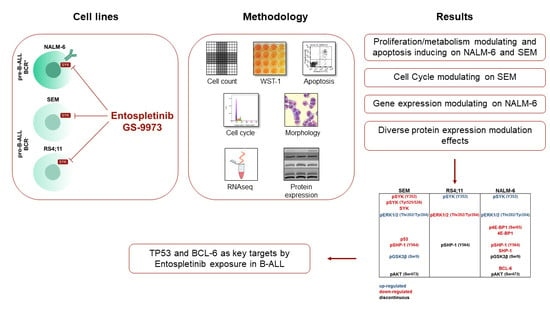
Precursor B-ALL Cell Lines Differentially Respond to SYK Inhibition by Entospletinib
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
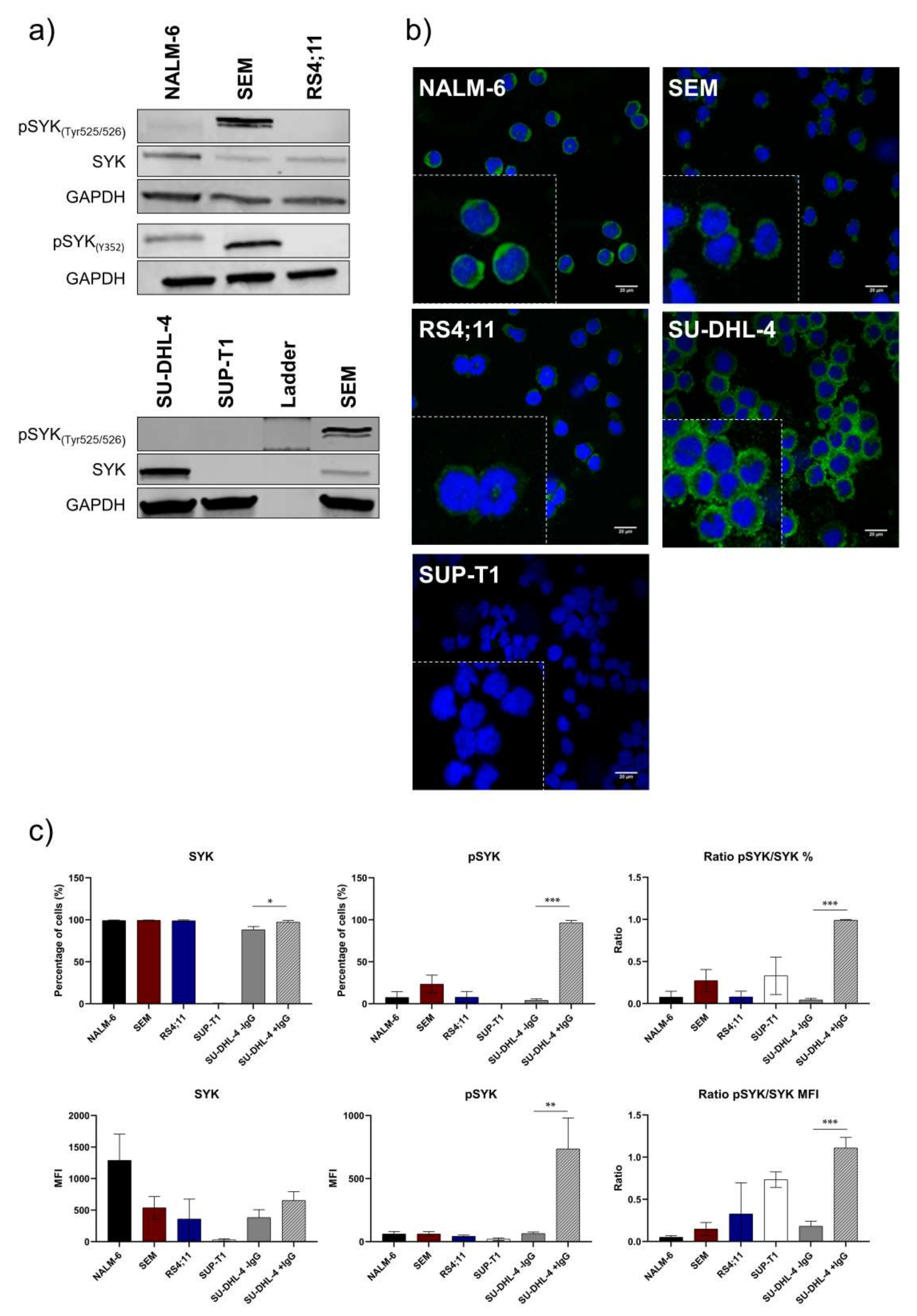
2.1. Pro-B-ALL Cell Line SEM is Characterized by High SYK and pSYK Expression
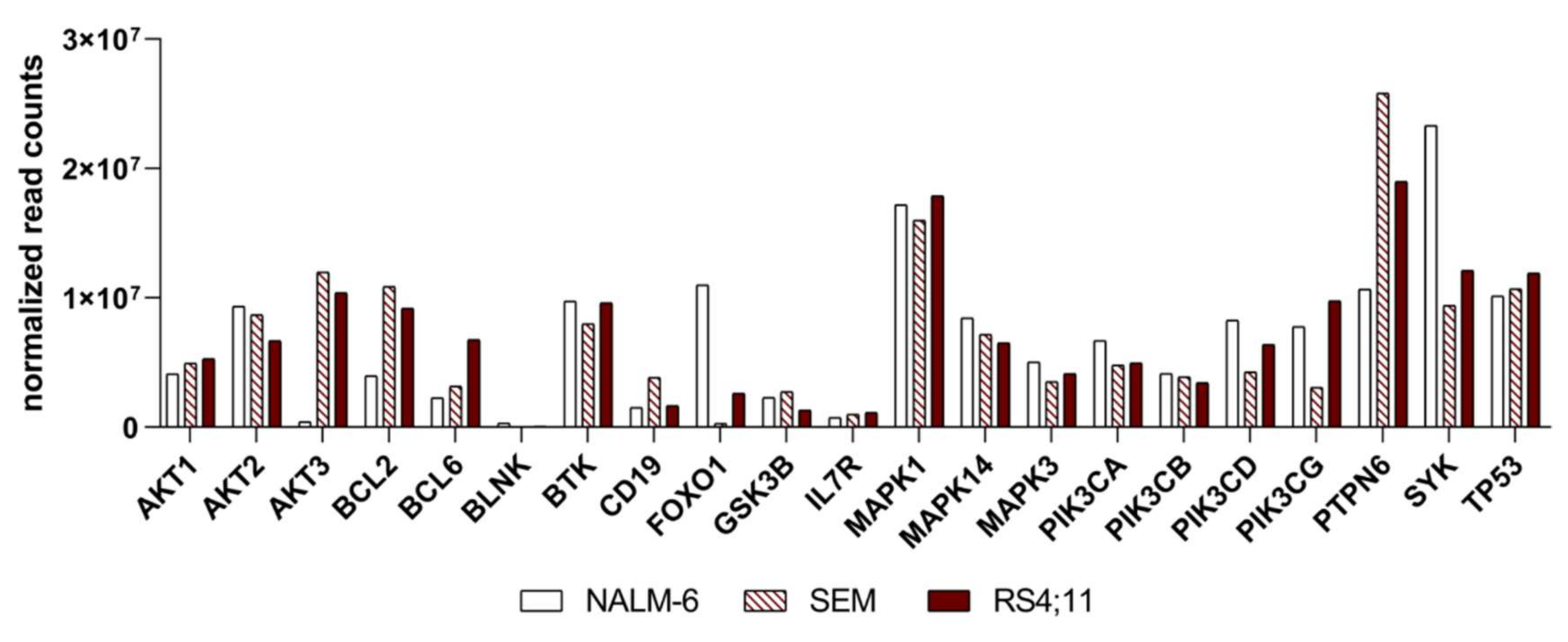
2.2. Basal Expression Analysis of Key B-Cell Receptor Genes in the B-Acute Lymphoblastic Cell Lines NALM-6, SEM and RS4;11
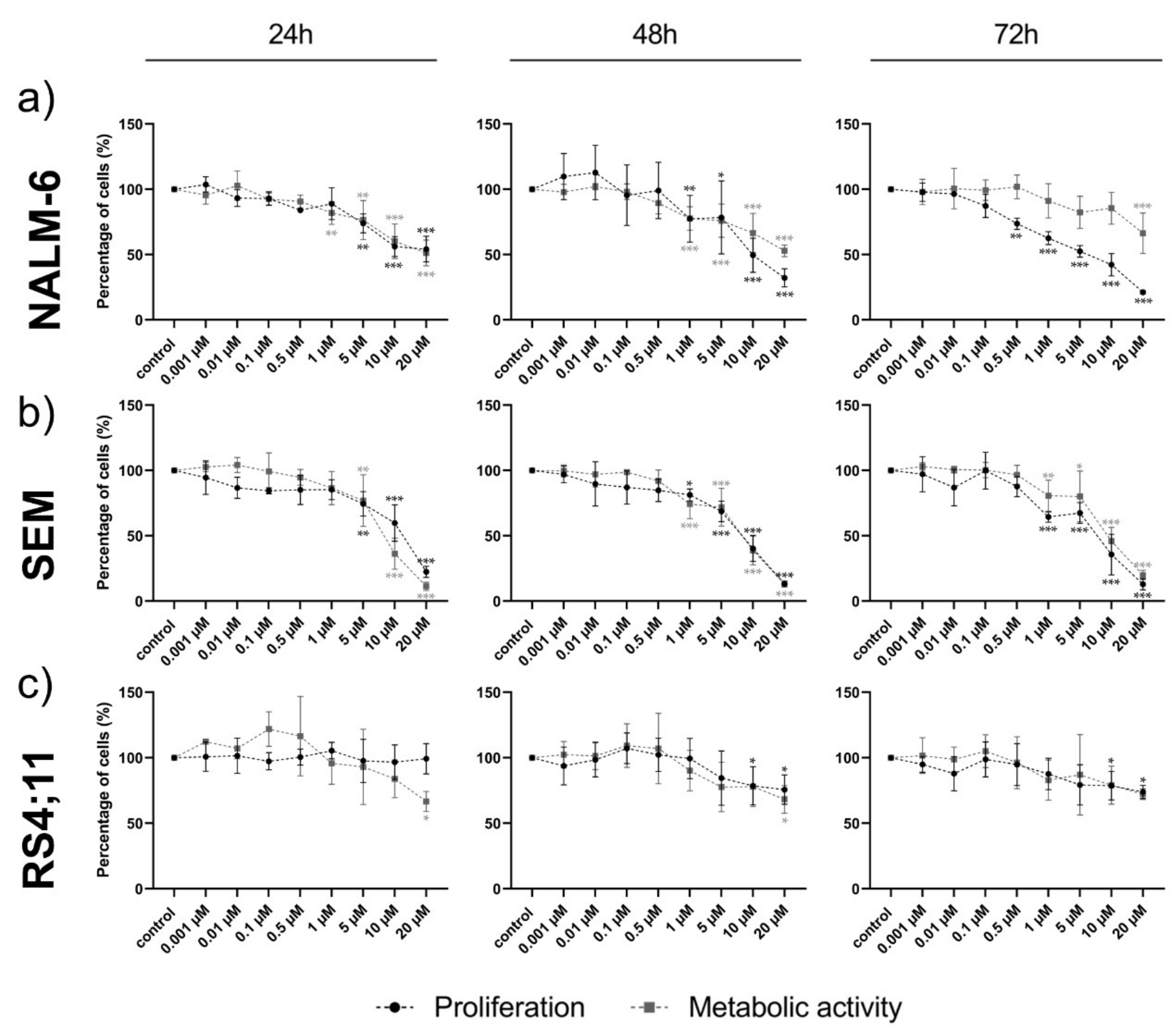
2.3. Ento Sensitivity Is Independent of the Pre-BCR Status
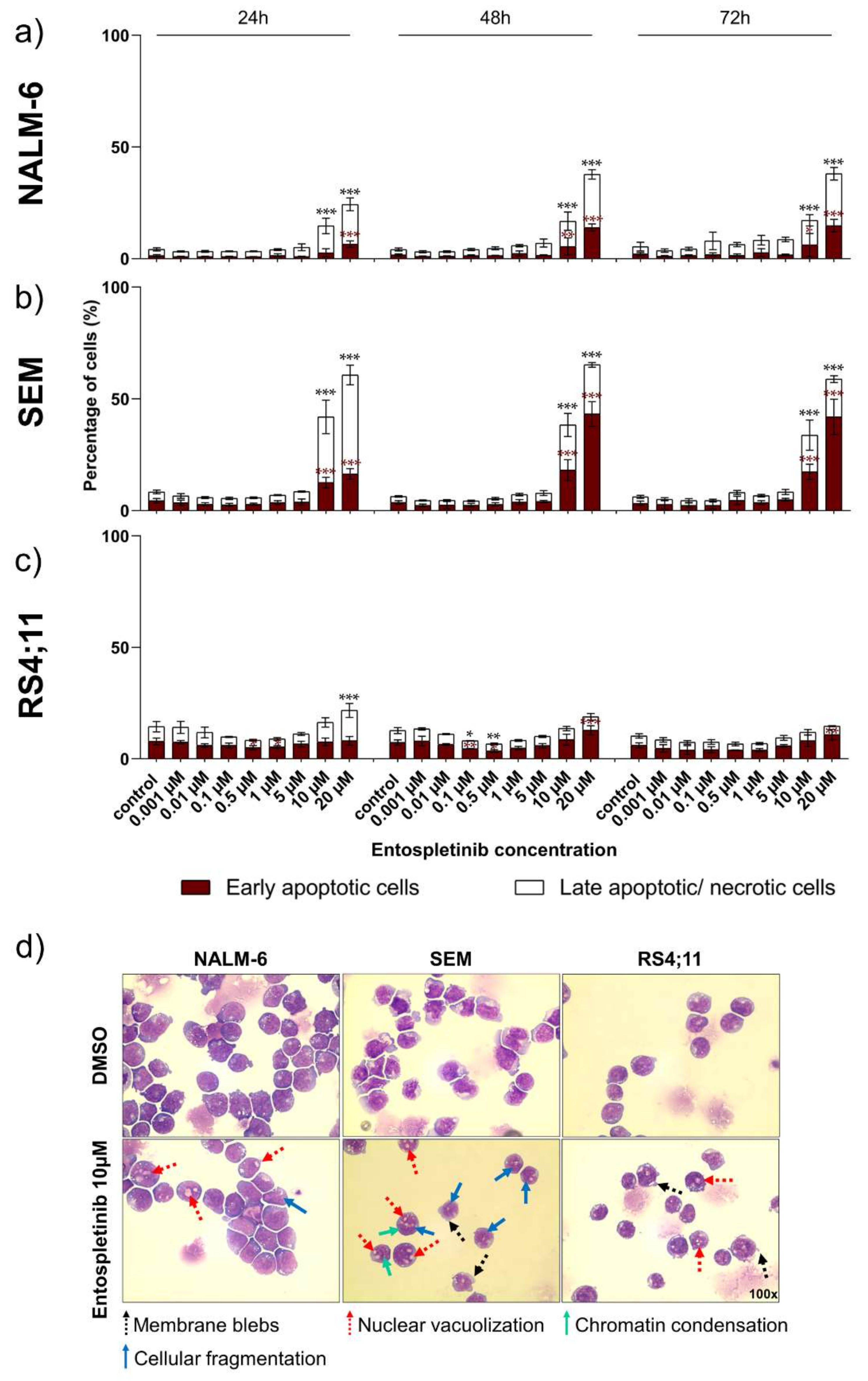
2.4. Pro-Apoptotic Effects Are Provoked by High Entospletinib Concentrations, Independent of Pre-BCR Dependency
2.5. Morphological Characterization Indicates Pro-Apoptotic Effects in Pre- and Pro-B-ALL Cell Lines In Vitro
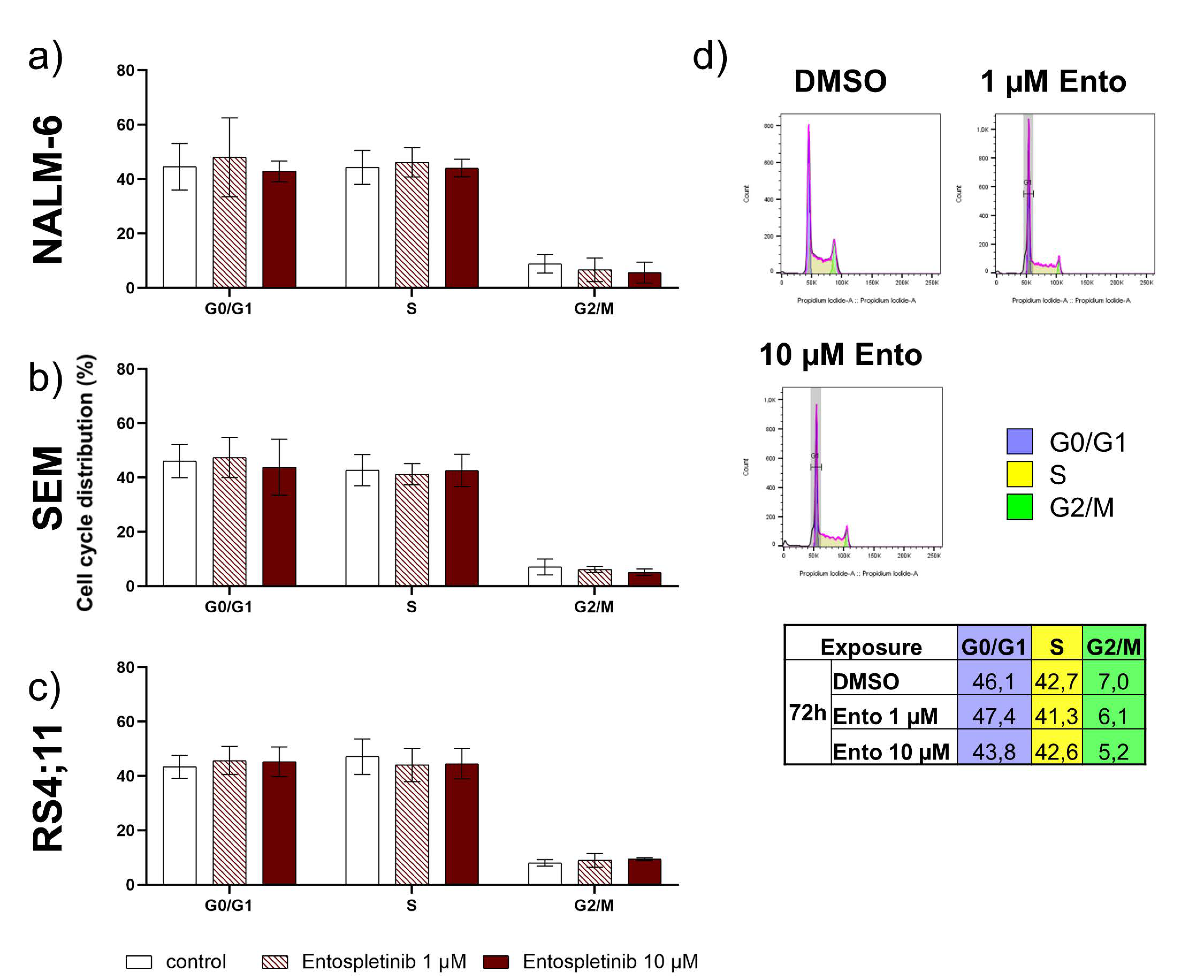
2.6. Entospletinib Does Not Induce Cell-Cycle Arrest in B-ALL Cell Lines
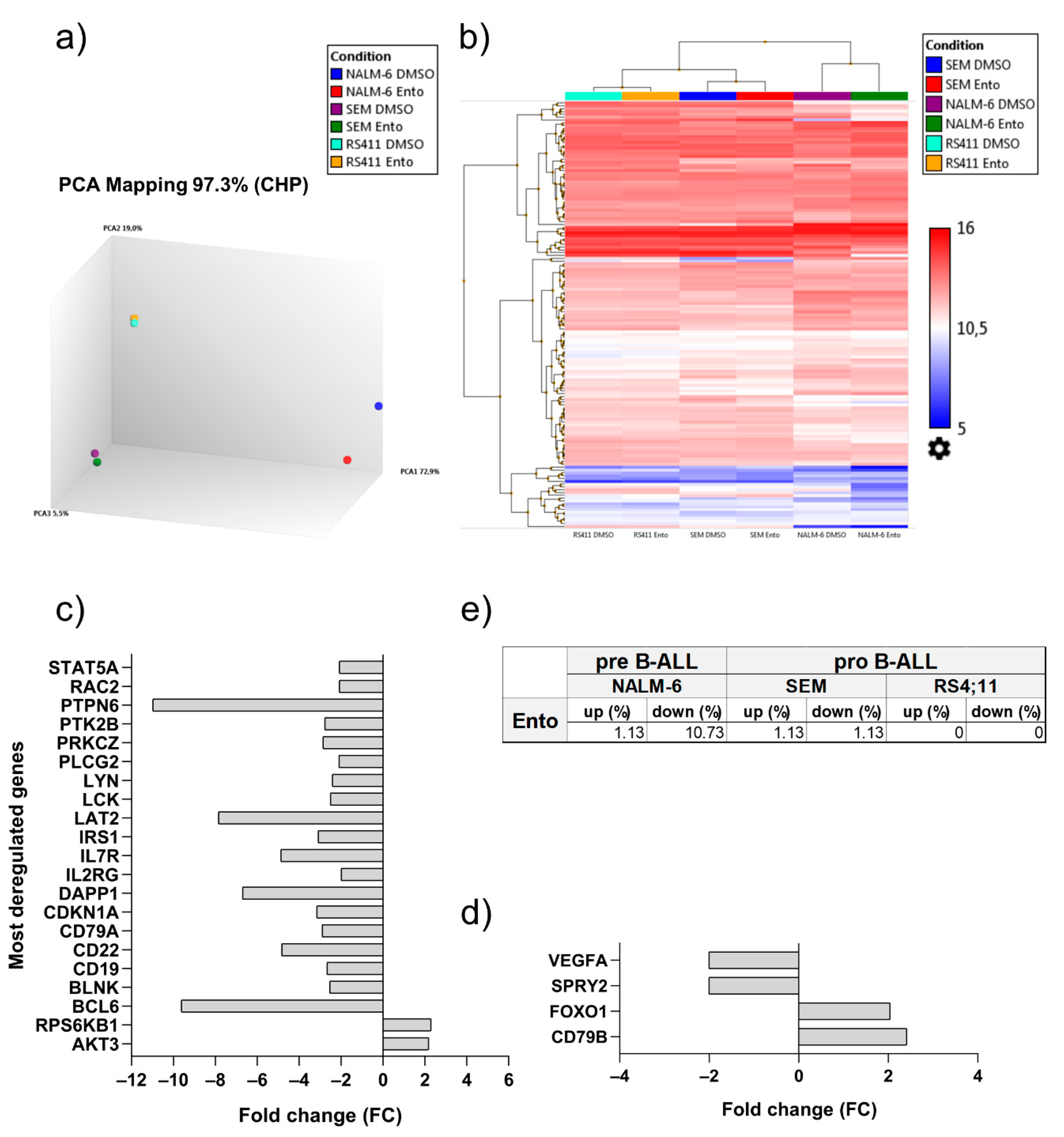
2.7. Entospletinib Downregulates Gene Expression of PTPN6 and BCL-6 in Pre-B-ALL NALM-6
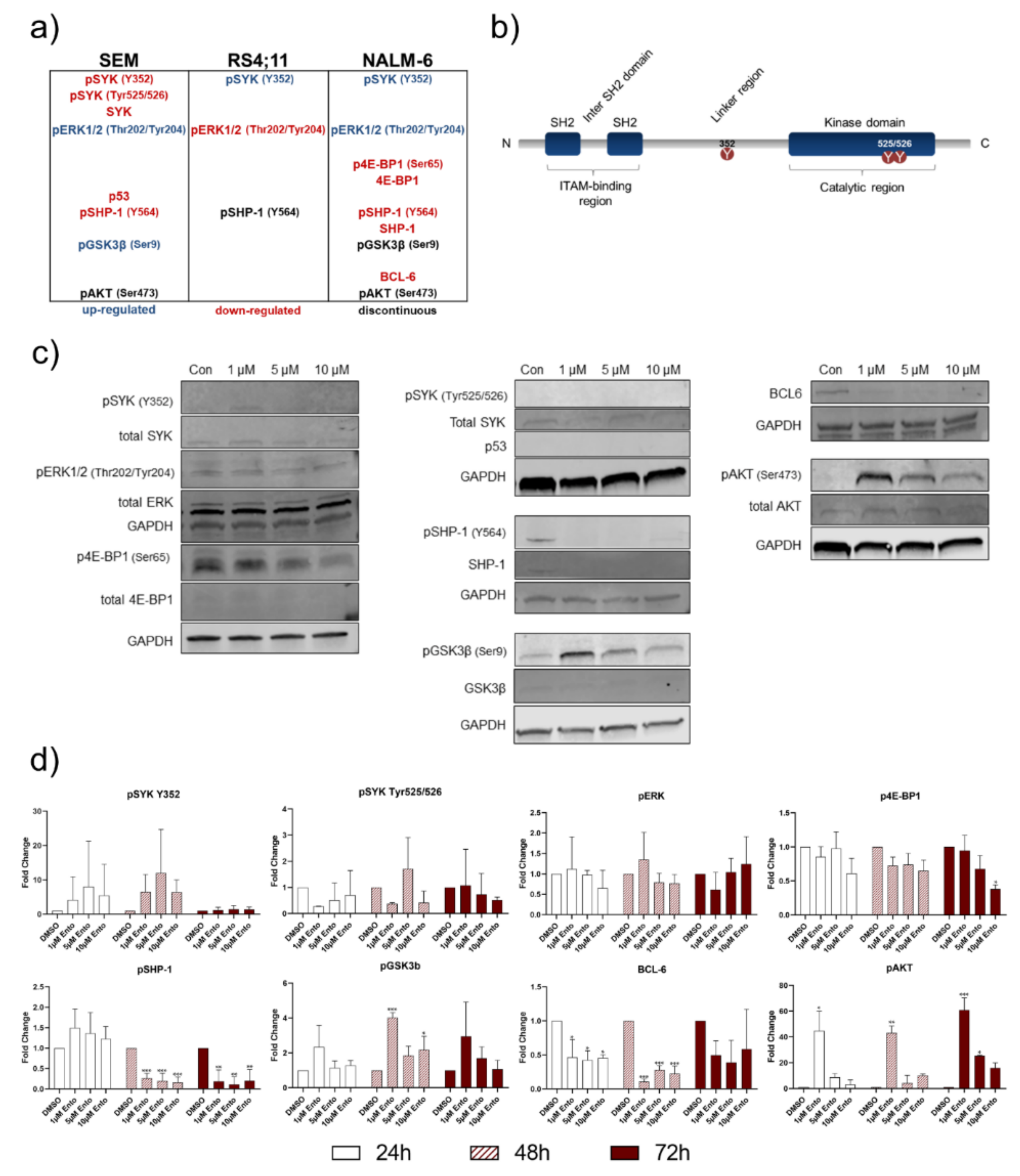
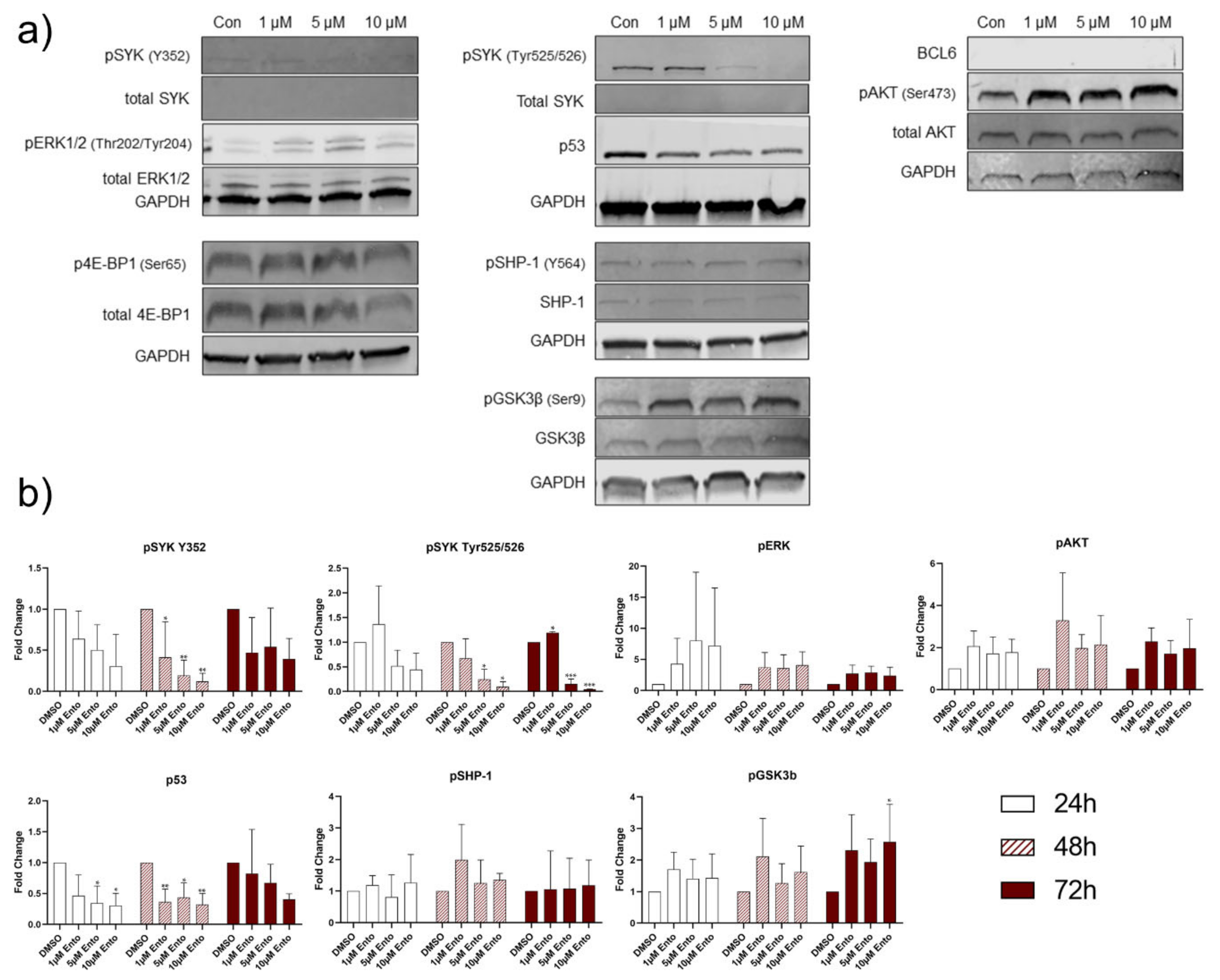
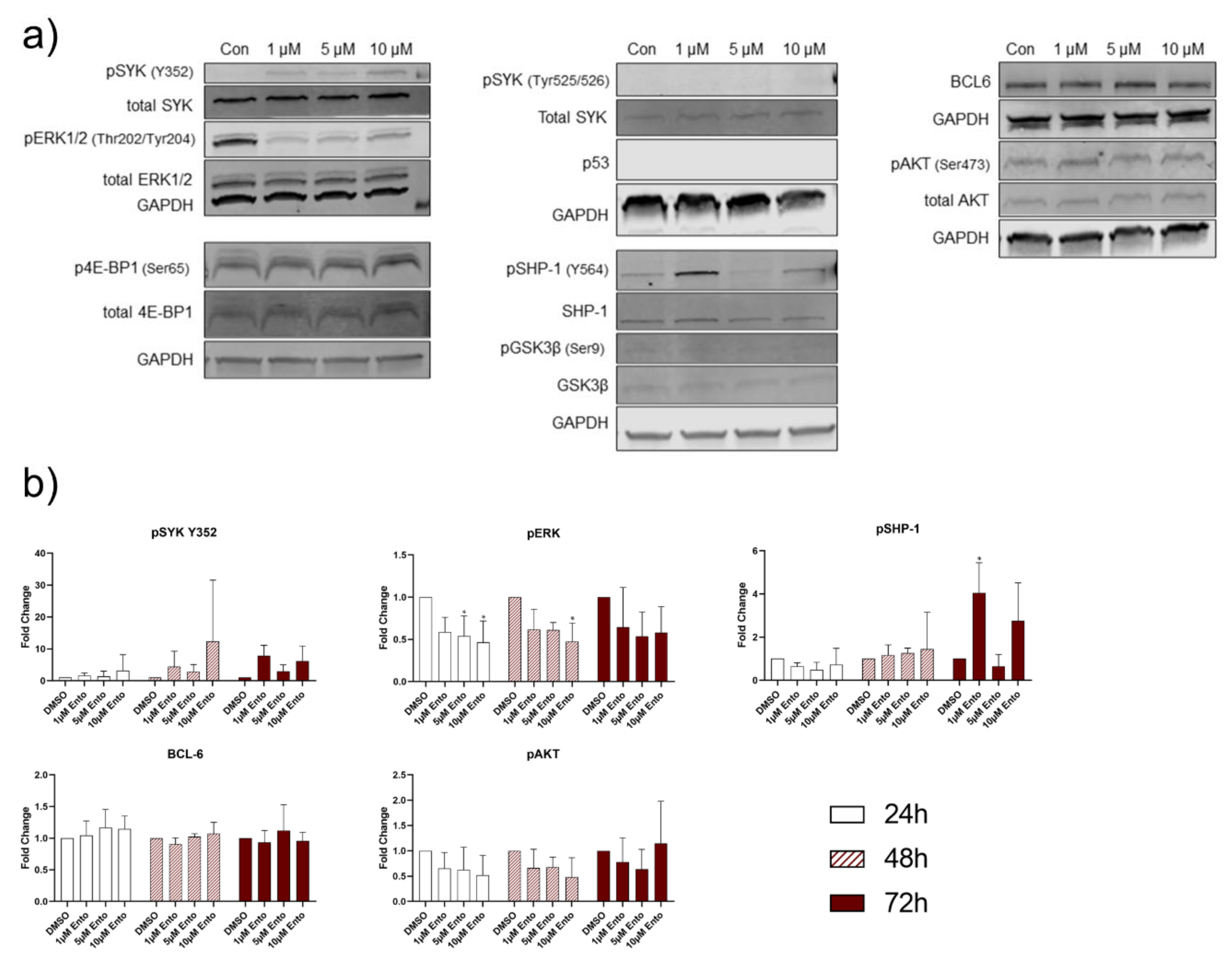
2.8. Downstream Protein Characterization Unveiled p53 and BCL-6 as Key Targets by Entospletinib Exposure
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Drug Exposure Experiments
4.3. Cell Proliferation
4.4. WST-1 Proliferation Assay
4.5. Apoptosis Assay
4.6. Cell-Cycle Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.8. Pappenheim Staining
4.9. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analyses
4.10. Intracellular Phospho-Specific Flow Cytometry and Stimulation
4.11. RNA Extraction and Isolation
4.12. Targeted RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
4.13. Statistics and Reproducibility
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4E-BP1 | Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4E |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| Avg | Average |
| B-ALL | B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| BCL-2 | BCL2 Apoptosis Regulator |
| BCL-6 | BCL6 Transcription Repressor |
| BCR | B-cell receptor |
| BCR- | B-cell receptor negative |
| BCR+ | B-cell receptor positive |
| BIM | Bcl-2-like protein 11 |
| BLNK | B Cell Linker |
| BTK | Bruton Tyrosine Kinase |
