From Liver Cirrhosis to Cancer: The Role of Micro-RNAs in Hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current and Emerging Therapeutic Options for HCC
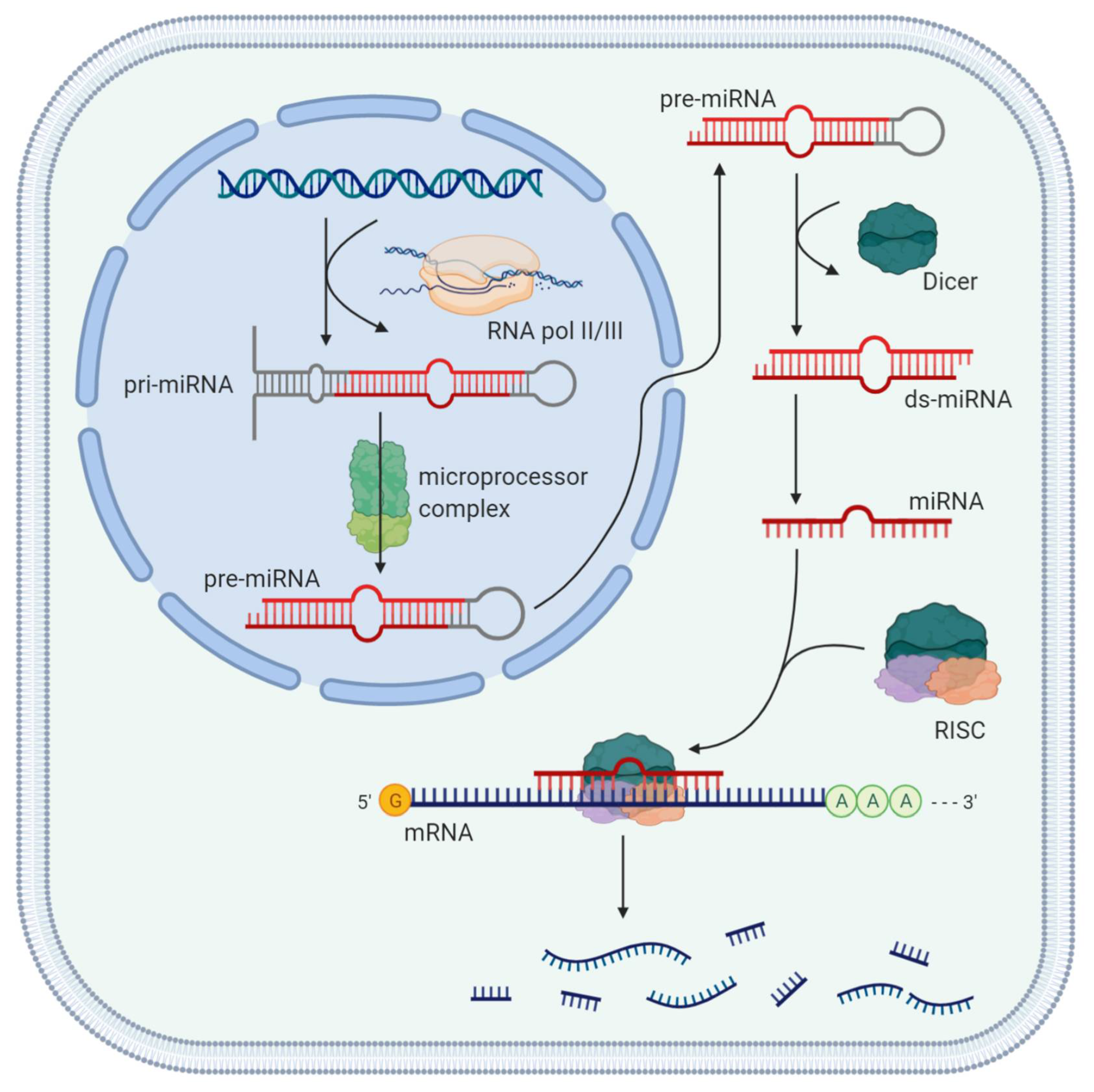
3. Role of miRNAs
4. Principal Physiological and Pathogenic Mechanisms of miRNAs
5. Clinical Application of miRNAs
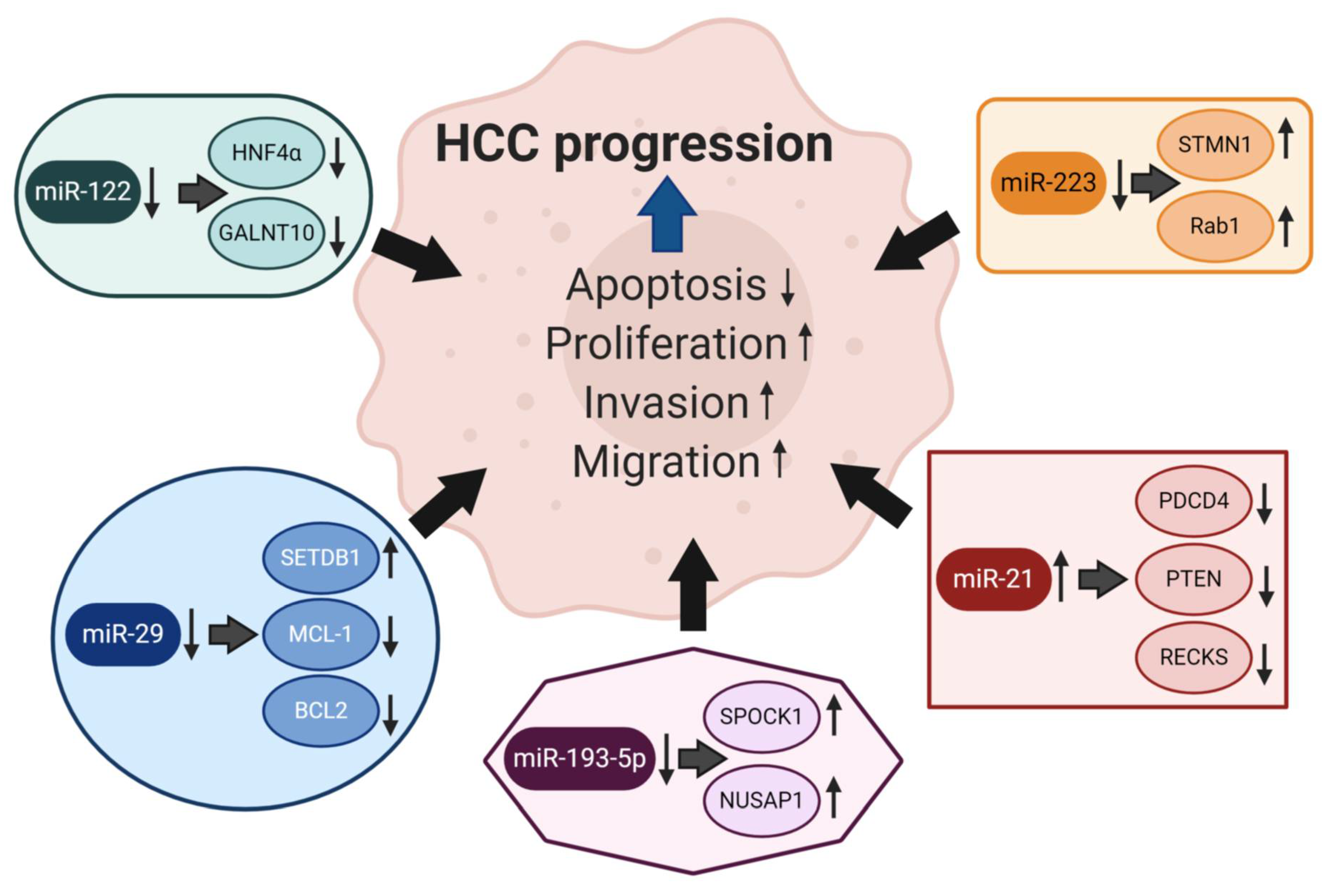
6. Specific miRNAs Involved in Hepatocarcinogenesis
6.1. miRNA-223
6.2. miRNA-21
6.3. miRNA-193a
6.4. miRNA-122
6.5. miRNA-29
6.6. miRNA34a/c
6.7. miRNA-199
7. Conclusion and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | adeno-associated virus |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AFP | alpha-fetoprotein |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| BCLC | Barcelona Clinic of Liver Cancer |
| BMF | Bcl2-modifying factor |
| C/EBP | CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein |
| ds-mi RNA | Double-stranded miRNA |
| FAK | focal adhesion kinase |
| ERBB4 | Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 4 |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HNF | hepatocyte nuclear factor |
| HNF4α | hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha |
| KLF6 | Kruppel-like factor 6 |
| MMP | matrix metallopeptidase |
| mTOR | mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| ncRNA | non-coding RNAs |
| NUSAP1 | Nucleolar and Spindle-Associated Protein 1 |
| OS | overall survival |
| PEG10 | paternally expressed gene 10 |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensing homolog |
| PDGFR | platelet-derived growth factor receptors |
| PD-1 | programmed cell death 1 |
| PDCD4 | programmed cell death 4 |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PKM2 | pyruvate kinase isoform M2 |
| Rab1 | Ras-related protein 1 |
| RECKS | reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| SPOCK1 | secreted protein/osteonectin, cwcv, and kazal-like domains proteoglycan 1 |
| SETDB1 | SET domain bifurcated 1 |
| STMN1 | Stathmin 1 |
| TKI | tyrosine-kinase inhibitors |
| GALNT10 | UDP-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine polypeptide N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-10 |
| VEGFR | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WNT1 | Wnt family member 1 |
References
- Shiels, M.S.; O’Brien, T.R. Recent Decline in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Rates in the United States. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1503–1505.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2020, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Abnet, C.C.; Neale, R.E.; Vignat, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global Burden of 5 Major Types of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 335–349.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Goossens, N.; Hoshida, Y. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 526–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekaran, G.; Bekki, Y.; Lourdusamy, V.; Schwartz, M. Surgical Treatments of Hepatobiliary Cancers. Hepatology 2021, 73, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ducreux, M.; Lencioni, R.; di Bisceglie, A.M.; Galle, P.R.; Dufour, J.F.; Greten, T.F.; Raymond, E.; Roskams, T.; de Baere, T.; et al. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Lenvatinib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Russo, D.; Verrienti, A.; Filetti, S. XL184 (cabozantinib) for medullary thyroid carcinoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kang, Y.-K.; Yen, C.-J.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; Assenat, E.; Brandi, G.; Pracht, M.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringelhan, M.; Pfister, D.; O’Connor, T.; Pikarsky, E.; Heikenwalder, M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-M.; Li, J.; Bai, C.-M.; Xu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Jia, R.; Lu, M.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Surufatinib in advanced well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: A multicenter, single-arm, open-label, phase Ib/II trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3486–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.; Ducreux, M.; Zhu, A.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; et al. IMbrave150: Efficacy and safety results from a ph III study evaluating atezolizumab (atezo) + bevacizumab (bev) vs sorafenib (Sor) as first treatment (tx) for patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, ix186–ix187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casak, S.J.; Donoghue, M.; Fashoyin-Aje, L.; Jiang, X.; Rodriguez, L.; Shen, Y.