Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation by Wogonin Attenuates Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 via Targeting pqs Quorum-Sensing System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
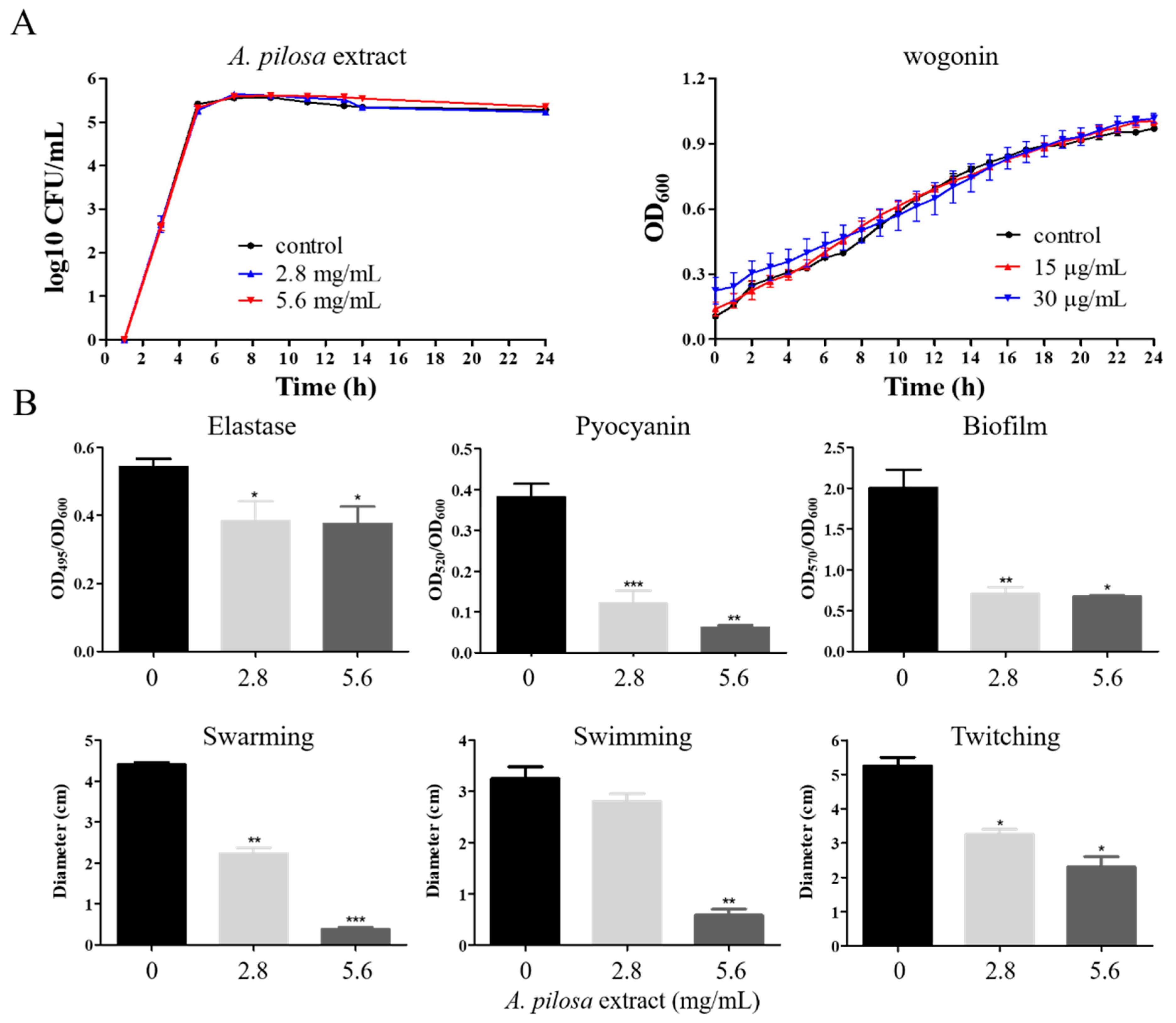
2.1. Inhibition of P. aeruginosa Virulence and Pathogenicity by the Crude Extracts of A. pilosa
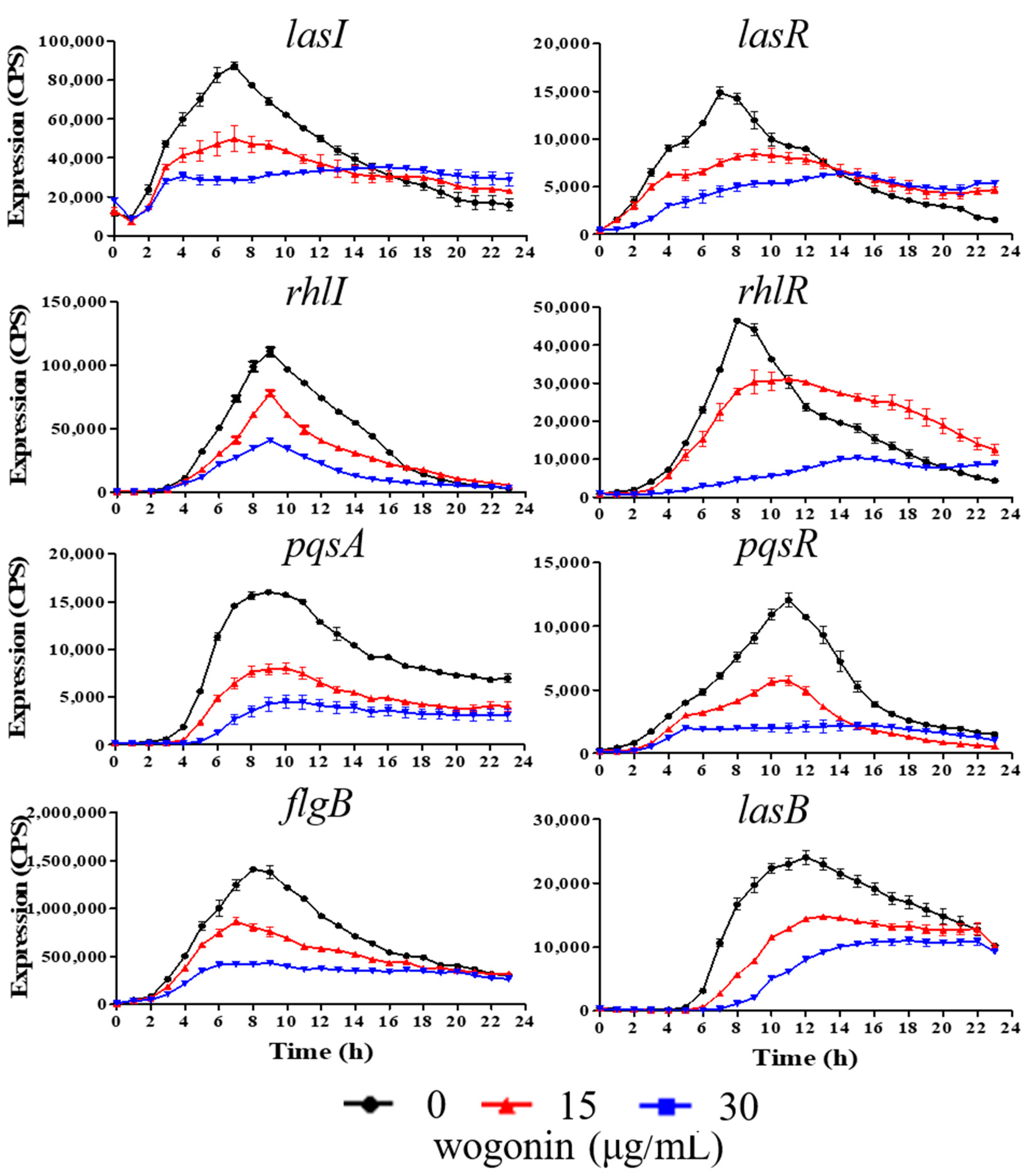
2.2. Wogonin Inhibited QS-Regulated Genes in P. aeruginosa PAO1
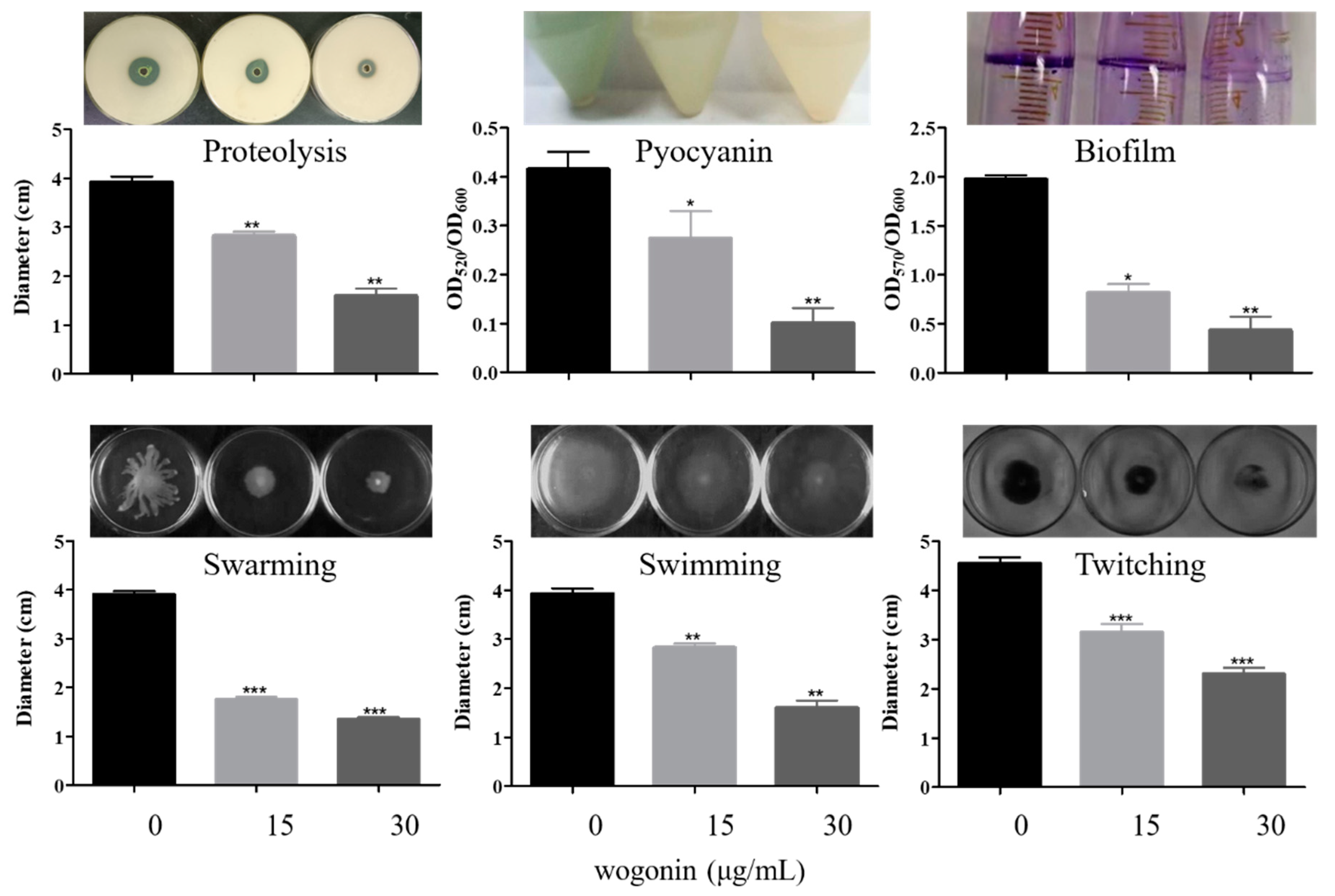
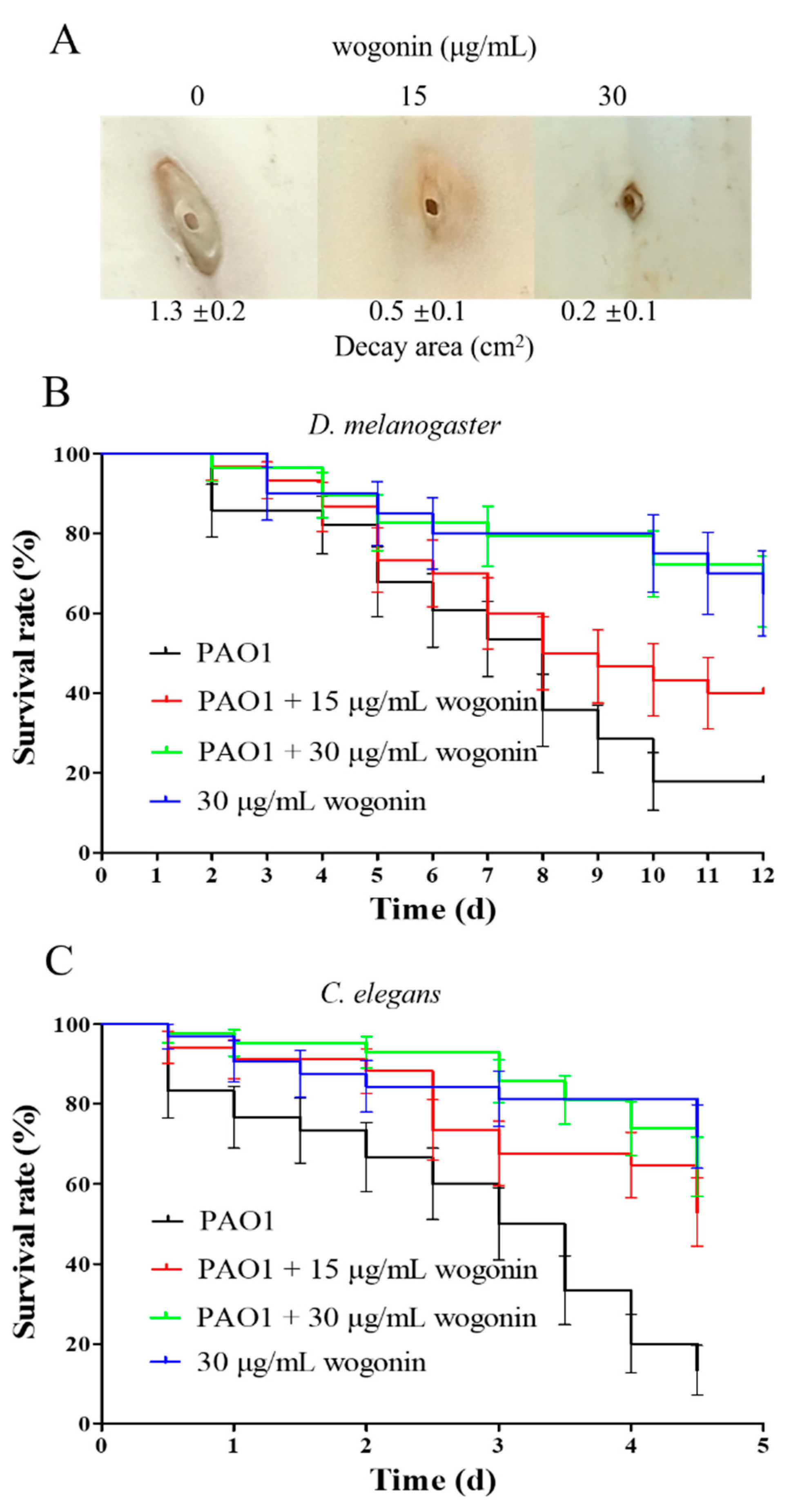
2.3. Inhibition of P. aeruginosa Virulence and Pathogenicity by Wogonin
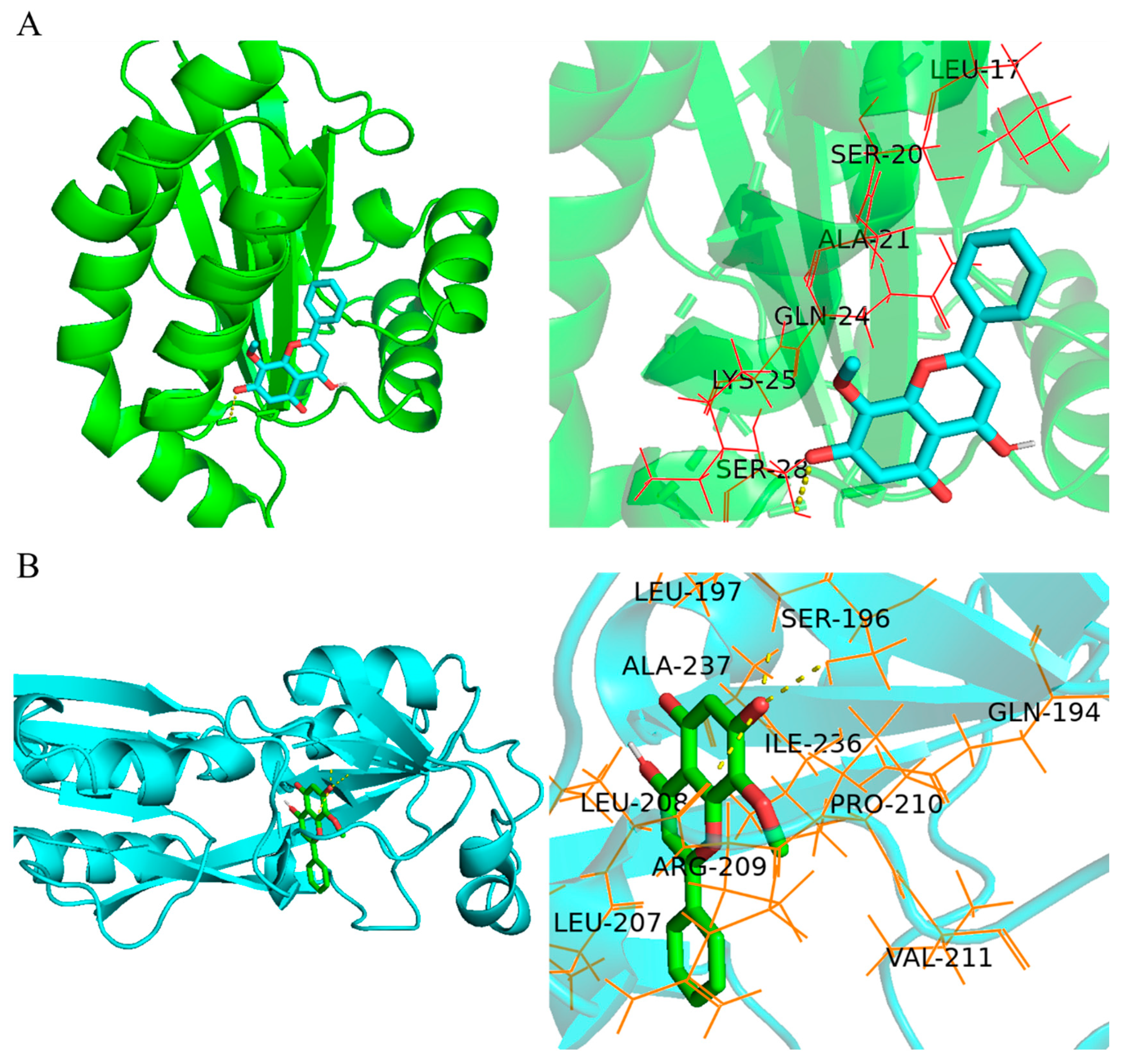
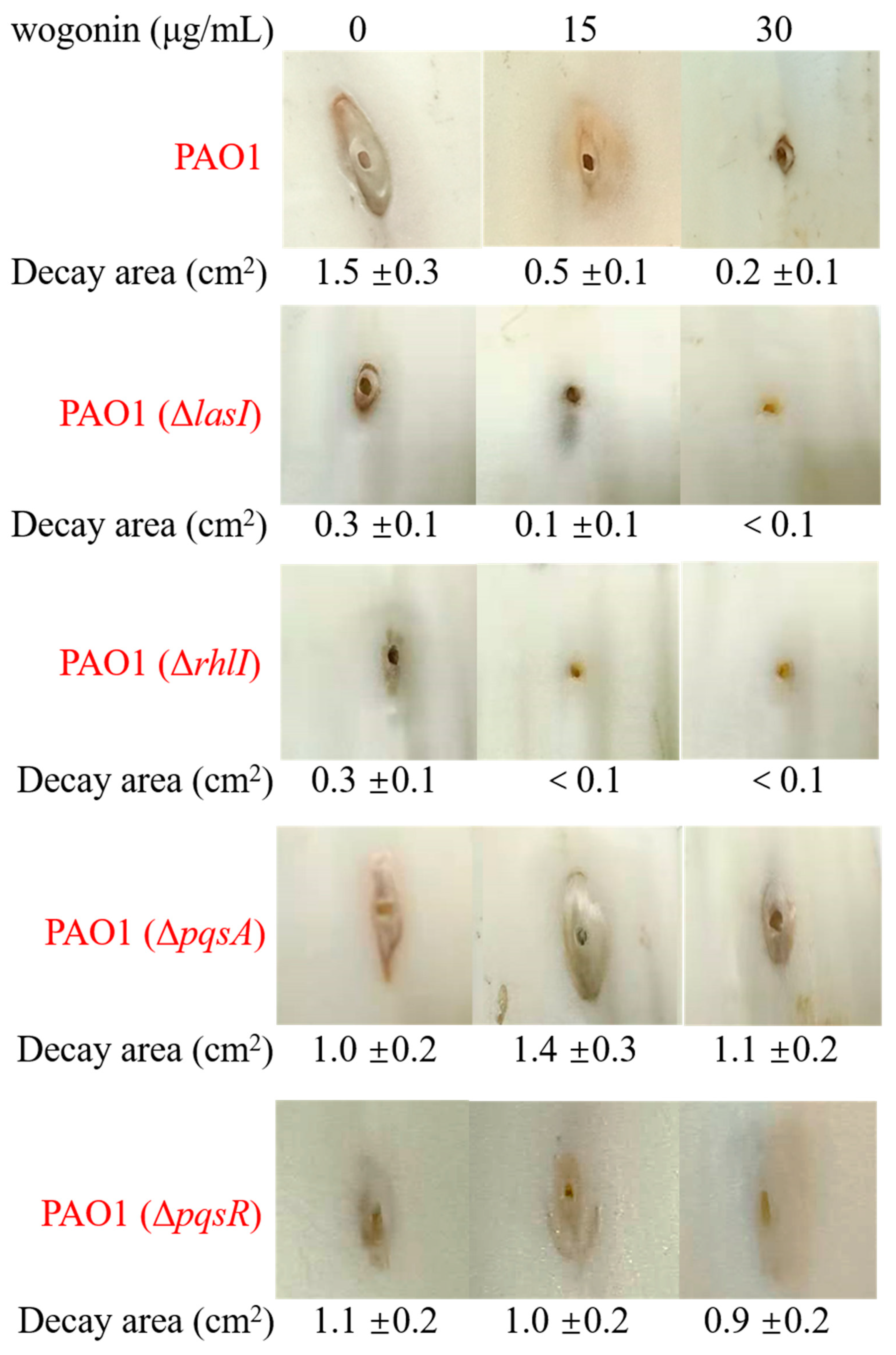
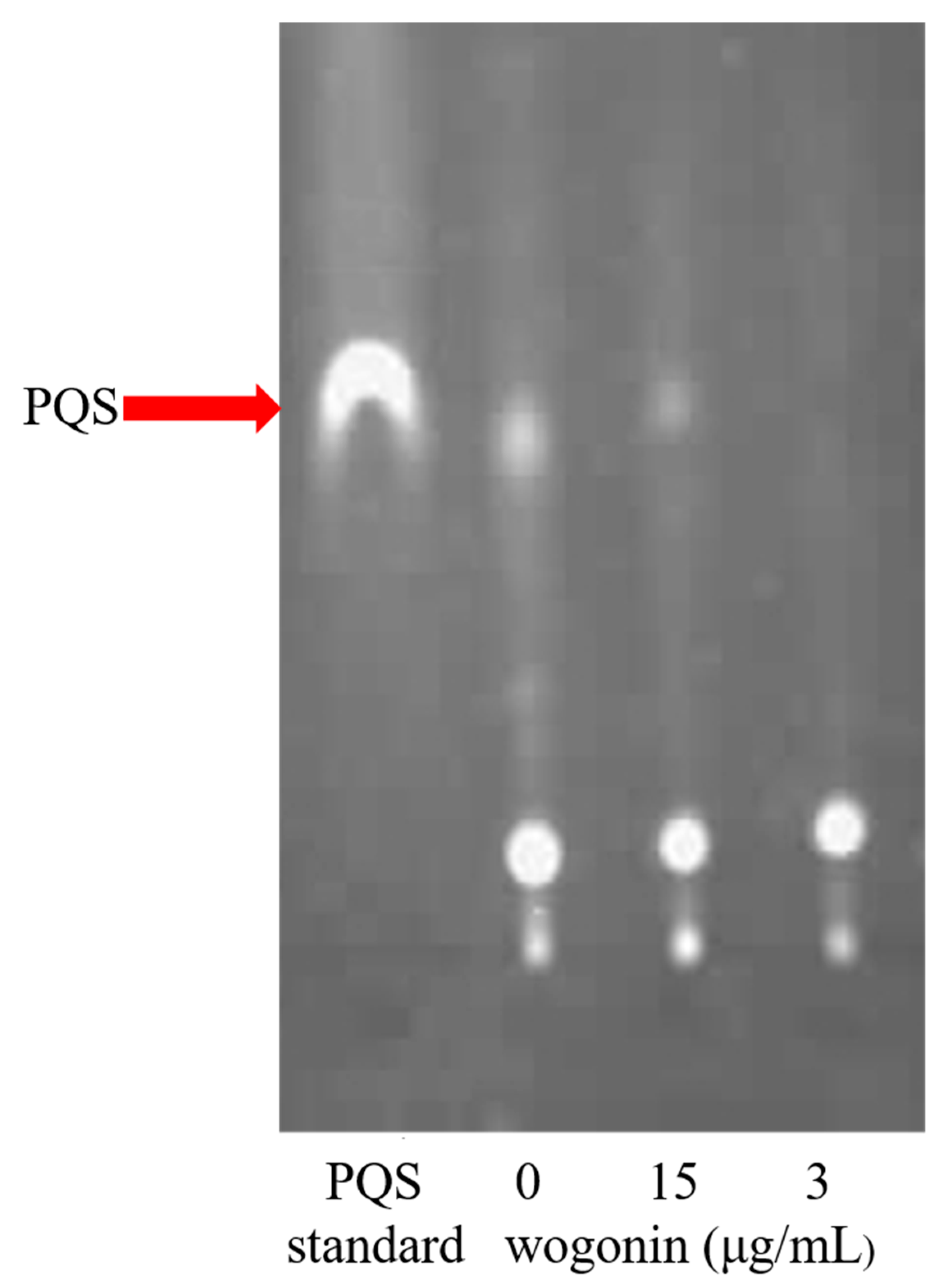
2.4. Wogonin Mainly Affected the pqs System of P. aeruginosa PAO1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Culture Conditions
4.2. Active Substance Extraction of Traditional Chinese Medicinal Herbs
4.3. Gene Expression Assay
4.4. Measurement of Virulence Factors
4.4.1. Pyocyanin
4.4.2. Biofilm Formation
4.4.3. Proteolytic Enzyme
4.4.4. Motility
4.4.5. Elastase
4.4.6. Exopolysaccharide Production Assay
4.4.7. Rhamnolipid Measurement
4.5. In Vivo Pathogenicity Assay
4.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4.7. PQS Signal Molecule Production Assay
4.8. Construction and Complementation of In-Frame Deletion Mutants
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, G.W.; Hassett, D.J.; Ran, H.; Kong, F. The role of pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usher, L.R.; Lawson, R.A.; Geary, I.; Taylor, C.J.; Bingle, C.D.; Taylor, G.W.; Taylor, G.; Whyte, M.K.B. Induction of neutrophil apoptosis by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin pyocyanin: A potential mechanism of persistent infection. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moradali, M.F.; Ghods, S.; Rehm, B.H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lifestyle: A Paradigm for Adaptation, Survival, and Persistence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.F. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 276–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkina, M.V.; Vikstrom, E. Bacteria-Host Crosstalk: Sensing of the Quorum in the Context of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. J. Innate Immun. 2019, 11, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, R.T.; Blasco, L.; Ambroa, A.; Gonzalez-Pedrajo, B.; Fernandez-Garcia, L.; Lopez, M.; Bleriot, I.; Bou, G.; García-Contreras, R.; Wood, T.K.; et al. Relationship Between Quorum Sensing and Secretion Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura-Alves, P.; Puyskens, A.; Stinn, A.; Klemm, M.; Guhlich-Bornhof, U.; Dorhoi, A.; Furkert, J.; Kreuchwig, A.; Protze, J.; Lozza, L.; et al. Host monitoring of quorum sensing during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Science 2019, 366, eaaw1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, P. Putting an end to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa IQS controversy. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, e962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuster, M.; Greenberg, E.P. A network of networks: Quorum-sensing gene regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, V. Regulation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pesci, E.C.; Milbank, J.B.J.; Pearson, J.P.; McKnight, S.; Kende, A.S.; Greenberg, E.; Iglewski, B.H. Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11229–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diggle, S.P.; Matthijs, S.; Wright, V.J.; Fletcher, M.P.; Chhabra, S.R.; Lamont, I.; Kong, X.; Hider, R.; Cornelis, P.; Cámara, M.; et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-Quinolone Signal Molecules HHQ and PQS Play Multifunctional Roles in Quorum Sensing and Iron Entrapment. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beury-Cirou, A.; Tannières, M.; Minard, C.; Soulère, L.; Rasamiravaka, T.; Dodd, R.H.; Queneau, Y.; Dessaux, Y.; Guillou, C.; Vandeputte, O.M.; et al. At a supra-physiological concentration, human sexual hormones act as quorum-sensing inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83564. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumari, J.; Borkotoky, S.; Reddy, D.; Mohanty, S.K.; Kumavath, R.; Murali, A.; Suchiang, K.; Busi, S. Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: Insights from in vitro, in vivo and in silico studies. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 226, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, X.; Fu, J. Effect of Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine with Antiquorum Sensing Activity on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 648257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Rudden, M.; Smyth, T.J.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Natural quorum sensing inhibitors effectively downregulate gene expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3521–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Priya, K.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G. Anti-quorum sensing activity of the traditional Chinese herb, Phyllanthus amarus. Sensors 2013, 13, 14558–14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Bhasme, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.Z.; Li, Y. Chinese medicinal herb extract inhibits PQS-mediated quorum sensing system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Chen, W. Okanin in Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt is a major quorum-sensing inhibitor against Chromobacterium violaceum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 260, 113017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Hao, S.; Zhao, L.; Shi, F.; Ye, G.; Zou, Y.