Effective Optical Image Assessment of Cellulose Paper Immunostrips for Blood Typing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
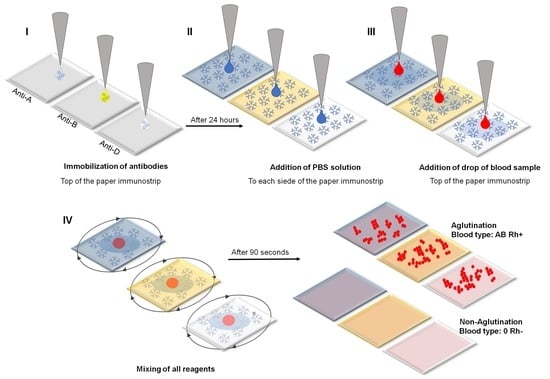
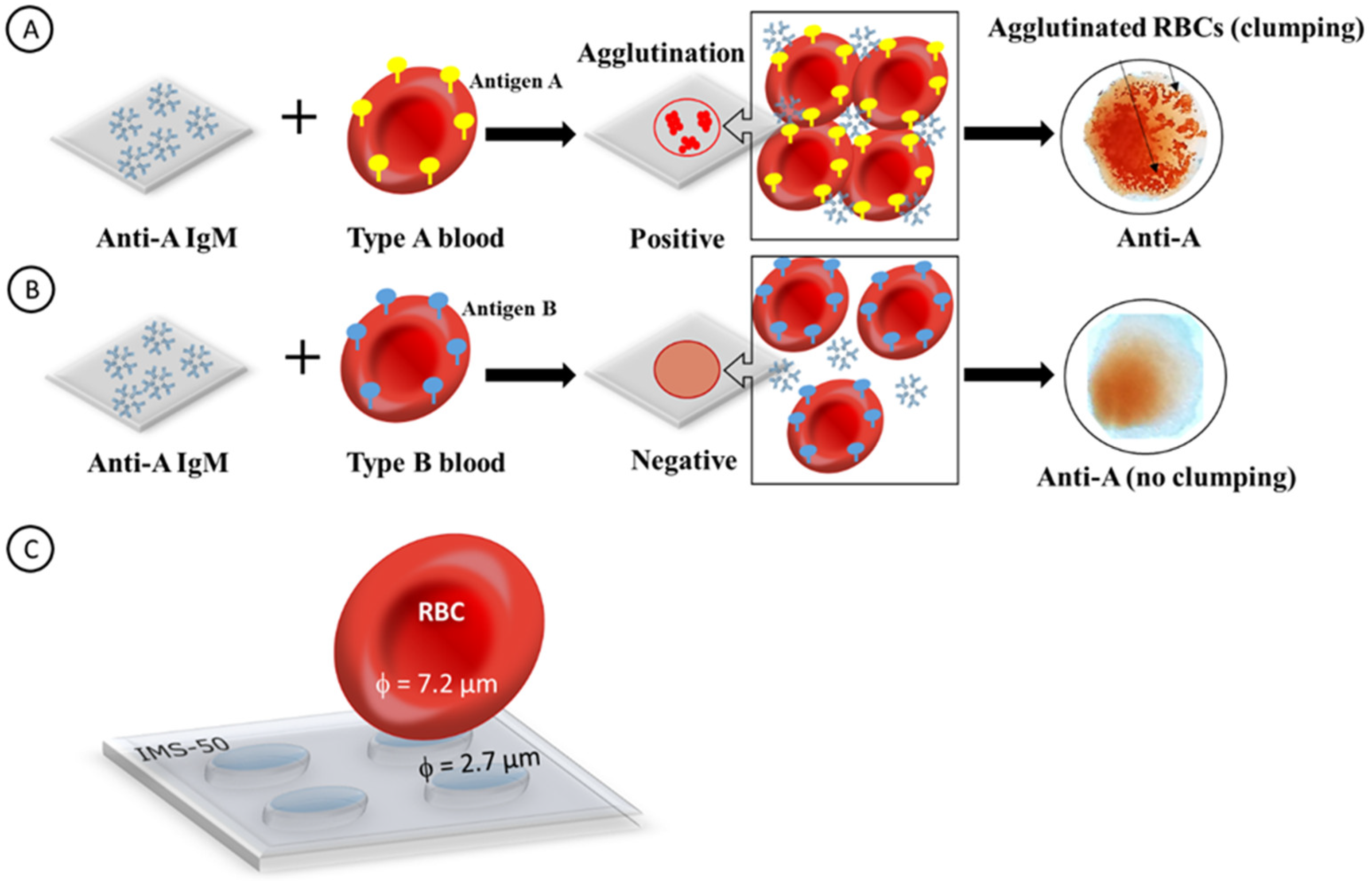
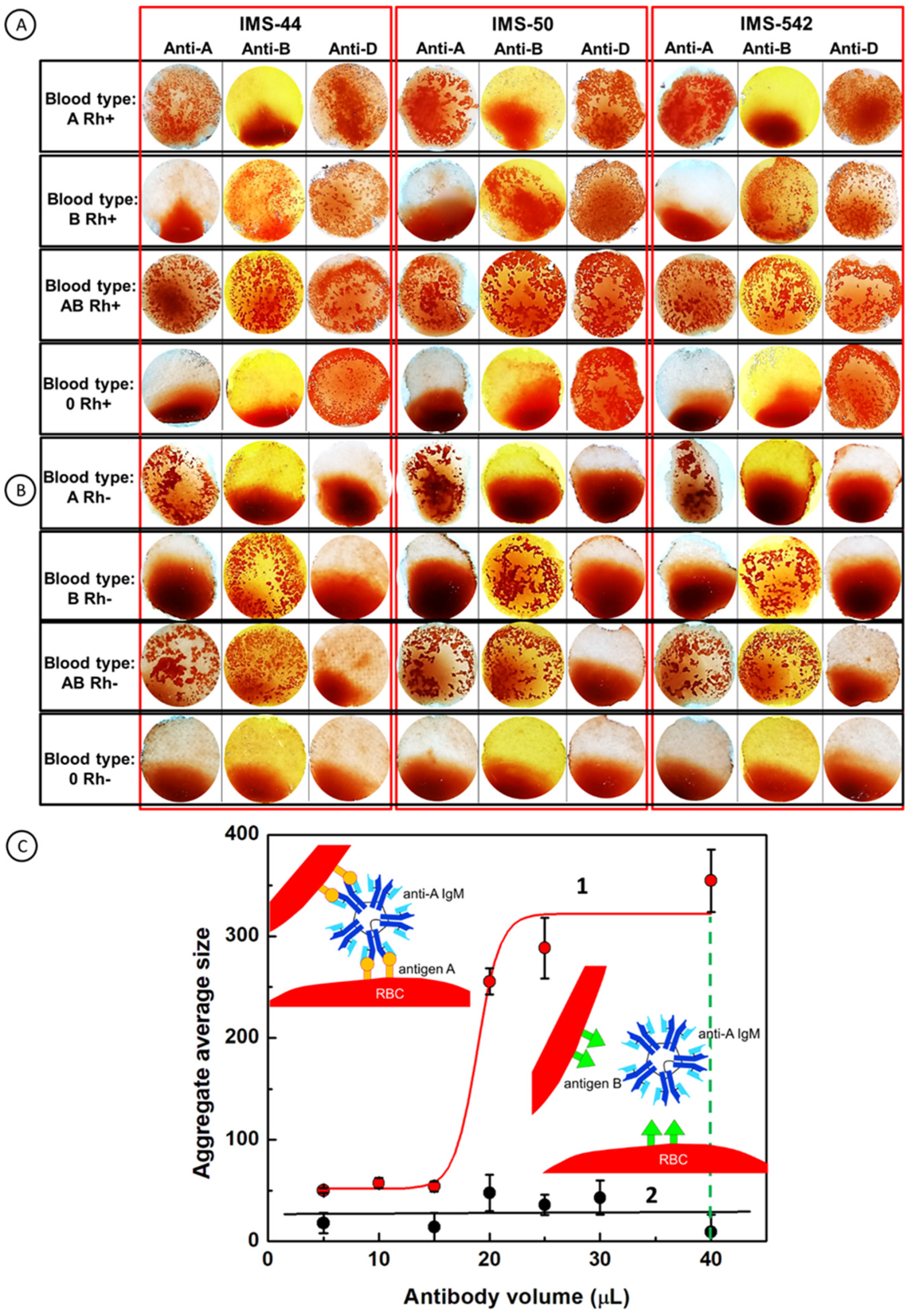
2.1. Principal Operation of Paper Immunostrips for Blood Typing