-L.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Patients with Advanced Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchert, G.M.; Lanier, W.; Davidson, B.L. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, L.-A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A Mammalian microRNA Expression Atlas Based on Small RNA Library Sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.M.; Robles, A.I.; Harris, C.C. Genetic variation in microRNA networks: The implications for cancer research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, F.; Roy, S.; Trautwein, C.; Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2008, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. MicroRNAs in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, J.; Mannaerts, I.; van Grunsven, L.A. The role of miRNAs in stress-responsive hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, J.; Verhulst, S.; Mannaerts, I.; Reynaert, H.; van Grunsven, L.A. Prospects in non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis: Liquid biopsy as the future gold standard? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864 Pt A, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, O.; Puri, P.; Eicken, C.; Contos, M.J.; Mirshahi, F.; Maher, J.W.; Kellum, J.M.; Min, H.; Luketic, V.A.; Sanyal, A.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic MicroRNA expression. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.-C.; Hsu, S.-D.; Hsu, C.-S.; Lai, T.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Tsai, T.-F.; et al. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, M.; Spasić, M.V.; Altamura, S.; Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Kiss, J.; Stolte, J.; Sparla, R.; D’Alessandro, L.A.; Klingmüller, U.; et al. The liver-specific microRNA miR-122 controls systemic iron homeostasis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esau, C.; Davis, S.; Murray, S.F.; Yu, X.X.; Pandey, S.K.; Pear, M.; Watts, L.; Booten, S.L.; Graham, M.; McKay, R.; et al. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Kim, H.; Jung, I.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.; Han, Y.-M. Expression profiles of miRNAs in human embryonic stem cells during hepatocyte differentiation. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatfield, D.; Le Martelot, G.; Vejnar, C.E.; Gerlach, D.; Schaad, O.; Fleury-Olela, F.; Ruskeepää, A.-L.; Oresic, M.; Esau, C.C.; Zdobnov, E.M.; et al. Integration of microRNA miR-122 in hepatic circadian gene expression. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Nakajima, M.; Kida, K.; Yamaura, Y.; Fukami, T.; Yokoi, T. MicroRNAs Regulate Human Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α, Modulating the Expression of Metabolic Enzymes and Cell Cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ju, W.; Wang, D.; Wu, L.; Zhu, X.; Guo, Z.; He, X. Down-Regulation of microRNA-26a Promotes Mouse Hepatocyte Proliferation during Liver Regeneration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Fu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Miao, M.; Jiao, B. Down-Regulation of MiR-127 Facilitates Hepatocyte Proliferation during Rat Liver Regeneration. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Verfaillie, C.M. MicroRNAs: The fine modulators of liver development and function. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, N.J.; Master, Z.R.; Le Lay, J.; Friedman, J.R. Hepatic function is preserved in the absence of mature microRNAs. Hepatology 2008, 49, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kota, J.; Chivukula, R.R.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hwang, H.-W.; Chang, T.-C.; Vivekanandan, P.; Torbenson, M.; Clark, K.R.; et al. Therapeutic microRNA Delivery Suppresses Tumorigenesis in a Murine Liver Cancer Model. Cell 2009, 137, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.-H.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Schmidt, C.R.; Lee, R.J.; Lee, L.J.; Jacob, S.T.; Ghoshal, K. Cationic lipid nanoparticles for therapeutic delivery of siRNA and miRNA to murine liver tumor. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borel, F.; Han, R.; Visser, A.; Petry, H.; Van Deventer, S.J.; Jansen, P.L.; Konstantinova, P. Adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter genes up-regulation in untreated hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated by cellular microRNAs. Hepatology 2012, 55, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindow, M.; Kauppinen, S. Discovering the first microRNA-targeted drug. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanford, R.E.; Hildebrandt-Eriksen, E.S.; Petri, A.; Persson, R.; Lindow, M.; Munk, M.E.; Kauppinen, S.; Ørum, H. Therapeutic Silencing of MicroRNA-122 in Primates with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Science 2009, 327, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.; Reesink, H.W.; Lawitz, E.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K.; Van Der Meer, A.J.; Patick, A.K.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Treatment of HCV Infection by Targeting MicroRNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, T.-Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.W.; Wang, R.; Cai, Q.; Qi, B.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wu, X.Z. Sulfatide epigenetically regulates miR-223 and promotes the migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Q.W.; Lung, R.W.; Law, P.T.; Lai, P.B.; Chan, K.Y.; To, K.; Wong, N. MicroRNA-223 Is Commonly Repressed in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Potentiates Expression of Stathmin1. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Plasma MicroRNA Panel to Diagnose Hepatitis B Virus–Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wu, C.; Che, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, T.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Tan, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol. Carcinog. 2010, 50, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Qi, R.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Bai, W.; Chang, X.; Hao, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. MiR-223 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through promoting apoptosis via the Rab1-mediated mTOR activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Yu, S.; Lavker, R.M.; Cai, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Chen, S. MicroRNA-21 acts as an oncomir through multiple targets in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe–Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 Regulates Expression of the PTEN Tumor Suppressor Gene in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, L.; Li, A.; Duan, Y.; Gao, H.; Song, X. Expression of Serum Exosomal MicroRNA-21 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 864894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimaru, Y.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; Wada, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Marubashi, S.; Tanemura, M.; Tomokuni, A.; Takemasa, I.; Umeshita, K.; et al. Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Mackowiak, B.; Gao, B. MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Seehawer, M.; Caruso, S.; Heinzmann, F.; Schneider, A.T.; Frank, A.K.; Cardenas, D.V.; Sonntag, R.; Luedde, M.; et al. microRNA 193a-5p Regulates Levels of Nucleolar- and Spindle-Associated Protein 1 to Suppress Hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1951–1966.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-T.; Wang, Z.-H. Role of miR-193a-5p in the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7233–7239. [Google Scholar]
- Loosen, S.H.; Wirtz, T.H.; Roy, S.; Vucur, M.; Castoldi, M.; Schneider, A.T.; Koppe, C.; Ulmer, T.F.; Roeth, A.A.; Bednarsch, J.; et al. Circulating levels of microRNA193a-5p predict outcome in early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Xiao, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L. MiR-139-5p, miR-940 and miR-193a-5p inhibit the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SPOCK1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cai, W.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, S. MiR-193a-3p and miR-193a-5p suppress the metastasis of human osteosarcoma cells by down-regulating Rab27B and SRR, respectively. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2016, 33, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hydbring, P.; Wang, Y.; Fassl, A.; Li, X.; Matia, V.; Otto, T.; Choi, Y.J.; Sweeney, K.E.; Suski, J.M.; Yin, H.; et al. Cell-Cycle-Targeting MicroRNAs as Therapeutic Tools against Refractory Cancers. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 576–590.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Liu, M.; SuYang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Fu, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. miR-193a-3p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Lung Cancer by Down-regulating ERBB4. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Liu, L.; Lin, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, J.; He, X.; Yao, M. MicroRNA-193a-3p and -5p suppress the metastasis of human non-small-cell lung cancer by downregulating the ERBB4/PIK3R3/mTOR/S6K2 signaling pathway. Oncogene 2015, 34, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.M.; Xu, Z.; Shek, F.H.; Wong, K.-F.; Lee, N.P.; Poon, R.T.; Chen, J.; Luk, J.M. miR-122 Targets Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Affects Metabolism of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Calin, G.A.; Giovannini, C.; Ferrazzi, E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Cyclin G1 Is a Target of miR-122a, a MicroRNA Frequently Down-regulated in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, M.; Schütte, K.; Malfertheiner, P.; Link, A. Prognostic value of serum microRNA-122 in hepatocellular carcinoma is dependent on coexisting clinical and laboratory factors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Baumert, T.F.; Zeisel, M.B. miR-122—A key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-H.; Hu, T.-H.; Lu, S.-N.; Kuo, F.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, J.-H.; Huang, C.-M.; Lee, C.-M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Yen, Y.-H.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for diagnosis of early hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis B virus. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; He, J.-H.; Xiao, Z.-D.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.-H. Liver-enriched transcription factors regulate MicroRNA-122 that targets CUTL1 during liver development. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsani, Z.; Mohammadi-Yeganeh, S.; Kia, V.; Karimkhanloo, H.; Zarghami, N.; Paryan, M. WNT1 Gene from WNT Signaling Pathway Is a Direct Target of miR-122 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 181, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyu, Y.-C.; Lee, T.-L.; Lu, M.-J.; Chen, J.-R.; Chien, R.-N.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, J.-F.; Tsou, A.-P.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsieh, C.-W.; et al. miR-122-mediated translational repression of PEG10 and its suppression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, H.-O.; Liu, Y.-D.; Liu, W.-S.; Pan, D.; Zhang, W.-J.; Yang, L.; Fu, Q.; Xu, J.-J.; Gu, J.-X. Decreased Expression of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α (Hnf4α)/MicroRNA-122 (miR-122) Axis in Hepatitis B Virus-associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Enhances Potential Oncogenic GALNT10 Protein Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1170–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parpart, S.; Roessler, S.; Dong, F.; Rao, V.; Takai, A.; Ji, J.; Qin, L.X.; Ye, Q.H.; Jia, H.L.; Tang, Z.Y.; et al. Modulation of miR-29 expression by α-fetoprotein is linked to the hepatocellular carcinoma epigenome. Hepatology 2014, 60, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Fang, J.-H.; Yun, J.-P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.-H.; Zhuang, S.-M. Effects of MicroRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 51, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-J.; Chong, Y.; Guo, Z.-W.; Xie, C.; Yang, X.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.-P.; Xiong, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Min, J.; et al. A serum microRNA classifier for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicentre, retrospective, longitudinal biomarker identification study with a nested case-control study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-M.; Wei, L.; Law, C.-T.; Ho, D.W.-H.; Tsang, F.H.-C.; Au, S.L.-K.; Sze, K.M.-F.; Lee, J.M.-F.; Wong, C.C.-L.; Ng, I.O.-L. Up-regulation of histone methyltransferase SETDB1 by multiple mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes cancer metastasis. Hepatology 2015, 63, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y. MicroRNA-34a inhibits liver cancer cell growth by reprogramming glucose metabolism. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4483–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.-Y.; Xie, H.-J.; Li, Z.; Kong, L.-F.; Gou, X.-N.; Li, D.-J.; Shi, Y.-J.; Ding, Y.-Z. miR-34a regulates HDAC1 expression to affect the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Tu, Y.; Zheng, L.L.; Liu, W.; Zuo, X.Y.; He, Y.M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhu, W.; Cao, J.P.; et al. MiR-34a regulates apoptosis in liver cells by targeting the KLF4 gene. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2014, 19, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryndyak, V.P.; Ross, S.A.; Beland, F.A.; Pogribny, I.P. Down-regulation of the microRNAs miR-34a, miR-127, and miR-200b in rat liver during hepatocarcinogenesis induced by a methyl-deficient diet. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, P.; Tang, C.; Hui, Y.; Wang, Z. miR-34c-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MARCKS. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 12728–12737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.-S.; Wang, Z.-G.; Guo, R.-P.; Lin, Z.-Q.; Ye, Z.-W.; Lu, C.-L. Hepatocellular carcinoma progression is protected by miRNA-34c-5p by regulating FAM83A. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6046–6054. [Google Scholar]
- Bharali, D.; Jebur, H.B.; Baishya, D.; Kumar, S.; Sarma, M.P.; Masroor, M.; Akhter, J.; Husain, S.A.; Kar, P. Expression Analysis of Serum microRNA-34a and microRNA-183 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 2561–2568. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-P.; Zhou, J.; Han, M.; Chen, C.-B.; Zheng, Y.-T.; He, X.-S.; Yuan, X.-P. MicroRNA-34a regulates liver regeneration and the development of liver cancer in rats by targeting Notch signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13264–13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Watari, H.; Hanley, S.J.B.; Konno, Y.; Ihira, K.; Yamada, T.; Kudo, M.; Yue, J.; Sakuragi, N. MiR-137 and miR-34a directly target Snail and inhibit EMT, invasion and sphere-forming ability of ovarian cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q. Chondroitin sulfate-functionalized polyamidoamine as a tumor-targeted carrier for miR-34a delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017, 57, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermeking, H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Glaser, S.S.; Francis, H.; Yang, F.; Han, Y.; Stokes, A.; Staloch, D.; McCarra, J.; Liu, J.; Venter, J.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of miR-34a Expression in Alcoholic Liver Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Saigo, K.; Urashima, T.; Toyoda, H.; Okanoue, T.; Shimotohno, K. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 2005, 25, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Hou, P.; Wu, Z.; Wang, T.; Nie, Y. Circulating miR-375 and miR-199a-3p as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4501–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudduluru, G.; Ceppi, P.; Kumarswamy, R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Papotti, M.; Allgayer, H. Regulation of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase expression by miR-34a and miR-199a/b in solid cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Milazzo, M.; Chieco, P.; Negrini, M.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Pollutri, D.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Gramantieri, L.; et al. MiR-199a-3p Regulates mTOR and c-Met to Influence the Doxorubicin Sensitivity of Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5184–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, U.J.; Kim, M.-N.; Lee, E.-J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Choung, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, Y.-C. MicroRNA miR-199a* Regulates the MET Proto-oncogene and the Downstream Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase 2 (ERK2). J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18158–18166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Q.; Cheng, H.Q.; Qian, X.; Bian, C.X.; Shi, Z.M.; Zhang, J.-P.; Jiang, B.-H.; Feng, Z.Q. Lentivirus-Mediated Overexpression of MicroRNA-199a Inhibits Cell Proliferation of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Biophys. 2011, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.C.; Park, J.K.; Jiang, J.; Kim, J.H.; Nagorney, D.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Banerjee, S.; Schmittgen, T.D. miR-199a-3p targets CD44 and reduces proliferation of CD44 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 403, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zheng, N.; Teng, F.; Bao, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M.; Guo, W.; Ding, G.; Wang, Q. MiR-199a/b-5p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by post-transcriptionally suppressing ROCK1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67169–67180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnnidis, J.B.; Harris, M.H.; Wheeler, R.T.; Stehling-Sun, S.; Lam, M.H.; Kirak, O.