Updated Insights on EGFR Signaling Pathways in Glioma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Understanding EGFR Features
3. Mechanisms of EGFR Pathway Activation
3.1. EGFR Activation Mechanisms in Normal Physiologic Status
3.1.1. Extracellular Domain Activation
3.1.2. Intracellular Domains Activation
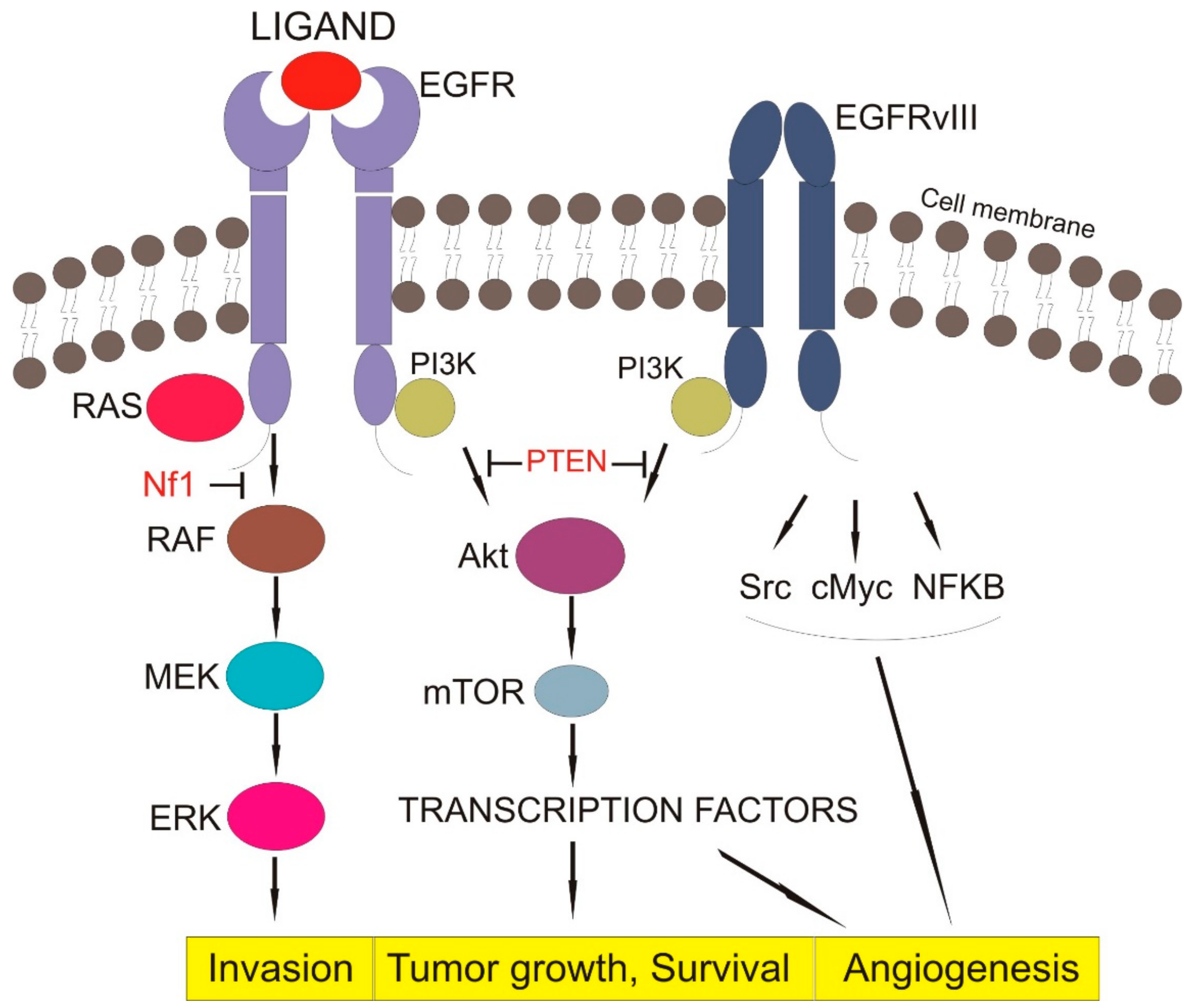
3.1.3. Downstream Signaling of EGFR
3.2. Oncogenic Status and EGFR Activation
3.2.1. Mutations of Cell Signaling Regulators
3.2.2. Overexpression and Gene Amplification
3.2.3. Rearrangements of Chromosomes
3.2.4. Activation by Autocrine Function
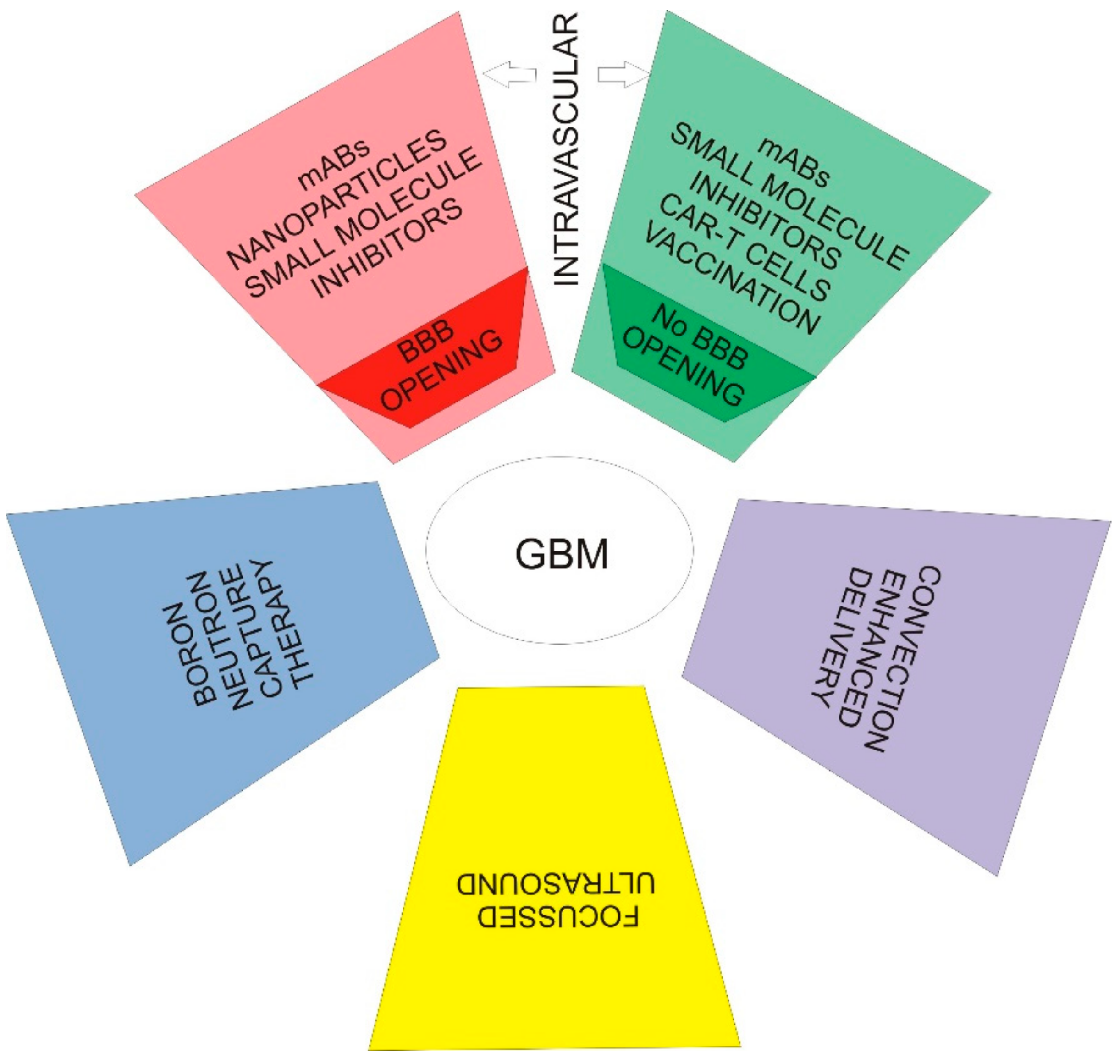
4. Applied Theory—Therapies Targeting EGFR
4.1. Small Molecule Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
4.2. Monoclonal Antibodies
4.3. Targeted Isotopes
4.4. Immunotherapy
4.4.1. CAR-T Cells Targeting EGFRvIII
4.4.2. EGFR as an Immunologic Target—Vaccination
4.5. Targeting the Regulation of EGFR Gene Expression
4.6. Nanoparticles
5. Facing a Real Challenge—Drug Resistance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, A.S.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Kruchko, C.; Rogers, L.; Peereboom, D.M.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Complete prevalence of malignant primary brain tumors registry data in the United States compared with other common cancers 2010. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, T.S.; Dirven, L.; Arons, D.; Bates, A.; Chang, S.M.; Coens, C.; Espinasse, C.; Gilbert, M.R.; Jenkinson, D.; Kluetz, P.; et al. Glioma patient-reported outcome assessment in clinical care and research: A Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology collaborative report. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e97–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, O.; Sevastre, A.S.; Castro, J.; Artene, S.A.; Tache, D.E.; Purcaru, O.S.; Sfredel, V.; Tataranu, L.G.; Dricu, A. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor and Ionizing Radiation in High Grade Glioma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, O.; Horescu, C.; Sevastre, A.S.; Cioc, C.E.; Baloi, C.; Oprita, A.; Dricu, A. Receptor tyrosine kinase targeting in glioblastoma: Performance, limitations and future approaches. Współczesna Onkol. 2020, 24, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastre, A.-S.; Horescu, C.; Carina Baloi, S.; Cioc, C.E.; Vatu, B.I.; Tuta, C.; Artene, S.A.; Danciulescu, M.M.; Tudorache, S.; Dricu, A. Benefits of Nanomedicine for Therapeutic Intervention in Malignant Diseases. Coatings 2019, 9, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.; KoprivnikarKrajnc, M.; Hrastar, B.; Breznik, B.; Majc, B.; Mlinar, M.; Rotter, A.; Porčnik, A.; Mlakar, J.; Stare, K.; et al. CCR5-Mediated Signaling Is Involved in Invasion of Glioblastoma Cells in Its Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, O.; Dragutescu, L.; Tătăranu, L.; Ciubotaru, V.; Sevastre, A.; Georgescu, A.M.; Purcaru, O.; Dănoiu, S.; Bäcklund, L.M.; Dricu, A. Helianthin induces antiproliferative effect on human glioblastoma cells in vitro. J. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 102, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Costa, A.; Osório, L.; Lago, R.C.; Linhares, P.; Carvalho, B.; Caeiro, C. Glioblastoma [Internet]. Current Standards of Care in Glioblastoma Therapy; De Vleeschouwer, S., Ed.; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2017; Chapter 11. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK469987/ (accessed on 22 June 2020). [CrossRef]
- Rajaratnam, V.; Islam, M.M.; Yang, M.; Slaby, R.; Ramirez, H.M.; Mirza, S.P. Glioblastoma: Pathogenesis and Current Status of Chemotherapy and Other Novel Treatments. Cancers 2020, 12, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horescu, C.; Cioc, C.E.; Tuta, C.; Sevastre, A.S.; Tache, D.E.; Alexandru, O.; Artene, S.A.; Danoiu, S.; Dricu, A.; Purcaru, S.O. The effect of temozolomide in combination with doxorubicin in glioblastoma cells in vitro. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2020, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöppler, M.C.; Shiel, W.C.; Credo Reference (Firm); WebMD (Firm). Webster’s New World Medical Dictionary, 3rd ed.; Credo Reference: Boston, MA, USA; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, iv1–iv86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirosh, I.; Suvà, M.L. Tackling the Many Facets of Glioblastoma Heterogeneity. Cell Stem Cell. 2020, 26, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carapancea, M.; Alexandru, O.; Fetea, A.S.; Dragutescu, L.; Castro, J.; Georgescu, A.; Popa-Wagner, A.; Bäcklund, M.L.; Lewensohn, R.; Dricu, A. Growth factor receptors signaling in glioblastoma cells: Therapeutic implications. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 92, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprita, A.; Sevastre, A.S. New pharmaceutical dosage forms used in the treatment of breast cancer. Polymeric micelles. Med. Oncol. 2020, 1, 38–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Lebrun, D.G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, V.F.; Li, M. Deregulated signaling pathways in glioblastoma multiforme: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Cancer Investig. 2012, 30, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, O.; Ciubotaru, V.; Tataranu, L.; Fetea, S.; Badea, P.; Dricu, A. The relationship between cognitive function, tumour histology and surgical treatment in patients with primary brain tumours. Communications of the European Neurological Society. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskilsson, E.; Røsland, G.V.; Solecki, G.; Wang, Q.; Harter, P.N.; Graziani, G.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Winkler, F.; Bjerkvig, R.; Miletic, H. EGFR heterogeneity and implications for therapeutic intervention in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T. Tyrosine phosphorylation: Thirty years and counting. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Aksoy, O.; Zheng, T.; Fan, Q.W.; Weiss, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFRvIII in glioblastoma: Signaling pathways and targeted therapies. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Berezov, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Drebin, J.; Murali, R.; Greene, M.I. ErbB receptors: From oncogenes to targeted cancer therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, E.R.; Truesdale, A.T.; McDonald, O.B.; Yuan, D.; Hassell, A.; Dickerson, S.H.; Ellis, B.; Pennisi, C.; Horne, E.; Lackey, K.; et al. A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): Relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6652–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, K.M. Structure-based view of epidermal growth factor receptor regulation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 37, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, S.R.; Till, J.H. Protein tyrosine kinase structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipov, A.; Shan, Y.; Das, R.; Endres, N.; Eastwood, M.; Wemmer, D.; Kuriyan, J.; Shaw, D. Architecture and Membrane Interactions of the EGF Receptor. Cell 2013, 152, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kawai, T.; O’Brien, S.; Thomas, W.; Harris, R.C.; Eguchi, S. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Transactivation: Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Potential Therapies in the Cardiovascular System. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 627–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, N.; Thiel, K.W.; Miller, F.J., Jr. The epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligands in cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20597–20613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, O.; Purcaru, S.O.; Tataranu, L.G.; Lucan, L.; Castro, J.; Folcuţi, C.; Artene, S.A.; Tuţă, C.; Dricu, A. The Influence of EGFR Inactivation on the Radiation Response in High Grade Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwatra, M.M. A Rational Approach to Target the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Glioblastoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2017, 17, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Hidalgo, L.; San-Miguel, T.; Megías, J.; Monleón, D.; Navarro, L.; Roldán, P.; Cerdá-Nicolás, M.; López-Ginés, C. Somatic copy number alterations are associated with EGFR amplification and shortened survival in patients with primary glioblastoma. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Weihua, Z. Rethink of EGFR in Cancer with Its Kinase Independent Function on Board. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jureczek, J.; Feldmann, A.; Bergmann, R.; Arndt, C.; Berndt, N.; Koristka, S.; Loureiro, L.R.; Mitwasi, N.; Hoffmann, A.; Kegler, A.; et al. Highly Efficient Targeting of EGFR-Expressing Tumor Cells with UniCAR T Cells via Target Modules Based on Cetuximab®. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 5515–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Nussinov, R. Emerging Allosteric Mechanism of EGFR Activation in Physiological and Pathological Contexts. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Jablons, D.M.; Yang, C.T.; You, L. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, P.P.; Cardone, C.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Belli, V.; Matrone, N.; Barra, G.; Napolitano, S.; Della Corte, C.; Turano, M.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinase-dependent PI3K activation is an escape mechanism to vertical suppression of the EGFR/RAS/MAPK pathway in KRAS-mutated human colorectal cancer cell lines. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, G.; Cohen, S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1979, 48, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullick, W.J.; Marsden, J.J.; Whittle, N.; Ward, B.; Bobrow, L.; Waterfield, M.D. Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors on Human Cervical, Ovarian, and Vulval Carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, J.T.; Parsons, S.J. Src family protein tyrosine kinases: Cooperating with growth factor and adhesion signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscardi, J.S.; Maa, M.C.; Tice, D.A.; Cox, M.E.; Leu, T.H.; Parsons, S.J. c-Src-mediated phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor on Tyr845 and Tyr1101 is associated with modulation of receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8335–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.P.; Berger, M.B.; Lin, C.C.; Schlessinger, J.; Lemmon, M.A.; Ferguson, K.M. Epidermal growth factor receptor dimerization and activation require ligand-induced conformational changes in the dimer interface. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7734–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervieu, A.; Kermorgant, S. The Role of PI3K in Met Driven Cancer: A Recap. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, T.; Schmitz-Peiffer, C.; Daly, R.J. Docking proteins. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 4356–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbanda, A.; Walter, D.; Gudiel, A.; Schek, N.; Feldser, D.; Witze, E. Blocking EGFR palmitoylation suppresses PI3K signaling and mutant KRAS lung tumorigenesis. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaax2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, I.A.; Arteaga, C.L. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoon, D.R.; Lamothe, B.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. The docking protein Gab1 is the primary mediator of EGF-stimulated activation of the PI-3K/Akt cell survival pathway. BMC Biol. 2004, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, E.Q.X.; Colόn, R.R.; Abounader, R. HGF/MET Signaling in Malignant Brain Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyatkin, A.; Aksamitiene, E.; Markevich, N.I.; Borisov, N.M.; Hoek, J.B.; Kholodenko, B.N. Scaffolding protein Grb2-associated binder 1 sustains epidermal growth factor-induced mitogenic and survival signaling by multiple positive feedback loops. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 19925–19938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawson, T. Specificity in signal transduction: From phosphotyrosine-SH2 domain interactions to complex cellular systems. Cell 2004, 116, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.F.; Braun, B.S.; Shannon, K.M. Targeting oncogenic Ras signaling in hematologic malignancies. Blood 2012, 120, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.P.; Mark, K.G.; Leslie, K.; Pao, W.; Motoi, N.; Gerald, W.L.; Travis, W.D.; Bornmann, W.; Veach, D.; Clarkson, B.; et al. Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3846–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.P.; Chang, Q.; Mao, N.; Daly, L.A.; Vogel, R.; Chan, T.; Liu, S.H.; Bournazou, E.; Schori, E.; Zhang, H.; et al. JAK2 inhibition sensitizes resistant EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padfield, E.; Ellis, H.P.; Kurian, K.M. Current Therapeutic Advances Targeting EGFR and EGFRvIII in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorissen, R.N.; Walker, F.; Pouliot, N.; Garrett, T.P.; Ward, C.W.; Burgess, A.W. Epidermal growth factor receptor: Mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 284, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Xu, A.M.; White, F.M. Oncogenic EGFR signaling networks in Glioma. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnari, F.B.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mischel, P.S. Heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor signalling networks in glioblastoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeineldin, R.; Ning, Y.; Hudson, L.G. The constitutive activity of epidermal growth factor receptor vIII leads to activation and differential trafficking of wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB2. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2010, 58, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsberg, J.; Hentschel, B.; Kaulich, K.; Gramatzki, D.; Zacher, A.; Malzkorn, B.; Kamp, M.; Sabel, M.; Simon, M.; Westphal, M.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Variant III (EGFRvIII) Positivity in EGFR-Amplified Glioblastomas: Prognostic Role and Comparison between Primary and Recurrent Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6846–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platten, M. EGFRvIII vaccine in glioblastoma-InACT-IVe or not ReACTive enough? Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1425–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struve, N.; Binder, Z.A.; Stead, L.F.; Brend, T.; Bagley, S.J.; Faulkner, C.; Ott, L.; Müller-Goebel, J.; Weik, A.-S.; Hoffer, K.; et al. EGFRvIII upregulates DNA mismatch repair resulting in increased temozolomide sensitivity of MGMT promoter methylated glioblastoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3041–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, C.; Azevedo, A.; Esteves, S.; Marques, A.R.; Martins, C.; Costa, I.; Mafra, M.; Bravo Marques, J.M.; Roque, L.; Pojo, M. Clinical insights gained by refining the 2016 WHO classification of diffuse gliomas with: EGFR amplification, TERT mutations, PTEN deletion and MGMT methylation. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Tachibana, O.; Sata, K.; Yonekawa, Y.; Kleihues, P.; Ohgaki, H. Overexpression of the EGF receptor and p53 mutations are mutually exclusive in the evolution of primary and secondary glioblastomas. Brain Pathol. 1996, 6, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisian, C.J.; Keister, B.A.; Stairs, D.B.; Boxer, R.B.; Moody, S.E.; Chodosh, L.A. Dose-dependent oncogene-induced senescence in vivo and its evasion during mammary tumorigenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Li, B.; Figueroa, J.M.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.C.; Carter, B.S.; Furnari, F.B. Mapping of genomic EGFRvIII deletions in glioblastoma: Insight into rearrangement mechanisms and biomarker development. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Gines, C.; Cerda-Nicolas, M.; Gil-Benso, R.; Pellin, A.; Lopez-Guerrero, J.A.; Callaghan, R.; Benito, R.; Roldan, P.; Piquer, J.; Llacer, J.; et al. Association of chromosome 7, chromosome 10 and EGFR gene amplification in glioblastoma multiforme. Clin. Neuropathol. 2005, 24, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Carpenter, G.; Coffey, R.J. EGF receptor ligands: Recent advances. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnarain, D.B.; Park, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Scoggin, S.O.; Out, H.; Libermann, T.A.; Raisanen, J.M.; Ashfaq, R.; Wong, E.T.; et al. Differential gene expression analysis reveals generation of an autocrine loop by a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Steck, P.A.; Yung, W.K. The autocrine loop of TGF-α/EGFR and brain tumors. J. Neurooncol. 1997, 35, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filmus, J.; Shi, W.; Spencer, T. Role of transforming growth factor α (TGF-α) in the transformation of ras-transfected rat intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 1993, 8, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Engelman, J.A. ErbB receptors: From oncogene discovery to basic science to mechanism-based cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell. 2014, 25, 282–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.; Chooback, N.; Ho, C.; Melosky, B. Outcome Differences Between First- and Second-generation EGFR Inhibitors in Advanced EGFR Mutated NSCLC in a Large Population-based Cohort. Clin. Lung Cancer. 2019, 20, e576–e583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Nabors, L.B.; Mason, W.P.; Perry, J.R.; Shapiro, W.; Kavan, P.; Mathieu, D.; Phuphanich, S.; Cseh, A.; Fu, Y.; et al. Phase I/randomized phase II study of afatinib, an irreversible ErbBfamily blocker, with or without protracted temozolomide in adults with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Khawaja, M.R.; Hong, D.S.; Amini, B.; Yungfang, J.; Liu, H.; Johnson, A.; Schrock, A.B.; Ali, S.M.; Sun, J.X.; et al. First-in-human trial of multikinase VEGF inhibitor regorafenib and anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab in advanced cancer patients. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e90380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda-Sánchez, J.M.; Vaz, M.Á.; Balañá, C.; Gil-Gil, M.; Reynés, G.; Gallego, Ó.; Martínez-García, M.; Vicente, E.; Quindós, M.; Luque, R.; et al. Phase II trial of dacomitinib, a pan-human EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in recurrent glioblastoma patients with EGFR amplification. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpel-Massler, G.; Westhoff, M.A.; Kast, R.E.; Wirtz, C.R.; Halatsch, M.E. Erlotinib in glioblastoma: Lost in translation? Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, J.N.; Reardon, D.A.; Peery, T.; Dowell, J.M.; Quinn, J.A.; Penne, K.L.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Van Duyn, L.B.; Dancey, J.E.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Phase II trial of gefitinib in recurrent glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiessen, B.; Stewart, C.; Tsao, M.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Schaiquevich, P.; Mason, W.; Easaw, J.; Belanger, K.; Forsyth, P.; McIntosh, L.; et al. A phase I/II trial of GW572016 (lapatinib) in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: Clinical outcomes, pharmacokinetics and molecular correlation. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 65, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.J.; Li, X.M.; Cai, L.B.; Sun, J.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, X.C.; Pang, X.L.; Deng, M.; Chen, F.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nimotuzumab in addition to radiotherapy and temozolomide for cerebral glioblastoma: A phase II multicenter clinical trial. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3214–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhlin, I.; Salinas, R.D.; Zhang, D.; Jacob, F.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H.; Saxena, D.; Dorsey, J.F.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Morrissette, J.J.; et al. Clinical activity of the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in EGFR-mutant glioblastoma. CNS Oncol. 2019, 8, CNS43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, L.; Shan, Q.; Cao, Q.; Yue, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; et al. The third-generation EGFR inhibitor AZD9291 overcomes primary resistance by continuously blocking ERK signaling in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagoya, G.; Kwatra, S.G.; Nanni, C.W.; Roberts, C.M.; Phillips, S.M.; Nullmeyergh, S.; Gilmore, S.P.; Spasojevic, I.; Corcoran, D.L.; Young, C.C.; et al. Efficacy of osimertinib against EGFRvIII+ glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, T.S.; Udayakumar, N.; Jani, A.H.; Hartman, Y.E.; Houson, H.A.; Moore, L.; Amm, H.M.; van den Berg, N.S.; Sorace, A.G. Warram JM. Comparison of Panitumumab-IRDye800CW and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid to Provide Optical Contrast in a Model of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Desjardins, A.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; O’Rourke, D.M.; Tran, D.D.; Fink, K.L.; Nabors, L.B.; Li, G.; Bota, D.A.; Lukas, R.V.; et al. Rindopepimut with Bevacizumab for Patients with Relapsed EGFRvIII-Expressing Glioblastoma (ReACT): Results of a Double-Blind Randomized Phase II Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisl, T.N.; McNeill, K.A.; Sul, J.; Iwamoto, F.M.; Shih, J.; Fine, H.A. A phase I/II trial of vandetanib for patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02844439 (accessed on 7 December 2020).