| CD22 | B-Lymphocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule |
| CD79B | B-Cell Antigen Receptor Complex-Associated Protein Beta Chain |
| CDC25C | Cell Division Cycle 25C |
| CDK1 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 |
| CLL | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| DAPP1 | Dual Adaptor Of Phosphotyrosine And 3-Phosphoinositides 1 |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| DN | Dominant negative |
| Ento | Entospletinib |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FL | Follicular lymphoma |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead Box O1 |
| GoF | Gain-of-function |
| GS-9973 | Entospletinib, SYK inhibitor |
| GSK3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta |
| IC50 | Half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| Igµ | Immunoglobulin heavy chains |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| Ig-α | Immunoglobulin (Ig)α cytoplasmic domain |
| Ig-β | Immunoglobulin (Ig)β cytoplasmic ddomain |
| IL7R | Interleukin 7 Receptor |
| ITAMs | Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs |
| LAT2 | Linker For Activation Of T Cells Family Member 2 |
| LoF | Loss-of-function |
| MAP | Mitogen-activated protein |
| MCL | Mantle cell lymphoma |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
| MFI | Mean fluorescence intensity |
| MLL | Mixed lineage leukemia |
| p | Phospho |
| p53 | Tumor Protein P53 |
| p63 | Tumor protein P63 |
| p73 | Tumor protein P73 |
| PCA | Principle component analysis |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PRT318 | SYK Inhibitor |
| PTPN6 | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-Receptor Type 6 |
| R406 | SYK Inhibitor |
| Raf | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| RAS | Rat sarcoma |
| RPS6KB1 | Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase B1 |
| S | Serine |
| Ser | Serine |
| SHP-1 | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-Receptor Type 6 |
| SPRY2 | Sprouty RTK Signaling Antagonist 2 |
| SYK | Spleen tyrosine kinase |
| TAC | Transcriptome Analysis Console |
| TCF3-PBX1 | Fusion gene Transcription Factor 3 and PBX Homeobox 1 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TP53 | Tumor Protein P53 |
| Tyr | Tyrosin |
| VEGFA | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A |
| wt | Wild type |
| Y | Tyrosin |
References