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Fleming, M.D.; Camargo, F.D. Regulation of progenitor cell proliferation and granulocyte function by microRNA-223. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 451, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneklaus, M.; Gerlic, M.; O’Neill, L.A.J.; Masters, S.L. miR-223: Infection, inflammation and cancer. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Zhang, T.; Lou, G.; Liu, Y. Role of miR-223 in the pathophysiology of liver diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, N.; Huang, C.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Q.; Yu, K.; Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; Shi, G. Serum MicroRNA Levels as a Noninvasive Diagnostic Biomarker for the Early Diagnosis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Liver Fibrosis. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giray, B.G.; Emekdas, G.; Tezcan, S.; Ulger, M.; Serin, M.S.; Sezgin, O.; Altintas, E.; Tiftik, E.N. Profiles of serum microRNAs; miR-125b-5p and miR223-3p serve as novel biomarkers for HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4513–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyöngyösi, B.; Végh, É.; Járay, B.; Székely, E.; Fassan, M.; Bodoky, G.; Schaff, Z.; Kiss, A. Pretreatment MicroRNA Level and Outcome in Sorafenib-treated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.-B.; Zhong, L.; Teng, M.-J.; Fan, J.-W.; Tang, H.-M.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.-W.; Qiu, G.-Q.; Peng, Z. Identification of recurrence-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma following liver transplantation. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stähler, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, C.; Besnier, M.; Shantikumar, S.; Shearn, A.I.; Rajakaruna, C.; Laftah, A.; Sessa, F.; Spinetti, G.; Petretto, E.; Angelini, G.D.; et al. Human Pericardial Fluid Contains Exosomes Enriched with Cardiovascular-Expressed MicroRNAs and Promotes Therapeutic Angiogenesis. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chai, J.; Xiao, X.; You, Y.; Zuo, X. MicroRNA-21 in Scleroderma Fibrosis and its Function in TGF-β-Regulated Fibrosis-Related Genes Expression. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarswamy, R.; Volkmann, I.; Thum, T. Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-T.; Wang, M.-C.; Zhou, J.; Peng, H.-H.; Lee, D.-Y.; Chiu, J.-J. Endothelial progenitors promote hepatocarcinoma intrahepatic metastasis through monocyte chemotactic protein-1 induction of microRNA-21. Gut 2014, 64, 1132–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yao, J.; Xie, M.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, M. Exosomal miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma development and clinical responses. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, Z.; Kusumanchi, P.; Han, S.; Liangpunsakul, S. Critical Role of microRNA-21 in the Pathogenesis of Liver Diseases. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Lv, X.; Lv, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. Circulating miR-21 serves as a serum biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma and correlated with distant metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44050–44058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, I.; Salvi, A.; Abeni, E.; Marchina, E.; De Petro, G. Biological Function of MicroRNA193a-3p in Health and Disease. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Rotem, A.; Struhl, K. Inhibition of miR-193a Expression by Max and RXRα Activates K-Ras and PLAU to Mediate Distinct Aspects of Cellular Transformation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5144–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Kirschner, M.B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Hanh, J.; Weiss, J.; Mugridge, N.; Wright, C.M.; Linton, A.; Kao, S.C.; Edelman, J.J.B.; et al. miR-193a-3p is a potential tumor suppressor in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23480–23495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wong, Y.S.; Goh, B.K.P.; Chan, C.Y.; Cheow, P.C.; Chow, P.K.H.; Lim, T.K.H.; Goh, G.B.B.; Krishnamoorthy, T.L.; Kumar, R.