A Novel L-Asparaginase from Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus sibiricus: Heterologous Expression and Characterization for Biotechnology Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
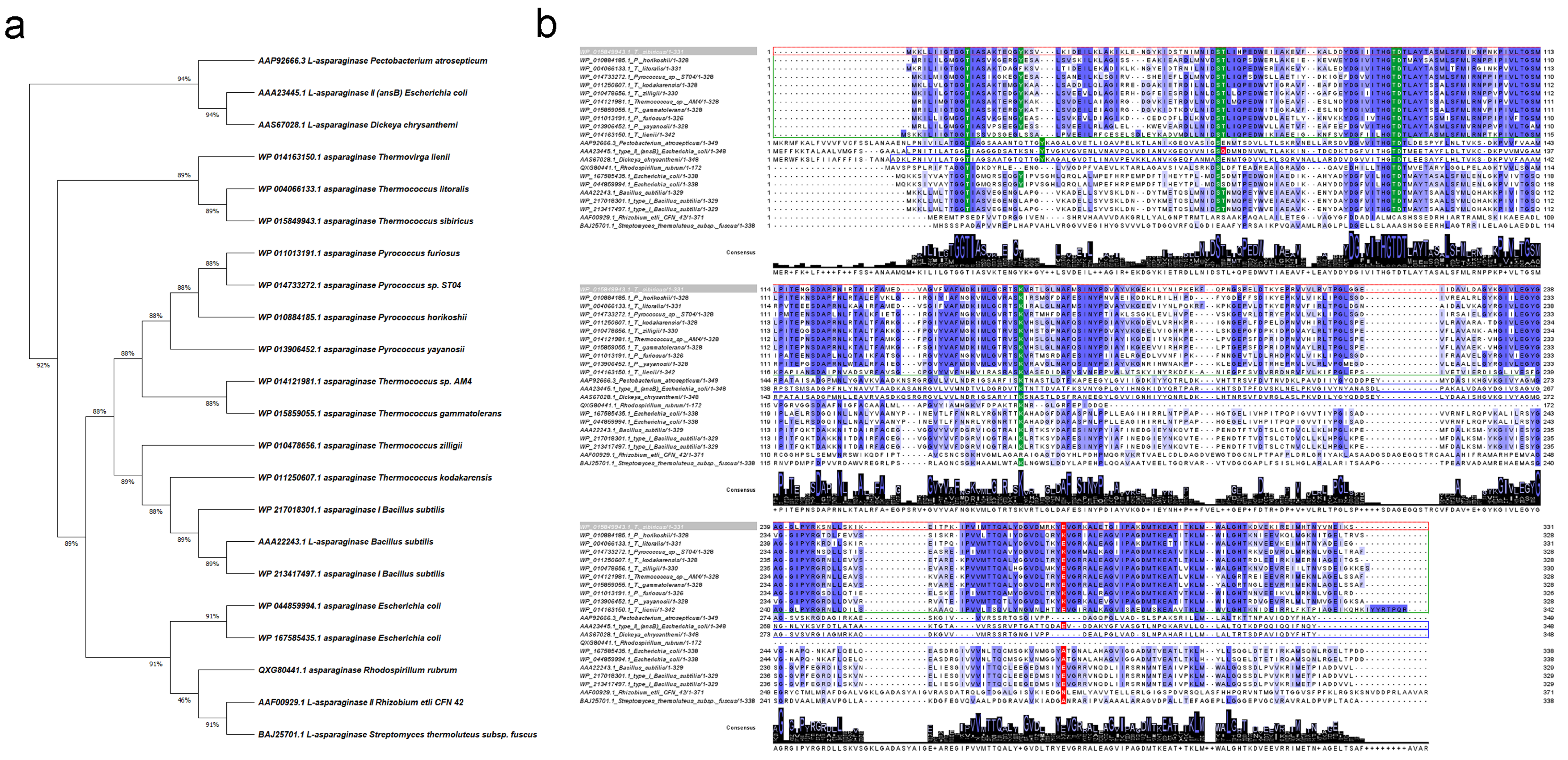
2.1. Identification and Sequence Comparison of TsA
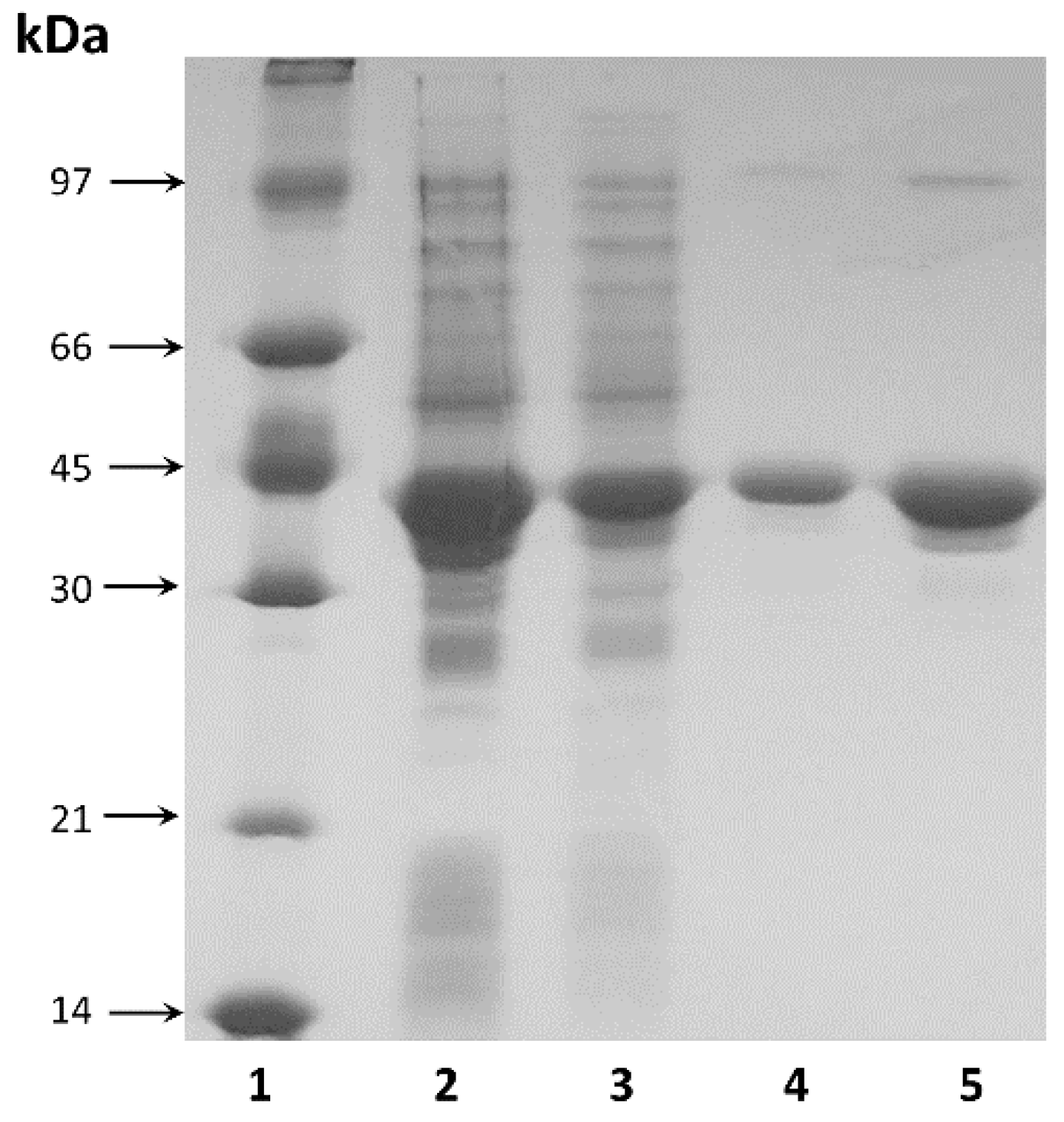
2.2. Gene Cloning, Expression and Recombinant Enzyme Purification
2.3. Specific Activity of TsA and Enzyme Kinetics
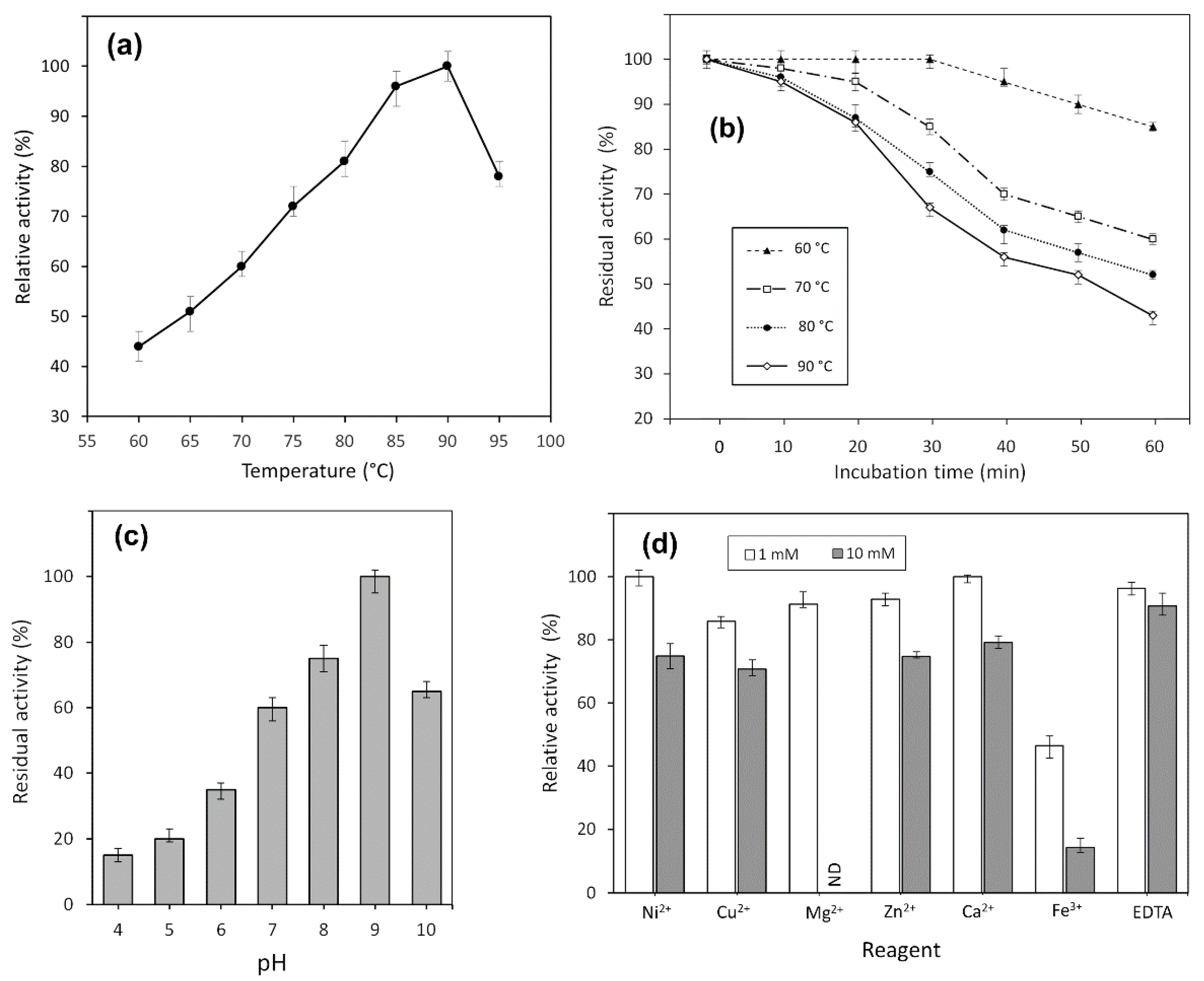
2.4. Effect of Temperature and pH on Enzyme Activity
2.5. Chemical Stability and Effect of Metal Ions on TsA Activity
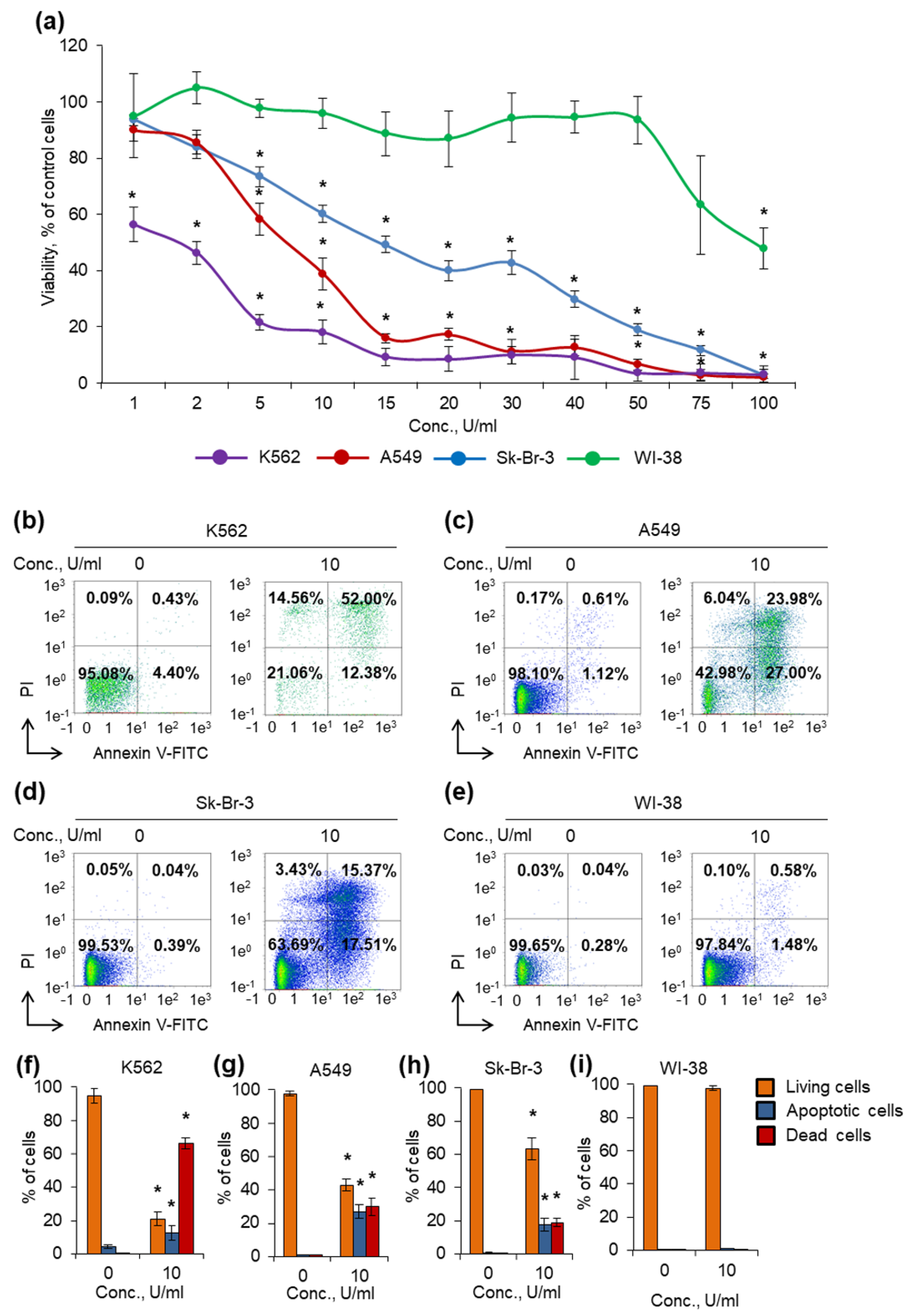
2.6. Determination of TsA Cytotoxic Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Enzymes and Chemicals
4.2. Strains and Cell Lines
4.3. Cloning of TsA Coding Sequences
4.4. Expression and Purification of Recombinant TsA
4.5. Enzyme Activity Assay and Determination of Kinetic Parameters of TsA
4.6. Effect of Temperature and pH
4.7. Chemical Denaturation Studies and Effect of Various Metal Ions
4.8. Determination of Cytotoxic Activity
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopes, A.M.; de Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Ribeiro, A.; Tairum, C.A.; Breyer, C.A.; de Oliveira, M.A.; Monteiro, G.; de Souza-Motta, C.M.; de Magalhães, P.O.; Avendaño, J.G.F.; et al. Therapeutic l-asparaginase: Upstream, downstream and beyond. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajitha, S.; Vidya, J.; Varsha, K.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Cloning and expression of l-asparaginase from E. coli in eukaryotic expression system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 102, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Ye, L.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Yang, P.; Cao, Z.; et al. Asparaginase induces apoptosis and cytoprotective autophagy in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3861–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-H. Asparaginase Therapy in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Focus on the Mode of Drug Resistance. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2015, 56, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.V.; Kumar, V.; Rajendran, V.; Saran, S.; Ghosh, P.C.; Saxena, R.K. Purification and Characterization of a Novel and Robust L-Asparaginase Having Low-Glutaminase Activity from Bacillus licheniformis: In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Cancerous Properties. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Naveed, M.; Ullah, A.; Ali, K.; Shah, S.A.; Fahad, S.; Mumtaz, A.S. L-asparaginase as a critical component to combat Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL): A novel approach to target ALL. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 771, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, S.P.; Lu, X.; Devidas, M.; Camitta, B.M.; Gaynon, P.S.; Winick, N.J.; Reaman, G.H.; Carroll, W.L. Improved Survival for Children and Adolescents With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Between 1990 and 2005: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möricke, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Reiter, A.; Henze, G.; Schrauder, A.; Gadner, H.; Ludwig, W.D.; Ritter, J.; Harbott, J.; Mann, G.; et al. Long-term results of five consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 2000. Leukemia 2009, 24, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrooman, L.M.; Stevenson, K.E.; Supko, J.G.; O’Brien, J.; Dahlberg, S.; Asselin, B.L.; Athale, U.H.; Clavell, L.A.; Kelly, K.M.; Kutok, J.L.; et al. Postinduction Dexamethasone and Individualized Dosing of Escherichia Coli L-Asparaginase Each Improve Outcome of Children and Adolescents With Newly Diagnosed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Results From a Randomized Study—Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium Protocol 00-01. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprivnikar, J.; McCloskey, J.; Faderl, S.H. Safety, efficacy, and clinical utility of asparaginase in the treatment of adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2017, 10, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Khan, A.A.; Khurshid, M.; Kalam, A.; Jain, S.K.; Singhal, P.K. Recent developments in l-asparaginase discovery and its potential as anticancer agent. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2016, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safary, A.; Moniri, R.; Hamzeh-Mivehroud, M.; Dastmalchi, S. Highly efficient novel recombinant L-asparaginase with no glutaminase activity from a new halo-thermotolerant Bacillus strain. BioImpacts 2019, 9, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.; Suciu, S.; Ferster, A.; Rialland, X.; Nelken, B.; Lutz, P.; Benoit, Y.; Robert, A.; Manel, A.-M.; Vilmer, E.; et al. Comparison of Escherichia coli-asparaginase with Erwinia-asparaginase in the treatment of childhood lymphoid malignancies: Results of a randomized European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Children’s Leukemia Group phase 3 trial. Blood 2002, 99, 2734–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Lorenzi, P.L.; Anishkin, A.; Purwaha, P.; Rogers, D.M.; Sukharev, S.; Rempe, S.B.; Weinstein, J.N. The glutaminase activity of l-asparaginase is not required for anticancer activity against ASNS-negative cells. Blood 2014, 123, 3596–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Xu, M.; He, B.; Rao, Z. Cloning, Expression, and Characterization of l-Asparaginase from a Newly Isolated Bacillus subtilis B11–06. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9428–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safary, A.; Khiavi, M.A.; Mousavi, R.; Barar, J.; Rafi, A.M. Enzyme replacement therapies: What is the best option? BioImpacts 2018, 8, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muso-Cachumba, J.J.; Antunes, F.A.F.; Peres, G.F.D.; Brumano, L.; Santos, J.; Da Silva, S.S. Current applications and different approaches for microbial l-asparaginase production. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.V.; Saran, S.; Kameswaran, K.; Kumar, V.; Saxena, R. Efficient production of l-asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis with low-glutaminase activity: Optimization, scale up and acrylamide degradation studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Toxicology Program. Report on Carcinogens, 14th ed.; Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2019.
