Research Progress in Chinese Herbal Medicines for Treatment of Sepsis: Pharmacological Action, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chinese Herbal Medicines
2.1. Chinese Patent Medicines
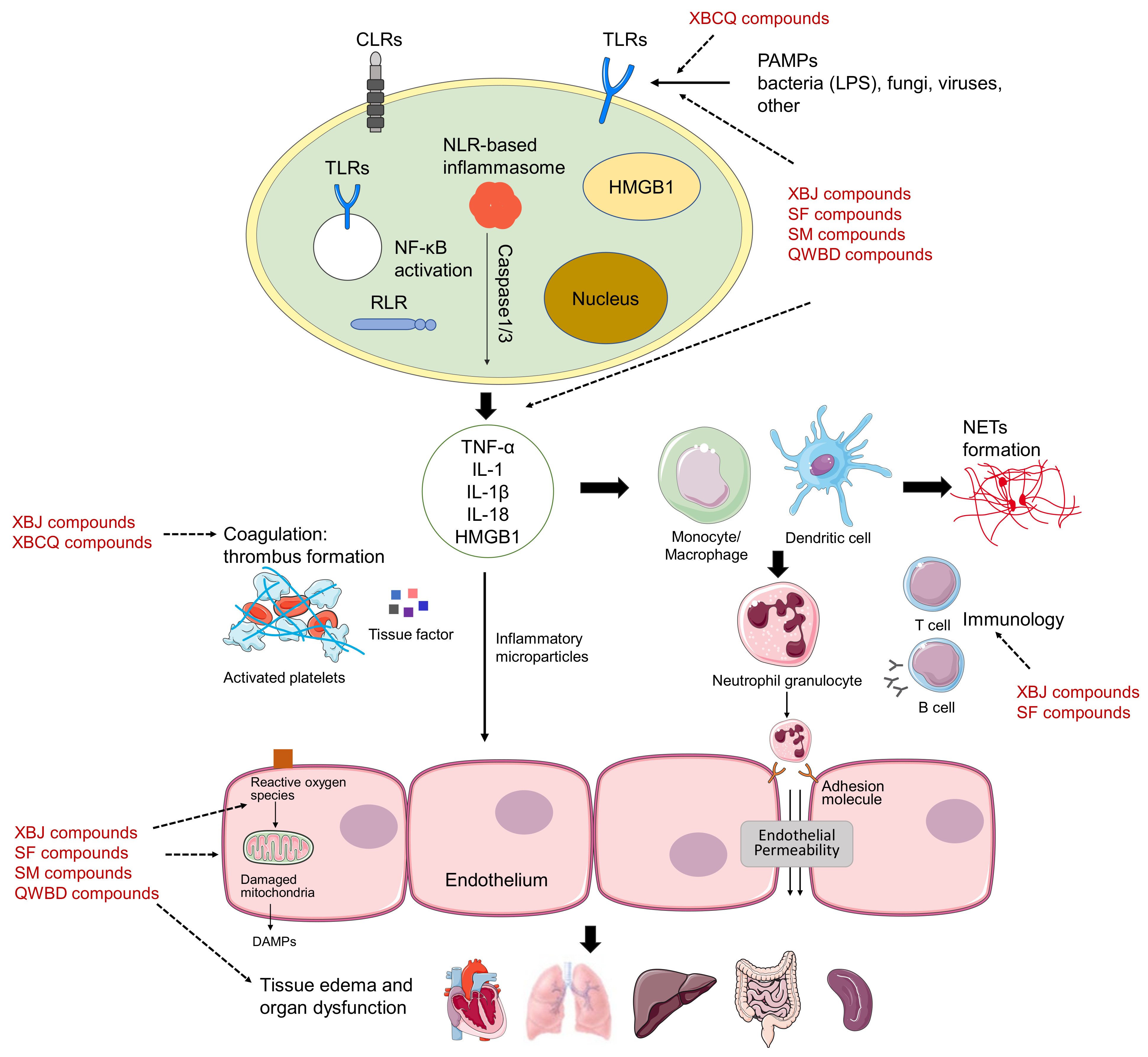
2.1.1. XueBiJing Injection
2.1.2. ShenFu Injection
2.2. Chinese Herbal Prescriptions
2.2.1. ShengMai Formula
2.2.2. Qingwen Baidu Decoction
2.2.3. Xuanbai Chengqi Decoction
2.3. Other Herbal Medicines
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADE | Adverse drug event |
| ADR | Adverse drug reaction |
| ALuI | Acute lung injury |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AMP | Adenosine 5′-monophosphate |
| APACHE II | Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| Cmax | Maximum plasma concentrations |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CHM | Chinese herbal medicines |
| CLP | Cecal ligation and puncture |
| Cr | Creatinine |
| HLA-DR | Human leukocyte antigen-DR |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| MLC | Myosin light chain |
| MLCK | Myosin light-chain kinase |
| MMP-2/9 | Matrix metalloproteinase 2/9 |
| MODS | Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome |
| OGD/R | Oxygen–glucose deprivation/reoxygenation |
| PEEP | Positive end-expiratory pressure |
| PSCC | Preventing Sepsis Campaign in China |
| QWBD | Qingwen Baidu decoction |
| ROCK | Rho-associated coil-forming protein kinase |
| SCCM | Society of Critical Care Medicine |
| SIRS | Systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
| 20(S)-protopanaxadiol type | ppd-type |
| 20(S)-protopanaxatriol type | ppt-type |
| SF | ShenFu injection |
| SM | ShengMai |
| SOCS1 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| SIRS | Systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
| t1/2 | Half-life |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| XBCQ | Xuanbai Chengqi decoction |
| XBJ | XueBiJing injection |
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.C.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, M.C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K.; on behalf of the International Forum Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Kang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Qin, B.; Ma, X.; Cao, X.; Chen, D.; Lu, W.; et al. The Epidemiology of Sepsis in Chinese ICUs. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e209–e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, A.L.; Katz, R.; Gostin, L.O. The Novel Coronavirus Originating in Wuhan, China Challenges for Global Health Governance. JAMA 2020, 323, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.-T.; Cheng, B.-L.; Fang, X.-M.; Chen, Y.-C.; Su, F. Application of Chinese Medicine in the Management of Critical Conditions: A Review on Sepsis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.R.; Moldawer, L.L.L.; Opal, S.M.; Reinhart, K.; Turnbull, I.I.; Vincent, J.-L. Sepsis and septic shock. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotts, J.E.; Matthay, M.A. Sepsis: Pathophysiology and clinical management. BMJ 2016, 353, i1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bone, R.C.; Balk, R.A.; Cerra, F.B.; Dellinger, R.P.; Fein, A.M.; Knaus, W.A.; Schein, R.M.H.; Sibbald, W.J. Definitions for Sepsis And Organ Failure and Guidelines for the Use of Innovative Therapies in Sepsis. Chest 1992, 101, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.M.; Fink, M.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Abraham, E.; Angus, D.; Cook, D.; Cohen, J.; Opal, S.M.; Vincent, J.L.; Ramsay, G. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Poll, T.; Van De Veerdonk, F.L.; Scicluna, B.; Netea, M.G. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; Van Der Poll, T. Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. New Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 486–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Vincent, J.-L.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Machado, F.R.; Angus, D.C.; Calandra, T.; Jaton, K.; Giulieri, S.; Delaloye, J.; Opal, S.; et al. Sepsis: A roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 581–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Lv, C.; Zhao, X. Chinese expert consensus on early prevention and intervention of sepsis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 13, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-Z.; Chen, R.-B.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.-H.; Xie, Y.-M.; Liao, X.; Yang, Y.-F.; Chen, T.-F.; Di, H.-R.; Shao, F.; et al. Clinical practice guideline on traditional Chinese medicine therapy alone or combined with antibiotics for sepsis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 43, 4776–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-Z.; Yao, Y.-M.; Zhou, R.-B. Chinese Guidelines for Emergency Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2018. J. Clin. Emerg. 2018, 38, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Chia, Y.-F. Chinese Emergency Medicine Expert Consensus on Diagnosis and Treatment of Sepsis Complicated with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Chin. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 29, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese National Health Commission and Chinese State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Diagnosis and Treatment of Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) (The Revised Eighth Version). 2021. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-04/15/5599795/files/e9ce837932e6434db998bdbbc5d36d32.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2021).