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, A.; Conde, I.; Abeni, E.; Arici, B.; Grossi, I.; Specchia, C.; Portolani, N.; Barlati, S.; De Petro, G. Effects of miR-193a and sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopling, C. Liver-specific microRNA-122: Biogenesis and function. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.; Jacquemin, E.; Munnich, A.; Lyonnet, S.; Henrion-Caude, A. miR-122, a paradigm for the role of microRNAs in the liver. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.-H.; Delgado, E.R.; Otero, P.A.; Teng, K.-Y.; Kutay, H.; Meehan, K.M.; Moroney, J.B.; Monga, J.K.; Hand, N.J.; Friedman, J.R.; et al. MicroRNA-122 regulates polyploidization in the murine liver. Hepatology 2016, 64, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, J.; Verhulst, S.; Reynaert, H.; van Grunsven, L.A. The miRFIB-Score: A Serological miRNA-Based Scoring Algorithm for the Diagnosis of Significant Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Ampuero, J.; Gil-Gómez, A.; Montero-Vallejo, R.; Rojas, Á.; Muñoz-Hernández, R.; Gallego-Durán, R.; Romero-Gómez, M. miRNAs in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, J.; Poortmans, P.J.; Verhulst, S.; Reynaert, H.; Mannaertsa, I.; Van Grunsven, L.A. Circulating ECV-Associated miRNAs as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Early Stage HBV and HCV Induced Liver Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Cheng, S.-Q.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.-F.; Gao, C.-F. Serum MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chinese Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, M.; Seidel, H.; Köchert, K.; Meinhardt, G.; Finn, R.S.; Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Biomarkers Associated With Response to Regorafenib in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, R.J.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Aubrecht, J.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Chalasani, N.; Fontana, R.J.; Goepfert, J.C.; Hackman, F.; King, N.M.P.; Kirby, S.; et al. Candidate biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of drug-induced liver injury: An international collaborative effort. Hepatology 2019, 69, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Deng, J.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Meng, Z.; Li, G.; Ye, H.; Zheng, S.; Wei, L.; Deng, X.; et al. LncRNA HOTAIR epigenetically suppresses miR-122 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma via DNA methylation. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Calin, G.A. miR-122 and hepatocellular carcinoma: From molecular biology to therapeutics. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.-W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.W.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2010, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.J.; Factora, T.D.; Dey, S.; Kota, J. A Systematic Review of miR-29 in Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 12, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Safarzadeh, A.; Beyranvand, F.; Ahmadpour, F.; Hajiasgharzadeh, K.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Baradaran, B. The potential role of miR-29 in health and cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19280–19297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Itami, S.; Kuroda, M.; Yoshizato, K.; Kawada, N.; Murakami, Y. MiR-29a Assists in Preventing the Activation of Human Stellate Cells and Promotes Recovery from Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-H.; Zhou, H.-C.; Zeng, C.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.-P.; Guan, X.-Y.; Zhuang, S.-M. MicroRNA-29b suppresses tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Ji, J.; Li, X.; Ding, N.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.W.; Calvisi, D.F.; Song, G.; Chen, X. Distinct anti-oncogenic effect of various microRNAs in different mouse models of liver cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6977–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, S. Combined low miRNA-29s is an independent risk factor in predicting prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: A Chinese population-based study. Medicine 2017, 96, e8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misso, G.; Di Martino, M.T.; De Rosa, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Lombardi, A.; Campani, V.; Zarone, M.R.; Gullà, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; et al. Mir-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H. MicroRNA-34a: A potential therapeutic target in human cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Hou, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, S.; Liu, Z.; Luo, R.; Li, L.; et al. Positive feedback loop of FAM83A/PI3K/AKT/c-Jun induces migration, invasion and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, A.E.D.; Rode, M.P.; Cisilotto, J.; Da Silva, T.E.; Fischer, J.; Matiollo, C.; Rateke, E.C.D.M.; Narciso-Schiavon, J.L.; Schiavon, L.L.