Immunomodulatory Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Can Vary in Genetically Modified Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
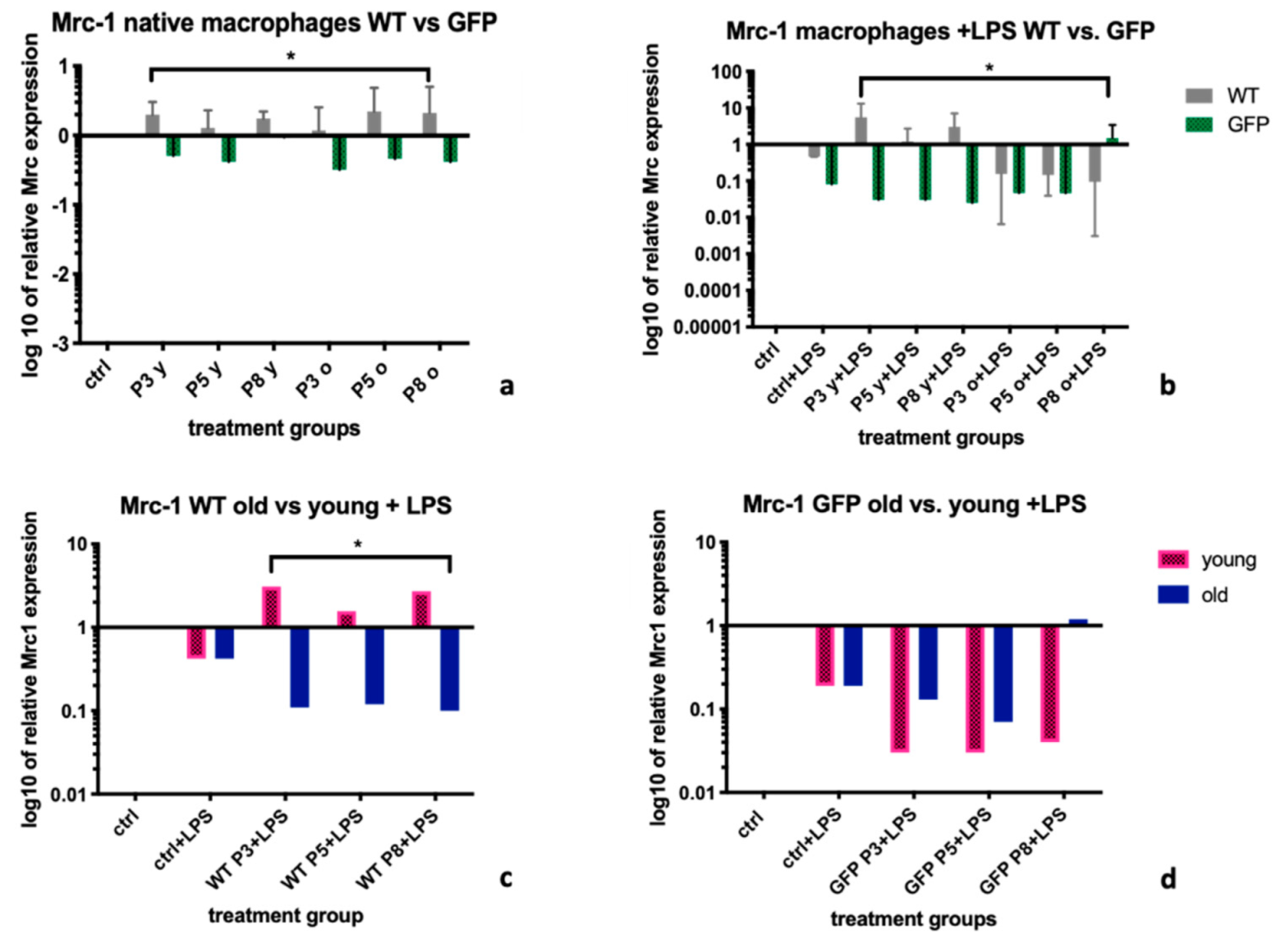
2.1. Mannose Receptor-1 (Mrc-1)
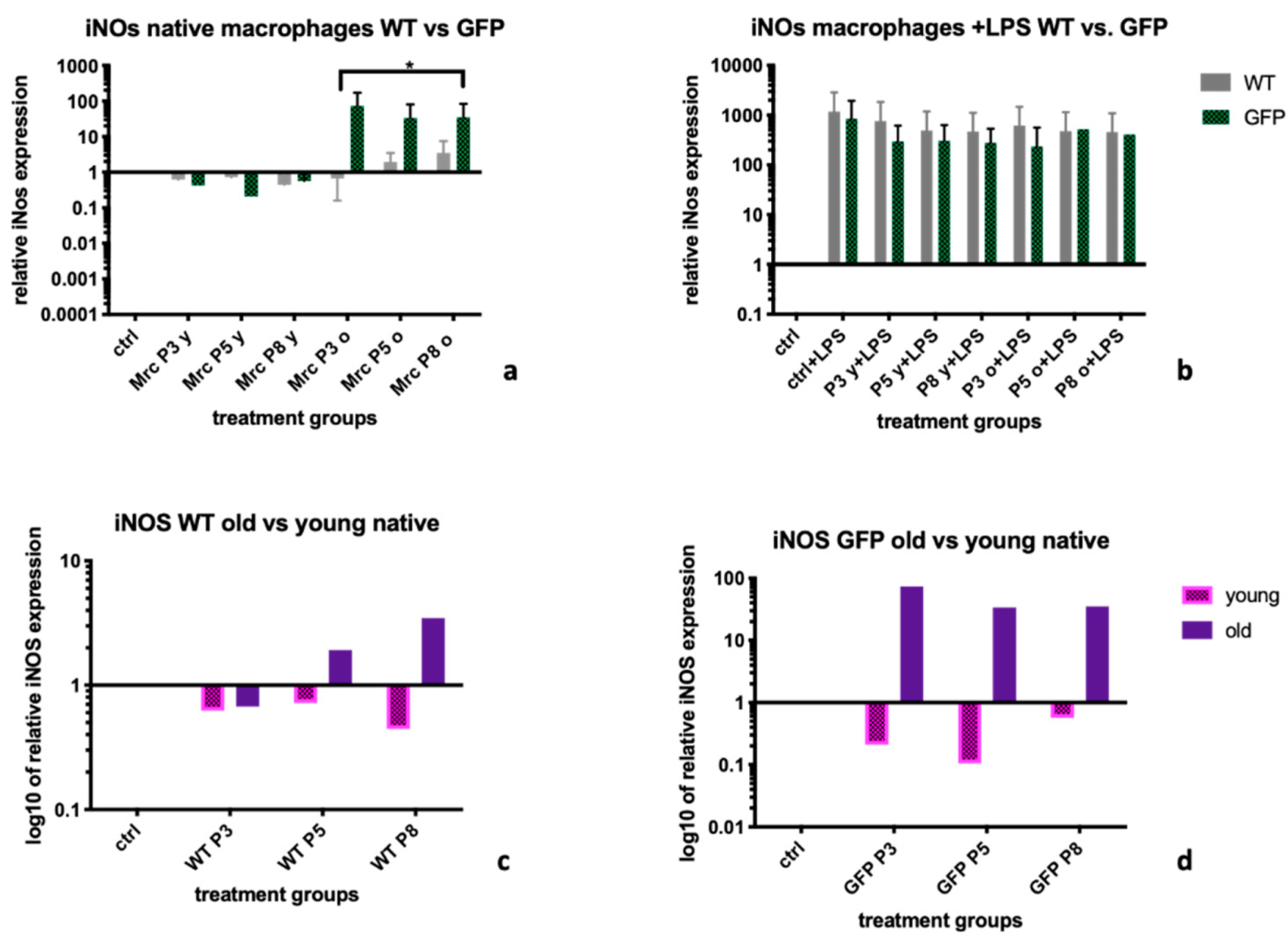
2.2. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS)