- Verma, N.; Kumar, K.; Kaur, G.; Anand, S.E. Colik-12 Asparaginase-Based Asparagine Biosensor for Leukemia. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Biotechnol. 2007, 35, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kataria, M.; Verma, N. Plant asparaginase-based asparagine biosensor for leukemia. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 41, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, A.; Koytepe, S.; Ates, B.; Yilmaz, I.; Seckin, T. Preparation of the L-Asparaginase-Based Biosensor with Polyimide Membrane Electrode for Monitoring L-Asparagine Levels in Leukemia. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2014, 63, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Bachas, L. Biosensor for Asparagine Using a Thermostable Recombinant Asparaginase from Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3336–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Khan, A.R.; Ullah, I.; Lee, C.; Park, C.K.; Shin, J.-H. Cloning, expression, and characterization of thermophilicL-asparaginase fromThermococcus kodakarensisKOD1. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarquis, M.I.D.M.; Oliveira, E.M.M.; Santos, A.S.; Da Costa, G.L. Production of L-asparaginase by filamentous fungi. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2004, 99, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, G.; Aiswarya, R. Overview on mitigation of acrylamide in starchy fried and baked foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4385–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumano, L.P.; da Silva, F.V.S.; Costa-Silva, T.A.; Apolinário, A.C.; Santos, J.H.P.M.; Kleingesinds, E.K.; Monteiro, G.; Rangel-Yagui, C.D.O.; Benyahia, B.; Junior, A.P. Development of L-Asparaginase Biobetters: Current Research Status and Review of the Desirable Quality Profiles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnapura, P.R.; Belur, P.D.; Subramanya, S. A critical review on properties and applications of microbial l-asparaginases. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 720–737. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, B.H.; Pekar, A.H.; Veros, A.J.; Ho, P.P. Crystalline L-asparaginase from Escherichia coli B. II. Physical properties, subunits, and reconstitution behavior. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.-K.; Nourse, A.; White, S.W.; Rock, C.O.; Heath, R.J. Crystal Structure and Allosteric Regulation of the Cytoplasmic Escherichia colil-Asparaginase I. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 369, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dasu, V.V.; Pakshirajan, K. Localization and production of novel l-asparaginase from Pectobacterium carotovorum MTCC 1428. Process. Biochem. 