The Inflammatory Profile of Obesity and the Role on Pulmonary Bacterial and Viral Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Mechanic Pulmonary Complications of Obesity
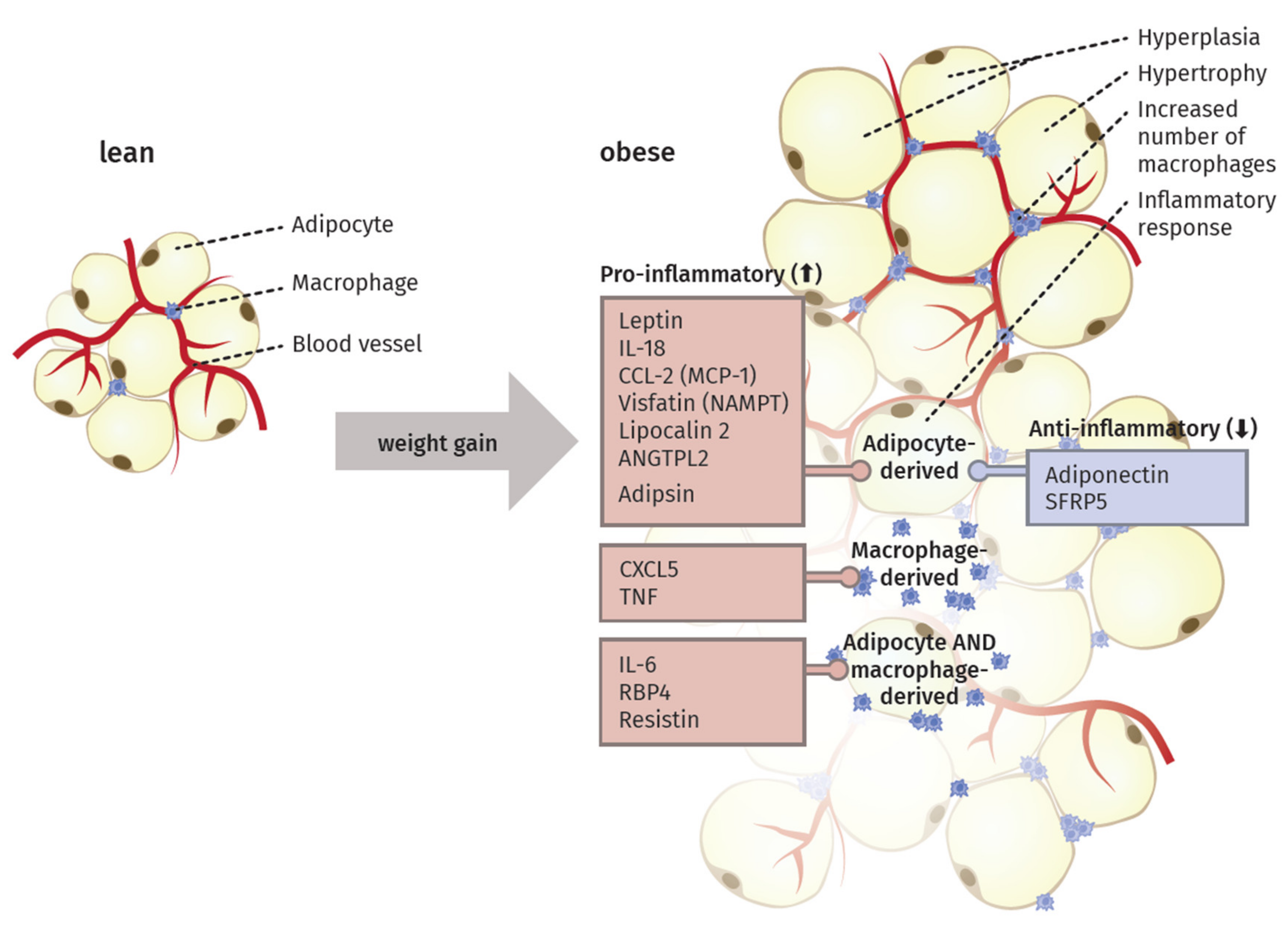
3. The Inflammatory Activity of Adipose Tissue
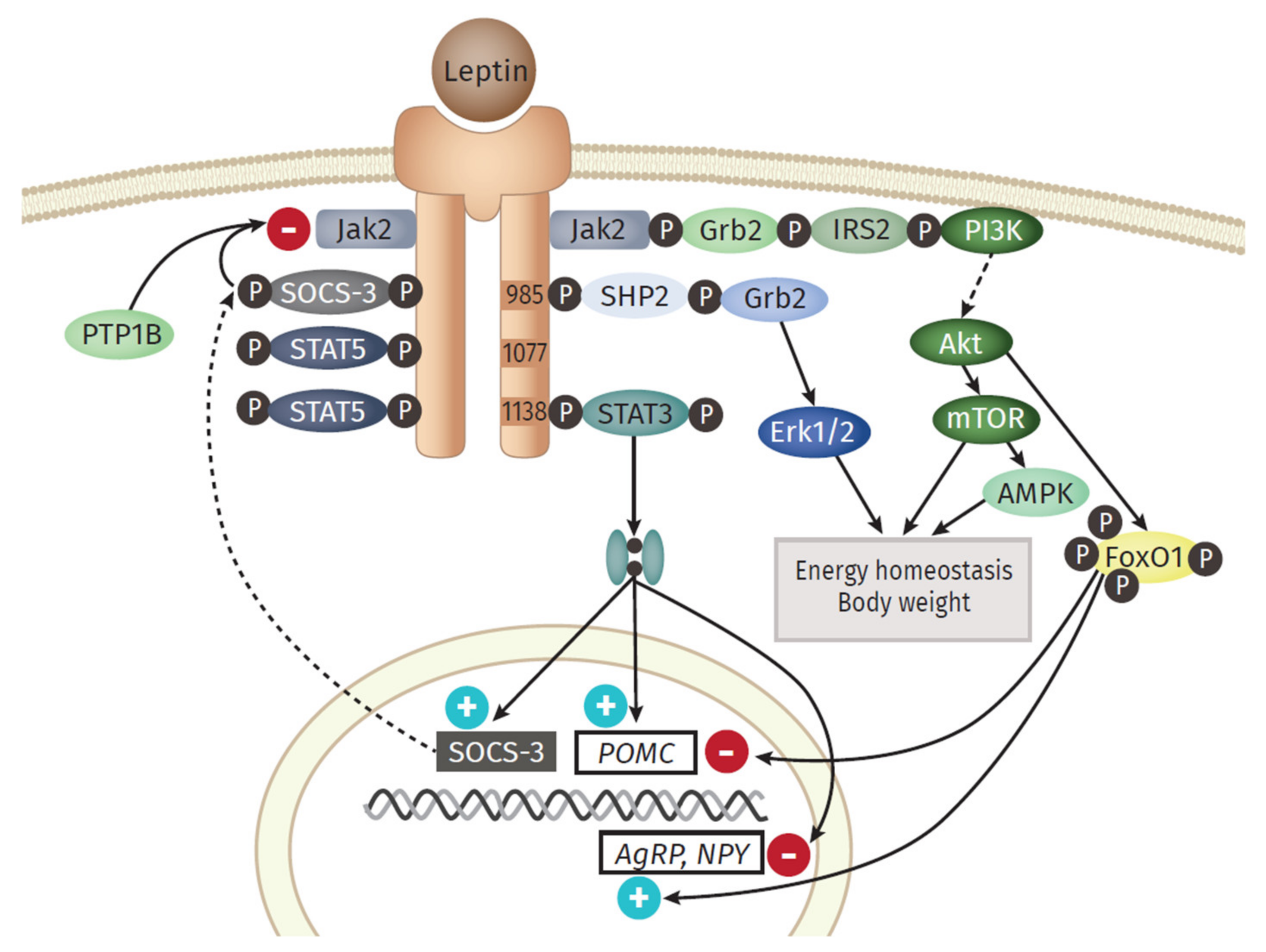
4. Adipocytokines Produced by Adipose Tissue
4.1. Pro-Inflammatory Molecules of the Adipose Tissue
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory Molecules of the Adipose Tissue
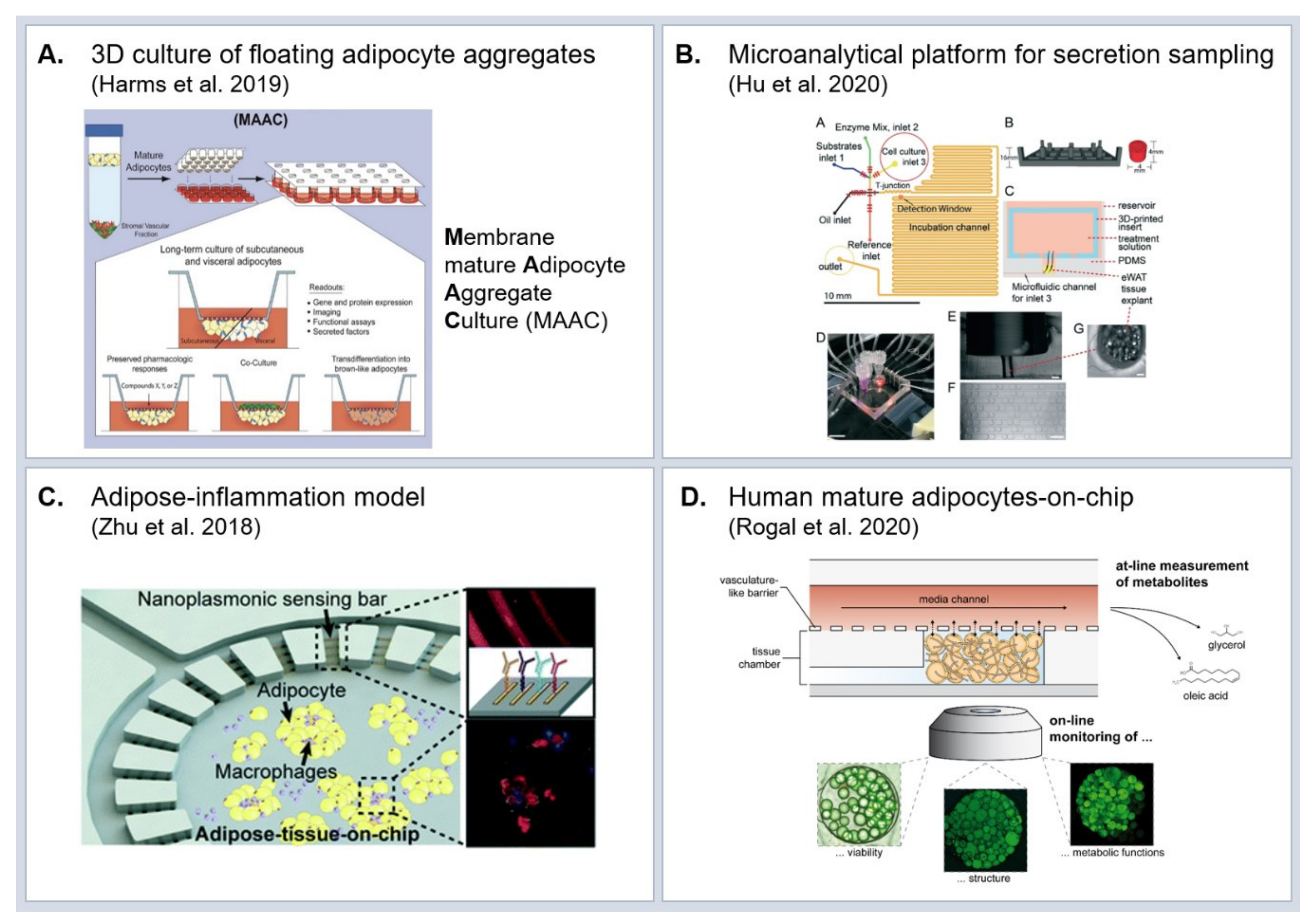
5. Experimental Model Systems to Study Molecular Effects of Obesity
5.1. In Vivo Models
5.2. In Vitro Models
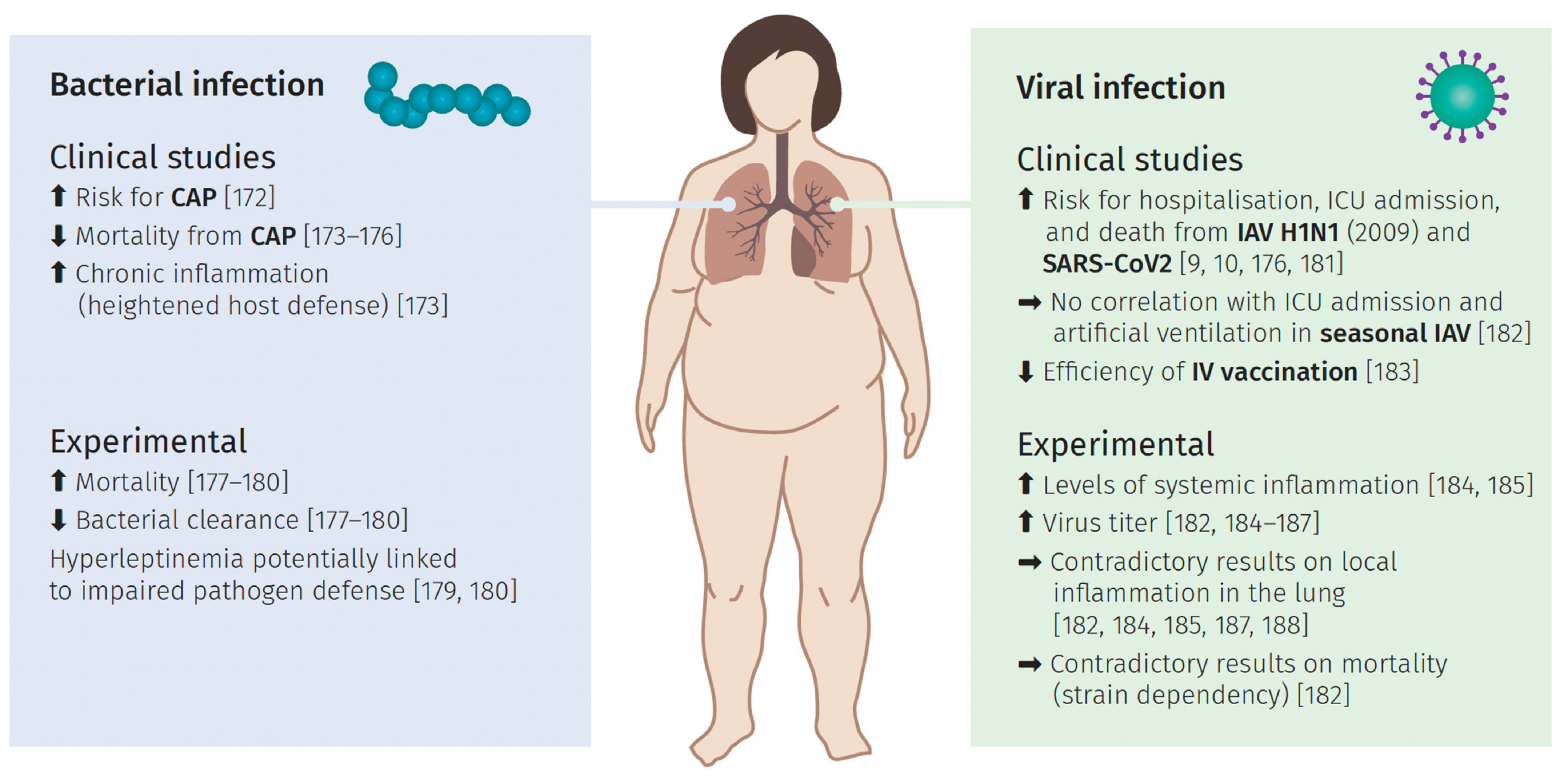
6. Pulmonary Infections and the Impact of Obesity
6.1. Bacterial Lung Infection
6.2. Viral Induced Lung Infection
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, D.S. Diagnosis and Prevalence of Obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1989, 73, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalki, S.B. The Clinical Biochemistry of Alcohol. In Scientific Foundations of Biochemistry in Clinical Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Quetelet, L.A. A Treatise on Man and the Development of His Faculties. 1842. Obes. Res. 1994, 2, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, K.M.; Martin, C.K.; Berthoud, H.R.; Heymsfield, S.B. Obesity: Pathophysiology and Management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P.T. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.M. Pulmonary Complications of Obesity. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2001, 321, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.; Swift-Scanlan, T.; Salyer, J.; Jones, T. The Obesity Paradox in Sepsis: A Theoretical Framework. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2020, 22, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Morris, A.M.; Nugent, R.; Ralston, J.; Barata Cavalcante, O.; Wilding, J. Strengthening Resistance to the COVID-19 Pandemic and Fostering Future Resilience Requires Concerted Action on Obesity. Glob. Health Action 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, F.M.; Islam, M.M. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Mortality Among COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Community Health 2020, 45, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.; Ventura, H.O. Obesity, Heart Disease, and Favorable Prognosis-Truth or Paradox? Am. J. Med. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.R.; Gold, A.R.; Schubert, N.; Stryzak, A.; Wise, R.A.; Permutt, S.; Smith, P.L. Effect of Weight Loss on Upper Airway Collapsibility in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 144, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, A.L.; Zwillich, C. The Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.T.; Henry, J.P.; Sweany, S.K.; Meadows, W.R.; Pietras, R.J. The Total Work of Breathing in Normal and Obese Men. J. Clin. Invest. 1964, 43, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, H.W.; Filler, J.; Fisthman, A.P.; Cournand, A. The Efficiency of Ventilation during Voluntary Hyperpnea: Studies in Normal Subjects and in Dyspneic Patients with Either Chronic Pulmonary Emphysema or Obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 1959, 38, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.T.; Druz, W.S.; Kondragunta, V.R. Diaphragmatic Responses to Body Position Changes in Obese Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 133, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, A.; Reddan, W.; Balke, B.; Rankin, J.; Ranrin, J. Work Capacity Determinants and Physiologic Cost of Weight-Supported Work in Obesity’ Work Mpacity Determinants and Physiologic Cost of Weight-Supported Work in Obesity. J. Appl. Physiol. 1966, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emirgil, C.; Sobol, B.J. The Effects of Weight Reduction on Pulmonary Function and the Sensitivity of the Respiratory Center in Obesity. Amer. Rev. Resp. Dis. 1973, 108, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvadori, A.; Fanari, P.; Mazza, P.; Agosti, R.; Longhini, E. Work Capacity and Cardiopulmonary Adaptation of the Obese Subject during Exercise Testing. Chest 1992, 101, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, R. Volume and PH of Gastric Juice in Obese Patients. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 1975, 43, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.A.; McNicol, G.P. Preoperative Prediction of Postoperative Deep Vein Thrombosis. Br. Med. J. 1976, 2, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, S.Z. A Prospective Study of Risk Factors for Pulmonary Embolism in Women. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1997, 277, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.A.; Webb, R.K.; Szekely, S.; Gillies, E.R.N.; Dreosti, A.V. Difficult Intubation: An Analysis of 2000 Incident Reports. Anaesth. Intensive Care 1993, 21, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choban, P.S.; Weireter, L.J.; Maynes, C. Obesity and Increased Mortality in Blunt Trauma. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 1991, 31, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose Tissue, Adipokines, and Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, J.; Bengtsson, T.; Cannon, B. Unexpected Evidence for Active Brown Adipose Tissue in Adult Humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S. White, Brown, Beige and Pink: A Rainbow in the Adipose Organ. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2019, 4, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himms-Hagen, J.; Melnyk, A.; Zingaretti, M.C.; Ceresi, E.; Barbatelli, G.; Cinti, S. Multilocular Fat Cells in WAT of CL-316243-Treated Rats Derive Directly from White Adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-α-Dependent Myokine That Drives Brown-Fat-like Development of White Fat and Thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, A.; Smorlesi, A.; Frontini, A.; Barbatelli, G.; Cint, S. White, Brown and Pink Adipocytes: The Extraordinary Plasticity of the Adipose Organ. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators Linking Adipose Tissue, Inflammation and Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity Is Associated with Macrophage Accumulation in Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frayn, K.N.; Karpe, F.; Fielding, B.A.; Macdonald, I.A.; Coppack, S.W. Integrative Physiology of Human Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, Stress, and Diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Kaaks, R. Overweight, Obesity and Cancer: Epidemiological Evidence and Proposed Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, G.H. The Role of Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. What We Talk about When We Talk about Fat. Cell 2014, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtue, S.; Vidal-Puig, A. Adipose Tissue Expandability, Lipotoxicity and the Metabolic Syndrome-An Allostatic Perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2010, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: A Multistep Process; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E.; Sun, K.