- Li, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Lei, X.; Liu, S.; Feng, Z.; Yao, Y.; Chang, B.; Liu, B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Xuebijing injection (a Chinese patent) for sepsis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 224, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, S.; Tan, D.; Ma, Q. Efficacy and Safety of Xuebijing Injection Combined with Ulinastatin as Adjunctive Therapy on Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kong, L.; Liu, S.; Feng, Z.; Shen, H.; Liu, Q. A prospective multicenter clinical study of Xuebijing injection in the treatment of sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Chin. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 27, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Li, C.-S. The Effectiveness of XueBiJing Injection in Therapy of Sepsis: A Multicenter Clinical Study. China J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 22, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qi, L. Clinical efficacy and safety of Xuebijing injection on sepsis: A Meta-analysis. Chin. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 32, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yao, C.; Yao, Y.; Han, H.; Zhao, X.; Yu, K.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; et al. XueBiJing Injection Versus Placebo for Critically Ill Patients with Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e735–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, W.; Xiang, M.; Wang, H.; Xiao, W.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Min, J.; Tu, Q. The preventive effect of Xuebijing injection against cytokine storm for severe patients with COVID-19: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 42, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Lei, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, S.; Feng, Z.; Shang, H. A real-world study on adverse drug reactions to Xuebijing injection: Hospital intensive monitoring based on 93 hospitals (31,913 cases). Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, Q.-P.; Ding, F.; Jiang, X.-D.; Tang, W.; Yu, M.-L.; Cheng, J.-Q. Reevaluation of the post-marketing safety of Xuebijing injection based on real-world and evidence-based evaluations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Olaleye, O.E.; Yu, X.; Jia, W.; Yang, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Duan, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. High degree of pharmacokinetic compatibility exists between the five-herb medicine XueBiJing and antibiotics comedicated in sepsis care. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Zhou, L.; Xu, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Kang, J.; Gao, G.; Du, S.; Sun, Z.; et al. Antiseptic Activity of Ethnomedicinal Xuebijing Revealed by the Metabolomics Analysis Using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L.; Zuo, L.; Jia, Q.; Du, S.; Kang, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z. Metabolomics approach in lung tissue of septic rats and the interventional effects of Xuebijing injection using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS. J. Biochem. 2018, 164, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Shen, X.; Pan, G.; Fan, G.; Gao, X.; Han, J.; Zhu, Y. Anti-sepsis protection of Xuebijing injection is mediated by differential regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory Th17 and T regulatory cells in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 211, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Zhou, M.; Han, Y.; Xing, L.; Zhao, H.; Dong, L.; Bai, G.; Luo, G. Identification of NF-κB Inhibitors in Xuebijing injection for sepsis treatment based on bioactivity-integrated UPLC-Q/TOF. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lai, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Wang, W.; Li, S. Network pharmacology to explore the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Xuebijing in the treatment of sepsis. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, J.; Bao, Y.; Yuan, D.; Huang, Z. Xuebijing injection alleviates cytokine-induced inflammatory liver injury in CLP-induced septic rats through induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qian, Y.; Miao, Z.; Zheng, P.; Shi, T.; Jiang, X.; Pan, L.; Qian, F.; Yang, G.; An, H.; et al. Xuebijing Injection Alleviates Pam3CSK4-Induced Inflammatory Response and Protects Mice from Sepsis Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Li, T.; Guo, X.; Pang, R.; Dong, L.; Duan, M. Xuebijing injection in septic rats mitigates kidney injury, reduces cortical microcirculatory disorders, and suppresses activation of local inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 276, 114199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.; Ling, B.; Wang, H.; Tan, D.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J. XueBiJing Injection Attenuates Hydrogen Sulfide-induced Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction by Upregulating Claudin-5 Expression. Chin. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 32, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zou, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y. GC/MS-based metabonomics approach reveals effects of Xuebijing injection in CLP induced septic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianyu, Z.; Liying, G. Identifying the molecular targets and mechanisms of xuebijing injection for the treatment of COVID-19 via network parmacology and molecular docking. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 2274–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Lv, J.-T.; Sa, R.-N.; Ma, B.-B.; Zhang, X.-M.; Lin, Z.-J. Molecular insight into the therapeutic promise of xuebijing injection against coronavirus disease 2019. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 6, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.-H.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Liu, L.-W.; Jiang, X.-F.; Wang, D.; Yan, S.-X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.-J. Mechanism of XueBiJing Injection in Anti-acute Lung Injury Based on Network Pharmacology. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2018, 49, 3541–3549. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.-Y.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-P.; Lian, Q.; Wang, Y.-M.; Luo, G.-A.; Wang, S.-M. Molecular Mechanism of XueBiJing Injection in Treatment of Sepsis according to Drug-target-pathway Network. Acta Pharmaceut Sin. 2017, 52, 556–562. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Zuo, L.; Sun, T.; Tang, J.; Ding, D.; Zhou, L.; Kang, J.; Zhang, X. Chemical profiling and quantification of XueBiJing injection, a systematic quality control strategy using UHPLC-Q Exactive hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Cao, X.-X.; Pu, W.-L.; Sun, L.-L.; Ren, X.-L. Research on Quality Control Method of XueBiJing Injection. Mod. Chin. Med. 2018, 20, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Sun, Z.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xue, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Bao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Suo, G.; et al. Rapid determination of 30 bioactive constituents in XueBiJing injection using ultra high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry coupled with principal component analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 137, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Fu, J.Z.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhao, H.Z.; Song, S.Y.; Ji, L.X.; Jiang, M.; Bai, G.; Luo, G.A. Simultaneous determination of thirteen main components and identification of eight major metabolites in Xuebijing Injection by UPLC/Q-TOF. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Yan, W.; Liu, X. Development and Validation of a HPLC Method for the Determination of Five Bioactive Compounds in the “Xuebijing” Injection. Anal. Lett. 2010, 43, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Cheng, C.; Olaleye, O.E.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Du, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Shi, Y.; et al. Pharmacokinetics-Based Identification of Potential Therapeutic Phthalides from XueBiJing, a Chinese Herbal Injection Used in Sepsis Management. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Jia, W.; Olaleye, O.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Pharmacokinetics of catechols in human subjects intravenously receiving XueBiJing injection, an emerging antiseptic herbal medicine. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 31, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Lin, J.-Z.; Li, L.; Yang, J.-L.; Jia, W.-W.; Huang, Y.-H.; Du, F.-F.; Wang, F.-Q.; Li, M.-J.; Li, Y.-F.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and disposition of monoterpene glycosides derived from Paeonia lactiflora roots (Chishao) after intravenous dosing of antiseptic XueBiJing injection in human subjects and rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D.; Xu, T.; Liu, L.; Gao, L.; Du, S.; Kang, J.; Zhang, X. Tissue distribution profiles of multiple major bioactive components in rats after intravenous administration of Xuebijing injection by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.