Impact of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid on Gene Expression in Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
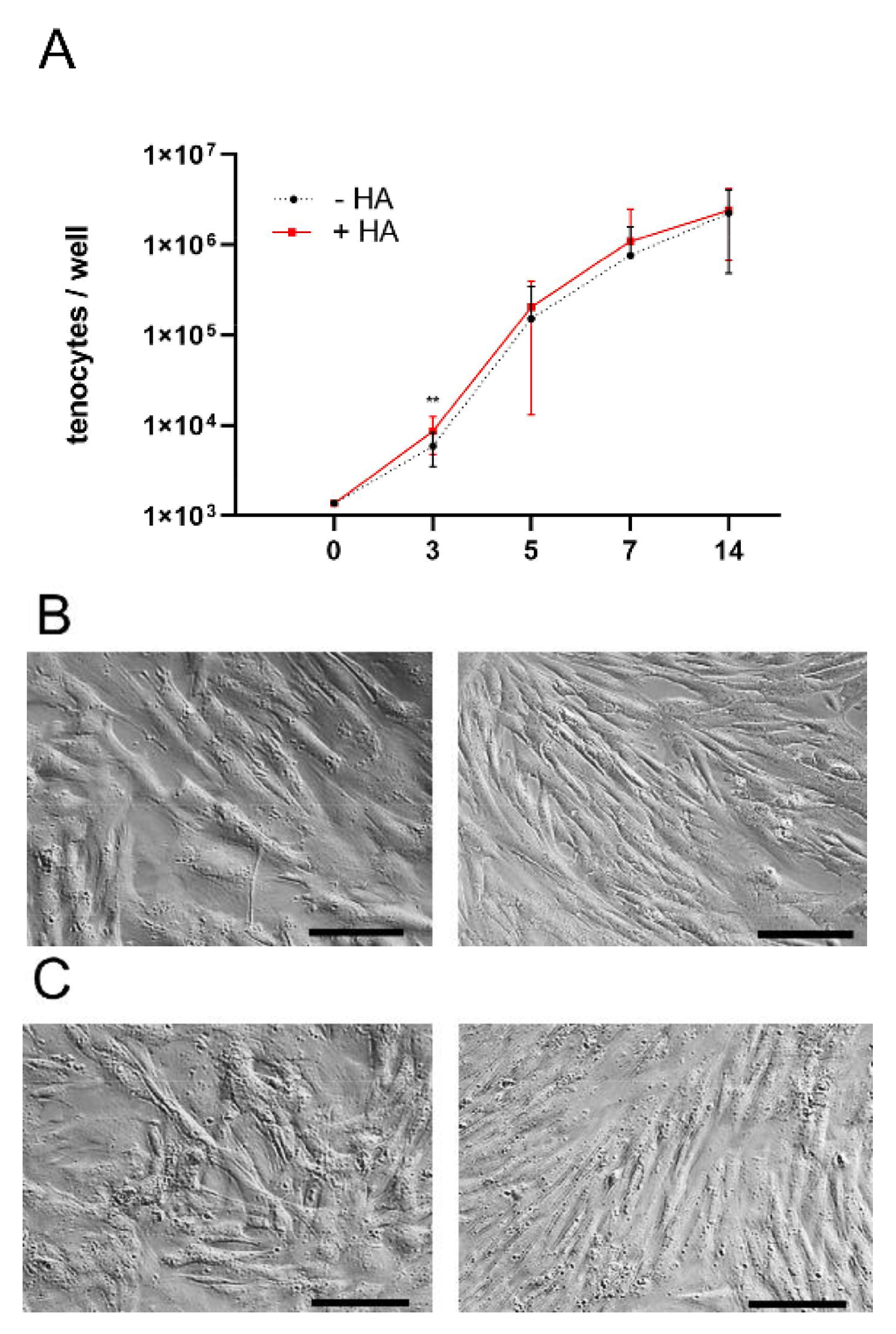
2.1. Proliferation of Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes
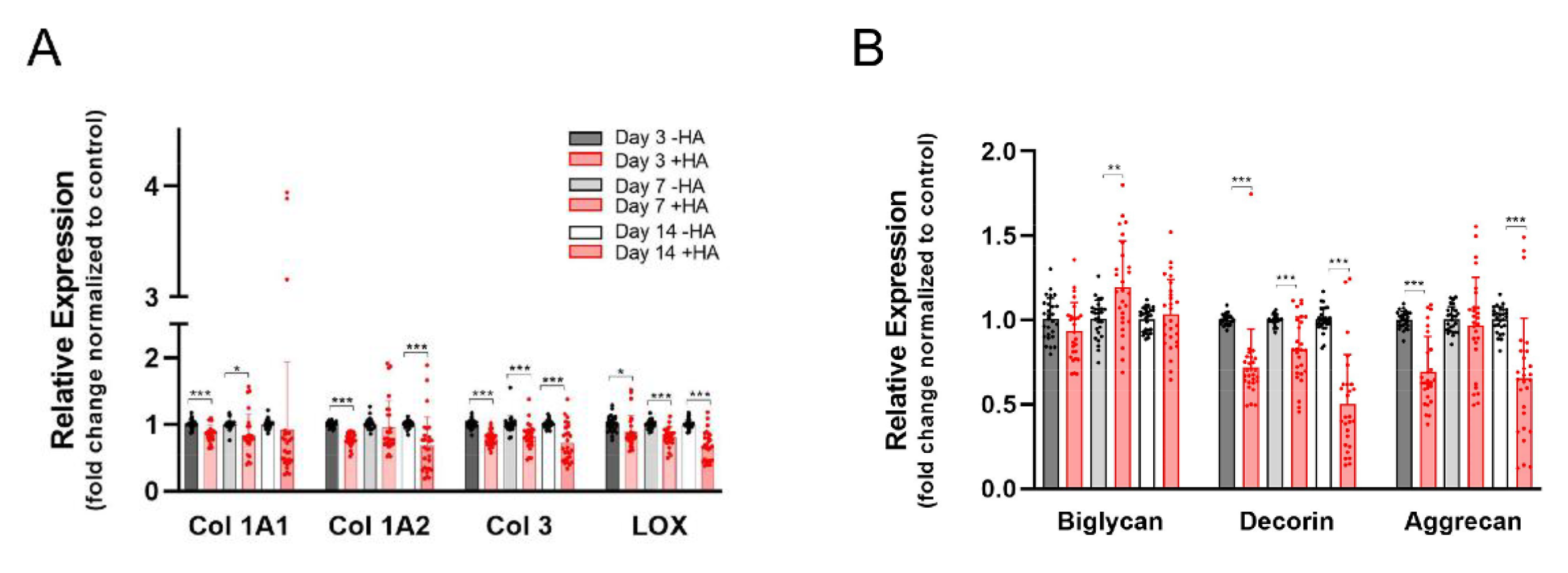
2.2. Gene Expression of Extracellular Matrix Markers
2.3. Gene Expression of Tendon Markers and Pro-Fibrotic Alpha-SMA
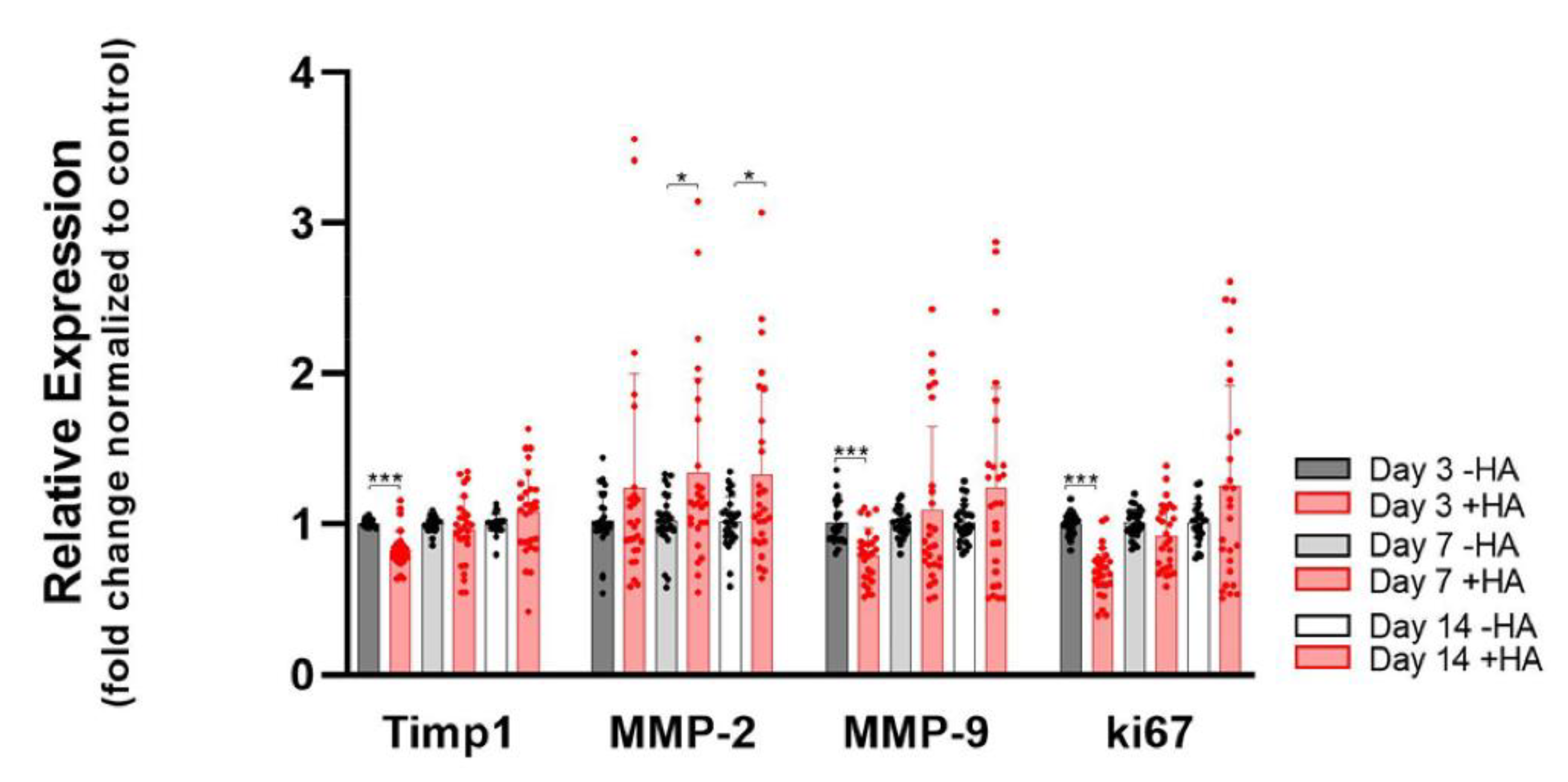
2.4. Remodeling Markers and Proliferation Marker ki67
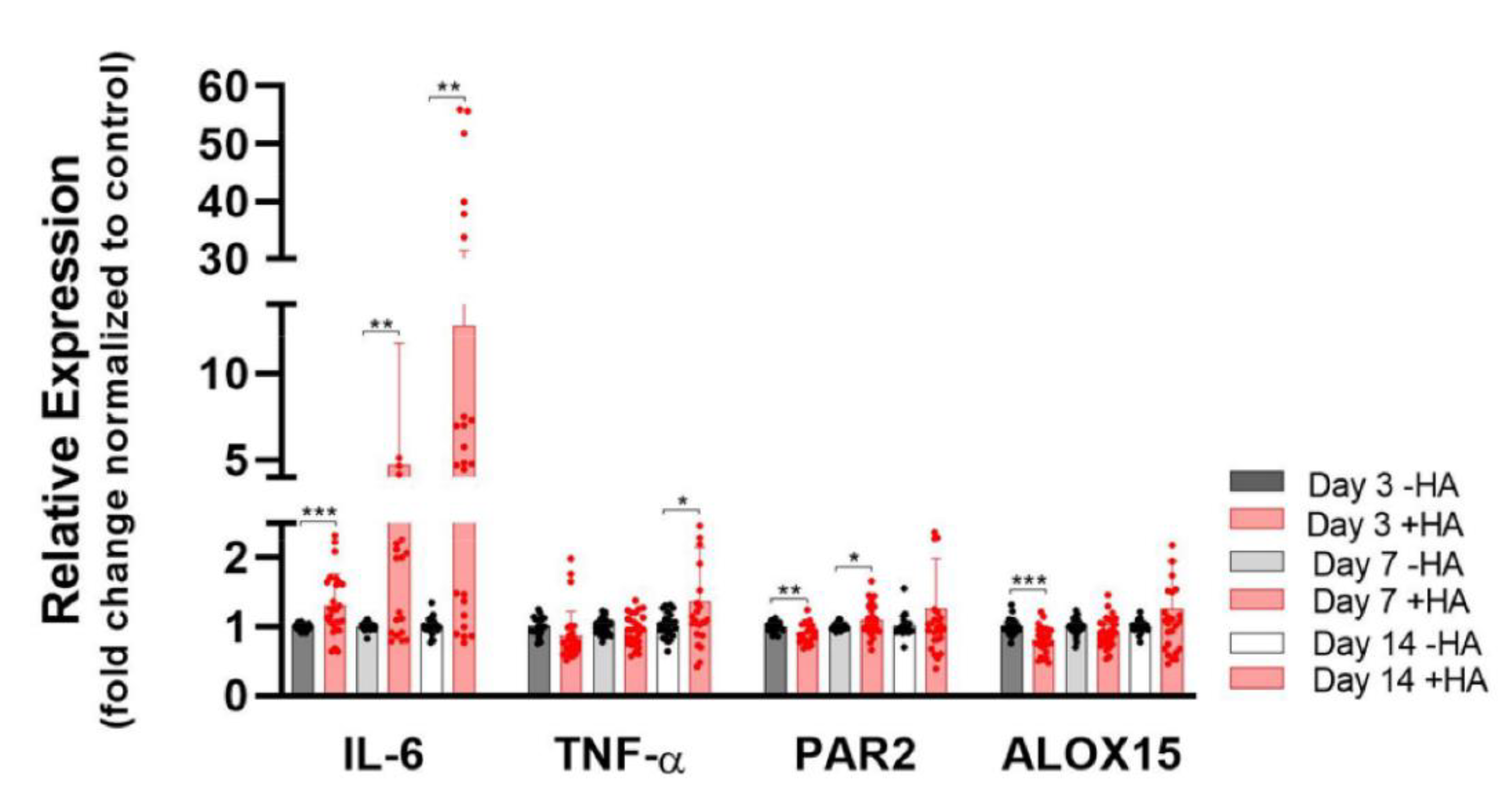
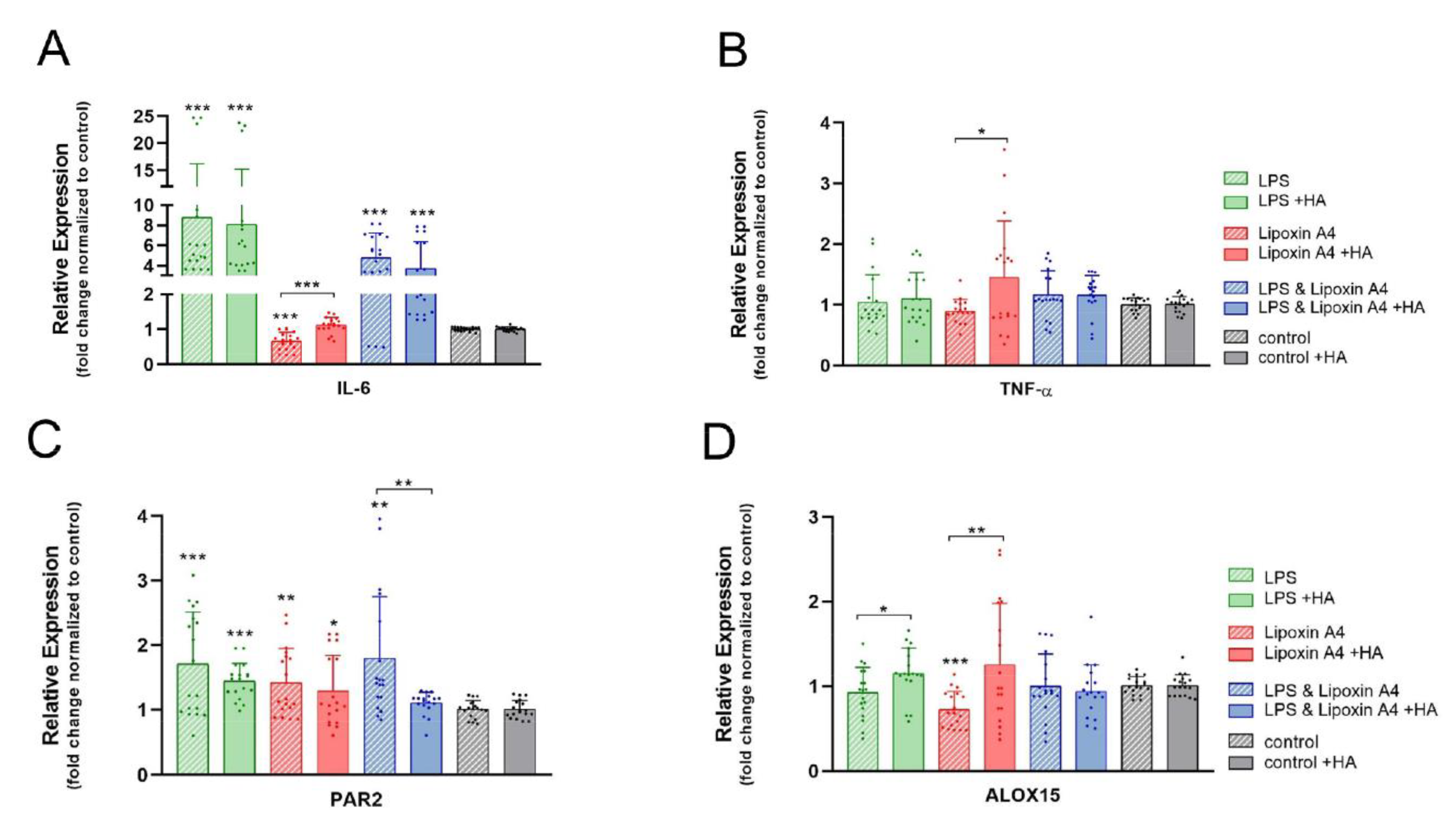
2.5. Pro-Inflammatory and Resolution Markers
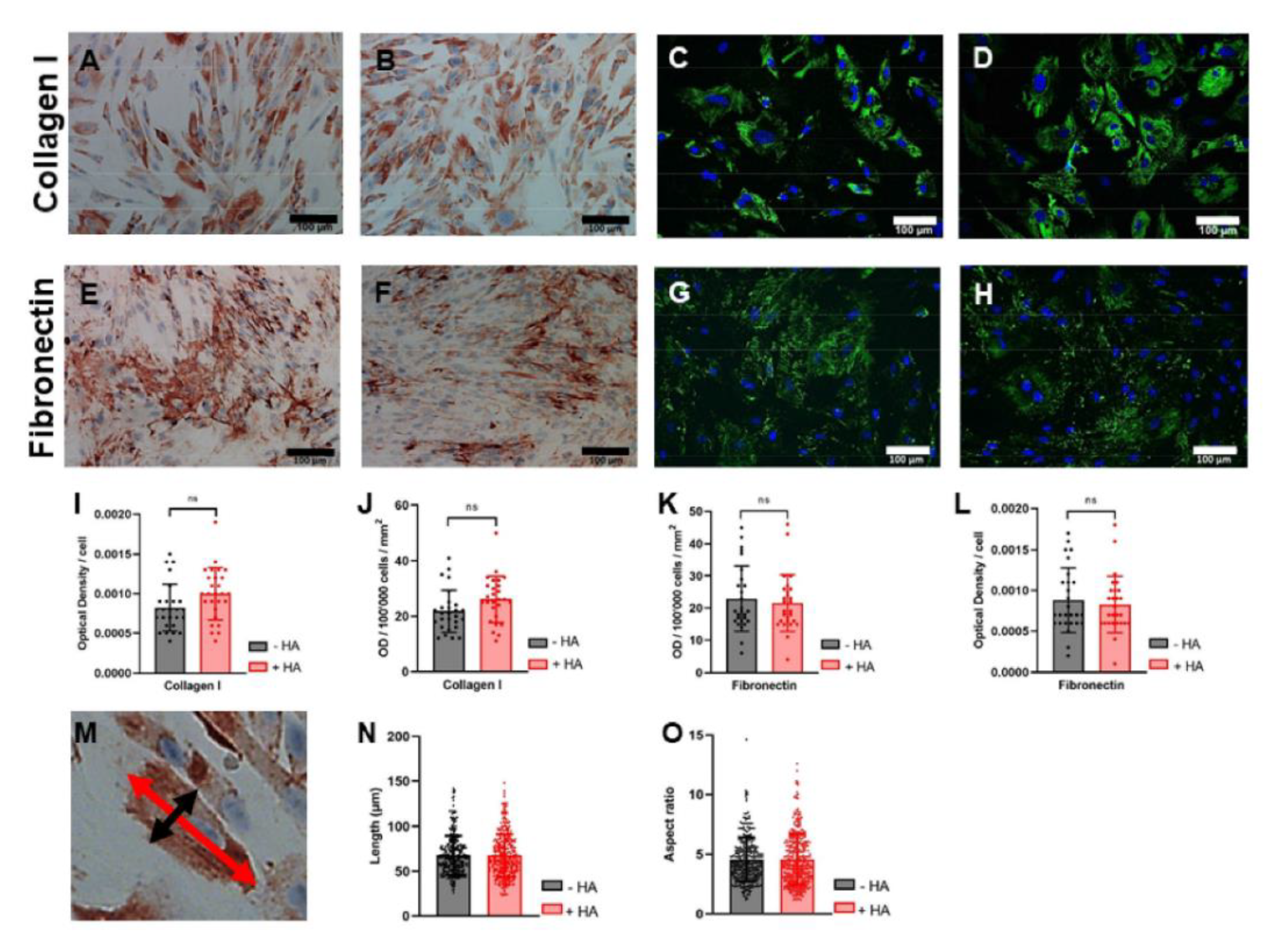
2.6. Immunocytochemistry for Collagen I and Fibronectin
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Isolation of Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes and Cell Culture
5.2. Cell Proliferation
5.3. Real-Time PCR
5.4. Pro-Inflammatory and Resolution Markers
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chartier, C.; ElHawary, H.; Baradaran, A.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Xu, L.; Efanov, J.I. Tendon: Principles of Healing and Repair. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliot, D.; Giesen, T. Primary Flexor Tendon Surgery. Hand Clin. 2013, 29, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.J.; Clitherow, H.D.; Singh, H.P.; Clarke, E.C.; Smith, B.J.; Tonkin, M.A. The Effect of Extensor Tendon Adhesions on Finger Motion. J. Hand Surg. 2019, 44, 903.e1–903.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Mashiah, R.; Seror, J.; Kadar, A.; Dolkart, O.; Pritsch, T.; Goldberg, R.; Klein, J. Lipid-hyaluronan synergy strongly reduces intrasynovial tissue boundary friction. Acta Biomater. 2018, 83, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Giavaresi, G.; Bellini, D.; Casagranda, V.; Pressato, D.; Fini, M. Evaluation of a new collagen-based medical device (ElastiCo®) for the treatment of acute Achilles tendon injury and prevention of peritendinous adhesions: An in vitro biocompatibility and in vivo investigation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Franchini, M.C.; Xu, K.; Locatelli, E.; Martin, R.C.; Monaco, I.; Cui, S. Controlled release of curcumin from curcumin-loaded nanomicelles to prevent peritendinous adhesion during Achilles tendon healing in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2873–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brochhausen, C.; Schmitt, V.H.; Rajab, T.K.; Planck, C.N.E.; Krämer, B.; Wallwiener, M.; Hierlemann, H.