Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Levels Are Associated with Progression of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
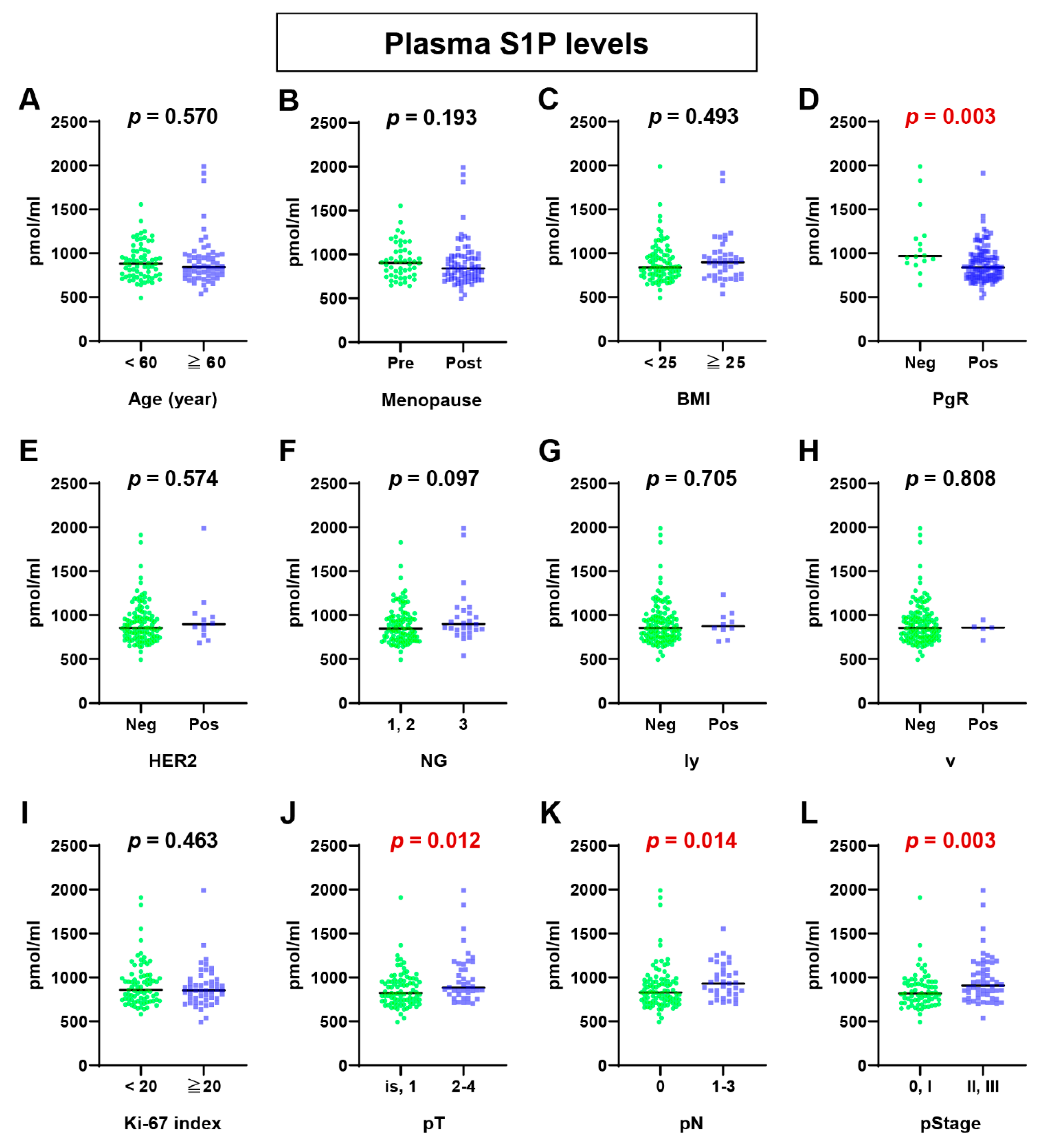
2.1. Plasma S1P Levels Were Higher in Advanced BC Patients
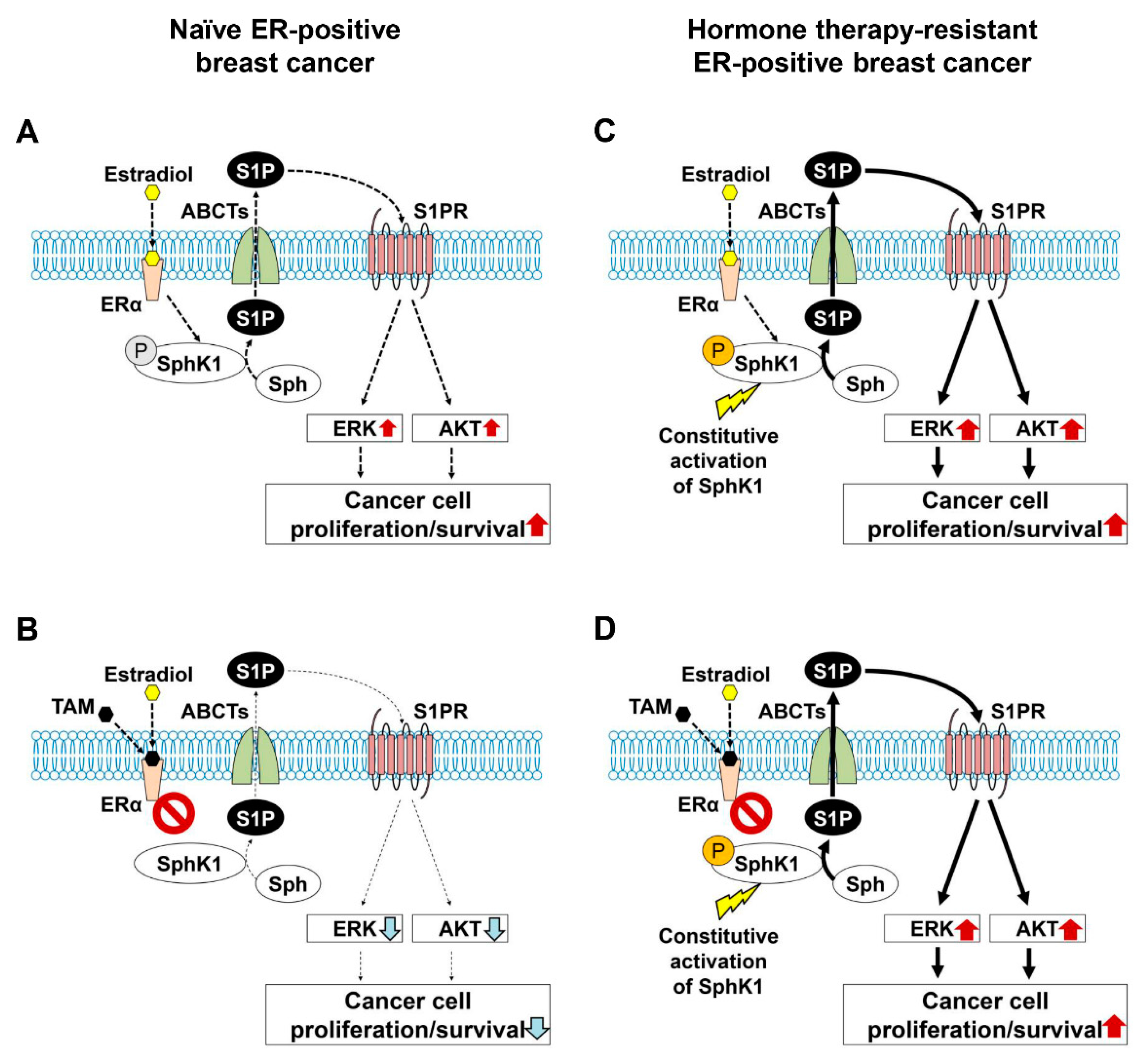
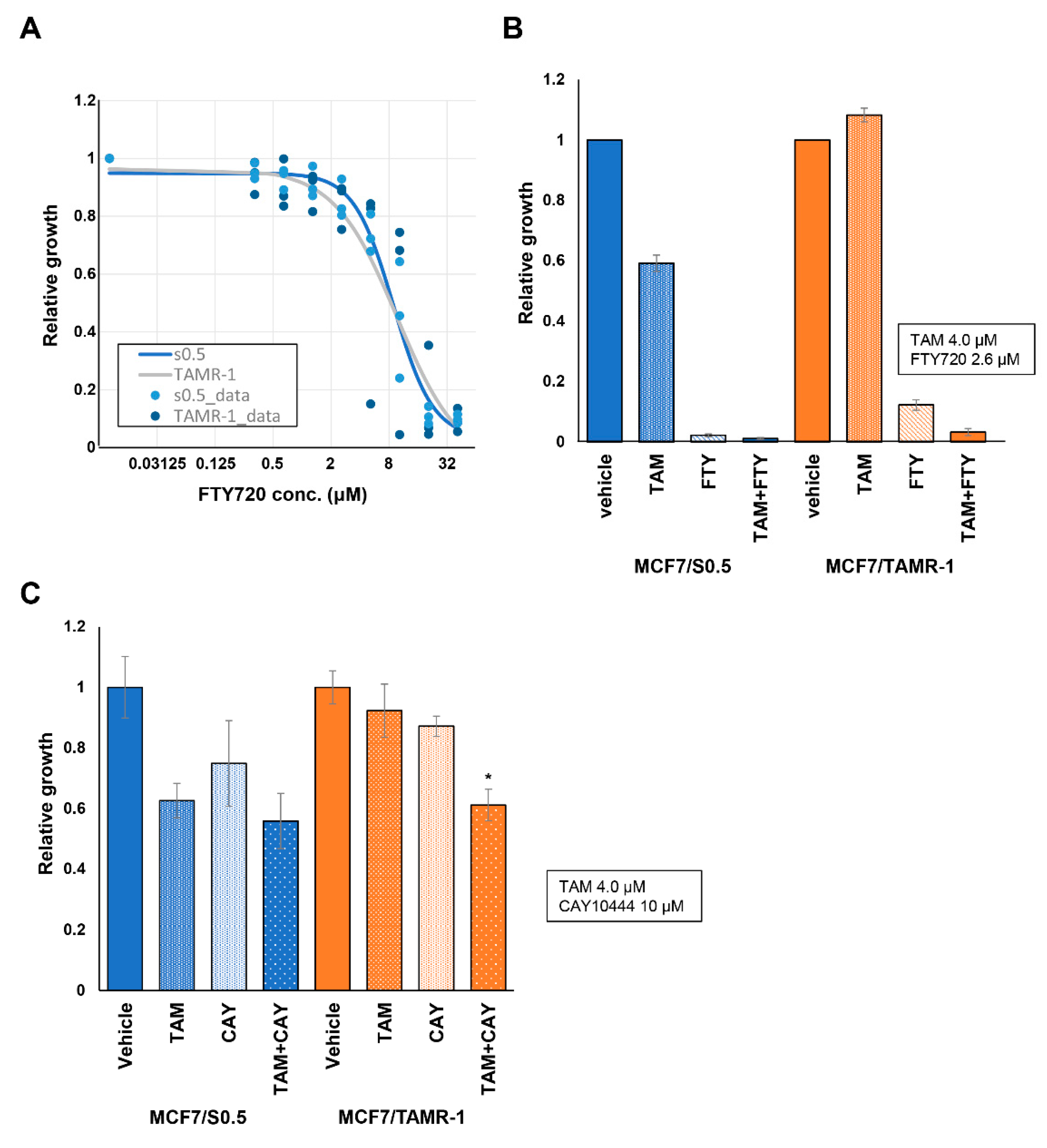
2.2. Possibility of Suppression of S1P Signaling in ER-Positive BC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasma Samples from BC Patients
4.2. Quantification of Sphingolipids by Mass Spectrometry
4.3. Comparison of Sphingolipid Levels in Plasma According to Clinicopathologic Characteristics of BC Patients
4.4. Cell Lines and Standard Culture Conditions
4.5. RNA Sequencing
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.P.; Massague, J. Cancer metastasis: Building a framework. Cell 2006, 127, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggio, A.I.; Varley, K.E.; Welm, A.L. The lingering mysteries of metastatic recurrence in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: An enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. The outs and the ins of sphingosine-1-phosphate in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogretmen, B.; Hannun, Y.A. Biologically active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahashi, M.; Takabe, K.; Terracina, K.P.; Soma, D.; Hirose, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Wakai, T. Sphingosine-1-phosphate transporters as targets for cancer therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 651727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, K.; Nagahashi, M.; Ramanathan, R.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. Resolvins and omega three polyunsaturated fatty acids: Clinical implications in inflammatory diseases and cancer. World J. Clin. Cases 2016, 4, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. Clinical Impact of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Breast Cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 2076239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moro, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsuchida, J.; Gabriel, E.; Qi, Q.; Yan, L.; Wakai, T.; Takabe, K.; Nagahashi, M. Ceramide species are elevated in human breast cancer and are associated with less aggressiveness. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19874–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moro, K.; Nagahashi, M.; Gabriel, E.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. Clinical application of ceramide in cancer treatment. Breast Cancer 2019, 26, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anelli, V.; Gault, C.R.; Snider, A.J.; Obeid, L.M. Role of sphingosine kinase-1 in paracrine/transcellular angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in vitro. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2727–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takabe, K.; Spiegel, S. Export of sphingosine-1-phosphate and cancer progression. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahashi, M.; Ramachandran, S.; Kim, E.Y.; Allegood, J.C.; Rashid, O.M.; Yamada, A.; Zhao, R.; Milstien, S.; Zhou, H.; Spiegel, S.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate produced by sphingosine kinase 1 promotes breast cancer progression by stimulating angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Kim, E.Y.; Harikumar, K.B.; Yamada, A.; Huang, W.C.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.C.; Price, M.M.; Avni, D.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate links persistent STAT3 activation, chronic intestinal inflammation, and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahashi, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Moro, K.; Tsuchida, J.; Soma, D.; Hirose, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Kosugi, S.; Takabe, K.; Komatsu, M.; et al. DNA damage response and sphingolipid signaling in liver diseases. Surg. Today 2016, 46, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahashi, M.; Yamada, A.; Miyazaki, H.; Allegood, J.C.; Tsuchida, J.; Aoyagi, T.; Huang, W.C.; Terracina, K.P.; Adams, B.J.; Rashid, O.M.; et al. Interstitial Fluid Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Murine Mammary Gland and Cancer and Human Breast Tissue and Cancer Determined by Novel Methods. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2016, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahashi, M.; Yamada, A.; Katsuta, E.; Aoyagi, T.; Huang, W.C.; Terracina, K.P.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.C.; Tsuchida, J.; Yuza, K.; et al. Targeting the SphK1/S1P/S1PR1 axis that links obesity, chronic inflammation and breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanyu, T.; Nagahashi, M.; Ichikawa, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Wakai, T. Expression of phosphorylated sphingosine kinase 1 is associated with diffuse type and lymphatic invasion in human gastric cancer. Surgery 2018, 163, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuza, K.; Nakajima, M.; Nagahashi, M.; Tsuchida, J.; Hirose, Y.; Miura, K.; Tajima, Y.; Abe, M.; Sakimura, K.; Takabe, K.; et al. Different Roles of Sphingosine Kinase 1 and 2 in Pancreatic Cancer Progression. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 232, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuza, K.; Nagahashi, M.; Shimada, Y.; Nakano, M.; Tajima, Y.; Kameyama, H.; Nakajima, M.