GABABR Modulation of Electrical Synapses and Plasticity in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
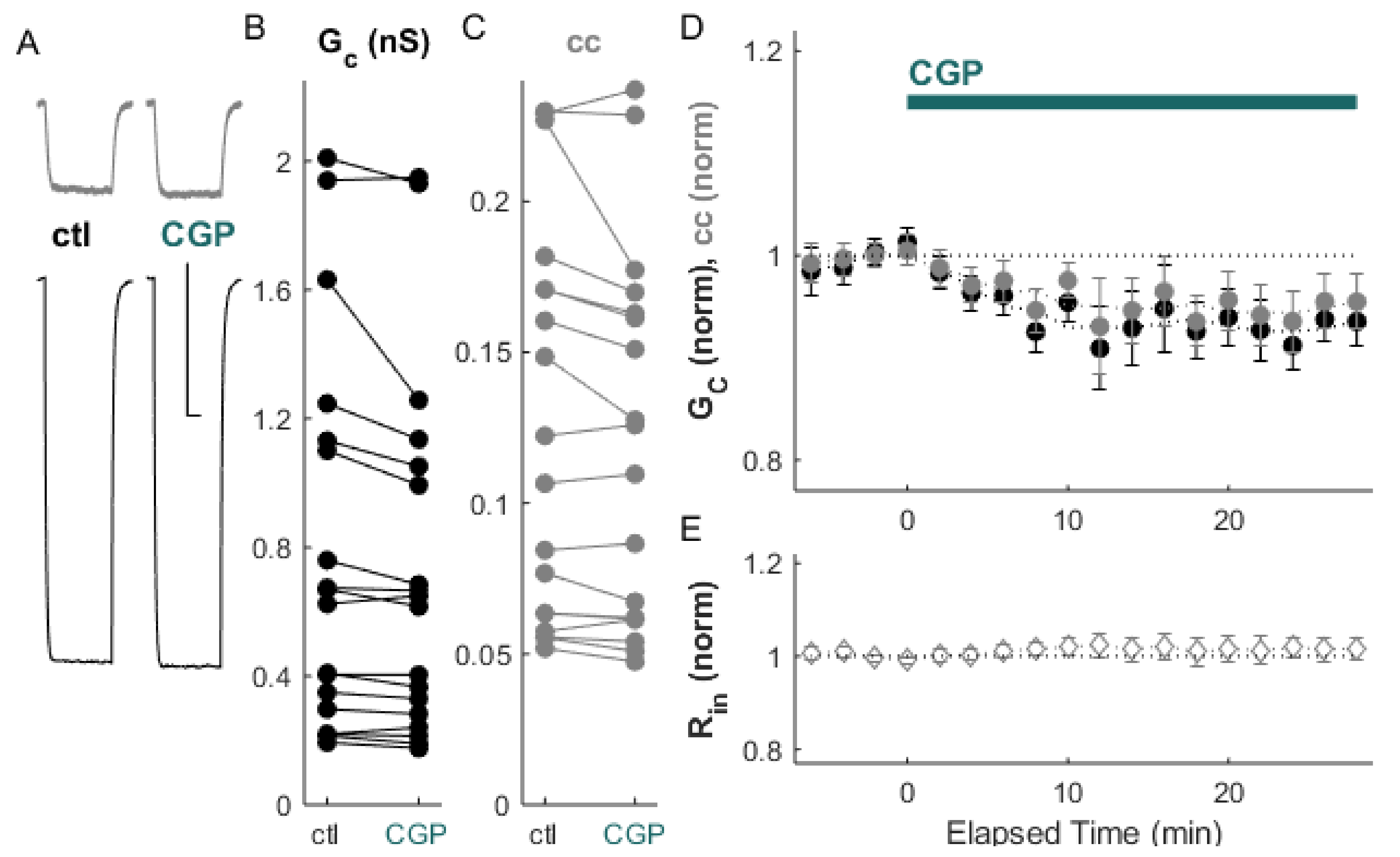
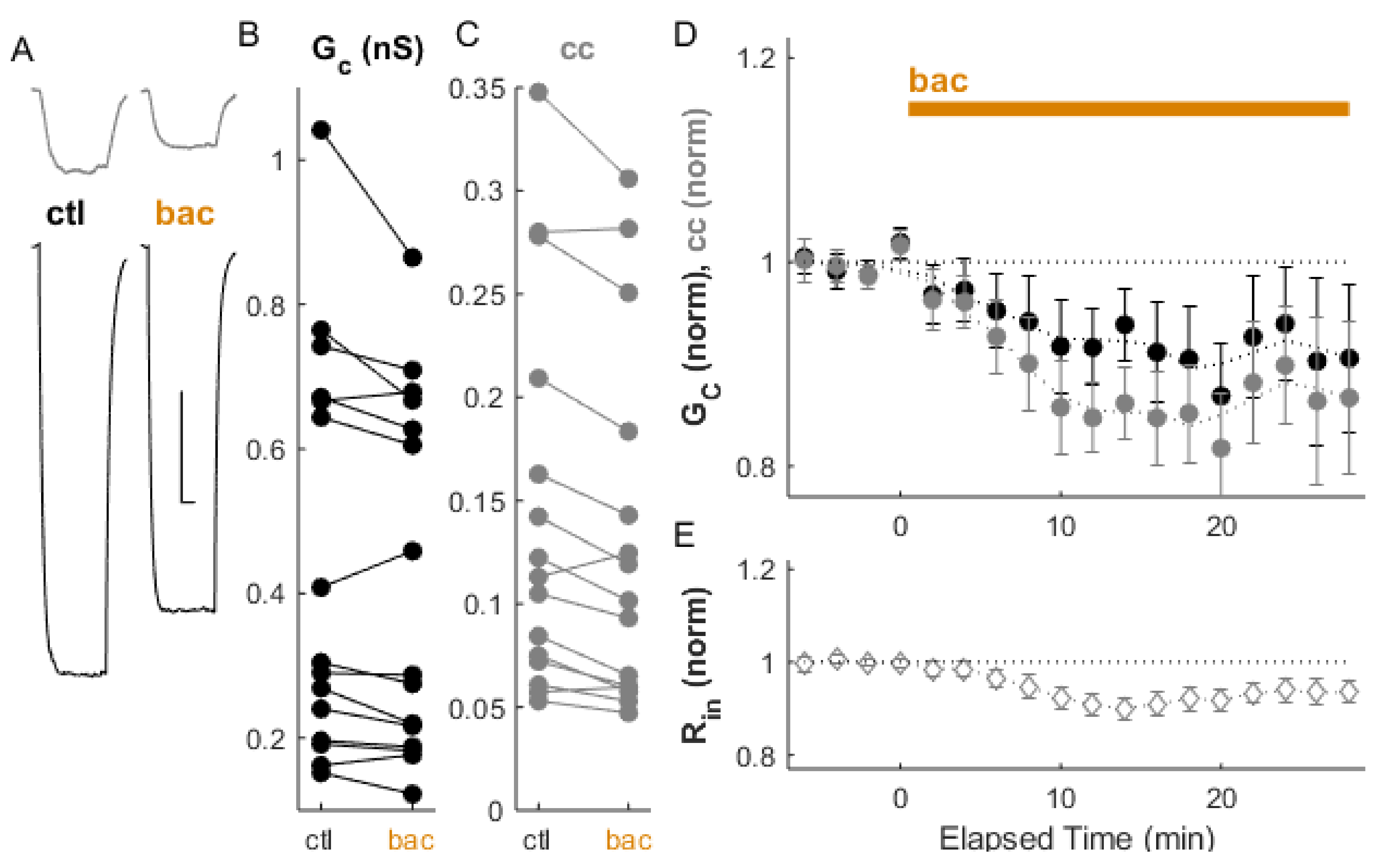
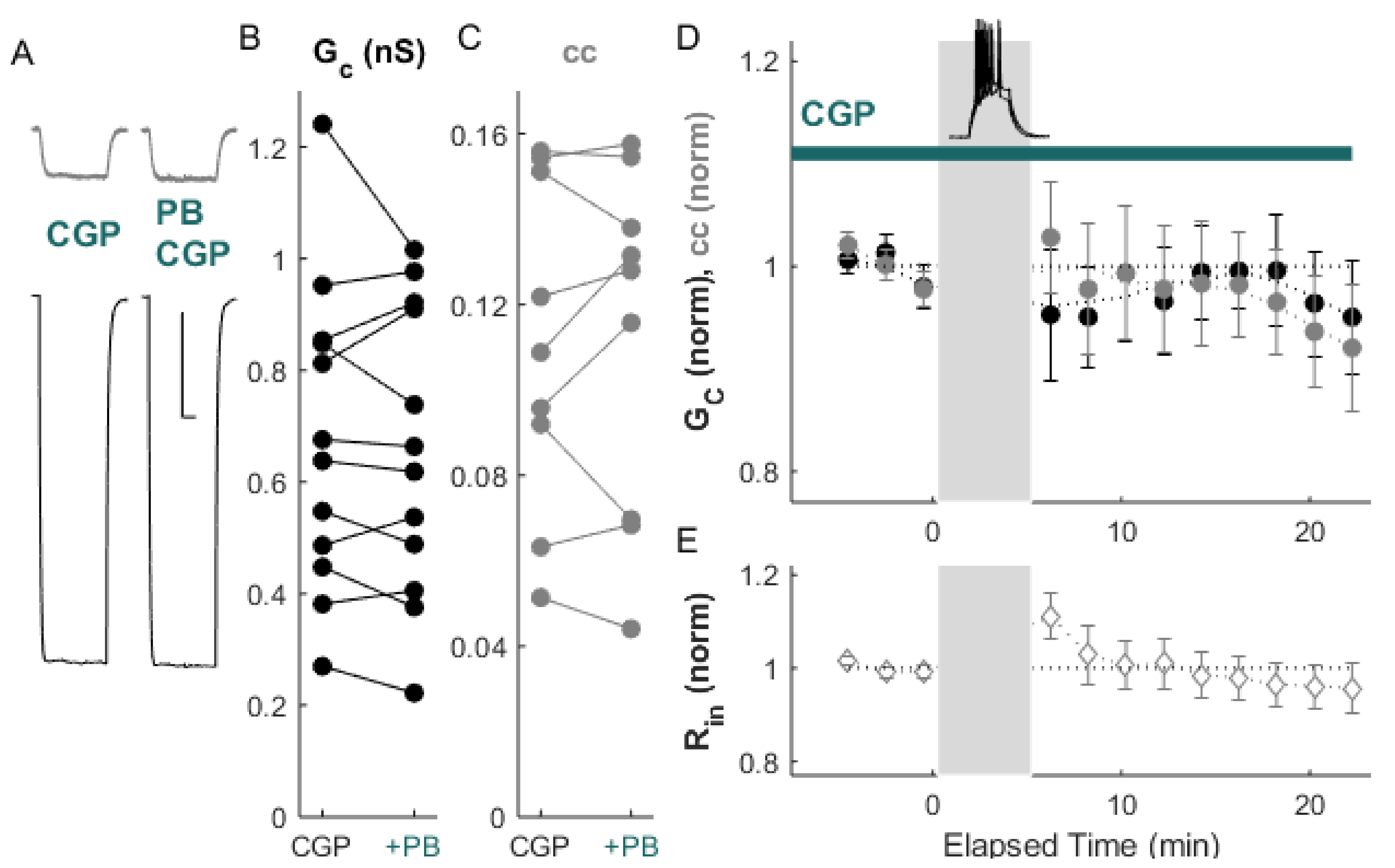
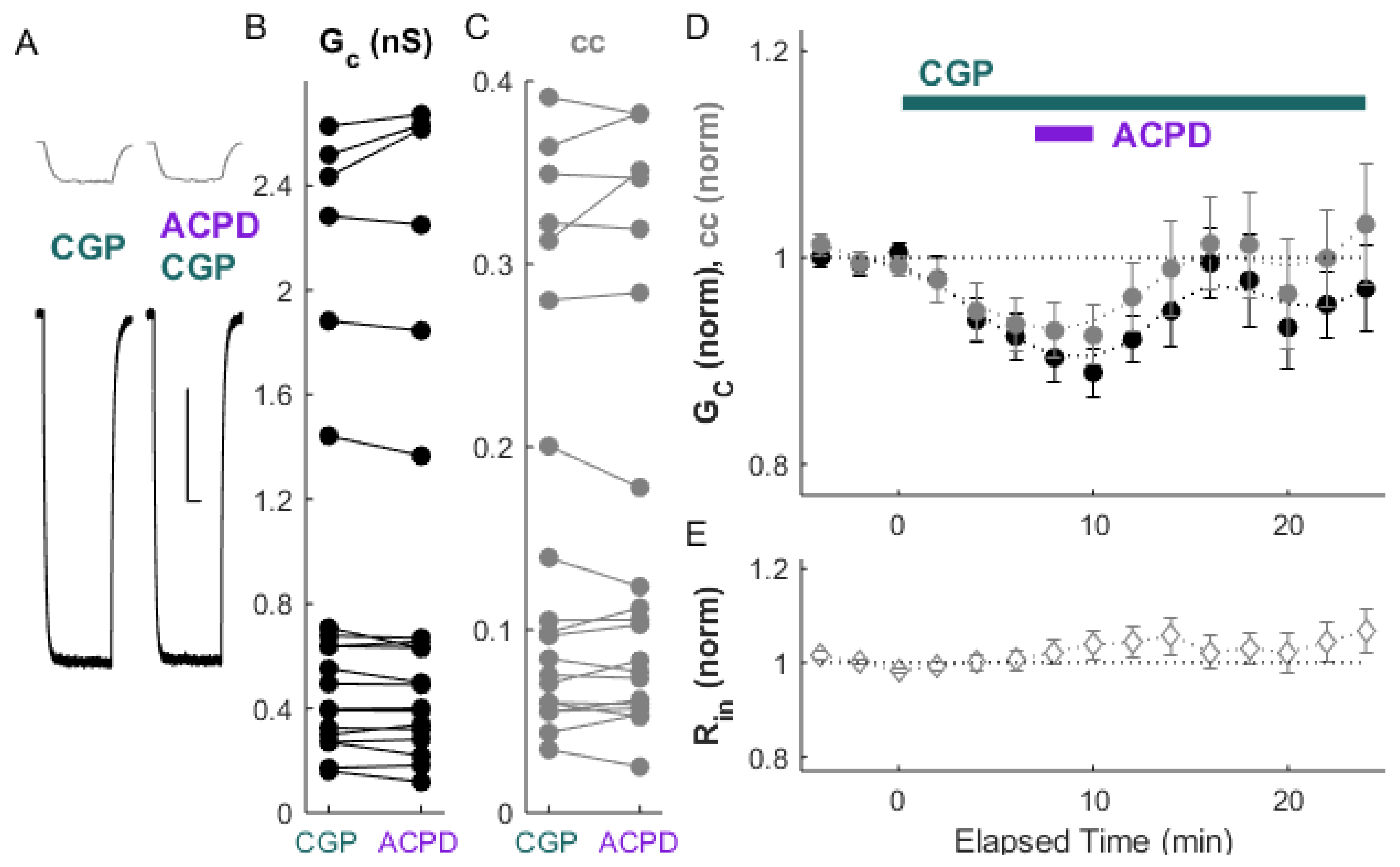
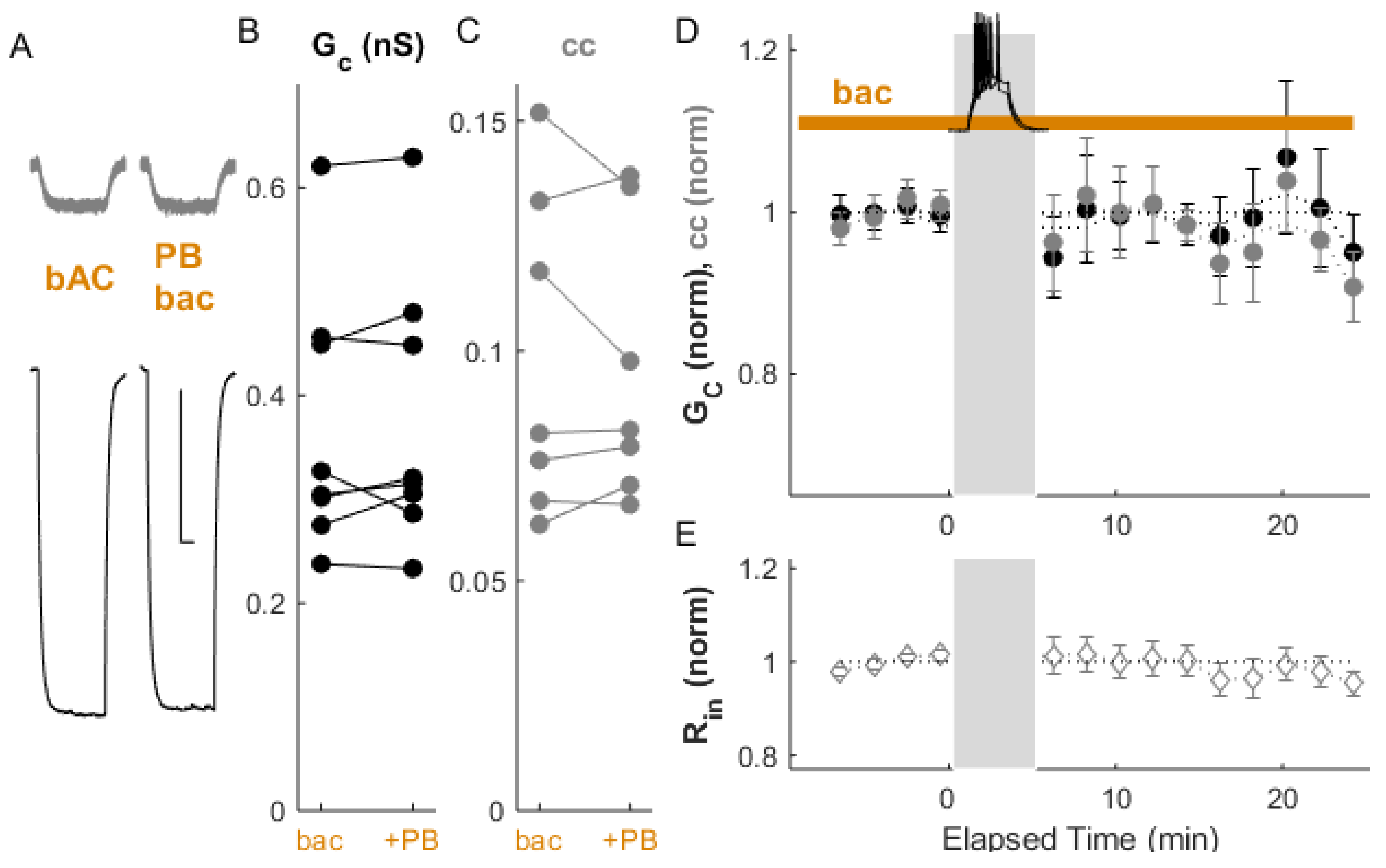
2. Results
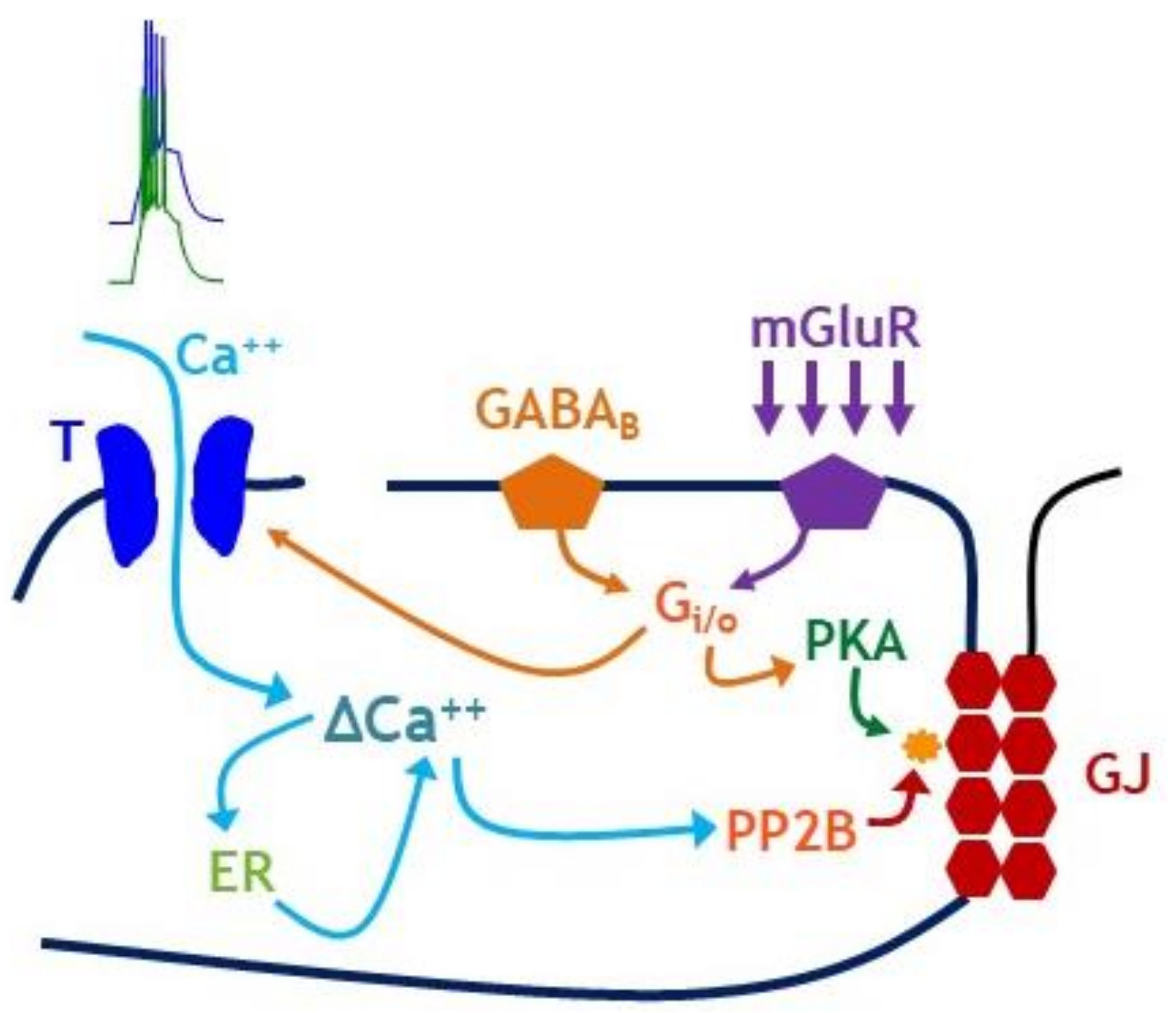
3. Discussion
4. Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steriade, M.; Domich, L.; Oakson, G.; Deschenes, M. The deafferented reticular thalamic nucleus generates spindle rhythmicity. J. Neurophysiol. 1987, 57, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, F. Function of the thalamic reticular complex: The searchlight hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4586–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAlonan, K.; Cavanaugh, J.; Wurtz, R.H. Attentional Modulation of Thalamic Reticular Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4444–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, P.T.; Lieberman, A.R. The thalamic reticular nucleus of the adult rat: Experimental anatomical studies. J. Neurocytol. 1985, 14, 365–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinault, D.; Deschenes, M. Projection and innervation patterns of individual thalamic reticular axons in the thalamus of the adult rat: A three-dimensional, graphic, and morphometric analysis. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 391, 180–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landisman, C.E.; Long, M.A.; Beierlein, M.; Deans, M.R.; Paul, D.L.; Connors, B.W. Electrical Synapses in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, G.; Smith, A.G.; Zhang, Z.-W. Lack of Intrinsic GABAergic Connections in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus of the Mouse. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7246–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steriade, M. Sleep, epilepsy and thalamic reticular inhibitory neurons. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Duysens, J.; Vossen, J.M.; Coenen, A.M. Thalamic multiple-unit activity underlying spike-wave discharges in anesthetized rats. Brain Res. 1993, 612, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguenard, J.; Prince, D.A. Intrathalamic rhythmicity studied in vitro: Nominal T-current modulation causes robust antioscillatory effects. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 5485–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von, M.K.; Bal, T.; McCormick, D.A. Cellular Mechanisms of a Synchronized Oscillation in the Thalamus. Science 1993, 261, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Destexhe, A. Spike-and-wave oscillations based on the properties of GABAB receptors. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9099–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, J.S.; Zavala, B.; Landisman, C.E. Activity-Dependent Long-Term Depression of Electrical Synapses. Science 2011, 334, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landisman, C.E.; Connors, B.W. Long-Term Modulation of Electrical Synapses in the Mammalian Thalamus. Science 2005, 310, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Neely, R.; Landisman, C.E. Activation of Group I and Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Causes LTD and LTP of Electrical Synapses in the Rat Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7616–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.B.; Jones, E.G. Predominance of corticothalamic synaptic inputs to thalamic reticular nucleus neurons in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 414, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.M.; Ohara, P.T.; Ralston, D.D.; Milroy, A.M.; Ralston, H.J. Analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acidergic synaptic contacts in the thalamic reticular nucleus of the monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 349, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paré, D.; Hazrati, L.