-Z.; He, J. Simultaneous determination of nine constituents of Xuebijing Injection in rat plasma and their pharmacokinetics by LC-MS/MS. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 3553–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, T.; Shi, Y.; Tang, J.; Du, S.; et al. Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of twelve bioactive compounds in rat plasma after intravenous administration of Xuebijing injection by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 146, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-M.; Wang, X.-W.; Luo, J.; Jia, P.; Wang, X.-Y.; Xiao, C.-N.; Wang, S.-X.; Liu, Q.-S.; Zheng, X.-H. Pharmacokinetic Studies of XueBiJing Injection in Rats. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 32, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Peng, W.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Y. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of hydroxysafflor yellow A in patients with traumatic brain injury after intravenous administration of Xuebijing using LC-MS/MS method. Xenobiotica 2019, 50, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Che, J.; Zhao, H.; Tang, J.; Shi, G. Paeoniflorin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis and adhesion molecule expression by autophagy enhancement in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9291–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Dong, L. Tanshinol upregulates the expression of aquaporin 5 in lung tissue of rats with sepsis. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, D.-P.; Qin, Z.; Wang, P.-Y.; Hu, B.-H.; Yu, J.-G.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, B.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lu, M.; et al. Protective cerebrovascular effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) on ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 818, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Hou, X.; Liu, W.; Deng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, K.; Li, R. Paeoniflorin inhibits activation of the IRAK1-NF-κB signaling pathway in peritoneal macrophages from lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 124, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Cui, D.; Wang, F.; Song, Y.; Cheng, L.; Gao, K.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Li, S.; et al. Protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A against acute kidney injury via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, N.; Ding, J.; Liu, Q. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Inhibits LPS-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via Binding to Xanthine Oxidase in Mouse RAW264.7 Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Z.; Pan, J.; Ma, X. Effects of Xuebijing injection on microcirculation in septic shock. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 202, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Duan, M.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y. Senkyunolide I protects rat brain against focal cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury by up-regulating p-Erk1/2, Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting caspase 3. Brain Res. 2015, 1605, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.-F.; Ji, H.-B.; Sang, D.-Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Li, C.-S. Shen-Fu Injection Reduces Impaired Myocardial Beta-adrenergic Receptor Signaling after Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cheng, M.; Yuan, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yu, Z. Protective Role of Shenfu on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of Rat Liver Grafts. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, F.; He, C.; Liu, X.; Tu, G.; Guo, F.; Yang, S. Protective effect of Shenfu injection on thromboangiitis obliterans model rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-H.; Leng, X.-S.; Zhu, J.-Y. Effect of Shenfu injection on ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat liver graft. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2006, 5, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Pan, T.; Lyu, L.; Zhang, W.; Tan, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L.; et al. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation and standard bundle therapy in patients with septic shock. Chin. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 31, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.-L.; Wang, J.-H.; Kong, L.; Zhang, F.-H.; Hao, H.; Tian, Z.-Y.; Yin, M.-X.; Fang, H.; Yang, H.-H.; Liu, Y. Effect of Shen-Fu Injection on Hemodynamics in Early Volume Resuscitation Treated Septic Shock Patients. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 25, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; Lv, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q.; Yu, X. Clinical Effect of Shenfu Injection in Patients with Septic Shock: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Guozhen, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhao, G.; Li, B.; Liu, Q. Efficacy and safety of Shenfu injection for septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, P.; Qiu, H.; Wei, J.; Cao, Y.; Pan, S.; Walline, J.; Qian, C.; Shan, Z.; et al. Effects of Shenfu Injection in the Treatment of Septic Shock Patients: A Multicenter, Controlled, Randomized, Open-Label Trial. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lou, T. Shenfu injection for improving cellular immunity and clinical outcome in patients with sepsis or septic shock. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.J.; Lai, D.P.; Wei, X.; Yan, Q.; Xia, J.M. The protective effect of Shenfu injection against elderly severe pneumonia. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2016, 43, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Sun, C.-Y.; Zang, B.-X. Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelium inflammatory injury. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2015, 22, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, W. Oxypaeoniflorin improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating the Sirt1/Foxo1 signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2020, 67, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Huang, M.; Bi, L.; Zhou, S. Paeoniflorin Reduced BLP-Induced Inflammatory Response by Inhibiting the NF-κB Signal Transduction in Pathway THP-1 Cells. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 39, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Seo, C.-S.; Lee, K.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Chang, H.-W.; Jung, J.-S.; Song, D.-K.; Son, J.-K. Protective constituents against sepsis in mice from the root cortex ofPaeonia suffruticosa. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2004, 27, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Li, P.; Zhu, C.-L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.-M.; Wang, J.-F. Senkyunolide I Protects against Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy by Attenuating Sleep Deprivation in a Murine Model of Cecal Ligation and Puncture. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Hu, S. Protective Effect of Ginsenosides Rg1 and Re on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis by Competitive Binding to Toll-Like Receptor 4. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5654–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.-K.; Jeong, T.C.; Lee, S.; Bae, J.-S. Ginsenosides Inhibit HMGB1-induced Inflammatory Responses in HUVECs and in Murine Polymicrobial Sepsis. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, 35, 2955–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Tao, T.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cao, L.; Deng, X.; Li, J. Ginsenoside Rg1 improves survival in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis by suppressing the inflammatory response and apoptosis of lymphocytes. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 183, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Du, Y.; Duan, S.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Fu, F. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via modulation of PPAR-γ/NF-κB signal pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55384–55393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.-Y. Ginsenoside Rb2 enhances the anti-inflammatory effect of ω-3 fatty acid in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by upregulating GPR120 expression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 38, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Yan, T.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, M.; et al. Ginsenosides Regulate PXR/NF-κB Signaling and Attenuate Dextran Sulfate Sodium–Induced Colitis. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-J.; Li, Y.-N.; Chen, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, T.