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. Upregulation of phosphorylated sphingosine kinase 1 expression in colitis-associated cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 231, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, Y.; Nagahashi, M.; Katsuta, E.; Yuza, K.; Miura, K.; Sakata, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Shimada, Y.; Kameyama, H.; et al. Generation of sphingosine-1-phosphate is enhanced in biliary tract cancer patients and is associated with lymphatic metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuchida, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Nakajima, M.; Katsuta, E.; Rashid, O.M.; Qi, Q.; Yan, L.; Okuda, S.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. Sphingosine Kinase 1 is Associated With Immune Cell-Related Gene Expressions in Human Breast Cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 256, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, M.; Ichikawa, H.; Nagahashi, M.; Hanyu, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kano, Y.; Muneoka, Y.; Wakai, T. Phospho-Sphingosine Kinase 1 Expression in Lymphatic Spread of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 234, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Nagahashi, M.; Prasoon, P.; Hirose, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Sakata, J.; Abe, M.; Sakimura, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Butash, A.L.; et al. Dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolic enzymes leads to high levels of sphingosine-1-phospate and ceramide in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2021, 51, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitson, S.M.; Xia, P.; Leclercq, T.M.; Moretti, P.A.; Zebol, J.R.; Lynn, H.E.; Wattenberg, B.W.; Vadas, M.A. Phosphorylation-dependent translocation of sphingosine kinase to the plasma membrane drives its oncogenic signalling. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takabe, K.; Kim, R.H.; Allegood, J.C.; Mitra, P.; Ramachandran, S.; Nagahashi, M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Hait, N.C.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Estradiol induces export of sphingosine 1-phosphate from breast cancer cells via ABCC1 and ABCG2. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10477–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Ota, I.; Kimura, M.; Shimizu, D.; Tanabe, M.; Chishima, T.; Sasaki, T.; Ichikawa, Y.; Morita, S.; et al. High expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCC11 in breast tumors is associated with aggressive subtypes and low disease-free survival. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 137, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahashi, M.; Kim, E.Y.; Yamada, A.; Ramachandran, S.; Allegood, J.C.; Hait, N.C.; Maceyka, M.; Milstien, S.; Takabe, K.; Spiegel, S. Spns2, a transporter of phosphorylated sphingoid bases, regulates their blood and lymph levels, and the lymphatic network. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takabe, K.; Paugh, S.W.