Dysregulated CD38 Expression on Peripheral Blood Immune Cell Subsets in SLE
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
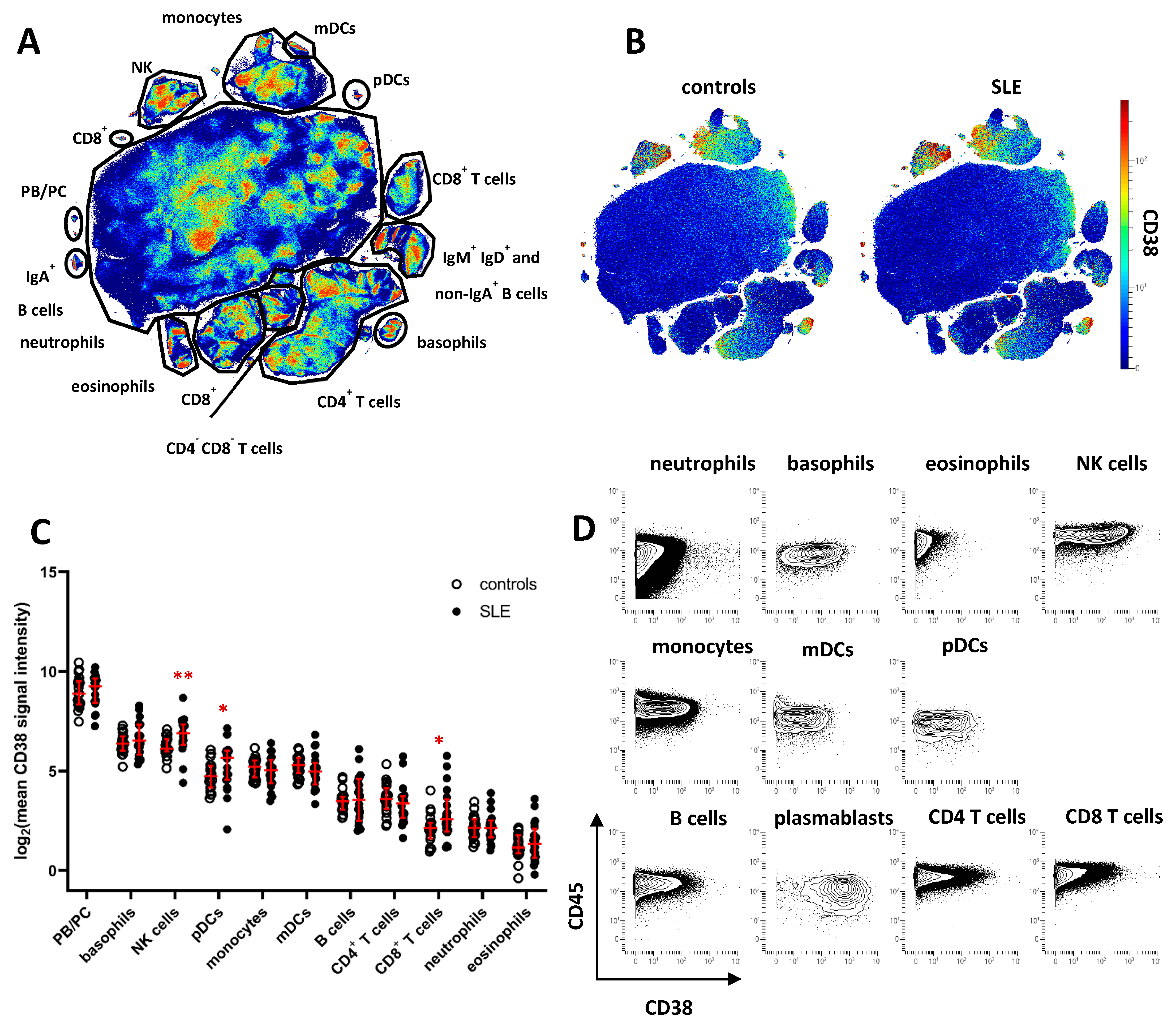
2.1. Increased CD38 Expression in Major SLE Leukocyte Subsets
2.2. CD38 Expression by NK Cells and Myeloid Immune Cells Is Associated with an Activated Phenotype
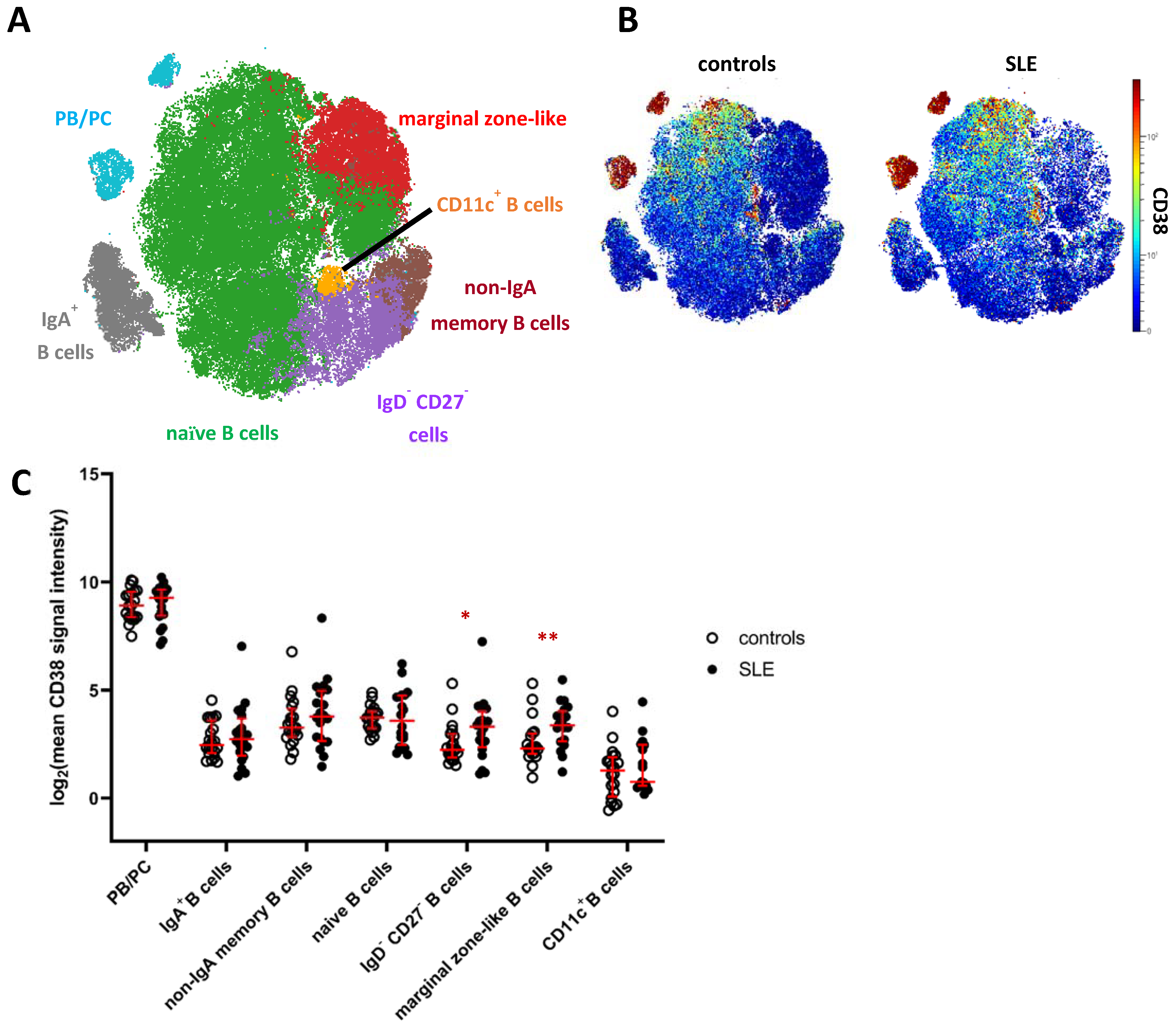
2.3. Increased Expression of CD38 on Distinct Subsets of Peripheral Blood B Cells in SLE
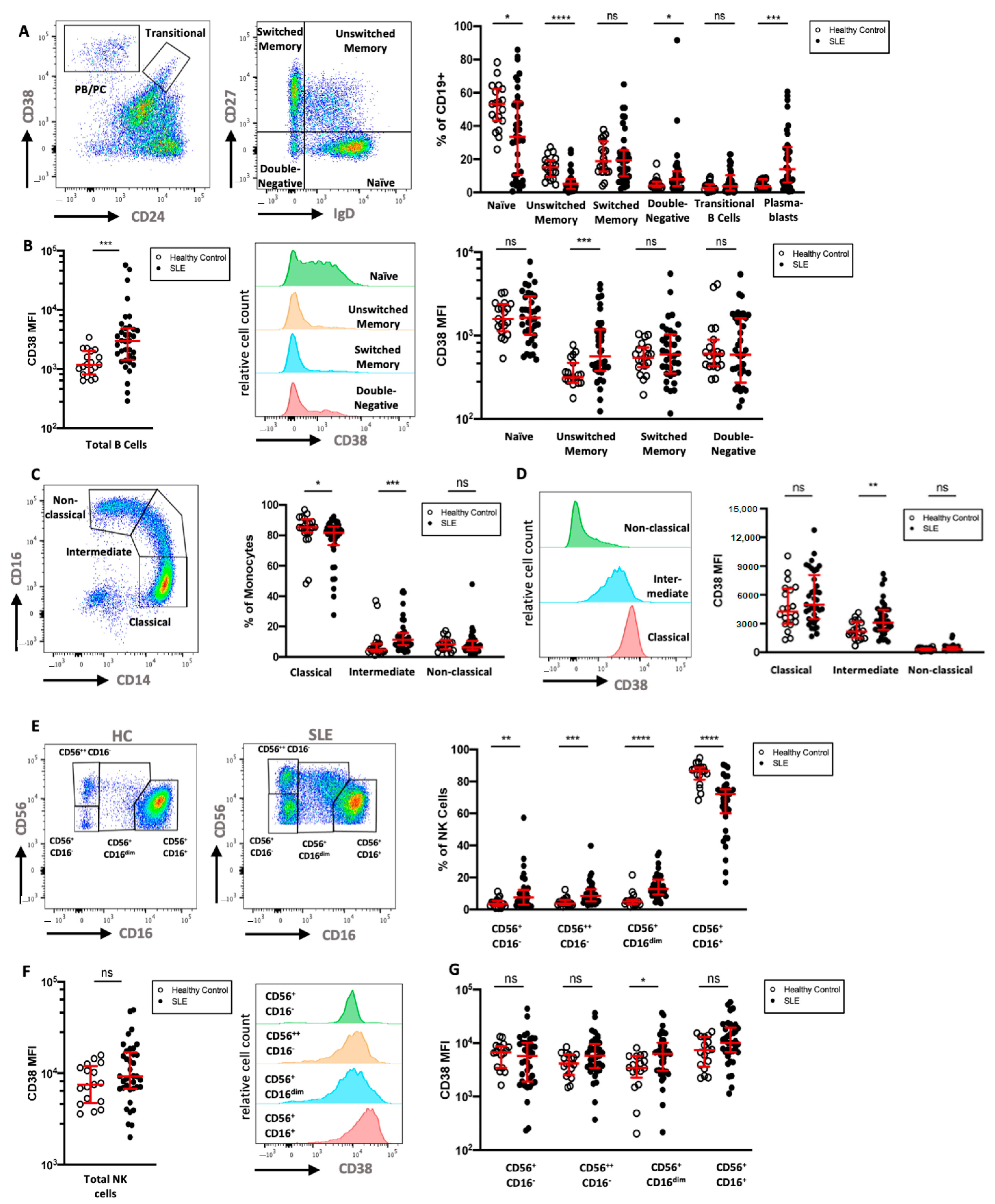
2.4. Circulating CD4+ and CD8+ Memory T Cell Subsets Express Increased Levels of CD38 in SLE
2.5. CD38 Expression Is Increased on Monocyte, NK Cell, and B Cell Subsets in an Independent SLE Cohort Flow Cytometry Cohort
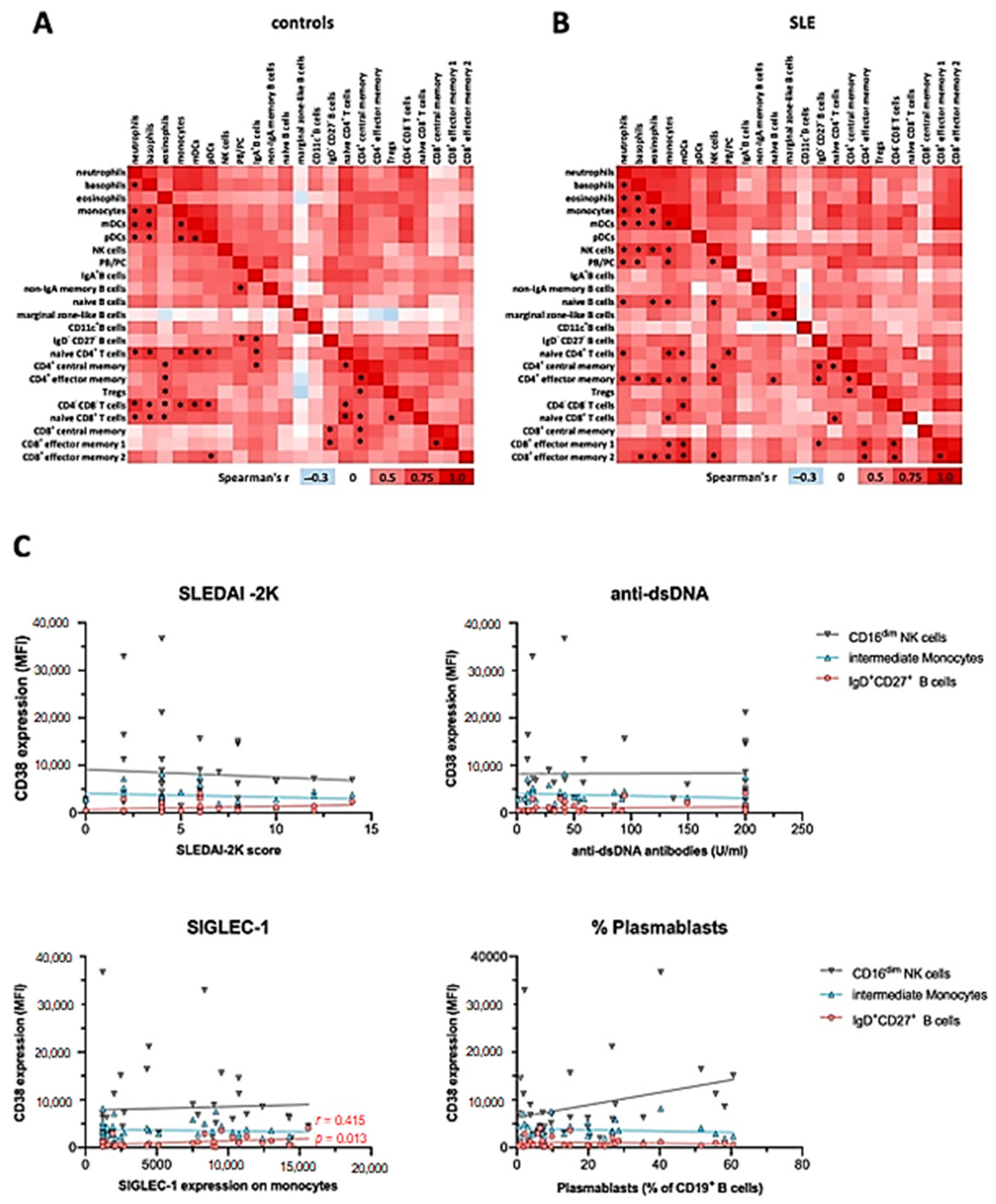
2.6. CD38 Expression Correlates between Individual Immune Cell Subsets
2.7. CD38 Expression Levels on Immune Cell Subsets Does Not Correlate with Severity or Clinical Manifestations of SLE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient and Control Blood Samples
4.2. Cryopreservation of Whole Blood Samples
4.3. Mass Cytometry
4.4. PBMC Isolation
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsokos, G.C. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2110–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lande, R.; Ganguly, D.; Facchinetti, V.; Frasca, L.; Conrad, C.; Gregorio, J.; Meller, S.; Chamilos, G.; Sebasigari, R.; Riccieri, V.; et al. Neutrophils Activate Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells by Releasing Self-DNA-Peptide Complexes in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesen, R.; Demir, C.; Barkhudarova, F.; Grün, J.R.; Steinbrich-Zöllner, M.; Backhaus, M.; Häupl, T.; Rudwaleit, M.; Riemekasten, G.; Radbruch, A.; et al. Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 1 expression in inflammatory and resident monocytes is a potential biomarker for monitoring disease activity and success of therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A. Plasma cells as an innovative target in autoimmune disease with renal manifestations. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, K.A.; Chini, C.C.S.; Chini, E.N. The Multi-faceted Ecto-enzyme CD38: Roles in Immunomodulation, Cancer, Aging, and Metabolic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaglio, S.; Morra, M.; Mallone, R.; Ausiello, C.M.; Prager, E.; Garbarino, G.; Dianzani, U.; Stockinger, H.; Malavasi, F. Human CD38 (ADP-ribosyl cyclase) is a counter-receptor of CD31, an Ig superfamily member. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 395–402. [Google Scholar]