-S. Total Ginsenosides Synergize with Ulinastatin against Septic Acute Lung Injury and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7385–7390. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Hu, B.-H.; Chang, X.; Yan, L.; Pan, C.-S.; Li, Q.; Fan, J.-Y.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced albumin leakage from rat mesenteric venules by intervening in both trans- and paracellular pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G289–G300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, E.-H.; Lee, I.-A.; Jung, I.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Ginsenoside Rb1 and its metabolite compound K inhibit IRAK-1 activation—The key step of inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Yang, Y.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Song, G.G.; Kim, M.-Y.; Rhee, M.H.; Cho, J.Y. Ginsenoside Rc from Panax ginseng exerts anti-inflammatory activity by targeting TANK-binding kinase 1/interferon regulatory factor-3 and p38/ATF-2. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Du, F.; Jia, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Niu, W.; Li, C. Molecular mechanisms governing different pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides and potential for ginsenoside-perpetrated herb–drug interactions on OATP1B3. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaleye, O.; Niu, W.; Du, F.-F.; Wang, F.-Q.; Xu, F.; Pintusophon, S.; Lu, J.-L.; Yang, J.-L.; Li, C. Multiple circulating saponins from intravenous ShenMai inhibit OATP1Bs in vitro: Potential joint precipitants of drug interactions. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintusophon, S.; Niu, W.; Duan, X.-N.; Olaleye, O.E.; Huang, Y.-H.; Wang, F.-Q.; Li, Y.-F.; Yang, J.-L.; Li, C. Intravenous formulation of Panax notoginseng root extract: Human pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides and potential for perpetrating drug interactions. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Chang, Y.; Li, W. Aqueous extract of Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via regulation of TLR4/NF-ΚB pathway. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimura, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Ishiuchi, K.; Ohsawa, M.; Makino, T. Neoline is the active ingredient of processed aconite root against murine peripheral neuropathic pain model, and its pharmacokinetics in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 241, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Y.-F.; Liu, X.-T.; Li, Y.-C.; Zhu, H.-M.; Sun, M.-R.; Li, P.; Liu, B.; Yang, H. Songorine promotes cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2 induction during sepsis. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Kan, H.; Ma, Y.; Men, L.; Pi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of drug interactions: Fritillary mediating the transport of alkaloids in caco-2 cells by p-glycoprotein. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Shin, J.A.; Jung, J.-S.; Hyun, J.-W.; Van Le, T.K.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, E.-M.; Kim, H.-S. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Compound K in Activated Microglia and Its Neuroprotective Effect on Experimental Stroke in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 341, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-S.; Ko, S.-R.; Cho, B.-G.; Shin, N.-M.; Yuk, J.-M.; Li, S.; Kim, J.-M.; Evans, R.M.; Jung, J.-S.; Song, N.-K.; et al. The ginsenoside metabolite compound K, a novel agonist of glucocorticoid receptor, induces tolerance to endotoxin-induced lethal shock. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Yao, N.; Wu, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.; Xiong, Y.; Xia, C. The major effective components in Shengmai Formula interact with sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, G.; Shang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Hao, H.; Xie, L. Differential effect of Shenmai injection, a herbal preparation, on the cytochrome P450 3A-mediated 1′-hydroxylation and 4-hydroxylation of midazolam. Chem. Interact. 2009, 180, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y. Ophiopogonin D and EETs ameliorate Ang II-induced inflammatory responses via activating PPARα in HUVECs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, X. Specific Turn-On Fluorescent Probe with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for SIRT1 Modulator Screening and Living-Cell Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5046–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, L.; Gao, M.; Jiang, W.; Shao, F.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Kou, J.; Yu, B. Ruscogenin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice: Involvement of tissue factor, inducible NO synthase and nuclear factor (NF)-κB. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Ding, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, F.; Yang, F. In vitro study on the effect of ophiopogonin D on the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Xenobiotica 2021, 51, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.-P.; Zhao, J.; Cao, Y.-F.; Hong, M.; Sun, D.-X.; Sun, X.-Y.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Z.-T.; Fang, Z.-Z. The Inhibition of the Components from Shengmai Injection towards UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lu, B. Schisantherin-A Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in WI-38 Cells. Curr. Top. Nutraceutical Res. 2021, 19, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Gong, J.; Choi, Y.-W.; Hwang, D. Novel Function of α-Cubebenoate Derived from Schisandra chinensis as Lipogenesis Inhibitor, Lipolysis Stimulator and Inflammasome Suppressor. Molecules 2020, 25, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-J.; Lu, C.-J.; Liu, Z.-J.; Zhang, P.; Guo, H.-L.; Wang, T.-T. Schizandrin B Protects LPS-Induced Sepsis via TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 Signaling Pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Kook, M.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Choi, Y.W.; Bae, Y.-S. Anti-septic activity of α-cubebenoate isolated from Schisandra chinensis. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, P.; Jiang, D. Berberine functions as a negative regulator in lipopolysaccharide -induced sepsis by suppressing NF-κB and IL-6 mediated STAT3 activation. Pathog. Dis. 2020, 78, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zuo, H.; Sun, Y.; Feng, A. Berberine Exerts a Protective Effect on Gut-Vascular Barrier via the Modulation of the Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway During Sepsis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-X.; Wang, X.-M.; Jiang, T.; Gong, J.-F.; Niu, L.-Y.; Li, N. Berberine Prevents Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Damage During Early Phase of Sepsis in Rat through the Toll-Like Receptors Signaling Pathway. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.-Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Yu, X.; Kou, J.-P.; Yu, B.-Y. Berberine inhibits LPS-induced TF procoagulant activity and expression through NF-κB/p65, Akt and MAPK pathway in THP-1 cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Piao, X.-L.; Lu, T.; Wang, D.; Kim, S.W. Preventive effect of Coptis chinensis and berberine on intestinal injury in rats challenged with lipopolysaccharides. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ekavali, K.C.; Mukherjee, M.; Pottabathini, R.; Dhull, D.K. Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 761, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Ma, J.Y.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, S.K. Inhibitory effects of Hwang-Ryun-Hae-Dok-Tang on cytochrome P450 in human liver microsomes. Xenobiotica 2014, 45, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Shen, D.-F.; Meng, Y.-Y.; Kong, C.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.-P.; Yan, L.; Tang, Q.-Z.; Ma, Z.-G. Geniposide protects against sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction through AMPKα-dependent pathway. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, N.; Shi, G.; Wang, H. Geniposide ameliorated sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by activating PPARγ. Aging 2020, 12, 22744–22758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.; Lee, S. Genipin alleviates sepsis-induced liver injury by restoring autophagy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.-Y. Fructus Gardenia (Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis) phytochemistry, pharmacology of cardiovascular, and safety with the perspective of new drugs development. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 15, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cai, Q.; He, J.; Chu, X.; Wei, M.; Feng, X.; Xie, X.; Huo, M.; Liu, J.; Wei, J.; et al. Geniposide, an Iridoid Glucoside Derived from Gardenia jasminoides, Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Li, B.; Cao, H.; Lu, Y.; Wei, G.