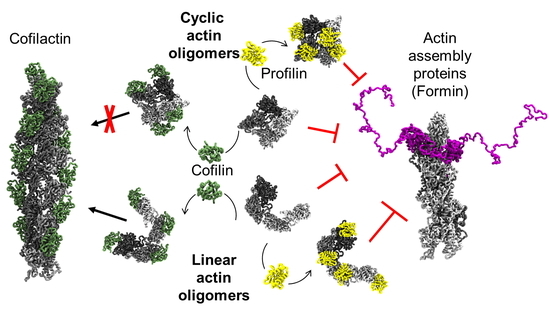
Rounding Out the Understanding of ACD Toxicity with the Discovery of Cyclic Forms of Actin Oligomers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
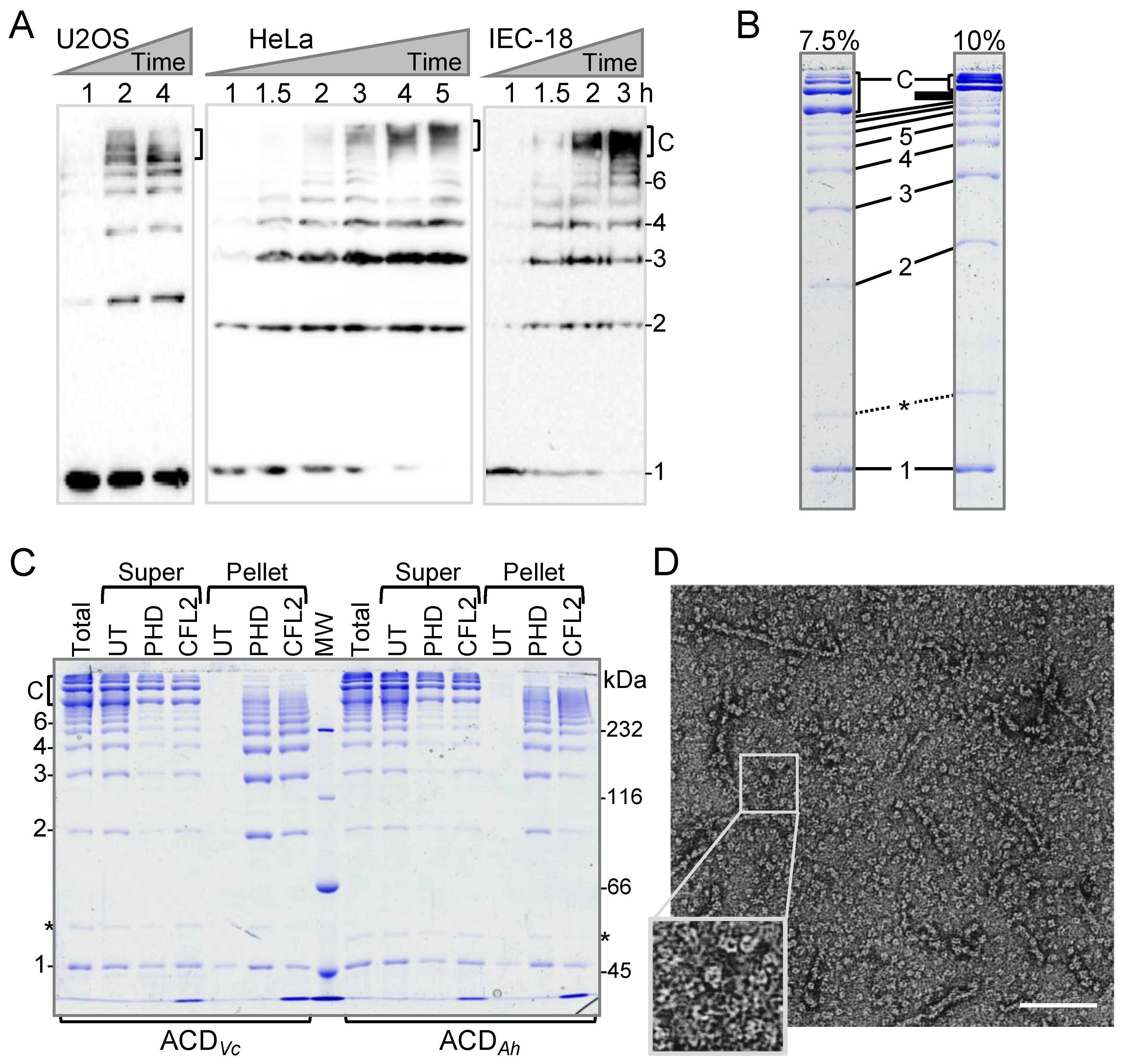
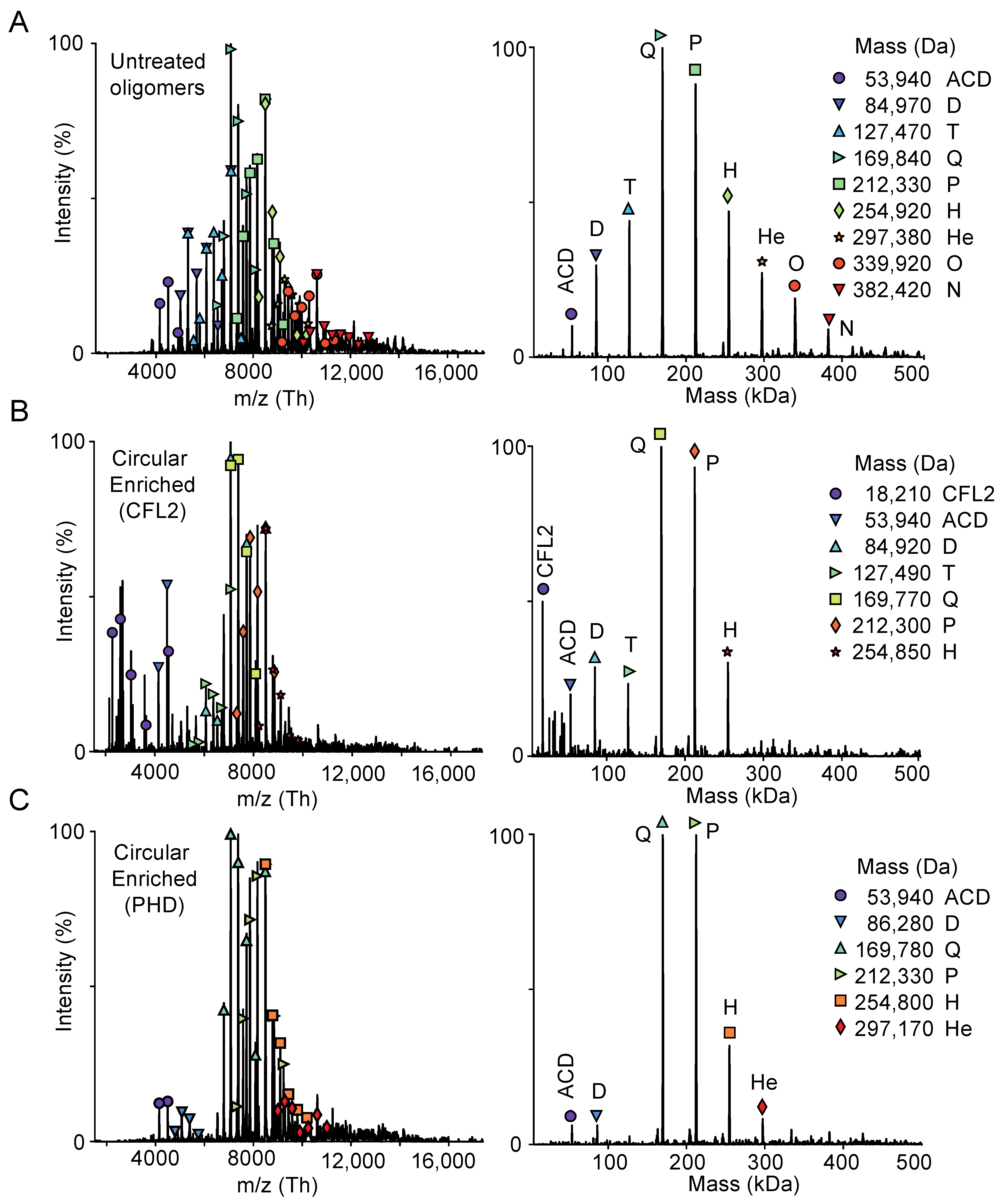
2.1. Discovery of a New Form of ACD-Cross-Linked Actin Oligomers
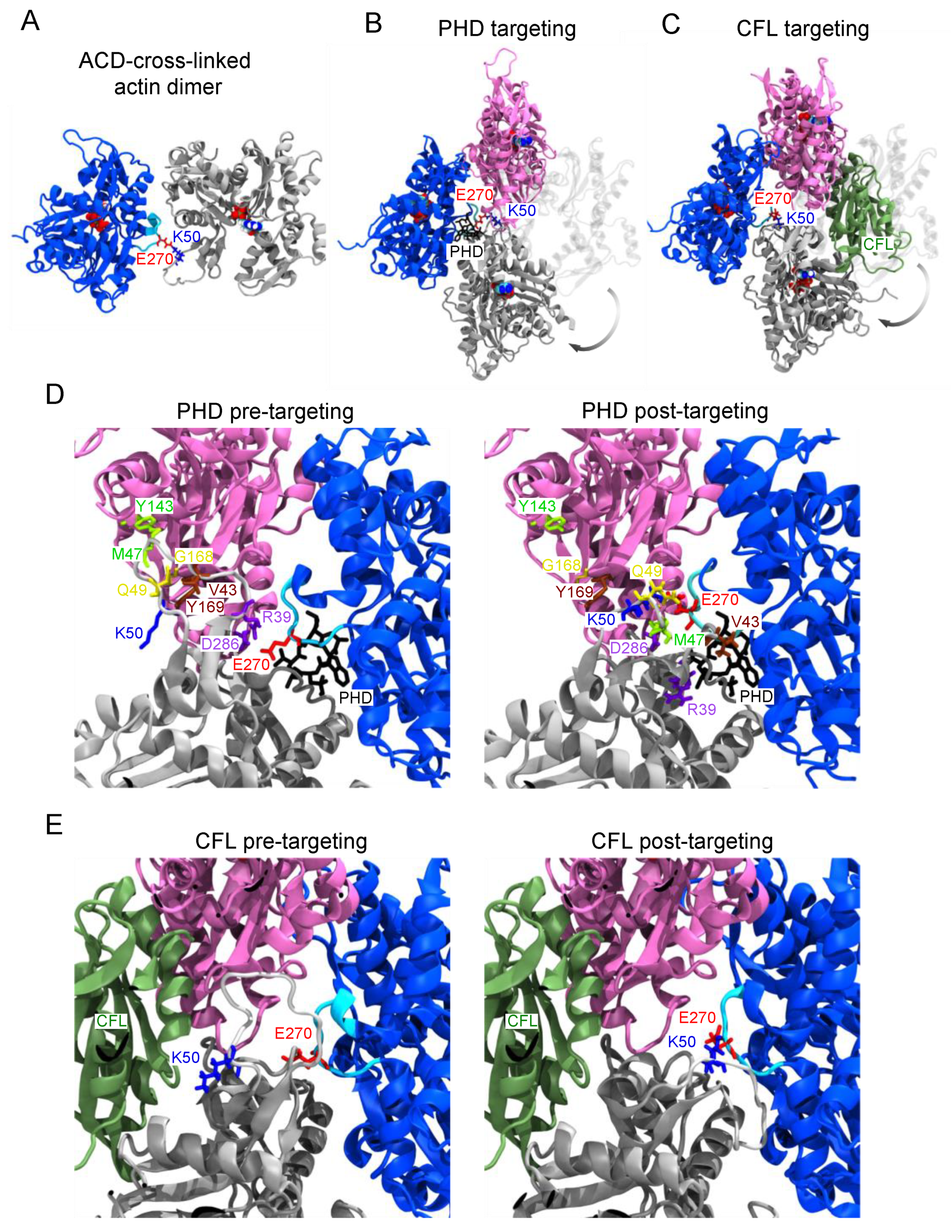
2.2. Structural Basis of Actin Oligomer Incorporation into F-Actin
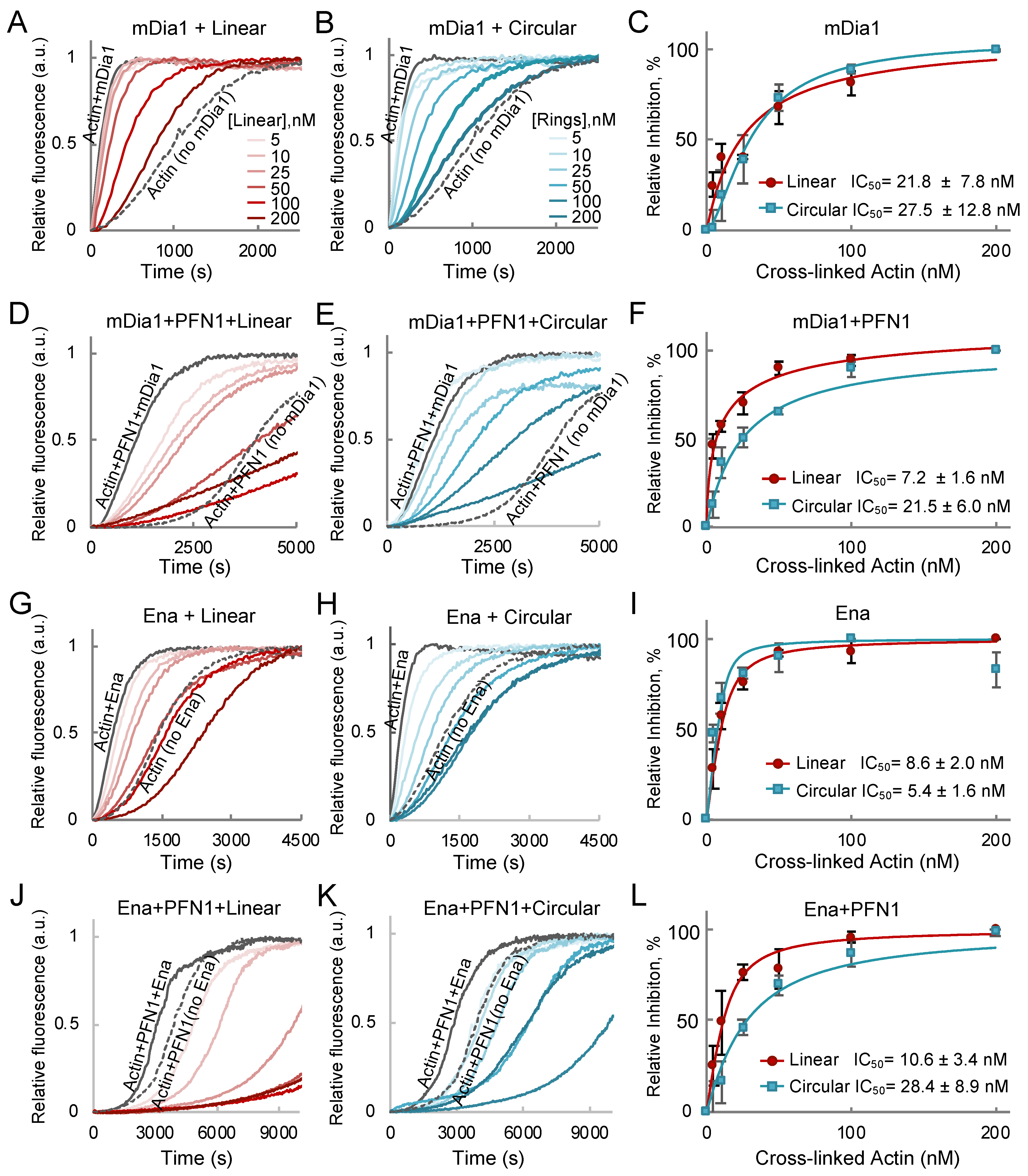
2.3. Linear and Cyclic AOs Inhibit Similarly Formin- and Ena/VASP-Driven Actin Assembly
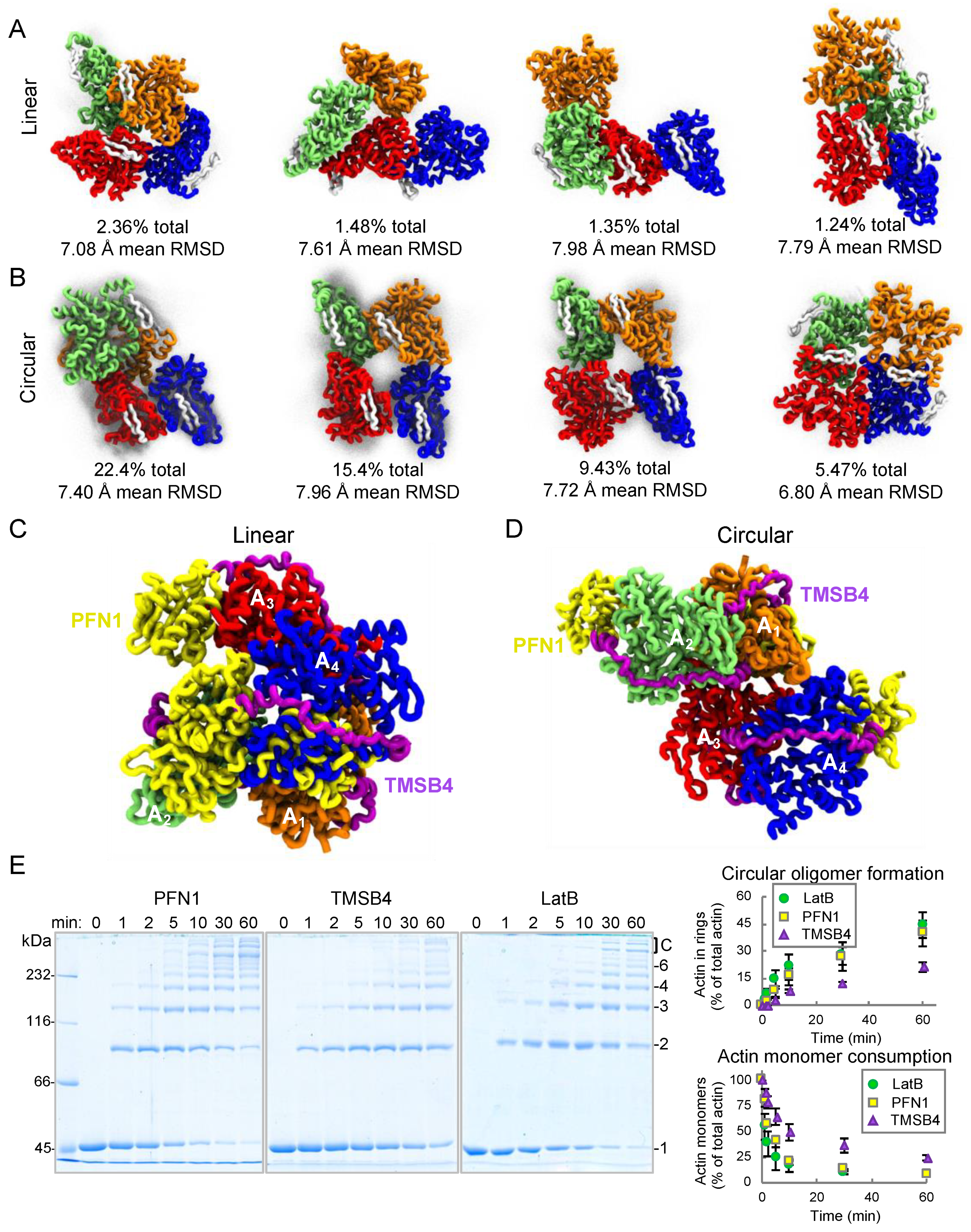
2.4. Coarse-Grained Simulations Predict Flexibility in AO Structure While Confirming that Profilin Binding Sites Stay Consistently Exposed
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Intracellular Actin Cross-Linking by ACD and Western Blotting
3.3. Protein Purification
3.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.5. Pyrenyl-Actin Polymerization Assays
3.6. In Vitro Actin Cross-Linking Assays
3.7. Mass Spectrometry
3.8. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.9. KH Model Coarse Graining
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACD | Actin cross-linking domain |
| AO | Actin oligomers |
| Atx | Anthrax toxin |
| β-ME | β-mercaptoethanol |
| CFL2 | Cofilin 2 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EGTA | Ethylene glycol-bis (β-aminoethyl ether)-N:N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid |
| FAB | F-actin binding domain |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GAB | G-actin binding domain |
| GS1 | Gelsolin segment 1 |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| IPTG | Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside |
| LatB | Latrunculin B |
| LFN | N-terminal fragment of lethal toxin |
| MARTX | Multifunctional auto-processing repeats-in-toxin |
| MOPS | 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| PA | Protective antigen |
| PFN1 | Profilin 1 |
| PHD | Phalloidin |
| PIPES | Piperazine-N,N’-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) |
| PMSF | Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
| PP | Polyproline |
| REMD | Replica exchange molecular dynamics |
| RMSD | Root-mean-square deviation |
| TMD | Targeted molecular dynamics |
| TMSB4 | Thymosin β4 |
| VASP | Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein |
| VgrG1 | Valine-glycine repeat protein G1 |
| WASP | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein |
| WH2 | WASP-homology motif 2 |
References
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Tan, Y.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Staiger, C.J.; Luo, Z.Q. A Legionella Effector Disrupts Host Cytoskeletal Structure by Cleaving Actin. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.E.; Qu, Z.; Schwan, C.; Silvan, U.; Unger, A.; Schoenenberger, C.A.; Aktories, K.; Mannherz, H.G. Actin ADP-ribosylation at Threonine148 by Photorhabdus luminescens toxin TccC3 induces aggregation of intracellular F-actin. Cell. Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurumura, T.; Tsumori, Y.; Qiu, H.; Oda, M.; Sakurai, J.; Nagahama, M.; Tsuge, H. Arginine ADP-ribosylation mechanism based on structural snapshots of iota-toxin and actin complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4267–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, E.; Heisler, D.B.; Kudryashov, D.S. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Actin Cross-Linking Toxins: Peeling Away the Layers. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 399, 87–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kudryashova, E.; Heisler, D.B.; Williams, B.; Harker, A.J.; Shafer, K.; Quinlan, M.E.; Kovar, D.R.; Vavylonis, D.; Kudryashov, D.S. Actin Cross-Linking Toxin Is a Universal Inhibitor of Tandem-Organized and Oligomeric G-Actin Binding Proteins. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, D.B.; Kudryashova, E.; Grinevich, D.O.; Suarez, C.; Winkelman, J.D.; Birukov, K.G.; Kotha, S.R.; Parinandi, N.L.; Vavylonis, D.; Kovar, D.R.; et al. ACTIN-DIRECTED TOXIN. ACD toxin-produced actin oligomers poison formin-controlled actin polymerization. Science 2015, 349, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukatzki, S.; Ma, A.T.; Revel, A.T.; Sturtevant, D.; Mekalanos, J.J. Type VI secretion system translocates a phage tail spike-like protein into target cells where it cross-links actin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15508–15513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woida, P.J.; Satchell, K.J.F. Coordinated delivery and function of bacterial MARTX toxin effectors. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 107, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, E.; Kalda, C.; Kudryashov, D.S. Glutamyl phosphate is an activated intermediate in actin crosslinking by actin crosslinking domain (ACD) toxin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, C.L.; Kudryashov, D.S.; Reisler, E.; Satchell, K.J. The Actin cross-linking domain of the Vibrio cholerae RTX toxin directly catalyzes the covalent cross-linking of actin. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32366–32374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashov, D.S.; Durer, Z.A.; Ytterberg, A.J.; Sawaya, M.R.; Pashkov, I.; Prochazkova, K.; Yeates, T.O.; Loo, R.R.; Loo, J.A.; Satchell, K.J.; et al. Connecting actin monomers by iso-peptide bond is a toxicity mechanism of the Vibrio cholerae MARTX toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18537–18542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, R. The WH2 Domain and Actin Nucleation: Necessary but Insufficient. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, N.M.; Janmey, P.A.; Almo, S.C. Structure of the profilin-poly-l-proline complex involved in morphogenesis and cytoskeletal regulation. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryashov, D.S.; Cordero, C.L.; Reisler, E.; Satchell, K.J. Characterization of the enzymatic activity of the actin cross-linking domain from the Vibrio cholerae MARTX Vc toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkin, V.E.; Orlova, A.; Schroder, G.F.; Egelman, E.H. Structural polymorphism in F-actin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospich, S.; Merino, F.; Raunser, S. Structural Effects and Functional Implications of Phalloidin and Jasplakinolide Binding to Actin Filaments. Structure 2020, 28, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ge, P.; Oztug Durer, Z.A.; Grintsevich, E.E.; Zhou, Z.H.; Reisler, E. D-loop Dynamics and Near-Atomic-Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of Phalloidin-Bound F-Actin. Structure 2020, 28, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoville, D.; Stamm, J.D.; Altenbach, C.; Shvetsov, A.; Kokabi, K.; Rubenstein, P.A.; Hubbell, W.L.; Reisler, E. Effects of binding factors on structural elements in F-actin. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oztug Durer, Z.A.; Diraviyam, K.; Sept, D.; Kudryashov, D.S.; Reisler, E. F-actin structure destabilization and DNase I binding loop: Fluctuations mutational cross-linking and electron microscopy analysis of loop states and effects on F-actin. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashov, D.S.; Phillips, M.; Reisler, E. Formation and destabilization of actin filaments with tetramethylrhodamine-modified actin. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bobkov, A.A.; Muhlrad, A.; Shvetsov, A.; Benchaar, S.; Scoville, D.; Almo, S.C.; Reisler, E. Cofilin (ADF) affects lateral contacts in F-actin. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 337, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobkov, A.A.; Muhlrad, A.; Kokabi, K.; Vorobiev, S.; Almo, S.C.; Reisler, E. Structural effects of cofilin on longitudinal contacts in F-actin. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 323, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashov, D.S.; Galkin, V.E.; Orlova, A.; Phan, M.; Egelman, E.H.; Reisler, E. Cofilin cross-bridges adjacent actin protomers and replaces part of the longitudinal F-actin interface. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 358, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huehn, A.R.; Bibeau, J.P.; Schramm, A.C.; Cao, W.; De La Cruz, E.M.; Sindelar, C.V. Structures of cofilin-induced structural changes reveal local and asymmetric perturbations of actin filaments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Takeda, S.; Mitsuoka, K.; Oda, T.; Kimura-Sakiyama, C.; Maeda, Y.; Narita, A. Structural basis for cofilin binding and actin filament disassembly. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlrad, A.; Kudryashov, D.; Michael Peyser, Y.; Bobkov, A.A.; Almo, S.C.; Reisler, E. Cofilin induced conformational changes in F-actin expose subdomain 2 to proteolysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, V.; Karplus, M. Analysis and elimination of a bias in targeted molecular dynamics simulations of conformational transitions: Application to calmodulin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 8584–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R.; Holmes, K.C. Actin structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 40, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durer, Z.A.; Kudryashov, D.S.; Sawaya, M.R.; Altenbach, C.; Hubbell, W.; Reisler, E. Structural states and dynamics of the D-loop in actin. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvetsov, A.; Galkin, V.E.; Orlova, A.; Phillips, M.; Bergeron, S.E.; Rubenstein, P.A.; Egelman, E.H.; Reisler, E. Actin hydrophobic loop 262-274 and filament nucleation and elongation. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, J.D.; Bilancia, C.G.; Peifer, M.; Kovar, D.R. Ena/VASP Enabled is a highly processive actin polymerase tailored to self-assemble parallel-bundled F-actin networks with Fascin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4121–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R. The beta-thymosin/WH2 fold: Multifunctionality and structure. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1112, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Diraviyam, K.; Sept, D. Nucleotide effects on the structure and dynamics of actin. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Hummer, G. Coarse-grained models for simulations of multiprotein complexes: Application to ubiquitin binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 375, 1416–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Tang, C.; Clore, G.M.; Hummer, G. Replica exchange simulations of transient encounter complexes in protein-protein association. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12855–12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, B.G.; Hall, A.R.; Vavylonis, D. Insights into Actin Polymerization and Nucleation Using a Coarse-Grained Model. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, B.G.; Zerze, G.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Vavylonis, D.; Mittal, J. Computational modeling highlights the role of the disordered Formin Homology 1 domain in profilin-actin transfer. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, R.C.; Melo, M.C.R.; Schulten, K. Enhanced sampling techniques in molecular dynamics simulations of biological systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhikara, D.J.; Emerson, D.J.; Roitberg, A.E. Exchange Often and Properly in Replica Exchange Molecular Dynamics. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2010, 6, 2804–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhikara, D.; Meng, Y.; Roitberg, A.E. Exchange frequency in replica exchange molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Aleman, R.; Hernandez-Castillo, D.; Caballero, J.; Montero-Cabrera, L.A. Quality Threshold Clustering of Molecular Dynamics: A Word of Caution. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uphoff, C.C.; Drexler, H.G. Detection of Mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2014, 106, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Leppla, S.H. Fusions of anthrax toxin lethal factor with shiga toxin and diphtheria toxin enzymatic domains are toxic to mammalian cells. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4955–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, J.C.; Blanke, S.R.; Hanna, P.C.; Collier, R.J. Protective antigen-binding domain of anthrax lethal factor mediates translocation of a heterologous protein fused to its amino- or carboxy-terminus. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 15, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesche, J.; Elliott, J.L.; Falnes, P.O.; Olsnes, S.; Collier, R.J. Characterization of membrane translocation by anthrax protective antigen. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 15737–15746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, E.; Quintyn, R.; Seveau, S.; Lu, W.; Wysocki, V.H.; Kudryashov, D.S. Human defensins facilitate local unfolding of thermodynamically unstable regions of bacterial protein toxins. Immunity 2014, 41, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, E.; Seveau, S.; Lu, W.; Kudryashov, D.S. Retrocyclins neutralize bacterial toxins by potentiating their unfolding. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, J.A.; Watt, S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 4866–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashova, E.; Heisler, D.; Zywiec, A.; Kudryashov, D.S. Thermodynamic properties of the effector domains of MARTX toxins suggest their unfolding for translocation across the host membrane. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 92, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purde, V.; Busch, F.; Kudryashova, E.; Wysocki, V.H.; Kudryashov, D.S. Oligomerization Affects the Ability of Human Cyclase-Associated Proteins 1 and 2 to Promote Actin Severing by Cofilins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehl, J.; Kudryashova, E.; Reisler, E.; Kudryashov, D.; Polenova, T. Structural Analysis of Human Cofilin 2/Filamentous Actin Assemblies: Atomic-Resolution Insights from Magic Angle Spinning NMR Spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz, E.M.; Ostap, E.M.; Brundage, R.A.; Reddy, K.S.; Sweeney, H.L.; Safer, D. Thymosin-beta(4) changes the conformation and dynamics of actin monomers. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.; Neidt, E.M.; Cui, J.; Feiger, Z.; Skau, C.T.; Gardel, M.L.; Kozmin, S.A.; Kovar, D.R. Identification and characterization of a small molecule inhibitor of formin-mediated actin assembly. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashov, D.S.; Grintsevich, E.E.; Rubenstein, P.A.; Reisler, E. A nucleotide state-sensing region on actin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 25591–25601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aernum, Z.L.; Busch, F.; Jones, B.J.; Jia, M.; Chen, Z.; Boyken, S.E.; Sahasrabuddhe, A.; Baker, D.; Wysocki, V.H. Rapid online buffer exchange for screening of proteins, protein complexes and cell lysates by native mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1132–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aernum, Z.L.; Gilbert, J.D.; Belov, M.E.; Makarov, A.A.; Horning, S.R.; Wysocki, V.H. Surface-Induced Dissociation of Noncovalent Protein Complexes in an Extended Mass Range Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3611–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, M.T.; Baldwin, A.J.; Marklund, E.G.; Hochberg, G.K.; Benesch, J.L.; Robinson, C.V. Bayesian deconvolution of mass and ion mobility spectra: From binary interactions to polydisperse ensembles. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4370–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. CHARMM36 all-atom additive protein force field: Validation based on comparison to NMR data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, M.V.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr. A smoothed backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins derived from adaptive kernel density estimates and regressions. Structure 2011, 19, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J. An Efficient Library for Parallel Ray Tracing and Animation. Master’s Thesis, University of Missouri-Rolla, Rolla, MO, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, J.C.; Hardy, D.J.; Maia, J.D.C.; Stone, J.E.; Ribeiro, J.V.; Bernardi, R.C.; Buch, R.; Fiorin, G.; Henin, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 044130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frishman, D.; Argos, P. Knowledge-based protein secondary structure assignment. Proteins 1995, 23, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.; Rodenkirch, P.; Siggel, M.; Bernardi, R.C.; Schulten, K.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Rudack, T. PyContact: Rapid, Customizable, and Visual Analysis of Noncovalent Interactions in MD Simulations. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular-Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, E.; Derrez, E.; Audoly, G.; Spinelli, S.; Ortiz-Lombardia, M.; Raoult, D.; Cascales, E.; Cambillau, C. Crystal structure of the VgrG1 actin cross-linking domain of the Vibrio cholerae type VI secretion system. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38190–38199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud-Agrawal, N.; Denning, E.J.; Woolf, T.B.; Beckstein, O. MDAnalysis: A toolkit for the analysis of molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutt, C.E.; Myslik, J.C.; Rozycki, M.D.; Goonesekere, N.C.; Lindberg, U. The structure of crystalline profilin-beta-actin. Nature 1993, 365, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, W.M.; Ayscough, K.R.; McLaughlin, P.J. Latrunculin alters the actin-monomer subunit interface to prevent polymerization. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Leyrat, C.; Grimes, J.M.; Robinson, R.C. Structural basis of thymosin-beta4/profilin exchange leading to actin filament polymerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4596–E4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chereau, D.; Kerff, F.; Graceffa, P.; Grabarek, Z.; Langsetmo, K.; Dominguez, R. Actin-bound structures of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)-homology domain 2 and the implications for filament assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16644–16649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, H.; Pinkerton, N.; Heisler, D.B.; Kudryashova, E.; Hall, A.R.; Karch, K.R.; Norris, A.; Wysocki, V.; Sotomayor, M.; Reisler, E.; et al. Rounding Out the Understanding of ACD Toxicity with the Discovery of Cyclic Forms of Actin Oligomers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020718
Smith H, Pinkerton N, Heisler DB, Kudryashova E, Hall AR, Karch KR, Norris A, Wysocki V, Sotomayor M, Reisler E, et al. Rounding Out the Understanding of ACD Toxicity with the Discovery of Cyclic Forms of Actin Oligomers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020718
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Harper, Nick Pinkerton, David B. Heisler, Elena Kudryashova, Aaron R. Hall, Kelly R. Karch, Andrew Norris, Vicki Wysocki, Marcos Sotomayor, Emil Reisler, and et al. 2021. "Rounding Out the Understanding of ACD Toxicity with the Discovery of Cyclic Forms of Actin Oligomers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020718
APA StyleSmith, H., Pinkerton, N., Heisler, D. B., Kudryashova, E., Hall, A. R., Karch, K. R., Norris, A., Wysocki, V., Sotomayor, M., Reisler, E., Vavylonis, D., & Kudryashov, D. S. (2021). Rounding Out the Understanding of ACD Toxicity with the Discovery of Cyclic Forms of Actin Oligomers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020718