- Partida-Sánchez, S.; Cockayne, D.A.; Monard, S.; Jacobson, E.L.; Oppenheimer, N.; Garvy, B.; Kusser, K.; Goodrich, S.; Howard, M.; Harmsen, A.; et al. Cyclic ADP-ribose production by CD38 regulates intracellular calcium release, extracellular calcium influx and chemotaxis in neutrophils and is required for bacterial clearance in vivo. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partida-Sánchez, S.; Goodrich, S.; Kusser, K.; Oppenheimer, N.; Randall, T.D.; Lund, F.E. Regulation of Dendritic Cell Traf-ficking by the ADP-Ribosyl Cyclase CD38. Immunity 2004, 20, 279–291. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuyama, E.; Suarez-Fueyo, A.; Bradley, S.J.; Mizui, M.; Marin, A.V.; Mulki, L.; Krishfield, S.; Malavasi, F.; Yoon, J.; Sui, S.J.H.; et al. The CD38/NAD/SIRTUIN1/EZH2 Axis Mitigates Cytotoxic CD8 T Cell Function and Identifies Patients with SLE Prone to Infections. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 112–123.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, E.J.; Zumaquero, E.; Rosal-Vela, A.; Khoo, K.-M.; Cerezo-Wallis, D.; García-Rodríguez, S.; Carrascal, M.; Abián, J.; Graeff, R.; Callejas-Rubio, J.-L.; et al. Increased CD38 expression in T cells and circulating anti-CD38 IgG autoantibodies differentially correlate with distinct cytokine profiles and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Cytokine 2013, 62, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostendorf, L.; Burns, M.; Durek, P.; Heinz, G.A.; Heinrich, F.; Garantziotis, P.; Enghard, P.; Richter, U.; Biesen, R.; Schneider, U.; et al. Targeting CD38 with Daratumumab in Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, D.J.; Titov, A.A.; Sobel, E.S.; Brusko, T.M.; Morel, L. Immunophenotyping reveals distinct subgroups of lupus patients based on their activated T cell subsets. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 221, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amici, S.A.; Young, N.A.; Narvaez-Miranda, J.; Jablonski, K.A.; Arcos, J.; Rosas, L.; Papenfuss, T.L.; Torrelles, J.B.; Jarjour, W.N.; Guerau-De-Arellano, M. CD38 Is Robustly Induced in Human Macrophages and Monocytes in Inflammatory Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlock, B.; Richardson, G.; García-Rodríguez, S.; Guerrero, S.; Zubiaur, M.; Sancho, J. The Role of CD38 on the Function of Regulatory B Cells in a Murine Model of Lupus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.; Walsh, A.; Yin, X.; Wechalekar, M.D.; Smith, M.D.; Proudman, S.M.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U.; Pitzalis, C.; Humby, F.; et al. Integrative analysis reveals CD38 as a therapeutic target for plasma cell-rich pre-disease and established rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. 2018, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheibe, F.; Ostendorf, L.; Reincke, S.M.; Prüss, H.; Von Brünneck, A.-C.; Köhnlein, M.; Alexander, T.; Meisel, C.; Meisel, A. Daratumumab treatment for therapy-refractory anti-CASPR2 encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2019, 267, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratuszny, D.; Skripuletz, T.; Wegner, F.; Groß, M.; Falk, C.; Jacobs, R.; Ruschulte, H.; Stangel, M.; Sühs, K.-W. Case Report: Daratumumab in a Patient With Severe Refractory Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, C.; Hoenig, M.; Moshous, D.; Weinstock, C.; Castelle, M.; Bendavid, M.; Shimano, K.; Tolbert, V.; Schulz, A.S.; Dvorak, C.C. Daratumumab in life-threatening autoimmune hemolytic anemia following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2550–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkina, A.C.; Ciccolella, C.O.; Anno, R.; Halpert, R.; Spidlen, J.; Snyder-Cappione, J.E. Automated optimized parameters for T-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding improve visualization and analysis of large datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.; Grützkau, A.; Hirseland, H.; Huscher, D.; Dähnrich, C.; Dzionek, A.; Ozimkowski, T.; Schlumberger, W.; Enghard, P.; Radbruch, A.; et al. IFNα and its response proteins, IP-10 and SIGLEC-1, are biomarkers of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 72, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odendahl, M.; Mei, H.; Hoyer, B.F.; Jacobi, A.M.; Hansen, A.; Muehlinghaus, G.; Berek, C.; Hiepe, F.; Manz, R.; Radbruch, A.; et al. Generation of migratory antigen-specific plasma