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. MicroRNA profiles in serum samples from patients with stable cirrhosis and miRNA-21 as a predictor of transplant-free survival. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 134, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.-K.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A.G.; Kim, S.; Hong, D.S. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daige, C.L.; Wiggins, J.F.; Priddy, L.; Nelligan-Davis, T.; Zhao, J.; Brown, D. Systemic Delivery of a miR34a Mimic as a Potential Therapeutic for Liver Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Tanaka, M.; Kuroda, M.; Harada, Y.; Matsuda, F.; Tajima, A.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Shimotohno, K. The Progression of Liver Fibrosis Is Related with Overexpression of the miR-199 and 200 Families. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Afdhal, N.H.; Albitar, M. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Gastroenterology 2011, 45, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, K.S.; Ezzat, W.M.; Elhosary, Y.A.; Hegazy, A.E.; Fahim, H.H.; Kamel, R.R. The potential role of miRNAs 21 and 199-a in early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene 2016, 575, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, E.; Elamin, B.K.; D’Abundo, L.; Falzoni, S.; Donvito, G.; Moshiri, F.; Milazzo, M.; Altavilla, G.; Giacomelli, L.; Fornari, F.; et al. Anti-Tumor Activity of a miR-199-dependent Oncolytic Adenovirus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| miRNA | Expression in Liver Tissue | Level in Circulation | Functions in HCC | Selected Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR223 | ↓ [49,50] | ↓ ↑ [51,52] | Inhibition of cell growth, induction of apoptosis [53] | STMN [50], Rab1 [53], integrin αV [49] |
| miR-21 | ↑ [54,55] | ↑ [52,56,57] | increased cell invasion, migration, proliferation | PTEN [54,55], PDCD4, RECKS [54], TIMP3 [58] |
| miR-193 | ↓ ↑ [59,60] | ↑ [61] | Increased cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis [33] | NUSAP1 [33], SPOCK1 [59,62], MCL1, ERBB4, S6K2 [63,64,65,66] |
| miR-122 | ↓ [67,68] | ↑ [28,52,69,70,71] | hepatocarcinogenesis, forming metastasis [28,67,68] | CUTL1 [72], WNT1, PEG10, PKM2 [67,68,73,74], HNF4α, GALNT10 [75], KLF6 [31,32] |
| miR-29 | ↓ [76,77] | ↑ [78] | promotes apoptosis [77], associated with HCC disease progression, cancer aggressiveness [79] | MCL-1, BCL2 [77], SETDB1 [79], DNMT3A [76] |
| miR-34 | ↓ [80,81,82,83,84,85] | ↓ [86] | inhibition of cell growth, increase in cell apoptosis rate [87] | NOTCH1 [87], HDAC1 [81], MARCKS [84], FAM83A [85], c-MYC, CDK6, c-MET [80,88,89,90,91], caspase-2, SIRT1 [92], BCL2 |
| miR-199 | ↓ [93] | ↓ [94] | inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion [95] | mTOR, c-Met, HIF-1α, CD44 [96,97,98,99], ROCK1 [100], Axl [95] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohr, R.; Özdirik, B.; Lambrecht, J.; Demir, M.; Eschrich, J.; Geisler, L.; Hellberg, T.; Loosen, S.H.; Luedde, T.; Tacke, F.; et al. From Liver Cirrhosis to Cancer: The Role of Micro-RNAs in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031492
Mohr R, Özdirik B, Lambrecht J, Demir M, Eschrich J, Geisler L, Hellberg T, Loosen SH, Luedde T, Tacke F, et al. From Liver Cirrhosis to Cancer: The Role of Micro-RNAs in Hepatocarcinogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031492
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohr, Raphael, Burcin Özdirik, Joeri Lambrecht, Münevver Demir, Johannes Eschrich, Lukas Geisler, Teresa Hellberg, Sven H. Loosen, Tom Luedde, Frank Tacke, and et al. 2021. "From Liver Cirrhosis to Cancer: The Role of Micro-RNAs in Hepatocarcinogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031492
APA StyleMohr, R., Özdirik, B., Lambrecht, J., Demir, M., Eschrich, J., Geisler, L., Hellberg, T., Loosen, S. H., Luedde, T., Tacke, F., Hammerich, L., & Roderburg, C. (2021). From Liver Cirrhosis to Cancer: The Role of Micro-RNAs in Hepatocarcinogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031492