- Schaller, T.H.; Foster, M.W.; Thompson, J.W.; Spasojevic, I.; Normantaite, D.; Moseley, M.A.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Sampson, J.H. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of a Novel Human EGFRvIII:CD3 Bispecific Antibody in Plasma and Whole Blood Using a High-Resolution Targeted Mass Spectrometry Approach. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, L. Convergence of EGFR glioblastoma mutations: Evolution and allostery rationalizing targeted therapy. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2019, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, T.S.; Brady, L.W. Radioimmunotherapy as a novel treatment regimen: 125I-labeled monoclonal antibody 425 in the treatment of high-grade brain gliomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 58, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, F.; Salinas, R.D.; Zhang, D.Y.; Nguyen, P.T.T.; Schnoll, J.G.; Wong, S.Z.H.; Thokala, R.; Sheikh, S.; Saxena, D.; Prokop, S.; et al. A Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Organoid Model and Biobank Recapitulates Inter- and Intra-tumoral Heterogeneity. Cell 2020, 180, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, C.T.; Krenciute, G. Next Generation CAR T Cells for the Immunotherapy of High-Grade Glioma. Front Oncol. 2019, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Pan, B.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, J.; Lu, J.; Yu, R.; Liu, H. Co-delivery of GOLPH3 siRNA and gefitinib by cationic lipid-PLGA nanoparticles improves EGFR-targeted therapy for glioma. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, A.; Okonechnikov, K.; Sahm, F.; Ryzhova, M.; Stichel, D.; Schrimpf, D.; Ghasemi, D.R.; Pajtler, K.W.; Antonelli, M.; Donofrio, V.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity (MBEN) reveals two clinically relevant tumor subsets with VSNL1 as potent prognostic marker. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, O.G.; Brzozowski, J.S.; Skelding, K.A. Glioblastoma Multiforme: An Overview of Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Chen, K.T.; Huang, C.Y.; Wei, K.C. Review ArticleNon-Invasive Focused Ultrasound-Based Synergistic Treatment of Brain Tumors. J. Cancer Res. Pract. 2016, 3, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.C.; Chu, P.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, P.Y.; Tsai, H.C.; Lu, Y.J.; Lee, P.Y.; Tseng, I.C.; Feng, L.Y.; et al. Focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening to enhance temozolomide delivery for glioblastoma treatment: A preclinical study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.; Maire, C.L.; Lamszus, K. EGFR as a Target for Glioblastoma Treatment: An Unfulfilled Promise. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.C.; Platt, S.R.; Holmes, S.; Kent, M.; Robinson, K.; Howerth, E.; Eagleson, J.; Bouras, A.; Kaluzova, M.; Hadjipanayis, C.G. Convection-enhanced delivery of cetuximab conjugated iron-oxide nanoparticles for treatment of spontaneous canine intracranial gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 137, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhm, J.H.; Ballman, K.V.; Wu, W.; Giannini, C.; Krauss, J.C.; Buckner, J.C.; James, C.D.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Behrens, R.J.; Flynn, P.J.; et al. Phase II evaluation of gefitinib in patients with newly diagnosed Grade 4 astrocytoma: Mayo/North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study N0074. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, A.; Wang, M.; Robins, H.I.; Lautenschlaeger, T.; Curran, W.J.; Brachman, D.G.; Schultz, C.J.; Choucair, A.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Christiansen, J.; et al. RTOG 0211: A phase 1/2 study of radiation therapy with concurrent gefitinib for newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, F.A.; Rodrigues Pereira, J.; Ciuleanu, T.; Tan, E.H.; Hirsh, V.; Thongprasert, S.; Campos, D.; Maoleekoonpiroj, S.; Smylie, M.; Martins, R.; et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peereboom, D.M.; Shepard, D.R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Brewer, C.J.; Agarwal, N.; Stevens, G.H.; Suh, J.H.; Toms, S.A.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Weil, R.J.; et al. Phase II trial of erlotinib with temozolomide and radiation in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 98, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.Y.; Chang, S.M.; Lamborn, K.R.; Kuhn, J.G.; Norden, A.D.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Robins, H.I.; Lieberman, F.S.; Gilbert, M.R.; Mehta, M.P.; et al. Phase I/II study of erlotinib and temsirolimus for patients with recurrent malignant gliomas: North American Brain Tumor Consortium trial 04-02. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raizer, J.J.; Giglio, P.; Hu, J.; Groves, M.; Merrell, R.; Conrad, C.; Phuphanich, S.; Puduvalli, V.K.; Loghin, M.; Paleologos, N.; et al. A phase II study of bevacizumab and erlotinib after radiation and temozolomide in MGMT unmethylated GBM patients. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 126, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Groves, M.D.; Wen, P.Y.; Nabors, L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Rosenfeld, S.; Raizer, J.; Barriuso, J.; McLendon, R.E.; Suttle, A.B.; et al. A phase I/II trial of pazopanib in combination with lapatinib in adult patients with relapsed malignant glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ide, J.L.; Norton, I.; Marchionni, M.A.; Ebling, M.C.; Wang, L.Y.; Davis, E.; Sauvageot, C.M.; Kesari, S.; Kellersberger, K.A.; et al. Molecular imaging of drug transit through the blood-brain barrier with MALDI mass spectrometry imaging. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassman, A.B.; Rossi, M.R.; Raizer, J.J.; Abrey, L.E.; Lieberman, F.S.; Grefe, C.N.; Lamborn, K.; Pao, W.; Shih, A.H.; Kuhn, J.G.; et al. Holland. Molecular study of malignant gliomas treated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: Tissue analysis from North American Brain Tumor Consortium Trials 01–03 and 00–01. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7841–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda, J.M.; Sánchez-Gómez, P.; Vaz Salgado, M.Á.; Gargini, R.; Balañá, C. Dacomitinib: An investigational drug for the treatment of glioblastoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=glioma&term=vandetanib&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyns, B.; Sadones, J.; Joosens, E.; Bouttens, F.; Verbeke, L.; Baurain, J.F.; D’Hondt, L.; Strauven, T.; Chaskis, C.; In’t Veld, P.; et al. Stratified phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Combined-therapeutic strategies synergistically potentiate glioblastoma multiforme treatment via nanotechnology. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3223–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Pigula, M.; Fang, Y.; Hasan, T. Immobilization of Photo-Immunoconjugates on Nanoparticles Leads to Enhanced Light-Activated Biological Effects. Small 2018, 14, e1800236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heun, J.; Holen, K.; Paul, P. Treatment with panitumumab after a severe infusion reaction to cetuximab in a patient with metastatic colorectal cancer: A case report. Clin. Colorectal. Cancer 2007, 6, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03510208 (accessed on 5 December 2020).
- Choi, B.D.; Kuan, C.T.; Cai, M.; Archer, G.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Gedeon, P.C.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Pastan, I.; Bigner, D.D.; Sampson, J.H. Systemic administration of a bispecific antibody targeting EGFRvIII successfully treats intracerebral glioma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, L.; Thorne, A.H.; Lema, R.; Gustavsson, J.; Parisian, A.D.; Hospital, A.; Cordeiro, T.N.; Bernadó, P.; Scott, A.M.; Brun-Heath, I.; et al. Oncogenic mutations at the EGFR ectodomain structurally converge to remove a steric hindrance on a kinase-coupled cryptic epitope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10009–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, T.G.; McKay, M.J.; Cvrljevic, A.N.; Gan, H.K.; Taylor, C.; Xu, H.; Smyth, F.E.; Scott, A.M. MAb 806 enhances the efficacy of ionizing radiation in glioma xenografts expressing the de2-7 epidermal growth factor receptor. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrich, J.G.; Brady, L.W.; Quang, T.S.; Class, R.; Miyamoto, C.; Black, P.; Rodeck, U. Radioiodinated (I-125) monoclonal antibody 425 in the treatment of high grade glioma patients: Ten-year synopsis of a novel treatment. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 25, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.A.; Scholler, J.; Ohkuri, T.; Kosaka, A.; Patel, P.R.; McGettigan, S.E.; Nace, A.K.; Dentchev, T.; Thekkat, P.; Loew, A.; et al. Rational development and characterization of humanized anti-EGFR variant III chimeric antigen receptor T cells for glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 275ra22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, A.; Sanchez, C.; Bullain, S.; Waterman, P.; Weissleder, R.; Carter, B.S. Development of third generation anti-EGFRvIII chimeric T cells and EGFRvIII-expressing artificial antigen presenting cells for adoptive cell therapy for glioma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical Trials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT01454596?term=CAR-T&cond=glioma&draw=3&rank=12 (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Binder, D.C.; Ladomersky, E.; Lenzen, A.; Zhai, L.; Lauing, K.L.; Otto-Meyer, S.D.; Lukas, R.V.; Wainwright, D.A. Lessons learned from rindopepimut treatment in patients with EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7 (Suppl. S4), S510–S513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, J.; Lai, R.K.; Recht, L.D.; Reardon, D.A.; Paleologos, N.A.; Groves, M.D.; Mrugala, M.M.; Jensen, R.; Baehring, J.M.; Sloan, A.; et al. A phase II, multicenter trial of rindopepimut (CDX-110) in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: The ACT III study. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Butowski, N.; Tran, D.D.; Recht, L.D.; Lim, M.; Hirte, H.; Ashby, L.; Mechtler, L.; Goldlust, S.A.; Iwamoto, F.; et al. Rindopepimut with temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed, EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ACT IV): A randomised, double-blind, international phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.; Ingram, A.; Al Saleh, H.A.; Platko, K.; Gabriel, K.; Kapoor, A.; Pinthus, J.; Majeed, F.; Qureshi, T.; Al-Nedawi, K. Nuclear transportation of exogenous epidermal growth factor receptor and androgen receptor via extracellular vesicles. Eur. J. Cancer. 2017, 70, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, F.; Mineo, M.; Rooj, A.K.; Nakano, I.; Charest, A.; Weissleder, R.; Breakefield, X.O.; Chiocca, E.A.; Godlewski, J.; Bronisz, A. Extracellular Vesicles from High-Grade Glioma Exchange Diverse Pro-oncogenic Signals That Maintain Intratumoral Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2876–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronisz, A.; Wang, Y.; Nowicki, M.O.; Peruzzi, P.; Ansari, K.; Ogawa, D.; Balaj, L.; De Rienzo, G.; Mineo, M.; Nakano, I.; et al. Extracellular vesicles modulate the glioblastoma microenvironment via a tumor suppression signaling network directed by miR-1. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.W.; Hsu, J.M.; Xia, W.; Wang, H.