Characterization of the Functional Cross-Talk between Surface GABAA and Dopamine D5 Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
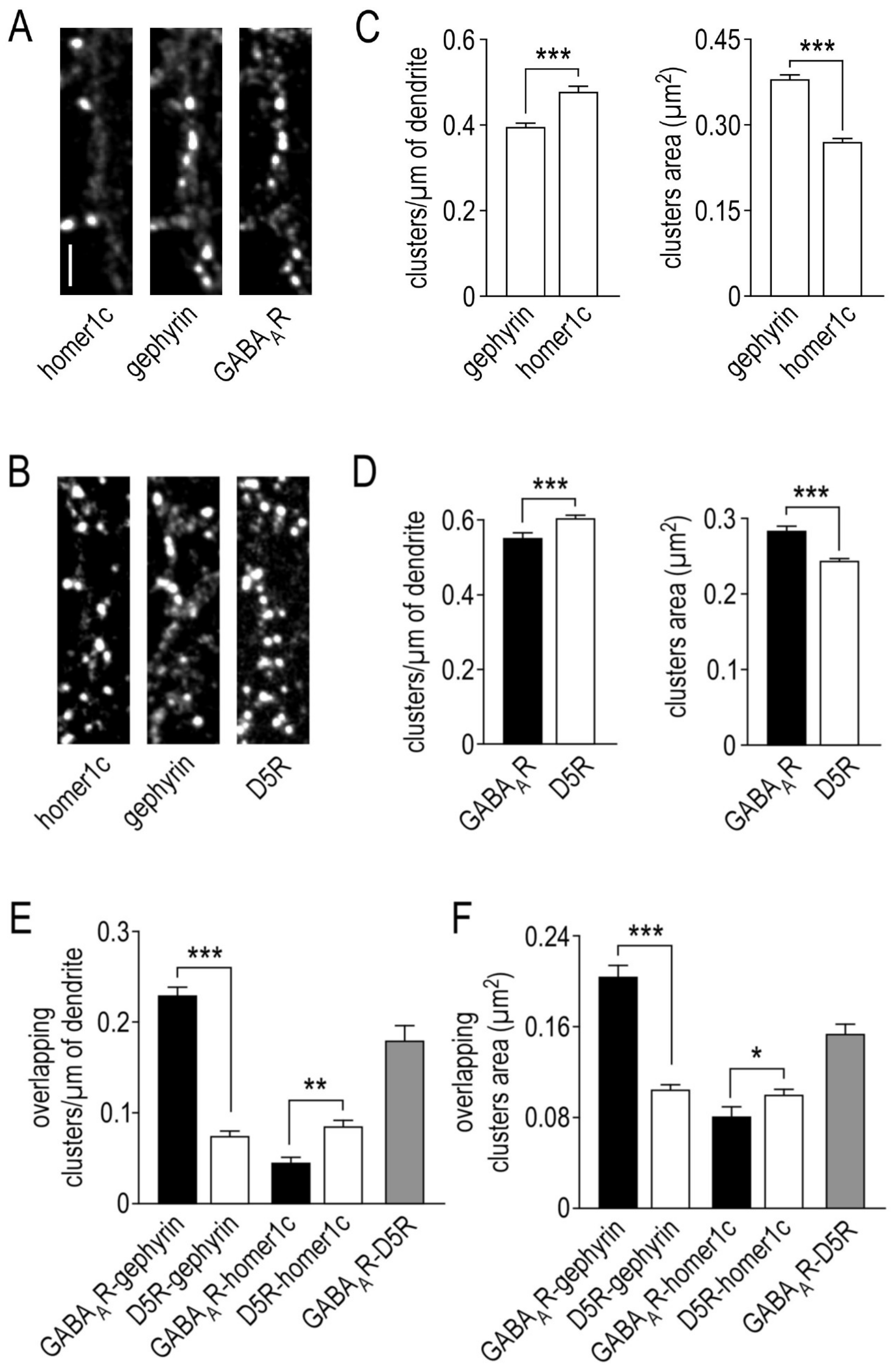
2.1. Organization of γ2-GABAA Receptors Clusters in Hippocampal Neurons
2.2. Organization of Dopamine D5 Receptors Clusters in Hippocampal Neurons
2.3. Physical Interaction between γ2-GABAA and Dopamine D5 Receptors
2.4. Surface Dynamics Properties of γ2-GABAA Receptors
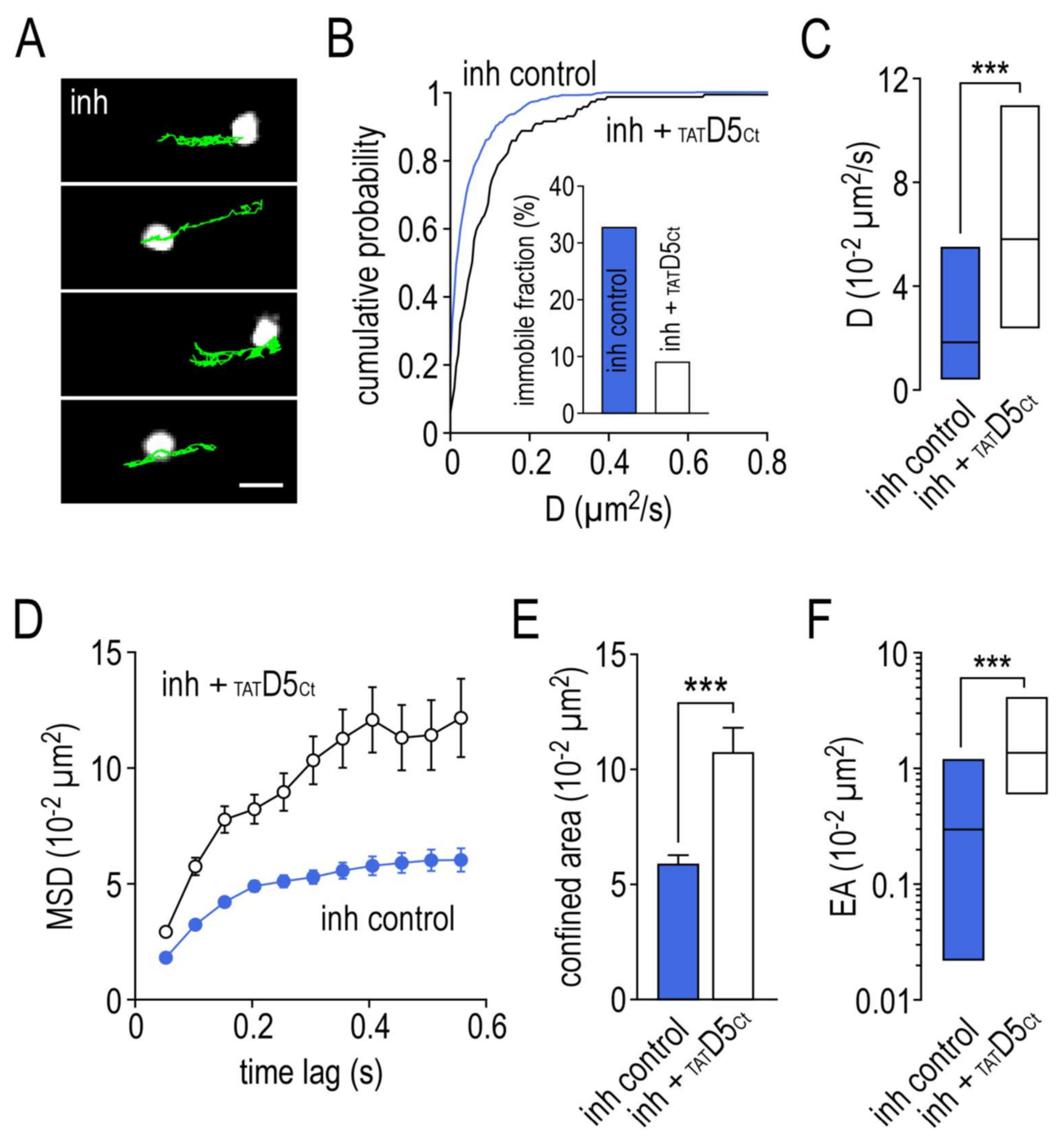
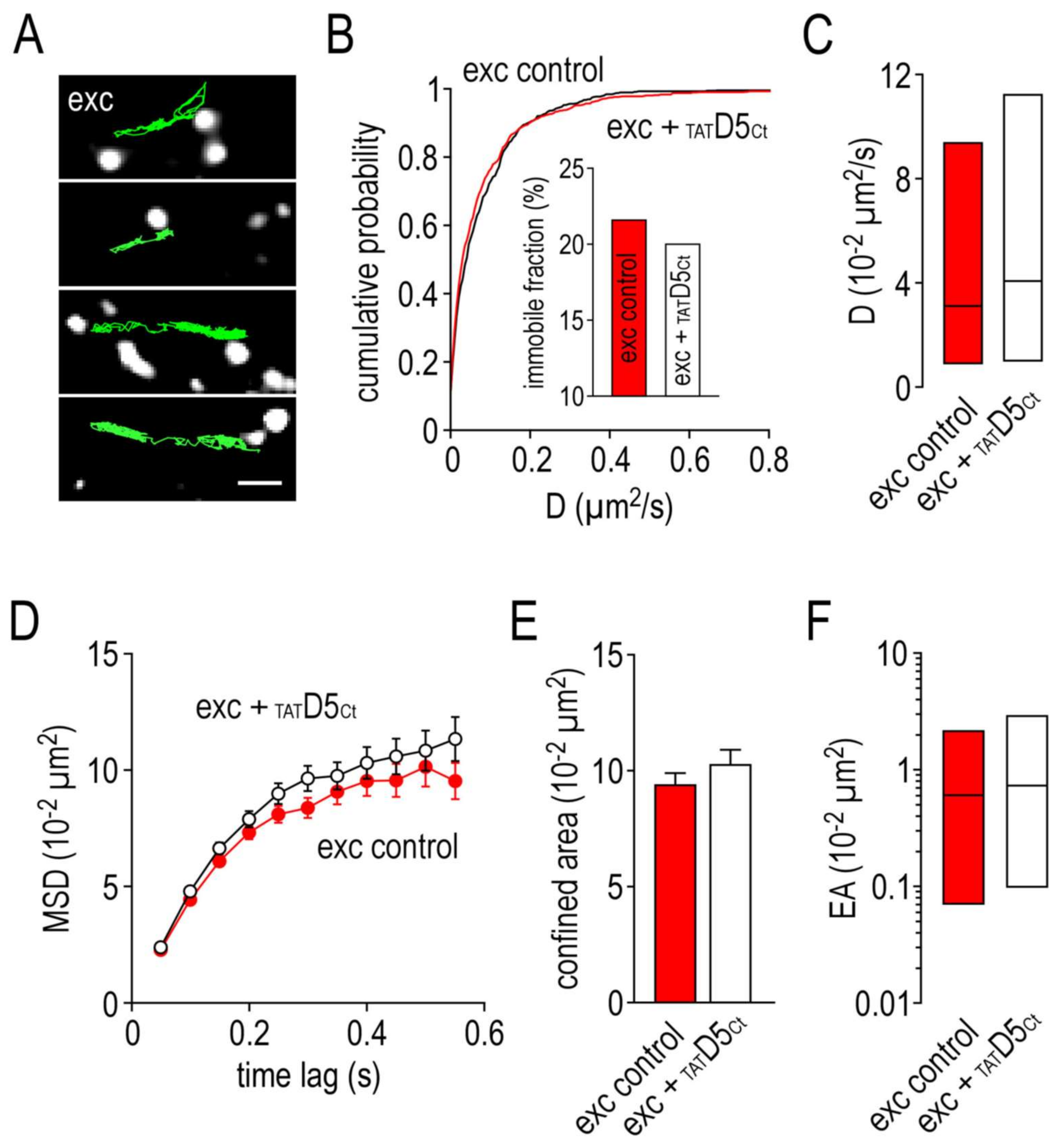
2.5. Impact of the Disrupting Peptide on the Surface Dynamics of γ2-GABAA Receptors
2.6. Surface Dynamics Properties of Dopamine D5 Receptors
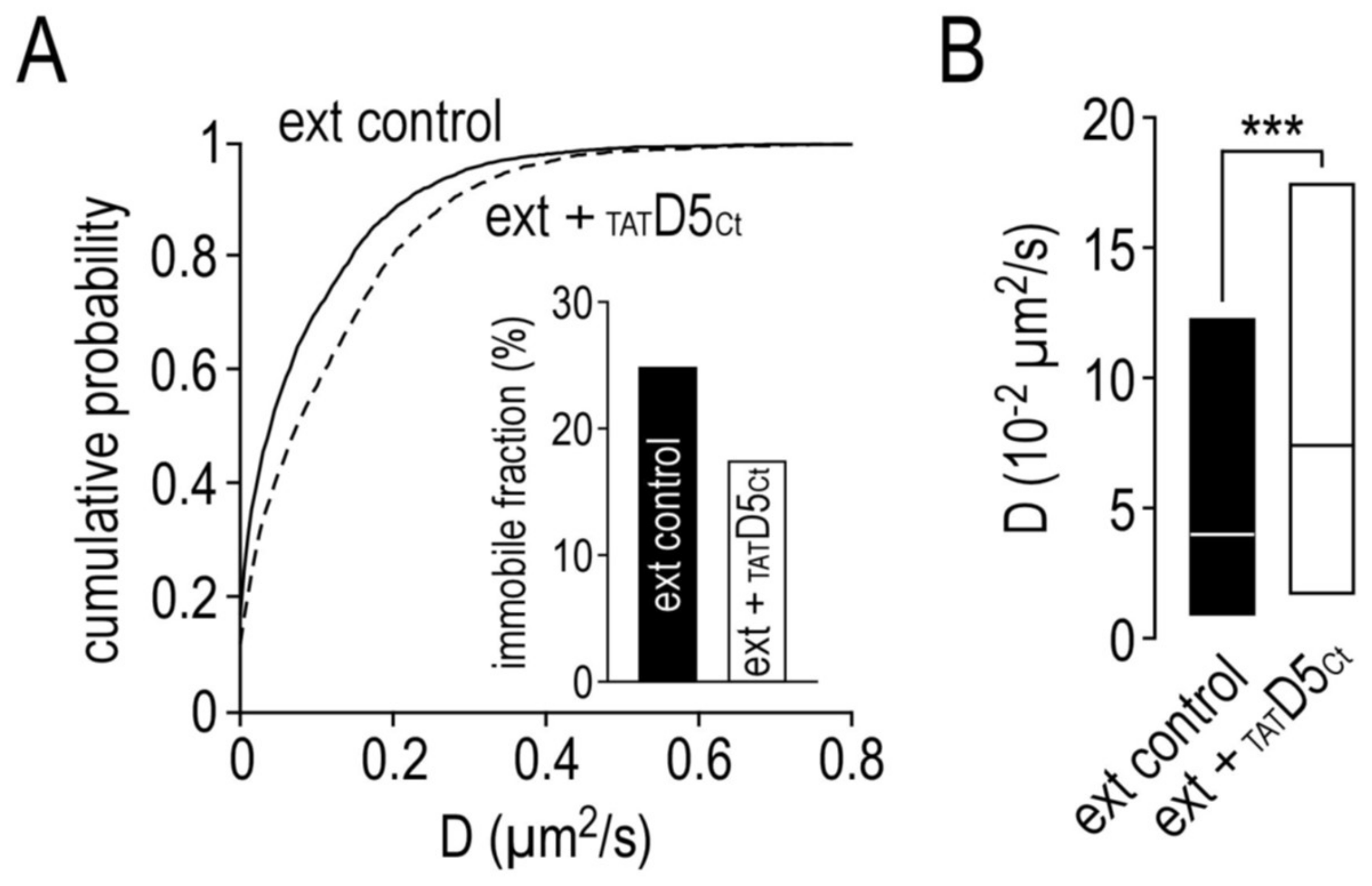
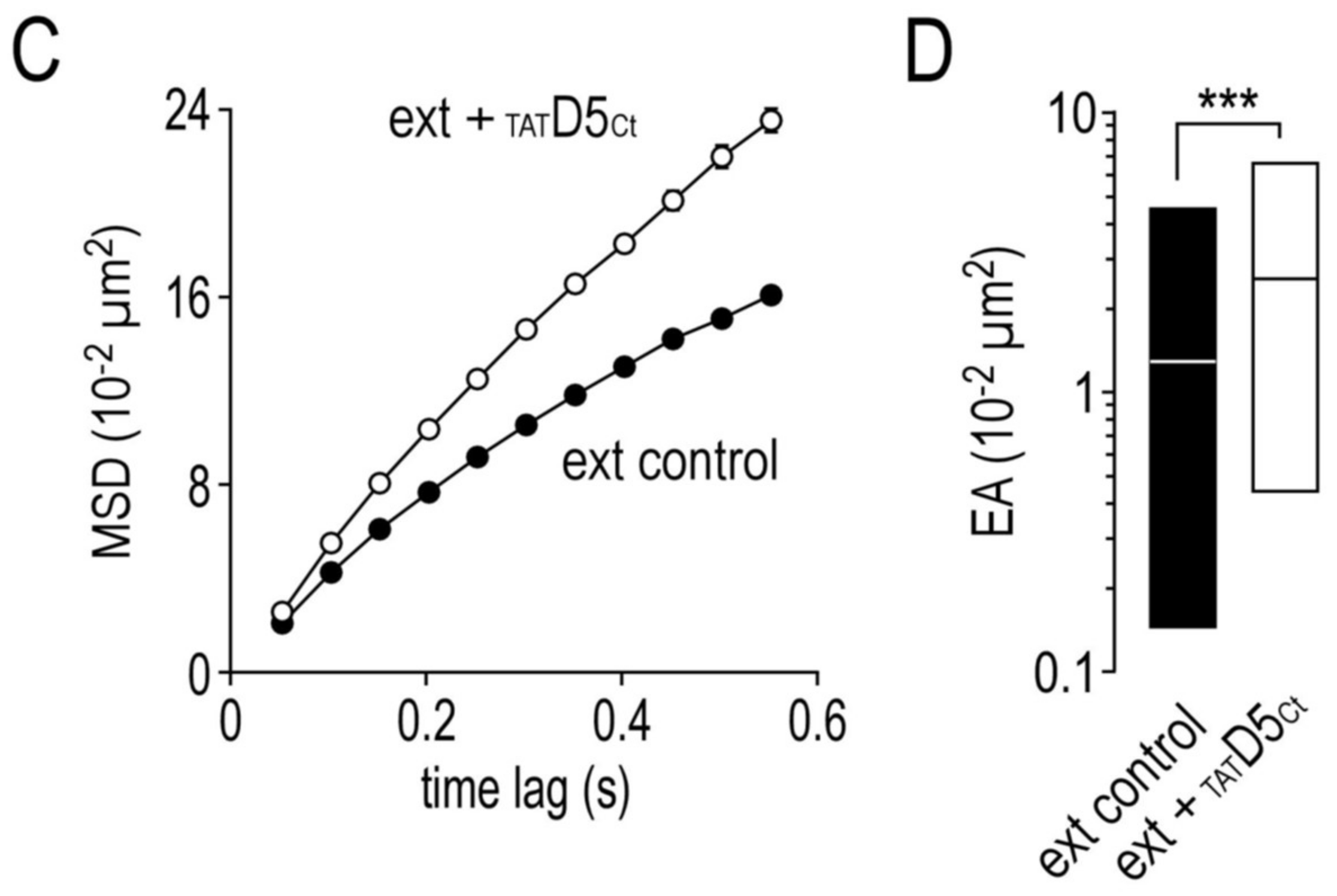
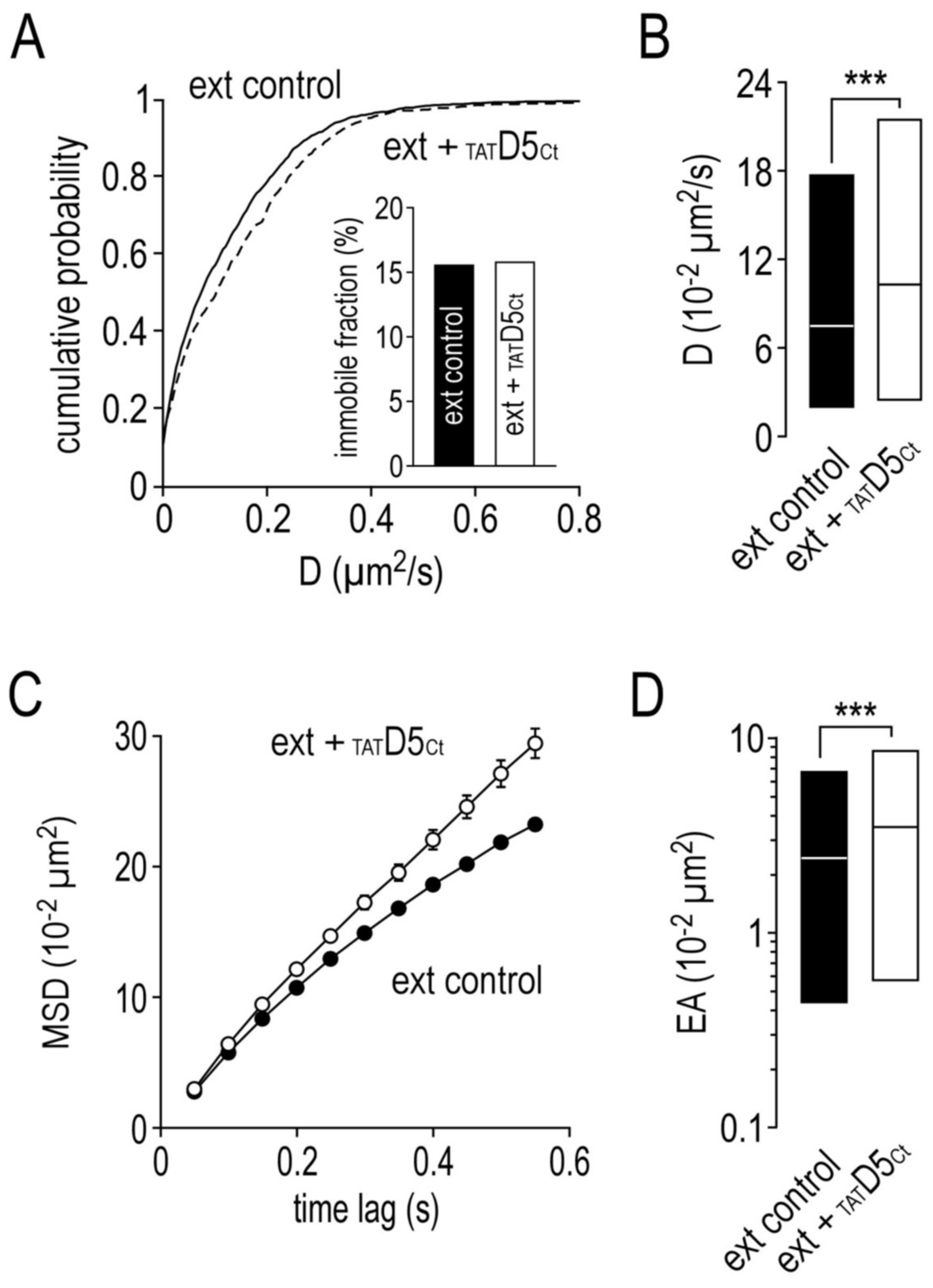
2.7. Impact of the Disrupting Peptide on the Surface Dynamics of Dopamine D5 Receptors
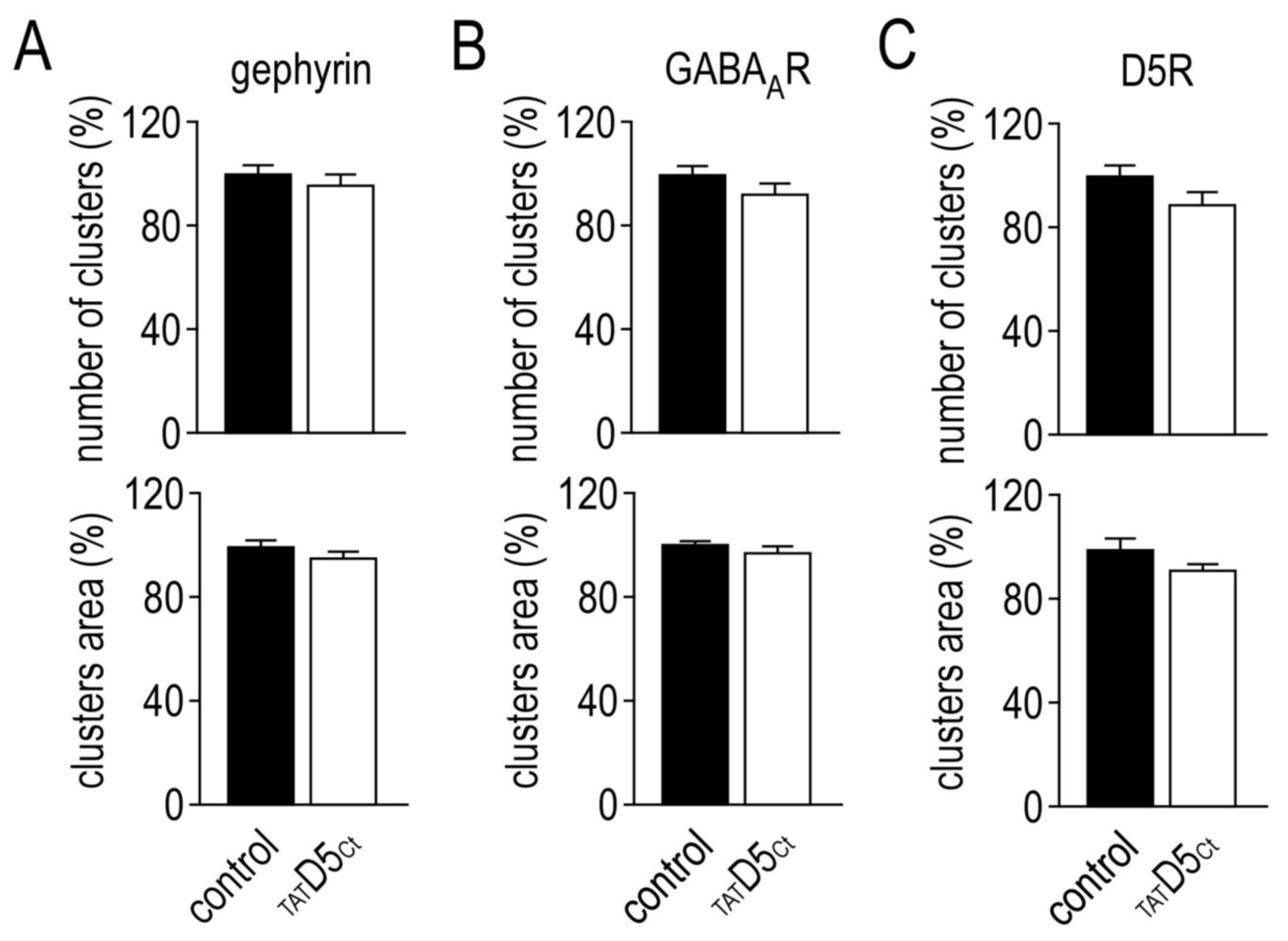
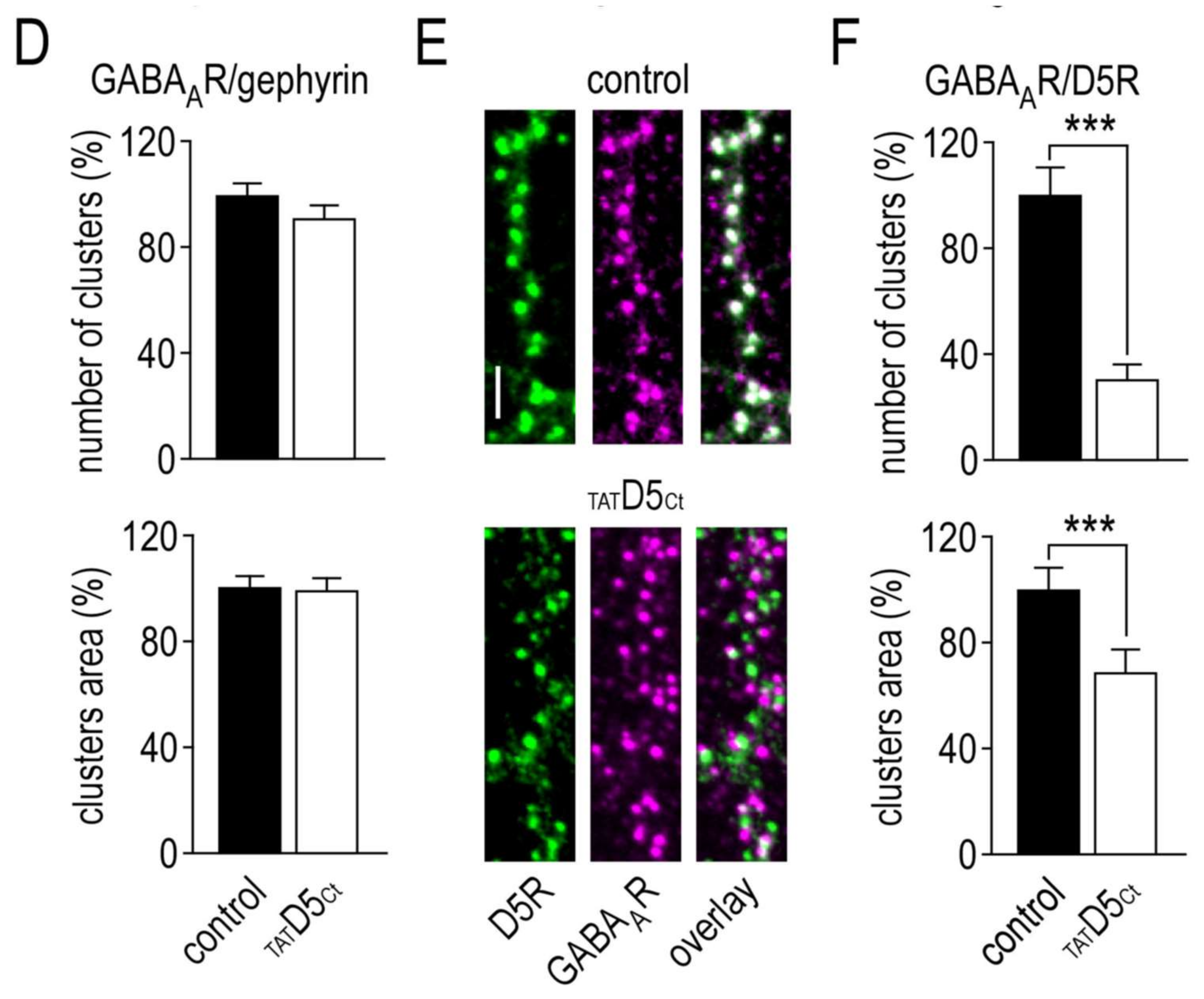
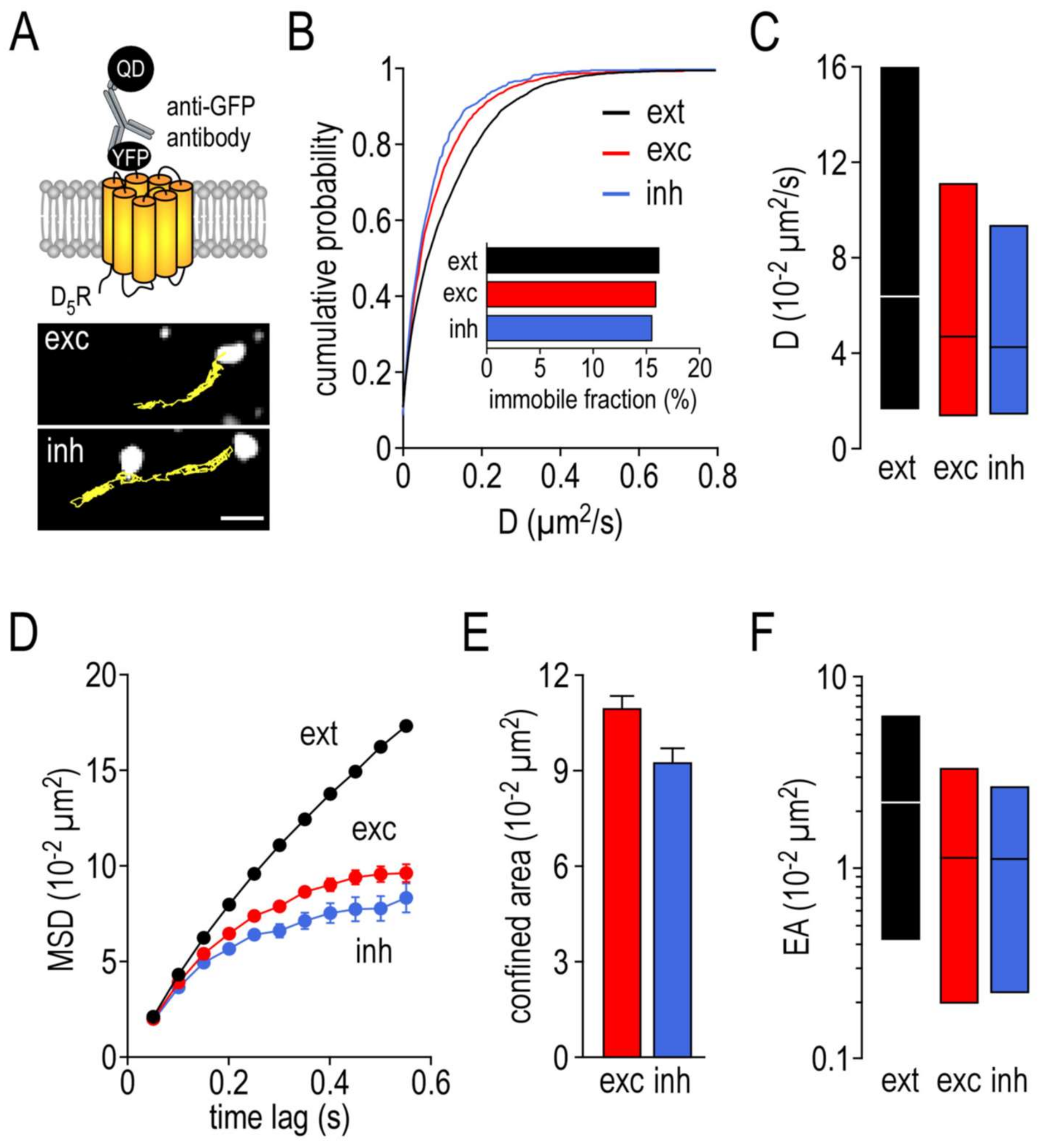
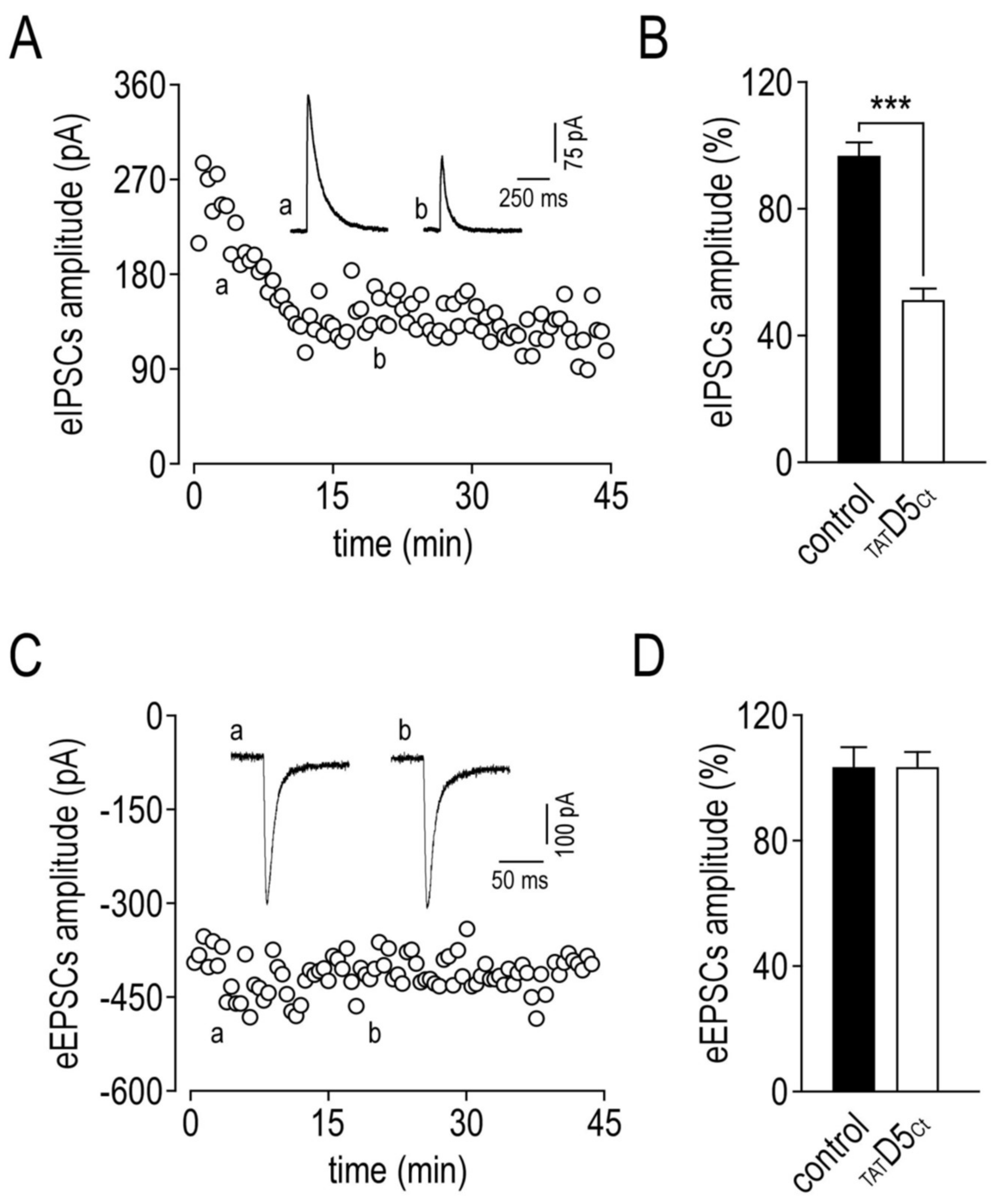
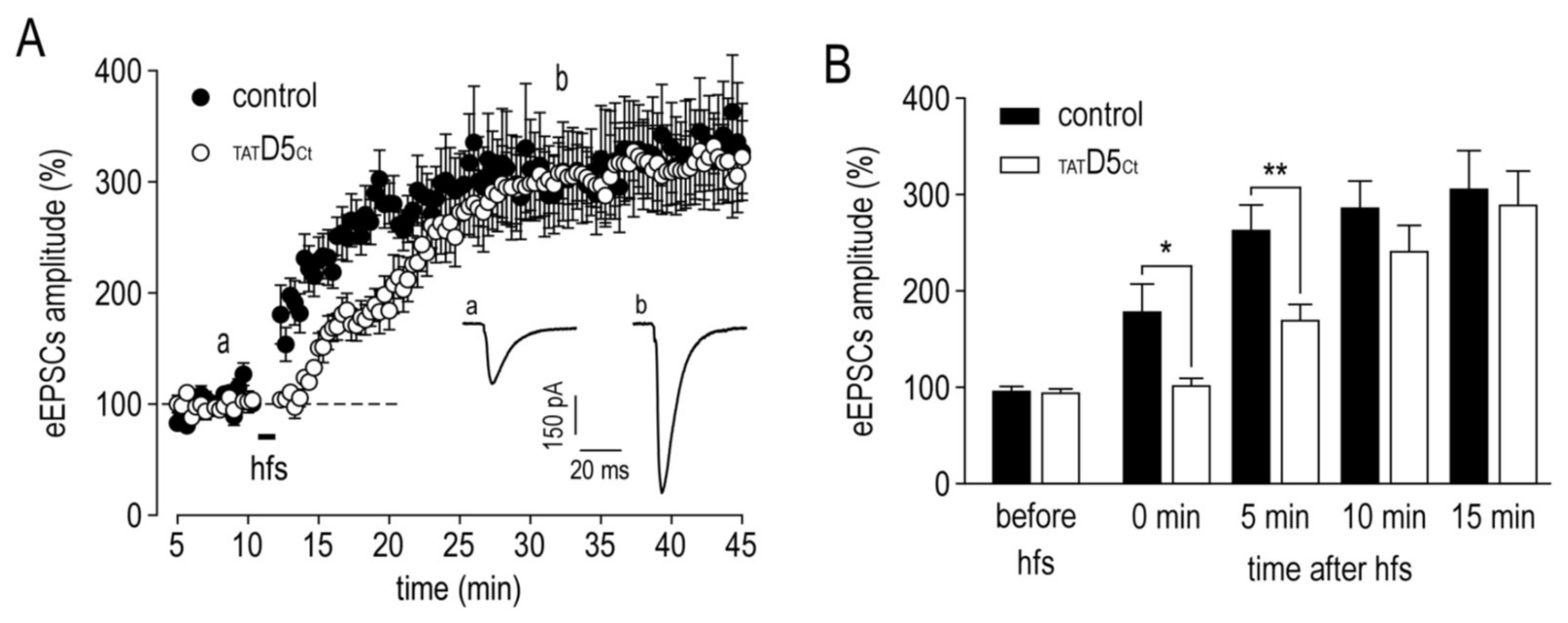
2.8. Functional Consequences of the Disruption of GABAAR–D5R Complexes
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Hippocampal Neuron Culture
4.2. Peptides Synthesis and Their Experimental Use
4.3. Immunocytochemistry Experimental Protocols
4.4. Single Nanoparticle Tracking Experimental Protocols
4.5. Patch-Clamp Experimental Protocols
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olsen, R.W.; Sieghart, W. International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors: Classification on the basis of subunit composition, pharmacology, and function. Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.W.; Sieghart, W. GABA A receptors: Subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mele, M.; Costa, R.O.; Duarte, C.B. Alterations in GABAA-Receptor Trafficking and Synaptic Dysfunction in Brain Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.R.; Kittler, J.T. The cell biology of synaptic inhibition in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.; Wakimoto, H.; Fujita, N.; Lalande, M.; Barnard, E.A. Analysis of the set of GABA(A) receptor genes in the human genome. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41422–41435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritschy, J.M.; Mohler, H. GABAA-receptor heterogeneity in the adult rat brain: Differential regional and cellular distribution of seven major subunits. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 359, 154–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusser, Z.; Sieghart, W.; Somogyi, P. Segregation of different GABAA receptors to synaptic and extrasynaptic membranes of cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, S.W.; Baur, R.; Sigel, E. Forced subunit assembly in alpha1beta2gamma2 GABAA receptors. Insight into the absolute arrangement. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46020–46025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, J.; Meyer, G.; Betz, H. Synaptic targeting of ionotropic neurotransmitter receptors. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, J.; Langosch, D.; Prior, P.; Littauer, U.Z.; Schmitt, B.; Betz, H. The 93-kDa glycine receptor-associated protein binds to tubulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 22242–22245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneussel, M.; Brandstatter, J.H.; Laube, B.; Stahl, S.; Muller, U.; Betz, H. Loss of postsynaptic GABA(A) receptor clustering in gephyrin-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 9289–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alldred, M.J.; Mulder-Rosi, J.; Lingenfelter, S.E.; Chen, G.; Luscher, B. Distinct gamma2 subunit domains mediate clustering and synaptic function of postsynaptic GABAA receptors and gephyrin. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essrich, C.; Lorez, M.; Benson, J.A.; Fritschy, J.M.; Luscher, B. Postsynaptic clustering of major GABAA receptor subtypes requires the gamma 2 subunit and gephyrin. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, C.; Balsiger, S.; Bluethmann, H.; Mansuy, I.M.; Fritschy, J.M.; Mohler, H.; Luscher, B. The gamma 2 subunit of GABA(A) receptors is required for maintenance of receptors at mature synapses. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 24, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, J.T.; Moss, S.J. Modulation of GABAA receptor activity by phosphorylation and receptor trafficking: Implications for the efficacy of synaptic inhibition. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, S.A.; Triller, A. Inhibitory Receptor Diffusion Dynamics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, N.; Jovanovic, J.; Moss, S. Multiple roles of protein kinases in the modulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptor function and cell surface expression. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 94, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardos, J.; Elster, L.; Damgaard, I.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Schousboe, A. Role of GABAB receptors in intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and possible interaction between GABAA and GABAB receptors in regulation of transmitter release in cerebellar granule neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 1994, 39, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Z.; Li, Z.W. Modulation by adenosine of GABA-activated current in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Physiol. 1997, 501, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunig, I.; Sommer, M.; Hatt, H.; Bormann, J. Dopamine receptor subtypes modulate olfactory bulb gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 2456–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kittler, J.T.; Moss, S.J.; Yan, Z. Dopamine D3 receptors regulate GABAA receptor function through a phospho-dependent endocytosis mechanism in nucleus accumbens. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Hernandez, J.; Hernandez, S.; Snyder, G.L.; Yan, Z.; Fienberg, A.A.; Moss, S.J.; Greengard, P.; Surmeier, D.J. D(1) dopamine receptor activation reduces GABA(A) receptor currents in neostriatal neurons through a PKA/DARPP-32/PP1 signaling cascade. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.J.; Ade, K.K.; Fu, Z.; Vicini, S. Dopamine modulation of GABA tonic conductance in striatal output neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 5116–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, P.; Yan, Z. Dopamine D4 receptors modulate GABAergic signaling in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9185–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritsch, N.X.; Sabatini, B.L. Dopaminergic modulation of synaptic transmission in cortex and striatum. Neuron 2012, 76, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.M.; Espinoza, S.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Dopamine receptors—IUPHAR Review 13. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missale, C.; Nash, S.R.; Robinson, S.W.; Jaber, M.; Caron, M.G. Dopamine receptors: From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 189–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wan, Q.; Pristupa, Z.B.; Yu, X.M.; Wang, Y.T.; Niznik, H.B. Direct protein-protein coupling enables cross-talk between dopamine D5 and gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors. Nature 2000, 403, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunahara, R.K.; Guan, H.C.; O’Dowd, B.F.; Seeman, P.; Laurier, L.G.; Ng, G.; George, S.R.; Torchia, J.; Van Tol, H.H.; Niznik, H.B. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature 1991, 350, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangarossa, G.; Longueville, S.; De Bundel, D.; Perroy, J.; Herve, D.; Girault, J.A.; Valjent, E. Characterization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing neurons in the mouse hippocampus. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.; Gutierrez, A.; Martin, R.; Penafiel, A.; Rivera, A.; de la Calle, A. Dopamine D5 receptors of rat and human brain. Neuroscience 2000, 100, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarinana, J.; Kitamura, T.; Kunzler, P.; Sultzman, L.; Tonegawa, S. Differential roles of the dopamine 1-class receptors, D1R and D5R, in hippocampal dependent memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8245–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergson, C.; Mrzljak, L.; Smiley, J.F.; Pappy, M.; Levenson, R.; Goldman-Rakic, P.S. Regional, cellular, and subcellular variations in the distribution of D1 and D5 dopamine receptors in primate brain. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 7821–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladepeche, L.; Dupuis, J.P.; Bouchet, D.; Doudnikoff, E.; Yang, L.; Campagne, Y.; Bezard, E.; Hosy, E.; Groc, L. Single-molecule imaging of the functional crosstalk between surface NMDA and dopamine D1 receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18005–18010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, M.; Schweizer, C.; Bannai, H.; Triller, A.; Levi, S. Diffusion barriers constrain receptors at synapses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.J.; Xue, S.; Pei, L.; Vukusic, B.; Chery, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Niznik, H.B.; Yu, X.M.; Liu, F. Dual regulation of NMDA receptor