The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
New Insights into Understanding Integration of Signals in Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Serotonin Neurons and Its Target Neurons and Their Relevance for Depression
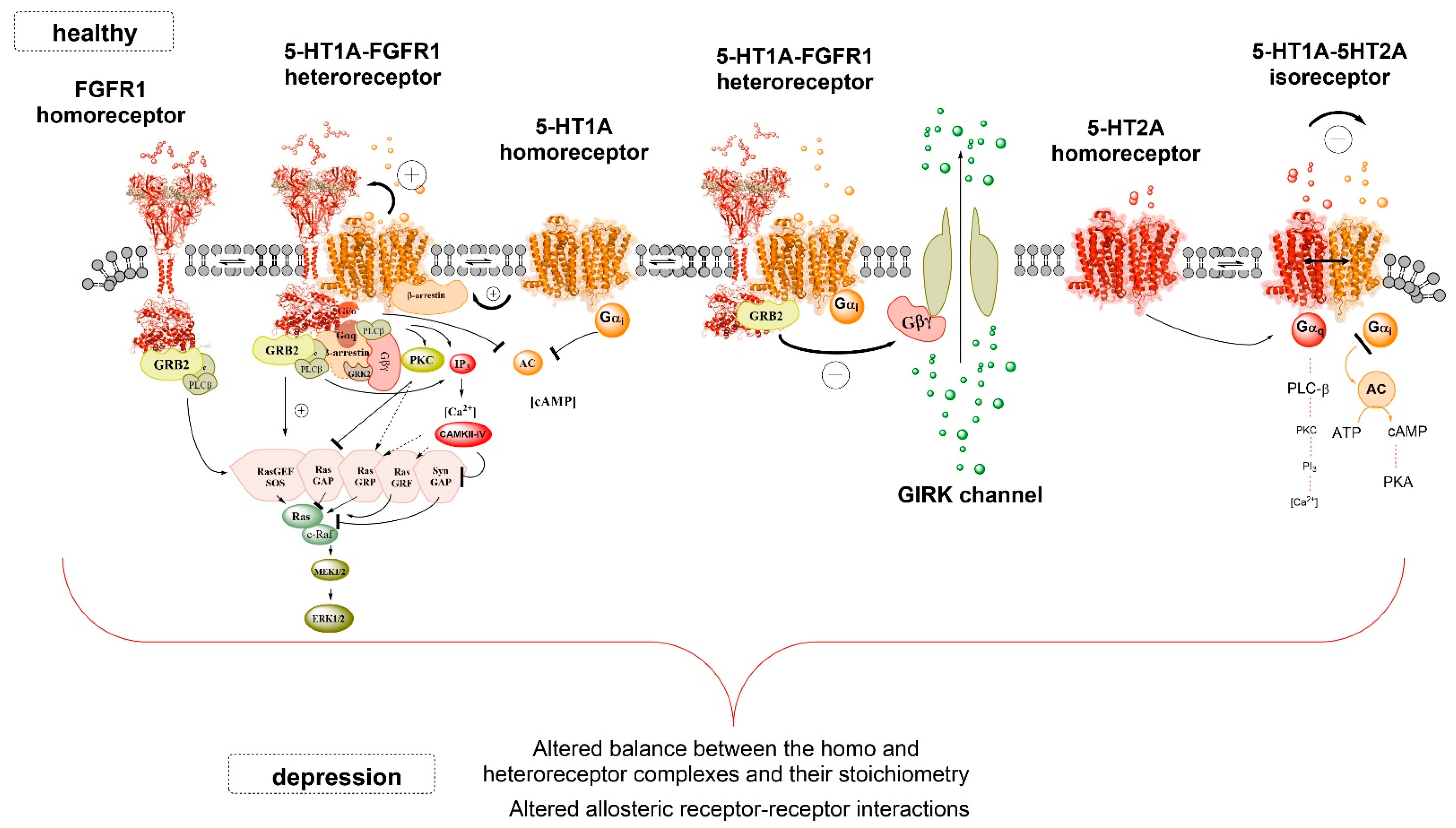
2. 5-HT1A-FGFR1 Heteroreceptor Complexes
2.1. The Flinders Sensitive Line (FSL) Model of Depression
2.2. A Novel Hypothesis on Depression
3. 5-HT1AR-5-HT2AR Isoreceptor Complexes
4. Oxytocin (OXTR)-5-HT2AR and OXTR-5-HT2CR Heterocomplexes
4.1. OXTR-5-HT2AR Heteroreceptor Complexes
4.2. OXTR-5-HT2CR Heteroreceptor Complexes
5. Implications for a Role of 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in Other Types of Brain Disease Besides Depression
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuxe, K. Evidence for the Existence of Monoamine Neurons in the Central Nervous System. Iv. Distribution of Monoamine Nerve Terminals in the Central Nervous System. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1965, 247, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe, K. Evidence for the Existence of Monoamine Neurons in the Central Nervous System. 3. The Monoamine Nerve Terminal. Zeitschrift fur Zellforschung und mikroskopische. Anatomie 1965, 65, 573–596. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlstroem, A.; Fuxe, K. Evidence for the Existence of Monoamine-Containing Neurons in the Central Nervous System. I. Demonstration of Monoamines in the Cell Bodies of Brain Stem Neurons. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1964, 232, 231–255. [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe, K.; Jonsson, G. The histochemical fluorescence method for the demonstration of catecholamines. Theory, practice and application. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 1973, 21, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, A.; Falck, B.; Fuxe, K.; Hillarp, N.A. Cellular Localization of Monoamines in the Spinal Cord. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1964, 60, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbusch, H.W. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-cell bodies and terminals. Neuroscience 1981, 6, 557–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxe, K.; Ungerstedt, U. Localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake in rat brain after intraventricular injection. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1967, 19, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, A.; Fuxe, K.; Ungerstedt, U. The effect of imipramine on central 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1968, 20, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxe, K.; Ungerstedt, U. Histochemical studies on the effect of (positive)-amphetamine, drugs of the imipramine group and tryptamine on central catecholamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons after intraventricular injection of catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1968, 4, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxe, K.; Ogren, S.O.; Agnati, L.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Jonsson, G. On the mechanism of action of the antidepressant drugs amitriptyline and nortriptyline. Evidence for 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor blocking activity. Neurosci. Lett. 1977, 6, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogren, S.O.; Fuxe, K.; Agnati, L.F.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Jonsson, G.; Holm, A.C. Reevaluation of the indoleamine hypothesis of depression. Evidence for a reduction of functional activity of central 5-HT systems by antidepressant drugs. J. Neural. Transm. 1979, 46, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannon, J.; Hoyer, D. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 195, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxe, K.; Hedlund, P.; von Euler, G.; Lundgren, K.; Martire, M.; Ogren, S.O.; Eneroth, P.; Agnati, L.F. Galanin/5-HT interactions in the rat central nervous system. Relevance for depression. In Galanin: A New Multifunctional Peptide in the Neuroendocrine System; Hokfelt, T., Bartfai, T., Jacobowitz, D.M., Ottoson, D., Eds.; MacMillan Press: London, UK, 1991; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe, K.; Dahlstroem, A.; Hoistad, M.; Marcellino, D.; Jansson, A.; Rivera, A.; Diaz-Cabiale, Z.; Jacobsen, K.; Tinner-Staines, B.; Hagman, B.; et al. From the Golgi-Cajal mapping to the transmitter-based characterization of the neuronal networks leading to two modes of brain communication: Wiring and volume transmission. Acta Morphol. Neerl. Scand. 2007, 55, 17–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descarries, L.; Berube-Carriere, N.; Riad, M.; Bo, G.D.; Mendez, J.A.; Trudeau, L.E. Glutamate in dopamine neurons: Synaptic versus diffuse transmission. Acta Morphol. Neerl. Scand. 2008, 58, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Romero-Fernandez, W.; Mudo, G.; Perez-Alea, M.; Ciruela, F.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Narvaez, M.; Di Liberto, V.; Agnati, L.F.; Belluardo, N.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1- 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A heteroreceptor complexes and their enhancement of hippocampal plasticity. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Narvaez, M.; Pérez-Alea, M.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Jiménez-Beristain, A.; Mudo, G.; Agnati, L.F.; Ciruela, F.; Belluardo, N.; Fuxe, K. Evidence for the existence of FGFR1–5-HT1A heteroreceptor complexes in the midbrain raphe 5-HT system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Pérez-Alea, M.; Narvaez, M.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Mudó, G.; Jiménez-Beristain, A.; Agnati, L.F.; Ciruela, F.; Belluardo, N.; Fuxe, K. Enhancement of the FGFR1 signaling in the FGFR1-5-HT1A heteroreceptor complex in midbrain raphe 5-HT neuron systems. Relevance for neuroplasticity and depression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Fuxe, K. FGFR1–5-HT1A Heteroreceptor Complexes: Implications for Understanding and Treating Major Depression. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Li, X.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Savelli, D.; Narváez, M.; Shumilov, K.; Andrade-Talavera, Y.; Jimenez-Beristain, A.; Pomierny, B.; Díaz-Cabiale, Z.; et al. Existence of Brain 5-HT1A–5-HT2A Isoreceptor Complexes with Antagonistic Allosteric Receptor–Receptor Interactions Regulating 5-HT1A Receptor Recognition. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 4779–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Narvaez, M.; Marcellino, D.; Parrado, C.; Narvaez, J.A.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Agnati, L.F.; Díaz-Cabiale, Z.; Fuxe, K. Galanin receptor-1 modulates 5-hydroxtryptamine-1A signaling via heterodimerization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Burgess, A.; Millón, C.; Gago, B.; Narváez, M.; Escuela, D.O.B.; Mengod, G.; Narváez, M.; Fuxe, K.; Santín, L.J.; Díaz-Cabiale, Z.; et al. Galanin (1-15) enhancement of the behavioral effects of Fluoxetine in the forced swimming test gives a new therapeutic strategy against depression. Neuropharmacology 2017, 118, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millon, C.; Flores-Burgess, A.; Narvaez, M.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Santin, L.; Gago, B.; Narvaez, J.A.; Fuxe, K.; Diaz-Cabiale, Z. Galanin (1-15) enhances the antidepressant effects of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT. Involvement of the ra-phe-hippocampal 5-HT neuron system. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol./Off. Sci. J. Coll. Int. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 221, 4491–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millón, C.; Flores-Burgess, A.; Narváez, M.