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Yin, Z.; He, X.; et al. Paeonol Attenuates Quorum-Sensing Regulated Virulence and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 692474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Yin, M.; Wu, K.; Lu, G.; Deng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, L.; Jia, X.; Ding, Y.; Gong, W.; et al. High-dose wogonin exacerbates DSS-induced colitis by up-regulating effector T cell function and inhibiting Treg cell. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sully, E.K.; Malachowa, N.; Elmore, B.O.; Alexander, S.M.; Femling, J.K.; Gray, B.M.; DeLeo, F.; Otto, M.; Cheung, A.L.; Edwards, B.S.; et al. Selective chemical inhibition of agr quorum sensing in Staphylococcus aureus promotes host defense with minimal impact on resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quave, C.L.; Lyles, J.T.; Kavanaugh, J.S.; Nelson, K.; Parlet, C.P.; Crosby, H.A.; Heilmann, K.P.; Horswill, A.R. Castanea sativa (European Chestnut) Leaf Extracts Rich in Ursene and Oleanene Derivatives Block Staphylococcus aureus Virulence and Pathogenesis without Detectable Resistance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mok, N.; Chan, S.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Chua, S.L. Vanillin inhibits PqsR-mediated virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6496–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.W.; Luo, H.Z.; Jiang, H.; Jian, T.K.; Chen, Z.Q.; Jia, A.Q. Hordenine: A Novel Quorum Sensing Inhibitor and Antibiofilm Agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, F.M.; Ahmad, I.; Al-Thubiani, A.S.; Abulreesh, H.H.; AlHazza, I.M.; Aqil, F. Leaf Extracts of Mangifera indica L. Inhibit Quorum Sensing—Regulated Production of Virulence Factors and Biofilm in Test Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, P.; Oliveira, J.; Fernandes, I.; Araújo, P.; Pereira, A.; Gameiro, P.; Bessa, L. Pyranoanthocyanins Interfering with the Quorum Sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.R.; Zeng, T.H.; Yao, J.W.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Xie, X.B.; Shi, Q.S. Diallyl sulfide from garlic suppresses quorum-sensing systems of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and enhances biosynthesis of three B vitamins through its thioether group. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sass, A.; Van Acker, H.; Wille, J.; Verhasselt, B.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Kaever, V.; Crabbé, A.; Coenye, T. Coumarin Reduces Virulence and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Affecting Quorum Sensing, Type III Secretion and C-di-GMP Levels. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.Y.; Yu, Q.M.; Kong, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, K.M.; Seo, J.S. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. Extract. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 8571207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Wang, H.; Kong, X.; Duan, R.; Dong, T.T.X.; Tsim, K.W.K. Flavonoids are identified from the extract of Scutellariae Radix to suppress inflammatory-induced angiogenic responses in cultured RAW 264.7 macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, J.P.; Pesci, E.C.; Iglewski, B.H. Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum-sensing systems in control of elastase and rhamnolipid biosynthesis genes. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5756–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brint, J.M.; Ohman, D.E. Synthesis of multiple exoproducts in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is under the control of RhlR-RhlI, another set of regulators in strain PAO1 with homology to the autoinducer-responsive LuxR-LuxI family. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 7155–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Li, L.; Kong, W.; Shen, L.; Duan, K. Identification of a novel regulator of the quorum-sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 293, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, K.; Dammel, C.; Stein, J.; Rabin, H.; Surette, M.G. Modulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa gene expression by host microflora through interspecies communication. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, T.T.; Karkhoff-Schweizer, R.R.; Kutchma, A.J.; Schweizer, H.P. A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: Application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 1998, 212, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditta, G.; Stanfield, S.; Corbin, D.; Helinski, D.R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: Construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7347–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, K.; Surette, M.G. Environmental regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Las and Rhl quorum-sensing systems. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 4827–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Li, L.; Dong, Z.; Surette, M.G.; Duan, K. The YebC family protein PA0964 negatively regulates the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal system and pyocyanin production. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6217–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoang, T.T.; Kutchma, A.J.; Becher, A.; Schweizer, H.P. Integration-proficient plasmids for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Site-specific integration and use for engineering of reporter and expression strains. Plasmid 2000, 43, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, K.; Neshat, S.; Krebes, K.; Heinrichs, D.E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the ferripyoverdine receptor gene fpvA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 4597–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becher, A.; Schweizer, H.P. Integration-proficient Pseudomonas aeruginosa vectors for isolation of single-copy chromosomal lacZ and lux gene fusions. BioTechniques 2000, 29, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Essar, D.W.; Eberly, L.; Hadero, A.; Crawford, I.P. Identification and characterization of genes for a second anthranilate synthase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Interchangeability of the two anthranilate synthases and evolutionary implications. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Hwang, H.M.; Aker, W.G.; Wang, P.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, X.; He, X. Synergistic combination of marine oligosaccharides and azithromycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Q.; Yan, L.; Ai, G.; Liu, H.; Ma, L.Z. Coordination of swarming motility, biosurfactant synthesis, and biofilm matrix exopolysaccharide production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6724–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohman, D.E.; Cryz, S.J.; Iglewski, B.H. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J. Bacteriol. 1980, 142, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberto, M.C.; Matera, G.; Quirino, A.; Lamberti, A.G.; Capicotto, R.; Puccio, R.; Barreca, G.S.; Focà, E.; Cascio, A.; Focà, A. Phenotypic and genotypic evaluation of slime production by conventional and molecular microbiological techniques. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fito-Boncompte, L.; Chapalain, A.; Bouffartigues, E.; Chaker, H.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Gicquel, G.; Bazire, A.; Madi, A.; Connil, N.; Véron, W.; et al. Full Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Requires OprF. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chugani, S.A.; Whiteley, M.; Lee, K.M.; D’Argenio, D.; Manoil, C.; Greenberg, E.P. QscR, A modulator of quorum-sensing signal synthesis and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2752–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarabhai, S.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. Ellagic acid derivatives from Terminalia chebula Retz. downregulate the expression of quorum sensing genes to attenuate Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 virulence. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajkumari, J.; Borkotoky, S.; Murali, A.; Suchiang, K.; Mohanty, S.K.; Busi, S. Attenuation of quorum sensing controlled virulence factors and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by pentacyclic triterpenes, betulin and betulinic acid. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfee, M.W.; Coleman, J.P.; Pesci, E.C. Interference with Pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis inhibits virulence factor expression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11633–11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Surette, M.; Duan, K. Characterization of a cryptic plasmid from Pseudomonas sp. and utilization of its temperature-sensitive derivatives for genetic manipulation. Plasmid 2010, 64, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chinese Medicinal Herbs | Extraction Solvent a | Concentration (mg/mL) | lasRb | lasI | rhlR | rhlI | pqsH | phzM | phzA1 | phzA2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agrimonia pilosa | water | 56 | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | - | ↑ | - | ↓ | ↓ |
| ethanol | 27 | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | - | - | ↓ | - | ↓ | |
| Sargentodoxa cuneata | water | 88 | - | - | ↓ | - | - | ↓ | - | - |
| ethanol | 34 | - | - | ↑ | - | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | - | |
| Ash bark | water | 60 | - | - | ↓ | - | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | - |
| ethanol | 13.4 | - | - | - | - | ↓ | - | - | - | |
| Rhizoma paridis | water | 78 | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | - | - | ↑ | - | - |
| ethanol | 47 | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | - | - | |
| Herba asari | water | 182 | - | - | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| ethanol | 17.5 | - | - | - | - | ↓ | - | - | - | |
| Stephania tetrandra | water | 40 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ethanol | 14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Lonicerae japonicae | water | 108 | - | ↑ | ↑ | - | - | ↑ | - | ↑ |
| ethanol | 36 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | - | |
| Tussilago farfart | water | 202 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | - |
| ethanol | 44 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | - | |
| Isatidids folium | water | 350 | - | - | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| ethanol | 34 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Balloon flower | water | 330 | - | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| ethanol | 52 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | |
| Radix arnebiae | water | 10 | ↓ | - | - | ↓ | - | ↓ | - | - |
| ethanol | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Hedyotis diffusa | water | 104 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ethanol | 12.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Herba lobeliae | water | 186 | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | - | ↑ | - | - | - |
