11β-HSD as a New Target in Pharmacotherapy of Metabolic Diseases
Abstract
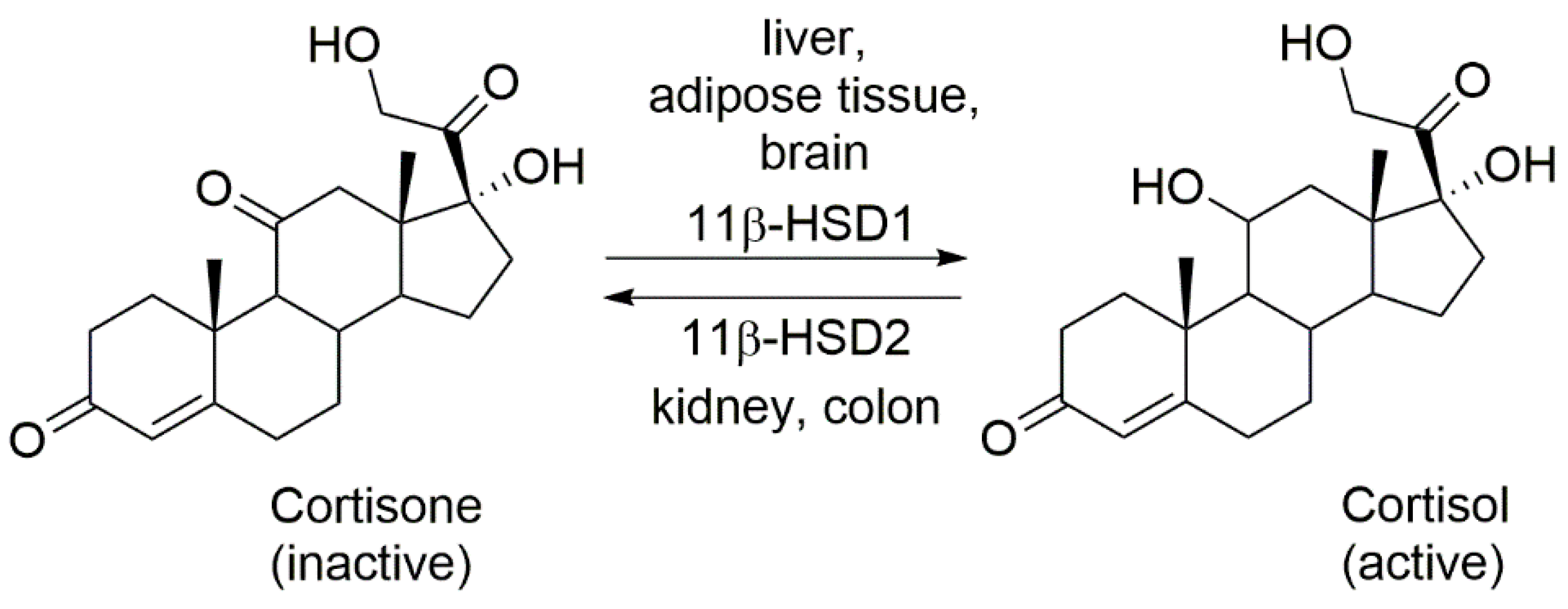
1. Regulation of the Local Action of Glucocorticoids
2. Isoforms Regulating the Local Action of Glucocorticoids
3. The Role of Glucocorticoids in Metabolic Syndrome
4. Metabolic Effects of 11β-HSD1 Deficiency
5. 11β-HSD1 Inhibitors in the Therapy of Components of the Metabolic Syndrome
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gensler, L.S. Glucocorticoids: Complications to anticipate and prevent. Neurohospitalist 2013, 3, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids: Mechanisms of Action in Health and Disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A General Introduction to Glucocorticoid Biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo-Payet, N.; Payet, M.D. Mechanism of action of ACTH: Beyond cAMP. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliver, T.; Eid, N. Effects of glucocorticoids on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in children and adults. Immunol Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2005, 25, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Engeland, W.C.; Ehrhart-Bornstein, M.; Herman, J.P. Dissociation of ACTH and glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 19, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.S.; Gillespie, C.F.; Neigh, G.N. Energetic stress: The reciprocal relationship between energy availability and the stress response. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 166, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.M.; Krozowski, Z.S. 11 beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Vitam. Horm. 1999, 57, 249–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kupczyk, D.; Studzińska, R.; Baumgart, S.; Bilski, R.; Kosmalski, T.; Kołodziejska, R.; Woźniak, A. A novel N-tert-butyl derivatives of pseudothiohydantoin as potential target in anti-cancer therapy. Molecules 2021, 26, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kloet, E.R.; de Kloet, S.F.; de Kloet, C.S.; de Kloet, A.D. Top-down and bottom-up control of stress-coping. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 31, e12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska, R.; Kupczyk, D.; Płazińska, A.; Kołodziejska, R.; Kosmalski, T.; Modzelewska-Banachiewicz, B. Thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidin-5-one derivatives as a novel class of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 81, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzaki, H.; Paterson, J.; Shinyama, H.; Morton, N.M.; Mullins, J.J.; Seckl, J.R.; Flier, J.S. A transgenic model of visceral obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Science 2001, 294, 2166–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.R. Is “Cushing’s disease of the omentum” an affliction of mouse and men? Diabetologia 2004, 47, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Anagnostis, P.; Katsiki, N.; Adamidou, F.; Athyros, V.G.; Karagiannis, A.; Kita, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P. 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors: Novel agents for the treatment of metabolic syndrome and obesity-related disorders? Metabolism 2013, 62, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttgereit, F.; Scheffold, A. Rapid glucocorticoid effects on immune cells. Steroids 2002, 67, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Hattori, T.; Nagasawa, K.; Matsuura, N.; Takahashi, K.; Murohara, T.; Nagata, K. Blockade of glucocorticoid receptors with RU486 attenuates cardiac damage and adipose tissue inflammation in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Hypertens. Res. 2015, 38, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.K.; Hutson, I.; Harris, C.A. Hepatic Glucocorticoid Receptor Plays a Greater Role Than Adipose GR in Metabolic Syndrome Despite Renal Compensation. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4943–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desarzens, S.; Faresse, N. Adipocyte glucocorticoid receptor has a minor contribution in adipose tissue growth. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 230, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, K.M.; Hartmann, K.; Kaltenecker, D.; Vettorazzi, S.; Bauer, M.; Mauser, L.; Amann, S.; Jall, S.; Fischer, K.; Esterbauer, H.; et al. Adipocyte Glucocorticoid Receptor Deficiency Attenuates Aging- and HFD-Induced Obesity and Impairs the Feeding-Fasting Transition. Diabetes 2017, 66, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Roh, H.C.; Kumari, M.; Rosen, E.D. Adipocyte glucocorticoid receptor is important in lipolysis and insulin resistance due to exogenous steroids, but not insulin resistance caused by high fat feeding. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, M.; Gültekin, H. Could serum total cortisol level at admission predict mortality due to coronavirus disease 2019 in the intensive care unit? A prospective study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2021, 139, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahat, R.K.; Rathore, V.; Singh, N.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.K.; Shah, R.K.; Garg, C. Lipid profile as an indicator of COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 45, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boechat, J.L.; Chora, I.; Morais, A.; Delgado, L. The immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 immunopathology—Current perspectives. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Via, M.A.; Mechanick, J.I. Obesity as a Disease. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2014, 3, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Gratteri, S.; Gualtieri, P.; Cammarano, A.; Bertucci, P.; Di Renzo, L. Why primary obesity is a disease? J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, D.N. Cushing’s syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.; Troop, N.; Connan, F.; Treasure, J.; Campbell, I.C. The effects of stress on body weight: Biological and psychological predictors of change in BMI. Obesity 2007, 15, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.D.; Azevedo, I.; Monteiro, R.; Martins, M.J. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1: Relevance of its modulation in the pathophysiology of obesity, the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.; Tomlinson, J.W. The dehydrogenase hypothesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 872, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Morton, N.M.; Dhillon, H.; Ramage, L.; Seckl, J.R.; Flier, J.S. Adipocyte-specific glucocorticoid inactivation protects against diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.; McQueen, A.; Chen, T.-C.; Wang, J.-C. Regulation of glucose homeostasis by glucocorticoids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 872, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliwad, S.K.; Gray, N.E.; Wang, J. Angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4). Adipocyte 2012, 1, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, M.-J.; Pramyothin, P.; Karastergiou, K.; Fried, S.K. Deconstructing the roles of glucocorticoids in adipose tissue biology and the development of central obesity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis. Dis. 2014, 1842, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaufrère, B.; Morio, B. Fat and protein redistribution with aging: Metabolic considerations. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Iozzo, P.; Virtanen, K.A.; Honka, M.J.; Bucci, M.; Nuutila, P. Adipose tissue and skeletal muscle insulin-mediated glucose uptake in insulin resistance: Role of blood flow and diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, P.; Bouchard, B. The Impact of Aging on Adipose Function and Adipokine Synthesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front. Med. 2013, 7, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, I.; Boudreau, A.; Stephens, J.M. Adipose tissue in health and disease. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erion, K.A.; Corkey, B.E. Hyperinsulinemia: A Cause of Obesity? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeman, N.M.; Skovsø, S.; Page, M.M.; Lim, G.E.; Johnson, J.D. A causal role for hyperinsulinemia in obesity. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, R173–R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markussen, J.; Damgaard, U.; Pingel, M.; Snel, L.; Sørensen, A.R.; Sørensen, E. Human insulin (Novo): Chemistry and characteristics. Diabetes Care 1983, 6, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reaven, G.M. Insulin resistance, the insulin resistance syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. Panminerva. Med. 2005, 47, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mlinar, B.; Marc, J.; Janez, A.; Pfeifer, M. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance and associated diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 375, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.M.; Pennings, N. Insulin Resistance. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, D.P.; Knight, B.L.; Soutar, A.K. Hormonal regulation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor activity in human hepatoma Hep G2 cells. Insulin increases LDL receptor activity and diminishes its suppression by exogenous LDL. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 174, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A. Insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of dyslipidemia. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Haffner, S.M. Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, P.A.; Thalhammer, C.; Schmied, C.; Spring, S.; Amann-Vesti, B.; Spinas, G.A.; Berneis, K. Small, dense LDL particles predict changes in intima media thickness and insulin resistance in men with type 2 diabetes and prediabetes—A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musunuru, K.; Orho-Melander, M.; Caulfield, M.P.; Li, S.; Salameh, W.A.; Reitz, R.E.; Berglund, G.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G.; Williams, P.T.; et al. Ion mobility analysis of lipoprotein subfractions identifies three independent axes of cardiovascular risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C. Glucose: A continuous risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Diabet. Med. 1997, 14, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, C.; Gerstein, H.C.; Yusuf, S.; Zhao, F.; Hilbrich, L.; Anderson, C.; Sleight, P.; Teo, K.; ONTARGET/TRANSCEND Investigators. Glucose levels predict hospitalization for congestive heart failure in patients at high cardiovascular risk. Circulation 2007, 115, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorisky, A. Effect of High Glucose Levels on White Adipose Cells and Adipokines-Fuel for the Fire. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahniwal, M.; Little, J.P.; Klegeris, A. High Glucose Enhances Neurotoxicity and Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion by Stimulated Human Astrocytes. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, P.; Timpel, P.; Harst, L.; Greaves, C.J.; Ali, M.K.; Lambert, J.; Weber, M.B.; Almedawar, M.M.; Morawietz, H. Blood Sugar Regulation for Cardiovascular Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: JACC Health Promotion Series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.H.; Swanson, R.E.; Lau, H.J.; Cheah, J.; Bishop, V.R.; Snell, K.; Reid, A.; Meddle, S.L.; Wingfield, J.C.; Krause, J.S. Tissue-specific expression of 11β-HSD and its effects on plasma corticosterone during the stress response. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb209346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. The Definition and Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotelevtsev, Y.; Holmes, M.C.; Burchell, A.; Houston, P.M.; Schmoll, D.; Jamieson, P.; Best, R.; Brown, R.; Edwards, C.R.; Seckl, J.R.; et al. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 knockout mice show attenuated glucocorticoid-inducible responses and resist hyperglycemia on obesity or stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14924–14929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dalmazi, G.; Pagotto, U.; Pasquali, R.; Vicennati, V. Glucocorticoids and type 2 diabetes: From physiology to pathology. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 525093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalestou, E.; Genser, L.; Rutter, G.A. Glucocorticoid Metabolism in Obesity and Following Weight Loss. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, N.M.; Paterson, J.M.; Masuzaki, H.; Holmes, M.C.; Staels, B.; Fievet, C.; Walker, B.R.; Flier, J.S.; Mullins, J.J.; Seckl, J.R. Novel adipose tissue-mediated resistance to diet-induced visceral obesity in 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1-deficient mice. Diabetes 2004, 53, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, N.; Walker, E.A.; Bujalska, I.J.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Chalder, S.M.; Arlt, W.; Lavery, G.G.; Bedendo, O.; Ray, D.W.; Laing, I.; et al. Mutations in the genes encoding 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase interact to cause cortisone reductase deficiency. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujalska, I.J.; Draper, N.; Michailidou, Z.; Tomlinson, J.W.; White, P.C.; Chapman, K.E.; Walker, E.A.; Stewart, P.M. Hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase confers oxo-reductase activity upon 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 34, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, R.C.; Rooyackers, O.; Walker, B.R. Effects of the 11--beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitor carbenoxolone on insulin sensitivity in men with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, T.C.; Andrew, R.; Homer, N.Z.; Andrews, R.C.; Smith, K.; Walker, B.R. Increased in vivo regeneration of cortisol in adipose tissue in human obesity and effects of the 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor carbenoxolone. Diabetes 2005, 54, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanesha, N.; Joharapurkar, A.; Shah, G.; Kshirsagar, S.; Dhote, V.; Sharma, A.; Jain, M. Inhibition of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 by carbenoxolone affects glucose homeostasis and obesity in db/db mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 39, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, T.; Morrow, L.; Hompesch, M.; Häring, H.U.; Kapitza, C.; Abt, M.; Ramsauer, M.; Magnone, M.C.; Fuerst-Recktenwald, S. Safety, efficacy and weight effect of two 11β-HSD1 inhibitors in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, P.; Shah, S.; Hermanowski-Vosatka, A.; Plotkin, D.; Springer, M.S.; Donahue, S.; Thach, C.; Klein, E.J.; Lai, E.; Kaufman, K.D. Effects of an 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, MK-0916, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Banarer, S.; Fonseca, V.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Sun, W.; Yao, W.; Hollis, G.; Flores, R.; Levy, R.; Williams, W.V.; et al. The 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor INCB13739 imporives hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by metofrmonmonotherapy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, M.; He, C.; Zhuo, J.; Burns, D.M.; Qian, D.Q.; Lin, Q.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, L.; Shi, E.; et al. Discovery of 1′-(1-phenylcyclopropane-carbonyl)-3H-spiro[isobenzofuran-1,3′-pyrrolidin]-3-one as a novel steroid mimetic scaffold for the potent and tissue-specific inhibition of 11β-HSD1 using a scaffold-hopping approach. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 69, 128782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Hermanowski-Vosatka, A.; Gibson, K.; Ruck, R.A.; Jia, G.; Zhang, J.; Hwang, P.M.; Ryan, N.W.; Langdon, R.B.; Feig, P.U. Efficacy and safety of the selective 11β-HSD-1 inhibitors MK-0736 and MK-0916 in overweight and obese patients with hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2011, 5, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.S.; Botfield, H.; Markey, K.; Mitchell, J.L.; Alimajstorovic, Z.; Westgate, C.; Sagmeister, M.; Fairclough, R.J.; Ottridge, R.S.; Yiangou, A.; et al. 11βHSD1 Inhibition with AZD4017 Improves Lipid Profiles and Lean Muscle Mass in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajjan, R.A.; Hensor, E.; Del Galdo, F.; Shams, K.; Abbas, A.; Fairclough, R.J.; Webber, L.; Pegg, L.; Freeman, A.; Taylor, A.E.; et al. Oral 11β-HSD1 inhibitor AZD4017 improves wound healing and skin integrity in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 186, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianzano, S.; Heise, T.; Jungnik, A.; Schepers, C.; Schölch, C.; Gräfe-Mody, U. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single oral doses of BI 187004, an inhibitor of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1, in healthy male volunteers with overweight or obesity. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaire, S.; Walzer, M.; Wang, T.; Krauwinkel, W.; Yuan, N.; Marek, G.J. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of ASP3662, a Novel 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Inhibitor, in Healthy Young and Elderly Subjects. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2019, 12, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.W.; Stewart, P.M. Mechanisms of disease: Selective inhibition of 11 betahydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 as a novel treatment for the metabolic syndrome. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 1, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, M.X. Inhibition of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 ameliorates obesity-related insulin resistance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbriere, R.; Vuaroqueaux, V.; Achard, V.; Boullu-Ciocca, S.; Labuhn, M.; Dutour, A.; Grino, M. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 mRNA is increased in both visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese patients. Obesity 2006, 14, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.M.; Di, W.J.; Zhu, T.; Xie, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Ding, G. Comparison of gene transcription between subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in Chinese adults. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Gao, Z.; Ye, J. Regulation of 11β-HSD1 expression during adipose tissue expansion by hypoxia through different activities of NF-κB and HIF-1α. American journal of physiology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariniello, B.; Ronconi, V.; Rilli, S.; Bernante, P.; Boscaro, M.; Mantero, F.; Giacchetti, G. Adipose tissue 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression in obesity and Cushing’s syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 155, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, R.; Carvajal, C.; Escalona, A.; Boza, C.; Pérez, G.; Ibáñez, L.; Fardella, C. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 is overexpressed in subcutaneous adipose tissue of morbidly obese patients. Obes. Surg. 2009, 19, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsamakis, G.; Anwar, A.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Shackleton, C.H.; McTernan, P.G.; Chetty, R.; Wood, P.J.; Banerjee, A.K.; Holder, G.; Barnett, A.H.; et al. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 activity in lean and obese males with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. 2004, 89, 4755–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, L.; Girola, A.; Gilardini, L.; Conti, A.; Cattaldo, S.; Micheletto, G.; Invitti, C. Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome are associated with increased expression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 in obese subjects. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudrand, R.; Carvajal, C.A.; Riquelme, A.; Morales, M.; Solis, N.; Pizarro, M.; Escalona, A.; Boza, C.; Pérez, G.; Domínguez, A.; et al. Overexpression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in hepatic and visceral adipose tissue is associated with metabolic disorders in morbidly obese patients. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devang, N.; Satyamoorthy, K.; Rai, P.S.; Nandini, M.; Rao, S.; Phani, N.M.; Adhikari, P. Association of HSD11B1 gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome in South Indian population. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 131, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.; Smith, K.; Jones, G.C.; Walker, B.R. Distinguishing the Activities of 11β-Hydroxysteroid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rask, E.; Walker, B.R.; Söderberg, S.; Livingstone, D.E.; Eliasson, M.; Johnson, O.; Andrew, R.; Olsson, T. Tissue-specific changes in peripheral cortisol metabolism in obese women: Increased adipose 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 activity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Di, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Yu, J.; Zha, J.; Lv, S.; Cheng, P.; et al. Adipose tissue-targeted 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor protects against diet-induced obesity. Endocr. J. 2011, 58, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, S.; Takahashi, T.; Iwamura, T.; Nakaki, J.; Sekiya, Y.; Yagi, M.; Kumagai, H.; Sato, M.; Sakami, S.; Nitta, A.; et al. HIS-388, a novel orally active and long-acting 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor, ameliorates insulin sensitivity and glucose intolerance in diet-induced obesity and nongenetic type 2 diabetic murine models. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanowski-Vosatka, A.; Balkovec, J.M.; Cheng, K.; Chen, H.Y.; Hernandez, M.; Koo, G.C.; Le Grand, C.B.; Li, Z.; Metzger, J.M.; Mundt, S.S.; et al. 11beta-HSD1 inhibition ameliorates metabolic syndrome and prevents progression of atherosclerosis in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooy, K.; Webster, S.P.; Noble, J.; Binnie, M.; Walker, B.R.; Seckl, J.R.; Yau, J.L. Partial deficiency or short-term inhibition of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 improves cognitive function in aging mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 30, 13867–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooy, K.; Noble, J.; McBride, A.; Binnie, M.; Yau, J.L.; Seckl, J.R.; Walker, B.R.; Webster, S.P. Cognitive and Disease-Modifying Effects of 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Inhibition in Male Tg2576 Mice, a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 4592–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, J.L.; Noble, J.; Kenyon, C.J.; Hibberd, C.; Kotelevtsev, Y.; Mullins, J.J.; Seckl, J.R. Lack of tissue glucocorticoid reactivation in 11beta -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 knockout mice ameliorates age-related learning impairments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4716–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, J.L.; Noble, J.; Seckl, J.R. 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 deficiency prevents memory deficits with aging by switching from glucocorticoid receptor to mineralocorticoid receptor-mediated cognitive control. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 31, 4188–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.L.; Wheelan, N.; Noble, J.; Walker, B.R.; Webster, S.P.; Kenyon, C.J.; Ludwig, M.; Seckl, J.R. Intrahippocampal glucocorticoids generated by 11β-HSD1 affect memory in aged mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska, R.; Kołodziejska, R.; Kupczyk, D.; Płaziński, W.; Kosmalski, T. A novel derivatives of thiazol 4(5H)one and their activity in the inhibition of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 79, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska, R.; Kołodziejska, R.; Płaziński, W.; Kupczyk, D.; Kosmalski, T.; Jasieniecka, K.; Modzelewska-Banachiewicz, B. Synthesis of the N-methyl derivatives of 2-aminothiazol-4(5H)–one and their interactions with 11βHSD1—Molecular modeling and in vitro studies. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupczyk, D.; Studzińska, R.; Bilski, R.; Baumgart, S.; Kołodziejska, R.; Woźniak, A. Synthesis of novel 2-(isopropylamino)thiazol-4(5H)-one derivatives and their inhibitory activity of 11β-HSD1 and 11β-HSD2 in aspect of carcinogenesis prevention. Molecules 2020, 25, 4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupczyk, D.; Studzińska, R.; Bilski, R.; Woźniak, A. Application of ELISA technique and human microsomes in the search for 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5747436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska, R.; Kupczyk, D.; Płaziński, W.; Baumgart, S.; Bilski, R.; Paprocka, R.; Kołodziejska, R. Novel 2-(Adamantan-1-ylamino)Thiazol-4(5H)-One Derivatives and Their Inhibitory Activity towards 11β-HSD1-Synthesis, Molecular Docking and In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kupczyk, D.; Bilski, R.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Studzińska, R.; Kędziora-Kornatowska, K.; Kosmalski, T.; Pedrycz-Wieczorska, A.; Głowacka, M. 11β-HSD as a New Target in Pharmacotherapy of Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168984
Kupczyk D, Bilski R, Kozakiewicz M, Studzińska R, Kędziora-Kornatowska K, Kosmalski T, Pedrycz-Wieczorska A, Głowacka M. 11β-HSD as a New Target in Pharmacotherapy of Metabolic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168984
Chicago/Turabian StyleKupczyk, Daria, Rafał Bilski, Mariusz Kozakiewicz, Renata Studzińska, Kornelia Kędziora-Kornatowska, Tomasz Kosmalski, Agnieszka Pedrycz-Wieczorska, and Mariola Głowacka. 2022. "11β-HSD as a New Target in Pharmacotherapy of Metabolic Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168984
APA StyleKupczyk, D., Bilski, R., Kozakiewicz, M., Studzińska, R., Kędziora-Kornatowska, K., Kosmalski, T., Pedrycz-Wieczorska, A., & Głowacka, M. (2022). 11β-HSD as a New Target in Pharmacotherapy of Metabolic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 8984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23168984