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Chang, W.C.; Arold, S.T.; Chou, C.K.; Tsou, P.H.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. PRMT1-mediated methylation of the EGF receptor regulates signaling and cetuximab response. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4529–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Palazzo, C.; Evrard, B.; Piel, G. Nanocarriers for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme: Current state-of-the-art. J. Control. Release 2016, 10, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, J.H.; Jeppesen, M.; Pilgaard, L.; Agger, R.; Duroux, M.; Zachar, V.; Moos, T. Targeted antiepidermal growth factor receptor (cetuximab) immunoliposomes enhance cellular uptake in vitro and exhibit increased accumulation in an intracranial model of glioblastoma multiforme. J. Drug Deliv. 2013, 2013, 209205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical Trials. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02340156?term=nanoparticles&cond=glioma&draw=2&rank=7 (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Kim, S.S.; Rait, A.; Kim, E.; Pirollo, K.F.; Chang, E.H. A tumor-targeting p53 nanodelivery system limits chemoresistance to temozolomide prolonging survival in a mouse model of glioblastoma multiforme. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, H.; Kulsoom, A.; Küçükosmanoglu, A.; Houweling, M.; Cornelissen, F.M.G.; Heiland, D.H.; Hegi, M.E.; Kouwenhoven, M.C.M.; Bailey, D.; Würdinger, T.; et al. The TICking clock of EGFR therapy resistance in glioblastoma: Target Independence or target Compensation. Drug Resist. Updates 2019, 43, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, D.A.; Gini, B.; Mottahedeh, J.; Visnyei, K.; Koga, T.; Gomez, G.; Eskin, A.; Hwang, K.; Wang, J.; Masui, K.; et al. Targeted therapy resistance mediated by dynamic regulation of extrachromosomal mutant EGFR DNA. Science 2014, 343, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Zhao, R.; Haeno, H.; Vivanco, I.; Michor, F. Mathematical modeling identifies optimum lapatinib dosing schedules for the treatment of glioblastoma patients. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018, 14, e1005924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Ahn, M.J.; Cho, B.C.; Gerber, D.E.; Natale, R.B.; Socinski, M.A.; Giri, N.; Quinn, S.; Sbar, E.; Zhang, H.; et al. Phase 2 study of intermittent pulse dacomitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer 2017, 112, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; Wang, J.; Shao, W.; Wu, C.P.; Chen, Z.P.; To, S.T.; Li, W.P. Recent advances in the use of PI3K inhibitors for glioblastoma multiforme: Current preclinical and clinical development. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettini, F.; De Santo, I.; Rea, C.G.; De Placido, P.; Formisano, L.; Giuliano, M.; Arpino, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Puglisi, F.; De Placido, S.; et al. CDK 4/6 Inhibitors as Single Agent in Advanced Solid Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Kong, S.; Shang, S.; Qi, Y. CDK4/6 inhibition suppresses tumour growth and enhances the effect of temozolomide in glioma cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5135–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Roberts, C.; Herpai, D.; Fokt, I.D.; Priebe, W.; Debinski, W. Drug Conjugates for Targeting Eph Receptors in Glioblastoma. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenstein, P.R.; Castro, M.G. Multiple Expressed Endogenous Glioma Epitopes as Novel Vaccines for Gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4760–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Valentini, D.; Rao, M.; Meng, Q.; von Landenberg, A.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Sinclair, G.; Paraschoudi, G.; Jäger, E.; Harvey-Peredo, I.; Dodoo, E.; et al. Identification of neoepitopes recognized by tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) from patients with glioma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19469–19480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alayo, Q.A.; Ito, H.; Passaro, C.; Zdioruk, M.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Grauwet, K.; Zhang, X.; Lawler, S.E.; Reardon, D.A.; Goins, W.F.; et al. Glioblastoma infiltration of both tumor- and virus-antigen specific cytotoxic T cells correlates with experimental virotherapy responses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Han, B.; Zha, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, P.; Qi, T.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Dual functionalized brain-targeting nanoinhibitors restrain temozolomide-resistant glioma via attenuating EGFR and MET signaling pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; King, P.J.; Antonescu, C.N.; Sugiyama, M.G.; Bhamra, A.; Surinova, S.; Angelopoulos, N.; Kragh, M.; Pedersen, M.W.; Hartley, J.A.; et al. Targeting of EGFR by a combination of antibodies mediates unconventional EGFR trafficking and degradation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Narayan, N.R.; Horton, L.; Patel, T.; Habib, A. The Role of EGFR-Met Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Glioblastoma and Resistance to Treatment. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2017, 17, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic Agent | Mechanism | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Afatinib (Tovok, BIBW2992) | Second-generation EGFR inhibitor | As a single agent, Afatinib proved good safety, but limited activity on GBM patients. It was promising in combination with TMZ in a case report.6 months progression-free survival (PFS) worse than TMZ: Afatinib alone 3% vs. Afatinib + TMZ 10% vs. TMZ alone 23% Ongoing clinical trials: NCT02423525 | [79] |