blasts and mobilization of resident plasma cells in a secondary immune response. Blood 2005, 105, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Autoimmunity Molecular Medicine Team; Wang, J.; Kumar, V.; Karnell, J.L.; Naiman, B.; Gross, P.S.; Rahman, S.; Zerrouki, K.; Hanna, R.; et al. IL-21 drives expansion and plasma cell differentiation of autoreactive CD11chiT-bet+ B cells in SLE. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnell, J.L.; Kumar, V.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Voynova, E.; Ettinger, R. Role of CD11c + T-bet + B cells in human health and disease. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 321, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, A.M.; Mei, H.; Hoyer, B.F.; Mumtaz, I.M.; Thiele, K.; Radbruch, A.; Burmester, G.-R.; Hiepe, F.; Dörner, T. HLA-DRhigh/CD27high plasmablasts indicate active disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 69, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.E.; Hahne, S.; Redlin, A.; Hoyer, B.F.; Wu, K.; Baganz, L.; Lisney, A.R.; Alexander, T.; Rudolph, B.; Dörner, T. Plasmablasts With a Mucosal Phenotype Contribute to Plasmacytosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odendahl, M.; Jacobi, A.; Hansen, A.; Feist, E.; Hiepe, F.; Burmester, G.R.; Lipsky, P.E.; Radbruch, A.; Dörner, T. Disturbed Peripheral B Lymphocyte Homeostasis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5970–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywacz, B.; Kataria, N.; Verneris, M.R. CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cells downregulate CD16 following target cell induced activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Leuk. 2007, 21, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Montes, C.; Santos-Argumedo, L. CD38 is expressed selectively during the activation of a subset of mature T cells with reduced proliferation but improved potential to produce cytokines. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 77, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, K.; Yoshida, T.; Ishida, S.; Takei, Y.; Kitanaka, A.; Shimoda, K.; Morishita, K.; Takihara, Y.; Ichinohe, T. All-trans retinoic acid and interferon-α increase CD38 expression on adult T-cell leukemia cells and sensitize them to T cells bearing anti-CD38 chimeric antigen receptors. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanichamy, A.; Barnard, J.; Zheng, B.; Owen, T.; Quach, T.; Wei, C.; Looney, R.J.; Sanz, I.; Anolik, J.H. Novel Human Transitional B Cell Populations Revealed by B Cell Depletion Therapy. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5982–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, G.P.; Ettinger, R.; Shirota, Y.; Yarboro, C.H.; Illei, G.G.; Lipsky, P.E. Identification and characterization of circulating human transitional B cells. Blood 2005, 105, 4390–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenca, C.; Merlo, A.; Zarcone, D.; Saverino, D.; Bruno, S.; De Santanna, A.; Ramarli, D.; Fabbi, M.; Pesce, C.; Deaglio, S.; et al. Death of T cell precursors in the human thymus: A role for CD38. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendall, S.C.; Davis, K.L.; Amir, E.-A.D.; Tadmor, M.D.; Simonds, E.F.; Chen, T.J.; Shenfeld, D.K.; Nolan, G.P.; Pe’Er, D. Single-Cell Trajectory Detection Uncovers Progression and Regulatory Coordination in Human B Cell Development. Cell 2014, 157, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, P.A.; Noreña, L.Y.; Flores-Borja, F.; Rawlings, D.J.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. CD19+CD24hiCD38hi B Cells Exhibit Regulatory Capacity in Healthy Individuals but Are Functionally Impaired in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Immunity 2010, 32, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Rezk, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Hilgenberg, E.; Touil, H.; Shen, P.; Moore, C.S.; Michel, L.; Althekair, F.; Rajasekharan, S.; et al. Proinflammatory GM-CSF–producing B cells in multiple sclerosis and B cell depletion therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 310ra166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deterre, P.; Berthelier, V.; Bauvois, B.; Dalloul, A.; Schuber, F.; Lund, F. CD38 in T-and B-cell functions. In Human CD38 and Related Molecules; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2000; Volume 75, pp. 146–168. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, D.T.; Wilson, M.D.; Rowan, W.C.; Soond, D.R.; Okkenhaug, K. The PI3K p110δ Regulates Expression of CD38 on Regulatory T Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quách, T.D.; Rodríguez-Zhurbenko, N.; Hopkins, T.J.; Guo, X.; Hernández, A.M.; Li, W.; Rothstein, T.L. Distinctions among Circulating Antibody-Secreting Cell Populations, Including B-1 Cells, in Human Adult Peripheral Blood. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.O.; Holodick, N.E.; Rothstein, T.L. Human B1 cells in umbilical cord and adult peripheral blood express the novel phenotype CD20+CD27+CD43+CD70−. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.O.; Rothstein, T.L. A small CD11b+ human B1 cell subpopulation stimulates T cells and is expanded in lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, T.; Deaglio, S.; Franco, L.; Calosso, L.; Badolato, R.; Garbarino, G.; Dianzani, U.; Malavasi, F. CD38 expression and functional activities are up-regulated by IFN-gamma on human monocytes and monocytic cell lines. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 69, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.; Tirumurugaan, K.G.; Deshpande, D.A.; Amrani, Y.; Panettieri, R.A.; Walseth, T.F.; Kannan, M.S. Transcriptional regulation of CD38 expression by tumor necrosis factor-α in human airway smooth muscle cells: Role of NF-κB and sensitivity to glucocor-ticoids. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahil, Z.; Leylek, R.; Schürch, C.M.; Chen, H.; Bjornson-Hooper, Z.; Christensen, S.R.; Gherardini, P.F.; Bhate, S.S.; Spitzer, M.H.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; et al. Landscape of coordinated immune responses to H1N1 challenge in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5800–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-W.; Kee, S.-J.; Cho, Y.-N.; Lee, E.-H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, E.-M.; Shin, M.-H.; Park, J.-J.; Kim, T.-J.; Lee, S.-S.; et al. Impaired differentiation and cytotoxicity of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepis, D.; Gunnarsson, I.; Eloranta, M.L.; Lampa, J.; Jacobson, S.H.; Kärre, K.; Berg, L. Increased proportion of CD56bright natural killer cells in active and inactive systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 2009, 126, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ibañez, M.; Urowitz, M.B. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 288–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zunder, E.R.; Finck, R.; Behbehani, G.K.; Amir, E.D.