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, J. Identification of a new anti-LPS agent, geniposide, from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, and its ability of direct binding and neutralization of lipopolysaccharide in vitro and in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.-F.; Shi, Y.-Q.; Ma, X.-Y.; Tao, L.; Liu, M.-W. Baicalin attenuates LPS-induced alveolar type II epithelial cell A549 injury by attenuation of the FSTL1 signaling pathway via increasing miR-200b-3p expression. Innate Immun. 2021, 27, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.-W.; Su, W.-L.; Chou, T.-C. Baicalin improves the survival in endotoxic mice and inhibits the inflammatory responses in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2020, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Lin, H. Baicalin Inhibits Renal Cell Apoptosis and Protects Against Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Sepsis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 5109–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Lou, S.-F.; Hsu, J.-H.; Chen, T.-J.; Cheng, T.-L.; Chiu, C.-C.; Yeh, J.-L. Baicalein Inhibits HMGB1 Release and MMP-2/-9 Expression in Lipopolysaccharide-induced Cardiac Hypertrophy. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.; Kang, Y.; Nepal, M.R.; Jeong, K.S.; Oh, D.G.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Baicalin-Induced Drug Interaction and Its Pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2016, 21, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Guo, W.; Tan, Y.; Niu, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Tao, K.; Chen, Z.; Dai, J. Wogonin alleviates liver injury in sepsis through Nrf2-mediated NF-κB signalling suppression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5782–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-Z.; Zhao, L.-F.; Ma, J.; Xue, W.-H.; Zhao, H. Protective mechanisms of wogonoside against Lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 780, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, W. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Wogonin on RAW 264.7 Mouse Macrophages Induced with Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid. Molecules 2015, 20, 6888–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Yang, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hou, G.; Guo, X.; Sun, N.; Liu, Y. Wogonoside Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Inflammation 2014, 37, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.-X.; Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, P.; Huang, M.; Luo, H.-B. The molecular basis for the inhibition of human cytochrome P450 1A2 by oroxylin and wogonin. Eur. Biophys. J. 2012, 41, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Zhou, R.; Yin, W. Oroxylin A alleviates immunoparalysis of CLP mice by degrading CHOP through interacting with FBXO15. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.-L.; Chen, M.-F.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Lee, T.J. OroxylinA reverses lipopolysaccharide-induced adhesion molecule expression and endothelial barrier disruption in the rat aorta. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 400, 115070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-F.; Wu, Y.-L.; Tseng, T.-L.; Chao, S.-W.; Lin, H.; Chen, H.-H. Inhibition of miR-155 potentially protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through the IRF2BP2-NFAT1 pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2020, 319, C1070–C1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Park, W. Anti-inflammatory effects of oroxylin A on RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages induced with polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.-K.; Han, M.-S.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Bae, J.-S. Inhibitory effects of oroxylin A on endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.-L.; Chen, M.-F.; Tsai, M.-J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-P.; Lee, T.J.F. Oroxylin-A Rescues LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Regulation of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Rodents. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Qin, Z.; Yang, N.; Chen, H.; Fu, K.; Lu, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Interactions between Oroxylin A with the solute carrier transporters and ATP-binding cassette transporters: Drug transporters profile for this flavonoid. Chem. Interact. 2020, 324, 109097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, M.; Qu, C. Verbascoside Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis-Like Symptoms in Mice via Its Potent Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 175, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, G.; Marchesini, J.; Bristot, L.; Monti, M.; Gambetti, S.; Pavasini, R.; Pollina, A.; Ferrari, R. The in vitro effects of verbascoside on human platelet aggregation. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2012, 34, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, L.; Franceschelli, S.; Pesce, M.; Reale, M.; Menghini, L.; Vinciguerra, I.; De Lutiis, M.A.; Felaco, M.; Grilli, A. Antiinflammatory effects in THP-1 cells treated with verbascoside. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Dong, L.; Duan, M.-L.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, M.-X.; Deng, J.-N.; Fan, J.-Y.; Wang, B.-E.; Han, J.-Y. Emodin Improves Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Microcirculatory Disturbance in Rat Mesentery. Microcirculation 2013, 20, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ye, B.; Chen, L.; Hong, G.; Zhao, G.; Lu, Z. Emodin alleviates LPS -induced myocardial injury through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 5203–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.-L.; Zhang, S.-J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Cai, X.; Luo, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, L. Emodin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Injury via Inhibiting the TLR4 Signaling Pathway in vitro and in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhang, W.; Feng, S.-J.; Yu, H.-P. Emodin suppresses LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells through a PPARγ-dependent pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 34, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.-T.; Wan, B.; Liu, D.-D.; Wan, S.-X.; Fu, H.-Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Emodin alleviates lung injury in rats with sepsis. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 202, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-K.; Xu, Y.-K.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.-T.; Fan, X.; Liu, D.-D.; Fu, H.-Y.; Wan, B. Emodin alleviates jejunum injury in rats with sepsis by inhibiting inflammation response. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-N.; Sun, L.-J.; Liu, S.-Q.; Song, J.; Cheng, J.-J.; Liu, J. Effect of Emodin on Aquaporin 5 Expression in Rats with Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 35, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.-H.; Yu, X.; Cao, F.; Cai, X.; Chen, P.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Pharmacokinetics of Anthraquinones from Medicinal Plants. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 638993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-Q.; Ma, J.-X.; Zhou, Y.-D. Investigation of Clinical Practice and Side Effects of Shenfu Injection. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 9, 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-F.; Yu, J.-Y.; Xie, Y.-M. Clinical safety imtensive hospital monitoring on Shenfu injection with 30 106 cases. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2017, 42, 2871–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.P. Gastrointestinal mucosal injury in experimental models of shock, trauma, and sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 1991, 19, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderinto-Adike, A.; Quigley, E.M.M. Gastrointestinal motility problems in critical care: A clinical perspective. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Jiang, R.; Wang, L.; Lei, S.; Zhi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Huang, L.; Xia, G.; Chen, Z. Shenfu injection alleviates intestine epithelial damage in septic rats. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; Varon, J. Sepsis: State of the art. Dis. Mon. 2001, 47, 462–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Jiang, R.; Lei, S.; Jin, L.; Zhu, C.; Feng, W.; Shen, Y. Shenfu injection prolongs survival and protects the intestinal mucosa in rats with sepsis by modulating immune response. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 30, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Dai, Z.; Wu, H.; Lin, M.; Tian, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Pu, X. Effect of Shenfu injection on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced septic shock in rabbits. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 234, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-J.; Rui, Q.-L.; Wang, Q.; Tian, F.; Wu, J.; Kong, X.-Q. Shenfu injection attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Xie, J.; Wen, Y.