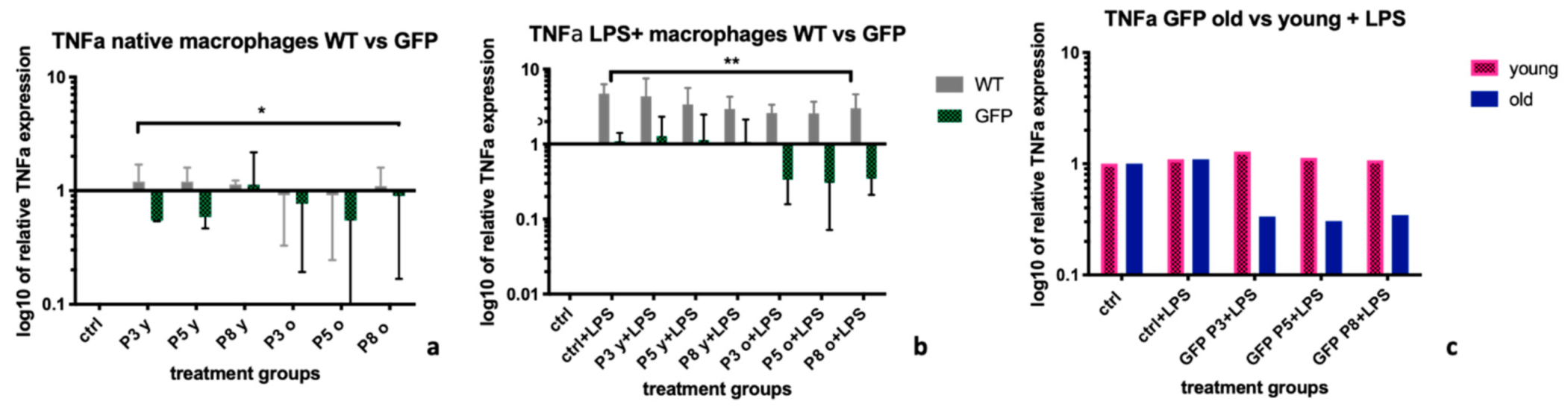
2.3. Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNFα)
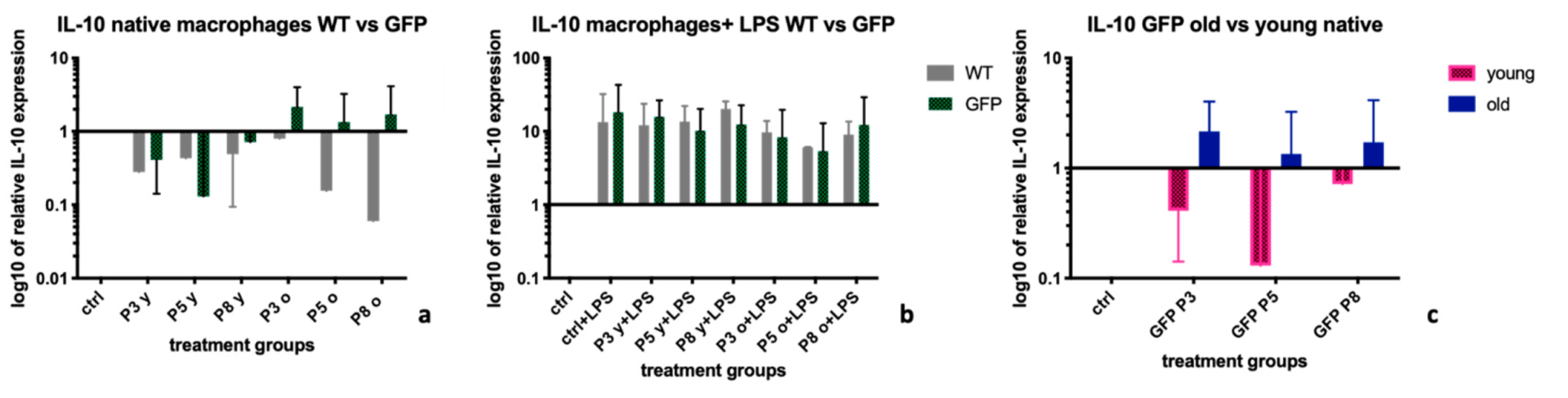