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose Tissue Remodeling and Obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Obesity-Induced Inflammatory Changes in Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 1785–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R.; Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity Induces a Phenotypic Switch in Adipose Tissue Macrophage Polarization Find the Latest Version: Obesity Induces a Phenotypic Switch in Adipose Tissue Macrophage Polarization. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Soldati, L.; Sarlo, F.; Calvani, M.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Di Renzo, L. New Obesity Classification Criteria as a Tool for Bariatric Surgery Indication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 681–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional Cloning of the Mouse Obese Gene and Its Human Homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, P.; Sereti, K.I.; Zhao, P.; Ali, S.R.; Weissman, I.L.; Ardehali, R. Parabiosis in Mice: A Detailed Protocol. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, e50556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, D.L. A Historical Perspective on Leptin. Nat. Med. 2010, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, L.A.; Dembski, M.; Weng, X.; Deng, N.; Culpepper, J.; Devos, R.; Richards, G.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Clark, F.T.; Deeds, J.; et al. Identification and Expression Cloning of a Leptin Receptor, OB-R. Cell 1995, 83, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar]
- La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. The Weight of Leptin in Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wauman, J.; Zabeau, L.; Tavernier, J. The Leptin Receptor Complex: Heavier than Expected? Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haniu, M.; Arakawa, T.; Bures, E.J.; Young, Y.; Hui, J.O.; Rohde, M.F.; Welcher, A.A.; Horan, T. Human Leptin Receptor: Determination of Disulfide Structure and N- Glycosylation Sites of the Extracellular Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28691–28699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kielar, D.; Clark, J.S.C.; Ciechanowicz, A.; Kurzawski, G.; Sulikowski, T.; Naruszewicz, M. Leptin Receptor Isoforms Expressed in Human Adipose Tissue. Metabolism 1998, 47, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Shimizu, H.; Horie, T.; Mori, M. Expression of Leptin Receptor in Lung: Leptin as a Growth Factor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 365, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, T.M.; Breininger, J.F.; Baskin, D.G.; Schwartz, M.W. Coexpression of Agrp and NPY in Fasting-Activated Hypothalamic Neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisse, C.; Halaas, J.L.; Horvath, C.M.; Darnell, J.E.; Stoffel, M.; Friedman, J.M. Leptin Activation of Stat3 in the Hypothalamus of Wild–Type and Ob/Ob Mice but Not Db/Db Mice. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørbaek, C.; Elmquist, J.K.; Daniel Frantz, J.; Shoelson, S.E.; Flier, J.S. Identification of SOCS-3 as a Potential Mediator of Central Leptin Resistance Cytokine-like Signal Transduction by Stimulating the JAK-STAT Pathway via the Long Leptin Receptor Isoform. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørbæk, C.; Buchholz, R.M.; Davis, S.M.; Bates, S.H.; Pierroz, D.D.; Gu, H.; Neel, B.G.; Myers, M.G.; Flier, J.S. Divergent Roles of SHP-2 in ERK Activation by Leptin Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4747–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T. Forkhead Protein FoxO1 Mediates Agrp-Dependent Effects of Leptin on Food Intake. Nat Med. 2006, 12, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, D.; Proulx, K.; Blake Smith, K.A.; Kozma, S.C.; Thomas, G.; Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J. Hypothalamic MTOR Signaling Regulates Food Intake. Science 2006, 312, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.-B.; Peroni, O.D.; Fryer, L.G.D.; Müller, C.; Carling, D.; Kahn, B.B. Leptin Stimulates Fatty-Acid Oxidation by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Nature 2002, 415, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Alquier, T.; Furukawa, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, A.; Xue, B.; Mu, J.; Foufelle, F.; Ferré, P.; Birnbaum, M.J.; et al. AMP-Kinase Regulates Food Intake by Responding to Hormonal and Nutrient Signals in the Hypothalamus. Nature 2004, 428, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauman, J.; Tavernier, J. Leptin Receptor Signaling: Pathways to Leptin Resistance. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 2771–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszubska, W.; Falls, H.D.; Schaefer, V.G.; Haasch, D.; Frost, L.; Hessler, P.; Kroeger, P.E.; White, D.W.; Jirousek, M.R.; Trevillyan, J.M. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Negatively Regulates Leptin Signaling in a Hypothalamic Cell Line. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 195, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in Inflammation and Metabolic Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Alvarez, J.; Goberna, R.; Sá Nchez-Margalet, V. Human Leptin Stimulates Proliferation and Activation of Human Circulating Monocytes. Cell Immunol. 1999, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Filho, G.; Mastronardi, C.; Franco, C.B.; Wang, K.B.; Wong, M.-L.; Licinio, J. Leptin: Molecular Mechanisms, Systemic pro-Inflammatory Effects, and Clinical Implications. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2012, 56, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Gao, B. Impaired Natural Killer (NK) Cell Activity in Leptin Receptor Deficient Mice: Leptin as a Critical Regulator in NK Cell Development and Activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cava, A.; Alviggi, C.; Matarese, G. Unraveling the Multiple Roles of Leptin in Inflammation and Autoimmunity. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, G.M.; Matarese, G.; Howard, J.K.; Baker, R.J.; Bloom, S.R.; Lechler, R.I. Leptin Modulates the T-Cell Immune Response and Reverses Starvation-Induced Immunosuppression. Nature 1998, 394, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bełtowski, J. Adiponectin and Resistin-New Hormones of White Adipose Tissue. Med Sci. Monitor. 2003, 9, RA55–RA61. [Google Scholar]