-S.; Zhang, G.-X.; Lu, S.-Q. Shenfu injection prevents sepsis-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 261, 113068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, R.-L.; Wang, L.-C.; Lei, S.; Xing, X.; Zhi, Y.-H.; Wu, J.-N.; Wu, Y.-C.; Zhu, M.-F.; Huang, L.-Q. Effect of Shenfu injection on intestinal mucosal barrier in a rat model of sepsis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ai, F.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Mei, L.; Miao, J.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Shenfu Injection against Acute Lung Injury through Inhibiting HMGB1-NF-κB Pathway in a Rat Model of Endotoxin Shock. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Shi, S.-P.; Song, Q.-Q.; Li, J.; Song, Y.-L.; Tu, P.-F. Simultaneous determination of 14 organic acids in Shenfu injection by hydrophilic interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 3342–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, A.-H.; Li, J.; Donnapee, S.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Liu, E.-W.; Kang, L.-Y.; Gao, X.-M.; Chang, Y.-X. Simultaneous determination of 2 aconitum alkaloids and 12 ginsenosides in Shenfu injection by ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with a photodiode array detector with few markers to determine multicomponents. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Gao, W.; Liu, K.; Qi, L.-W.; Li, P. Direct and comprehensive analysis of ginsenosides and diterpene alkaloids in Shenfu injection by combinatory liquid chromatography–mass spectrometric techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 92, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, N.; Shi, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P. Large-scale qualitative and quantitative characterization of components in Shenfu injection by integrating hydrophilic interaction chromatography, reversed phase liquid chromatography, and tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1407, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lv, B.; Jiang, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, X.; Chang, N.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Identification of NF-κB inhibitors following Shenfu injection and bioactivity-integrated UPLC/Q-TOF-MS and screening for related anti-inflammatory targets in vitro and in silico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q. Simultaneous determination of seven ginsenosides in rat plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry: Application to pharmacokinetics of Shenfu injection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Du, F.; Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Niu, W.; Wang, F.; Mao, Y.; et al. Absorption and Disposition of Ginsenosides after Oral Administration of Panax notoginseng Extract to Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-L.; Zhou, S.-S.; Ma, Z.-C.; Liang, Q.-D.; Wang, Y.-G.; Tan, H.-L.; Xiao, C.-R.; Tang, X.-L.; Gao, Y. Material Basis of Shenfu Injection Based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2014, 30, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Mao, J.; Tian, J.; Ding, J. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of Shenfu Injection in beagle dogs after intravenous drip administration. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Xia, Y.; Ferrelli, R.M.; Fauci, A.; Guerra, R.; Hu, L. Clinical practice of traditional Chinese medicines for chronic heart failure. Hear. Asia 2010, 2, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Duan, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X. Shengmai injection as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 43, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.-H.; Xi, R.; Sun, J. Adverse Reaction Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Shengmai Injections. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 24, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.-X.; Wang, X.-P.; Huang, P.; Zhuang, R.; Xu, X.-L.; Li, B.; Liu, Q.-Q. Effect of Shengmai Injection on Septic Shock, a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Emerg. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 28, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Chai, R.-P.; Lyu, X.-K.; Deng, M.-H.; Hu, M.-G.; Qi, Y.; Chen, X. Mechanism of Shengmai Injection on Anti-Sepsis and Protective Activities of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Han, X.; Pan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, X.; Xiao, W.; Rong, J.; Chen, F.; He, J.; Zou, L.; et al. Emerging protective roles of shengmai injection in septic cardiomyopathy in mice by inducing myocardial mitochondrial autophagy via caspase-3/Beclin-1 axis. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.-P.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Lu, J.; Wang, T.-J.; Chen, X. Research on Mechanism of Shengmai Injection in the Treatment of Sepsis Based on Metabolomics. China J. Pharm. Econ. 2019, 14, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.-H.; Zhan, S.-Y.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Feng, Y.-H.; Fang, M.-T.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Liu, G.-Q.; Li, M.-J. Research Progress on Material Composition, Pre-clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Studies of Shengmai Injection. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2020, 51, 5360–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Hao, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, G.; Sang, G.; Liang, Y.; Xie, L.; Xia, C.; Yao, X. Diagnostic fragment-ion-based extension strategy for rapid screening and identification of serial components of homologous families contained in traditional Chinese medicine prescription using high-resolution LC-ESI- IT-TOF/MS: Shengmai injection as an example. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 44, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, H.; Miao, P.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Z. A Strategy for Selecting "Q-Markers" of Chinese Medical Preparation via Components Transfer Process Analysis with Application to the Quality Control of Shengmai Injection. Molecules 2019, 24, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Sun, H.; Wei, W.; Han, Y.; Wang, P.; Dong, T.; Yan, G.; Wang, X. Rapid and global detection and characterization of the constituents in ShengMai San by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-high-definition mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 3194–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Tsai, T.-H. Analysis of Sheng-Mai-San, a Ginseng-Containing Multiple Components Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Physical Examination by Electron and Light Microscopies. Molecules 2016, 21, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Fan, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Z.; Xu, N.; Huang, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, S.; Cao, H.; et al. Overall quality control of the chemical and bioactive consistency of ShengMai Formula. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 189, 113411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Jia, W.; Xie, G. A Metabolomics-Based Strategy for the Quality Control of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Shengmai Injection as a Case Study. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Cheng, T.-F.; Dong, X.; Li, P.; Yang, H. Global analysis of chemical constituents in Shengmai injection using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 117, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Lyu, X.; Chai, R.; Yu, Y.; Deng, M.; Zhan, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, X. Investigation of the Mechanism of Shengmai Injection on Sepsis by Network Pharmacology Approaches. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Guo, G.; Li, F.; Yu, B.; Kou, J. The Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound, GRS, Alleviates Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.; Shao, Q.; Fan, X.; Li, Z. Development of a sensitive LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of eleven constituents in rat serum and its application to a pharmacokinetic study of a Chinese medicine Shengmai injection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.-Y.; Shao, Q.; Fan, X.-H.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Y.-Y. Tissue distribution and excretion of herbal components after intravenous administration of a Chinese medicine (Shengmai injection) in rat. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, A.; Wu, F.; Wei, W.; Dong, T.; Wang, X. Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Study of Multiple Constituents from Shengmai San. In Serum Pharmacochemistry of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Wang, X., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wei, W.; Wang, X. Characterization of multiple constituents in rat plasma after oral administration of Shengmai San using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization/quadrupole-time-of-flight high-definition mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, T.