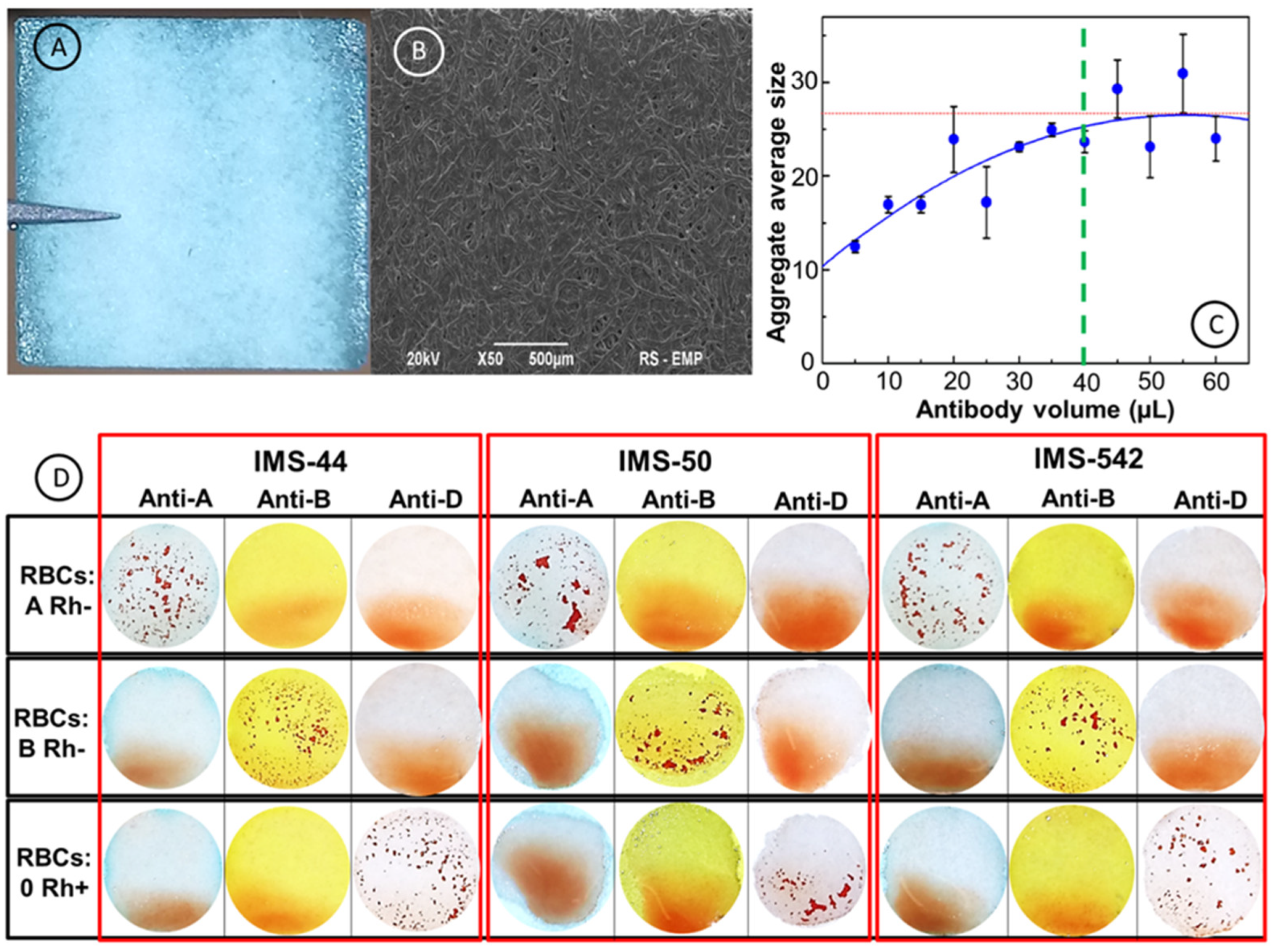
2.2. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
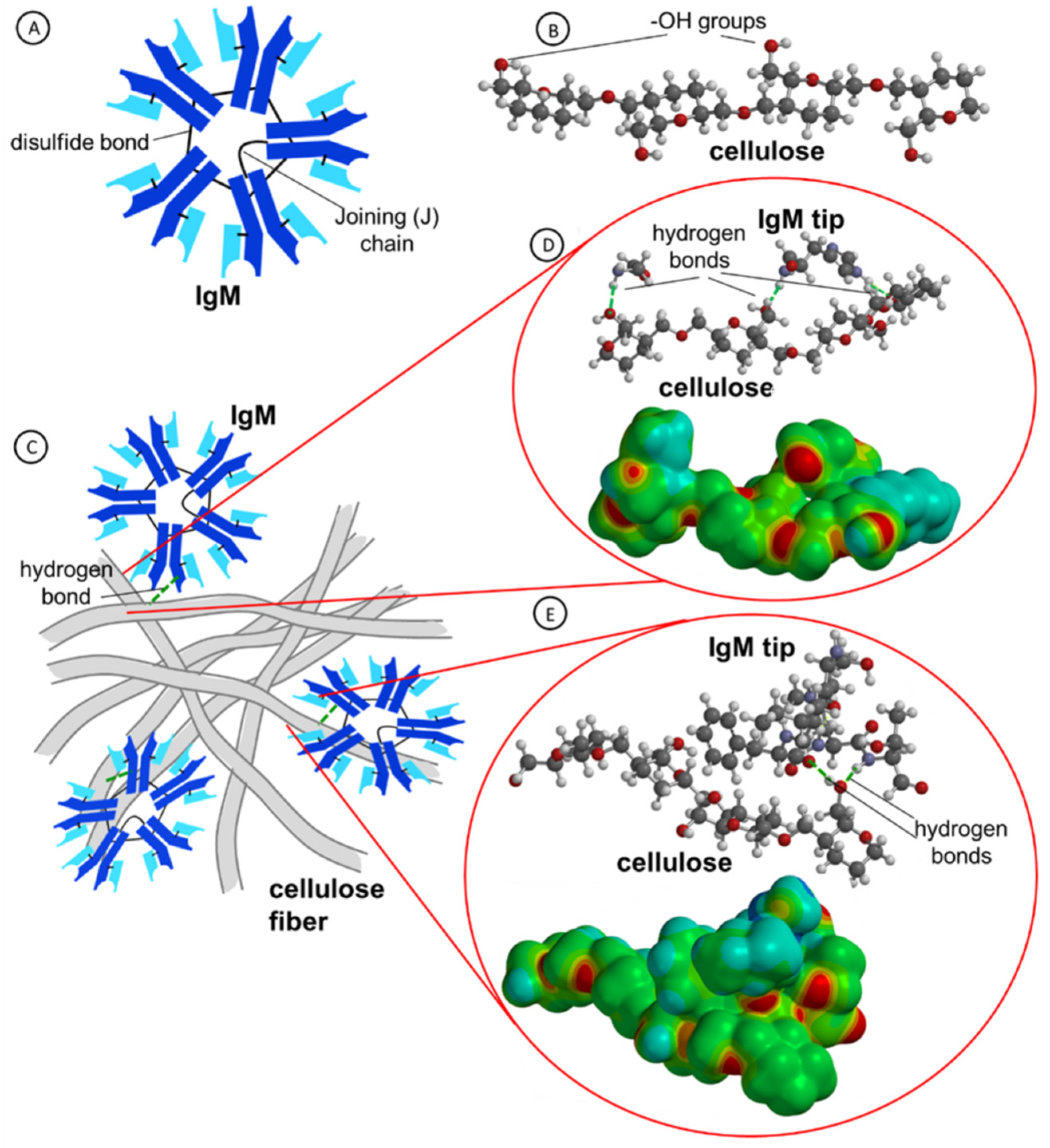
2.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of IgM Interactions with Cellulose Fibers
2.4. Morphology and Surface Structure of Cellulose Membranes
