Solution Structure, Dynamics, and New Antifungal Aspects of the Cysteine-Rich Miniprotein PAFC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
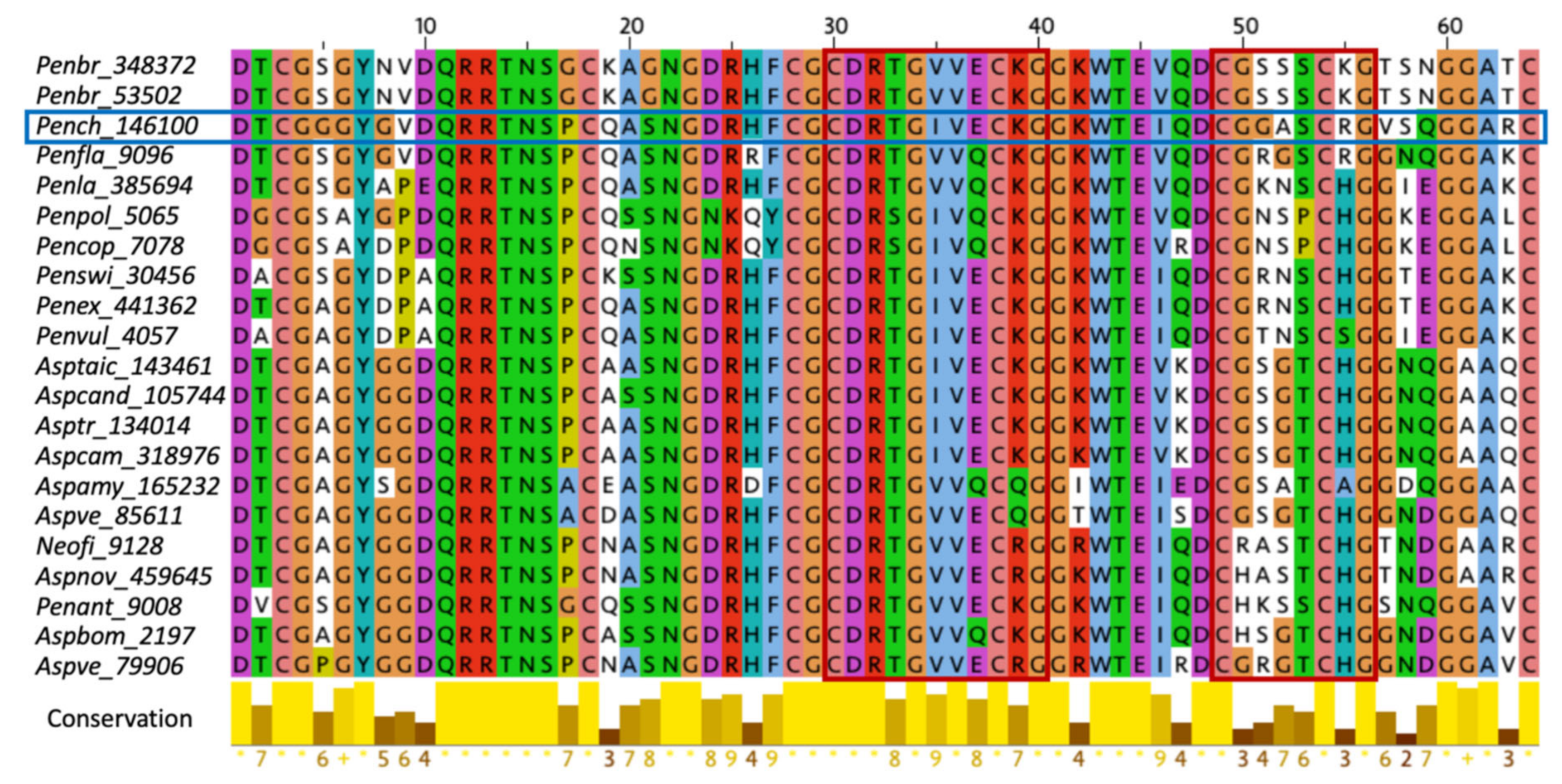
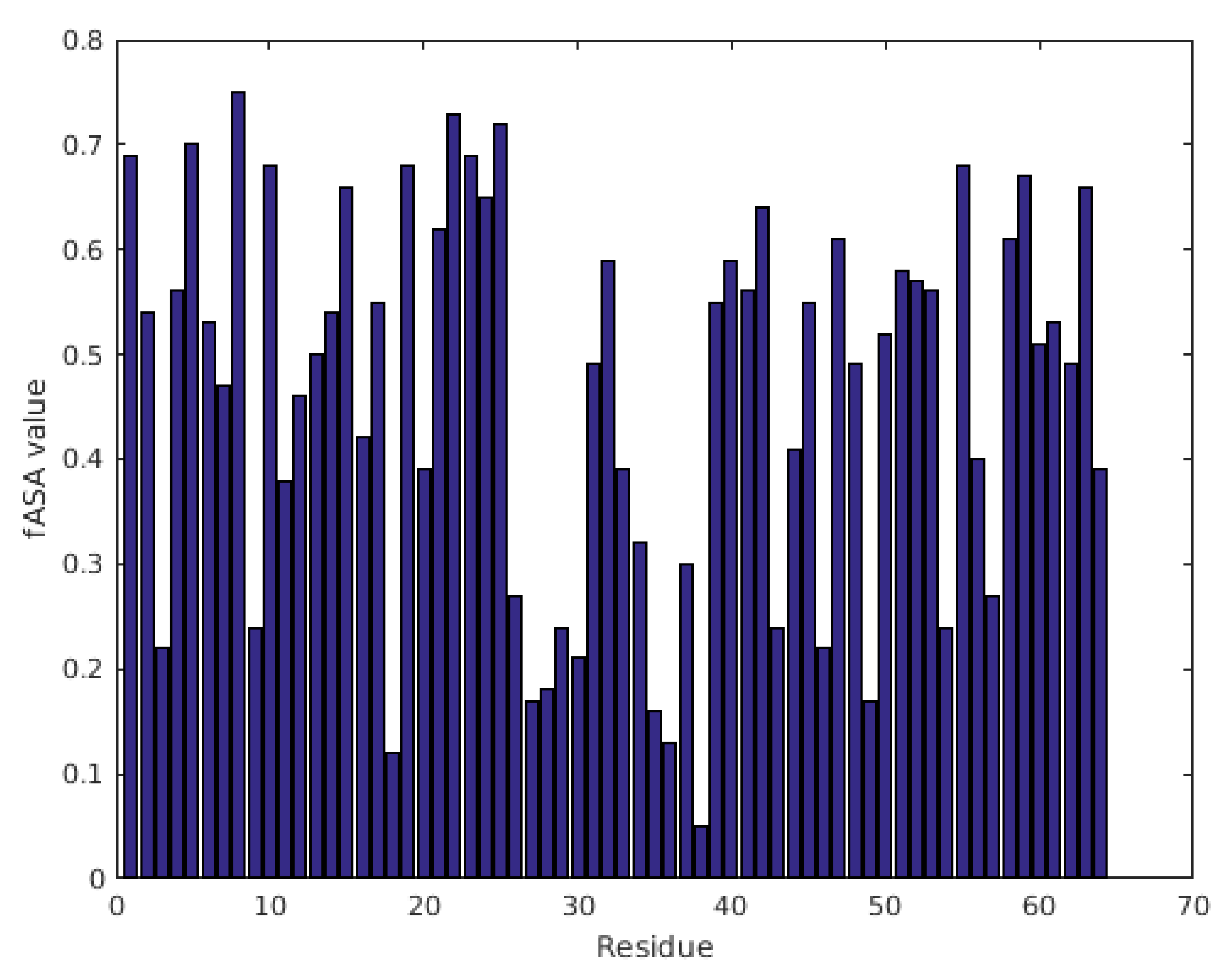
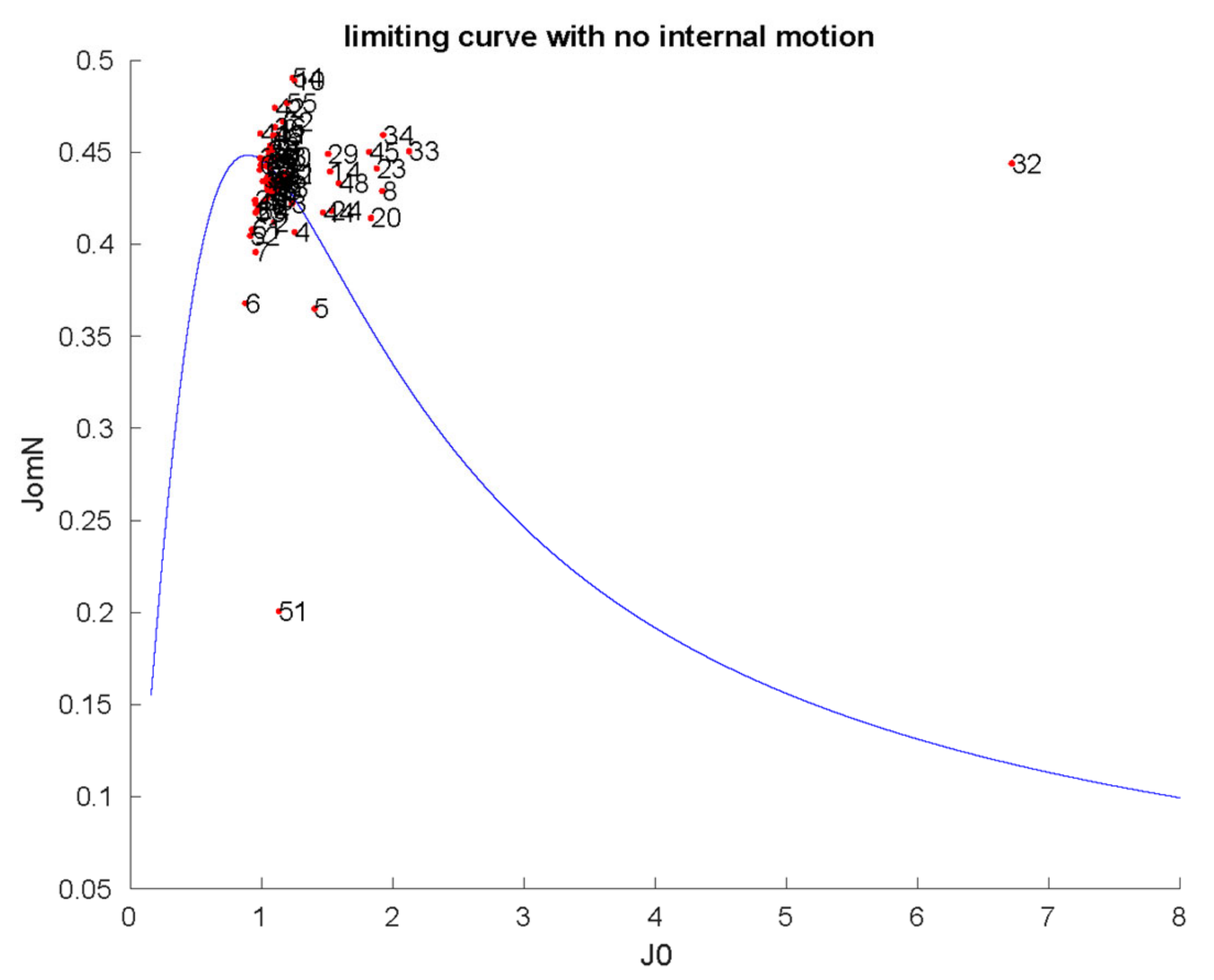
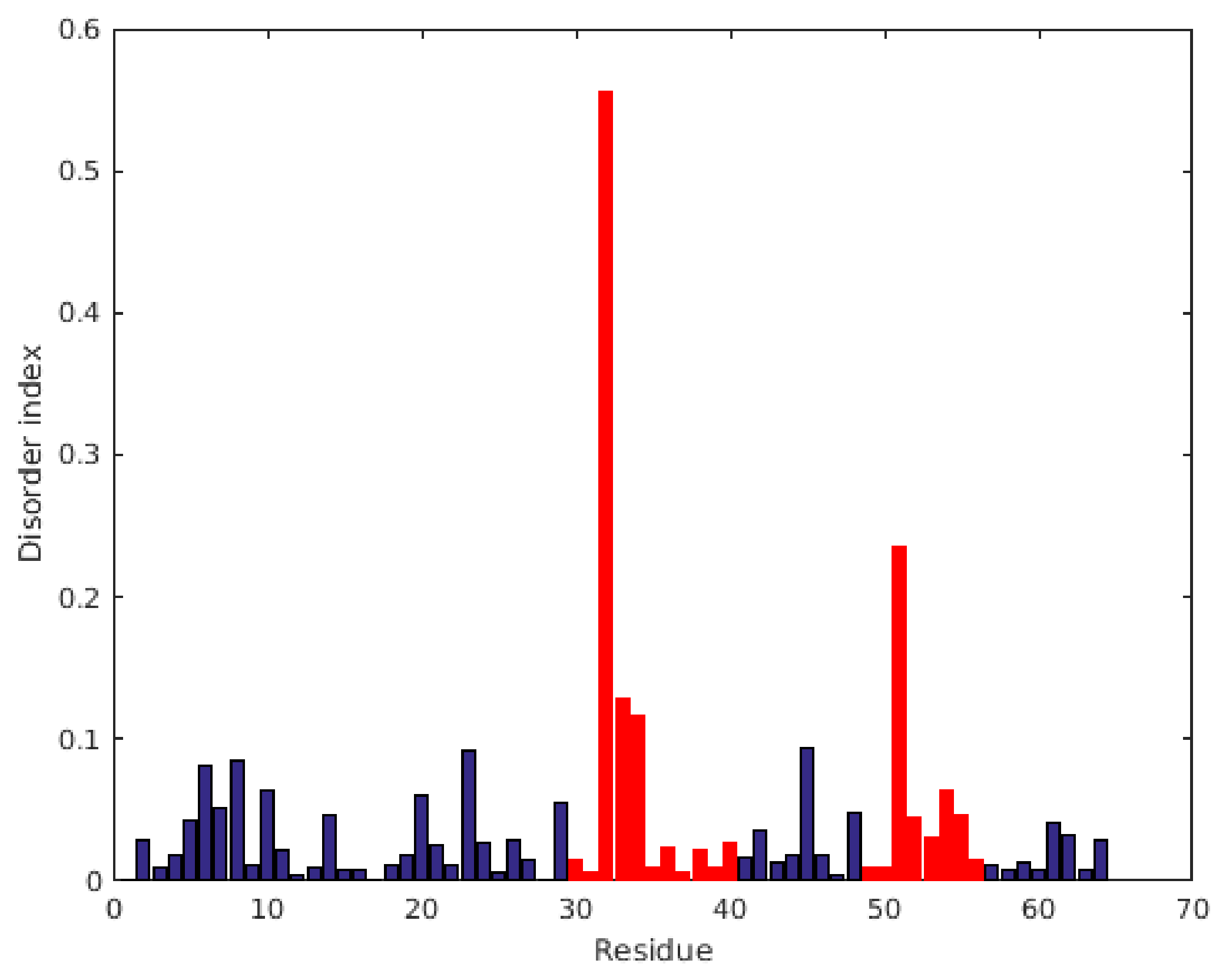
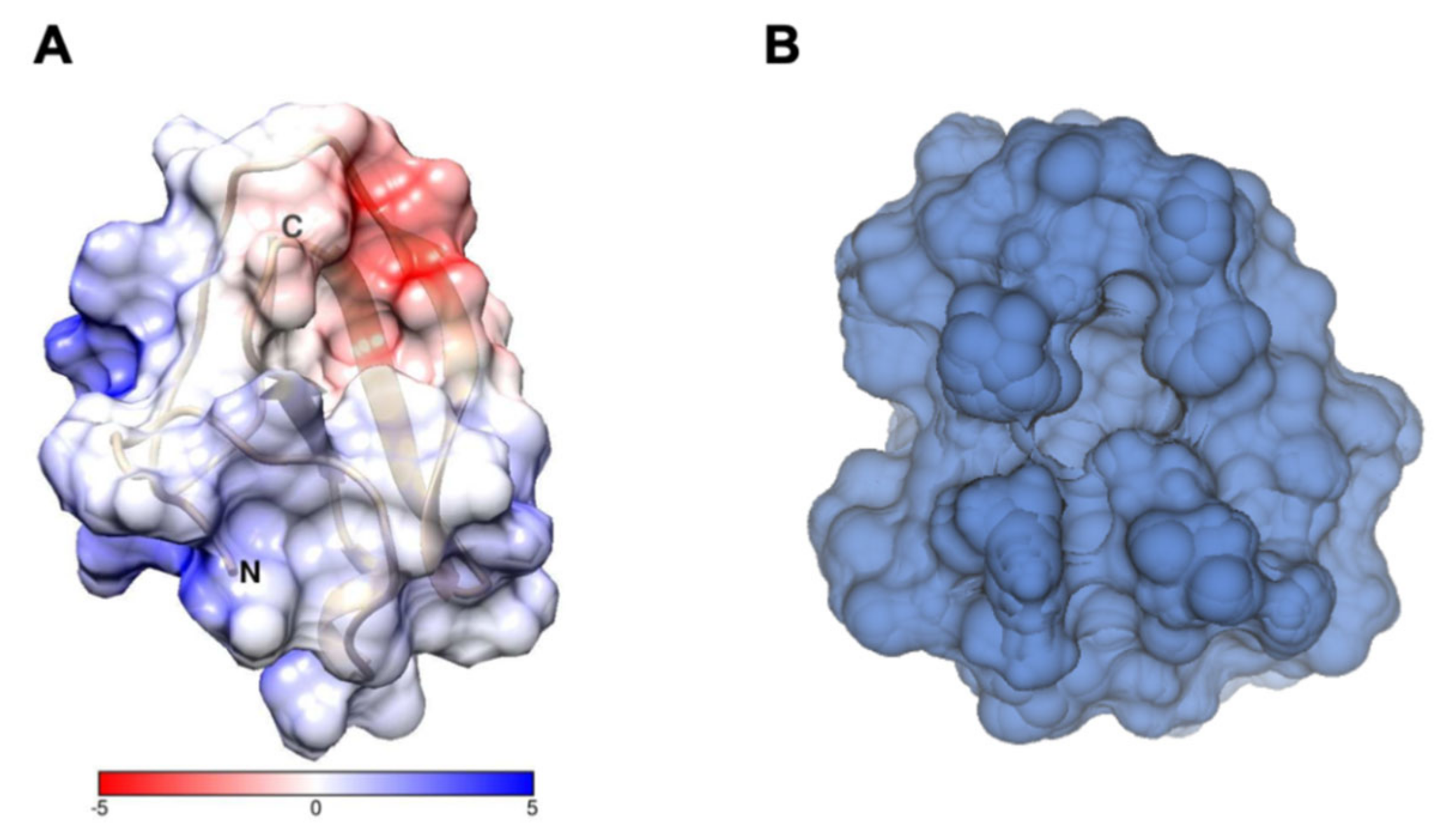
2.1. Characterization of Structural and Dynamical Properties of PAFC
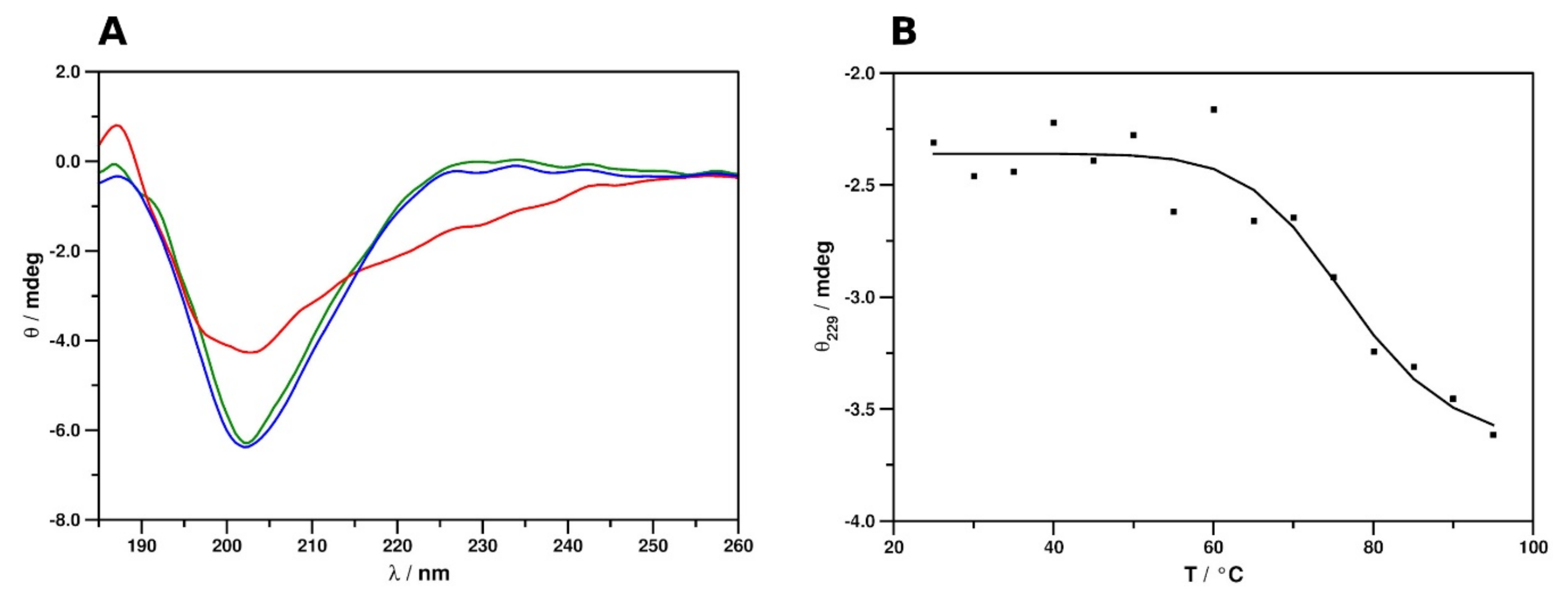
2.2. Secondary Structure and Thermal Stability Analysis of PAFC Using Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
2.3. Microbial Growth Inhibitory Activity of PAFC
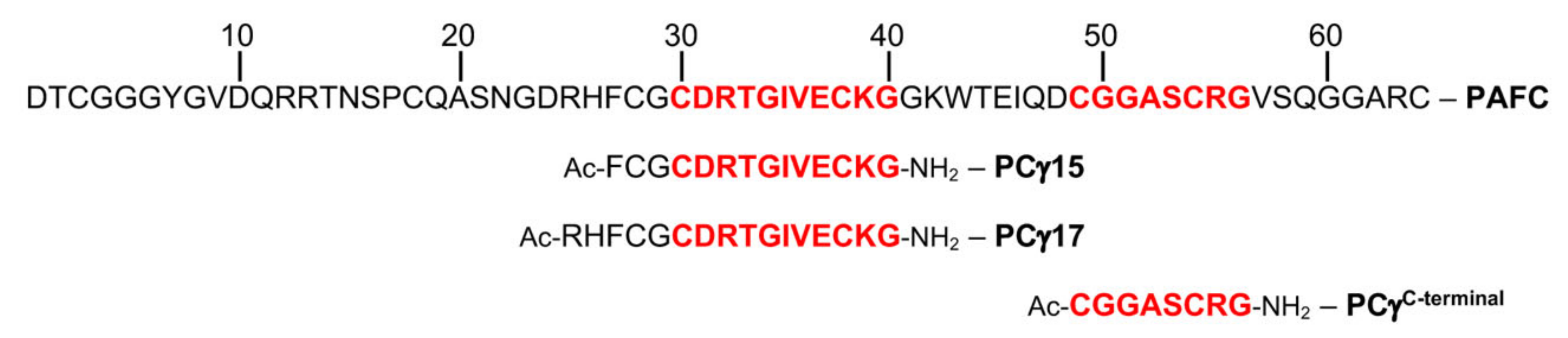
2.4. The Role of the γ-Core Motif in the Antifungal Activity of PAFC
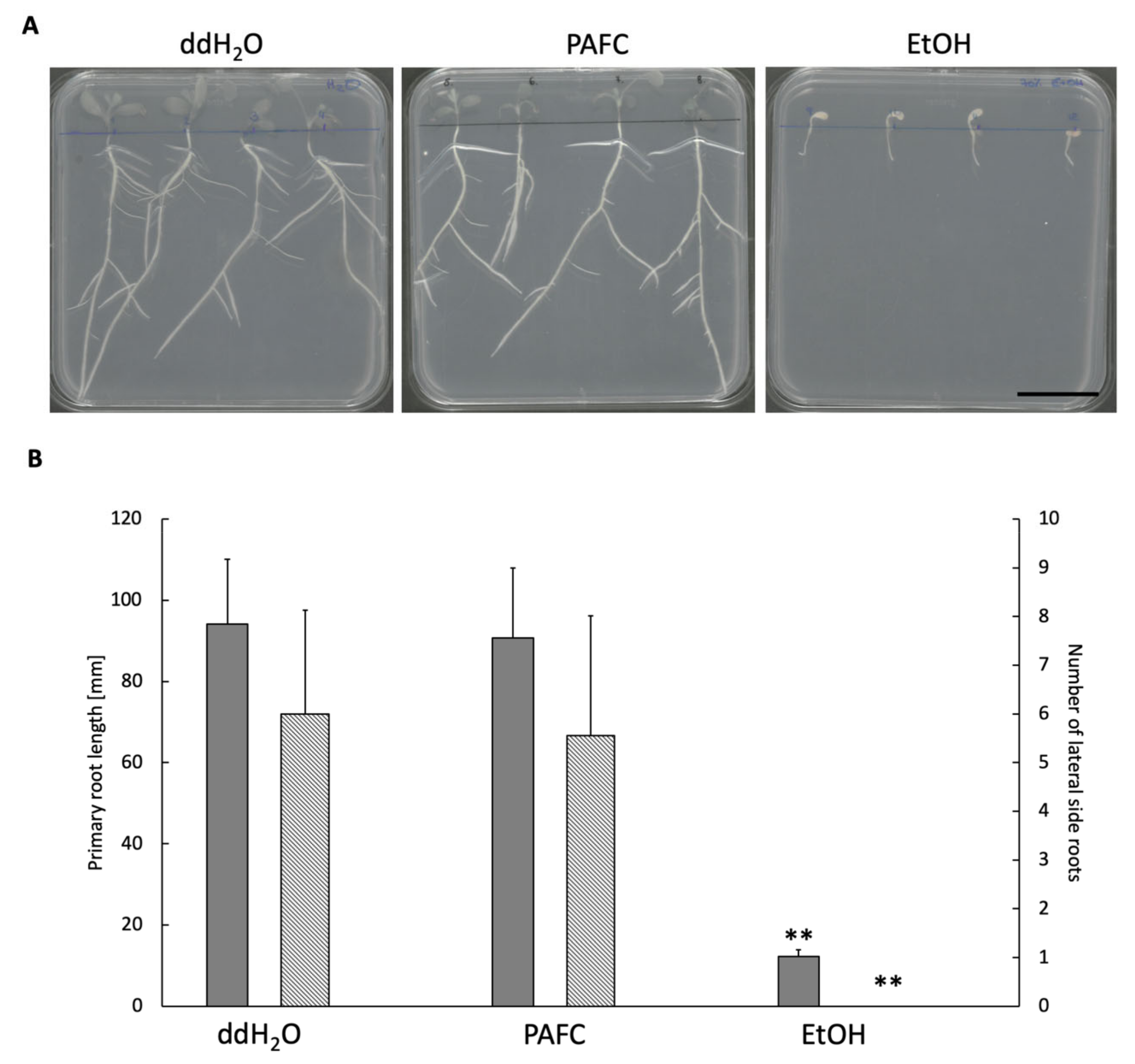
2.5. Effect of PAFC on Medicago truncatula Seedlings
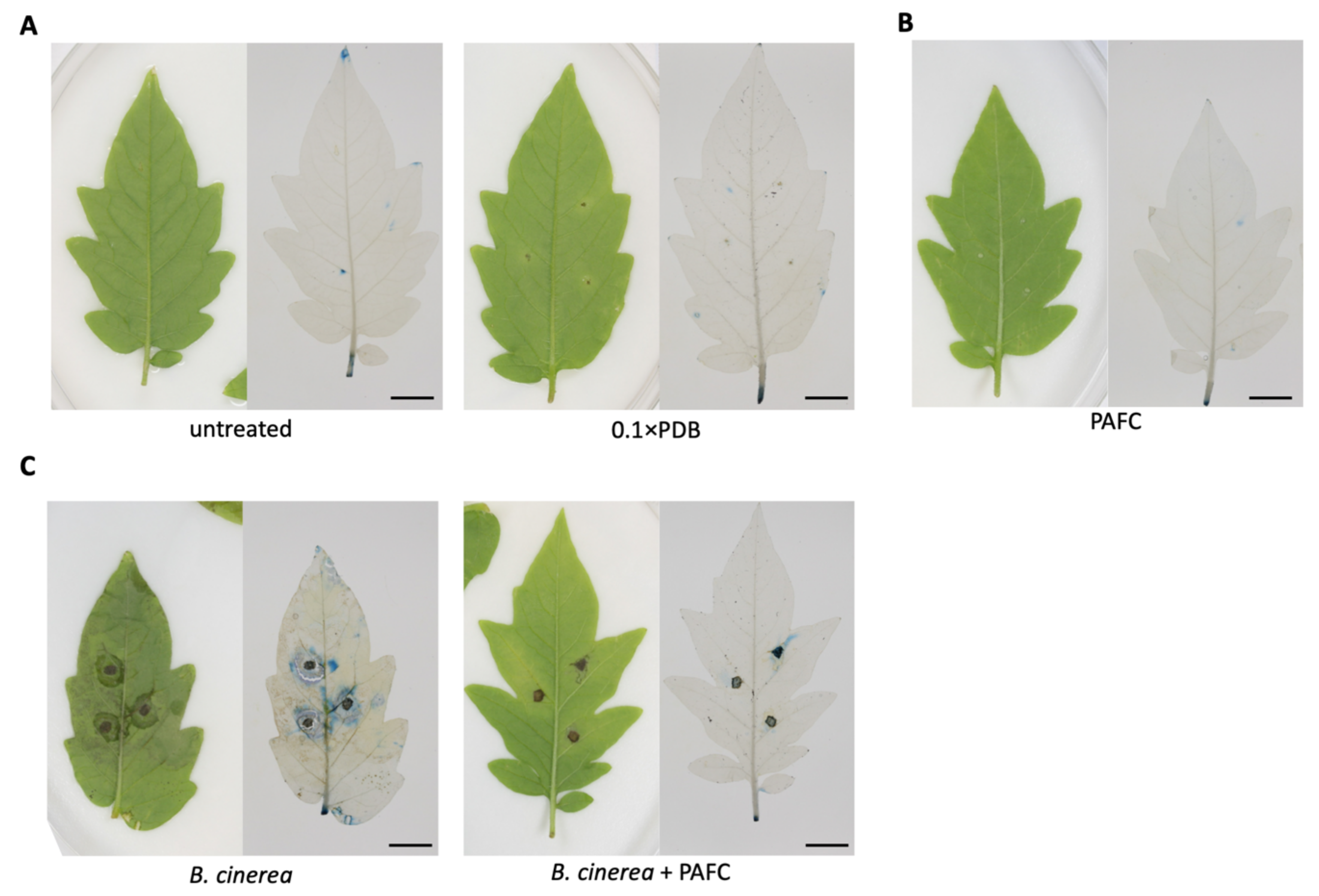
2.6. Protection of Tomato Plant Leaves from Botrytis cinerea Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microbial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. PAFC Production
4.3. NMR Measurements, Signal Assignment, and Structure Calculations
4.4. ECD Spectroscopy
4.5. Synthesis of γ-Core Peptides PCγ15, PCγ17, and PCγC-terminal
4.6. Determination of Antimicrobial Activity
4.7. Toxicity Tests with Medicaco truncatula Seedlings
4.8. Plant Protection Experiments
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aa | Amino acid |
| BP | Penicillium brevicompactum bubble protein |
| BMRB | Biological magnetic resonance data bank |
| CDSSTR | Circular dichroism spectra secondary structure |
| CPMG-RD | Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill relaxation dispersion |
| DSSP | Dictionary secondary structures of protein |
| DI | Disorder index |
| ECD | Electronic circular dichroism |
| fASA | Fractional associated solvent area |
| GRAVY | Grand average of hydropathy value |
| HI-HSQC | Heteronuclear in-phase single quantum coherence |
| IC90 | Inhibitory concentration reducing microbial growth by ≥90% |
| kDa | kiloDalton |
| K | Kelvin |
| MP(s) | Miniprotein(s) |
| NFAP | Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| NOE | Nuclear Overhauser effect |
| OD | Optical density |
| PAF | Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein |
| PdAfp | Penicillium digitatum antifungal protein |
| PeAfp | Penicillium expansum antifungal protein |
| pdb | Protein Data Bank |
| RCI | Random coil index |
| RMSD | Root-mean-square deviation |
References
- Fisher, M.C.; Gurr, S.J.; Cuomo, C.A.; Blehert, D.S.; Jin, H.L.; Stukenbrock, E.H.; Stajich, J.E.; Kahmann, R.; Boone, C.; Denning, D.W.; et al. Threats posed by the fungal kingdom to humans, wildlife, and agriculture. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Sahl, H.-G. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Cationic host defense (antimicrobial) peptides. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Weerden, N.L.; Bleackley, M.R.; Anderson, M.A. Properties and mechanisms of action of naturally occurring antifungal peptides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3545–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelabh; Singh, K.; Rani, J. Sequential and structural aspects of antifungal peptides from animals, bacteria and fungi based on bioinformatics tools. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2016, 8, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgóczy, L.; Yap, A.; Marx, F. Cysteine-Rich antifungal proteins from filamentous fungi are promising bioactive natural compounds in anti-Candida therapy. Isr. J. Chem. 2019, 59, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, F. Small, basic antifungal proteins secreted from filamentous ascomycetes: A comparative study regarding expression, structure, function and potential application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.; Galgóczy, L.; Váradi, G.; Holzknecht, J.; Kakar, A.; Malanovic, N.; Leber, R.; Koch, J.; Keller, M.A.; Batta, G.; et al. Two small, cysteine-rich and cationic antifungal proteins from Penicillium chrysogenum: A comparative study of PAF and PAFB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.; Hajdu, D.; Bratschun-Khan, D.; Gáspári, Z.; Varbanov, M.; Philippot, S.; Fizil, Á.; Czajlik, A.; Kele, Z.; Sonderegger, C.; et al. New antimicrobial potential and structural properties of PAFB: A cationic, cysteine-rich protein from Penicillium chrysogenum Q176. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, F.; Binder, U.; Leiter, E.; Pócsi, I. The Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF, a promising tool for the development of new antifungal therapies and fungal cell biology studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palicz, Z.; Gall, T.; Leiter, E.; Kollár, S.; Kovács, I.; Miszti-Blasius, K.; Pócsi, I.; Csernoch, L.; Szentesi, P. Application of a low molecular weight antifungal protein from Penicillium chrysogenum (PAF) to treat pulmonary aspergillosis in mice. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, L.; Boros, E.; Poór, P.; Ördög, A.; Kele, Z.; Váradi, G.; Holzknecht, J.; Bratschun-Khan, D.; Nagy, I.; Tóth, G.K.; et al. The potential use of the Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF, the designed variant PAFopt and its γ-core peptide Pγopt in plant protection. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzknecht, J.; Kühbacher, A.; Papp, C.; Farkas, A.; Váradi, G.; Marcos, J.F.; Manzanares, P.; Tóth, G.K.; Galgóczy, L.; Marx, F. The Penicillium chrysogenum Q176 antimicrobial protein PAFC effectively inhibits the growth of the opportunistic human pathogen Candida albicans. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedüs, N.; Leiter, É.; Kovács, B.; Tömöri, V.; Kwon, N.