-T.; Li, Y.-P.; Wang, X.-L. Inhibitory Effect of Shengmai Injection on CYP450 Enzyme and Transporter in Vitro. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2021, 52, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.-Y.; Wang, H.-J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Tan, E.C.-H.; Lee, I.-J.; Yun, C.-H.; Ueng, Y.-F. Effects of Shengmai San on key enzymes involved in hepatic and intestinal drug metabolism in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Rao, T.; Zhou, L.; Xing, R.; Wang, Q.; Fu, H.; Hao, K.; Xie, L.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Compatibility of Ginsenosides and Schisandra Lignans in Shengmai-san: From the Perspective of P-Glycoprotein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, H.; Tong, Y.; Wei, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.; Jing, M.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y. Potential therapeutic effect of Qingwen Baidu Decoction against Corona Virus Disease 2019: A mini review. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Huang, H.; Zhong, J.; Cai, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Cao, Q.; Peng, X. Qinwen Baidu decoction for sepsis A Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e14761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-J.; Wang, J.-D. Clinical observation on treatment of 18 patients with pulmonary infection after renal transplantation by integrative traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2005, 25, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-M.; Liu, Z.-H.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Q. Anti-inflammatory effect of Qingwen Baidu Decoction in sepsis rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 20, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-R.; Zhu, N.; Li, Z.-Y.; Tang, S.-H. Intervention mechanism of Qingwen Baidu Yin on cytokine storm based on network pharmacology. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2020, 45, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Zhang, K.-X.; Liu, Y.; Gai, X.-H.; Ren, T.; Liu, S.-X.; Tian, C.-W. Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Actions of Rehmannia Glutinosa. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2021, 52, 1772–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Duan, J.-A.; Wang, M.; Shang, E.; Guo, J.; Tang, Y. Analysis of active components of rhinoceros, water buffalo and yak horns using two-dimensional electrophoresis and ethnopharmacological evaluation. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H. Huang-Lian Jie-Du decoction: A review on phytochemical, pharmacological and pharmacokinetic investigations. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.; Tao, W.; Wang, P.; Tian, X.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis: Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological and industrial applications of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Platycodon grandiflorus—An Ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-L.; Wang, S.; Kuang, Y.; Hu, Z.-M.; Qiao, X.; Ye, M. A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, pharmacology, and flavonoid biosynthesis of Scutellaria baicalensis. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dan, Y.; Yang, D.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Cui, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. The genus Anemarrhena Bunge: A review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.-Q.; Chen, H.-W.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.-J. Efficacy, Chemical Constituents, and Pharmacological Actions of Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Shen, Z.-Y.; Qin, L.-P.; Zhu, B. Pharmacology, phytochemistry, and traditional uses of Scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, W.; Mei, X.; Luo, J.; Shan, M.; Lin, R.; Zou, D.; et al. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and future research of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 318–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Review on Research of the Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Lophatherum Gracile Brongn. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2014, 10, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, X.; Song, W.; Ji, S.; Wang, Q.; Guo, D.-A.; Ye, M. Separation and characterization of phenolic compounds and triterpenoid saponins in licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) using mobile phase-dependent reversed-phase×reversed-phase comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1402, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, C.; Peng, Y.; Chen, F.; Xiao, P. Origins, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Analytical Methods and Safety of Cortex Moutan (Paeonia suffruticosa Andrew): A Systematic Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Fan, C.; Zeng, H.; Huang, H.; Tian, C.; Lu, Z.; Cao, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, L. Holistic quality evaluation of Qingwen Baidu Decoction and its anti-inflammatory effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lei, H.-M.; Wang, P.-L.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.-J.; Nie, J.; Chen, S.-J.; Han, W.-J.; Wang, Q.; et al. Bioactive Components from Qingwen Baidu Decoction against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats. Molecules 2017, 22, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Wang, H. Effects of Xuanbai Chengqi decoction on lung compliance for patients with exogenous pulmonary acute respiratory distress syndrome. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, T.; Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Ma, F.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y. Analysis of medication characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine in treating COVID-19 based on data mining. J. Zhejiang Univ. Med. Sci 2020, 49, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.-L.; Xiong, X.-J. Treatment strategy and thought on classical herbal formulae for coronavirus disease 2019. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2021, 46, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Cheng, N.; Zhu, J. Xuanbai Chengqi decoction plus Western Medicine in treatment of severe pneumonia with symptom pattern of phlegm-heat obstructing lung: A Meta-analysis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 41, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelubre, C.; Vincent, J.-L. Mechanisms and treatment of organ failure in sepsis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, B.W.; Wiersinga, W.J. The role of the gut microbiota in sepsis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborin, A.; Smith, D.; Garfield, K.; Quensen, J.; Shakhsheer, B.; Kade, M.; Tirrell, M.; Tiedje, J.; Gilbert, J.A.; Zaborina, O.; et al. Membership and Behavior of Ultra-Low-Diversity Pathogen Communities Present in the Gut of Humans during Prolonged Critical Illness. mBio 2014, 5, e01361-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; De Vos, W.M. The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 996–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitch, E.A. Bacterial translocation or lymphatic drainage of toxic products from the gut: What is important in human beings? Surgery 2002, 131, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.P.; Singer, B.; Newstead, M.W.; Falkowski, N.R.; Erb-Downward, J.R.; Standiford, T.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. Enrichment of the lung microbiome with gut bacteria in sepsis and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Zhang, J.; Du, S.; Zhu, M.; Wei, W.; Xiang, J.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H.; et al. Gut microbiota modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of Xuanbai Chengqi decoction in septic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Shan, C.; Li, X.; Tan, B.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, A. Mechanism of protective effect of xuan-bai-cheng-qi decoction on LPS-induced acute lung injury based on an integrated network pharmacology and RNA-sequencing approach. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.-J.; Pu, Z.-J.; Tang, Y.-P.; Shen, J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Kang, A.; Zhou, G.-S.; Duan, J.-A. Advances in bio-active constituents, pharmacology and clinical applications of rhubarb. Chin. Med. 2017, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarbashi, D.; Jahanbin, K.; Tafaghodi, M.; Fahmideh-Rad, E. Prunus armeniaca gum exudates: An overview on purification, structure, physicochemical properties, and applications. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1240–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabuprapap, W.; Suksamrarn, A. Chemical Constituents of the Genus Trichosanthes (Cucurbitaceae) and Their Biological Activities: A Review. Scienceasia 2021, 47, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zhi, Y.; Lu, J.; Lei, S.; Huang, L.; Zhu, M.; Fang, K.