Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 420 with a Chromosomally Inserted Virulence Plasmid
Abstract
:1. Background
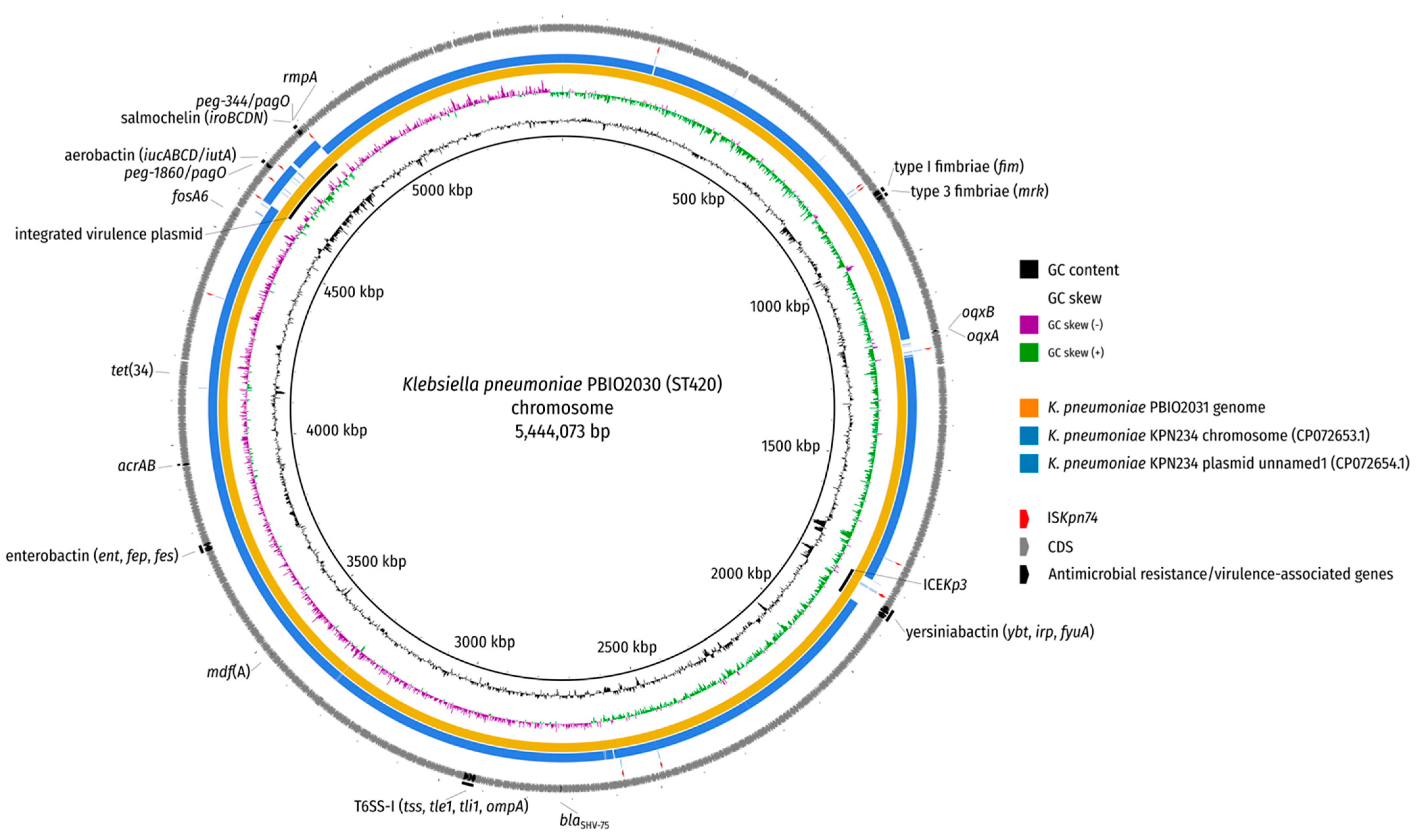
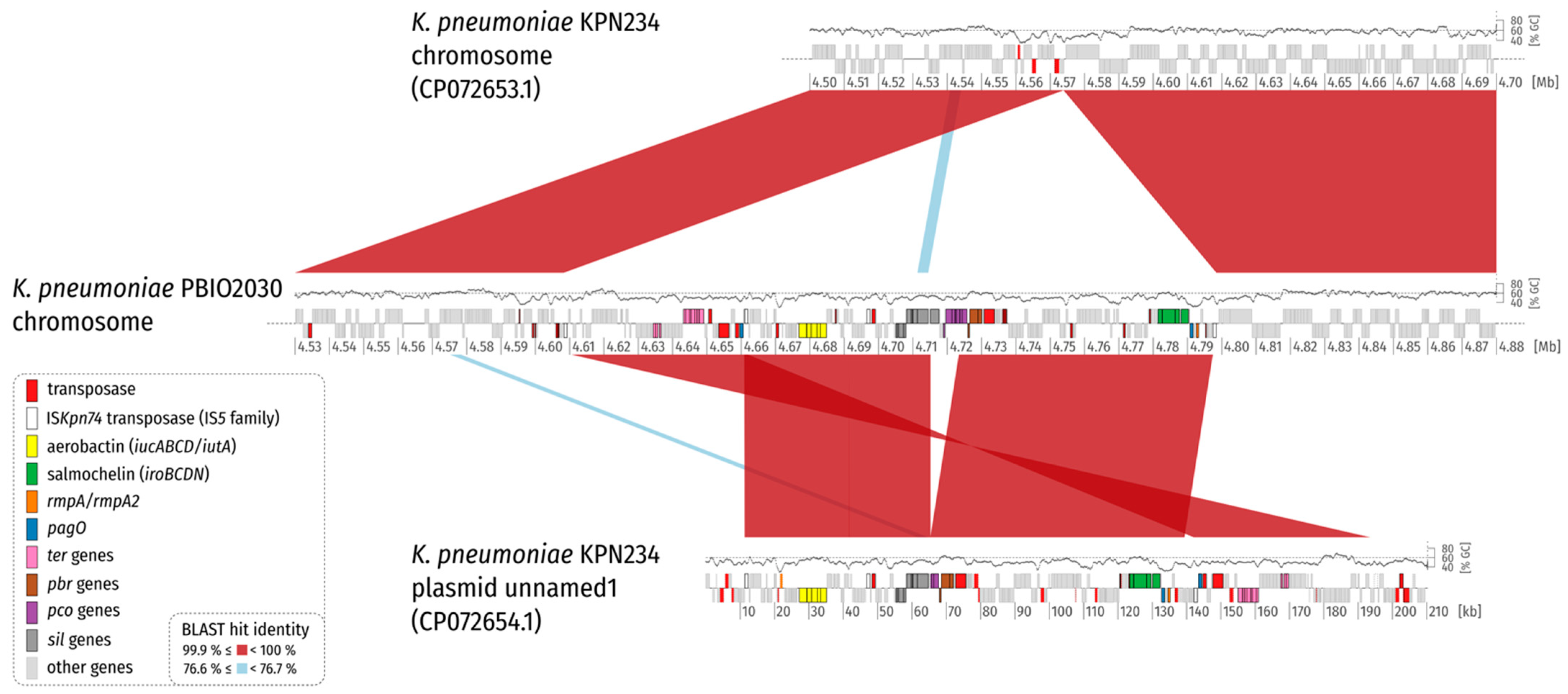
2. Results and Discussion
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Strain Origin and Clinical Background
3.2. Bacterial Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.3. Phenotypic Analyses
3.4. Genomic Analysis
3.5. Validity of Plasmid Integration (In Silico and PCR Analysis)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AbST | aerobactin sequence type |
| AST | antimicrobial susceptibility testing |
| bp | base pairs |
| CAS | Chromazurol S |
| CFU | colony-forming unit |
| cKp | classic K. pneumoniae |
| DR | direct repeat |
| hvKp | hypervirulent K. pneumoniae |
| ICE | integrative conjugative element |
| Inc | incompatibility group |
| IR | inverted repeat |
| IS | insertion sequence |
| kb | kilo base pairs |
| µL | microliter |
| mL | milliliter |
| MLST | multi-locus sequence typing |
| OD | optical density |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| SmST | salmochelin sequence type |
| SNP | single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| SNV | single-nucleotide variant |
| ST | sequence type |
| YbST | yersiniabactin sequence type |
References
- Fazili, T.; Sharngoe, C.; Endy, T.; Kiska, D.; Javaid, W.; Polhemus, M. Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess: An Emerging Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 351, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Podschun, R.; Ullmann, U. Klebsiella spp. as Nosocomial Pathogens: Epidemiology, Taxonomy, Typing Methods, and Pathogenicity Factors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marr, C.M.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new public health threat. Expert Rev. Anti-Infective Ther. 2019, 17, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heiden, S.E.; Hübner, N.-O.; Bohnert, J.A.; Heidecke, C.-D.; Kramer, A.; Balau, V.; Gierer, W.; Schaefer, S.; Eckmanns, T.; Gatermann, S.; et al. A Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 outbreak clone from Germany demonstrates features of extensive drug resistance, hypermucoviscosity, and enhanced iron acquisition. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Marimuthu, K.; Teo, J.; Venkatachalam, I.; Cherng, B.P.Z.; De Wang, L.; Prakki, S.R.S.; Xu, W.; Tan, Y.H.; Nguyen, L.C.; et al. Acquisition of Plasmid with Carbapenem-Resistance Gene blaKPC2 in Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, Singapore. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catalán-Nájera, J.C.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Barrios-Camacho, H. Hypervirulence and hypermucoviscosity: Two different but complementary Klebsiella spp. phenotypes? Virulence 2017, 8, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulger, J.; MacDonald, U.; Olson, R.; Beanan, J.; Russo, T.A. Metabolite Transporter PEG344 Is Required for Full Virulence of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain hvKP1 after Pulmonary but Not Subcutaneous Challenge. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00093-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; Fang, C.-T.; Stoesser, N.; Miller, M.; MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Barker, J.H.; La Hoz, R.M.; Johnson, J.R. Identification of Biomarkers for Differentiation of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from Classical K. pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00776-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.M.; Grossman, A.D. Integrative and Conjugative Elements (ICEs): What They Do and How They Work. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankar, C.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Nabarro, L.E.B.; Ravi, R.; Ragupathi, N.K.D.; Rupali, P. Whole genome analysis of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from community and hospital acquired bloodstream infection. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, L.; Yang, J. Molecular epidemiology and virulence factors of pyogenic liver abscess causing Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O818–O824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thuy, D.B.; Campbell, J.; Thuy, C.T.; Hoang, N.V.M.; Vinh, P.V.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Minh, C.N.N.; Pham, D.T.; Rabaa, M.A.; Lan, N.P.H.; et al. Colonization with Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae causes infections in a Vietnamese intensive care unit. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. High Prevalence of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in China: Geographic Distribution, Clinical Characteristics, and Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6115–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wyres, K.L.; Judd, L.M.; Wick, R.R.; Jenney, A.; Brisse, S.; Holt, K.E. Tracking key virulence loci encoding aerobactin and salmochelin siderophore synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russo, T.A.; Gill, S.R. Draft Genome Sequence of the Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain hvKP1, Isolated in Buffalo, New York. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e0006513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Wu, C.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Lai, Y.C.; Peng, H.L. RmpA Regulation of Capsular Polysaccharide Biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3144–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; MacDonald, U.; Metzger, D.; Maltese, L.M.; Drake, E.J.; Gulick, A. Aerobactin Mediates Virulence and Accounts for Increased Siderophore Production under Iron-Limiting Conditions by Hypervirulent (Hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-L.; Chen, F.-H.; Huang, L.-Y.; Chang, J.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Tsai, Y.-K.; Chang, F.-Y.; Lin, J.