- Kenkre, V.P.; Kahl, B.S. The Future of B-Cell Lymphoma Therapy: The B-Cell Receptor and its Downstream Pathways. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2012, 7, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mócsai, A.; Ruland, J.; Tybulewicz, V.L.J. The SYK tyrosine kinase: A crucial player in diverse biological functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.; Mee, P.J.; Costello, P.S.; Williams, O.; Price, A.A.; Duddy, L.P.; Furlong, M.T.; Geahlen, R.L.; Tybulewicz, V.L. Perinatal lethality and blocked B-cell development in mice lacking the tyrosine kinase Syk. Nature 1995, 378, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhrer, S.; Havranek, O.; Seyfried, F.; Hurtz, C.; Coffey, G.P.; Kim, E.; Hacken, E.T.; Jäger, U.; Vanura, K.; O’Brien, S.; et al. Pre-BCR signaling in precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia regulates PI3K/AKT, FOXO1 and MYC, and can be targeted by SYK inhibition. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornall, R.J.; Cheng, A.M.; Pawson, T.; Goodnow, C.C. Role of Syk in B-cell development and antigen-receptor signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.M.; Rowley, B.; Pao, W.; Hayday, A.; Bolen, J.B.; Pawson, T. Syk tyrosine kinase required for mouse viability and B-cell development. Nature 1995, 378, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reth, M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature 1989, 338, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, T. Molecular dissection of B cell antigen receptor signaling (review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 1998, 1, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toapanta, F.R.; Bernal, P.J.; Sztein, M.B. Diverse phosphorylation patterns of B cell receptor-associated signaling in naïve and memory human B cells revealed by phosphoflow, a powerful technique to study signaling at the single cell level. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Matsushita, M.; Watanabe, D.; Kishimoto, T.; Kurosaki, T.; Tsukada, S. BLNK mediates Syk-dependent Btk activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2582–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T.; Sanjo, H.; Pagès, G.; Kawano, Y.; Karasuyama, H.; Pouysségur, J.; Ogata, M.; Kurosaki, T. Erk Kinases Link Pre-B Cell Receptor Signaling to Transcriptional Events