| ethanol | 18 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | |
| Dwarf lilyturf | water | 396 | - | - | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| ethanol | 50 | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | - | - | |
| Pulsa tilia radix | water | 68 | - | - | - | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | - | - |
| ethanol | 40 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Subprostrate sophra | water | 106 | - | ↑ | ↑ | - | ↑ | - | - | - |
| ethanol | 35 | - | - | - | - | - | ↓ | ↓ | - | |
| Asteris rasix | water | 288 | ↑ | ↑ | - | - | ↓ | ↓ | - | - |
| ethanol | 73 | - | ↓ | - | - | - | - | ↓ | ↓ | |
| Cortex dictamni | water | 170 | - | - | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| ethanol | 34 | - | - | ↑ | - | ↓ | - | - | - |
| Strains/Plasmids | Description | Source or Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| E. coli DH10B | F– mcrA Δ(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) φ80dlacZ ΔM15 ΔlacX74 recA1 araΔ139 Δ(ara leu)7697 galU galK rpsL (StrR) endA1 nupG | Invitrogen |
| PAO1 | P. aeruginosa wild type strain | This lab |
| PAO1 (ΔlasI) | lasI deletion mutant of PAO1 | [36] |
| PAO1 (ΔrhlI) | rhlI deletion mutant of PAO1 | [37] |
| PAO1 (ΔpqsA) | pqsA deletion mutant of PAO1 | This study |
| PAO1 (ΔpqsR) | pqsR deletion mutant of PAO1 | [38] |
| ΔpqsA/CTX-pqsA | CTX-pqsA integrated into PAO1(ΔpqsA) chromosome; Tcr | This study |
| ΔpqsA/pAK-pqsA/CTX-pqsA | ΔpqsA/CTX-pqsA complemented by plasmid pAK-pqsA; Cbr | This study |
| ΔpqsR/CTX-pqsA | CTX-pqsA integrated into PAO1(ΔpqsR) chromosome; Tcr | This study |
| ΔpqsR/pAK-pqsR/CTX-pqsA | ΔpqsR/CTX-pqsA complemented by plasmid pAK-pqsR; Cbr | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pMS402 | Expression reporter vector carrying the promoterless luxCDABE; Kanr, Tmpr | [39] |
| pEX18-Tc | Broad host range gene replacement vector; sacB, Tcr | [40] |
| pRK2013 | Broad host range helper vector; Traþ, Kanr | [41] |
| pKD-lasI | pMS402-containing lasI promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | [42] |
| pKD-lasR | pMS402-containing lasR promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | [42] |
| pKD-lasB | pMS402-containing lasB promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | This lab |
| pKD-rhlI | pMS402-containing rhlI promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | [42] |
| pKD-rhlR | pMS402-containing rhlR promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | [42] |
| pKD-rhlA | pMS402-containing rhlA promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | This lab |
| pKD-pqsA | pMS402-containing pqsA promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | [43] |
| pKD-pqsR | pMS402-containing pqsR promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | [43] |