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Gonzalez, V.D.; Lorang, C.G.; Bjornson, Z.; Spitzer, M.H.; Bodenmiller, B.; et al. Palladium-based mass tag cell barcoding with a doublet-filtering scheme and single-cell deconvolution algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.H.; Tordesillas, L.; Berin, M.C. Heparin reduces nonspecific eosinophil staining artifacts in mass cytometry experiments. Cytom. Part A 2016, 89, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.E.; Leipold, M.D.; Schulz, A.R.; Chester, C.; Maecker, H.T. Barcoding of Live Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells for Multiplexed Mass Cytometry. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, L.R.; Leipold, M.D.; Pedersen, C.B.; Maecker, H.T. The anatomy of single cell mass cytometry data. Cytom. Part A 2019, 95, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, S.; Crowell, H.L.; Zanotelli, V.R.; Engler, S.; Robinson, M.D.; Bodenmiller, B. Compensation of Signal Spillover in Suspension and Imaging Mass Cytometry. Cell Syst. 2018, 6, 612–620.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzinski, L.; Schulz, A.R.; Baumgart, S.; Burns, T.; Rose, T.; Hirseland, H.; Mei, H.E. Osmium-Labeled Microspheres for Bead-Based Assays in Mass Cytometry. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostendorf, L.; Mothes, R.; Van Koppen, S.; Lindquist, R.L.; Bellmann-Strobl, J.; Asseyer, S.; Ruprecht, K.; Alexander, T.; Niesner, R.A.; Hauser, A.E.; et al. Low-Density Granulocytes Are a Novel Immunopathological Feature in Both Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarizza, A.; Chang, H.; Radbruch, A.; Acs, A.; Adam, D.; Adam-Klages, S.; Agace, W.W.; Aghaeepour, N.; Akdis, M.; Allez, M.; et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (second edition). Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 1457–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, version 3.6; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gassen, S.; Callebaut, B.; Van Helden, M.J.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Demeester, P.; Dhaene, T.; Saeys, Y. FlowSOM: Using self-organizing maps for visualization and interpretation of cytometry data. Cytom. Part A 2015, 87, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, M.; Krieg, C.; Crowell, H.L.; Weber, L.M.; Hartmann, F.J.; Guglietta, S.; Becher, B.; Levesque, M.P.; Robinson, R.B. CyTOF