- Steppan, C.M.; Wang, J.; Whiteman, E.L.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Lazar, M.A. Activation of SOCS-3 by Resistin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degawa-Yamauchi, M.; Bovenkerk, J.E.; Juliar, B.E.; Watson, W.; Kerr, K.; Jones, R.; Zhu, Q.; Considine, R.V. Serum Resistin (FIZZ3) Protein Is Increased in Obese Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5452–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppan, C.M.; Bailey, S.T.; Bhat, S.; Brown, E.J.; Banerjee, R.R.; Wright, C.M.; Patel, H.R.; Ahima, R.S.; Lazar, M.A. The Hormone Resistin Links Obesity to Diabetes. Nature 2001, 409, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, D.B.; Sewter, C.P.; Klenk, E.S.; Segal, D.G.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Considine, R.V.; O’Rahilly, S. Resistin / Fizz3 Expression in Relation to Obesity and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Action in Humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.R.; Lazar, M.A. Resistin: Molecular History and Prognosis. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokarewa, M.; Nagaev, I.; Dahlberg, L.; Smith, U.; Tarkowski, A. Resistin, an Adipokine with Potent Proinflammatory Properties. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5789–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Li, S.H.; Wang, C.H.; Fedak, P.W.M.; Li, R.K.; Weisel, R.D.; Mickle, D.A.G. Resistin Promotes Endothelial Cell Activation: Further Evidence of Adipokine-Endothelial Interaction. Circulation 2003, 108, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revollo, J.R.; Körner, A.; Mills, K.F.; Satoh, A.; Wang, T.; Garten, A.; Dasgupta, B.; Sasaki, Y.; Wolberger, C.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin Regulates Insulin Secretion in β Cells as a Systemic NAD Biosynthetic Enzyme. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, D.G.; Schindler, K.; Schaller, G.; Prager, G.; Wolzt, M.; Ludvik, B. Increased Plasma Visfatin Concentrations in Morbidly Obese Subjects Are Reduced after Gastric Banding. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1578–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.S.; Min, H.Y.; Johnson, D.; Chaplinsky, R.J.; Flier, J.S.; Hunt, C.R.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipsin: A Circulating Serine Protease Homolog Secreted by Adipose Tissue and Sciatic Nerve. Science 1987, 237, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.T.; Damm, D.; Hancock, N.; Rosen, B.S.; Lowell, B.B.; Usher, P.; Flier, J.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Human Adipsin Is Identical to Complement Factor D and Is Expressed at High Levels in Adipose Tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9210–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flier, J.S.; Cook, K.S.; Usher, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Severely Impaired Adipsin Expression in Genetic and Acquired Obesity. Science 1987, 237, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Lowell, B.B.; Damm, D.; Leibel, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Jimerson, D.C.; Lesem, M.D.; Van Dyke, D.C.; Daly, P.A.; Chatis, P.; et al. Concentrations of Adipsin in Blood and Rates of Adipsin Secretion by Adipose Tissue in Humans with Normal, Elevated and Diminished Adipose Tissue Mass. Int. J. Obes. 1994, 18, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, J.C.; Ljubicic, S.; Leibiger, B.; Kern, M.; Leibiger, I.B.; Moede, T.; Kelly, M.E.; Chatterjee Bhowmick, D.; Murano, I.; Cohen, P.; et al. Adipsin is an Adipokine That Improves β Cell Function in Diabetes. Cell 2014, 158, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, J.M.; Zhang, J.G.; Bandala-Sanchez, E.; Naselli, G.; Liu, R.; Ritchie, M.; Smyth, G.K.; O’Brien, P.E.; Harrison, L.C. Interferon-Gamma Released from Omental Adipose Tissue of Insulin-Resistant Humans Alters Adipocyte Phenotype and Impairs Response to Insulin and Adiponectin Release. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendar, J.; Frohberger, S.J.; Karunakaran, I.; Schmitt, V.; Stamminger, W.; Neumann, A.-L.; Wilhelm, C.; Hoerauf, A.; Hübner, M.P. Adiponectin Limits IFN-γ and IL-17 Producing CD4 T Cells in Obesity by Restraining Cell Intrinsic Glycolysis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, V.Z.; Libby, P. Obesity, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2009, 6, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, L.; Di Renzo, L.; Anania, C.; Osborn, J.F.; Ippoliti, F.; Schiavo, E.; Chiesa, C. Increased T-Helper Interferon-γ-Secreting Cells in Obese Children. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 154, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, V.; Weber, F. Interferon and Cytokine Responses to SARS-Coronavirus Infection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.A.; Saghizadeh, M.; Ong, J.M.; Bosch, R.J.; Deem, R.; Simsolo, R.B. The Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor in Human Adipose Tissue: Regulation by Obesity, Weight Loss, and Relationship to Lipoprotein Lipase. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 95, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Budavari, A.; Murray, D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Reduced Tyrosine Kinase Activity of the Insulin Receptor in Obesity- Diabetes. Central Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. J. Clin. Invest. 1994, 94, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, J.N.; Madan, A.K.; Hiler, M.L.; Cheema, P.; Bahouth, S.W. Comparison of the Release of Adipokines by Adipose Tissue, Adipose Tissue Matrix, and Adipocytes from Visceral and Subcutaneous Abdominal Adipose Tissues of Obese Humans. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.K.; Bunkin, D.A.; Greenberg, A.S. Omental and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissues of Obese Subjects Release Interleukin-6: Depot Difference and Regulation by Glucocorticoid 1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senn, J.J.; Klover, P.J.; Nowak, I.A.; Zimmers, T.A.; Koniaris, L.G.; Furlanetto, R.W.; Mooney, R.A. Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling-3 (SOCS-3), a Potential Mediator of Interleukin-6-Dependent Insulin Resistance in Hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 13740–13746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Pontillo, A.; Ciotola, M.; Di Palo, C.; Grella, E.; Nicoletti, G.; Giugliano, D. Weight Loss Reduces Interleukin-18 Levels in Obese Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3864–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.W.; Liu, X.; Bi, X.P.; Xing, S.S.; Li, L.; Gong, H.P.