2010, 45, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollersrud, O.K.; Aronson, N.N. Purification and characterization of rat liver glycosylasparaginase. Biochem. J. 1989, 260, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Gnaneswari, D.; Mishra, P.; Kundu, B. Structural stability and functional analysis of L-asparaginase from Pyrococcus furiosus. Biochemistry 2010, 75, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, S.M.; Rashid, N. TK1656, a thermostable l-asparaginase from Thermococcus kodakaraensis, exhibiting highest ever reported enzyme activity. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elleuche, S.; Schröder, C.; Sahm, K.; Antranikian, G. Extremozymes—Biocatalysts with unique properties from extremophilic microorganisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 29, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, R.A. A perspective on the biotechnological potential of extremophiles. Trends Biotechnol. 1992, 10, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishino, S.; Ishino, Y. DNA polymerases as useful reagents for biotechnology—The history of developmental research in the field. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlechild, J.A. Archaeal Enzymes and Applications in Industrial Biocatalysts. Archaea 2015, 2015, 147671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.B.; Carvalho, I. Diketopiperazines: Biological activity and synthesis. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 9923–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, J.A. Extremophiles and biotechnology: Current uses and prospects. F1000Research 2016, 5, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J. Overview of extremophiles and their food and medical applications. Physiol. Biotechnol. Asp. Extrem. 2020, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Coker, A.R.; Wood, S.P.; Cooper, J.B.; Chohan, S.M.; Rashidc, N.; Akhtar, M. Structure and function of the thermostable L-asparaginase from Thermococcus kodakarensis. Acta Cryst. 2017, 73, 889–895. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, S.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W. Reduction of acrylamide level through blanching with treatment by an extremely thermostable l-asparaginase during French fries processing. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Xue, D.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W. Biochemical characterization of an extremely thermostable l-asparaginase from Thermococcus gammatolerans EJ3. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 109, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Yang, T.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Zhang, H.; Fang, H.; et al. Simultaneous cell disruption and semi-quantitative activity assays for high-throughput screening of thermostable L-asparaginases. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; Srivastava, A.; Mukherjee, G.; Pandey, R.; Verma, A.K.; Mishra, P.; Kundu, B. Hyperthermophilic asparaginase mutants with enhanced substrate affinity and antineoplastic activity: Structural insights on their mechanism of action. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.K.; Kundu, B. Hyperthermophilic l -asparaginase bypasses monomeric intermediates during folding to retain cooperativity and avoid amyloid assembly. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 622, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, D.K.; Tomar, R.; Dhoke, R.R.; Srivastava, A.; Kundu, B. Domains of Pyrococcus furiosus l-asparaginase fold sequentially and assemble through strong intersubunit associative forces. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Yasutake, Y.; Morita, H.; Tanaka, I. Structure of the type IL-asparaginase from the hyperthermophilic archaeonPyrococcus horikoshiiat 2.16 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2005, 61, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, S.M.; Rashid, N.; Sajed, M.; Imanaka, T. Pcal_0970: An extremely thermostable l-asparaginase from Pyrobaculum calidifontis with no detectable glutaminase activity. Folia Microbiol. 2019, 64, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miroshnichenko, M.L.; Hippe, H.; Stackebrandt, E.; Kostrikina, N.A.; Chernyh, N.A.; Jeanthon, C.; Nazina, T.N.; Belyaev, S.S.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. Isolation and characterization of Thermococcus sibiricus sp. nov. from a Western Siberia high-temperature oil reservoir. Extremophiles 2001, 5, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Svetlitchnyi, V.A.; Beletsky, A.V.; Miroshnichenko, M.L.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Skryabin, K.G. Metabolic Versatility and Indigenous Origin of the Archaeon Thermococcus sibiricus, Isolated from a Siberian Oil Reservoir, as Revealed by Genome Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Svetlitchnyi, V.A.; Beletsky, A.V.; Miroshnichenko, M.L.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A.; Skryabin, K.G. Thermococcus Sibiricus MM 739, Complete Genome. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NC_012883.1 (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Dumina, M.V.; Eldarov, M.A.; Zdanov, D.D.; Sokolov, N.N. L-Asparaginases of Extremophilic Microorganisms in Biomedicine. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2020, 14, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhossein, M.; Korbekandi, H. Cloning, expression, purification and characterisation of Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase in Escherichia coli. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzia, G.A.; Labrou, N.E. Cloning, expression and characterisation of Erwinia carotovoral-asparaginase. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 119, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Aleksandrova, S.S.; Pokrovsky, V.; Veselovsky, A.V.; Grishin, D.V.; Abakumova, O.Y.; Podobed, O.V.; Mishin, A.A.