Extracellular Matrix Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
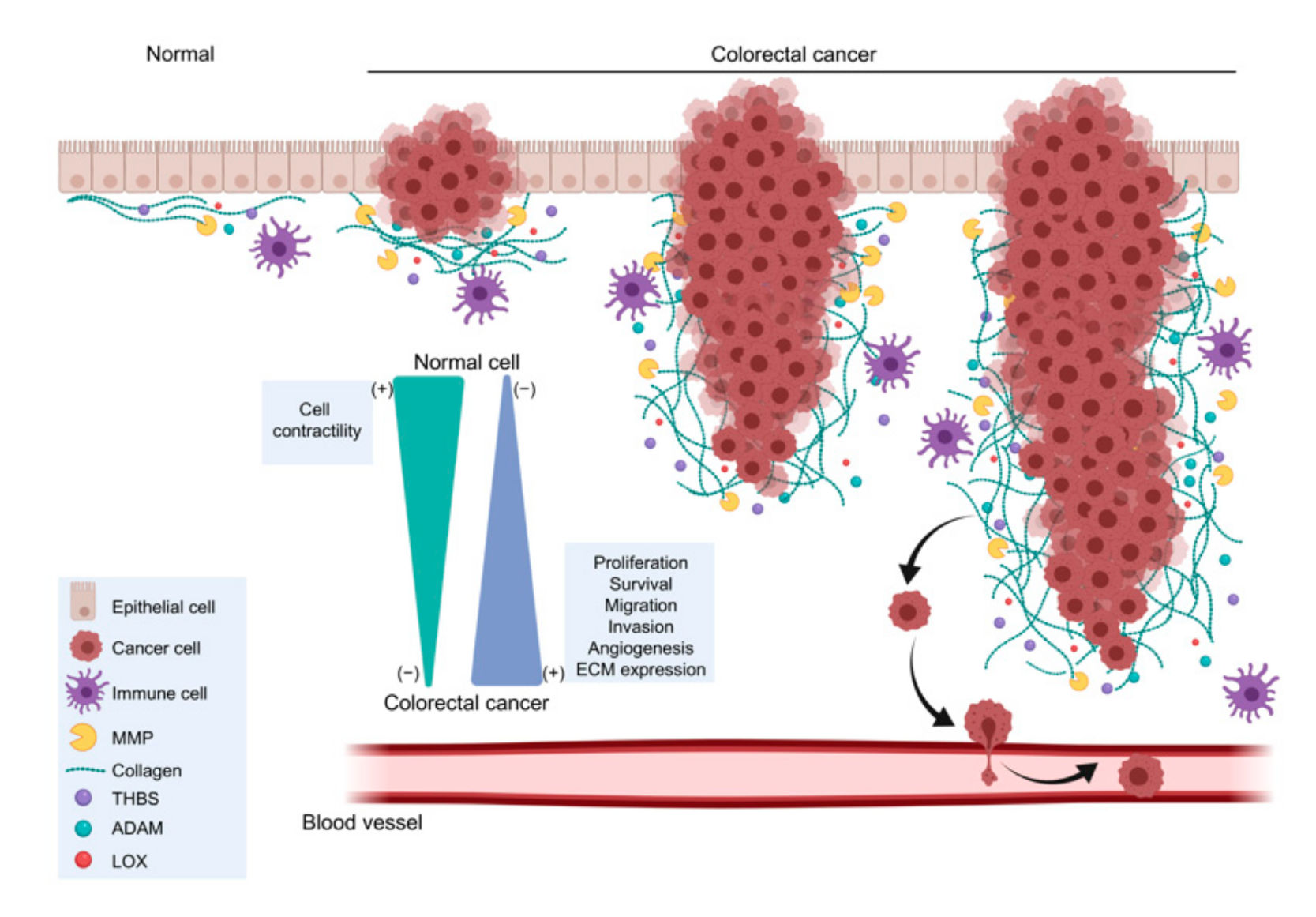
1. Introduction
2. Collagen
3. Laminin
4. Matrix Metalloproteinases
5. LOX
6. ADAM
7. Proteoglycan
8. Thrombospondin
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nature Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Lian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Cao, K.; et al. Role of tumor microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, E.; Nandigama, R.; Ergun, S. Extracellular Matrix in the Tumor Microenvironment and Its Impact on Cancer Therapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiry, S.; Kim, G.; Filippou, P.S.; Sanchez, L.R.; Entenberg, D.; Marks, D.K.; Oktay, M.H.; Karagiannis, G.S. The Cancer Cell Dissemination Machinery as an Immunosuppressive Niche: A New Obstacle Towards the Era of Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 654877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanos, N.K. Extracellular matrix: Key structural and functional meshwork in health and disease. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2826–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanos, N.K.; Piperigkou, Z.; Theocharis, A.D.; Watanabe, H.; Franchi, M.; Baud, S.; Brézillon, S.; Götte, M.; Passi, A.; Vigetti, D.; et al. Proteoglycan Chemical Diversity Drives Multifunctional Cell Regulation and Therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9152–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iozzo, R.V.; Gubbiotti, M.A. Extracellular matrix: The driving force of mammalian diseases. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuzhalin, A.E.; Lim, S.Y.; Kutikhin, A.G.; Gordon-Weeks, A.N. Dynamic matrisome: ECM remodeling factors licensing cancer progression and metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Campbell, J.M.; Inman, D.R.; White, J.G.; Keely, P.J. Collagen reorganization at the tumor-stromal interface facilitates local invasion. BMC Med. 2006, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egeblad, M.; Rasch, M.G.; Weaver, V.M. Dynamic interplay between the collagen scaffold and tumor evolution. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkovic, I. Extracellular matrix remodelling: The role of matrix metalloproteinases. J. Pathol. 2003, 200, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.V.; Chudakova, D.A.; Skorova, E.Y.; Anikin, V.; Reshetov, I.V.; Mynbaev, O.A. The Extracellular Matrix-Derived Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Personalized Therapy of Malignant Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 575569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissell, M.J.; Hines, W.C. Why don’t we get more cancer? A proposed role of the microenvironment in restraining cancer progression. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gout, S.; Huot, J. Role of cancer microenvironment in metastasis: Focus on colon cancer. Cancer Microenviron. Off. J. Int. Cancer Microenviron. Soc. 2008, 1, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, H.; Naredi, P.; Berglund, A.; Palmqvist, R.; Tavelin, B.; Sund, M. Liver-metastatic potential of colorectal cancer is related to the stromal composition of the tumour. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 5183–5191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanjore, H.; Kalluri, R. The role of type IV collagen and basement membranes in cancer progression and metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Huang, G.; Qin, J.; Li, H.; Nong, F.; Wen, B. Prognostic significance of abnormal matrix collagen remodeling in colorectal cancer based on histologic and bioinformatics analysis. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1671–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.; Li, M.; Luo, T.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Y. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumorigenesis: An evolving paradigm. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3853–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjin, G.; White, E.S.; Faiz, A.; Sicard, D.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Mahar, A.; Kable, E.P.W.; Burgess, J.K. Lysyl oxidases regulate fibrillar collagen remodelling in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Dis. Model Mech. 2017, 10, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Choi, H.S.; Wu, M.; Myung, J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Ro, S.; Ha, S.E.; Bartlett, A.; Wei, L.; et al. Potential Role of PDGFRbeta-Associated THBS4 in Colorectal Cancer Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wan, D.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Lin, S.; Qiao, Y. Extracellular matrix and its therapeutic potential for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Liu, L. The role of collagen in cancer: From bench to bedside. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.J.; Sugimoto, H.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Type I collagen deletion in alphaSMA(+) myofibroblasts augments immune suppression and accelerates progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 548–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conklin, M.W.; Keely, P.J. Why the stroma matters in breast cancer: Insights into breast cancer patient outcomes through the examination of stromal biomarkers. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2012, 6, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, R.N.; Yousof, M.; Ly, K.L.; Gombedza, F.C.; Luo, X.; Bandyopadhyay, B.C.; Raub, C.B. Microstructural densification and alignment by aspiration-ejection influence cancer cell interactions with three-dimensional collagen networks. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1826–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatcott, C.J.; Diep, C.H.; Jiang, P.; Watanabe, A.; LoBello, J.; Sima, C.; Hostetter, G.; Shepard, H.M.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Han, H. Desmoplasia in Primary Tumors and Metastatic Lesions of Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3561–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beam, J.; Botta, A.; Ye, J.; Soliman, H.; Matier, B.J.; Forrest, M.; MacLeod, K.M.; Ghosh, S. Excess Linoleic Acid Increases Collagen I/III Ratio and “Stiffens” the Heart Muscle Following High Fat Diets. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23371–23384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauchle, E.; Kasper, J.; Daum, R.; Schierbaum, N.; Falch, C.; Kirschniak, A.; Schäffer, T.E.; Schenke-Layland, K. Biomechanical and biomolecular characterization of extracellular matrix structures in human colon carcinomas. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, M.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness and degradation as cancer drivers. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, K.; Smid, M.; Dawes, R.P.; Timmermans, M.A.; Salzman, P.; van Deurzen, C.H.; Beer, D.G.; Foekens, J.A.; Brown, E. Using second harmonic generation to predict patient outcome in solid tumors. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantola, T.; Väyrynen, J.P.; Klintrup, K.; Mäkelä, J.; Karppinen, S.M.; Pihlajaniemi, T.; Autio-Harmainen, H.; Karttunen, T.J.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Tuomisto, A. Serum endostatin levels are elevated in colorectal cancer and correlate with invasion and systemic inflammatory markers. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Fang, C.Y.; Chen, S.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Cui, S.J.; Liu, X.