functions by direct protein-protein interactions with the dopamine D1 receptor. Cell 2002, 111, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Teissere, J.A.; Raju, D.V.; Hall, R.A. Hetero-oligomerization between GABAA and GABAB receptors regulates GABAB receptor trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18840–18850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, A.; Waters, N.; Holm-Waters, S.; Tedroff, J.; Nilsson, M.; Carlsson, M.L. Interactions between monoamines, glutamate, and GABA in schizophrenia: New evidence. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Lipina, T.V.; Wang, M.; Lai, T.K.; Lee, F.H.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, D.; Ferguson, S.S.; et al. A dopamine D2 receptor-DISC1 protein complex may contribute to antipsychotic-like effects. Neuron 2014, 84, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.K.Y.; Su, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F. Development of a peptide targeting dopamine transporter to improve ADHD-like deficits. Mol. Brain 2018, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, T.; Collingridge, G.L. Persistent memories of long-term potentiation and the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, R.A. A Brief History of Long-Term Potentiation. Neuron 2017, 93, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquet, D.; Triller, A. The role of receptor diffusion in the organization of the postsynaptic membrane. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Shi, S.H.; Esteban, J.A.; Piccini, A.; Poncer, J.C.; Malinow, R. Driving AMPA receptors into synapses by LTP and CaMKII: Requirement for GluR1 and PDZ domain interaction. Science 2000, 287, 2262–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, H.; Malinow, R. AMPA receptor incorporation into synapses during LTP: The role of lateral movement and exocytosis. Neuron 2009, 64, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groc, L.; Choquet, D. Linking glutamate receptor movements and synapse function. Science 2020, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, M.; Groc, L.; Frischknecht, R.; Beique, J.C.; Lounis, B.; Rumbaugh, G.; Huganir, R.L.; Cognet, L.; Choquet, D. Surface mobility of postsynaptic AMPARs tunes synaptic transmission. Science 2008, 320, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausrat, T.J.; Muhia, M.; Gerrow, K.; Thomas, P.; Hirdes, W.; Tsukita, S.; Heisler, F.F.; Herich, L.; Dubroqua, S.; Breiden, P.; et al. Radixin regulates synaptic GABAA receptor density and is essential for reversal learning and short-term memory. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, E.; Ravasenga, T.; Petrini, E.M.; Polenghi, A.; Nieus, T.; Guazzi, S.; Barberis, A. Inter-Synaptic Lateral Diffusion of GABAA Receptors Shapes Inhibitory Synaptic Currents. Neuron 2017, 95, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, L.S.; Jones, M.V.; Westbrook, G.L. Slow desensitization regulates the availability of synaptic GABA(A) receptors. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7914–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trussell, L.O.; Zhang, S.; Raman, I.M. Desensitization of AMPA receptors upon multiquantal neurotransmitter release. Neuron 1993, 10, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, C.M.; Rajappa, R.; Katchan, L.; Taylor, C.R.; Tsai, M.C.; Smith, C.M.; de Jong, J.W.; Arnold, D.B.; Lammel, S.; Kramer, R.H. Relocation of an Extrasynaptic GABAA Receptor to Inhibitory Synapses Freezes Excitatory Synaptic Strength and Preserves Memory. Neuron 2021, 109, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyzio, R.; Represa, A.; Jorquera, I.; Ben-Ari, Y.; Gozlan, H.; Aniksztejn, L. The establishment of GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses on CA1 pyramidal neurons is sequential and correlates with the development of the apical dendrite. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10372–10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ari, Y.; Gaiarsa, J.L.; Tyzio, R.; Khazipov, R. GABA: A pioneer transmitter that excites immature neurons and generates primitive oscillations. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1215–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffin, D.; Ali, A.B.; Rampersaud, N.; Harkavyi, A.; Fuchs, C.; Whitton, P.S.; Nairn, A.C.; Jovanovic, J.N. Dopamine-dependent tuning of striatal inhibitory synaptogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 2935–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruusmagi, M.; Kumar, S.; Zelenin, S.; Brismar, H.; Aperia, A.; Scott, L. Functional differences between D(1) and D(5) revealed by high resolution imaging on live neurons. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaech, S.; Banker, G. Culturing hippocampal neurons. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2406–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maingret, F.; Groc, L. Characterization of the Functional Cross-Talk between Surface GABAA and Dopamine D5 Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094867
Maingret F, Groc L. Characterization of the Functional Cross-Talk between Surface GABAA and Dopamine D5 Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094867
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaingret, François, and Laurent Groc. 2021. "Characterization of the Functional Cross-Talk between Surface GABAA and Dopamine D5 Receptors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094867
APA StyleMaingret, F., & Groc, L. (2021). Characterization of the Functional Cross-Talk between Surface GABAA and Dopamine D5 Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094867