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. “Inside-out” signaling of sphingosine-1-phosphate: Therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matloubian, M.; Lo, C.G.; Cinamon, G.; Lesneski, M.J.; Xu, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Allende, M.L.; Proia, R.L.; Cyster, J.G. Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature 2004, 427, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.H.; Okada, T.; Matloubian, M.; Lo, C.G.; Cyster, J.G. S1P1 receptor signaling overrides retention mediated by G alpha i-coupled receptors to promote T cell egress. Immunity 2008, 28, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahashi, M.; Tsuchida, J.; Moro, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Tatsuda, K.; Woelfel, I.A.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. High levels of sphingolipids in human breast cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 204, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuchida, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Nakajima, M.; Moro, K.; Tatsuda, K.; Ramanathan, R.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. Breast cancer sphingosine-1-phosphate is associated with phospho-sphingosine kinase 1 and lymphatic metastasis. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 205, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nava, V.E.; Hobson, J.P.; Murthy, S.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase type 1 promotes estrogen-dependent tumorigenesis of breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 281, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Maceyka, M.; Hait, N.C.; Paugh, S.W.; Sankala, H.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase 1 is required for migration, proliferation and survival of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5313–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sukocheva, O.; Wadham, C.; Holmes, A.; Albanese, N.; Verrier, E.; Feng, F.; Bernal, A.; Derian, C.K.; Ullrich, A.; Vadas, M.A.; et al. Estrogen transactivates EGFR via the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor Edg-3: The role of sphingosine kinase-1. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukocheva, O.; Wadham, C.; Xia, P. Estrogen defines the dynamics and destination of transactivated EGF receptor in breast cancer cells: Role of S1P(3) receptor and Cdc42. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maczis, M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and estrogen signaling in breast cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2016, 60, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amin, M.B. (Ed.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C.; Long, J.S.; Orange, C.; Tannahill, C.L.; Mallon, E.; McGlynn, L.M.