Divergent Effect of Central Incretin Receptors Inhibition in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Peripheral Changes Were More Pronounced following Central Gipr Inhibition
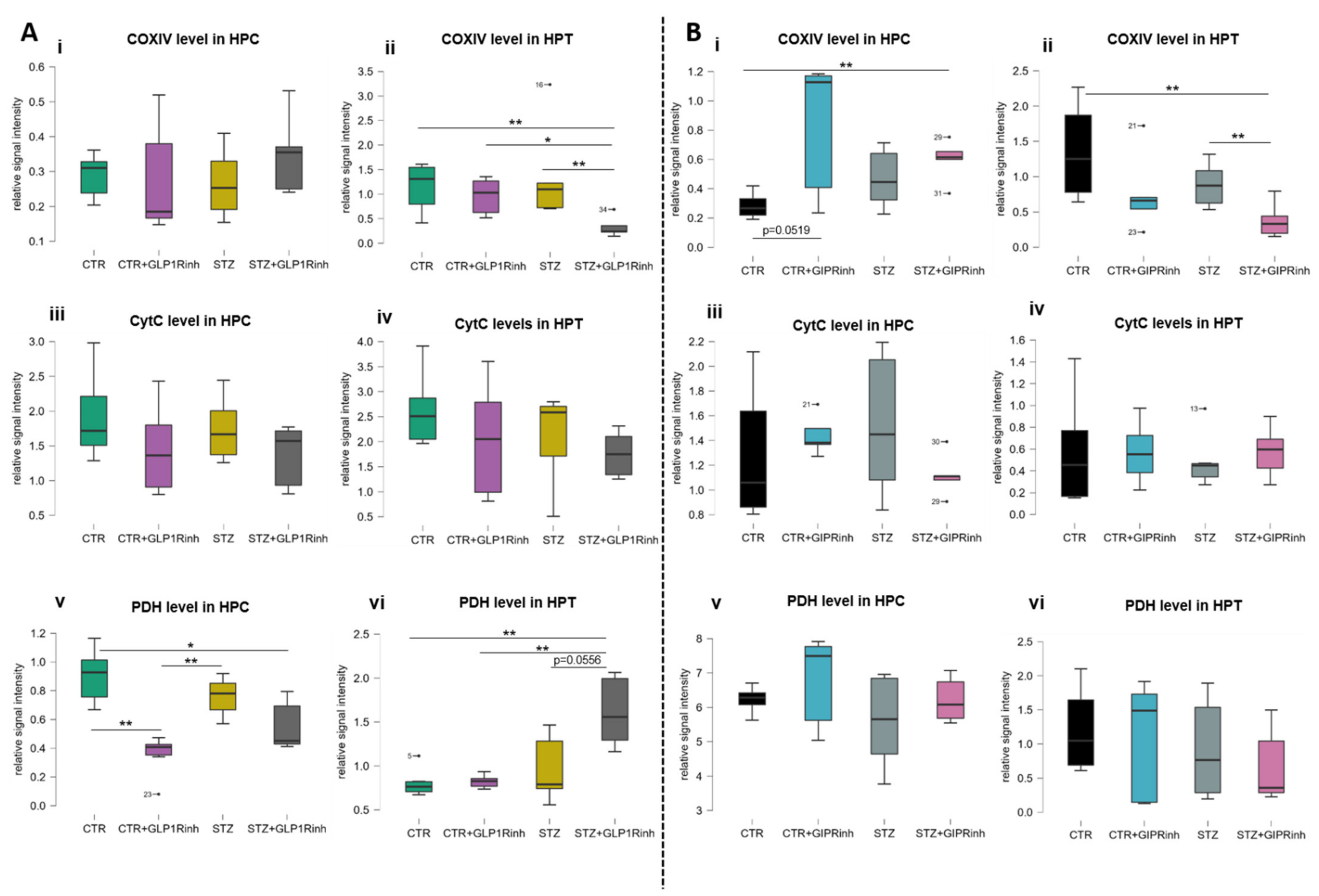
2.2. Central GLP-1R Inhibition Has a Stronger Impact on Brain Proteins Involved in Cell Energy
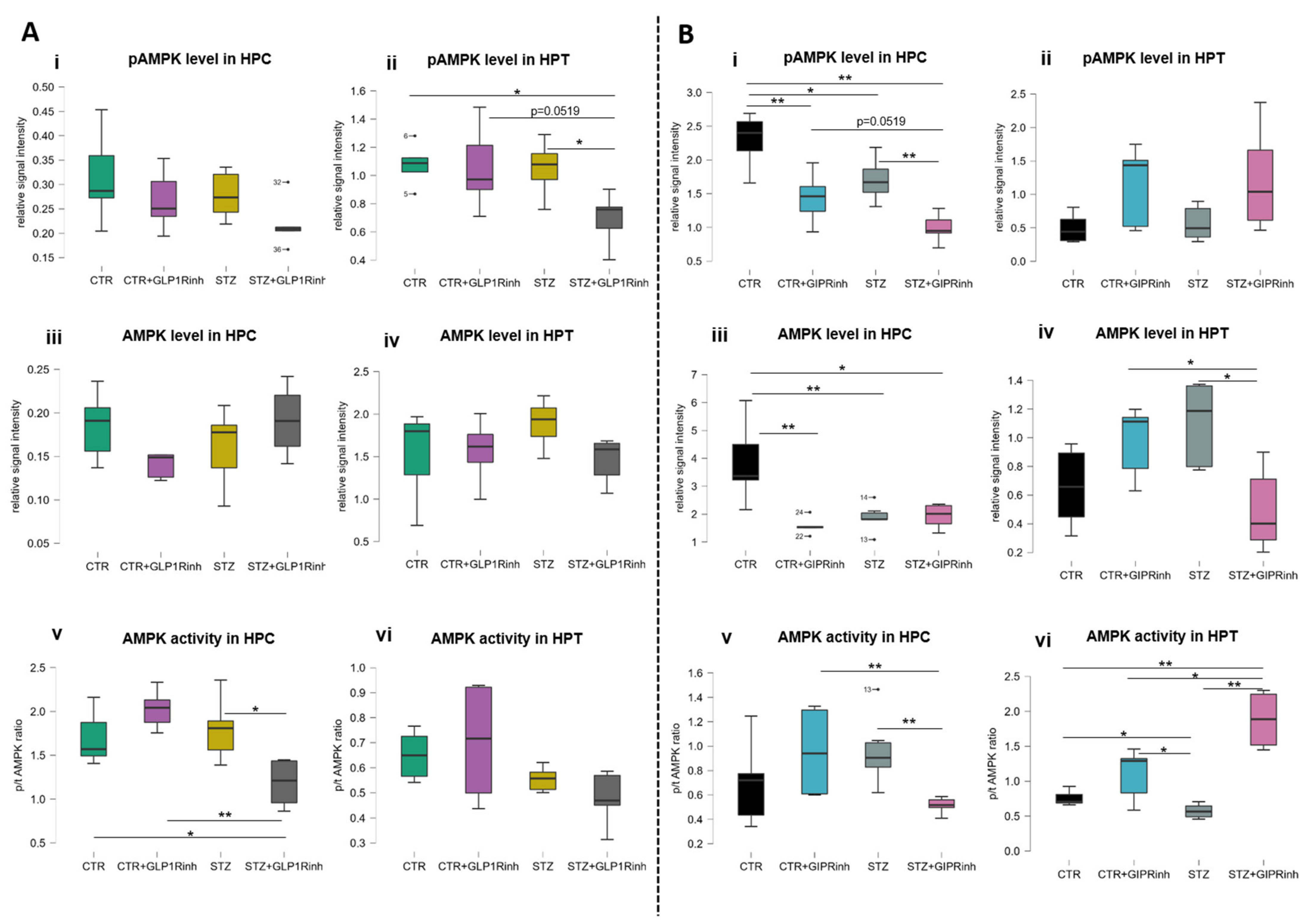
2.3. Central Inhibition of the GIPR Has a More Pronounced Impact on Ampk Protein Levels and Activity
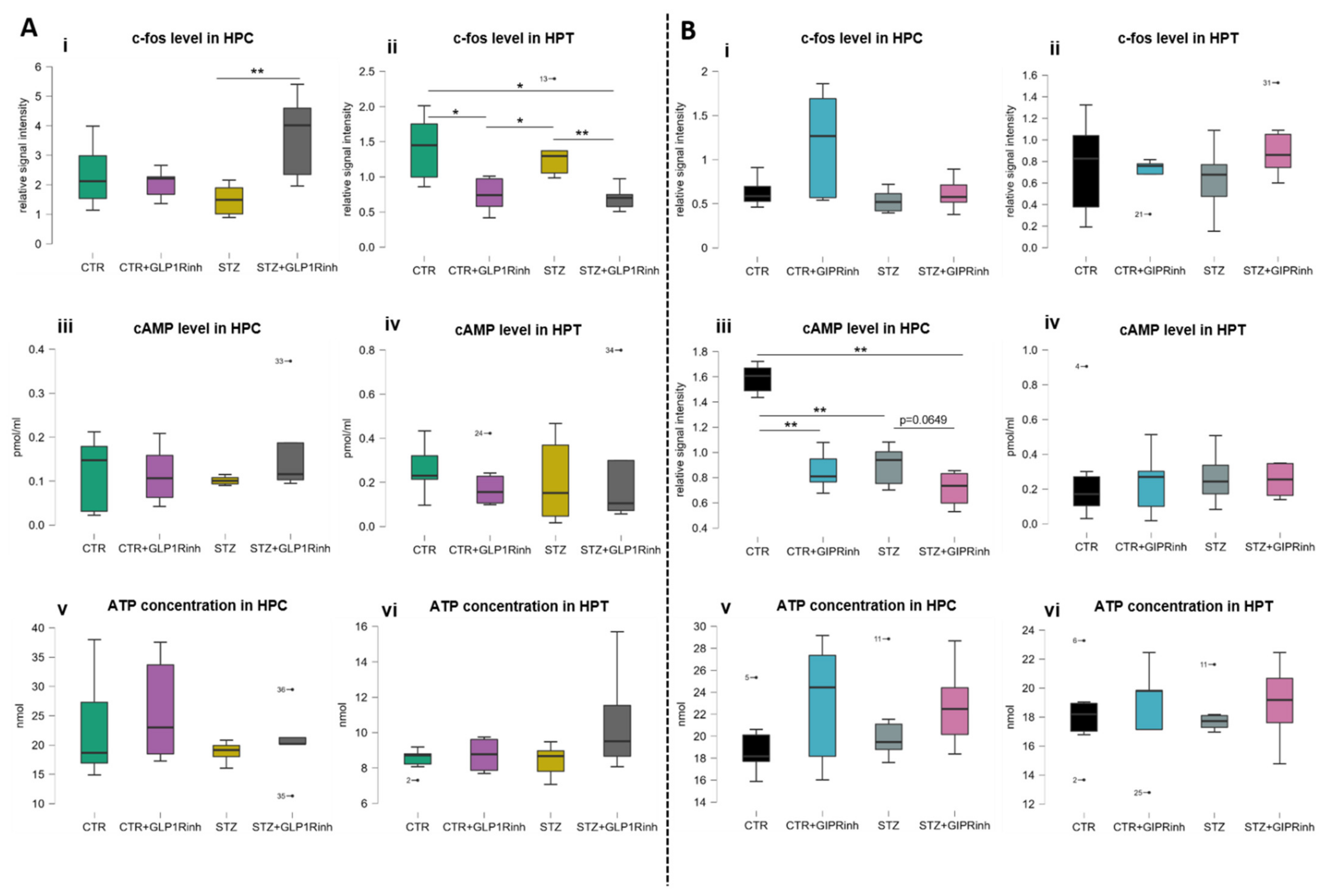
2.4. Central Inhibition of GLP-1R Affects the Level of the Neuronal Activity Marker C-Fos, While GIPR Inhibition Decreases cAMP
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Ethics
4.3. Materials
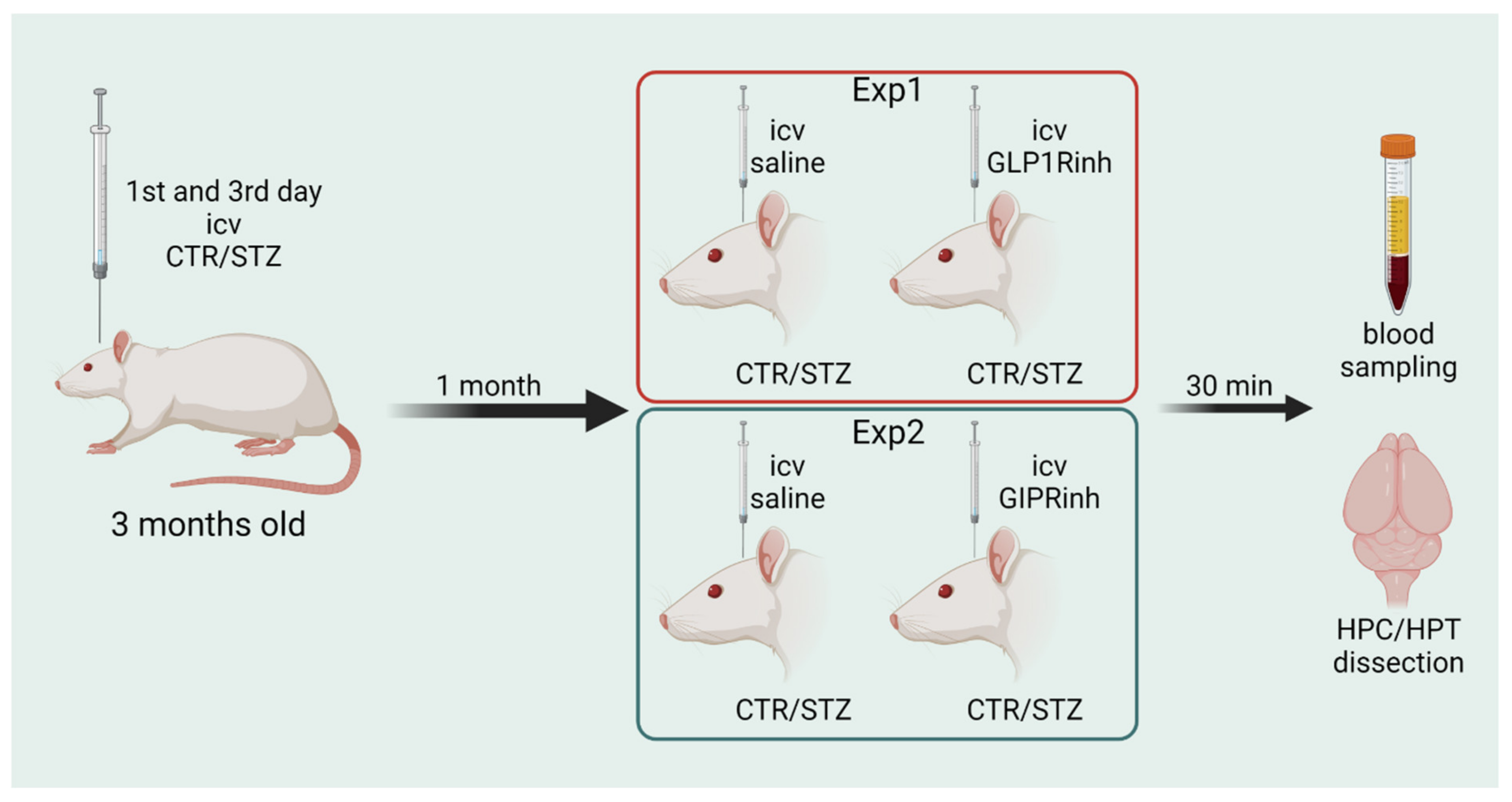
4.4. Experimental Design
4.5. Tissue Preparation and Blood Sampling
4.6. Biochemical Analysis
4.7. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kellar, D.; Craft, S. Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femminella, G.D.; Frangou, E.; Love, S.B.; Busza, G.; Holmes, C.; Ritchie, C.; Lawrence, R.; McFarlane, B.; Tadros, G.; Ridha, B.H.; et al. Evaluating the effects of the novel GLP-1 analogue liraglutide in Alzheimer’s disease: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (ELAD study). Trials 2019, 20, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gejl, M.; Gjedde, A.; Egefjord, L.; Møller, A.; Hansen, S.B.; Vang, K.; Rodell, A.; Brændgaard, H.; Gottrup, H.; Schacht, A.; et al. In Alzheimer’s disease, 6-month treatment with GLP-1 analog prevents decline of brain glucose metabolism: Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölscher, C. Drugs developed for treatment of diabetes show protective effects in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2014, 66, 497–510. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, D.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Physiology of Proglucagon Peptides: Role of Glucagon and GLP-1 in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 513–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, D.; Seino, Y. Two incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP: Comparison of their actions in insulin secretion and β cell preservation. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 107, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Yabe, D. GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J. Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of Incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaman, L. Ascending projections from the caudal visceral nucleus of the solitary tract to brain regions involved in food intake and energy expenditure. Brain Res. 2010, 1350, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. The glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide signaling axis in the central nervous system. Peptides 2020, 125, 170194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Fu, Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Cordonier, E.L.; Mo, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yao, T.; Naylor, J.; Howard, V.; Saito, K.; et al. Gut-derived GIP activates central Rap1 to impair neural leptin sensitivity during overnutrition. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3786–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Jarboe, L.A.; Landau, S.B.; Williams, E.K.; Wolfe, M.M. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide: Structure of the precursor and tissue-specific expression in rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1992–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Roland, B.; Tomaselli, K.; Dolman, C.S.; Lowe, C.; Heilig, J.S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 in the rat brain: Distribution of expression and functional implication. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 2235–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallwitz, B. Preclinical and clinical data on extraglycemic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2009, 6, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athauda, D.; Foltynie, T. The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP) receptor as a therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms of action. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Patil, I.; Cadenas, E. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkovic-Petrisic, M.; Hoyer, S. Central insulin resistance as a trigger for sporadic Alzheimer-like pathology: An experimental approach. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2007, 72, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, S.C.; Santos, R.X.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X.; IMoreira, P.I.; Smith, M.A. Insulin-resistant brain state: The culprit in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease? Ageing Res. Rev. 2011, 10, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, H.; Liu, S.; Yan, N.; Xing, Y.; Hölscher, C.; Wang, Z. The novel GLP-1/GIP analogue DA5-CH reduces tau phosphorylation and normalizes theta rhythm in the icv. STZ rat model of AD. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladugu, L.; Gharaibeh, A.; Kolli, N.; Learman, C.; Hall, T.C.; Li, L.; Rossignol, J.; Maiti, P.; Dunbar, G.L. Liraglutide has anti-inflammatory and anti-amyloid properties in streptozotocin-induced and 5xFAD mouse models of alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölscher, C. Novel dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists show neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease models. Neuropharmacology 2018, 136, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, F.; Ramos-Espiritu, L.S.; Buck, J.; Levin, L.R.; Manfredi, G. cAMP and mitochondria. Physiology 2013, 28, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, F.; Raciti, G.A.; Nigro, C.; Mannino, G.C.; Procopio, T.; Davalli, A.M.; Beguinot, F.; Sesti, G.; Miele, C.; Folli, F. The GLP-1 receptor agonists exenatide and liraglutide activate Glucose transport by an AMPK-dependent mechanism. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojakovic, A.; Trushin, S.; Sheu, A.; Khalili, L.; Chang, S.Y.; Li, X.; Christensen, T.; Salisbury, J.L.; Geroux, R.E.; Gateno, B.; et al. Partial inhibition of mitochondrial complex I ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and cognition in APP/PS1 female mice. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhai, H.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xu, G. AMPK-dependent regulation of GLP1 expression in L-like cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 57, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, J.L.S. Structure and Regulation of Pyruvate Dehydrogenases. In Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry: Second Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 321–328. ISBN 9780123786319. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Xie, Y.; Ren, L.; Qi, L.; Wu, L.; Pan, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L. GLP-1 improves the supportive ability of astrocytes to neurons by promoting aerobic glycolysis in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Metab. 2021, 47, 101180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Helsted, M.M.; Hartmann, B.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Veedfald, S.; Stensen, S.; Lanng, A.R.; Bergmann, N.C.; Christensen, M.B.; Vilsbøll, T.; et al. GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Antagonism During a Meal in Healthy Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, dgz175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Bergmann, N.C.; Stensen, S.; Christensen, M.B.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Holst, J.J.; Nauck, M.; Knop, F.K. Evaluation of the incretin effect in humans using GIP and GLP-1 receptor antagonists. Peptides 2020, 125, 170183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wolfe, M.M. Effect of GIP and GLP-1 antagonists on insulin release in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 276, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, V.A.; O’Harte, F.P.M.; Harriott, P.; Mooney, M.H.; Green, B.D.; Flatt, P.R. Effects of the novel (Pro3)GIP antagonist and exendin(9-39)amide on GIP- and GLP-1-induced cyclic AMP generation, insulin secretion and postprandial insulin release in obese diabetic (ob/ob) mice: Evidence that GIP is the major physiological incretin. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, M.D.; O’Shea, D.; Gunn, I.; Beak, S.A.; Edwards, C.M.B.; Meeran, K.; Choi, S.J.; Taylor, G.M.; Heath, M.M.; Lambert, P.D.; et al. A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 1996, 379, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gault, V.A.; McClean, P.L.; Cassidy, R.S.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. Chemical gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor antagonism protects against obesity, insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and associated disturbances in mice fed high-fat and cafeteria diets. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, R.S.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. Effects of gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) and related analogues on glucagon release at normo- and hyperglycaemia in Wistar rats and isolated islets. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClean, P.L.; Irwin, N.; Cassidy, R.S.; Holst, J.J.; Gault, V.A.; Flatt, P.R. GIP receptor antagonism reverses obesity, insulin resistance, and associated metabolic disturbances induced in mice by prolonged consumption of high-fat diet. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, 1746–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, A.C.; Li, C.; Gallagher, P.R.; Stanley, C.A.; De León, D.D. GLP-1 Receptor Antagonist Exendin-(9-39) Elevates Fasting Blood Glucose Levels in Congenital Hyperinsulinism Owing to Inactivating Mutations in the ATP-Sensitive K+ Channel. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2585–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauf, C.; Cani, P.D.; Perrin, C.; Iglesias, M.A.; Maury, J.F.; Bernard, E.; Benhamed, F.; Grémeaux, T.; Drucker, D.J.; Kahn, C.R.; et al. Brain glucagon-like peptide-1 increases insulin secretion and muscle insulin resistance to favor hepatic glycogen storage. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3554–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonghe, B.C.; Holland, R.A.; Olivos, D.R.; Rupprecht, L.E.; Kanoski, S.E.; Hayes, M.R. Hindbrain GLP-1 receptor mediation of cisplatin-induced anorexia and nausea. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 153, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Cong, W.; Ji, S.; Rothman, S.; Maudsley, S.; Martin, B. Metabolic Dysfunction in Alzheimers Disease and Related Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Metabolic Dysregulation Contributes to the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homolak, J.; Perhoc, A.B.; Knezovic, A.; Barilar, J.O.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Failure of the brain glucagon-like peptide-1-mediated control of intestinal redox homeostasis in a rat model of sporadic alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavropoulou, M.P.; Kotsa, K.; Anastasiou, O.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Pappas, T.N.; Yovos, J.G. Effect of intracerebroventricular infusion of insulin on glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide in dogs. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 460, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.B.; Shade, R.E.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Garcia-Forey, M.; Tejero, M.E.; Voruganti, V.S.; Cole, S.A.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Folli, F. CNS Control of Metabolism: Central GIP signaling stimulates peripheral GIP release and promotes insulin and pancreatic polypeptide secretion in nonhuman primates. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Hansen, L.S.; Svendsen, B.; Christensen, M.; Knop, F.K.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Species-specific action of (Pro3)GIP—A full agonist at human GIP receptors, but a partial agonist and competitive antagonist at rat and mouse GIP receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, L.; Smith, E.P.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.; Herman, J.P.; Seeley, R.J.; Sandoval, D.; D’Alessio, D. Central Nervous System GLP-1 Receptors Regulate Islet Hormone Secretion and Glucose Homeostasis in Male Rats. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, D.A.; Bagnol, D.; Woods, S.C.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Seeley, R.J. Arcuate glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors regulate glucose homeostasis but not food intake. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudurí, E.; Beiroa, D.; Porteiro, B.; López, M.; Diéguez, C.; Nogueiras, R. Acute but not chronic activation of brain glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezovic, A.; Osmanovic Barilar, J.; Babic, A.; Bagaric, R.; Farkas, V.; Riederer, P.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 mediates effects of oral galactose in streptozotocin-induced rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2018, 135, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrang, N.; Hansen, M.; Larsen, P.J.; Tang-Christensen, M. Characterization of brainstem preproglucagon projections to the paraventricular and dorsomedial hypothalamic nuclei. Brain Res. 2007, 1149, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, J.; Anderson, M.F.; Meister, B.; Alborn, A.M.; Ström, A.K.; Brederlau, A.; Illerskog, A.C.; Nilsson, O.; Kieffer, T.J.; Hietala, M.A.; et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide is expressed in adult hippocampus and induces progenitor cell proliferation. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, G.S.; Craft, S. The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Implications for treatment. CNS Drugs 2003, 17, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhenthi, S.; Qin, L.; Reddy, P.H. Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Xue, G.