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.Y.; et al. Stroma derived COL6A3 is a potential prognosis marker of colorectal carcinoma revealed by quantitative proteomics. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29929–29946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Ding, F.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q. Co-expression Network Analysis Identified COL8A1 Is Associated with the Progression and Prognosis in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovbjerg, H.; Anthonsen, D.; Lothe, I.M.; Tveit, K.M.; Kure, E.H.; Vogel, L.K. Collagen mRNA levels changes during colorectal cancer carcinogenesis. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, X.; Crous-Bou, M.; Cordero, D.; Olivares, D.; Guinó, E.; Sanz-Pamplona, R.; Rodriguez-Moranta, F.; Sanjuan, X.; de Oca, J.; Salazar, R.; et al. Discovery and validation of new potential biomarkers for early detection of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzhalin, A.E.; Gordon-Weeks, A.N.; Tognoli, M.L.; Jones, K.; Markelc, B.; Konietzny, R.; Fischer, R.; Muth, A.; O’Neill, E.; Thompson, P.R.; et al. Colorectal cancer liver metastatic growth depends on PAD4-driven citrullination of the extracellular matrix. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. COL1A1: A potential therapeutic target for colorectal cancer expressing wild-type or mutant KRAS. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, R. COL1A1 promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating the WNT/PCP pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5037–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodia, M.T.; Ugolini, G.; Mattei, G.; Montroni, I.; Zattoni, D.; Ghignone, F.; Veronese, G.; Marisi, G.; Lauriola, M.; Strippoli, P.; et al. Systematic large-scale meta-analysis identifies a panel of two mRNAs as blood biomarkers for colorectal cancer detection. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30295–30306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Feng, B.; Dong, T.; Yan, G.; Tan, B.; Shen, H.; Huang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, P.; et al. Up-regulation of type I collagen during tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer revealed by quantitative proteomic analysis. J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willumsen, N.; Bager, C.; Karsdal, M.A. Matrix Metalloprotease Generated Fragments of Type VI Collagen Have Serum Biomarker Potential in Cancer-A Proof of Concept Study. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlet, S.N.; Sanz-Pamplona, R.; Brix, S.; Leeming, D.J.; Karsdal, M.A.; Moreno, V. Excessive collagen turnover products are released during colorectal cancer progression and elevated in serum from metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröker, M.E.; Lalmahomed, Z.S.; Roest, H.P.; van Huizen, N.A.; Dekker, L.J.; Calame, W.; Verhoef, C.; Ijzermans, J.N.; Luider, T.M. Collagen peptides in urine: A new promising biomarker for the detection of colorectal liver metastases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalmahomed, Z.S.; Bröker, M.E.; van Huizen, N.A.; Coebergh van den Braak, R.R.; Dekker, L.J.; Rizopoulos, D.; Verhoef, C.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Luider, T.M.; JN, I.J. Hydroxylated collagen peptide in urine as biomarker for detecting colorectal liver metastases. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nyström, H.; Tavelin, B.; Björklund, M.; Naredi, P.; Sund, M. Improved tumour marker sensitivity in detecting colorectal liver metastases by combined type IV collagen and CEA measurement. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 9839–9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, H.; Naredi, P.; Hafström, L.; Sund, M. Type IV collagen as a tumour marker for colorectal liver metastases. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Surg. Oncol. Br. Assoc. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 37, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, N.I.; Kehlet, S.; Boisen, M.K.; Liljefors, M.; Jensen, C.; Johansen, A.Z.; Johansen, J.S.; Erler, J.T.; Karsdal, M.; Mortensen, J.H.; et al. Prognostic value of blood-based fibrosis biomarkers in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy and bevacizumab. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Cai, J.; Zuo, Z.; Li, J. Collagen facilitates the colorectal cancer stemness and metastasis through an integrin/PI3K/AKT/Snail signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, S.C. Type I collagen inhibits differentiation and promotes a stem cell-like phenotype in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Stenling, R.; Rubio, C.; Lindblom, A. Colorectal carcinogenesis is associated with stromal expression of COL11A1 and COL5A2. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Salahshor, S.; Stenling, R.; Björk, J.; Lindmark, G.; Iselius, L.; Rubio, C.; Lindblom, A. COL11A1 in FAP polyps and in sporadic colorectal tumors. BMC Cancer 2001, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptman, N.; Boštjančič, E.; Žlajpah, M.; Ranković, B.; Zidar, N. Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals Most Prominent Gene Candidates to Distinguish Colorectal Adenoma from Adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9416515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Y. Integrated bioinformatics analysis of expression and gene regulation network of COL12A1 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4743–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.; Nielsen, S.H.; Mortensen, J.H.; Kjeldsen, J.; Klinge, L.G.; Krag, A.; Harling, H.; Jørgensen, L.N.; Karsdal, M.A.; Willumsen, N. Serum type XVI collagen is associated with colorectal cancer and ulcerative colitis indicating a pathological role in gastrointestinal disorders. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4619–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grässel, S.; Tan, E.M.; Timpl, R.; Chu, M.L. Collagen type XVI expression is modulated by basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta. FEBS Lett. 1998, 436, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, H.; Ito, N.; Tamura, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Inada, M.; Yabuuchi, I.; Imai, Y.; Nagashima, R.; Misawa, H.; Takeda, H.; et al. Circulating transforming growth factor beta 1 as a predictor of liver metastasis after resection in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Moilanen, J.M.; Kokkonen, N.; Löffek, S.; Väyrynen, J.P.; Syväniemi, E.; Hurskainen, T.; Mäkinen, M.; Klintrup, K.; Mäkelä, J.; Sormunen, R.; et al. Collagen XVII expression correlates with the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Lin, S.P.; Hsu, H.S.; Yang, S.H.; Lin, C.H.; Yang, M.H.; Hung, M.C.; Hung, S.C. Suspension survival mediated by PP2A-STAT3-Col XVII determines tumour initiation and metastasis in cancer stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K. Laminin-5 (laminin-332): Unique biological activity and role in tumor growth and invasion. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumailley, M. The laminin family. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Rodin, S.; Simonson, O.E.; Hollande, F. Laminins and cancer stem cells: Partners in crime? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 45, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Weeks, A.; Yuzhalin, A.E. Cancer Extracellular Matrix Proteins Regulate Tumour Immunity. Cancers 2020, 12, 3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Akimoto, S.; Moriya, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Kitajima, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Prognostic significance of laminin-5 gamma2 chain expression in colorectal carcinoma: Immunohistochemical analysis of 103 cases. Dis. Colon Rectum 2002, 45, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Shembrey, C.; Smith, J.; Paquet-Fifield, S.; Behrenbruch, C.; Beyit, L.M.; Thomson, B.N.J.; Heriot, A.G.; Cao, Y.; Hollande, F. Laminin 521 enhances self-renewal via STAT3 activation and promotes tumor progression in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 476, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinto, E.; Tsuda, H.; Ueno, H.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Hase, K.; Tamai, S.; Mochizuki, H.; Inazawa, J.; Matsubara, O. Prognostic implication of laminin-5 gamma 2 chain expression in the invasive front of colorectal cancers, disclosed by area-specific four-point tissue microarrays. Lab. Investig. J. Techn. Methods Pathol. 2005, 85, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Du, C.; Ji, D.; Xi, J.; Gu, J. Overexpression of LAMC2 predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients and promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2017, 39, 1010428317705849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukazawa, S.; Shinto, E.; Tsuda, H.; Ueno, H.; Shikina, A.; Kajiwara, Y.; Yamamoto, J.; Hase, K. Laminin β3 expression as a prognostic factor and a predictive marker of chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Lim, H.S.; Lin, H.L.; Tan, H.T.; Lim, T.K.; Cheong, W.K.; Cheah, P.Y.; Tang, C.L.; Chow, P.K.; Chung, M.C. Analysis of colorectal cancer glyco-secretome identifies laminin β-1 (LAMB1) as a potential serological biomarker for colorectal cancer. Proteomics 2015, 15, 3905–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatenko, V.V.; Maltseva, D.V.; Galatenko, A.V.; Rodin, S.; Tonevitsky, A.G. Cumulative prognostic power of laminin genes in colorectal cancer. BMC Med. Genomics 2018, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, W.J.; Kang, H.G.; Jang, J.H.; Choi, I.J.; Chun, K.H.; Kim, S.J. Upregulation of LAMB1 via ERK/c-Jun Axis Promotes Gastric Cancer Growth and Motility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, C.C.; Lazaris, A.C. Colorectal cancer and basement membranes: Clinicopathological correlations. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 580159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Oh, T.; Chung, H.; Rha, S.; Kim, C.; Moon, Y.; Hoehn, B.D.; Jeong, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.; et al. Identification of GABRA1 and LAMA2 as new DNA methylation markers in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.; Janson, C.; Seveus, L.; Miyazaki, K.; Virtanen, I.; Venge, P. Uncoordinated production of Laminin-5 chains in airways epithelium of allergic asthmatics. Respir Res. 2005, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivinus-Nebot, M.; Rousselle, P.; Breittmayer, J.P.; Cenciarini, C.; Berrih-Aknin, S.; Spong, S.; Nokelainen, P.; Cottrez, F.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Bernard, A. Mature human thymocytes migrate on laminin-5 with activation of metalloproteinase-14 and cleavage of CD44. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sime, W.; Lunderius-Andersson, C.; Enoksson, M.; Rousselle, P.; Tryggvason, K.; Nilsson, G.; Harvima, I.; Patarroyo, M. Human mast cells adhere to and migrate on epithelial and vascular basement membrane laminins LM-332 and LM-511 via alpha3beta1 integrin. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4657–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondimu, Z.; Geberhiwot, T.; Ingerpuu, S.; Juronen, E.; Xie, X.; Lindbom, L.; Doi, M.; Kortesmaa, J.; Thyboll, J.; Tryggvason, K.; et al. An endothelial laminin isoform, laminin 8 (α4β1γ1), is secreted by blood neutrophils, promotes neutrophil migration and extravasation, and protects neutrophils from apoptosis. Blood 2004, 104, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioce, V.; Castronovo, V.; Shmookler, B.M.; Garbisa, S.; Grigioni, W.F.; Liotta, L.A.; Sobel, M.E. Increased expression of the laminin receptor in human colon cancer. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 1991, 82, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.H.; Raufman, J.P.; Xie, G. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2014, 6, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.W.; Ko, Y.T.; Kim, N.K.; Chung, H.C.; Min, B.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, J.P.; Kim, H. A comparative study of protein expression in primary colorectal cancer and synchronous hepatic metastases: The significance of matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression as a predictor of liver metastasis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vočka, M.; Langer, D.; Fryba, V.; Petrtyl, J.; Hanus, T.; Kalousova, M.; Zima, T.; Petruzelka, L. Serum levels of TIMP-1 and MMP-7 as potential biomarkers in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2019, 34, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkiewicz, K.; Kozieł, P.; Bednarczyk, M.; Błażelonis, A.; Mazurek, U.; Muc-Wierzgoń, M. Expression of Migration-Related Genes in Human Colorectal Cancer and Activity of a Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 17. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8208904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, D.; Xiang, L.; Lv, M.; Tao, L.; Ni, T.; Deng, J.; Gu, X.; Masatara, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. TIMP-2 inhibits metastasis and predicts prognosis of colorectal cancer via regulating MMP-9. Cell Adh. Migration 2019, 13, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Oshima, T.; Yoshihara, K.; Tamura, S.; Kanazawa, A.; Inagaki, D.; Yamamoto, N.; Sato, T.; Fujii, S.; Numata, K.; et al. Overexpression of MMP-13 gene in colorectal cancer with liver metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2693–2699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benbow, U.; Schoenermark, M.P.; Mitchell, T.I.; Rutter, J.L.; Shimokawa, K.; Nagase, H.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. A novel host/tumor cell interaction activates matrix metalloproteinase 1 and mediates invasion through type I collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25371–25378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airola, K.; Karonen, T.; Vaalamo, M.; Lehti, K.; Lohi, J.; Kariniemi, A.L.; Keski-Oja, J.; Saarialho-Kere, U.K. Expression of collagenases-1 and -3 and their inhibitors TIMP-1 and -3 correlates with the level of invasion in malignant melanomas. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Ito, M.; Shiozawa, J.; Naito, S.; Kanematsu, T.; Sekine, I. Expression of the MMP-1 in human pancreatic carcinoma: Relationship with prognostic factor. Modern Pathol. Off. J. US Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc 1999, 12, 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori, Y.; Matsushima, M.; Minaguchi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Sagae, S.; Kudo, R.; Terakawa, N.; Nakamura, Y. Correlation between expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene in ovarian cancers and an insertion/deletion polymorphism in its promoter region. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4225–4227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, G.I.; Duncan, M.E.; O’Neil, P.; Melvin, W.T.; Fothergill, J.E. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczko, B.; Groblewska, M.; Okulczyk, B.; Kedra, B.; Szmitkowski, M. The diagnostic value of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) determination in the sera of colorectal adenoma and cancer patients. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2010, 25, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, K.; Mimori, K.; Iinuma, H.; Iwatsuki, M.; Yokobori, T.; Ishii, H.; Anai, H.; Kitano, S.; Mori, M. Serum matrix-metalloproteinase-1 is a bona fide prognostic marker for colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ii, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Adachi, Y.; Maruyama, Y.; Shinomura, Y. Role of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) in human cancer invasion, apoptosis, growth, and angiogenesis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 231, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskensalo, S.; Louhimo, J.; Nordling, S.; Hagström, J.; Haglund, C. MMP-7 as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2011, 32, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenskiöld, M.; Ivarsson, M.L.; Holmdahl, L.; Falk, P.; Kåbjörn-Gustafsson, C.; Angenete, E. Intestinal mucosal MMP-1-a prognostic factor in colon cancer. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, S.; Vacirca, J. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Meta. Rev. 2004, 23, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragutinović, V.V.; Radonjić, N.V.; Petronijević, N.D.; Tatić, S.B.; Dimitrijević, I.B.; Radovanović, N.S.; Krivokapić, Z.V. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and -9 (MMP-9) in preoperative serum as independent prognostic markers in patients with colorectal cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 355, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Estévez, O.; De Chiara, L.; Rodríguez-Girondo, M.; Rodríguez-Berrocal, F.J.; Cubiella, J.; Castro, I.; Hernández, V.; Martínez-Zorzano, V.S. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 in colorectal cancer family-risk population screening. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annaházi, A.; Ábrahám, S.; Farkas, K.; Rosztóczy, A.; Inczefi, O.; Földesi, I.; Szűcs, M.; Rutka, M.; Theodorou, V.; Eutamene, H.; et al. A pilot study on faecal MMP-9: A new noninvasive diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langers, A.M.; Verspaget, H.W.; Hawinkels, L.J.; Kubben, F.J.; van Duijn, W.; van der Reijden, J.J.; Hardwick, J.C.; Hommes, D.W.; Sier, C.F. MMP-2 and MMP-9 in normal mucosa are independently associated with outcome of colorectal cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Jung, A.; Dag, S.; Hlubek, F.; Kirchner, T. beta-catenin regulates the expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-7 in human colorectal cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, J.; Nadal, C.; Garcia-Albeniz, X.; Gallego, R.; Carcereny, E.; Almendro, V.; Mármol, M.; Gallardo, E.; Maria Augé, J.; Longarón, R.; et al. Serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 levels identifies poor prognosis advanced colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimori, K.; Yamashita, K.; Ohta, M.; Yoshinaga, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Ishii, H.; Utsunomiya, T.; Barnard, G.F.; Inoue, H.; Mori, M. Coexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor in colorectal cancer: An EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor is effective against MMP-7-expressing cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8243–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, X.T.; Lv, G.Y. Prognostic significance of MMP-7 expression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Yankui, L.; Jingjie, F.; Linfang, J.; Yong, P.; Dong, H.; Xiaowei, Q. The Expression and Significance of CXCR5 and MMP-13 in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 73, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.Y.; Chang, H.J.; Chung, F.Y.; Yang, M.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Lin, S.R. MMP13 is a potential prognostic marker for colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wernicke, A.K.; Churin, Y.; Sheridan, D.; Windhorst, A.; Tschuschner, A.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Roderfeld, M.; Roeb, E. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 refines pathological staging of precancerous colorectal lesions. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73552–73557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Cai, F.; Ding, Z.; Gao, L. MMP14 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 83, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Gao, J.; Rao, Z.; Shen, Q. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of α5β1-integrin and MMP-14 expressions in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma 2013, 60, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesanakurti, D.; Chetty, C.; Dinh, D.H.; Gujrati, M.; Rao, J.S. Role of MMP-2 in the regulation of IL-6/Stat3 survival signaling via interaction with α5β1 integrin in glioma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozevich, G.; Kozlova, N.; Cheglakov, I.; Ushakova, N.; Berman, A. Integrin alpha5beta1 controls invasion of human breast carcinoma cells by direct and indirect modulation of MMP-2 collagenase activity. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Sottile, J. MT1-MMP regulates the turnover and endocytosis of extracellular matrix fibronectin. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 4039–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Têtu, B.; Brisson, J.; Wang, C.S.; Lapointe, H.; Beaudry, G.; Blanchette, C.; Trudel, D. The influence of MMP-14, TIMP-2 and MMP-2 expression on breast cancer prognosis. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2006, 8, R28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yana, I.; Sagara, H.; Takaki, S.; Takatsu, K.; Nakamura, K.; Nakao, K.; Katsuki, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Aoki, T.; Sato, H.; et al. Crosstalk between neovessels and mural cells directs the site-specific expression of MT1-MMP to endothelial tip cells. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.Z.; Yao, H.; Staszewski, E.D.; Rockwood, K.F.; Markwart, S.M.; Fay, K.S.; Spalding, A.C.; Livant, D.L. alpha(5)beta(1) Integrin Ligand PHSRN Induces Invasion and alpha(5) mRNA in Endothelial Cells to Stimulate Angiogenesis. Transl. Oncol. 2009, 2, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.; Peng, Z.; Yin, J.; Yang, Z.; Shang, J. Expression of MMP-14 and prognosis in digestive system carcinoma: A meta-analysis and databases validation. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhou, X.; Liang, C.; Zheng, X.; Lei, P.; Fang, J.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; Qi, C.; Wei, H. Human colorectal cancer progression correlates with LOX-induced ECM stiffening. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, H.E.; Cox, T.R.; Erler, J.T. The rationale for targeting the LOX family in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, H.M.; Li, W. Lysyl oxidase: Properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of the cell. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 88, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.M.; Cox, T.R.; Bird, D.; Lang, G.; Murray, G.I.; Sun, X.F.; Southall, S.M.; Wilson, J.R.; Erler, J.T. The role of lysyl oxidase in SRC-dependent proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.M.; Bird, D.; Welti, J.C.; Gourlaouen, M.; Lang, G.; Murray, G.I.; Reynolds, A.R.; Cox, T.R.; Erler, J.T. Lysyl oxidase plays a critical role in endothelial cell stimulation to drive tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Liang, Z.; Mei, Z.; Wu, T.; Cui, A.; Liu, C.; Cui, L. Lysyl oxidase: A colorectal cancer biomarker of lung and hepatic metastasis. Thoracic Cancer 2018, 9, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiszar, K.; Fong, S.F.; Ujfalusi, A.; Krawetz, S.A.; Salvati, E.P.; Mackenzie, J.W.; Boyd, C.D. Somatic mutations of the lysyl oxidase gene on chromosome 5q23.1 in colorectal tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wu, C.; Mao, B.; Maruthi Prasad, E.; Wang, Y.; Chin, Y.E. LOXL1 modulates the malignant progression of colorectal cancer by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of YAP. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2020, 18, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.G.; Jo, S.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.K.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, H.; Park, J.H.; et al. Role of LOXL2 in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and colorectal cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80325–80335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1Wang, F.; Sun, G.; Peng, C.; Chen, J.; Quan, J.; Wu, C.; Lian, X.; Tang, W.; Xiang, D. ZEB1 promotes colorectal cancer cell invasion and disease progression by enhanced LOXL2 transcription. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 14, 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Hu, L.; Jiang, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bu, Y. Identification and characterization of the promoter of cancer-related gene LOXL2. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 387, 111786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Wang, G.; Shen, W.; Huang, Z.; He, H.; Cui, L. Lysyl oxidase-like 2 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer cells and promotes the development of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, J. Prognostic utility and clinical significance of lysyl oxidase-like 2 protein expression in digestive system cancers. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 20713–20720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, V.; Lazaris, A.; Mayer, T.Z.; Petrillo, S.K.; Alamri, H.; Rada, M.; Jarrouj, G.; Park, W.Y.; Gao, Z.H.; McDonald, P.P.; et al. Neutrophils expressing lysyl oxidase-like 4 protein are present in colorectal cancer liver metastases resistant to anti-angiogenic therapy. J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrlich, P.; Herrlich, A. ADAM Metalloprotease-Released Cancer Biomarkers. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Huo, L.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Expression of A disintegrin and metalloprotease 8 is associated with cell growth and poor survival in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Merritt, R.; Fu, L.; Pan, Z. Targeting calcium signaling in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sinica. B 2017, 7, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.L.; Park, S.Y.; Oh, H.H.; Chung, M.W.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Myung, D.S.; Cho, S.B.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, H.S.; et al. A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease 12 Promotes Tumor Progression by Inhibiting Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, H.; Han, F.; Zhang, H.; Xu, E. Methylation status of ADAM12 promoter are associated with its expression levels in colorectal cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 221, 153449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattern, J.; Roghi, C.S.; Hurtz, M.; Knauper, V.; Edwards, D.R.; Poghosyan, Z. ADAM15 mediates upregulation of Claudin-1 expression in breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutz, A.; Hartig, W.; Wobus, M.; Grosche, J.; Wittekind, C.; Aust, G. Expression of ADAM15 in lung carcinomas. Virchows. Arch. 2005, 446, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Sha, K.; Song, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X. The microRNA miR-3174 Suppresses the Expression of ADAM15 and Inhibits the Proliferation of Patient-Derived Bladder Cancer Cells. Onco. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 4157–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdelski, C.; Fitzner, M.; Hube-Magg, C.; Kluth, M.; Heumann, A.; Simon, R.; Krech, T.; Clauditz, T.; Buscheck, F.; Steurer, S.; et al. Overexpression of the A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase ADAM15 is linked to a Small but Highly Aggressive Subset of Prostate Cancers. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuefer, R.; Day, K.C.; Kleer, C.G.; Sabel, M.S.; Hofer, M.D.; Varambally, S.; Zorn, C.S.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rubin, M.A.; Day, M.L. ADAM15 disintegrin is associated with aggressive prostate and breast cancer disease. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, N.; Day, M.L. The role of the disintegrin metalloproteinase ADAM15 in prostate cancer progression. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 106, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.L.; Poghosyan, Z.; Pennington, C.J.; Scott, X.; Handsley, M.M.; Warn, A.; Gavrilovic, J.; Honert, K.; Kruger, A.; Span, P.N.; et al. Distinct functions of natural ADAM-15 cytoplasmic domain variants in human mammary carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B.; Deane, N.G.; No, Y.; Shiou, S.R.; Schmidt, C.; Neff, J.; Washington, M.K.; Beauchamp, R.D. Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toquet, C.; Colson, A.; Jarry, A.; Bezieau, S.; Volteau, C.; Boisseau, P.; Merlin, D.; Laboisse, C.L.; Mosnier, J.F. ADAM15 to α5β1 integrin switch in colon carcinoma cells: A late event in cancer progression associated with tumor dedifferentiation and poor prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, N.B.; Voskresensky, I.; Rogers, C.M.; Lafleur, B.; Dempsey, P.J.; Graves-Deal, R.; Revetta, F.; Foutch, A.C.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Washington, M.K.; et al. TACE/ADAM-17: A component of the epidermal growth factor receptor axis and a promising therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyula, J.N.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Doherty, J.; Fenning, C.S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Chemotherapy-induced activation of ADAM-17: A novel mechanism of drug resistance in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3378–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.D.; Zhao, C.H.; Ding, H.W.; Wu, Q.; Ren, T.S.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.Q.; Zhao, Q.C. A novel inhibitor of ADAM17 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to 5-Fluorouracil by reversing Notch and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in vivo. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ye, X.; Bhattacharya, R.; Boulbes, D.R.; Fan, F.; Xia, L.; Ellis, L.M. A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase Domain 17 Regulates Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells and Chemosensitivity Via Notch1 Signaling. Stem Cells Translat. Med. 2016, 5, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, G. Knockdown of ADAM17 inhibits cell proliferation and increases oxaliplatin sensitivity in HCT-8 colorectal cancer through EGFR-PI3K-AKT activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosch, J.; Ziemke, E.; Wan, S.; Luker, K.; Welling, T.; Hardiman, K.; Fearon, E.; Thomas, S.; Flynn, M.; Rios-Doria, J.; et al. Targeting ADAM17 inhibits human colorectal adenocarcinoma progression and tumor-initiating cell frequency. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65090–65099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Kyula, J.N.; Fenton, A.; Fenning, C.S.; Sasazuki, T.; Shirasawa, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Oncogenic Kras promotes chemotherapy-induced growth factor shedding via ADAM17. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Wang, X.; Gong, L.F.; Chen, W.J.; Hao, Z.; Feng, S.W.; Wu, Y.B.; Ye, T.; Cai, Y.K. Nox1 promotes colon cancer cell metastasis via activation of the ADAM17 pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4474–4481. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Chen, B.; Wu, J.; Jiang, C.; Fan, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xu, Y. Epigenetic Regulation of a Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM) Transcription in Colorectal Cancer Cells: Involvement of β-Catenin, BRG1, and KDM4. Front. Cell Develop. Biol. 2020, 8, 581692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.B.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, D. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose suppresses the migration and reverses the drug resistance of colon cancer cells through ADAM expression regulation. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2017, 28, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.B.; Kim, D. TLR4-mediated galectin-1 production triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells through ADAM10- and ADAM17-associated lactate production. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 425, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.B.; Kim, D. Insulin-like growth factor-1 activates different catalytic subunits p110 of PI3K in a cell-type-dependent manner to induce lipogenesis-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the regulation of ADAM10 and ADAM17. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 439, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitovic, D.; Berdiaki, A.; Spyridaki, I.; Krasanakis, T.; Tsatsakis, A.; Tzanakakis, G.N. Proteoglycans-Biomarkers and Targets in Cancer Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, W. SRGN Promotes Colorectal Cancer Metastasis as a Critical Downstream Target of HIF-1α. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 48, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpetinou, A.; Papachristou, D.J.; Lampropoulou, A.; Bouris, P.; Labropoulou, V.T.; Noulas, A.; Karamanos, N.K.; Theocharis, A.D. Increased Expression of Serglycin in Specific Carcinomas and Aggressive Cancer Cell Lines. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 690721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.T.; Guo, E.N.; Dong, B.G.; Chen, L.S. Prognostic and clinical significance of syndecan-1 in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zuo, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, R.; He, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhou, L.; Deng, T.; Wang, X.; et al. Shed Syndecan-1 is involved in chemotherapy resistance via the EGFR pathway in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Katakam, S.; Tria, V.; Sim, W.C.; Yip, G.W.; Molgora, S.; Karnavas, T.; Elghonaimy, E.A.; Pelucchi, P.; Piscitelli, E.; Ibrahim, S.A.; et al. The heparan sulfate proteoglycan syndecan-1 regulates colon cancer stem cell function via a focal adhesion kinase-Wnt signaling axis. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 486–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Cao, B.; Yang, H.; Jin, L.; Cui, M.; Mao, Y. Syndecan-1 suppresses cell growth and migration via blocking JAK1/STAT3 and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in human colorectal carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.; Yu, J.; Yan, X.; Ni, Q.; Zhi, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, B.; Zhu, J. Syndecan-2 in colorectal cancer plays oncogenic role via epithelial-mesenchymal transition and MAPK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, C.M.; Ricci, R.; Nader, H.B.; Toma, L. Syndecan-2 is upregulated in colorectal cancer cells through interactions with extracellular matrix produced by stromal fibroblasts. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.J.; Oh, H.I.; Seo, Y.Y.; Jeong, D.; Kim, C.; Kang, H.W.; Han, Y.D.; Chung, H.C.; Kim, N.K.; An, S. Feasibility of quantifying SDC2 methylation in stool DNA for early detection of colorectal cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.; Wen, J.; Fu, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, R.; Wu, S.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Stool DNA Test of Methylated Syndecan-2 for the Early Detection of Colorectal Neoplasia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2017, 26, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.D.; Oh, T.J.; Chung, T.H.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, Y.N.; An, S.; Kim, N.K. Early detection of colorectal cancer based on presence of methylated syndecan-2 (SDC2) in stool DNA. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, H.; Song, C.; Gong, Y.; Xing, X. Up-regulated biglycan expression correlates with the malignancy in human colorectal cancers. Clin. Exp. Med. 2012, 12, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Gu, X.; Ma, T.; Ye, H. Biglycan up-regulated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and promoted angiogenesis in colon cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Pohl, N.M.; Qian, Z.; Yang, G.R.; Gou, Y.; Guzman, G.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Iozzo, R.V.; Yang, W. Decorin-mediated inhibition of colorectal cancer growth and migration is associated with E-cadherin in vitro and in mice. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Yang, J.; Yue, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Fan, D.; Zhang, Q.; Buraschi, S.; Iozzo, R.V.; Bi, X. Decorin deficiency promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and colon cancer metastasis. Matrix Biol. 2021, 95, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwanska, A.; Litwin, M.; Nowak, D.; Baczynska, D.; Wegrowski, Y.; Maquart, F.X.; Malicka-Blaszkiewicz, M. Overexpression of lumican affects the migration of human colon cancer cells through up-regulation of gelsolin and filamentous actin reorganization. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 2312–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, M.; Boncela, J.; Perreau, C.; Karamanou, K.; Chatron-Colliet, A.; Proult, I.; Przygodzka, P.; Chakravarti, S.; Maquart, F.X.; Kowalska, M.A.; et al. Lumican Inhibits SNAIL-Induced Melanoma Cell Migration Specifically by Blocking MMP-14 Activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, M.; Belt, E.J.; Delis-van Diemen, P.M.; Carvalho, B.; Coupe, V.M.; Stockmann, H.B.; Bril, H.; Belien, J.A.; Fijneman, R.J.; Meijer, G.A. Lumican and versican are associated with good outcome in stage II and III colon cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 Suppl 3, S348–S359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, M.; Carvalho, B.; Delis-van Diemen, P.M.; van Alphen, C.; Belien, J.A.M.; Meijer, G.A.; Fijneman, R.J.A. Lumican and versican protein expression are associated with colorectal adenoma-to-carcinoma progression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpino, V.; Brock, M.; Gill, S.E. The role of TIMPs in regulation of extracellular matrix proteolysis. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44-46, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Lawler, J. The interaction of Thrombospondins with extracellular matrix proteins. J. Cell. Commun. Signal 2009, 3, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, A.A.; Adams, J.C. The evolution of thrombospondins and their ligand-binding activities. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, K.L.; Hankenson, K.; Veerisetty, A.C.; Bornstein, P.; Lawler, J.; Hecht, J.T. Skeletal abnormalities in mice lacking extracellular matrix proteins, thrombospondin-1, thrombospondin-3, thrombospondin-5, and type IX collagen. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.C.; Monk, R.; Taylor, A.L.; Ozbek, S.; Fascetti, N.; Baumgartner, S.; Engel, J. Characterisation of Drosophila thrombospondin defines an early origin of pentameric thrombospondins. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 328, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, Y.; Sakai, H. Thrombospondin-1 in urological cancer: Pathological role, clinical significance, and therapeutic prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12249–12272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenina-Adognravi, O.; Muppala, S.; Gajeton, J. Thrombospondins and remodeling of the tumor microenvironment. Vessel. Plus 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-P.; Wu, L.-W.; Chou, C.-Y. The anticancer potential of thrombospondin-1 by inhibiting angiogenesis and stroma reaction during cervical carcinogenesis. Gynecol. Minim. Invasive Ther. 2016, 5, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.H.; Bhang, D.; Zaslavsky, A.; Wang, L.C.; Vachani, A.; Kim, C.F.; Albelda, S.M.; Evan, G.I.; Ryeom, S. Thrombospondin-1 mediates oncogenic Ras-induced senescence in premalignant lung tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4375–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucera, C.; Porrello, A.; Antonello, Z.A.; Mekel, M.; Nehs, M.A.; Giordano, T.J.; Gerald, D.; Benjamin, L.E.; Priolo, C.; Puxeddu, E.; et al. B-Raf(V600E) and thrombospondin-1 promote thyroid cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10649–10654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, W.S.; Mizukami, Y.; Duerr, E.M.; Zukerberg, L.R.; Chung, D.C. Wnt signaling can repress thrombospondin-1 expression in colonic tumorigenesis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanaga, K.; Kato, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumura, M.; Amaya, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Chiba, Y.; Tanaka, K. Expression and role of thrombospondin-1 in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 3941–3948. [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Sipes, J.M.; Martin-Manso, G.; Westwood, B.; Morris, N.L.; Ghosh, A.; Emenaker, N.J.; Roberts, D.D. Dietary fat overcomes the protective activity of thrombospondin-1 signaling in the Apc(Min/+) model of colon cancer. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, C.D.; O’Byrne, K.; Goddard, J.C.; Marshall, L.J.; Jones, L.; Garcea, G.; Dennison, A.R.; Poston, G.; Lloyd, D.M.; Berry, D.P. Expression of thrombospondin-1 in resected colorectal liver metastases predicts poor prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6567–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, P.; Hultine, S.; Smith, L.M.; Dews, M.; Fox, J.L.; Biyashev, D.; Schelter, J.M.; Huang, Q.; Cleary, M.A.; Volpert, O.V.; et al. p53-responsive miR-194 inhibits thrombospondin-1 and promotes angiogenesis in colon cancers. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7490–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, T.; Nakamura, M.; Oshika, Y.; Abe, Y.; Ozeki, Y.; Fukushima, Y.; Hatanaka, H.; Sadahiro, S.; Kijima, H.; Tsuchida, T.; et al. Thrombospondin 2 expression is correlated with inhibition of angiogenesis and metastasis of colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Oshika, Y.; Fukushima, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Hatanaka, H.; Kijima, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Ueyama, Y.; Tamaoki, N.; Miura, S.; et al. Expression of angiostatic factors in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 1999, 15, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Gong, L.; Mou, Y.; Han, Y.; Zheng, S. MicroRNA203a3p is a candidate tumor suppressor that targets thrombospondin 2 in colorectal carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, I.W.; Sheu, M.J.; Li, C.F.; Lee, S.W.; Lin, L.C.; Lee, Y.E.; He, H.L. Low thrombospondin 2 expression is predictive of low tumor regression after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 2423–2432. [Google Scholar]
- Jubb, A.M.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Bai, W.; Holmgren, E.B.; Tobin, P.; Guerrero, A.S.; Kabbinavar, F.; Holden, S.N.; Novotny, W.F.; Frantz, G.D.; et al. Impact of vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression, thrombospondin-2 expression, and microvessel density on the treatment effect of bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla-Torre, C.A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Lee, C.H.; Joshua, A.M.; de Toledo, S.R.; Petrilli, A.S.; Andrade, J.A.; Chilton-MacNeill, S.; Zielenska, M.; Squire, J.A. Effects of THBS3, SPARC and SPP1 expression on biological behavior and survival in patients with osteosarcoma. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCart Reed, A.E.; Song, S.; Kutasovic, J.R.; Reid, L.E.; Valle, J.M.; Vargas, A.C.; Smart, C.E.; Simpson, P.T. Thrombospondin-4 expression is activated during the stromal response to invasive breast cancer. Virchows Arch. 2013, 463, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turashvili, G.; Bouchal, J.; Baumforth, K.; Wei, W.; Dziechciarkova, M.; Ehrmann, J.; Klein, J.; Fridman, E.; Skarda, J.; Srovnal, J.; et al. Novel markers for differentiation of lobular and ductal invasive breast carcinomas by laser microdissection and microarray analysis. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.; Gretschel, S.; Jons, T.; Yashiro, M.; Kemmner, W. THBS4, a novel stromal molecule of diffuse-type gastric adenocarcinomas, identified by transcriptome-wide expression profiling. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Yashiro, M.; Sera, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kushitani, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Kushiyama, S.; Nishimura, S.; Togano, S.; Okuno, T.; et al. The clinicopathological significance of Thrombospondin-4 expression in the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, D.; Ren, M.; Lu, G.; Zhang, X.; He, S.; Li, Y. THBS4 promotes HCC progression by regulating ITGB1 via FAK/PI3K/AKT pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 10668–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.Y.; Zeng, X.F.; Tang, D.; Deng, W.; Liu, H.F.; Xie, Y.K. Expression and prognostic significance of thrombospondin gene family in gastric cancer. J. Gastrointest Oncol. 2021, 12, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Zhao, J.; Qin, S.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhu, F.; Ou, Y.; et al. Over-expression of Thrombospondin 4 correlates with loss of miR-142 and contributes to migration and vascular invasion of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23277–23288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, T.; Chengedza, S.; Lightfoot, S.; Pan, Y.; Dedmond, D.; Cole, L.; Tang, Y.; Benbrook, D.M. Flexible heteroarotinoid (Flex-Het) SHetA2 inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Invest. New Drugs 2009, 27, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncati, L.; Barbolini, G.; Sartori, G.; Siopis, E.; Pusiol, T.; Maiorana, A. Loss of CDKN2A Promoter Methylation Coincides With the Epigenetic Transdifferentiation of Uterine Myosarcomatous Cells. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Gynecol. Pathol. 2016, 35, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncati, L.; Gasparri, P.; Gallo, G.; Bernardelli, G.; Zanelli, G.; Manenti, A. Appendix Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1226, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, S.A.; Chia, J.; Inglis, K.J.; Cozzi, S.J.; Ramsnes, I.; Buttenshaw, R.L.; Spring, K.J.; Boyle, G.M.; Worthley, D.L.; Leggett, B.A.; et al. Thrombospondin-4 is a putative tumour-suppressor gene in colorectal cancer that exhibits age-related methylation. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000113296-THBS4/pathology/colorectal+cancer/COAD (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Iozzo, R.V.; Theocharis, A.D.; Neill, T.; Karamanos, N.K. Complexity of matrix phenotypes. Matrix Biol. Plus 2020, 6–7, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.J.; Nedergaard, A.F.; Sun, S.; Veidal, S.S.; Larsen, L.; Zheng, Q.; Suetta, C.; Henriksen, K.; Christiansen, C.; Karsdal, M.A.; et al. The neo-epitope specific PRO-C3 ELISA measures true formation of type III collagen associated with liver and muscle parameters. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2013, 5, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Li, H.; Han, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Z.; Lv, B.; et al. Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell. Death Dis. 2020, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Tsai, M.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chu, P.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, Y.H. MIR29A Impedes Metastatic Behaviors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Targeting LOX, LOXL2, and VEGFA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deek, S.E.M.; Abdel-Ghany, S.M.; Hana, R.S.; Mohamed, A.A.R.; El-Melegy, N.T.; Sayed, A.A. Genetic polymorphism of lysyl oxidase, glutathione S-transferase M1, glutathione-S-transferase T1, and glutathione S-transferase P1 genes as risk factors for lung cancer in Egyptian patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4221–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, S.; Xie, J. miR-20b reduces 5-FU resistance by suppressing the ADAM9/EGFR signaling pathway in colon cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furini, S.; Falciani, C. Expression and Role of Heparan Sulfated Proteoglycans in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Hama, S.; Yamasaki, F.; Takayasu, T.; Nosaka, R.; Onishi, S.; Muragaki, Y.; Kawamata, T.; Kurisu, K. High Expression of Glypican-1 Predicts Dissemination and Poor Prognosis in Glioblastomas. World Neurosurg. 2017, 105, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charni, F.; Friand, V.; Haddad, O.; Hlawaty, H.; Martin, L.; Vassy, R.; Oudar, O.; Gattegno, L.; Charnaux, N.; Sutton, A. Syndecan-1 and syndecan-4 are involved in RANTES/CCL5-induced migration and invasion of human hepatoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Yang, S.; Park, H.; Choi, S.; Jung, K.C.; Lee, S.T.; Seong, J.K.; Han, I.O.; Oh, E.S. Syndecan-2 functions as a docking receptor for pro-matrix metalloproteinase-7 in human colon cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35692–35701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Kojima, S.; Sugawara, S.; Kato, M.; Okato, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Regulation of antitumor miR-144-5p targets oncogenes: Direct regulation of syndecan-3 and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongaarts, A.; de Jong, J.M.; Broekaart, D.W.M.; van Scheppingen, J.; Anink, J.J.; Mijnsbergen, C.; Jansen, F.E.; Spliet, W.G.M.; den Dunnen, W.F.A.; Gruber, V.E.; et al. Dysregulation of the MMP/TIMP Proteolytic System in Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytomas in Patients With Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Modulation of MMP by MicroRNA-320d In Vitro. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 79, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Function | Gene Name | Expression (Verse Normal Tissue/Cells) | Tumor Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen | Cell adhesion | COL1A1, COL3A2, COL4A3, COL4A6, PRO-C3, PRO-C6, C6M, C6Mα3, ColXIA1, COL12A1 | Upregulated | Tumor stroma, lung tumor, thyroid cancer, colorectal cancer, osteosarcoma, breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian cancer | [17,37,38,39,40,41,42,47,52,53,209] |
| Laminin | Tumor angiogenesis, cell infiltration, metastasis, drug resistance | LAMA2, Laminin β-1, Laminin γ2 | Upregulated | Colorectal cancer, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma | [60,63,65,210] |
| Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) | tumor invasion, progression, metastasis | MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, MMP-13, TIMP-1, TIMP-2 | Upregulated | Colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, breast cancer, lung tumor | [83,84,85,91,95,97] |
| Lysyl oxidase (LOX) | ECM remodeling, tumor growth | LOXL1, LOXL2, LOXL3 LOXL4 | Upregulated | Hepatocellular cancer, colorectal cancer, lung tumor | [211,212] |
| A disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) | Regulation of cytokines and growth factors, cell proliferation | ADAM-8, ADAM-10, ADAM-12, ADAM-15 | Upregulated: ADAM-8, ADAM-12, ADAM-15 (lung tumor, pancreatic cancer) Downregulated: ADAM-10, ADAM-15 (Colorectal cancer) | Colorectal cancer, lung tumor, pancreatic cancer | [129,133,142,144,145,148,151,152,213] |
| Proteoglycan (PG) | Enhancement of cell viability, cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, regulation of cytokine, cell adhesion and migration, angiogenesis | Serglycin, Glypican (GPC)-1, GPC-4, GPC-5, Syndecan (SDC)-1, SDC-2, SDC-3, SDC-4, HSPG2 | Upregulated: Serglycin, GPC-1, GPC-4, SDC-1 (Pancreatic cancer, breast cancer), SDC-2, SDC-3, HSPG2 Downregulated: SDC-1 (Colorectal cancer), SDC-4, GPC-5, | Nasopharyngeal cancer, glioblastoma, hepatocellular cancer, colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer | [155,160,161,214,215,216,217,218] |
| Thrombospondin (THBS) | Cell proliferation, carcinogenesis, fibroblast apoptosis, vascular homeostasis | THBS1, THBS2, THBS3, THBS4, THBS5 | Upregulated | Lung tumor, thyroid cancer, colorectal cancer, osteosarcoma, breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma | [176,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192,193,195,196,198,199,200,201,202,206] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-S.; Ha, S.-E.; Wu, M.; Zogg, H.; Ronkon, C.F.; Lee, M.-Y.; Ro, S. Extracellular Matrix Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179185
Kim M-S, Ha S-E, Wu M, Zogg H, Ronkon CF, Lee M-Y, Ro S. Extracellular Matrix Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179185
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Seob, Se-Eun Ha, Moxin Wu, Hannah Zogg, Charles F. Ronkon, Moon-Young Lee, and Seungil Ro. 2021. "Extracellular Matrix Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179185
APA StyleKim, M.-S., Ha, S.-E., Wu, M., Zogg, H., Ronkon, C. F., Lee, M.-Y., & Ro, S. (2021). Extracellular Matrix Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179185