-J.; Emri, T.; Marx, F.; Batta, G.; Csernoch, L.; Haas, H.; et al. The small molecular mass antifungal protein of Penicillium chrysogenum—A mechanism of action oriented review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2011, 51, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, É.; Szappanos, H.; Oberparleiter, C.; Kaiserer, L.; Csernoch, L.; Pusztahelyi, T.; Emri, T.; Pócsi, I.; Salvenmoser, W.; Marx, F. Antifungal protein PAF severely affects the integrity of the plasma membrane of Aspergillus nidulans and induces an apoptosis-like phenotype. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, U.; Bencina, M.; Fizil, Á.; Batta, G.; Chhillar, A.K.; Marx, F. Protein kinase A signaling and calcium ions are major players in PAF mediated toxicity against Aspergillus niger. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, U.; Chu, M.; Read, N.D.; Marx, F. The antifungal activity of the Penicillium chrysogenum protein PAF disrupts calcium homeostasis in Neurospora crassa. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batta, G.; Barna, T.; Gáspári, Z.; Sándor, S.; Kövér, K.E.; Binder, U.; Sarg, B.; Kaiserer, L.; Chhillar, A.K.; Eigentler, A.; et al. Functional aspects of the solution structure and dynamics of PAF—A highly-stable antifungal protein from Penicillium chrysogenum. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2875–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.; Oemer, G.; Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K.; Kovács, L.; Salvenmoser, W.; Zschocke, J.; Keller, M.A.; Marx, F. Membrane sphingolipids regulate the fitness and antifungal protein susceptibility of Neurospora crassa. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonderegger, C.; Váradi, G.; Galgóczy, L.; Kocsubé, S.; Posch, W.; Borics, A.; Dubrac, S.; Tóth, G.K.; Wilflingseder, D.; Marx, F. The evolutionary conserved γ-core motif influences the anti-Candida activity of the Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yount, N.Y.; Yeaman, M.R. Multidimensional signatures in antimicrobial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7363–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yount, N.Y.; Yeaman, M.R. Emerging themes and therapeutic prospects for anti-infective peptides. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.G.; Flensburg, C.; Olsen, O.; Seibold, M.; Bricogne, G.; Henriksen, A. Solving the structure of the bubble protein using the anomalous sulfur signal from single-crystal in-house Cu K α diffraction data only. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, S.; Gandia, M.; Castillo, L.; Coca, M.; Marx, F.; Marcos, J.F.; Manzanares, P. Three antifungal proteins from Penicillium expansum: Different patterns of production and antifungal activity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.Z.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizil, Á.; Gáspári, Z.; Barna, T.; Marx, F.; Batta, G. “Invisible” conformers of an antifungal disulfide protein revealed by constrained cold and heat unfolding, CEST-NMR experiments, and molecular dynamics calculations. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 5136–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virágh, M.; Vörös, D.; Kele, Z.; Kovács, L.; Fizil, Á.; Lakatos, G.; Maróti, G.; Batta, G.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Galgóczy, L. Production of a defensin-like antifungal protein NFAP from Neosartorya fischeri in Pichia pastoris and its antifungal activity against filamentous fungal isolates from human infections. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 94, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, L.; Virágh, M.; Tako, M.; Papp, T.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Galgóczy, L. Isolation and characterization of Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein (NFAP). Peptides 2011, 32, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, D.; Huber, A.; Czajlik, A.; Tóth, L.; Kele, Z.; Kocsubé, S.; Fizil, Á.; Marx, F.; Galgóczy, L.; Batta, G. Solution structure and novel insights into phylogeny and mode of action of the Neosartorya (Aspergillus) fischeri antifungal protein (NFAP). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Rajarathnam, K. C-13 NMR chemical shifts can predict disulfide bond formation. J. Biomol. NMR 2000, 18, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berjanskii, M.V.; Wishart, D.S. Application of the random coil index to studying protein flexibility. J. Biomol. NMR 2008, 40, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, F.; Grzesiek, S. Direct observation of hydrogen bonds in proteins by interresidue 3hJNC’ scalar couplings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 1601–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsa, N.E.; Arndt, D.; Wishart, D.S. Accessible surface area from NMR chemical shifts. J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 62, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: Pattern-Recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, N.A.; Muhandiram, R.; Singer, A.U.; Pascal, S.M.; Kay, C.M.; Gish, G.; Shoelson, S.E.; Pawson, T.; Formankay, J.D.; Kay, L.E. Backbone dynamics of a free and a phosphopeptide-complexed src homology-2 domain studied by N-15 NMR relaxation. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5984–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipari, G.; Szabo, A. Model-Free approach to the interpretation of nuclear magnetic-resonance relaxation in macromolecules.1. Theory and range of validity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 4546–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneller, J.M.; Lu, M.; Bracken, C. An effective method for the discrimination of motional anisotropy and chemical exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1852–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, J.F.; Dayie, K.T.; Peng, J.W.; Wagner, G. Internal mobility in the partially folded DNA binding and dimerization domains of GAL4: NMR analysis of the N-H spectral density functions. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2674–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonderegger, C.; Galgóczy, L.; Garrigues, S.; Fizil, Á.; Borics, A.; Manzanares, P.; Hegedüs, N.; Huber, A.; Marcos, J.F.; Batta, G.; et al. A Penicillium chrysogenum-based expression system for the production of small, cysteine-rich antifungal proteins for structural and functional analyses. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrigues, S.; Gandia, M.; Borics, A.; Marx, F.; Manzanares, P.; Marcos, J.F. Mapping and identification of antifungal peptides in the putative antifungal protein AfpB from the filamentous fungus Penicillium digitatum. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgóczy, L.; Borics, A.; Virágh, M.; Ficze, H.; Váradi, G.; Kele, Z.; Marx, F. Structural determinants of Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein (NFAP) for folding, stability and antifungal activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, L.; Váradi, G.; Borics, A.; Batta, G.; Kele, Z.; Vendrinszky, A.; Tóth, R.; Ficze, H.; Tóth, G.K.; Vágvölgyi, C.; et al. Anti-Candidal activity and functional mapping of recombinant and synthetic Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein 2 (NFAP2). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, E.D.; Taveira, G.B.; Carvalho, A.D.; Gomes, V.M. Improved smallest peptides based on positive charge increase of the γ-core motif from PnuD-1 and their mechanism of action against Candida species. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, L.; Váradi, G.; Boros, E.; Borics, A.; Ficze, H.; Nagy, I.; Tóth, G.K.; Rákhely, G.; Marx, F.; Galgóczy, L. Biofungicidal potential of Neosartorya (Aspergillus) fischeri antifungal protein NFAP and novel synthetic γ-core peptides. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.G.; Pfaff, T.; Moreau, D.; Groves, E.; Ruffel, S.; Lepetit, M.; Whitehand, S.; Maillet, F.; Nair, R.M.; Journet, E.P. Growing M. Truncatula: Choice of substrates and growth conditions. In Medicago Truncatula Handbook; Mathesius, U., Journet, E.P., Sumner, L.W., Eds.; Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation: Ardmore, OK, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-9754303-1-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jurrus, E.; Engel, D.; Star, K.; Monson, K.; Brandi, J.; Felberg, L.E.; Brookes, D.H.; Wilson, L.; Chen, J.H.; Liles, K.; et al. Improvements to the APBS biomolecular solvation software suite. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehr, D.D.; Nussinov, R.; Wright, P.E. The role of dynamic conformational ensembles in biomolecular recognition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.T.; Ao, J.Q.; Yang, W.C.; Jiao, L.P.; Zheng, T.L.; Chen, X.H. Purification and characterization of a novel antifungal protein secreted by Penicillium chrysogenum from an arctic sediment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 10381–10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, S.; Gandia, M.; Popa, C.; Borics, A.; Marx, F.; Coca, M.; Marcos, J.F.; Manzanares, P. Efficient