| pKD-flgB | pMS402-containing flgB promoter region; Kanr, Tmpr | This lab |
| mini-CTX-lacZ | Integration plasmid-containing attP site for integration at chromosomal attB site; Tcr | [44] |
| CTX-pqsA | mini-CTX-lacZ-containing pqsA gene region | This study |
| pAK1900 | E. coli-P. aeruginosa shuttle cloning vector carrying plac upstream of MCS; Ampr, Cbr | [45] |
| pAK-pqsA | pAK1900-containing pqsA gene region | This study |
| pAK-pqsR | pAK1900-containing pqsR gene region | This study |
| Primers | Sequence (5′→3′) | Restriction Sites | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| pKD-pqsA-up | CATCTCGAGCCAGGGTCAGTGTCC | Xho I | Luminous reporter construction |
| pKD-pqsA-down | TGTGGATCCCAGAACCTCGGTCAG | BamH I | Luminous reporter construction |
| pqsA-up1 | CAGGAAACAGCTATGACCATGATTACGAAGTACCTTGGAAGTCGAGC | - | pqsA knockout |
| pqsA-down1 | CAACATGCCCGTTCCTCGGAACAGAACCTCGGTC | - | pqsA knockout |
| pqsA-up 2 | GACCGAGGTTCTGTTCCGAGGAACGGGCATGTTG | - | pqsA knockout |
| pqsA-down 2 | CGACGGCCAGTGCCAAGCTTCGAACGGATCGAAGCTG | - | pqsA knockout |
| pAK-pqsA-up | TATGAGCTCCCGTGGTTCTTCTCC | Sac I | pqsA complement |
| pAK-pqsA-down | CGTTCTAGAGCATCAGCATCTCGTC | Xba I | pqsA complement |
| pAK-pqsR-up | TATTTAGGTGACACTATAGAATACTCAAGCTTGAATAAGGGATGCCTATTC | Hind III | pqsR complement |
| pAK-pqsR-down | GAATTGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGAATTCGAGCTCCCACGGCCAGCGTC | EcoR I | pqsR complement |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Han, X.; Cai, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Shen, L. Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation by Wogonin Attenuates Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 via Targeting pqs Quorum-Sensing System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312699
Wang S, Feng Y, Han X, Cai X, Yang L, Liu C, Shen L. Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation by Wogonin Attenuates Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 via Targeting pqs Quorum-Sensing System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312699
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shiwei, Yuqi Feng, Xiaofeng Han, Xinyu Cai, Liu Yang, Chaolan Liu, and Lixin Shen. 2021. "Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation by Wogonin Attenuates Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 via Targeting pqs Quorum-Sensing System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312699
APA StyleWang, S., Feng, Y., Han, X., Cai, X., Yang, L., Liu, C., & Shen, L. (2021). Inhibition of Virulence Factors and Biofilm Formation by Wogonin Attenuates Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 via Targeting pqs Quorum-Sensing System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312699