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J.; Edwards, J. High expression of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors, S1P1 and S1P3, sphingosine kinase 1, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 is associated with development of tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maczis, M.A.; Maceyka, M.; Waters, M.R.; Newton, J.; Singh, M.; Rigsby, M.F.; Turner, T.H.; Alzubi, M.A.; Harrell, J.C.; Milstien, S.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 activation by estrogen receptor alpha36 contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Tang, G.; Pogue-Geile, K.L.; Costantino, J.P.; Baehner, F.L.; Baker, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Watson, D.; Shak, S.; Bohn, O.L.; et al. Estrogen receptor (ESR1) mRNA expression and benefit from tamoxifen in the treatment and prevention of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dowsett, M.; Allred, C.; Knox, J.; Quinn, E.; Salter, J.; Wale, C.; Cuzick, J.; Houghton, J.; Williams, N.; Mallon, E.; et al. Relationship between quantitative estrogen and progesterone receptor expression and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) status with recurrence in the Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Placido, S.; De Laurentiis, M.; Carlomagno, C.; Gallo, C.; Perrone, F.; Pepe, S.; Ruggiero, A.; Marinelli, A.; Pagliarulo, C.; Panico, L.; et al. Twenty-year results of the Naples GUN randomized trial: Predictive factors of adjuvant tamoxifen efficacy in early breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoyagi, T.; Nagahashi, M.; Yamada, A.; Takabe, K. The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in breast cancer tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2012, 10, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takabe, K.; Yamada, A.; Rashid, O.M.; Adams, B.J.; Huang, W.C.; Aoyagi, T.; Nagahashi, M. Twofer anti-vascular therapy targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate for breast cancer. Gland Surg. 2012, 1, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Maceyka, M.; Strub, G.M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Singh, S.K.; Luo, C.; Marmorstein, R.; Kordula, T.; Milstien, S.; et al. Regulation of histone acetylation in the nucleus by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 2009, 325, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, R.; Raza, A.; Sturgill, J.; Lyon, D.; Young, J.; Hait, N.C.; Takabe, K. Paradoxical Association of Postoperative Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate with Breast Cancer Aggressiveness and Chemotherapy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5984819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuchida, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Rashid, O.M.; Takabe, K.; Wakai, T. At what age should screening mammography be recommended for Asian women? Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpino, G.; Weiss, H.; Lee, A.V.; Schiff, R.; De Placido, S.; Osborne, C.K.; Elledge, R.M. Estrogen receptor-positive, progesterone receptor-negative breast cancer: Association with growth factor receptor expression and tamoxifen resistance. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruckhaberle, E.; Rody, A.; Engels, K.; Gaetje, R.; von Minckwitz, G.; Schiffmann, S.; Grosch, S.; Geisslinger, G.; Holtrich, U.; Karn, T.; et al. Microarray analysis of altered sphingolipid metabolism reveals prognostic significance of sphingosine kinase 1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 112, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahashi, M.; Yamada, A.; Aoyagi, T.; Allegood, J.; Wakai, T.; Spiegel, S.; Takabe, K. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in the lymphatic fluid determined by novel methods. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, Y.; Lee, S.; Snyder, A.H.; Sheasley-O′neill, S.L.; Morris, M.A.; Setiady, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zigler, M.A.; Burcin, T.L.; Ley, K.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 2 is required for modulation of lymphocyte traffic by FTY720. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36865–36872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanna, M.G.; Wang, S.K.; Gonzalez-Cabrera, P.J.; Don, A.; Marsolais, D.; Matheu, M.P.; Wei, S.H.; Parker, I.; Jo, E.; Cheng, W.C.; et al. Enhancement of capillary leakage and restoration of lymphocyte egress by a chiral S1P1 antagonist in vivo. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pchejetski, D.; Bohler, T.; Brizuela, L.; Sauer, L.; Doumerc, N.; Golzio, M.; Salunkhe, V.; Teissie, J.; Malavaud, B.; Waxman, J.; et al. FTY720 (fingolimod) sensitizes prostate cancer cells to radiotherapy by inhibition of sphingosine kinase-1. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8651–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonelli, F.; Lim, K.G.; Loveridge, C.; Long, J.; Pitson, S.M.; Tigyi, G.; Bittman, R.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J. FTY720 and (S)-FTY720 vinylphosphonate inhibit sphingosine kinase 1 and promote its proteasomal degradation in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle, breast cancer and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.G.; Tonelli, F.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Bittman, R.; Pyne, S.; Pyne, N.J. FTY720 analogues as sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitors: Enzyme inhibition kinetics, allosterism, proteasomal degradation, and actin rearrangement in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 18633–18640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paugh, S.W.; Payne, S.G.; Barbour, S.E.