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Intraperitoneal adhesions-an ongoing challenge between biomedical engineering and the life sciences. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 98, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terčič, D.; Božič, B. The Basis of the Synovial Fluid Analysis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2001, 39, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myant, C.; Cann, P. On the matter of synovial fluid lubrication: Implications for Metal-on-Metal hip tribology. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 34, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohrs, R.T.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Y.-L.; Jay, G.D.; Zhang, L.; Warman, M.L.; An, K.-N.; Amadio, P.C. Tendon fascicle gliding in wild type, heterozygous, and lubricin knockout mice. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 29, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.; Fasanello, D.; Stefanovski, D.; Schurer, S.; Caracappa, K.; D’Agostino, A.; Costello, E.; Freer, H.; Rollins, A.; Read, C.; et al. Investigation of synovial fluid lubricants and inflammatory cytokines in the horse: A comparison of recombinant equine interleukin 1 beta-induced synovitis and joint lavage models. BMC Veter-Res. 2021, 17, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, K.C.; Campos, M.G.N.; Mei, L.H.I. Hyaluronic acid electrospinning: Challenges, applications in wound dressings and new perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Chanmee, T.; Itano, N. Hyaluronan: Metabolism and Function. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aya, K.L.; Stern, R. Hyaluronan in wound healing: Rediscovering a major player. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayahin, J.E.; Buhrman, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Koh, T.J.; Gemeinhart, R.A. High and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Differentially Influence Macrophage Activation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, V.; Stellavato, A.; Cimini, D.