-F.; Li, G.; Li, D.; Hölscher, C. Neuroprotective effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 27, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, T.; Faivre, E.; Hölscher, C. Impairment of synaptic plasticity and memory formation in GLP-1 receptor KO mice: Interaction between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, E.; Gault, V.A.; Thorens, B.; Hölscher, C. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor knockout mice are impaired in learning, synaptic plasticity, and neurogenesis. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 105, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox, R.R.; Moffett, C.; Porter, D.W.; Irwin, N.; Gault, V.A.; Flatt, P.R. Effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor knockout and a high-fat diet on cognitive function and hippocampal gene expression in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoizumi, M.; Sato, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kato, S.; Tsukiyama, K.; Narita, T.; Fujita, H.; Morii, T.; Sassa, M.H.; Seino, Y.; et al. Inhibition of GIP signaling extends lifespan without caloric restriction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Fortin, S.M.; Arnold, M.; Grill, H.J.; Hayes, M.R. Peripheral and central GLP-1 receptor populations mediate the anorectic effects of peripherally administered GLP-1 receptor agonists, liraglutide and exendin-4. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, H.M. AMPK and exercise: Glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Metab. J. 2013, 37, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timón-Gómez, A.; Nývltová, E.; Abriata, L.A.; Vila, A.J.; Hosler, J.; Barrientos, A. Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis: Recent developments. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 76, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezovic, A.; Osmanovic-Barilar, J.; Curlin, M.; Hof, P.R.; Simic, G.; Riederer, P.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Staging of cognitive deficits and neuropathological and ultrastructural changes in streptozotocin-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salkovic-Petrisic, M.; Knezovic, A.; Hoyer, S.; Riederer, P. What have we learned from the streptozotocin-induced animal model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, about the therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s research. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic Perhoc, A.; Osmanovic Barilar, J.; Knezovic, A.; Farkas, V.; Bagaric, R.; Svarc, A.; Grünblatt, E.; Riederer, P.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Cognitive, behavioral and metabolic effects of oral galactose treatment in the transgenic Tg2576 mice. Neuropharmacology 2019, 148, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaki, I.; Winther, K.; Catrina, S.B.; Svenningsson, P. Repurposing GLP1 agonists for neurodegenerative diseases. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 155, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlessi, R.; Chen, Y.; Rowlands, J.; Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.N.; Egan, L.; Mamotte, C.; Stokes, R.; Gunton, J.E.; de Bittencourt, P.I.H.; et al. GLP-1 receptor signalling promotes β-cell glucose metabolism via mTOR-dependent HIF-1α activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Lin, H.Y.; Mo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Suganami, T.; Ravn, P.; Fukuda, M. Gut Hormone GIP Induces Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in the Hypothalamus. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, E.P.; Wurtman, R.J.; Axelrod, J. A simple and rapid method for injecting H3-norepinephrine into the lateral ventricle of the rat brain. Life Sci. 1967, 6, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanovic Barilar, J.; Knezovic, A.; Grünblatt, E.; Riederer, P.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Nine-month follow-up of the insulin receptor signalling cascade in the brain of streptozotocin rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarić, Đ. Učinak Antagonista Receptora Glukagonu Sličnog Peptida-1 na Biokemijske Promjene u Mozgu Štakora. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Pharmacy and Biochemistry, Department of Pharmacology, Zagreb, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.M.; Tang, F.; Seeholzer, S.H.; Zou, Y.; De León, D.D. Population pharmacokinetics of exendin-(9-39) and clinical dose selection in patients with congenital hyperinsulinism. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, A. N-2-(4-[18F]-Fluorobenzamido)ethylmaleimide coupled to cysteine-tagged on the C- or N-terminal of exendin-4. In Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD); National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osmanovic Barilar, J.; Knezovic, A.; Homolak, J.; Babic Perhoc, A.; Salkovic-Petrisic, M. Divergent Effect of Central Incretin Receptors Inhibition in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010548
Osmanovic Barilar J, Knezovic A, Homolak J, Babic Perhoc A, Salkovic-Petrisic M. Divergent Effect of Central Incretin Receptors Inhibition in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010548
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsmanovic Barilar, Jelena, Ana Knezovic, Jan Homolak, Ana Babic Perhoc, and Melita Salkovic-Petrisic. 2022. "Divergent Effect of Central Incretin Receptors Inhibition in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010548
APA StyleOsmanovic Barilar, J., Knezovic, A., Homolak, J., Babic Perhoc, A., & Salkovic-Petrisic, M. (2022). Divergent Effect of Central Incretin Receptors Inhibition in a Rat Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010548