production and characterization of the novel and highly active antifungal protein AfpB from Penicillium digitatum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paege, N.; Jung, S.; Schape, P.; Muller-Hagen, D.; Ouedraogo, J.P.; Heiderich, C.; Jedamzick, J.; Nitsche, B.M.; van den Hondel, C.A.; Ram, A.F.; et al. A transcriptome meta-analysis proposes novel biological roles for the antifungal protein AnAFP in Aspergillus niger. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, A.; Lerchster, H.; Marx, F. Nutrient excess triggers the expression of the Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAFB. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.L.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elad, Y.; Vivier, M.; Fillinger, S. Botrytis, the good, the bad and the ugly. In Botrytis—The Fungus, the Pathogen and its Management in Agricultural Systems; Fillinger, S., Elad, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, M.; Hamada, M.S.; Li, G.Q.; Luo, C.X. Detection and molecular characterization of resistance to the dicarboximide and benzamide fungicides in Botrytis cinerea from tomato in Hubei province, China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbey, J.A.; Percival, D.; Abbey, L.; Asiedu, S.K.; Prithiviraj, B.; Schilder, A. Biofungicides as alternative to synthetic fungicide control of grey mould (Botrytis cinerea)—Prospects and challenges. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero-Hernandez, E.D.; Moraga, J.; Collado, I.G.; Echeverri, F. Natural compounds that modulate the development of the fungus Botrytis cinerea and protect Solanum lycopersicum. Plants 2019, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, M.; Hamada, M.S.; Hahn, M.; Li, G.; Luo, C. Fungicide resistance of Botrytis cinerea from strawberry to procymidone and zoxamide in Hubei, China. Phytopathol. Res. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R. The Computer Aided Resonance Assignment Tutorial; Cantina Verlag: Goldau, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, M.; Schleucher, J.; Griesinger, C. Heteronuclear multidimensional NMR experiments for the structure determination of proteins in solution employing pulsed field gradients. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1999, 34, 93–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranken, W.F.; Boucher, W.; Stevens, T.J.; Fogh, R.H.; Pajon, A.; Llinas, P.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L.; Ionides, J.; Laue, E.D. The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: Development of a software pipeline. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2005, 59, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Bax, A. Protein backbone and sidechain torsion angles predicted from NMR chemical shifts using artificial neural networks. J. Biomol. NMR 2013, 56, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Delaglio, F.; Cornilescu, G.; Bax, A. TALOS plus: A hybrid method for predicting protein backbone torsion angles from NMR chemical shifts. J. Biomol. NMR 2009, 44, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, T.; Güntert, P.; Wüthrich, K. Protein NMR structure determination with automated NOE-identification in the NOESY spectra using the new software ATNOS. J. Biomol. NMR 2002, 24, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, T.; Güntert, P.; Wüthrich, K. Protein NMR structure determination with automated NOE assignment using the new software CANDID and the torsion angle dynamics algorithm DYANA. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 319, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, M.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Palmer, A.G. Disulfide bond isomerization in basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor: Multisite chemical exchange quantified by CPMG relaxation dispersion and chemical shift modeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14324–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.G.; Koss, H. Chemical exchange. In Biological NMR, Pt B; Wand, A.J., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 615, pp. 177–236. [Google Scholar]
- Sreerama, N.; Woody, R.W. Estimation of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra: Comparison of CONTIN, SELCON, and CDSSTR methods with an expanded reference set. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 287, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poór, P.; Gémes, K.; Horváth, F.; Szepesi, A.; Simon, M.L.; Tari, I. Salicylic acid treatment via the rooting medium interferes with stomatal response, CO2 fixation rate and carbohydrate metabolism in tomato, and decreases harmful effects of subsequent salt stress. Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Oirdi, M.; Trapani, A.; Bouarab, K. The nature of tobacco resistance against Botrytis cinerea depends on the infection structures of the pathogen. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Oirdi, M.; Abd El Rahman, T.; Rigano, L.; El Hadrami, A.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Daayf, F.; Vojnov, A.; Bouarab, K. Botrytis cinerea manipulates the antagonistic effects between immune pathways to promote disease development in tomato. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2405–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Miura, E.; Matsushima, R.; Sakamoto, W. White leaf sectors in yellow variegated2 are formed by viable cells with undifferentiated plastids. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
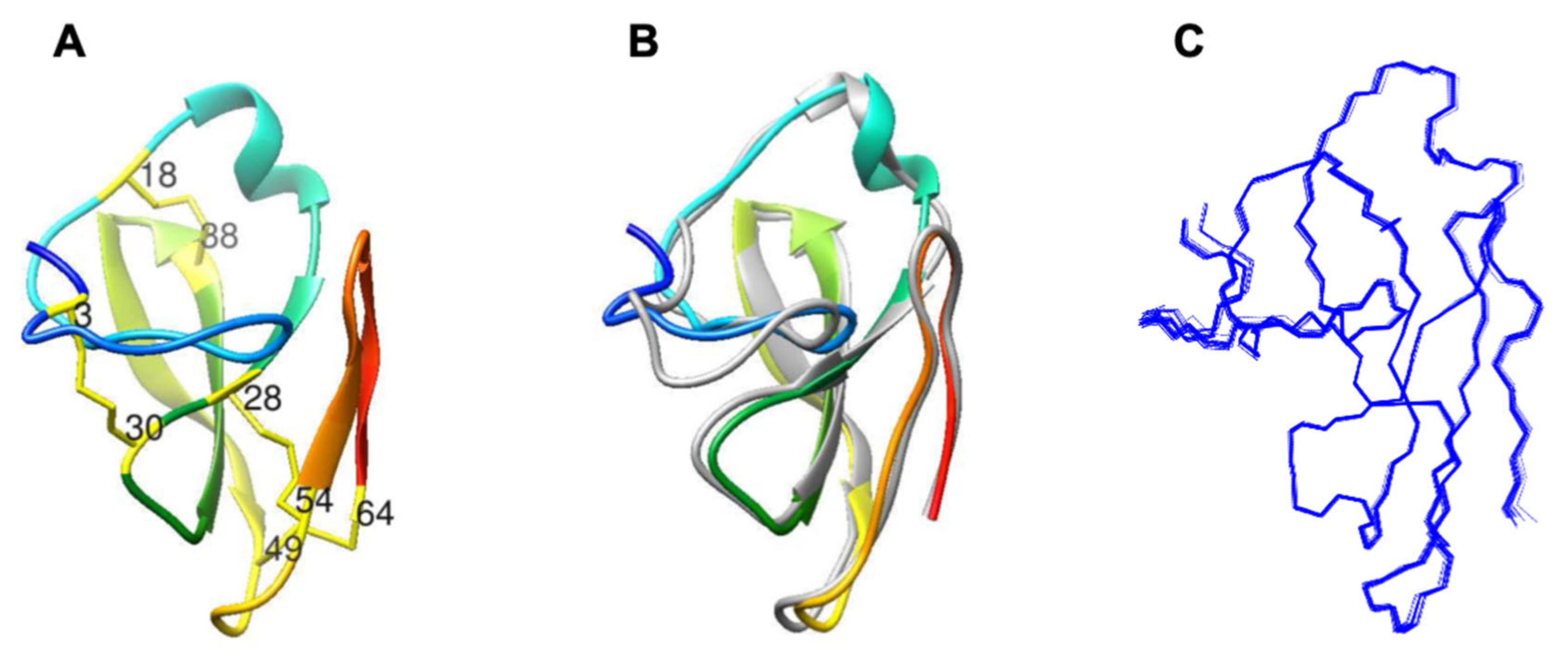
| Secondary Structure Elements | Residue with Amide Hydrogen | Residue with Carbonyl Oxygen |
|---|---|---|
| β1-β2 | 29Gly | 34Gly |
| β1-β2 | 36Val | 27Phe |
| β1-β2 | 27Phe | 36Val |
| β2-β3 | 35Ile | 47Gln |
| β2-β3 | 37Glu | 44Thr |
| β2-β3 | 39Lys | 42Lys |
| β2-β3 | 44Thr | 37Glu |
| β2-β3 | 46Ile | 35Ile |
| β2-β3 | 49Cys | 33Thr |
| β4-β5 | 55Arg | 63Arg |