2.4. Interleukin-10 (IL-10)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
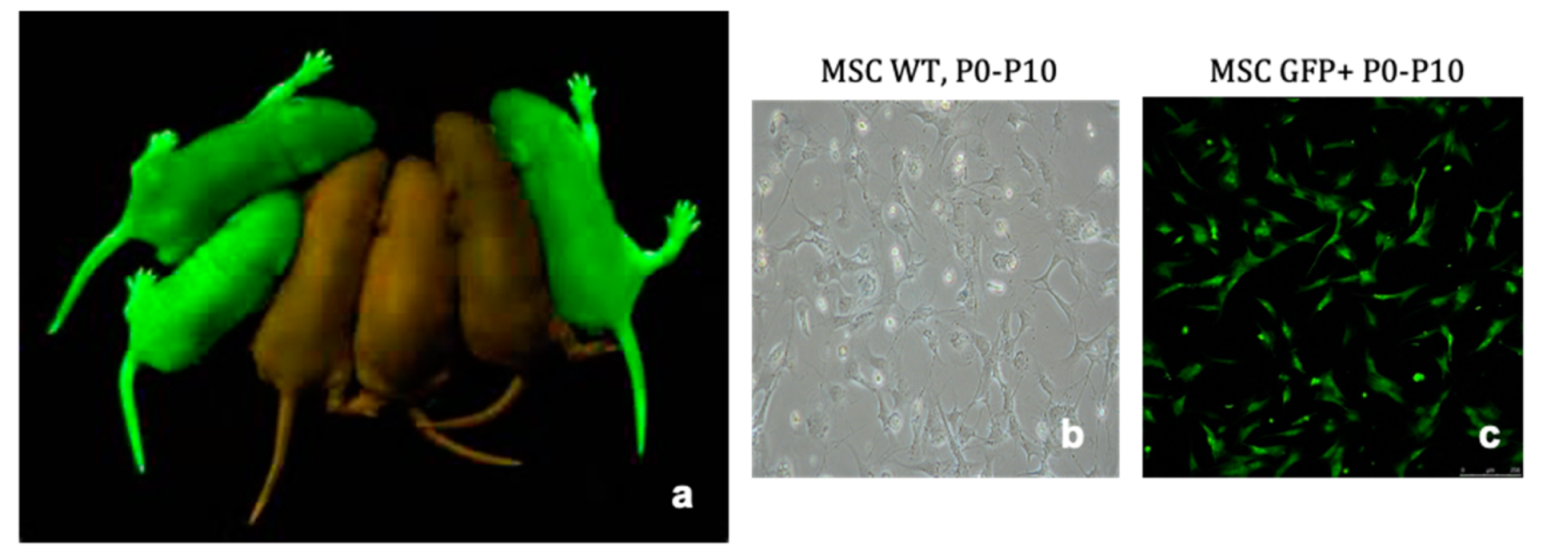
4.1. Extraction and Culture of Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
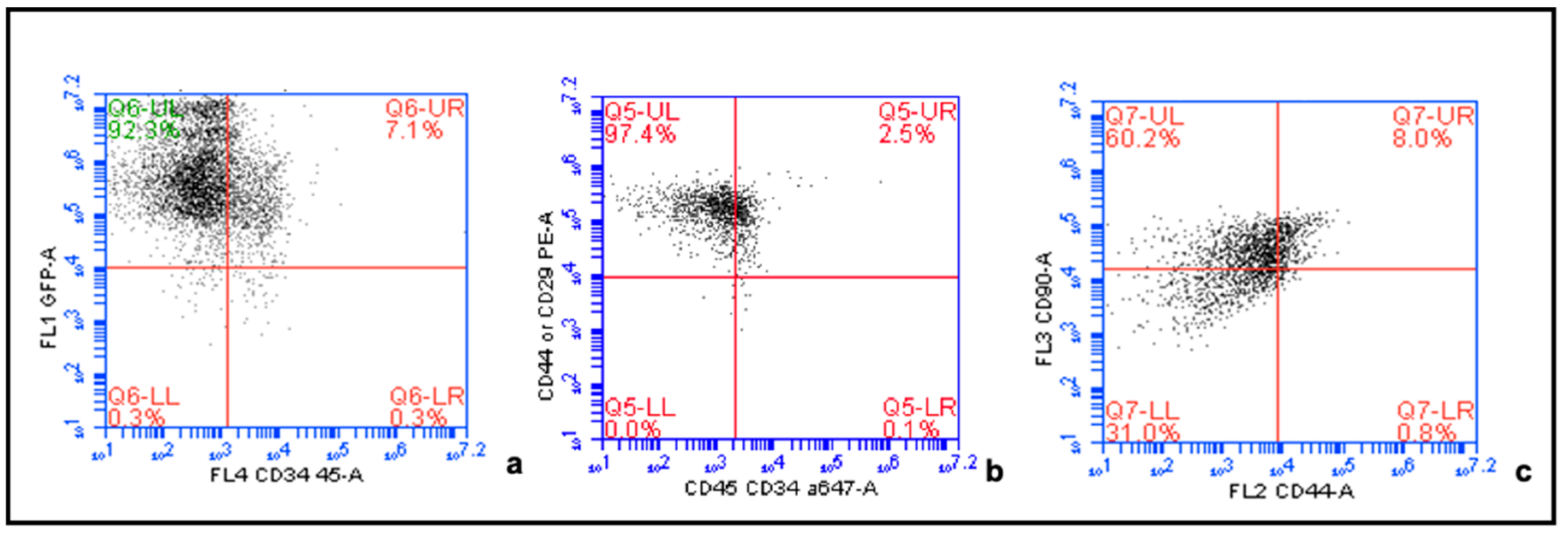
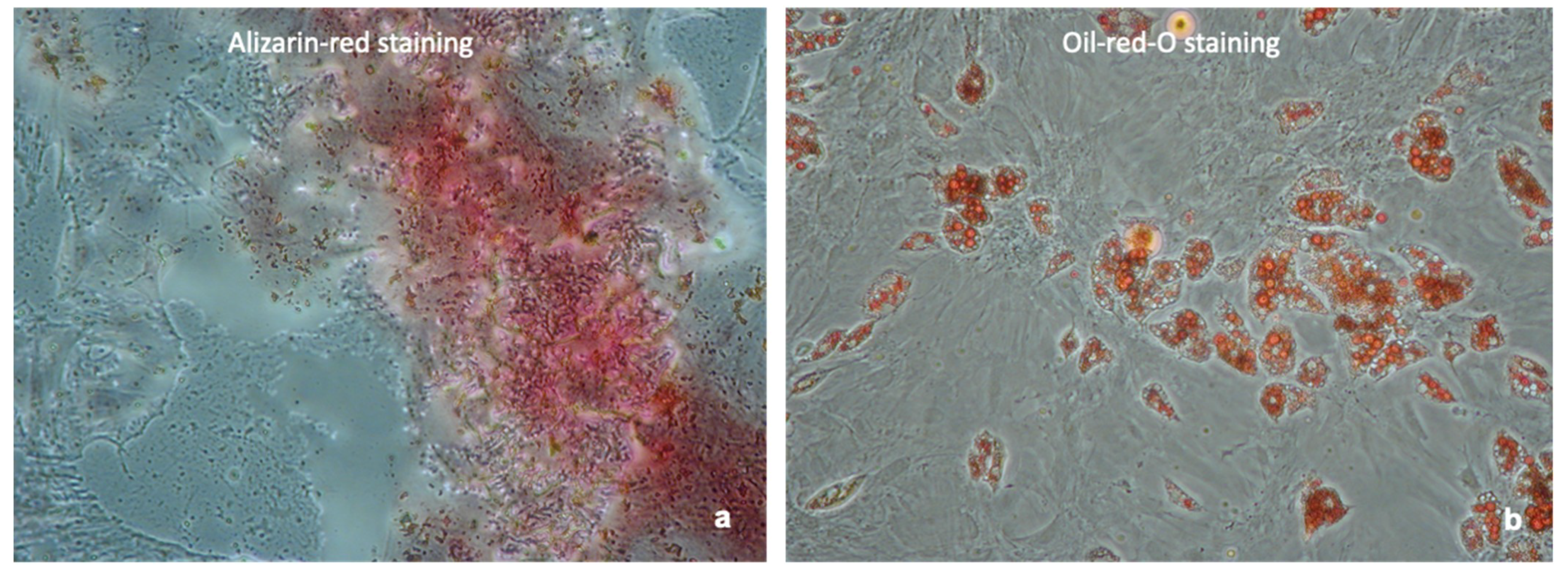
4.2. Confirmation of MSC Phenotype