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. The immunosuppressant FTY720 is phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase type 2. FEBS Lett. 2003, 554, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hait, N.C.; Avni, D.; Yamada, A.; Nagahashi, M.; Aoyagi, T.; Aoki, H.; Dumur, C.I.; Zelenko, Z.; Gallagher, E.J.; Leroith, D.; et al. The phosphorylated prodrug FTY720 is a histone deacetylase inhibitor that reactivates ERalpha expression and enhances hormonal therapy for breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2015, 4, e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | |
| <60 | 68 (54%) |
| ≥60 | 58 (46%) |
| Menopausal status | |
| Premenopause | 50 (40%) |
| Postmenopause | 75 (59%) |
| N.D. | 1 (1%) |
| Body mass index | |
| <25 | 85 (67%) |
| ≥25 | 41 (33%) |
| Estrogen receptor expression | |
| Negative | 0 (0%) |
| Positive | 126 (100%) |
| Progesterone receptor expression | |
| Negative | 16 (13%) |
| Positive | 110 (87%) |
| HER2 overexpression/amplification | |
| Negative | 107 (85%) |
| Positive | 12 (10%) |
| N.D. | 7 (6%) |
| NSAS nuclear grade | |
| 1 | 73 (58%) |
| 2 | 24 (19%) |
| 3 | 27 (21%) |
| N.D. | 2 (2%) |
| Lymphatic invasion (ly) | |
| Absent | 116 (92%) |
| Present | 10 (8%) |
| Venous invasion (v) | |
| Absent | 121 (96%) |
| Present | 5 (4%) |
| Ki-67 labeling index | |
| <20 | 77 (61%) |
| ≥20 | 49 (39%) |
| Pathological primary tumor (pT) category * | |
| pTis | 19 (15%) |
| pT1 | 65 (52%) |
| pT2 | 32 (25%) |
| pT3 | 9 (7%) |
| pT4 | 1 (1%) |
| Pathological regional lymph node (pN) category * | |
| pN0 | 90 (72%) |
| pN1 | 23 (18%) |
| pN2 | 8 (6%) |
| pN3 | 4 (3%) |
| pNX | 1 (1%) |
| Pathological stage (pStage) * | |
| pStage 0 | 19 (15%) |
| pStage I | 50 (39%) |
| pStage II | 41 (33%) |
| pStage III | 15 (12%) |
| N.D. | 1 (1%) |
| DHS1P (pmol/mL) | Sph (pmol/mL) | DHSph (pmol/mL) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Median | (IQR) | p | Median | (IQR) | p | Median | (IQR) | p | |
| Age (year) | 0.573 | 0.200 | 0.795 | |||||||
| 60 | 68 | 181.5 | (52.4) | 20.30 | (10.0) | 14.53 | (7.31) | |||
| ≥60 | 58 | 169.3 | (68.3) | 18.65 | (8.02) | 13.74 | (6.54) | |||
| Menopause | 0.823 | 0.051 | 0.774 | |||||||
| Premenopause | 50 | 179.7 | (57.3) | 21.65 | (10.59) | 14.48 | (6.88) | |||
| Postmenopause | 75 | 172.4 | (60.5) | 18.65 | (8.22) | 14.00 | (6.70) | |||
| Body mass index | 0.630 | 0.409 | 0.452 | |||||||
| 25 | 85 | 184.6 | (62.6) | 19.77 | (9.47) | 13.32 | (7.41) | |||
| ≥25 | 41 | 168.8 | (55.4) | 18.65 | (8.31) | 14.83 | (6.39) | |||
| PgR expression | 0.069 | 0.369 | 0.026 | |||||||
| Negative | 16 | 201.6 | (56.2) | 21.83 | (9.79) | 16.54 | (6.92) | |||
| Positive | 110 | 175.5 | (59.1) | 19.02 | (8.74) | 13.42 | (6.97) | |||
| HER2 expression | 0.934 | 0.196 | 0.873 | |||||||
| Negative | 107 | 182.2 | (60.0) | 19.07 | (8.91) | 14.11 | (6.70) | |||
| Positive | 12 | 168.5 | (69.3) | 18.11 | (6.93) | 12.43 | (8.31) | |||
| NSAS nuclear grade | 0.029 | 0.104 | 0.085 | |||||||