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. IL-18 Overexpression Promotes Vascular Inflammation and Remodeling in a Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2010, 208, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Graham, T.E.; Mody, N.; Preitner, F.; Peroni, O.D.; Zabolotny, J.M.; Kotani, K.; Quadro, L.; Kahn, B.B. Serum Retinol Binding Protein 4 Contributes to Insulin Resistance in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Nature 2005, 436, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, T.E.; Yang, Q.; Blüher, M.; Hammarstedt, A.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Henry, R.R.; Wason, C.J.; Oberbach, A.; Jansson, P.-A.; Smith, U.; et al. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 and Insulin Resistance in Lean, Obese, and Diabetic Subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2552–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broch, M.; Ramírez, R.; Auguet, M.T.; Alcaide, M.J.; Aguilar, C.; Garcia-España, A.; Richart, C.; Xxiii, C.; Guasch, M. Macrophages Are Novel Sites of Expression and Regulation of Retinol Binding Protein-4 (RBP4). Physiol. Res. 2010, 59, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Kadomatsu, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Miyata, K.; Ito, Y.; Endo, M.; Urano, T.; Zhu, H.J.; Tsukano, H.; Tazume, H.; et al. Angiopoietin-like Protein 2 Promotes Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Obesity-Related Systemic Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Kraegen, E.W.; Sweeney, G.; Zhang, J.; Tso, A.W.; Chow, W.-S.; Wat, N.M.; Xu, J.Y.; Hoo, R.L.; et al. Lipocalin-2 Is an Inflammatory Marker Closely Associated with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Hyperglycemia in Humans. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, H.; Tateya, S.; Tamori, Y.; Kotani, K.; Hiasa, K.I.; Kitazawa, R.; Kitazawa, S.; Miyachi, H.; Maeda, S.; Egashira, K.; et al. MCP-1 Contributes to Macrophage Infiltration into Adipose Tissue, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic Steatosis in Obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavey, C.; Lazennec, G.; Lagarrigue, S.; Clapé, C.; Iankova, I.; Teyssier, J.; Annicotte, J.S.; Schmidt, J.; Mataki, C.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. CXC Ligand 5 Is an Adipose-Tissue Derived Factor That Links Obesity to Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartipy, P.; Loskutoff, D.J. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7265–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Liang, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. AdipoQ Is a Novel Adipose-Specific Gene Dysregulated in Obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffes, M.W.; Gross, M.D.; Schreiner, P.J.; Yu, X.; Hilner, J.E.; Gingerich, R.; Jacobs, D.R. Serum Adiponectin in Young Adults-Interactions with Central Adiposity, Circulating Levels of Glucose, and Insulin Resistance: The CARDIA Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Walsh, K. Obesity, Adiponectin and Vascular Inflammatory Disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischon, T.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Rimm, E.B. Adiponectin: Stability in Plasma over 36 Hours and within-Person Variation over 1 Year. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waki, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Uchida, S.; Kita, S.; Hara, K.; Hada, Y.; Vasseur, F.; Froguel, P.; et al. Impaired Multimerization of Human Adiponectin Mutants Associated with Diabetes. Molecular Structure and Multimer Formation of Adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40352–40363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Yago, H.; Miyazaki, O.; Ebinuma, H.; Imai, Y.; Nagai, R.; Kadowaki, T. Measurement of the High-Molecular Weight Form of Adiponectin in Plasma Is Useful for the Prediction of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of Adiponectin Receptors That Mediate Antidiabetic Metabolic Effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin Stimulates Glucose Utilization and Fatty-Acid Oxidation by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turer, A.T.; Khera, A.; Ayers, C.R.; Turer, C.B.; Grundy, S.M.; Vega, G.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose Tissue Mass and Location Affect Circulating Adiponectin Levels. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2515–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, N.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Suhail, A.; Sweeney, G.; Wheeler, M.B. Adiponectin-Induced ERK and Akt Phosphorylation Protects against Pancreatic Beta Cell Apoptosis and Increases Insulin Gene Expression and Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33623–33631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Du, X.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. The Adipocyte-Secreted Protein Acrp30 Enhances Hepatic Insulin Action. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffler, A.; Schölmerich, J.; Büchler, C. Mechanisms of Disease: Adipocytokines and Visceral Adipose Tissue-Emerging Role in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, I.; Kelesidis, T.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin and Cancer: A Systematic Review. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischon, T.; Girman, C.J.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Rifai, N.; Hu, F.B.; Rimm, E.B. Plasma Adiponectin Levels and Risk of Myocardial Infarction in Men. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyagarajan, B.; Jacobs, D.R.; Smith, L.J.; Kalhan, R.; Gross, M.D.; Sood, A. Serum Adiponectin Is Positively Associated with Lung Function in Young Adults, Independent of Obesity: The CARDIA Study. Respir. Res. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulster-Radcliffe, M.C.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Wang, J.; Christian, J.A.; Spurlock, M.E. Adiponectin Differentially Regulates Cytokines in Porcine Macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Novel Modulator for Endothelial Adhesion Molecules: Adipocyte-Derived Plasma Protein Adiponectin. Circulation 1999, 100, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryo, M.; Nakamura, T.; Kihara, S.; Kumada, M.; Shibazaki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nagai, M.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T. Adiponectin as a Biomarker of the Metabolic Syndrome. Circ. J. 2004, 68, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosogai, N.; Fukuhara, A.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Segawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Tochino, Y.; Komuro, R.; Matsuda, M.; et al. Adipose Tissue Hypoxia in Obesity and Its Impact on Adipocytokine Dysregulation. Diabetes 2007, 56, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, M.