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Sokolov, N.N. Identification of Functional Regions in the Rhodospirillum rubrum l-Asparaginase by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2015, 57, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovskaya, M.; Aleksandrova, S.; Veselovsky, A.; Zdanov, D.; Pokrovsky, V.; Eldarov, M.; Grishin, D.; Gladilina, Y.; Toropigin, I.; Sokolov, N. Physical-Chemical Properties of L-asparaginase Mutants from Rhodospirillum Rubrum which Showed Antitelomerase Activity. Biomed. Chem. Res. Methods 2019, 2, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechkova, E.; Fiordoro, S.; Sokolov, N.; Pokrovsky, V.; Pokrovskaya, M.; Aleksandrova, S.; Veselovsky, L.; Bragazzi, N.; Giannini, M.; Pellegrino, L.; et al. LB Crystallization and Preliminary X-ray Diffraction Analysis of L-Asparaginase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. NanoWorld J. 2017, 3, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Nishimura, H.; Saito, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Kamisaki, Y.; Wada, H.; Sako, M.; Tsujino, G.; Inada, Y. Characterization of polyethylene glycol-modified L-asparaginase from Escherichia coli and its application to therapy of leukemia. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1986, 77, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhdanov, D.D.; Pokrovsky, V.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Alexandrova, S.S.; Eldarov, M.A.; Grishin, D.V.; Basharov, M.M.; Gladilina, Y.; Podobed, O.V.; Sokolov, N.N. Rhodospirillum rubrum l-asparaginase targets tumor growth by a dual mechanism involving telomerase inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, A.L.; Jaskolski, M.; Housset, D.; Rao, J.K.; Wlodawer, A. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase, an enzyme used in cancer therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, M.P.; Daniel, R.M.; Guy, G.R.; Morgan, H.W. A specific l-asparaginase from Thermus aquaticus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1985, 241, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentahir, M.; Feller, G.; Aittaleb, M.; Lamotte-Brasseur, J.; Himri, T.; Chessa, J.-P.; Gerday, C. Structural, Kinetic, and Calorimetric Characterization of the Cold-active Phosphoglycerate Kinase from the AntarcticPseudomonas sp. TACII18. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11147–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thomas, T.M.; Scopes, R.K. The effects of temperature on the kinetics and stability of mesophilic and thermophilic 3-phosphoglycerate kinases. Biochem. J. 1998, 330, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, W.H.; Nealon, A.D.; Rej, R. Effects of temperature on measurement of alkaline phosphatase activity. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, M.; Wasagu, R.; Umar, M. Kinetic Studies of Alkaline Phosphatase from the Liver of Agama agama Lizard. Niger. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2013, 21, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mahesh, M.; Guleria, N.; Rajesh, T. Isolation and characterization of extracellular thermostable alkaline phosphatase enzyme from Bacillus spp. Int. J. Appl. Biol. Pharm. Technol. 