-N.; Parent, A.; Steriade, M. Substantia nigra pars reticulata projects to the reticular thalamic nucleus of the cat: A morphological and electrophysiological study. Brain Res. 1990, 535, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanuma, C. Axonal arborizations of a magnocellular basal nucleus input and their relation to the neurons in the thalamic reticular nucleus of rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4746–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jourdain, A.; Semba, K.; Fibiger, H.C. Basal forebrain and mesopontine tegmental projections to the reticular thalamic nucleus: An axonal collateralization and immunohistochemical study in the rat. Brain Res. 1989, 505, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickford, M.E.; Günlük, A.E.; van Horn, S.C.; Sherman, S.M. GABAergic projection from the basal forebrain to the visual sector of the thalamic reticular nucleus in the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 348, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandia, J.; Heras, S.D.L.; García, M.; Giménez-Amaya, J.M. Afferent projections to the reticular thalamic nucleus from the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra in the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 1993, 32, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halassa, M.M.; Acsády, L. Thalamic Inhibition: Diverse Sources, Diverse Scales. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cornwall, J.; Cooper, J.; Phillipson, O.T. Projections to the rostral reticular thalamic nucleus in the rat. Exp. Brain Res. 1990, 80, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.G.; Cadavieco, M.C.; Jego, S.; Ponomarenko, A.; Korotkova, T.M.; Adamantidis, A.R. Hypothalamic feedforward inhibition of thalamocortical network controls arousal and consciousness. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munoz, A.; Huntsman, M.M.; Jones, E.G. GABA(B) receptor gene expression in monkey thalamus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 394, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta-Mitrovic, M.; Mitrovic, I.; Riley, R.C.; Jan, L.Y.; Basbaum, A.I. Immunohistochemical localization of GABA(B) receptors in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 405, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, S.M.; Garcia, E.; Waheed, Z.; Jones, K.L.; Bushell, T.J.; Snutch, T.P. GABAB receptors suppress burst-firing in reticular thalamic neurons. Channels 2017, 11, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coulon, P.; Herr, D.; Kanyshkova, T.; Meuth, P.; Budde, T.; Pape, H.-C. Burst discharges in neurons of the thalamic reticular nucleus are shaped by calcium-induced calcium release. Cell Calcium 2009, 46, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, D.; Bettler, B. GABAB receptors: Synaptic functions and mechanisms of diversity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevetson, J.; Fittro, S.; Heckman, E.; Haas, J.S. A calcium-dependent pathway underlies activity-dependent plasticity of electrical synapses in the thalamic reticular nucleus. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4417–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karschin, C.; Dißmann, E.; Stühmer, W.; Karschin, A. IRK(1–3) and GIRK(1–4) Inwardly Rectifying K+Channel mRNAs Are Differentially Expressed in the Adult Rat Brain. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iftinca, M.C.; Zamponi, G.W. Regulation of neuronal T-type calcium channels. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Pereda, A.E. Chemical synaptic activity modulates nearby electrical synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4849–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereda, A.E. Electrical synapses and their functional interactions with chemical synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsiros, V.; Maccaferri, G. Noradrenergic Modulation of Electrical Coupling in GABAergic Networks of the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1804–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McHahon, D.G.; Knapp, A.G.; Dowling, J.E. Horizontal cell gap junctions: Single-channel conductance and modulation by dopamine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 7639–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fricker, B.; Heckman, E.; Cunningham, P.C.; Wang, H.; Haas, J.S. Activity-dependent long-term potentiation of electrical synapses in the mammalian thalamus. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 125, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, J.W.; Lodge, D.; Bashir, Z.I.; Isaac, J.T.R. GABAA, NMDA and mGlu2 receptors tonically regulate inhibition and excitation in the thalamic reticular nucleus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 37, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, J.S.; Landisman, C.E. State-Dependent Modulation of Gap Junction Signaling by the Persistent Sodium Current. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohmann, D.; Lüttjohann, A.; Seidenbecher, T.; Coulon, P.; Pape, H.-C. Short-term depression of gap junctional coupling in reticular thalamic neurons of absence epileptic rats. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5695–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Patrick, S.L.; Richardson, K.A.; Connors, B.W. Two functionally distinct networks of gap junction-coupled inhibitory neurons in the thalamic reticular nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 13170–13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palacios-Prado, N.; Chapuis, S.; Panjkovich, A.; Fregeac, J.; Nagy, J.I.; Bukauskas, F.F. Molecular determinants of magnesium-dependent synaptic plasticity at electrical synapses formed by connexin36. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, P.R.L.; Cruikshank, S.J.; Connors, B. Stability of Electrical Coupling despite Massive Developmental Changes of Intrinsic Neuronal Physiology. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9761–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sevetson, J.; Haas, J.S. Asymmetry and modulation of spike timing in electrically coupled neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zolnik, T.A.; Connors, B.W. Electrical synapses and the development of inhibitory circuits in the thalamus. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 2579–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belluardo, N.; Mudò, G.; Salinaro, A.T.; Le Gurun, S.; Charollais, A.; Serre-Beinier, V.; Amato, G.; Haefliger, J.-A.; Meda, P.; Condorelli, D.F. Expression of Connexin36 in the adult and developing rat brain. Brain Res. 2000, 865, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, D.F.; Belluardo, N.; Salinaro, A.T.; Mudò, G. Expression of Cx36 in mammalian neurons. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 32, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, J.; Meier, C.; Van Der Giessen, R.S.; Söhl, G.; Petrasch-Parwez, E.; Urschel, S.; Dermietzel, R.; Schilling, K.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; Willecke, K. Expression pattern of lacZ reporter gene representing connexin36 in transgenic mice. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 473, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.A.; Jones, E.G. Maturation of Neuronal Form and Function in a Mouse Thalamo-Cortical Circuit. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blethyn, K.L.; Hughes, S.W.; Crunelli, V. Evidence for electrical synapses between neurons of the nucleus reticularis thalami in the adult brain in vitro. Thalamus Relat. Syst. 2008, 4, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Yu, S.; Yi, R.; Luo, D.; Fu, X. Effects of Propofol on Electrical Synaptic Strength in Coupling Reticular Thalamic GABAergic Parvalbumin-Expressing Neurons. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleuze, C.; Huguenard, J.R. Distinct Electrical and Chemical Connectivity Maps in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus: Potential Roles in Synchronization and Sensation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 8633–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozsádi, D.A. Organization of cortical afferents to the rostral, limbic