Required for Early B Cell Expansion. Immunity 2008, 28, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, S.; Hug, E.; Meixlsperger, S.; Paik, J.; DePinho, R.A.; Reth, M.; Jumaa, H. SLP-65 regulates immunoglobulin light chain gene recombination through the PI(3)K-PKB-Foxo pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchner, M.; Fuchs, S.; Prinz, G.; Pfeifer, D.; Bartholomé, K.; Burger, M.; Chevalier, N.; Vallat, L.; Timmer, J.; Gribben, J.G.; et al. Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Is Overexpressed and Represents a Potential Therapeutic Target in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5424–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Monti, S.; Juszczynski, P.; Daley, J.; Chen, W.; Witzig, T.E.; Habermann, T.M.; Kutok, J.L.; Shipp, M.A. SYK-dependent tonic B-cell receptor signaling is a rational treatment target in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, A.; Kwee, I.; Taborelli, M.; Largo, C.; Uccella, S.; Martin, V.; Poretti, G.; Gaidano, G.; Calabrese, G.; Martinelli, G.; et al. Genomic and expression profiling identifies the B-cell associated tyrosine kinase Syk as a possible therapeutic target in mantle cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 132, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, J.M.; Czerwinski, D.K.; Nolan, G.P.; Levy, R. Altered B-cell receptor signaling kinetics distinguish human follicular lymphoma B cells from tumor-infiltrating nonmalignant B cells. Blood 2006, 108, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, M.; Jennings, C.D.; Bondada, S. Cutting Edge: Constitutive B Cell Receptor Signaling Is Critical for Basal Growth of B Lymphoma. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5715–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, P.A.; Wood, C.M.; Vassilev, A.; Mao, C.; Uckun, F.M. Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) deficiency in childhood pro-B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perova, T.; Grandal, I.; Nutter, L.M.J.; Papp, E.; Matei, I.R.; Beyene, J.; Kowalski, P.E.; Hitzler, J.K.; Minden, M.D.; Guidos, C.J. Therapeutic potential of spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition for treating high-risk precursor B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 