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; Alfano, A.; Cammarota, M.; Balato, G.; D’Addona, A.; Ruosi, C.; Schiraldi, C. Unsulfated biotechnological chondroitin by itself as well as in combination with high molecular weight hyaluronan improves the inflammation profile in osteoarthritis in vitro model. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, J.; Calcagni, M.; Bürgisser, G.M.; Bonavoglia, E.; Neuenschwander, P.; Milleret, V.; Giovanoli, P. Synthesis, characterization and histomorphometric analysis of cellular response to a new elastic DegraPol® polymer for rabbit Achilles tendon rupture repair. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2012, 9, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgisser, G.M.; Calcagni, M.; Müller, A.; Bonavoglia, E.; Fessel, G.; Snedeker, J.G.; Giovanoli, P.; Buschmann, J. Prevention of Peritendinous Adhesions Using an Electrospun DegraPol Polymer Tube: A Histological, Ultrasonographic, and Biomechanical Study in Rabbits. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 656240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Morozkina, S.; Uspenskaya, M.; Olekhnovich, R. Hyaluronan-Based Nanofibers: Fabrication, Characterization and Application. Polymers 2019, 11, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgisser, G.M.; Calcagni, M.; Bachmann, E.; Fessel, G.; Snedeker, J.; Giovanoli, P.; Buschmann, J. Rabbit Achilles tendon full transection model—Wound healing, adhesion formation and biomechanics at 3, 6 and 12 weeks post-surgery. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, E.A.; Watson, D.; Duff, I.F.; Roseman, S. Hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid. I. Molecular parameters of hyaluronic acid in normal and arthritic human fluids. Arthritis Care Res. 1967, 10, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaibaji, M. Advances in the Biology of Zone II Flexor Tendon Healing and Adhesion Formation. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2000, 45, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.H.; Al-Youha, S.; Van Agtmael, T.; Lu, Y.; Wong, J.; McGrouther, D.A.; Kadler, K.E. Tendon Is Covered by a Basement Membrane Epithelium That Is Required for Cell Retention and the Prevention of Adhesion Formation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halper, J.; Kjaer, M. Basic Components of Connective Tissues and Extracellular Matrix: Elastin, Fibrillin, Fibulins, Fibrinogen, Fibronectin, Laminin, Tenascins and Thrombospondins. In Progress in Heritable Soft Connective Tissue Diseases; Halper, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, T.; Elliot, D. Avoidance of unfavourable results following primary flexor tendon surgery. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2013, 46, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgisser, G.M.; Evrova, O.; Heuberger, D.M.; Wolint, P.; Rieber, J.; Miescher, I.; Schüpbach, R.A.; Giovanoli, P.; Calcagni, M.; Buschmann, J. Electrospun tube reduces adhesion in rabbit Achilles tendon 12 weeks post-surgery without PAR-2 overexpression. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docheva, D.; Müller, S.A.; Majewski, M.; Evans, C.H. Biologics for tendon repair. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 84, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgese, G.; Benetti, E.M.; Zenobi-Wong, M. Molecularly Engineered Biolubricants for Articular Cartilage. Adv. Health Mater. 2018, 7, e1701463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, F.; Marsilio, E.; Asparago, G.; Frizziero, A.; Berardi, A.C.; Maffulli, N. The Impact of Hyaluronic Acid on Tendon Physiology and Its Clinical Application in Tendinopathies. Cells 2021, 10, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serri, C.; Frigione, M.; Ruponen, M.; Urtti, A.; Borzacchiello, A.; Biondi, M.; Itkonen, J.; Mayol, L. Electron dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and degradation properties of hyaluronic acid decorated microparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Shah, R.; Gashi, B.; Zhang, S.; Bhavnani, K.; Wartzack, S.; Rosenkranz, A. Exploring the Lubrication Mechanisms of Synovial Fluids for Joint Longevity—A Perspective. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pien, N.; Peeters, I.; Deconinck, L.; Van Damme, L.; De Wilde, L.; Martens, A.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Mignon, A. Design and development of a reinforced tubular electrospun construct for the repair of ruptures of deep flexor tendons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 119, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imere, A.; Ligorio, C.; O’Brien, M.; Wong, J.K.; Domingos, M.; Cartmell, S.H. Engineering a cell-hydrogel-fibre composite to mimic the structure and function of the tendon synovial sheath. Acta Biomater. 