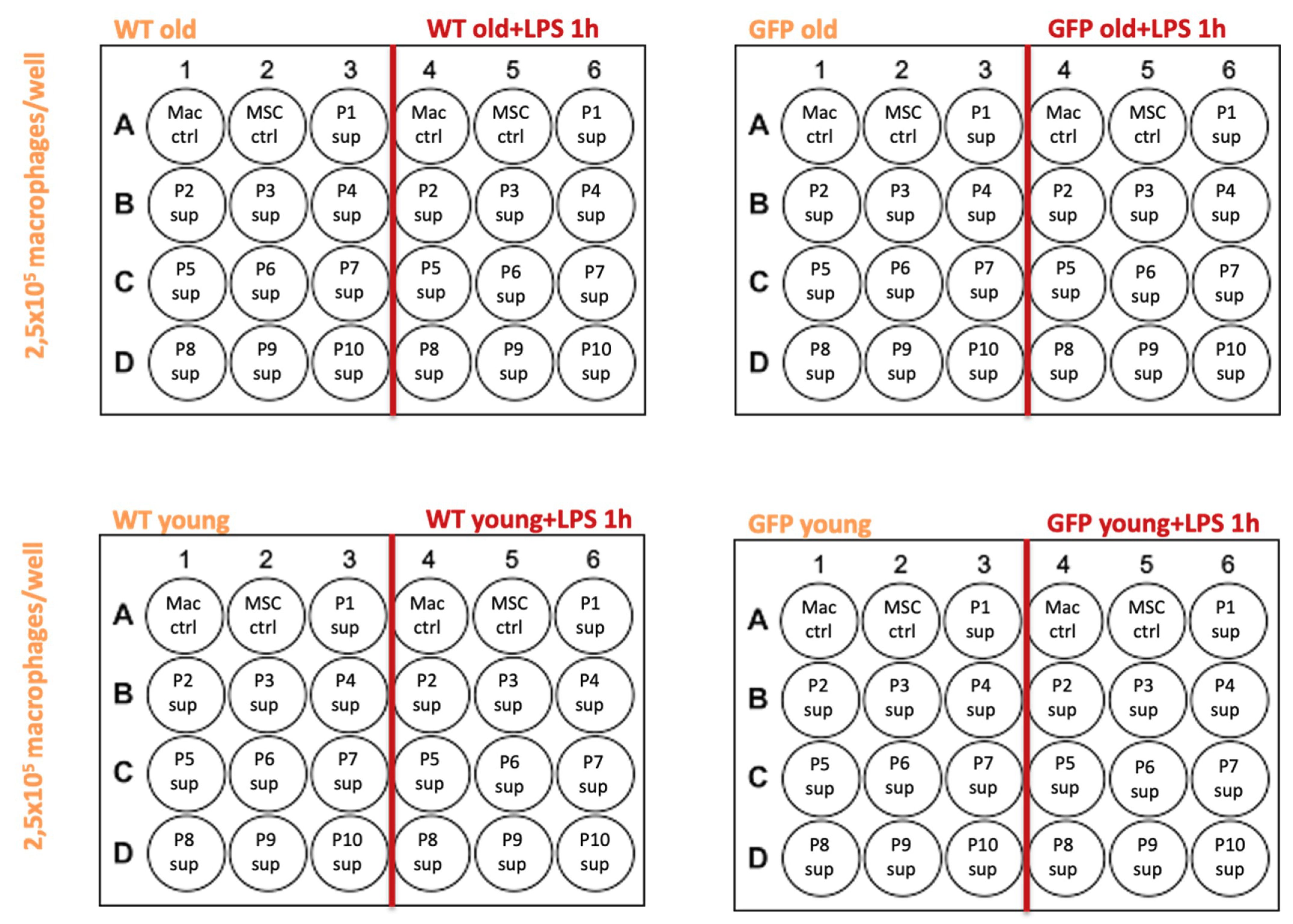
4.3. MSC Supernatants
- MSC-wt young, P1-P10: supernatants from MSCs in culture, extracted from a 6 week old WKY-wt rat, passages 1–10.