sector of the rat thalamic reticular nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 341, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.G. Some aspects of the organization of the thalamic reticular complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 1975, 162, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.-W.; Sherman, S.M. Functional Organization of the Thalamic Input to the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6791–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Perez, A.; Makinson, S.R.; Higashikubo, B.; Brovarney, S.; Cho, F.S.; Urry, A.; Holden, S.S.; Wimer, M.; Dávid, C.; Fenno, L.E.; et al. Distinct Thalamic Reticular Cell Types Differentially Modulate Normal and Pathological Cortical Rhythms. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2130–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Lopez-Huerta, V.G.; Adiconis, X.; Levandowski, K.; Choi, S.; Simmons, S.K.; Arias-Garcia, M.A.; Guo, B.; Yao, A.Y.; Blosser, T.R.; et al. Distinct subnetworks of the thalamic reticular nucleus. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 583, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, R.I.; Voelcker, B.; Zaltsman, J.B.; Patrick, S.L.; Stevens, T.R.; Connors, B.; Cruikshank, S.J. Two dynamically distinct circuits drive inhibition in the sensory thalamus. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 583, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathy, A.; Clark, B.A.; Häusser, M. Synaptically Induced Long-Term Modulation of Electrical Coupling in the Inferior Olive. Neuron 2014, 81, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefler, Y.; Yarom, Y.; Uusisaari, M.Y. Cerebellar Inhibitory Input to the Inferior Olive Decreases Electrical Coupling and Blocks Subthreshold Oscillations. Neuron 2014, 81, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turecek, J.; Yuen, G.S.; Han, V.Z.; Zeng, X.-H.; Bayer, K.U.; Welsh, J.P. NMDA Receptor Activation Strengthens Weak Electrical Coupling in Mammalian Brain. Neuron 2014, 81, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, J.S. A new measure for the strength of electrical synapses. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham, T.; Haas, J.S. Electrical synapses between inhibitory neurons shape the responses of principal neurons to transient inputs in the thalamus: A modeling study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.; Haas, J.S. Electrical synapses regulate both subthreshold integration and population activity of principal cells in response to transient inputs within canonical feedforward circuits. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curti, S.; Pereda, A.E. Voltage-dependent enhancement of electrical coupling by a subthreshold sodium current. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 3999–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curti, S.; Hoge, G.; Nagy, J.I.; Pereda, A.E. Synergy between Electrical Coupling and Membrane Properties Promotes Strong Synchronization of Neurons of the Mesencephalic Trigeminal Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4341–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, P.A. Detecting and estimating rectification of gap junction conductance based on simulations of dual-cell recordings from a pair and a network of coupled cells. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 265, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Haas, J.S. GABABR Modulation of Electrical Synapses and Plasticity in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212138
Wang H, Haas JS. GABABR Modulation of Electrical Synapses and Plasticity in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212138
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huaixing, and Julie S. Haas. 2021. "GABABR Modulation of Electrical Synapses and Plasticity in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212138
APA StyleWang, H., & Haas, J. S. (2021). GABABR Modulation of Electrical Synapses and Plasticity in the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212138