workflow: Differential discovery in high-throughput high-dimensional cytometry datasets. F1000Research 2019, 6, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mass Cytometry Cohort | Flow Cytometry Cohort | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Controls | SLE Patients | p Value | Healthy Controls | SLE Patients | p Value | |
| Number | 20 | 20 | 19 | 36 | ||
| Age (median, IQR) | 39 (30–46) | 39 (30–47) | 0.732 | 28 (24–30) | 40 (31–46) | 0.001 |
| Sex (n% female) | 18 (90.0%) | 18 (90.0%) | 1.00 | 11 (57.9%) | 33 (91.7%) | 0.003 |
| SLEDAI-2K (median, range) | – | 8 (2–14) | – | 4.5 (0–14) | ||
| Clinically active SLE (clinical SLEDAI-2K > 0) | – | 17 (85.0%) | – | 24 (66.7%) | ||
| Serologically active SLE (serological SLEDAI-2K > 0) | – | 18 (90%) | – | 29 (80.6%) | ||
| Prednisolone Dose (mg/d; median, range) | – | 5.0 (0–20.0) | – | 5.0 (0–25.0) | ||
| Other Immunosuppressive Medication (n) | – | HCQ: 17 (85.0%) AZA: 4 (20.0%) MTX: 3 (15.0%) BEL: 3 (15.0%) MMF: 1 (5.0%) | – | HCQ: 24 (66.7%) MMF: 9 (25.0%) AZA: 9 (25.0%) CsA: 4 (11.1%) BEL: 4 (11.1%) RTX: 3 (8.3%) UST: 1 (2.8%) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burns, M.; Ostendorf, L.; Biesen, R.; Grützkau, A.; Hiepe, F.; Mei, H.E.; Alexander, T. Dysregulated CD38 Expression on Peripheral Blood Immune Cell Subsets in SLE. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052424
Burns M, Ostendorf L, Biesen R, Grützkau A, Hiepe F, Mei HE, Alexander T. Dysregulated CD38 Expression on Peripheral Blood Immune Cell Subsets in SLE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(5):2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052424
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurns, Marie, Lennard Ostendorf, Robert Biesen, Andreas Grützkau, Falk Hiepe, Henrik E. Mei, and Tobias Alexander. 2021. "Dysregulated CD38 Expression on Peripheral Blood Immune Cell Subsets in SLE" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 5: 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052424
APA StyleBurns, M., Ostendorf, L., Biesen, R., Grützkau, A., Hiepe, F., Mei, H. E., & Alexander, T. (2021). Dysregulated CD38 Expression on Peripheral Blood Immune Cell Subsets in SLE. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(5), 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052424