- MSC-GFP+ young, P1-P10: supernatants from MSCs in culture, extracted from a 6 week old WKY-GFP+ rat, passages 1–10.
- MSC-wt old, P1-P10: supernatants from MSCs in culture, extracted from a 6 month old WKY-wt rat, passages 1–10.
- MSC-GFP+ old, P1-P10: supernatants from MSCs in culture, extracted from a 6 month old WKY-GFP+ rat, passages 1–10.
4.4. Extraction of Bone Marrow Derived Macrophages
4.5. Supernatant Transfer Experiments
4.6. qRT-PCR
4.7. MTT Viability Assay
4.8. Statistical Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMDM | Bone Marrow Derived Macrophages |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| GVHD | Graft versus host disease |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| ISCT | International Society for Stem Cell Therapy |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| MSC | Mesenchymal Stromal Cells |
| Mrc-1 | Mannose receptor-1 |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor α |
| WKY | Wistar Kyoto |
| WT | Wild type |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
Appendix A
References
- Rhijn, M.R.-V.; Weimar, W.; Hoogduijn, M.J. Mesenchymal stem cells. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2012, 17, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, F.; Remuzzi, G.; Perico, N. Mesenchymal stromal cells to promote kidney transplantation tolerance. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2014, 19, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, D.K.; Schaapherder, A.F.M.; Reinders, M.E.J. Mesenchymal stromal cells in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blanc, K.; Frassoni, F.; Ball, L.; Locatelli, F.; Roelofs, H.; Lewis, I.; Lanino, E.; Sundberg, B.; Bernardo, M.E.; Remberger, M.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase II study. Lancet 2008, 371, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duijvestein, M.; Vos, A.C.W.; Roelofs, H.; Wildenberg, M.E.; Wendrich, B.B.; Verspaget, H.W.; Kooy-Winkelaar, E.M.C.; Koning, F.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Fidder, H.H.; et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment for refractory luminal Crohn’s disease: Results of a phase I study. Gut 2010, 59, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, F.; Perico, N.; Cortinovis, F.C.M.; Remuzzi, N.P.G. Mesenchymal stromal cells in renal transplantation: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquesa, M.; Hoogduijn, M.J.; Reinders, M.E.J.; Eggenhofer, E.; Engela, A.U.; Mensah, F.K.; Torras, J.; Pileggi, A.; Van Kooten, C.; Mahon, B.P.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Solid Organ Transplantation (MiSOT) Fourth Meeting. Transplant. 2013, 96, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders, M.E.J.; Fibbe, W.E.; Rabelink, T.J. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in renal disease and kidney transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 25, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, E.M.; Prockop, D.J.; Fitzpatrick, L.A.; Koo, W.W.K.; Gordon, P.L.; Neel, M.; Sussman, M.; Orchard, P.; Marx, J.C.; Pyeritz, R.E.; et al. Transplantability and therapeutic effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, N.G.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Mechanisms of Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, W.; Jiang, J.; Arp, J.; Liu, W.; Garcia, B.; Wang, H. Regulatory T-Cell Generation and Kidney Allograft Tolerance Induced by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Associated With Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Expression. Transplantation 2010, 90, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Ting, J.; Alfonso, Z.; Strem, B.M.; Fraser, J.K.; Rutenberg, J.; Kuo, H.-C.; Pinkernell, K. Fresh and cryopreserved, uncultured adipose tissue-derived stem and regenerative cells ameliorate ischemia–reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 3874–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, R.; Lanzoni, G.; Stignani, M.; Campioni, D.; Alviano, F.; Ricci, F.; Tazzari, P.L.; Melchiorri, L.; Scalinci, S.Z.; Cuneo, A.; et al. A simple method for identifying bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells with a high immunosuppressive potential. Cytotherapy 2011, 13, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggenhofer, E.; Hoogduijn, M.J. Mesenchymal stem cell-educated macrophages. Transplant. Res. 2012, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hematti, P. Mesenchymal stem cell–educated macrophages: A novel type of alternatively activated macrophages. Exp. Hematol. 2009, 37, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qin, C.; Zheng, G.; Lai, D.