| β4-β5 | 57Val | 60Gly |
| β4-β5 | 63Arg | 55Arg |
| N-terminal-β1 | 12Arg | 28Cys |
| N-terminal-β1 | 28Cys | 10Asp |
| N-terminal-β3 | 15Asn | 43Trp |
| N-terminal-β3 | 43Trp | 16Ser |
| loop1-β4 | 54Cys | 32Arg |
| N-terminal region | 13Arg | 1Asp |
| Secondary Structural Elements/% | PAFC 25 °C | PAFC 95 °C | PAFC 25 °C after Heating | BP Crystallographic Structure (1UOY) § | PAFC Solution NMR Structure (6TRM) § |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α- or 310-helix | 13 | 15 | 14 | 5 | 6 |
| β-strand, extended | 28 | 26 | 28 | 39 | 38 |
| β- or γ-turns, bends | 26 | 26 | 25 | 31 | 33 |
| unordered | 33 | 34 | 32 | 25 | 23 |
| Microorganism | IC90 | |
|---|---|---|
| µM | μg mL−1 | |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | >30 | 199 |
| Aspergillus nidulans | 30 | 199 |
| Aspergillus niger | >30 | 199 |
| Neurospora crassa | 15 | 99 |
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 50 | 331 |
| Microsporum gypseum | 7 | 46 |
| Trichophyton rubrum | 5 | 33 |
| Bacillus subtilis | >50 | 331 |
| Escherichia coli | >50 | 331 |
| Protein/Peptide | Molecular Mass (kDa) | Charge (pH 7.0) | GRAVY | IC90 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. crassa | C. albicans | ||||||
| μM | μg mL−1 | μM | μg mL−1 | ||||
| PAFC | 6.6 | +0.6 | −0.767 | 12.5 | 83 | 2.5 | 17 |
| PCγ15 | 1.5 | −0.2 | +0.087 | >100 | 66 | >100 | 66 |
| PCγ17 | 1.8 | +1.1 | −0.367 | 25 | 166 | >100 | 66 |
| PCγC-terminal | 0.7 | +0.8 | +0.038 | >100 | 66 | >100 | 66 |
| PAFC (mg mL−1) | Diameter of Inhibition Zone (mm) |
|---|---|
| 0.25 | 16.5 ± 0.71 |
| 0.5 | 17.0 ± 0.00 |
| 0.75 | 18.5 ± 0.71 |
| 1.0 | 20.0 ± 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czajlik, A.; Holzknecht, J.; Galgóczy, L.; Tóth, L.; Poór, P.; Ördög, A.; Váradi, G.; Kühbacher, A.; Borics, A.; Tóth, G.K.; et al. Solution Structure, Dynamics, and New Antifungal Aspects of the Cysteine-Rich Miniprotein PAFC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031183
Czajlik A, Holzknecht J, Galgóczy L, Tóth L, Poór P, Ördög A, Váradi G, Kühbacher A, Borics A, Tóth GK, et al. Solution Structure, Dynamics, and New Antifungal Aspects of the Cysteine-Rich Miniprotein PAFC. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031183
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzajlik, András, Jeanett Holzknecht, László Galgóczy, Liliána Tóth, Péter Poór, Attila Ördög, Györgyi Váradi, Alexander Kühbacher, Attila Borics, Gábor K. Tóth, and et al. 2021. "Solution Structure, Dynamics, and New Antifungal Aspects of the Cysteine-Rich Miniprotein PAFC" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031183
APA StyleCzajlik, A., Holzknecht, J., Galgóczy, L., Tóth, L., Poór, P., Ördög, A., Váradi, G., Kühbacher, A., Borics, A., Tóth, G. K., Marx, F., & Batta, G. (2021). Solution Structure, Dynamics, and New Antifungal Aspects of the Cysteine-Rich Miniprotein PAFC. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031183