2010, 1, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Pindi, P.K.; Dube, S.; Sundareswaran, V.R.; Shivaji, S. Importance of trmE for Growth of the Psychrophile Pseudomonas syringae at Low Temperatures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richer, H.B.; Brewer, J.; Fahlman, G.G.; Gibson, B.; Hansen, B.M.; Ibata, R.; Kalirai, J.S.; Limongi, M.; Rich, R.M.; Saviane, I.; et al. The Lower Main Sequence and Mass Function of the Globular Cluster Messier 4. Astrophys. J. 2002, 574, L151–L154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warangkar, S.C.; Khobragade, C.N. Purification, Characterization, and Effect of Thiol Compounds on Activity of the Erwinia carotovora L-Asparaginase. Enzym. Res. 2010, 2010, 165878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, T.; Usuki, H.; Arima, J.; Uesugi, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Yamasato, A.; Mukaihara, T. Extracellular Production and Characterization of Two Streptomyces l-Asparaginases. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 163, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Relling, M.V.; Storm, M.C.; Woo, M.H.; Ribeiro, R.; Pui, C.-H.; Hak, L.J. Evaluation of immunologic crossreaction of antiasparaginase antibodies in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoma patients. Leukemia 2003, 17, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Pokrovskiy, V.S.; Aleksandrova, S.S.; Anisimova, N.; Andrianov, R.M.; Treschalina, E.M.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Sokolov, N.N. Recombinant intracellular Rhodospirillum rubrum L-asparaginase with low L-glutaminase activity and antiproliferative effect. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2012, 6, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, A.A.; El’Darov, A.M.; Zhgun, A.A.; Aleksandrova, S.S.; Omel’Ianiuk, N.M.; Sokov, B.N.; Berezov, T.T.; Sokolov, N.N. Purification and properties of recombinant Erwinia carotovora L-asparaginase expressed in E.coli cells. Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya 2005, 49, 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak, J.; Grossberg, S.E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 79, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wriston, J.C.; Yellin, T.O. L-Asparaginase: A Review. In Advances in Enzymology—And Related Areas of Molecular Biology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 39, pp. 185–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, H.E.; Robinson, H.K.; Phillips, B.W. Asparaginase and Glutaminase Activities of Bacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1971, 69, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizot, F.; Lang, R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 89, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, D.D.; Pokrovsky, V.S.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Alexandrova, S.S.; Eldarov, M.A.; Grishin, D.V.; Basharov, M.M.; Gladilina, Y.A.; Podobed, O.V.; Sokolov, N.N. Inhibition of telomerase activity and induction of apoptosis by Rhodospirillum rubrum L-asparaginase in cancer Jurkat cell line and normal human CD4+ T lymphocytes. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2697–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Purification Step | Total Protein, mg | Total Activity, U | Specific Activity, U/mg | Yield, % | Purification Fold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| crude enzyme | 165.0 | 86,361.0 | 523.4 | 100.0 | - |