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, G.; Ge, M.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Educated Macrophages Ameliorate LPS-Induced Systemic Response. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Okusa, M.D. Macrophages, Dendritic Cells, and Kidney Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2010, 30, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Huang, C.; Lin, Z.; Zhan, S.; Kong, L.; Fang, C.; Li, J. Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.I.G.; Moyon, B.; Coan, P.M.; Alfazema, N.; Venda, L.; Woollard, K.; Aitman, T.J. New Wistar Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rat transgenic models with ubiquitous expression of green fluorescent protein. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannam, S.; Bouffi, C.; Djouad, F.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells: Mechanisms and clinical applications. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2010, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggini, J.; Mirkin, G.; Bognanni, I.; Holmberg, J.; Piazzón, I.M.; Nepomnaschy, I.; Costa, H.; Cañones, C.; Raiden, S.; Vermeulen, M.; et al. Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Turn Activated Macrophages into a Regulatory-Like Profile. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, P.-C.; Chiu, L.-Y.; Srivastava, P.; Trento, C.; Dazzi, F.; Petretto, E.; Cook, H.T.; Behmoaras, J. Unique Regulatory Properties of Mesangial Cells Are Genetically Determined in the Rat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-H.K. Aging of mesenchymal stem cells: Implication in regenerative medicine. Regen. Ther. 2018, 9, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.H.; Rousche, K.T.; Tuan, R.S. Technology Insight: Adult stem cells in cartilage regeneration and tissue engineering. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2006, 2, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halme, J. Release of tumor necrosis factor-α by human peritoneal macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1989, 161, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Chi, M.; Laplace-Builhe, B.; Travnickova, J.; Luz-Crawford, P.; Tejedor, G.; Phan, Q.T.; Duroux-Richard, I.; Levraud, J.-P.; Kissa, K.; Lutfalla, G.; et al. Identification of polarized macrophage subsets in zebrafish. eLife 2015, 4, e07288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Ma, Y.; Iyer, R.P.; DeLeon-Pennell, K.Y.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Garrett, M.R.; Lindsey, M.L. IL-10 improves cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by stimulating M2 macrophage polarization and fibroblast activation. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2017, 112, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Sequence | Tm | Product Length (bp) | Concentration Used in PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPRT for | GCACGAGGGACTTACCTCAC | 63.7 °C | 128 bp | 100 nM |
| HPRT rev | TAATCACGACGCTGGGACTG | 66.2 °C | 128 bp | 100 nM |
| IL-10 for | TAAAAGCAAGGCAGTGGAGC | 64.3 °C | 147 bp | 100 nM |
| IL-10 rev | TGCCGGGTGGTTCAATTTTTC | 69.7 °C | 147 bp | 100 nM |
| TNFα for | ATGGGCTCCCTCTCATCAGT | 65 °C | 106 bp | 100 nM |
| TNFα rev | GCTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGAC | 64.5 °C | 106 bp | 100 nM |
| NOs-2 for | TCAGGCTTGGGTCTTGTTAGC | 65.4 °C | 110 bp | 100 nM |
| NOs-2 rev | GAAGAGAAACTTCCAGGGGCA | 66.5 °C | 110 bp | 100 nM |
| Mrc-1 for | TGATTCCGGTCGCTGTTCAA | 68.9 °C | 99 bp | 100 nM |
| Mrc-1 rev | GAACGGAGATGGCGCTTAGA | 66.5 °C | 99 bp | 100 nM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vallant, N.; Sandhu, B.; Hamaoui, K.; Prendecki, M.; Pusey, C.; Papalois, V. Immunomodulatory Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Can Vary in Genetically Modified Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031181
Vallant N, Sandhu B, Hamaoui K, Prendecki M, Pusey C, Papalois V. Immunomodulatory Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Can Vary in Genetically Modified Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031181
Chicago/Turabian StyleVallant, Natalie, Bynvant Sandhu, Karim Hamaoui, Maria Prendecki, Charles Pusey, and Vassilios Papalois. 2021. "Immunomodulatory Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Can Vary in Genetically Modified Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031181
APA StyleVallant, N., Sandhu, B., Hamaoui, K., Prendecki, M., Pusey, C., & Papalois, V. (2021). Immunomodulatory Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Can Vary in Genetically Modified Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031181