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Maeda, K.; Nagaretani, H.; Kishida, K.; Maeda, N.; et al. Adiponectin Specifically Increased Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 Through Interleukin-10 Expression in Human Macrophages. Circulation 2004, 109, 2046–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Parker, J.L.; Ouchi, N.; Higuchi, A.; Vita, J.A.; Gokce, N.; Pedersen, A.A.; Kalthoff, C.; Tullin, S.; Sams, A.; et al. Adiponectin Promotes Macrophage Polarization toward an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 6153–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Higuchi, A.; Ohashi, K.; Oshima, Y.; Gokce, N.; Shibata, R.; Akasaki, Y.; Shimono, A.; Walsh, K. Sfrp5 Is an Anti-Inflammatory Adipokine That Modulates Metabolic Dysfunction in Obesity. Science 2010, 329, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Deng, H.; Qu, H. Plasma SFRP5 Levels Are Decreased in Chinese Subjects with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes and Negatively Correlated with Parameters of Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 99, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashima, Y.; Katsuya, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Ouchi, N.; Ohishi, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Fu, Y.; Motone, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsuo, A.; et al. Hypoadiponectinemia Is an Independent Risk Factor for Hypertension. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α: Direct Role in Obesity-Linked Insulin Resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, C.; Raun, K.; Yan, F.F.; Larsen, M.O.; Tang-Christensen, M. Laboratory Animals as Surrogate Models of Human Obesity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingalls, A.M.; Dickie, M.M.; Shell, G.D. Obese, a New Mutation in the House Mouse. J. Hered. 1950, 41, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederich, R.C.; Lollmann, B.; Hamann, A.; Napolitano-Rosen, A.; Kahn, B.B.; Lowell, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Expression of Ob MRNA and Its Encoded Protein in Rodents. Impact of Nutrition and Obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 96, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberg, L.; Coleman, D.L. Laboratory Animals Exhibiting Obesity and Diabetes Syndromes. Metabolism 1977, 26, 59–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, K.P.; Dickie, M.M.; Coleman, D.L. Diabetes, a New Mutafton in the Mouse. Science 1966, 153, 1127–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricker, L.D.; Leiter, E.H. Peptides, Enzymes and Obesity: New Insights from a “dead” Enzyme. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, T.F.; Zucker, L.M. Hereditary Obesity in the Rat Associated with High Serum Fat and Cholesterol. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1962, 110, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, I.S.; Jebb, S.A.; Langmack, G.; Lawrence, E.; Cheetham, C.H.; Prentice, A.M.; Hughes, I.A.; McCamish, M.A.; O’Rahilly, S. Effects of Recombinant Leptin Therapy in a Child with Congenital Leptin Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G.; Cowley, M.A.; Münzberg, H. Mechanisms of Leptin Action and Leptin Resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G.; Leibel, R.L.; Seeley, R.J.; Schwartz, M.W. Obesity and Leptin Resistance: Distinguishing Cause from Effect. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, N.J.; Stock, M.J. The Cafetaria Diet as a Tool for Studies of Thermogenesis. J. Nutr. 1988, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, B.E.; Hogan, S.; Sullivan, A.C. Initiation and Perpetuation of Obesity and Obesity Resistance in Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1989, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, A.; Stemple, D.L.; Barroso, I. The Emerging Use of Zebrafish to Model Metabolic Disease. DMM Dis. Models Mech. 2013, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Maddison, L.A.; Chen, W. Zebrafish as a Model for Obesity and Diabetes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestas, J.; Hughes, C.C.W. Of Mice and Not Men: Differences between Mouse and Human Immunology. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greek, R.; Menache, A. Systematic Reviews of Animal Models: Methodology versus Epistemology. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Worp, H.B.; Howells, D.W.; Sena, E.S.; Porritt, M.J.; Rewell, S.; O’Collins, V.; Macleod, M.R. Can Animal Models of Disease Reliably Inform Human Studies? PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmad, H.F.; Daouk, R.; Azar, J.; Sapudom, J.; Teo, J.C.M.; Abou-Kheir, W.; Al-Sayegh, M. Modeling Adipogenesis: Current and Future Perspective. Cells 2020, 9, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Easley, C.J. Microfluidic Systems for Studying Dynamic Function of Adipocytes and Adipose Tissue. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, A.C.; Omengo, B.; Gehrke, S.; Kluger, P.J. Comparing the Use of Differentiated Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Mature Adipocytes to Model Adipose Tissue in Vitro. Differentiation 2019, 110, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, U.; Akabane, T.; Andersson, T.B.; Baker, E.; Beilmann, M.; Beken, S.; Brendler-Schwaab, S.; Cirit, M.; David, R.; Dehne, E.M.; et al. Biology-Inspired Microphysiological Systems to Advance Patient Benefit and Animal Welfare in Drug Development. ALTEX 2020, 37, 364–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, J.; Zbinden, A.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Loskill, P. Stem-Cell Based Organ-on-a-Chip Models for Diabetes Research. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 140, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhutz, A.J.; Gourronc, F.A.; Chaly, A.; Wadkins, D.A.; Burand, A.J.; Markan, K.R.; Idiga, S.O.; Wu, M.; Potthoff, M.J.; Ankrum, J.A. Scaffold-Free Generation of Uniform Adipose Spheroids for Metabolism Research and Drug Discovery. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Sellin, J.; Kuerschner, L.; Krähl, L.; Majlesain, Y.; Förster, I.; Thiele, C.; Weighardt, H.; Weber, E. Generation of Immune Cell Containing Adipose Organoids for in Vitro Analysis of Immune Metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Ader, I.; Creff, J.; Leménager, H.; Achard, P.; Casteilla, L.; Sensebé, L.; Carrière, A.; Deschaseaux, F. Human Adipose Stromal-Vascular Fraction Self-Organizes to Form Vascularized Adipose Tissue in 3D Cultures. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.D.; Wang, R.Y.; Reagan, M.R.; Chen, Y.; Borowsky, F.E.; Zieba, A.; Marra, K.G.; Rubin, J.P.