| purified enzyme | 45.0 | 68,014.3 | 2164.0 | 78.8 | 4.1 |
| Cell Line | IC50, U/mL | IC90, U/mL |
|---|---|---|
| K562 | 1.5 | 13.6 |
| A549 | 6.6 | 45.4 |
| Sk-Br-3 | 15.8 | 82.1 |
| WI-38 | 97.1 | ˃300 |
| Microorganism | Molecular Weight, kDa | Optimum t, °C | Optimum pH | Hydrolysis of L-Asparagine, U/mg | Hydrolysis of L-Glutamine, U/mg | KM, mM | Vmax, μM * min−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. sibiricus | 37.5 | 90.0 | 9.0 | 2164 | 151 | 2.801 | 1200 | This study |
| Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1 | 37.0 | 90.0 | 8.0 | 978.7 | Not determined | 2.6 | 1121 | [24] |
| T. kodakarensis KOD1 | 35.5 | 85.0 | 9.5 | 2350 | - | 5.5 | 3300 | [34] |
| T. zilligii | 36.0 | 90.0 | 8.5 | 5278 ± 32 | Not determined | 6.08 | [43] | |
| T.gammatolerans EJ3 | 36.5 | 85.0 | 8.5 | 7622 | +2926 | 10.0 | [44] | |
| P. yayanosii CH1 | 36.1 | 95.0 | 8.0 | 1483.8 | Not determined | 6.5 | 2929 | [45] |
| P.furiosus | ~37.0 | ~85.0 | 9.0 | 550 | - | 80 °C, pH 8.2 12.1 ± 0.05 37 °C, pH 7.4 8.12 ± 0.3 | [33,46] | |
| Pyrobaculum calidifontis | 32 | ≥100 | 6.5 | - | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 355 ± 13 | [50] | |
| Archaeoglobus fulgidus | 70.0 | 9.2 | + | 37 °C 0.08 70 °C 0.005 | [23] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumina, M.; Zhgun, A.; Pokrovskaya, M.; Aleksandrova, S.; Zhdanov, D.; Sokolov, N.; El’darov, M. A Novel L-Asparaginase from Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus sibiricus: Heterologous Expression and Characterization for Biotechnology Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189894
Dumina M, Zhgun A, Pokrovskaya M, Aleksandrova S, Zhdanov D, Sokolov N, El’darov M. A Novel L-Asparaginase from Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus sibiricus: Heterologous Expression and Characterization for Biotechnology Application. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(18):9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189894
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumina, Maria, Alexander Zhgun, Marina Pokrovskaya, Svetlana Aleksandrova, Dmitry Zhdanov, Nikolay Sokolov, and Michael El’darov. 2021. "A Novel L-Asparaginase from Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus sibiricus: Heterologous Expression and Characterization for Biotechnology Application" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 18: 9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189894
APA StyleDumina, M., Zhgun, A., Pokrovskaya, M., Aleksandrova, S., Zhdanov, D., Sokolov, N., & El’darov, M. (2021). A Novel L-Asparaginase from Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus sibiricus: Heterologous Expression and Characterization for Biotechnology Application. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(18), 9894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189894







