TG 2 (mg/dL) | - | 77.75 ± 31.64 | 116.11 ± 60.04 | 103.57 ± 49.04 | 129.61 ± 69.45 | 117.77 ± 62.18 | 118.62 ± 60.74 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | - | 4.1225 ± 0.26 | 4.1223 ± 0.44 | 4.22 ± 0.40 | 4.01 ± 0.48 | 4.04 ± 0.41 | 4.22 ± 0.47 |
| Protein/Group/Coefficient | Variables | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANSS-P | PANSS-N | PANSS-G | PANSS-T | SAAS | Glucose (mg/dL) | TC1 (mg/dL) | TG2 (mg/dL) | Albumin (g/dL) | |||
| IGF-2 (ng/mL) | FE (n = 15) | r | 0.003 | −0.314 | −0.286 | −0.282 | −0.336 | 0.002 | −0.674 | 0.003 | −0.147 |
| p | 0.991 | 0.255 | 0.301 | 0.308 | 0.241 | 0.993 | 0.016 * | 0.992 | 0.648 | ||
| FE_1 (n = 9) | r | 0.745 s | 0.862 s | 0.445 s | 0.767 s | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p | 0.021 * | 0.003 * | 0.230 | 0.016 * | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| ∆FE (n = 9) | r | 0.800 s,%↓ | 0.150 s, %↓ | 0.117 s, %↓ | 0.533 s, %↓ | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p | 0.014 * | 0.708 | 0.776 | 0.148 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| ME (n = 40) | r | 0.135 s | 0.162 | −0.035 | 0.075 | 0.026 s | 0.08 | 0.054 | 0.142 | 0.160 | |
| p | 0.407 | 0.318 | 0.829 | 0.644 | 0.879 | 0.673 | 0.788 | 0.479 | 0.435 | ||
| ME_R (n = 19) | r | 0.226 | 0.168 | −0.090 | 0.125 | −0.271 | 0.269 | −0.275 s | 0.015 | 0.347 | |
| p | 0.353 | 0.491 | 0.714 | 0.609 | 0.277 | 0.314 | 0.342 s | 0.958 | 0.224 | ||
| ME_NR (n = 21) | r | −0.085 | 0.257 s | 0.008 | 0.049 | 0.259 | −0.258 s | 0.450 | 0.284 | −0.04 | |
| p | 0.715 | 0.261 s | 0.974 | 0.834 | 0.270 | 0.374 s | 0.123 | 0.347 | 0.891 | ||
| ME_A (n = 16) | r | −0.084 s | −0.169 | −0.273 | −0.235 | 0.095 s | −0.466 s | 0.138 | 0.110 | 0.201 | |
| p | 0.757 s | 0.530 | 0.307 | 0.381 | 0.748 s | 0.108 s | 0.653 | 0.720 | 0.491 | ||
| ME_T (n = 23) | r | 0.267 | 0.256 s | 0.141 | 0.296 | −0.008 s | 0.219 | −0.007 | 0.207 | 0.094 | |
| p | 0.217 | 0.238 s | 0.522 | 0.170 | 0.971 s | 0.416 | 0.983 | 0.498 | 0.770 | ||
| Protein/Group/Coefficient | Variables | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANSS-P | PANSS-N | PANSS-G | PANSS-T | SAAS | Glucose (mg/dL) | TC1 (mg/dL) | TG2 (mg/dL) | Albumin (g/dL) | |||
| IGFBP-7 (ng/mL) | FE (n = 15) | r | −0.176 | 0.41 | 0.252 | 0.265 | −0.03 | −0.172 | 0.067 | 0.177 | −0.079 |
| p | 0.548 | 0.145 | 0.385 | 0.36 | 0.918 | 0.556 | 0.83 | 0.583 | 0.808 | ||
| FE_1 (n = 11) | r | 0.068 | 0.128 | −0.119 | −0.036 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p | 0.841 | 0.709 | 0.727 | 0.915 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| ∆FE (n = 11) | r | 0.136 s, %↓ | −0.209 s, %↓ | −0.200 s, %↓ | −0.100 s, %↓ | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p | 0.694 | 0.539 | 0.557 | 0.776 | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| ME (n = 40) | r | 0.081 s | 0.322 | 0.241 | 0.276 | 0.325 s | −0.168 | 0.038 | 0.037 | 0.098 | |
| p | 0.62 | 0.043 * | 0.135 | 0.085 | 0.047 * | 0.374 | 0.849 | 0.855 | 0.633 | ||
| ME_R (n = 19) | r | 0.048 | 0.137 | 0.123 | 0.123 | 0.021 | −0.324 | −0.288 s | −0.301 | −0.398 | |
| p | 0.845 | 0.576 | 0.615 | 0.617 | 0.933 | 0.221 | 0.318 s | 0.296 | 0.158 | ||
| ME_NR (n = 21) | r | 0.246 | 0.435 s | 0.311 | 0.384 | 0.384 | 0.075 s | 0.263 | 0.185 | 0.441 | |
| p | 0.283 | 0.049 s | 0.170 | 0.086 | 0.094 | 0.799 s | 0.385 | 0.545 | 0.151 | ||
| ME_A (n = 16) | r | −0.013 s | 0.330 | 0.288 | 0.250 | 0.407 s | −0.219 s | −0.171 | −0.182 | 0.049 | |
| p | 0.961 s | 0.212 | 0.279 | 0.349 | 0.149 s | 0.472 s | 0.577 | 0.552 | 0.869 | ||
| ME_T (n = 23) | r | 0.172 | 0.316 s | 0.178 | 0.276 | 0.363 s | −0.132 | 0.284 | 0.353 | 0.099 | |
| p | 0.433 | 0.142 s | 0.417 | 0.203 | 0.089 s | 0.625 | 0.347 | 0.236 | 0.76 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Pereira, C.; Penedo, M.A.; Rivera-Baltanas, T.; Fernández-Martínez, R.; Ortolano, S.; Olivares, J.M.; Agís-Balboa, R.C. Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF-2) and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP-7) Are Upregulated after Atypical Antipsychotics in Spanish Schizophrenia Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179591
Fernández-Pereira C, Penedo MA, Rivera-Baltanas T, Fernández-Martínez R, Ortolano S, Olivares JM, Agís-Balboa RC. Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF-2) and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP-7) Are Upregulated after Atypical Antipsychotics in Spanish Schizophrenia Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(17):9591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179591
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Pereira, Carlos, Maria Aránzazu Penedo, Tania Rivera-Baltanas, Rafael Fernández-Martínez, Saida Ortolano, José Manuel Olivares, and Roberto Carlos Agís-Balboa. 2022. "Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF-2) and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP-7) Are Upregulated after Atypical Antipsychotics in Spanish Schizophrenia Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 17: 9591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179591
APA StyleFernández-Pereira, C., Penedo, M. A., Rivera-Baltanas, T., Fernández-Martínez, R., Ortolano, S., Olivares, J. M., & Agís-Balboa, R. C. (2022). Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF-2) and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP-7) Are Upregulated after Atypical Antipsychotics in Spanish Schizophrenia Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(17), 9591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179591