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Kaplan, D.L. The Use of Silk as a Scaffold for Mature, Sustainable Unilocular Adipose 3D Tissue Engineered Systems. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.D.; Kimmerling, E.P.; Cairns, D.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a Biomaterial to Support Long-Term Three-Dimensional Tissue Cultures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 21861–21868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, B.; Borchers, K.; Tovar, G.E.M.; Kluger, P.J. Methacrylated Gelatin and Mature Adipocytes Are Promising Components for Adipose Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 30, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, F.; Kitano, S.; Mano, J.F.; Matsusaki, M. 3D Collagen Microfibers Stimulate the Functionality of Preadipocytes and Maintain the Phenotype of Mature Adipocytes for Long Term Cultures. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.D.; Borowsky, F.E.; Alonzo, C.A.; Zieba, A.; Georgakoudi, I.; Kaplan, D.L. Variability in Responses Observed in Human White Adipose Tissue Models. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, F.H.; Vogel, K.; Luckett, J.P.; Hunt, M.; Meyer, A.; Rogers, C.L.; Tessler, O.; Dupin, C.L.; St. Hilaire, H.; Islam, K.N.; et al. Sandwiched White Adipose Tissue: A Microphysiological System of Primary Human Adipose Tissue. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2018, 24, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, M.J.; Li, Q.; Lee, S.; Zhang, C.; Kull, B.; Hallen, S.; Thorell, A.; Alexandersson, I.; Hagberg, C.E.; Peng, X.R.; et al. Mature Human White Adipocytes Cultured under Membranes Maintain Identity, Function, and Can Transdifferentiate into Brown-like Adipocytes. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 213–225.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.; Brown, T.; Alarcon, A.; Williams, C.; Wu, X.; Abbott, R.D.; Gimble, J.; Frazier, T. Fat-On-A-Chip Models for Research and Discovery in Obesity and Its Metabolic Comorbidities. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2020, 26, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, L.A.; Brooks, J.C.; Hoepfner, L.D.; Wanders, D.; Judd, R.L.; Easley, C.J. A Microfluidic Interface for the Culture and Sampling of Adiponectin from Primary Adipocytes. Analyst 2015, 140, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, J.; Easley, C.J. Automated Microfluidic Droplet Sampling with Integrated, Mix-and-Read Immunoassays to Resolve Endocrine Tissue Secretion Dynamics. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2926–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, X.; Judd, R.L.; Easley, C.J. Rapid Lipolytic Oscillations in: Ex Vivo Adipose Tissue Explants Revealed through Microfluidic Droplet Sampling at High Temporal Resolution. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; He, J.; Verano, M.; Brimmo, A.T.; Glia, A.; Qasaimeh, M.A.; Chen, P.; Aleman, J.O.; Chen, W. An Integrated Adipose-Tissue-on-Chip Nanoplasmonic Biosensing Platform for Investigating Obesity-Associated Inflammation. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3550–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kongsuphol, P.; Chiam, S.Y.; Zhang, Q.X.; Gourikutty, S.B.N.; Saha, S.; Biswas, S.K.; Ramadan, Q. Adipose-on-a-Chip: A Dynamic Microphysiological in Vitro Model of the Human Adipose for Immune-Metabolic Analysis in Type II Diabetes. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, J.; Binder, C.; Kromidas, E.; Roosz, J.; Probst, C.; Schneider, S.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Loskill, P. WAT-on-a-Chip Integrating Human Mature White Adipocytes for Mechanistic Research and Pharmaceutical Applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogal, J.; Probst, C.; Loskill, P. Integration Concepts for Multi-Organ Chips: How to Maintain Flexibility?! Futur. Sci. OA 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, O.; Misun, P.M.; Fluri, D.A.; Hengstler, J.G.; Hierlemann, A. Reconfigurable Microfluidic Hanging Drop Network for Multi-Tissue Interaction and Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edington, C.D.; Chen, W.L.K.; Geishecker, E.; Kassis, T.; Soenksen, L.R.; Bhushan, B.M.; Freake, D.; Kirschner, J.; Maass, C.; Tsamandouras, N.; et al. Interconnected Microphysiological Systems for Quantitative Biology and Pharmacology Studies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Rennert, K.; Schicke, E.; Cseresnyés, Z.; Windolph, M.; Nietzsche, S.; Heller, R.; Siwczak, F.; Haupt, K.F.; Carlstedt, S.; et al. Co-Infection with Staphylococcus Aureus after Primary Influenza Virus Infection Leads to Damage of the Endothelium in a Human Alveolus-on-a-Chip Model. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Lerner, S.A. Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Lancet 1998, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Streja, E.; Molnar, M.Z.; Flegal, K.M.; Gillen, D.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Obesity Paradox in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales-Medina, V.F.; Valayam, J.; Serpa, J.A.; Rueda, A.M.; Musher, D.M. The Obesity Paradox in Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e54–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singanayagam, A.; Singanayagam, A.; Chalmers, J.D. Obesity Is Associated with Improved Survival in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, M.C.; He, S.Y.; Li, X.P.; Shen, D. Lower Long-Term Mortality in Obese Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Possible Role of CRP. Clinics 2019, 74, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, N.; Hoess, C.; Kutz, A.; Christ-Crain, M.; Thomann, R.; Henzen, C.; Zimmerli, W.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Obesity Paradox in Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Is Inflammation the Missing Link? Nutrition 2017, 33, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, I.; Curhan, G.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Bendich, A.; Willett, W.C.; Fawzi, W.W. A Prospective Study of Age and Lifestyle Factors in Relation to Community-Acquired Pneumonia in US Men and Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 3082–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, A.; Aronoff, D.M.; Phipps, J.; Goel, D.; Mancuso, P. Leptin Improves Pulmonary Bacterial Clearance and Survival in Ob/Ob Mice during Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 150, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, P.; Gottschalk, A.; Phare, S.M.; Peters-Golden, M.; Lukacs, N.W.; Huffnagle, G.B. Leptin-Deficient Mice Exhibit Impaired Host Defense in Gram-Negative Pneumonia. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4018–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, P.; O’brien, E.; Prano, J.; Goel, D.; Aronoff, D.M. No Impairment in Host Defense against Streptococcus Pneumoniae in Obese CPEfat/Fat Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubags, N.D.J.; Burg, E.; Antkowiak, M.; Wallace, A.M.; Dilli, E.; Bement, J.; Wargo, M.J.; Poynter, M.E.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Suratt, B.T. A Comparative Study of Lung Host Defense in Murine Obesity Models: Insights into Neutrophil Function. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Q.A.A.; Niederman, M.S. Respiratory Infection in the Chronically Critically Ill Patient: Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia and Tracheobronchitis. Clin. Chest Med. 2001, 22, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, K.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Shu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, C.; Liu, W. Histopathological Changes Caused by Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Diet-Induced-Obese Mouse Following Experimental Lung Injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, T.; Yuan, G.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Cui, H.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Deng, J.; et al. Diet-Induced Obese Mice Exhibit Altered Immune Responses to Acute Lung Injury Induced by Escherichia Coli. Obesity 2016, 24, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zuo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, K.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Shu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Geng, Y.; Ouyang, P. Delayed Pulmonary Apoptosis of Diet-Induced Obesity Mice Following Escherichia Coli Infection through the Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubags, N.D.J.; Stapleton, R.D.; Vernooy, J.H.J.; Burg, E.; Bement, J.; Hayes, C.M.; Ventrone, S.; Zabeau, L.; Tavernier, J.; Poynter, M.E.; et al. Hyperleptinemia Is Associated with Impaired Pulmonary Host Defense. JCI Insight 2016, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Després, J.P. Excess Visceral Adipose Tissue/Ectopic Fat: The Missing Link in the Obesity Paradox? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1887–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.P.; Tam, J.S.; Assossou, O.M.; Kieny, M.P. The 2009 A (H1N1) Influenza Virus Pandemic: A Review. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, V.S.; Webster, R.G.; Turnert, B. Novel Influenza A Viruses Isolated from Canadian Feral Ducks: Including Strains Antigenically Related to Swine Influenza (HswlN1) Viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1985, 288, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, I.H. The Epidemiology and Evolution of Influenza Viruses in Pigs. In Veterinary Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 74, pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Kamimoto, L.; Bramley, A.M.; Schmitz, A.M.; Benoit, S.R.; Louie, J.; Sugerman, D.E.; Druckenmiller, J.K.; Ritger, K.A.; Chugh, R.; et al. Hospitalized Patients with 2009 H1N1 Influenza in the United States, April–June 2009. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fezeu, L.; Julia, C.; Henegar, A.; Bitu, J.; Hu, F.B.; Grobbee, D.E.; Kengne, A.P.; Hercberg, S.; Czernichow, S. Obesity Is Associated with Higher Risk of Intensive Care Unit Admission and Death in Influenza A (H1N1) Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, O.W.; Bramley, A.; Fowlkes, A.; Freedman, D.S.; Taylor, T.H.; Gargiullo, P.; Belay, B.; Jain, S.; Cox, C.; Kamimoto, L.; et al. Morbid Obesity as a Risk Factor for Hospitalization and Death Due to 2009 Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1) Disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, E.S.; Crawford, F.W.; Desai, M.M.; Meek, J.; Kirley, P.D.; Miller, L.; Anderson, E.J.; Oni, O.; Ryan, P.; Lynfield, R.; et al. Obesity Not Associated with Severity among Hospitalized Adults with Seasonal Influenza Virus Infection. Infection 2015, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easterbrook, J.D.; Dunfee, R.L.; Schwartzman, L.M.; Jagger, B.W.; Sandouk, A.; Kash, J.C.; Memoli, M.J.; Taubenberger, J.K. Obese Mice Have Increased Morbidity and Mortality Compared to Non-Obese Mice during Infection with the 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Virus. Influenza Other Respi. Viruses 2011, 5, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.J.X.; To, K.K.W.; Li, C.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Poon, V.K.M.; Chan, C.C.S.; Zheng, B.J.; Hung, I.F.N.; Lam, K.S.L.; Xu, A.; et al. Leptin Mediates the Pathogenesis of Severe 2009 Pandemic Influenza A(H1N1) Infection Associated with Cytokine Dysregulation in Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, J.J.; Rebeles, J.; Dhungana, S.; Stewart, D.A.; Sumner, S.C.J.; Meyers, M.H.; Mancuso, P.; Beck, M.A. Obesity Increases Mortality and Modulates the Lung Metabolome during Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection in Mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4846–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radigan, K.A.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Soberanes, S.; Nicholson, T.; Nigdelioglu, R.; Cho, T.; Chi, M.; Hamanaka, R.B.; Misharin, A.V.; Perlman, H.; et al. Impaired Clearance of Influenza a Virus in Obese, Leptin Receptor Deficient Mice Is Independent of Leptin Signaling in the Lung Epithelium and Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.G.; Sheridan, P.A.; Harp, J.B.; Beck, M.A. Diet-Induced Obese Mice Have Increased Mortality and Altered Immune Responses When Infected with Influenza Virus. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, P.G. Inhibitory Activity of Unstimulated Alveolar Macrophages on T-Lymphocyte Blastogenic Response. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 118, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, E.C.; Trost, L.; Aarons, S.; Jewell, W.R. Study of Function and Maturation of Monocytes in Morbidly Obese Individuals. J. Surg. Res. 1982, 33, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Naka, T.; Kubo, M. SOCS Proteins, Cytokine Signalling and Immune Regulation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, E.A.; Sheridan, P.A.; Beck, M.A. Diet-Induced Obesity Impairs the T Cell Memory Response to Influenza Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlotides, G.; Sörensen, A.S.; Kopp, F.; Zitzmann, K.; Cengic, N.; Brand, S.; Zachoval, R.; Auernhammer, C.J. SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 Inhibit IFN-α-Induced Expression of the Antiviral Proteins 2,5-OAS and MxA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, E.K.; Schmolke, M.; Wolff, T.; Viemann, D.; Roth, J.; Bode, J.G.; Ludwig, S. Influenza A Virus Inhibits Type I IFN Signaling via NF-ΚB-Dependent Induction of SOCS-3 Expression. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yan, R.; Chen, B.; Pan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.-L. Influenza Virus-Induced Robust Expression of SOCS3 Contributes to Excessive Production of IL-6. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paich, H.A.; Sheridan, P.A.; Handy, J.; Karlsson, E.A.; Schultz-Cherry, S.; Hudgens, M.G.; Noah, T.L.; Weir, S.S.; Beck, M.A. Overweight and Obese Adult Humans Have a Defective Cellular Immune Response to Pandemic H1N1 Influenza a Virus. Obesity 2013, 21, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidich, S.D.; Green, W.D.; Rebeles, J.; Karlsson, E.A.; Schultz-Cherry, S.; Noah, T.L.; Chakladar, S.; Hudgens, M.G.; Weir, S.S.; Beck, M.A. Increased Risk of Influenza among Vaccinated Adults Who Are Obese. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.J.; Nam, J.H.; Shim, S.M.; Choi, Y.K.; Lee, C.H.; Poo, H. Diet-Induced Obesity Dramatically Reduces the Efficacy of a 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Vaccine in a Mouse Model. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.G.; Sheridan, P.A.; Tseng, R.J.; Sheridan, J.F.; Beck, M.A. Selective Impairment in Dendritic Cell Function and Altered Antigen-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Responses in Diet-Induced Obese Mice Infected with Influenza Virus. Immunology 2009, 126, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaraju, R.; Guesdon, W.; Crouch, M.J.; Teague, H.L.; Sullivan, E.M.; Karlsson, E.A.; Schultz-Cherry, S.; Gowdy, K.; Bridges, L.C.; Reese, L.R.; et al. B Cell Activity Is Impaired in Human and Mouse Obesity and is Responsive to an Essential Fatty Acid upon Murine Influenza Infection. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4738–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regina, J.; Papadimitriou-Olivgeris, M.; Burger, R.; Le Pogam, M.-A.; Niemi, T.; Filippidis, P.; Tschopp, J.; Desgranges, F.; Viala, B.; Kampouri, E.; et al. Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Clinical Course of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients in a Swiss University Hospital: An Observational Retrospective Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Schulze, M.B. Global Pandemics Interconnected—Obesity, Impaired Metabolic Health and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.C.; Mendez, S.R.; Stevenson, E.K.; Guseh, J.S.; Chung, M.; Silverman, M.G. Obesity and the Risk of Intubation or Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e1097–e1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grippo, F.; Navarra, S.; Orsi, C.; Manno, V.; Grande, E.; Crialesi, R.; Frova, L.; Marchetti, S.; Pappagallo, M.; Simeoni, S.; et al. The Role of COVID-19 in the Death of SARS-CoV-2–Positive Patients: A Study Based on Death Certificates. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungnak, W.; Huang, N.; Bécavin, C.; Berg, M.; Queen, R.; Litvinukova, M.; Talavera-López, C.; Maatz, H.; Reichart, D.; Sampaziotis, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Entry Factors Are Highly Expressed in Nasal Epithelial Cells Together with Innate Immune Genes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Qi, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Meng, Z.; Tang, J.; Dai, Z. Obesity as a Potential Predictor of Disease Severity in Young COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study. Obesity 2020, 28, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, E.; Kassim, G.; Soffer, S.; Freeman, R.; Levin, M.A.; Reich, D.L. Severe Obesity as an Independent Risk Factor for COVID-19 Mortality in Hospitalized Patients Younger than 50. Obesity 2020, 28, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizinga, G.P.; Singer, B.H.; Singer, K. The Collision of Meta-Inflammation and SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic Infection. Endocrinology 2020, 161, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.B.; June, C.H. Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19. Science 2020, 368, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krams, I.A.; Luoto, S.; Rantala, M.J.; Jõers, P.; Krama, T. Covid-19: Fat, Obesity, Inflammation, Ethnicity, and Sex Differences. Pathogens 2020, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, S.; Pedone, C.; Napoli, N.; Russo, E.; Agnoletti, V.; Nigra, S.G.; Dengo, C.; Mughetti, M.; Conte, C.; Pozzilli, P.; et al. Computed Tomography Highlights Increased Visceral Adiposity Associated with Critical Illness in Covid-19. Diabetes Care 2020, e129–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavazos, A.E.; Corsi Romanelli, M.M.; Bandera, F.; Iacobellis, G. Targeting the Adipose Tissue in COVID-19. Obesity 2020, 28, 1178–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, M.; Oliveira, T.; Fernandes, R. Biochemistry of Adipose Tissue: An Endocrine Organ. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Somers, K.R.; Becari, C.; Polonis, K.; Pfeifer, M.A.; Allen, A.M.; Kellogg, T.A.; Covassin, N.; Singh, P. Comparative Expression of Renin-Angiotensin Pathway Proteins in Visceral Versus Subcutaneous Fat. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasllieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greeneugh, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Is a Functional Receptor for the SARS Coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deinhardt-Emmer, S.; Wittschieber, D.; Sanft, J.; Kleemann, S.; Elschner, S.; Haupt, K.; Vau, V.; Häring, C.; Rödel, J.; Henke, A.; et al. Early Postmortem Mapping of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Patients with COVID-19 and Correlation to Tissue Damage. bioRxiv 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Cell Receptor Gene ACE2 in a Wide Variety of Human Tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hornung, F.; Rogal, J.; Loskill, P.; Löffler, B.; Deinhardt-Emmer, S. The Inflammatory Profile of Obesity and the Role on Pulmonary Bacterial and Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073456
Hornung F, Rogal J, Loskill P, Löffler B, Deinhardt-Emmer S. The Inflammatory Profile of Obesity and the Role on Pulmonary Bacterial and Viral Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073456
Chicago/Turabian StyleHornung, Franziska, Julia Rogal, Peter Loskill, Bettina Löffler, and Stefanie Deinhardt-Emmer. 2021. "The Inflammatory Profile of Obesity and the Role on Pulmonary Bacterial and Viral Infections" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073456
APA StyleHornung, F., Rogal, J., Loskill, P., Löffler, B., & Deinhardt-Emmer, S. (2021). The Inflammatory Profile of Obesity and the Role on Pulmonary Bacterial and Viral Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073456