| 1, 2 | 97 | 169.7 | (61.4) | 18.92 | (7.98) | 13.36 | (7.04) | |||
| 3 | 27 | 195.5 | (49.9) | 23.50 | (13.1) | 15.78 | (8.92) | |||
| Lympatic invasion | 0.518 | 0.468 | 0.281 | |||||||
| Negative | 116 | 179.3 | (62.8) | 19.49 | (8.89) | 13.74 | (7.08) | |||
| Positive | 10 | 189.3 | (61.3) | 16.66 | (8.98) | 15.88 | (5.06) | |||
| Vascular invasion | 0.151 | 0.942 | 0.372 | |||||||
| Negative | 121 | 182.2 | (62.6) | 19.23 | (8.98) | 14.00 | (6.78) | |||
| Positive | 5 | 161.6 | (28.4) | 18.65 | (9.44) | 15.83 | (8.68) | |||
| Ki-67 labeling index | 0.568 | 0.667 | 0.897 | |||||||
| 20 | 77 | 181.9 | (58.4) | 19.23 | (8.45) | 14.46 | (6.32) | |||
| ≥20 | 49 | 176.7 | (64.9) | 18.86 | (12.44) | 14.11 | (7.46) | |||
| pT | 0.066 | 0.332 | 0.261 | |||||||
| is, 1 | 85 | 177.3 | (58.4) | 18.75 | (9.26) | 13.48 | (7.28) | |||
| 2–4 | 41 | 193.1 | (69.8) | 20.19 | (7.17) | 15.31 | (6.83) | |||
| pN | 0.347 | 0.024 | 0.319 | |||||||
| 0 | 90 | 176.7 | (62.0) | 18.83 | (8.63) | 13.34 | (8.42) | |||
| 1–3 | 35 | 184.4 | (60.3) | 20.83 | (10.25) | 15.54 | (6.64) | |||
| pStage | 0.036 | 0.037 | 0.241 | |||||||
| 0, I | 69 | 168.8 | (61.5) | 18.54 | (9.45) | 12.84 | (7.29) | |||
| II, III | 56 | 186.1 | (60.3) | 20.45 | (7.57) | 15.28 | (7.25) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikarashi, M.; Tsuchida, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Takeuchi, S.; Moro, K.; Toshikawa, C.; Abe, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Shimada, Y.; Sakata, J.; et al. Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Levels Are Associated with Progression of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413367
Ikarashi M, Tsuchida J, Nagahashi M, Takeuchi S, Moro K, Toshikawa C, Abe S, Ichikawa H, Shimada Y, Sakata J, et al. Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Levels Are Associated with Progression of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(24):13367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413367
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkarashi, Mayuko, Junko Tsuchida, Masayuki Nagahashi, Shiho Takeuchi, Kazuki Moro, Chie Toshikawa, Shun Abe, Hiroshi Ichikawa, Yoshifumi Shimada, Jun Sakata, and et al. 2021. "Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Levels Are Associated with Progression of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 24: 13367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413367
APA StyleIkarashi, M., Tsuchida, J., Nagahashi, M., Takeuchi, S., Moro, K., Toshikawa, C., Abe, S., Ichikawa, H., Shimada, Y., Sakata, J., Koyama, Y., Sato, N., Hait, N. C., Ling, Y., Okuda, S., Takabe, K., & Wakai, T. (2021). Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Levels Are Associated with Progression of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(24), 13367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413367