| Cetuximab (Erbitux, DTXSID70142901) | Antibody targeting the L2 domain of EGFR | Cetuximab was not very effective in GBM clinical trials. 6-month PFS was 33%, and median PFS was 16 weeks Ongoing clinical trials: NCT02800486 NCT02861898 | [80] |
| Dacomitinib (Vizimpro, PF299804) | Second-generation EGFR inhibitor | Dacomitinib proved to be promising in pre-clinical models. 6-months PFS was 10.6% with a median PFS of 2.7 months Ongoing clinical trials: NCT01112527 NCT01520870 | [81] |
| Erlotinib (Tarceva, OSI-774) | First-generation EGFR inhibitor | Erlotinib showed poor results in GBM clinical trials. The median PFS: 1.8 months Erlotinib vs. 2.4 months TMZ/BCNU (bis-chloroethylnitrosourea) Ongoing clinical trials: NCT01257594 NCT02239952 | [82] |
| Gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839) | First-generation EGFR inhibitor | Gefitinib showed poor results in GBM clinical trials. The median overall survival time from treatment initiation was 39.4 weeks | [83] |
| Lapatinib (Tykerb, GSK 572016) | First-generation EGFR inhibitor | Lapatinib demonstrated poor results in GBM clinical trials. The studies lacked objective responses, with early progression rate of 76%. Ongoing clinical trials: NCT01591577 NCT02101905 | [84] |
| Nimotuzumab (OSAG101) | Antibody targeting the L2 domain of EGFR | Nimotuzumab in addition to standard treatment is well tolerated and has increased survival rates in EGFR positive expression newly diagnosed GBM patients. The PFS and OS rates were 49.3% and 83.3% for 1-year and 29.0% and 51.1% for 2-year. Ongoing clinical trials: NCT03620032 | [85] |
| Osimertinib (AZD9291) | Third-generation EGFR inhibitor | Osimertinib is in phase I/II clinical trial. Compared to other EGFR-TKIs, AZD9291 demonstrated improved ability to inhibit GBM cells proliferation.Complete response of left frontal lobe tumor after 4 weeks of osimertinib. | [86,87,88] |
| Panitumumab (Vectibix, ABX-EGF) | Antibody targeting the L2 domain of EGFR | Panitumumab was not very effective in GBM clinical trials.Panitumumab-IRDye800CW specificities for tumor core and margin were slightly higher than those of 5-ALA. Ongoing clinical trials: NCT03510208 | [89] |
| Rindopepimut (CDX110) | Vaccine | When co-administrated with Bevacizumab, Rindopepimut significantly prolonged patient survival. 6 months PFS was 28% (rindopepimut), compared with 16% (control)Phase II trial (NCT00458601) was completed in 2018. | [90] |
| Vandetanib (Caprelsa, ZD6474) | Second-generation EGFR inhibitor | Vandetanib was a moderately tolerated drug, with no significant activity as a single agent in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Median overall survival was 6.3 months. Ongoing clinical trials: NCT02239952 | [91] |
| Tesevatinib (KD019) | Second-generation EGFR inhibitor | Tesevatinib is in Phase II study in patients with recurrent glioblastoma, with no results posted. Ongoing clinical trials: NCT02844439 | [92] |
| bscEGFRvIIIxCD3 | Antibody BisAbs | Fully human bispecific single chain antibody fragments bi-scFv (EGFRvIII:CD3 bi-scFv) was recently developed with the aim to redirect CD3-expressing T cells to target malignant EGFRvIII-expressing glioma. | [93] |
| mAB806 | Antibody targeting the EGFRvIII-specific sequence | Structural extracellular mutations lead to a similar intermediate conformation, that can be synergistically targeted intra- and extracellularly by mAb806 antibody. Lapatinib co-treatment sensitized unresponsive wild type (WT)-EGFR to mAb806. | [94] |
| 125I mAB425 | Antibody toxin or radioactive isotope conjugated | Single or in combination with TMZ, 125I mAB425 prolonged patient survival (median survival of 20.4 months, compared to 14.5 months for 125I mAB425 alone), with minimal toxicity in normal tissue. | [95] |
| Chimeric anti-gen receptor T cell therapy (CAR-T cells) | Chimeric antigen receptor therapy (CARs) targeting EGFRvIII | Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells are in phase I clinical trials in high-grade glioma (HGG) patients. Pre-clinical models proved to be promising. Ongoing clinical trials: NCT02331693 NCT02844062 NCT02209376 NCT01454596 NCT02664363 | [96,97] |
| Antisense oligonucleotides, siRNA, ribozymes, and miRNA-based therapy | RNA-based therapies | Feasibility of RNA-based therapies must be further evaluated using pre-clinical models. | [98,99] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oprita, A.; Baloi, S.-C.; Staicu, G.-A.; Alexandru, O.; Tache, D.E.; Danoiu, S.; Micu, E.S.; Sevastre, A.-S. Updated Insights on EGFR Signaling Pathways in Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020587
Oprita A, Baloi S-C, Staicu G-A, Alexandru O, Tache DE, Danoiu S, Micu ES, Sevastre A-S. Updated Insights on EGFR Signaling Pathways in Glioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020587
Chicago/Turabian StyleOprita, Alexandru, Stefania-Carina Baloi, Georgiana-Adeline Staicu, Oana Alexandru, Daniela Elise Tache, Suzana Danoiu, Elena Simona Micu, and Ani-Simona Sevastre. 2021. "Updated Insights on EGFR Signaling Pathways in Glioma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020587
APA StyleOprita, A., Baloi, S.-C., Staicu, G.-A., Alexandru, O., Tache, D. E., Danoiu, S., Micu, E. S., & Sevastre, A.-S. (2021). Updated Insights on EGFR Signaling Pathways in Glioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020587