-C.; Siu, L.K. Effect in virulence of switching conserved homologous capsular polysaccharide genes from Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K1 into K20. Virulence 2017, 8, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, K.S. The contribution of capsule polysaccharide genes to virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Virulence 2017, 8, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siguier, P.; Gourbeyre, E.; Varani, A.; Ton-Hoang, B.; Chandler, M. Everyman’s Guide to Bacterial Insertion Sequences. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 555–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siguier, P.; Perochon, J.; Lestrade, L.; Mahillon, J.; Chandler, M. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavakoli, N.P.; Derbyshire, K.M. Tipping the balance between replicative and simple transposition. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2923–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Medina, N.; Martínez-Romero, E.; De La Cruz, M.A.; Ares, M.A.; Valdovinos-Torres, H.; Silva-Sánchez, J.; Lozano-Aguirre, L.; Martínez-Barnetche, J.; Andrade, V.; Garza-Ramos, U. A Klebsiella variicola Plasmid Confers Hypermucoviscosity-Like Phenotype and Alters Capsule Production and Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 579612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-L.; Chiang, M.-K.; Liou, W.-J.; Chen, Y.-T.; Peng, H.-L.; Chiou, C.-S.; Liu, K.-S.; Lu, M.-C.; Tung, K.-C.; Lai, Y.-C. Correlation between Klebsiella pneumoniae carrying pLVPK-derived loci and abscess formation. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Torres, V.V.; Liu, H.; Rocker, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Bi, W.; Lin, J.; et al. An Outbreak of Carbapenem-Resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in an Intensive Care Unit of a Major Teaching Hospital in Wenzhou, China. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Scholz, J.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Ewers, C.; Müller, S.; Pickard, D.J.; Schierack, P.; Tedin, K.; Ahmed, N.; et al. ESBL-plasmid carriage in E. coli enhances in vitro bacterial competition fitness and serum resistance in some strains of pandemic sequence types without overall fitness cost. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierack, P.; Heiden, S.E.; Khan, M.M.; Nikolaus, L.; Kolenda, R.; Stubbe, M.; Lkhagvasuren, D.; Rödiger, S.; Guenther, S.; Schaufler, K. Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of an ESBL-Producing E. coli ST1159 Clonal Lineage From Wild Birds in Mongolia. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himpsl, S.D.; Mobley, H.L.T. Siderophore Detection Using Chrome Azurol S and Cross-Feeding Assays. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2019, 2021, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K.; Verma, M. Modified microplate method for rapid and efficient estimation of siderophore produced by bacteria. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mike, L.A.; Stark, A.J.; Forsyth, V.S.; Vornhagen, J.; Smith, S.N.; Bachman, M.; Mobley, H.L.T. A systematic analysis of hypermucoviscosity and capsule reveals distinct and overlapping genes that impact Klebsiella pneumoniae fitness. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.S.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An Integrated Tool for Comprehensive Microbial Variant Detection and Genome Assembly Improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Jin, Q.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2019: A comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Hasman, H. PlasmidFinder and In Silico pMLST: Identification and Typing of Plasmid Replicons in Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS). Cardiovasc. Dev. 2020, 2075, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Rensing, C.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. BacMet: Antibacterial biocide and metal resistance genes database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D737–D743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alikhan, N.-F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.S.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Gorrie, C.; Jenney, A.; Follador, R.; Thomson, N.R.; Holt, K.E. Identification of Klebsiella capsule synthesis loci from whole genome data. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, L.; Kultima, J.R.; Andersson, S.G.E. genoPlotR: Comparative gene and genome visualization in R. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2334–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, I.; Stephen, G.; Bayer, M.; Cock, P.; Pritchard, L.; Cardle, L.; Shaw, P.D.; Marshall, D. Using Tablet for visual exploration of second-generation sequencing data. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Strain (Origin, Purpose) | String Test Result |
|---|---|
| W3110 (E. coli; negative control) | Negative |
| ATCC700603 (K. pneumoniae; negative control) | Negative |
| PBIO1953 (reference I) | Negative |
| hvKP1 (reference II) | Positive |
| PBIO2030 (wound) | Positive |
| PBIO2031 (blood culture) | Positive |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eger, E.; Heiden, S.E.; Becker, K.; Rau, A.; Geisenhainer, K.; Idelevich, E.A.; Schaufler, K. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 420 with a Chromosomally Inserted Virulence Plasmid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179196
Eger E, Heiden SE, Becker K, Rau A, Geisenhainer K, Idelevich EA, Schaufler K. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 420 with a Chromosomally Inserted Virulence Plasmid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179196
Chicago/Turabian StyleEger, Elias, Stefan E. Heiden, Karsten Becker, Andrea Rau, Katharina Geisenhainer, Evgeny A. Idelevich, and Katharina Schaufler. 2021. "Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 420 with a Chromosomally Inserted Virulence Plasmid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179196
APA StyleEger, E., Heiden, S. E., Becker, K., Rau, A., Geisenhainer, K., Idelevich, E. A., & Schaufler, K. (2021). Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 420 with a Chromosomally Inserted Virulence Plasmid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179196