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Traditional Chinese medicine bundle therapy for septic acute gastrointestinal injury: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 47, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Yang, X.; Wu, J.; Huang, F. Sini decoction ameliorates interrelated lung injury in septic mice by modulating the composition of gut microbiota. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 140, 103956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.; Zhou, G.; Mai, S.; Qin, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, D.; Weng, Y.; Du, J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Sini Decoction Improves Adrenal Function and the Short-Term Outcome of Septic Rats through Downregulation of Adrenal Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Yu, P.; Sheng, L.; Ye, J.; Qin, Z. Fangjifuling Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Renal Injury via Inhibition of Inflammatory and Apoptotic Response in Mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 2124–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Lai, H.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Cai, Y.; Huang, Q. Effect of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction Pretreatment on Myocardium in Sepsis Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 2939307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Qian, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Shen, M.; Ding, C.; Guo, J. Shengjiang Powder ameliorates myocardial injury in septic rats by downregulating the phosphorylation of P38-MAPK. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yan, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, L.; Li, P. Network pharmacology based research into the effect and mechanism of Xijiao Dihuang decoction against sepsis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: Theory, methodology and application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.-F.; Olaleye, O.E.; Lu, J.-L.; Yang, W.; Du, F.-F.; Yang, J.-L.; Cheng, C.; Shi, Y.-H.; Wang, F.-Q.; Zeng, X.-S.; et al. Pharmacokinetics-based identification of pseudoaldosterogenic compounds originating from Glycyrrhiza uralensis roots (Gancao) after dosing LianhuaQingwen capsule. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Du, F.; Yu, K.; Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Olaleye, O.E.; Yang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhong, C.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and Disposition of Circulating Iridoids and Organic Acids in Rats Intravenously Receiving ReDuNing Injection. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
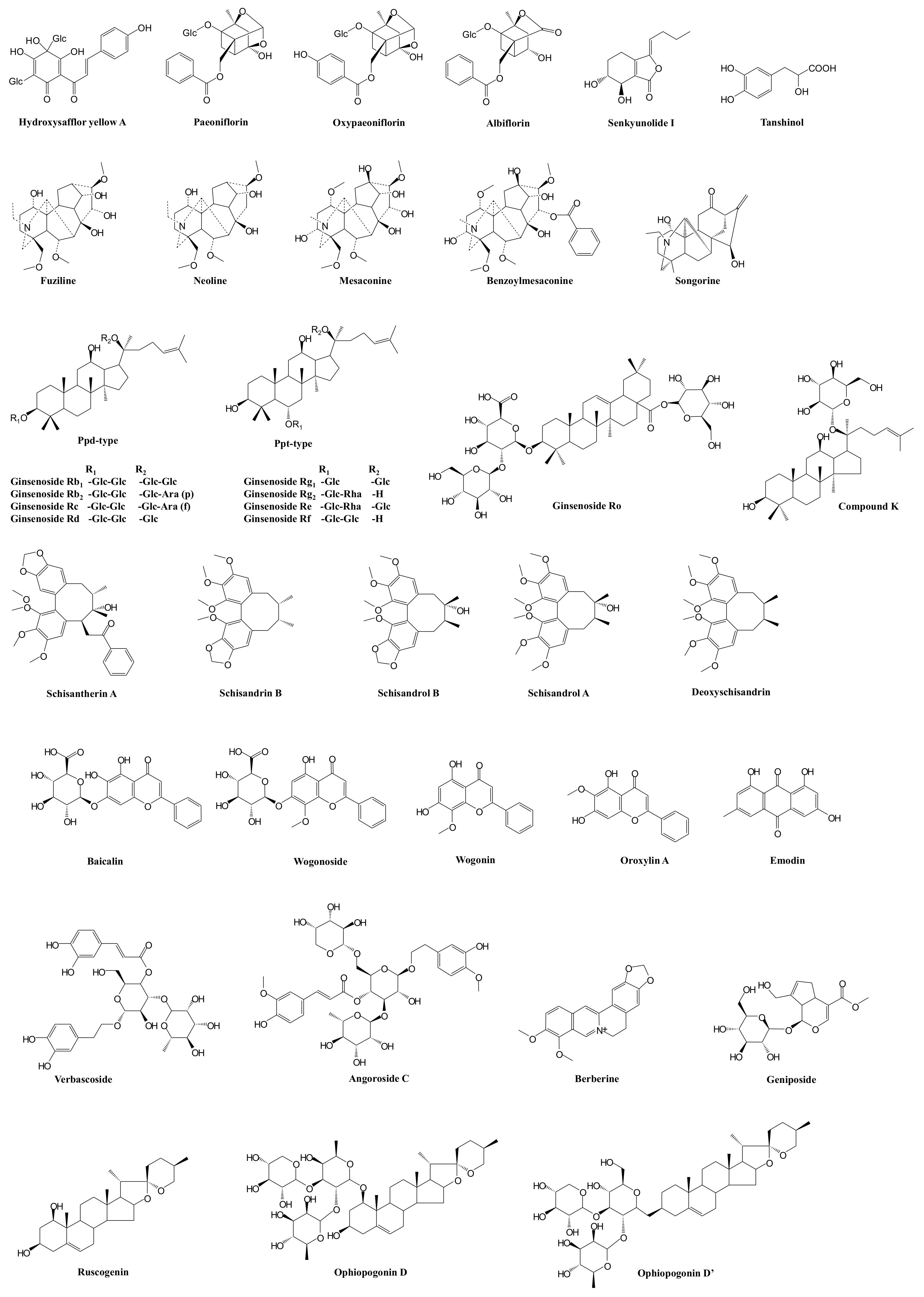
| Prescription | Component Herbs | Chemical Composition | Pharmacological Actions | Bioactive and Bioavailable Compounds | Potential Target Pathway | Potential DDI Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XueBiJing injection | Carthamus tinctorius flower (Honghua in Chinese), Paeonia lactiflora root (Chishao), Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome (Chuanxiong), Angelica sinensis root (Danggui), and Salvia miltiorrhiza root (Danshen) | Flavonoids, monoterpene glycosides, catechols, phthalides, organic acids, etc. | Exhibit anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, endothelium-protective, immunoregulatory, antioxidant, and organ-protective activities; inhibit ox-LDL-induced apoptosis; improve microcirculation and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury | Hydroxysafflor yellow A | TLR4/NF-κB; NLRP3; Rac1/Akt; NF-κB/ICAM-1 | — | [59,61,62,76] |
| Paeoniflorin Oxypaeoniflorin Albiflorin | SIRT1; IRAK1-NF-κB; IκB; PI3K/Akt; TLR2; Sirt1/Foxo1 | — | [33,57,60,77,78,79] | ||||
| Senkyunolide I | p-Erk1/2; Nrf2/HO-1; Caspase 3; MAPK; TLRs | As victim: UGT2B15 | [29,33,64,80] | ||||
| Tanshinol | cAMP-PKA | As victim: OAT1/2 | [29,58] | ||||
| ShenFu injection | Panax ginseng steamed root (Hongshen) and processed Aconitum carmichaelii root (Fuzi) | Ginsenosides, aconitum alkaloids, organic acids, etc. | Regulate oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, inhibit HMGB1-mediated severe inflammatory response, restore endothelial integrity, attenuate the proinflammatory response, enhance innate immunity, preserve adaptive immunity, alleviate neuropathic pain | Ginsenosides Rb1, Rc, Rb2, Rf, Rd, Rg1, etc. | TLR4; PXR/NF-κB; TLRs/IRAK-1; TBK-1/IκB kinase ε/IRF-3; p38/ATF-2 | As substrate: OATP1B3 (for Ginsenosides Rg1, Rf) As perpetrator: OATP1B1/1B3 (for Ginsenosides Rb1, Rc, Rb2, Rd) | [81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93] |
| Benzoylmesaconine Fuziline Mesaconine Neoline Songorine | TLR4/NF-κB; Nrf2 | As victim: P-gp (for benzoylmesaconine) | [94,95,96,97] | ||||
| ShengMai formula | Panax ginseng root (Renshen), Ophiopogon japonicus root (Maidong), and Schisandra chinensis fruit (Wuweizi) | Ginsenosides, lignans, steroidal saponins, and homoisoflavanones | Exhibit anti-inflammatory or antioxidant, hepatoprotective activities | Ginsenosides Rb₁, Rb2, Rc, Rd, Re, Rg1, Rh1, Compound K, Rf, and Rg2 | TLR4; PXR/NF-κB; TLRs/IRAK-1; TBK-1/IκB kinase ε/IRF-3; p38/ATF-2 | As substrate: OATP1B1/1B3 (for Ginsenoside Rg2) OATP1B3 (for Ginsenosides Rg1, Rf, Re) As perpetrator: OATP1B1/1B3 (for Ginsenosides Rb1, Rc, Rb2, Rd) NTCP (for Rg1) CYP3A (for Rd) | [81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,98,99,100,101] |
| Ophiopogonin D Ophiopogonin D’ Ruscogenin | PPARα; NF-κB/IκBα; SIRT1; TLR4; TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 | As perpetrator: CYP3A4, 2C9, and 2E1 (for Ophiopogonin D) UGT1A6/1A8 (for Ophiopogonin D) UGT1A6/1A10 (for Ophiopogonin D’) NTCP (for Ophiopogonin D’) CYP3A (for Ophiopogonin D) As victim: OATP1B1/1B3 (for Ophiopogonin D) | [92,101,102,103,104,105,106] | ||||
| Schisandrol A Schisandrol B Schizandrin A Schizandrin B Deoxyschisandrin | iNOS; COX-2; PGE2; MAPK; TLR4/NF-κB/MyD88 | As perpetrator: NTCP (for Schizandrin A) | [100,107,108,109,110] | ||||
| Qingwen Baidu decoction | Rehmannia glutinosa root (Dihuang), Rhinoceros unicornis horn (Xijiao), Coptidis chinensis rhizome (Huanglian), Gardenia jasminoides fruit (Zhizi), Platycodon grandiflorum root (Jiegeng), Scutellaria baicalensis root (Huangqin), Anemarrhena asphodeloides rhizome (Zhimu), Paeonia lactiflora root (Chishao), Scrophularia ningpoensis root (Xuanshen), Forsythia suspense fruit (Lianqiao), Lophatherum gracile stem and leaf(Danzhuye), Glycyrrhiza uralensis root and rhizome (Gancao), Paeonia suffruticosa root cortex (Danpi), and Gypsum Fibrosum (Shigao) | Alkaloids, iridoids, flavonoids, etc. | Reduce LPS-induced intestinal damage; treat inflammation; alleviate LPS-induced acute kidney injury; alleviate liver injury in sepsis; exhibit anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and cardioprotective effects | Berberine | TLRs; NF-κB; STAT3; Wnt/β-catenin; PI3K/Akt; MAPK/JNK/p38/ERK | As perpetrator: CYP3A4, CYP2D6 As victim: P-gp | [111,112,113,114,115,116,117] |
| Geniposide Genipin | NF-κB; MAPK; PPARγ; AMPK; NLRP3; AKT-mTOR | — | [118,119,120,121,122,123] | ||||
| Baicalin | iNOS; COX-2; NF-κB; HMGB1 | As perpetrator: CYP1A2/3A/2E1, OATP1B1, P-gp | [124,125,126,127,128] | ||||
| Wogonoside Wogonin | TLR4; NF-κB; Nrf2; NLRP3 | As perpetrator: CYP1A2 (for Wogonin) | [129,130,131,132,133] | ||||
| Oroxylin A | JAK/STAT; IRF2BP2-NFAT1; NF-κB | As perpetrator: CYP1A2, OATP1B1, OAT1/3 and BCRP | [133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140] | ||||
| Verbascoside | iNOS | — | [141,142,143] | ||||
| XuanBai Chengqi decoction | Rheum palmatum rhizome and root (Dahuang), Gypsum Fibrosum (Shigao), Prunus armeniaca seed (Kuxingren), and Trichosanthes kirilowii fruit (Gualou) | Anthraquinones, etc. | Attenuate LPS-induced microcirculatory disturbance | Emodin | TLR4/NF-κB/ICAM-1; JAK1/STAT3; MAPK; cAMP-PKA; NLRP3; PPARγ | As victim: CYP1A2, UGT1A8/1A10/12B7 | [144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.; Yu, X. Research Progress in Chinese Herbal Medicines for Treatment of Sepsis: Pharmacological Action, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011078
Cheng C, Yu X. Research Progress in Chinese Herbal Medicines for Treatment of Sepsis: Pharmacological Action, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacokinetics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(20):11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011078
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chen, and Xuan Yu. 2021. "Research Progress in Chinese Herbal Medicines for Treatment of Sepsis: Pharmacological Action, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacokinetics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 20: 11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011078
APA StyleCheng, C., & Yu, X. (2021). Research Progress in Chinese Herbal Medicines for Treatment of Sepsis: Pharmacological Action, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacokinetics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(20), 11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011078