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Santin, L.J.; Parrado, C.; Narváez, J.A.; Fuxe, K.; Díaz-Cabiale, Z. A Role for Galanin N-Terminal Fragment (1–15) in Anxiety-and Depression-Related Behaviors in Rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Narvaez, M.; Di Palma, M.; Calvo, F.; Rodríguez, D.; Millón, C.; Carlsson, J.; Agnati, L.F.; Garriga, P.; Díaz-Cabiale, Z.; et al. Preferential activation by galanin 1–15 fragment of the GalR1 protomer of a GalR1–GalR2 heteroreceptor complex. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tena-Campos, M.; Ramon, E.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Fuxe, K.; Garriga, P. The zinc binding receptor GPR39 interacts with 5-HT1A and GalR1 to form dynamic heteroreceptor complexes with signaling diversity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellekens, H.; McNamara, O.; Dinan, T.G.; McCarthy, J.V.; McGlacken, G.P.; Cryan, J.F. Semagacestat, a γ-secretase inhibitor, activates the growth hormone secretagogue (GHS-R1a) receptor. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J.F. Taking two to tango: A role for ghrelin receptor heterodimerization in stress and reward. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellekens, H.; De Francesco, P.N.; Kandil, D.; Theeuwes, W.F.; McCarthy, T.; Van Oeffelen, W.E.P.A.; Perelló, M.; Giblin, L.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Ghrelin’s Orexigenic Effect Is Modulated via a Serotonin 2C Receptor Interaction. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chruścicka, B.; Fitzsimons, S.E.W.; Escuela, D.O.B.; Druelle, C.; Stamou, P.; Nally, K.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Fuxe, K.; Schellekens, H. Attenuation of Oxytocin and Serotonin 2A Receptor Signaling through Novel Heteroreceptor Formation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3225–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chruścicka, B.; Cowan, C.S.; Fitzsimons, S.E.W.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Druelle, C.M.; Stamou, P.; Bergmann, C.A.; Dinan, T.G.; Slattery, D.A.; Fuxe, K.; et al. Molecular, biochemical and behavioural evidence for a novel oxytocin receptor and serotonin 2C receptor heterocomplex. Neuropharmacology 2021, 183, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Narváez, M.; Ambrogini, P.; Ferraro, L.; Brito, I.; Romero-Fernández, W.; Andrade-Talavera, Y.; Flores-Burgess, A.; Millón, C.; Gago, B.; et al. Receptor–Receptor Interactions in Multiple 5-HT1A Heteroreceptor Complexes in Raphe-Hippocampal 5-HT Transmission and Their Relevance for Depression and Its Treatment. Molecules 2018, 23, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Carlsson, J.; Ambrogini, P.; Narváez, M.; Wydra, K.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Li, X.; Millón, C.; Ferraro, L.; Cuppini, R.; et al. Understanding the Role of GPCR Heteroreceptor Complexes in Modulating the Brain Networks in Health and Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yohn, C.N.; Gergues, M.M.; Samuels, B.A. The role of 5-HT receptors in depression. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Takayanagi, Y.; Inoue, K.; Kimura, T.; Young, L.J.; Onaka, T.; Nishimori, K. Evidence That Oxytocin Exerts Anxiolytic Effects via Oxytocin Receptor Expressed in Serotonergic Neurons in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uvnäs-Moberg, K.; Ahlenius, S.; Hillegaart, V.; Alster, P. High doses of oxytocin cause sedation and low doses cause an anxiolytic-like effect in male rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 49, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas, F. Serotonin receptors involved in antidepressant effects. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 137, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas, F. Developments in the field of antidepressants, where do we go now? Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blier, P.; El Mansari, M. Serotonin and beyond: Therapeutics for major depression. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamon, M.; Blier, P. Monoamine neurocircuitry in depression and strategies for new treatments. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 45, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Corrales, F.; Narvaez, M.; Oflijan, J.; Agnati, L.F.; Palkovits, M.; Fuxe, K. Dynamic modulation of FGFR1–5-HT1A heteroreceptor complexes. Agonist treatment enhances participation of FGFR1 and 5-HT1A homodimers and recruitment of β-arrestin2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuela, D.O.B.; Dupont, C.M.; Li, X.; Savelli, D.; Lattanzi, D.; Srivastava, I.; Narváez, M.; Di Palma, M.; Barbieri, E.; Andrade-Talavera, Y.; et al. Disturbances in the FGFR1-5-HT1A Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Raphe-Hippocampal 5-HT System Develop in a Genetic Rat Model of Depression. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitti, F.L.; Siegelbaum, S.A. The hippocampal CA2 region is essential for social memory. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 508, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, C.; Jan, L.Y.; Stoffel, M.; Malenka, R.C.; Nicoll, R.A. G Protein-Coupled Inwardly Rectifying K+ Channels (GIRKs) Mediate Postsynaptic but Not Presynaptic Transmitter Actions in Hippocampal Neurons. Neuron 1997, 19, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbano, A.; Corradetti, R.; Mlinar, B. Pharmacological Characterization of 5-HT1A Autoreceptor-Coupled GIRK Channels in Rat Dorsal Raphe 5-HT Neurons. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krystal, J.H. N- methyl-D-aspartate Glutamate Receptor Antagonists and the Promise of Rapid-Acting Antidepressants. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystal, J.H.; Sanacora, G.; Duman, R.S. Rapid-Acting Glutamatergic Antidepressants: The Path to Ketamine and Beyond. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, C.G.; Adams, T.G.; Kelmendi, B.; Esterlis, I.; Sanacora, G.; Krystal, J.H. KETAMINE’S MECHANISM OF ACTION: A PATH TO RAPID-ACTING ANTIDEPRESSANTS. Depress. Anxiety 2016, 33, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magara, S.; Holst, S.; Lundberg, S.; Roman, E.; Lindskog, M. Altered explorative strategies and reactive coping style in the FSL rat model of depression. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blier, P.; Ward, N.M. Is there a role for 5-HT1A agonists in the treatment of depression? Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celada, P.; Bortolozzi, A.; Artigas, F. Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptors as Targets for Agents to Treat Psychiatric Disorders: Rationale and Current Status of Research. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blier, P.; Szabo, S.T. Potential mechanisms of action of atypical antipsychotic medications in treatment-resistant depression and anxiety. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66 (Suppl. 8), 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, P.R.; Le François, B.; Millar, A.M. Transcriptional dysregulation of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in mental illness. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarakanov, A.O.; Fuxe, K. Triplet Puzzle: Homologies of Receptor Heteromers. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2010, 41, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitre, M.; Marlin, B.J.; Schiavo, J.K.; Morina, E.; Norden, S.E.; Hackett, T.A.; Aoki, C.J.; Chao, M.V.; Froemke, R.C. A Distributed Network for Social Cognition Enriched for Oxytocin Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 2517–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottolese, R.; Redouté, J.; Costes, N.; Le Bars, D.; Sirigu, A. Switching brain serotonin with oxytocin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8637–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurek, B.; Neumann, I.D. The Oxytocin Receptor: From Intracellular Signaling to Behavior. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1805–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, E.H.V.D.; Hegoburu, C. Modulation of expression of fear by oxytocin signaling in the central amygdala: From reduction of fear to regulation of defensive behavior style. Neuropharmacology 2020, 173, 108130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Fernandez, W.; O Borroto-Escuela, D.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K. Evidence for the existence of dopamine d2-oxytocin receptor heteromers in the ventral and dorsal striatum with facilitatory receptor–receptor interactions. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 849–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Mora, M.P.; Pérez-Carrera, D.; Crespo-Ramírez, M.; Tarakanov, A.; Fuxe, K.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O. Signaling in dopamine D2 receptor-oxytocin receptor heterocomplexes and its relevance for the anxiolytic effects of dopamine and oxytocin interactions in the amygdala of the rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsing, D.E.; Anastasio, N.C.; Miszkiel, J.M.; Gilbertson, S.R.; Allen, J.A.; Cunningham, K.A. Biophysical validation of serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor interaction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brea, J.; Castro, M.; Giraldo, J.; López-Giménez, J.F.; Padín, J.F.; Quintián, F.; Cadavid, M.I.; Vilaró, M.T.; Mengod, G.; Berg, K.A.; et al. Evidence for Distinct Antagonist-Revealed Functional States of 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A Receptor Homodimers. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Cimadevila, M.; Cadavid, M.I.; Loza, M.I.; Brea, J. Serotonin-2A homodimers are needed for signalling via both phospholipase A 2 and phospholipase C in transfected CHO cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 800, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick-Davis, K.; Grinde, E.; Mazurkiewicz, J.E. Biochemical and Biophysical Characterization of Serotonin 5-HT2CReceptor Homodimers on the Plasma Membrane of Living Cells. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 13963–13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dölen, G.; Darvishzadeh, A.; Huang, K.W.; Malenka, R.C. Social reward requires coordinated activity of nucleus accumbens oxytocin and serotonin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 501, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, S.; King, M.V.; Williams, S.; Edwards, A.; Ballard, T.M.; Steward, L.J.; Alberati, D.; Fone, K.C. Oxytocin attenuates phencyclidine hyperactivity and increases social interaction and nucleus accumben dopamine release in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefevre, A.; Richard, N.; Jazayeri, M.; Beuriat, P.-A.; Fieux, S.; Zimmer, L.; Duhamel, J.-R.; Sirigu, A. Oxytocin and Serotonin Brain Mechanisms in the Nonhuman Primate. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6741–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölen, G.; Malenka, R.C. The Emerging Role of Nucleus Accumbens Oxytocin in Social Cognition. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 354–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutkine, I.; Quentin, E.; Guiard, B.P.; Maroteaux, L.; Doly, S. Heterodimers of serotonin receptor subtypes 2 are driven by 5-HT2Cprotomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 6352–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Pediani, J.D.; Godin, A.G.; Milligan, G. Regulation of Oligomeric Organization of the Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2C (5-HT2C) Receptor Observed by Spatial Intensity Distribution Analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 12844–12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvnäs-Moberg, K.; Bruzelius, G.; Alster, P.; Bileviciute, I.; Lundeberg, T. Oxytocin increases and a specific oxytocin antagonist decreases pain threshold in male rats. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1992, 144, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Deurwaerdère, P.; Di Giovanni, G. Serotonin in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giovanni, G. Dopamine Interaction with other Neurotransmitter Systems: Relevance in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of CNS Disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2010, 16, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toneatti, R.; Shin, J.M.; Shah, U.H.; Mayer, C.R.; Saunders, J.M.; Fribourg, M.; Arsenovic, P.T.; Janssen, W.G.; Sealfon, S.C.; López-Giménez, J.F.; et al. Interclass GPCR heteromerization affects localization and trafficking. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaaw3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, U.H.; González-Maeso, J. Serotonin and Glutamate Interactions in Preclinical Schizophrenia Models. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3068–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plach, M.; Schäfer, T.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Weikert, D.; Gmeiner, P.; Fuxe, K.; Friedland, K. Differential allosteric modulation within dopamine D2R—Neurotensin NTS1R and D2R—Serotonin 5-HT2AR receptor complexes gives bias to intracellular calcium signalling. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Romero-Fernandez, W.; Narvaez, M.; Oflijan, J.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K. Hallucinogenic 5-HT2AR agonists LSD and DOI enhance dopamine D2R protomer recognition and signaling of D2-5-HT2A heteroreceptor complexes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Romero-Fernandez, W.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Marcellino, D.; Ciruela, F.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K. Dopamine D2 and 5-hydroxytryptamine 5-HT2A receptors assemble into functionally interacting heteromers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 401, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Romero-Fernandez, W.; Garriga, P.; Ciruela, F.; Narvaez, M.; Tarakanov, A.O.; Palkovits, M.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K. G Protein–Coupled Receptor Heterodimerization in the Brain. Methods Enzymol. 2013, 521, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.E.; Sholler, D.J.; Stutz, S.J.; Anastasio, N.C.; Cunningham, K.A. Endogenous Serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C Receptors Associate in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3241–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangeli, R.; Di Maio, R.; Pierucci, M.; Deidda, G.; Casarrubea, M.; Di Giovanni, G. Synergistic action of CB1 and 5-HT2B receptors in preventing pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 125, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Ambrogini, P.; Chruścicka, B.; Lindskog, M.; Crespo-Ramirez, M.; Hernández-Mondragón, J.C.; Perez de la Mora, M.; Schellekens, H.; Fuxe, K. The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041927
Borroto-Escuela DO, Ambrogini P, Chruścicka B, Lindskog M, Crespo-Ramirez M, Hernández-Mondragón JC, Perez de la Mora M, Schellekens H, Fuxe K. The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041927
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorroto-Escuela, Dasiel O., Patrizia Ambrogini, Barbara Chruścicka, Maria Lindskog, Minerva Crespo-Ramirez, Juan C. Hernández-Mondragón, Miguel Perez de la Mora, Harriët Schellekens, and Kjell Fuxe. 2021. "The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041927
APA StyleBorroto-Escuela, D. O., Ambrogini, P., Chruścicka, B., Lindskog, M., Crespo-Ramirez, M., Hernández-Mondragón, J. C., Perez de la Mora, M., Schellekens, H., & Fuxe, K. (2021). The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041927