236ra62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedberg, J.W.; Sharman, J.; Sweetenham, J.; Johnston, P.B.; Vose, J.M.; Lacasce, A.; Schaefer-Cutillo, J.; de Vos, S.; Sinha, R.; Leonard, J.P.; et al. Inhibition of Syk with fostamatinib disodium has significant clinical activity in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 2578–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.; Hawkins, M.; Kolibaba, K.; Boxer, M.; Klein, L.; Wu, M.; Hu, J.; Abella, S.; Yasenchak, C. An open-label phase 2 trial of entospletinib (GS-9973), a selective spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 2336–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, S.M.; Feldman, T.A.; Hess, B.T.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Munoz, J.; Patel, M.R.; Phillips, T.J.; Smith, S.D.; Smith, S.M.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of the Dual SYK/JAK Inhibitor Cerdulatinib Demonstrates Good Tolerability and Clinical Response in Relapsed/Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma and Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. FDA approves first-in-class SYK inhibitor. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, K.S.; Kropf, J.E.; Lee, T.; Blomgren, P.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Gallion, S.; Whitney, J.A.; Maclin, D.; Lansdon, E.B.; et al. Discovery of GS-9973, a Selective and Orally Efficacious Inhibitor of Spleen Tyrosine Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3856–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, R.T.; Meadows, S.; Loriaux, M.M.; Currie, K.S.; Mitchell, S.A.; Maciejewski, P.; Clarke, A.S.; Dipaolo, J.A.; Druker, B.J.; Lannutti, B.J.; et al. A potential therapeutic strategy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia by combining idelalisib and GS-9973, a novel spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grädler, U.; Schwarz, D.; Dresing, V.; Musil, D.; Bomke, J.; Frech, M.; Greiner, H.; Jäkel, S.; Rysiok, T.; Müller-Pompalla, D.; et al. Structural and Biophysical Characterization of the Syk Activation Switch. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Hurtz, C.; Lenz, K.B.; Chen, Z.; Baumjohann, D.; Thompson, S.; Goloviznina, N.A.; Chen, W.; Huan, J.; LaTocha, D.; et al. Self-enforcing feedback activation between BCL6 and pre-B cell receptor signaling defines a distinct subtype of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, C.; Rowland, T.A.; Sreekantham, B.; Godbersen, C.; Best, S.R.; Kaur, P.; Loriaux, M.M.; Spurgeon, S.E.F.; Danilova, O.V.; Danilov, A.V. SYK inhibition thwarts the BAFF-B-cell receptor crosstalk and thereby antagonizes Mcl-1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-κB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponader, S.; Chen, S.-S.; Buggy, J.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Gandhi, V.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; O’Brien, S.; Chiorazzi, N.; Burger, J.A. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 thwarts chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival and tissue homing in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2012, 119, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Coffey, G.P.; Zhang, X.H.; Shaknovich, R.; Song, Z.; Lu, P.; Pandey, A.; Melnick, A.M.; Sinha, U.; Wang, Y.L. SYK inhibition and response prediction in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 6342–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uckun, F.M.; Ma, H.; Ozer, Z.; Goodman, P.; Zhang, J.; Qazi, S. A previously unknown unique challenge for inhibitors of SYK ATP-binding site: Role of SYK as a cell cycle checkpoint regulator. EBioMedicine 2014, 1, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Althubiti, M. Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Modulates p53 Activity. J. Cell Death 2017, 10, 1179066017731564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauet, O.; Fenouille, N.; Abbe, P.; Robert, G.; Rocchi, S.; Gonthier, N.; Denoyelle, C.; Ticchioni, M.; Ortonne, J.; Ballotti, R.; et al. Spleen tyrosine kinase functions as a tumor suppressor in melanoma cells by inducing senescence-like growth arrest. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 748–2756. [Google Scholar]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lane, D.P. p53 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoth, C.; McLellan, M.D.; Vandin, F.; Ye, K.; Niu, B.; Lu, C.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Q.; McMichael, J.F.; Wyczalkowski, M.A.; et al. Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature 2013, 502, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, H.C.; Joerger, A.C.; Mayer, S.; Fersht, A.R. Effects of Common Cancer Mutations on Stability and DNA Binding of Full-length p53 Compared with Isolated Core Domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21934–21941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.L.; Gallo, C.V.D.M.; Costa, D.C.; Rangel, L.P. Prion-like aggregation of mutant p53 in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Reumers, J.; Couceiro, J.R.; De Smet, F.; Gallardo, R.; Rudyak, S.; Cornelis, A.; Rozenski, J.; Zwolinska, A.; Marine, J.-C.; et al. Gain of function of mutant p53 by coaggregation with multiple tumor suppressors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE). Available online: http://www.broadinstitute.org/ccle (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Sasi, B.K.; Martines, C.; Xerxa, E.; Porro, F.; Kalkan, H.; Fazio, R.; Turkalj, S.; Bojnik, E.; Pyrzynska, B.; Stachura, J.; et al. Inhibition of SYK or BTK augments venetoclax sensitivity in SHP1-negative/BCL-2-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2416–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Abrams, S.L.; Lee, J.T.; Chang, F.; Bertrand, F.E.; Navolanic, P.M.; Terrian, D.M.; Franklin, R.A.; D’Assoro, A.B.; et al. Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 2006, 46, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremer, A.; Ellegast, J.M.; Pikman, Y.; Alexe, G.; Ross, L.; Goodale, A.; Piccioni, F.; Frank, E.S.; Oellerich, T.; Stegmaier, K. Resistance Mechanisms to SYK Inhibition in AML. Blood 2018, 132, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, A.; Ellegast, J.M.; Alexe, G.; Frank, E.S.; Ross, L.; Chu, S.H.; Pikman, Y.; Robichaud, A.; Goodale, A.; Haupl, B.; et al. Resistance Mechanisms to SYK Inhibition in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2019, 10, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dustin, L.B.; Plas, D.R.; Wong, J.; Hu, Y.T.; Soto, C.; Chan, A.C.; Thomas, M.L. Expression of dominant-negative src-homology domain 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 results in increased Syk tyrosine kinase activity and B cell activation. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müschen, M. Autoimmunity checkpoints as therapeutic targets in B cell malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 132, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neel, B.G. Role of phosphatases in lymphocyte activation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1997, 9, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadeq, A.; Hobeika, E.; Medgyesi, D.; Kläsener, K.; Reth, M. The Role of the Syk/Shp-1 Kinase-Phosphatase Equilibrium in B Cell Development and Signaling. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtz, C.; Chan, L.N.; Geng, H.; Ballabio, E.; Xiao, G.; Deb, G.; Khoury, H.; Chen, C.-W.; Armstrong, S.A.; Chen, J.; et al. Rationale for targeting BCL6 in MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara-Konishi, J.; Oizumi, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Kikuchi, E.; Mizugaki, H.; Kinoshita, I.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Nishimura, M. Expression of Bim, Noxa, and Puma in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, A.C.; Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Chung, E.; Incio, J.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Pollack, S.F.; Song, Y.; et al. BIM Expression in Treatment-Naïve Cancers Predicts Responsiveness to Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscan, C.E.; Jing, D.; Mayoh, C.; Lock, R.B. Reversal of glucocorticoid resistance in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is dependent on restoring BIM expression. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sender, S.; Sekora, A.; Villa Perez, S.; Chabanovska, O.; Becker, A.; Ngezahayo, A.; Junghanss, C.; Murua Escobar, H. Precursor B-ALL Cell Lines Differentially Respond to SYK Inhibition by Entospletinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020592
Sender S, Sekora A, Villa Perez S, Chabanovska O, Becker A, Ngezahayo A, Junghanss C, Murua Escobar H. Precursor B-ALL Cell Lines Differentially Respond to SYK Inhibition by Entospletinib. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020592
Chicago/Turabian StyleSender, Sina, Anett Sekora, Simon Villa Perez, Oleksandra Chabanovska, Annegret Becker, Anaclet Ngezahayo, Christian Junghanss, and Hugo Murua Escobar. 2021. "Precursor B-ALL Cell Lines Differentially Respond to SYK Inhibition by Entospletinib" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020592
APA StyleSender, S., Sekora, A., Villa Perez, S., Chabanovska, O., Becker, A., Ngezahayo, A., Junghanss, C., & Murua Escobar, H. (2021). Precursor B-ALL Cell Lines Differentially Respond to SYK Inhibition by Entospletinib. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020592