2.5. Blood Typing using Paper Immunostrips
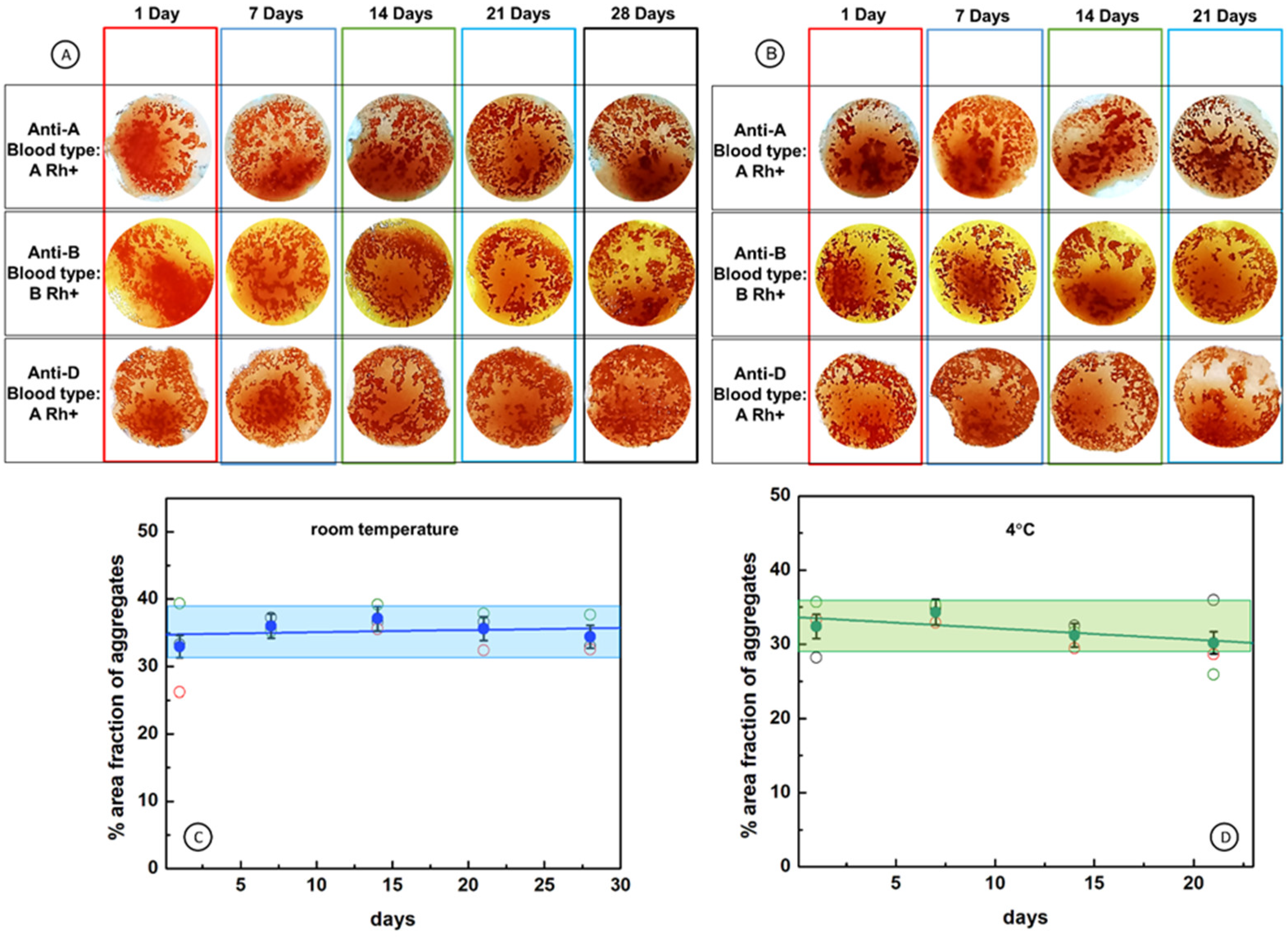
2.6. Durability of Cellulose Paper Immunostrips
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Modification of Cellulose Paper Immunostrips with Blood Typing Reagents
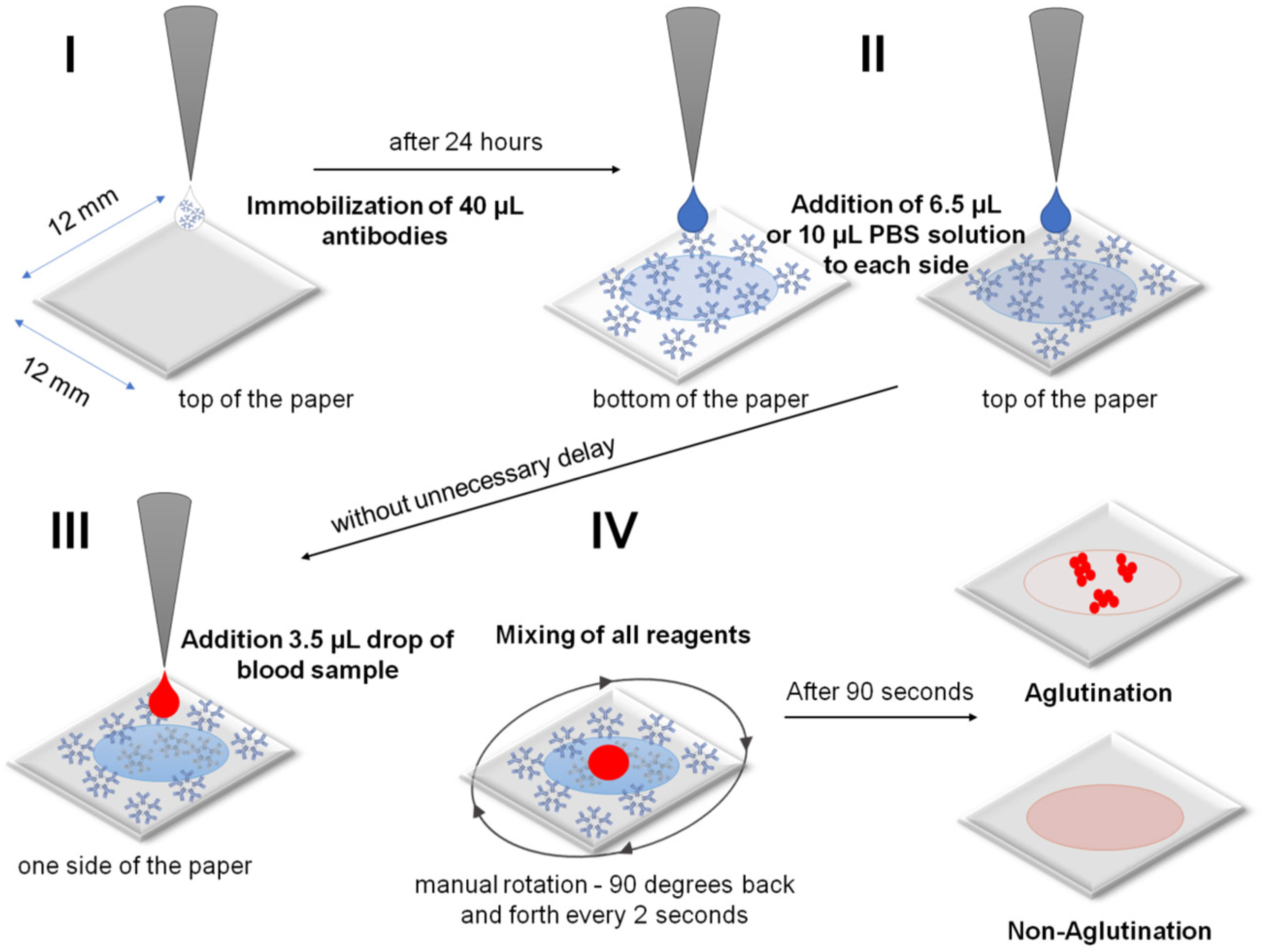
3.3. Steps in the RBCs and Blood Typing Procedure
- I.
- Immobilization of an antibody on a cellulose membrane to form the active biosensing membrane able to interact with antigens of RBCs in blood samples. A 40 µL sample of antibodies was dosed directly from the manufacturer’s reagent without dilution. Unfortunately, the absolute antibody concentration was not provided by the manufacturer.
- II.
- Beginning of analysis: wetting of a dry antibody-modified paper biosensor by sequentially dropping a PBS solution on both sides of the paper immunostrip (i.e., bilateral wetting): 6.5 µL of PBS for IMS-50 and 10 µL of PBS for IMS-44 and IMS-542 membranes.
- III.