2020, 119, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titan, A.L.; Foster, D.S.; Chang, J.; Longaker, M.T. Flexor Tendon. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 639e–647e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Lin, Z.Y.; Pan, G.; He, F.; Li, F.; Fan, C.; Cui, W. Optimization of intrinsic and extrinsic tendon healing through controllable water-soluble mitomycin-C release from electrospun fibers by mediating adhesion-related gene expression. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K.; Uversky, V.N. What Macromolecular Crowding Can Do to a Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23090–23140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwe, M.; Kalacheva, M.; Boersma, A.J.; Kedrov, A. The more the merrier: Effects of macromolecular crowding on the structure and dynamics of biological membranes. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 5039–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendi, D.; Marzi, J.; Linthicum, W.; Rickards, A.; Dolivo, D.; Keller, S.; Kauss, M.; Wen, Q.; McDevitt, T.; Dominko, T.; et al. Hyaluronic acid as a macromolecular crowding agent for production of cell-derived matrices. Acta Biomater. 2019, 100, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrova, O.; Kellenberger, D.; Calcagni, M.; Vogel, V.; Buschmann, J. Supporting Cell-Based Tendon Therapy: Effect of PDGF-BB and Ascorbic Acid on Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, S.D.; Miele, A.E.; Uciechowska-Kaczmarzyk, U.; Liwo, A.; Duclos, B.; Samsonov, S.A.; Ricard-Blum, S. Insights into the structure and dynamics of lysyl oxidase propeptide, a flexible protein with numerous partners. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.G.; Eivers, S.B.; Dervan, E.W.; O’Brien, C.J.; Wallace, D. Lysyl Oxidase Like 1: Biological roles and regulation. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 193, 107975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifi, M.A.; Godugu, C. Inhibition of lysyl oxidase ameliorates renal injury by inhibiting CD44-mediated pericyte detachment and loss of peritubular capillaries. Life Sci. 2020, 243, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zeng, Y.; Wei, J.; Yang, D.; Ding, G.; Liu, J.; Shang, J.; Kang, Y.; Ji, X. Knockdown of LOXL1 inhibits TGF-β1-induced proliferation and fibrogenesis of hepatic stellate cells by inhibition of Smad2/3 phosphorylation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.J.; Melrose, J. Aggrecan, the Primary Weight-Bearing Cartilage Proteoglycan, Has Context-Dependent, Cell-Directive Properties in Embryonic Development and Neurogenesis: Aggrecan Glycan Side Chain Modifications Convey Interactive Biodiversity. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Halper, J. Tendon proteoglycans: Biochemistry and function. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2005, 5, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Corps, A.N.; Robinson, A.H.N.; Movin, T.; Costa, M.L.; Hazleman, B.L.; Riley, G.P. Increased expression of aggrecan and biglycan mRNA in Achilles tendinopathy. Rheumatology 2005, 45, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.A.; Sun, M.; Barnum, C.E.; Weiss, S.N.; Huegel, J.; Shetye, S.S.; Lin, L.; Saez, D.; Adams, S.M.; Iozzo, R.V.; et al. Decorin and biglycan are necessary for maintaining collagen fibril structure, fiber realignment, and mechanical properties of mature tendons. Matrix Biol. 2017, 64, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antoni, M.L.; Risse, P.-A.; Ferraro, P.; Martin, J.G.; Ludwig, M.S. Effects of decorin and biglycan on human airway smooth muscle cell adhesion. Matrix Biol. 2012, 31, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midwood, K.S.; Chiquet, M.; Tucker, R.P.; Orend, G. Tenascin-C at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 4321–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, S.; Lu, P.; Zhu, T.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Yin, Z.; Heng, B.C.; et al. Mohawk Promotes the Tenogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Activation of the TGFβ Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells 2014, 33, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, T.; Mori, M.; Ito, Y.; Matsushima, T.; Nakamichi, R.; Suzuki, H.; Ichinose, S.; Saito, M.; Marumo, K.; Asahara, H. Gtf2ird1 -Dependent Mohawk Expression Regulates Mechanosensing Properties of the Tendon. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, R.; Chee, S.M.L.; Raghunath, M.; Wohland, T. Macromolecular crowding gives rise to microviscosity, anomalous diffusion and accelerated actin polymerization. Phys. Biol. 2015, 12, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docheva, D.; Hunziker, E.B.; Fässler, R.; Brandau, O. Tenomodulin Is Necessary for Tenocyte Proliferation and Tendon Maturation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dex, S.; Alberton, P.; Willkomm, L.; Söllradl, T.; Bago, S.; Milz, S.; Shakibaei, M.; Ignatius, A.; Bloch, W.; Clausen-Schaumann, H.; et al. Tenomodulin is Required for Tendon Endurance Running and Collagen I Fibril Adaptation to Mechanical Load. eBioMedicine 2017, 20, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.M. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in health and disease: An overview. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, H.; El-Rehany, M.; Roeb, E.; Abdel-Ghany, H.; Ramzy, M.; Gaber, S. Mutant matrix metalloproteinase-9 reduces postoperative peritoneal adhesions in rats. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 26, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanabad, A.F.; Zarzycki, A.; Jeon, K.; Deniset, J.; Fedak, P. Post-Operative Adhesions: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ren, S.; Macarak, E.; Rosenbloom, J. Pathobiological mechanisms of peritoneal adhesions: The mesenchymal transition of rat peritoneal mesothelial cells induced by TGF-β1 and IL-6 requires activation of Erk1/2 and Smad2 linker region phosphorylation. Matrix Biol. 2016, 51, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, J.; Denson, J.L.; Brüning, J.C. Versatile functions for IL-6 in metabolism and cancer. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, M.; Rhodes, D.H.; Castellanos, K.J.; Hall, A.R.; Cabay, R.J.; Chennuri, R.; Grady, E.F.; Fantuzzi, G. Role of IL-6 in the resolution of pancreatitis in obese mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.G.; Cassali, G.D.; Poole, S.; Teixeira, M.M. Effects of inhibition of PDE4 and TNF-α on local and remote injuries following ischaemia and reperfusion injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 134, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, T.; Coldewey, S.M.; Chen, J.; McArthur, S.; le Faouder, P.; Cenac, N.; Flower, R.J.; Thiemermann, C.; Perretti, M. Nonredundant protective properties of FPR2/ALX in polymicrobial murine sepsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18685–18690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.A.; Sousa, L.P.; Pinho, V.; Perretti, M.; Teixeira, M.M. Resolution of Inflammation: What Controls Its Onset? Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowska, M.; Chen, L.-Y.; Eberlein, M.; Anton, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Alsaaty, S.; Qi, H.-Y.; Logun, C.; Horton, M.; Shelhamer, J.H. Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronan Activates Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α and Eicosanoid Production in Monocytes and Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4470–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakin, S.G.; Colas, R.A.; Wheway, K.; Watkins, B.; Appleton, L.; Rees, J.; Gwilym, S.; Little, C.; Dalli, J.; Carr, A.J. Proresolving Mediators LXB4 and RvE1 Regulate Inflammation in Stromal Cells from Patients with Shoulder Tendon Tears. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefer, A.M.; Stahl, G.L.; Lefer, D.J.; Brezinski, M.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Veale, C.; Abe, Y.; Smith, J.B. Lipoxins A4 and B4: Comparison of icosanoids having bronchoconstrictor and vasodilator actions but lacking platelet aggregatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8340–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miescher, I.; Wolint, P.; Opelz, C.; Snedeker, J.G.; Giovanoli, P.; Calcagni, M.; Buschmann, J. Impact of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid on Gene Expression in Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147926
Miescher I, Wolint P, Opelz C, Snedeker JG, Giovanoli P, Calcagni M, Buschmann J. Impact of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid on Gene Expression in Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(14):7926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147926
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiescher, Iris, Petra Wolint, Christine Opelz, Jess G. Snedeker, Pietro Giovanoli, Maurizio Calcagni, and Johanna Buschmann. 2022. "Impact of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid on Gene Expression in Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 14: 7926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147926
APA StyleMiescher, I., Wolint, P., Opelz, C., Snedeker, J. G., Giovanoli, P., Calcagni, M., & Buschmann, J. (2022). Impact of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid on Gene Expression in Rabbit Achilles Tenocytes In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147926