- Application of a 3.5 µL drop of whole blood sample of known blood type (A+, B+, AB+, 0+, A, B, AB−, and 0−) dosed from the standard EDTA tube without dilution onto the top side of the paper immunostrip. The dosing procedure was the same for experiments with commercially available solutions of RBCs (concentration ~5 × 106 RBCs/µL).
- IV.
- Mixing of all reagents and waiting 90 s for agglutination, followed by drying with room temperature air stream and image recording. Mixing involved a manual rotation of 90 degrees back and forth every 2 s.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Yang, Y.; Du, M. Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Membranes for Their Sensing Applications. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9157–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, K.; Stobiecka, M. High-Performance Modified Cellulose Paper-Based Biosensors for Medical Diagnostics and Early Cancer Screening: A Concise Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, H.; Asghar, W.; Inci, F.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Jahangir, M.; Zhang, M.H.; Durmus, N.G.; Gurkan, U.A.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Demirci, U. Paper and Flexible Substrates as Materials for Biosensing Platforms to Detect Multiple Biotargets. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, S.K.; Linder, V.; Parviz, B.A.; Siegel, A.; Whitesides, G.M. An Integrated Approach to a Portable and Low-Cost Immunoassay for Resource-Poor Settings. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, P.; Edwards, T.; Fu, E.; Helton, K.; Nelson, K.; Tam, M.R.; Weigl, B.H. Microfluidic Diagnostic Technologies for Global Public Health. Nature 2006, 442, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kenz, H.; Corazza, F. Automated Point-of-Care Testing for ABO Agglutination Test: Proof of Concept and Validation. Vox Sang. 2015, 109, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primiceri, E.; Chiriacò, M.S.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Crocamo, A.; Ardissino, D.; Cereda, M.; Bramanti, A.P.; Bianchessi, M.A.; Giannelli, G.; Maruccio, G. Key Enabling Technologies for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Sensors 2018, 18, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Setya, D.; Aggarwal, G.; Arora, D.; Dara, R.C.; Ratan, A.; Bhardwaj, G.; Acharya, D.P. Evaluation of New Indigenous “Point-of-Care” ABO and Rh Grouping Device. J. Lab. Physicians 2018, 10, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, G.; Bromilow, I. Techniques used in Blood Grouping. In Essential Guide to Blood Groups, 3rd ed.; Daniels, G., Bromilow, I., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Malomgré, W.; Neumeister, B. Recent and Future Trends in Blood Group Typing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A.; Dickert, F.L. Blood Group Typing: From Classical Strategies to the Application of Synthetic Antibodies Generated by Molecular Imprinting. Sensors 2015, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, H.G.; Anstee, D.J. Mollison’s Blood Transfusion in Clinical Medicine, 12th ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Linden, J.V.; Wagner, K.; Voytovich, A.E.; Sheehan, J. Transfusion Errors in New York State: An Analysis of 10 Years’ Experience. Transfusion 2000, 40, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-J.; Ho, C.-Y.; Zhou, X.-M.; Yen, H.-R. Determination of Degree of RBC Agglutination for Blood Typing Using a Small Quantity of Blood Sample in a Microfluidic System. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrière, K.; Rouleau, A.; Gaiffe, O.; Fertey, J.; Morel, P.; Bourcier, V.; Pieralli, C.; Boireau, W.; Pazart, L.; Wacogne, B. Biochip Technology Applied to an Automated ABO Compatibility Test at the Patient Bedside. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-J.; Fan, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Lee, K.-H.; Lou, L.-Y. An Automatic Lab-on-Disc System for Blood Typing. SLAS Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2018, 23, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashiba, H.; Fujimaki, M.; Awazu, K.; Tanaka, T.; Makishima, M. Microfluidic Chips for Forward Blood Typing Performed with a Multichannel Waveguide-Mode Sensor. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2016, 7, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chou, H.-H.; Wang, C.-P.; Chen, C.-F. Rapid and Inexpensive Blood Typing on Thermoplastic Chips. Lab. Chip 2015, 15, 4533–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makulska, S.; Jakiela, S.; Garstecki, P. A Micro-Rheological Method for Determination of Blood Type. Lab. Chip 2013, 13, 2796–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, E.; Albahrani, M.; Alostad, J.; Ebraheem, H.K.; Alnaser, M.; Alkhateeb, N. Novel Optical Biosensor Method to Identify Human Blood Types Using Free-Space Frequency-Modulated Wave of NIR Photon Technology. Med. Devices 2018, 12, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szittner, Z.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; van der Donk, E.; Ligthart, P.C.; Lissenberg-Thunnissen, S.; van der Schoot, C.E.; Vidarsson, G. Multiplex Blood Group Typing by Cellular Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging. Transfusion 2019, 59, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Then, W.L.; Aguilar, M.-I.; Garnier, G. Quantitative Blood Group Typing Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 73, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, O.; Mann, K.-J.; Krassnig, S.; Dickert, F.L. Biomimetic ABO Blood-Group Typing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2626–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tamimi, M.; Shen, W.; Zeineddine, R.; Tran, H.; Garnier, G. Validation of Paper-Based Assay for Rapid Blood Typing. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Park, J.; Le, H.T.N.; Santhosh, M.; Kadam, A.N.; Cho, S. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Paper-Based Electrochemiluminescence Analytical Devices for Point-of-Care Testing Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Cao, R.; Tian, J.; McLiesh, H.; Garnier, G.; Shen, W. A Preliminary Study on the Stabilization of Blood Typing Antibodies Sorbed into Paper. Cellulose 2014, 21, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Tian, J.; Cao, R.; Li, M.; Cai, Z.; Shen, W. Barcode-Like Paper Sensor for Smartphone Diagnostics: An Application of Blood Typing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11362–11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarujamrus, P.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Siripinyanond, A.; Shiowatana, J.; Shen, W. Mechanisms of Red Blood Cells Agglutination in Antibody-Treated Paper. Analyst 2012, 137, 2205–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Thouas, G.; Shen, W.; Whyte, G.; Garnier, G. Paper Diagnostic for Instantaneous Blood Typing. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4158–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Shen, W. Control Performance of Paper-Based Blood Analysis Devices through Paper Structure Design. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21624–21631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tian, J.; Ballerini, D.; Li, M.; Shen, W. A Study of the Transport and Immobilisation Mechanisms of Human Red Blood Cells in a Paper-Based Blood Typing Device Using Confocal Microscopy. Analyst 2013, 138, 4933–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeow, N.; McLiesh, H.; Guan, L.; Shen, W.; Garnier, G. Paper-Based Assay for Red Blood Cell Antigen Typing by the Indirect Antiglobulin Test. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5231–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Chandra, P. Paper-Based Miniaturized Immunosensor for Naked Eye ALP Detection Based on Digital Image Colorimetry Integrated with Smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, P.; Abolfathi, N. A Novel Method for Blood-Typing Using Nitrocellulose. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Cui, C.; Meng, L.; Hao, S.; Dai, R.; Yang, J. Emerging Cellulose-Derived Materials: A Promising Platform for the Design of Flexible Wearable Sensors toward Health and Environment Monitoring. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 2051–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.; Khattab, T.A. Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Biosensors for Medical Diagnosis. Biosensors 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tavakoli, H.; Ma, L.; Bautista, C.; Li, X. Chapter 12—Rapid Disease Diagnosis Using Low-Cost Paper and Paper-Hybrid Microfluidic Devices. In Multidisciplinary Microfluidic and Nanofluidic Lab-On-A-chip; Li, X., Yang, C., Li, P.C.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 325–360. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi Fana, S.; Paknejad, M.; Aminian, M. Paper Based Analytical Devices for Blood Grouping: A Comprehensive Review. Biomed. Microdevices 2021, 23, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertaeg, M.J.; Tabor, R.F.; McLiesh, H.; Garnier, G. A Rapid Paper-Based Blood Typing Method from Droplet Wicking. Analyst 2021, 146, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishat, S.; Jafry, A.T.; Martinez, A.W.; Awan, F.R. Paper-Based Microfluidics: Simplified Fabrication and Assay Methods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 336, 129681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songjaroen, T.; Primpray, V.; Manosarn, T.; Khumchanta, W.; Sakuldamrongpanich, T.; Kulkeratiyut, S.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. A Simple and Low-Cost Portable Paper-Based ABO Blood Typing Device for Point-of-Care Testing. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2018, 39, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songjaroen, T.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. Simultaneous Forward and Reverse ABO Blood Group Typing Using a Paper-Based Device and Barcode-like Interpretation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 921, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Guo, K. Blood Group Testing. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 827619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czajkowsky, D.M.; Shao, Z. The Human IgM Pentamer Is a Mushroom-Shaped Molecule with a Flexural Bias. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14960–14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saber, R.; Sarkar, S.; Gill, P.; Nazari, B.; Faridani, F. High Resolution Imaging of IgG and IgM Molecules by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy in Air Condition. Sci. Iran. 2011, 18, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putnam, F.W.; Florent, G.; Paul, C.; Shinoda, T.; Shimizu, A. Complete Amino Acid Sequence of the Mu Heavy Chain of a Human IgM Immunoglobulin. Science 1973, 182, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharimalla, A.; Deshmukh, S.; Patil, P.G.; Nadanathangam, V. Micro/Nano-Fibrillated Cellulose from Cotton Linters as Strength Additive in Unbleached Kraft Paper: Experimental, Semi-Empirical, and Mechanistic Studies. BioResour. 2017, 12, 5682–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
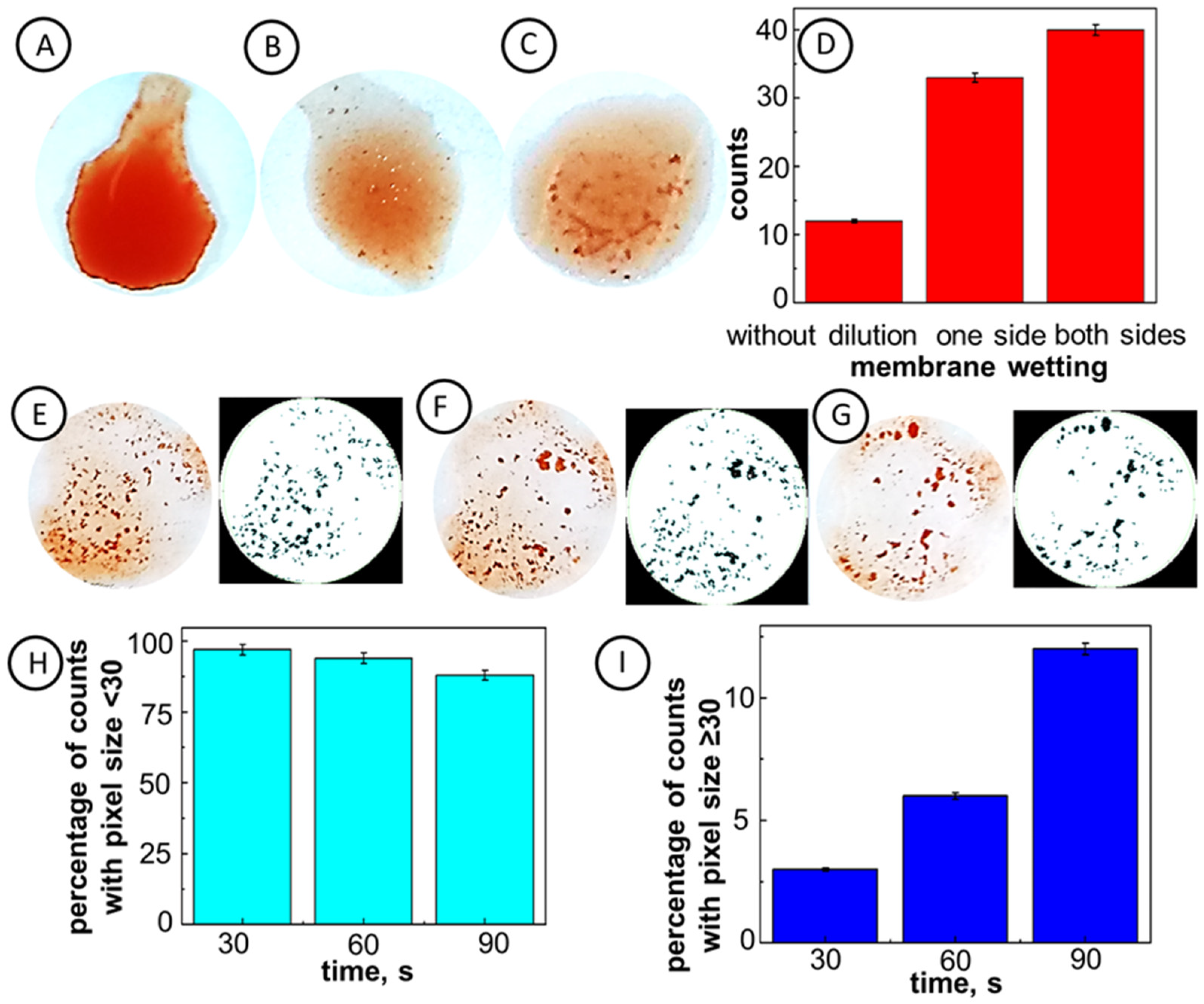

| Clinical Level No. | Aggregate Area, % | Agglutination Strength |
|---|---|---|
| - | 35.0 | Max |
| 4+ | 28.0 | Strong |
| 3+ | 21.0 | Heavy |
| 2+ | 14.0 | Moderate |
| 1+ | 7.0 | Mild |
| 0 | 0 | None |
| Immunostrip | Membrane Characteristic | Basis Weight [g/m2] | Pore Size [μm] | Thickness [μm] | Speed [s/100 mL] | Membrane Whatman Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMS-50 | High density | 97 | 2.7 | 115 | 2685 | 50 |
| IMS-542 | Medium density | 93 | 2.7 | 150 | 2510 | 542 |
| IMS-44 | Low density | 80 | 3 | 180 | 995 | 44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ratajczak, K.; Sklodowska-Jaros, K.; Kalwarczyk, E.; Michalski, J.A.; Jakiela, S.; Stobiecka, M. Effective Optical Image Assessment of Cellulose Paper Immunostrips for Blood Typing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158694
Ratajczak K, Sklodowska-Jaros K, Kalwarczyk E, Michalski JA, Jakiela S, Stobiecka M. Effective Optical Image Assessment of Cellulose Paper Immunostrips for Blood Typing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158694
Chicago/Turabian StyleRatajczak, Katarzyna, Karolina Sklodowska-Jaros, Ewelina Kalwarczyk, Jacek A. Michalski, Slawomir Jakiela, and Magdalena Stobiecka. 2022. "Effective Optical Image Assessment of Cellulose Paper Immunostrips for Blood Typing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158694
APA StyleRatajczak, K., Sklodowska-Jaros, K., Kalwarczyk, E., Michalski, J. A., Jakiela, S., & Stobiecka, M. (2022). Effective Optical Image Assessment of Cellulose Paper Immunostrips for Blood Typing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158694