Adenosine and Inflammation: Here, There and Everywhere
Abstract
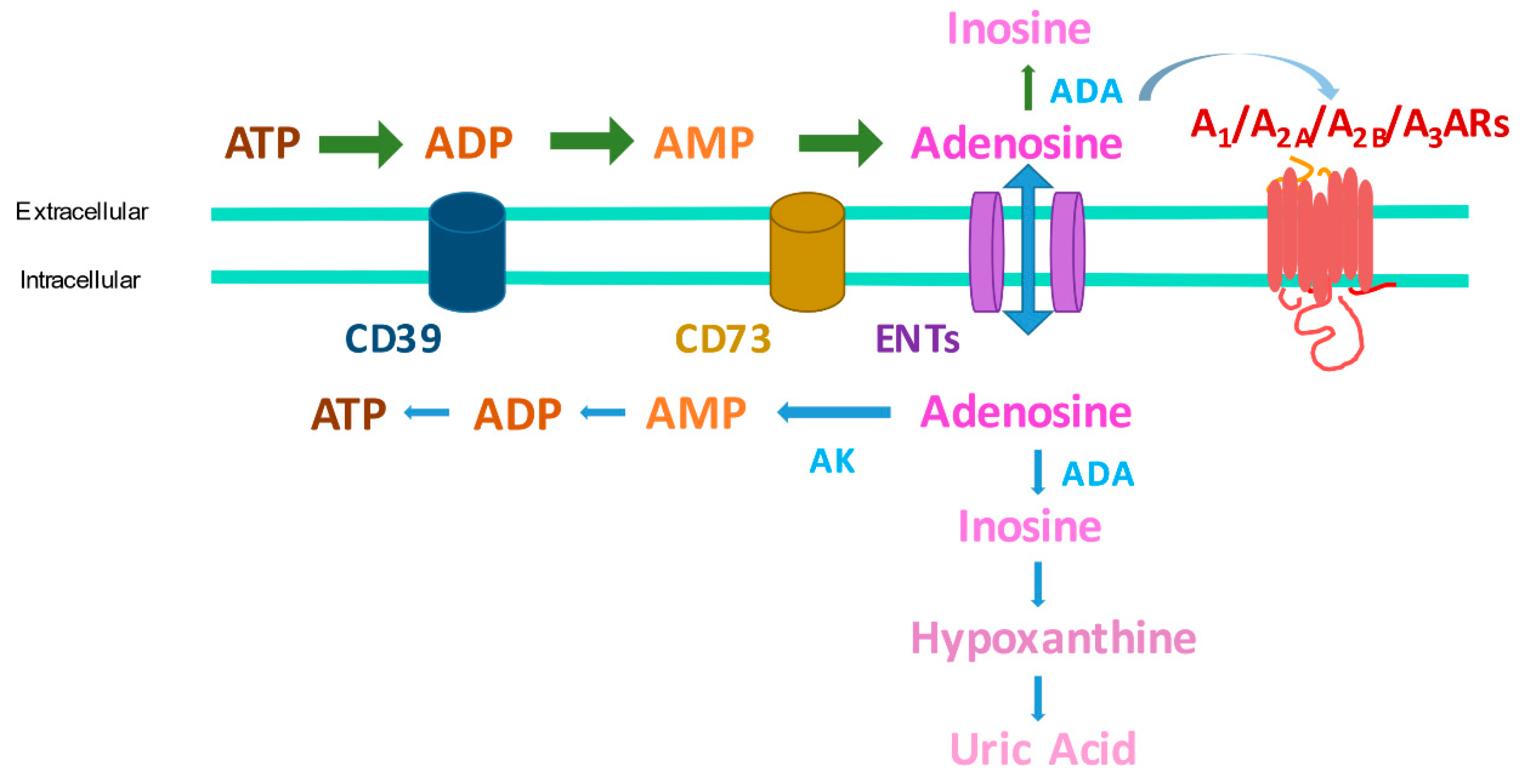
1. Introduction
2. Regulation of Immune Cells
3. Rheumatic Diseases and Osteoarthritis
4. Chronic Lung Diseases and Pulmonary Inflammation
5. Intestinal Inflammation
6. Neuroinflammation
7. Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Adenylate cyclase |
| ADA | Adenosine deaminase |
| ADP | Adenosine diphosphate |
| AMP | Adenosine monophosphate |
| ARs | Adenosine receptors |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CD39 | Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase |
| CD73 | Ecto-5′-nucleotidase |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| CXCL | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand |
| DNBS | Dinitrobenzenesulfonic acid |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| EAE | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| ENT | Equilibrative nucleoside transporter |
| GC | Germinal center |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| IBDs | Inflammatory bowel diseases |
| IDO-1 | Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase |
| IFN-γ | Interferon γ |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MIP | Macrophage inflammatory protein |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| PEMFs | Pulsed electromagnetic fields |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TGF-β | Tissue growth factor β |
| TNBS | 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Haskó, G. Adenosine Signaling and the Immune System: When a Lot Could Be Too Much. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 205, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskó, G.; Linden, J.; Cronstein, B.; Pacher, P. Adenosine Receptors: Therapeutic Aspects for Inflammatory and Immune Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: The State of the Art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pathological Overproduction: The Bad Side of Adenosine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Varani, K. Adenosine as a Multi-Signalling Guardian Angel in Human Diseases: When, Where and How Does It Exert Its Protective Effects? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine--a Physiological or Pathophysiological Agent? J. Mol. Med. Berl. Ger. 2014, 92, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Csóka, B.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Kókai, E.; Blandizzi, C.; Haskó, G. Adenosine and Inflammation: What’s New on the Horizon? Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, A.; Kronstein, R.; Wetzel, A.; Gerth, A.; Nieber, K.; Hauschildt, S. Regulation of Adenosine Receptor Subtypes during Cultivation of Human Monocytes: Role of Receptors in Preventing Lipopolysaccharide-Triggered Respiratory Burst. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, N.D.; Postow, M.; Danielsson, J.; Cronstein, B.N. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Prevents Desensitization of Gαs-Coupled Receptors by Regulating GRK2 Association with the Plasma Membrane. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, N.D.; Montesinos, M.C.; Reiss, A.B.; Delano, D.; Awadallah, N.; Cronstein, B.N. Inflammatory Cytokines Regulate Function and Expression of Adenosine A2A Receptors in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4026–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskó, G.; Pacher, P.; Deitch, E.A.; Vizi, E.S. Shaping of Monocyte and Macrophage Function by Adenosine Receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-S.; Chung, H.-J.; Lee, H.W.; Jeong, L.S.; Lee, S.K. Suppression of Inflammation Response by a Novel A3 Adenosine Receptor Agonist Thio-Cl-IB-MECA through Inhibition of Akt and NF-ΚB Signaling. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, A.; Sitkovsky, M. Role of G-Protein-Coupled Adenosine Receptors in Downregulation of Inflammation and Protection from Tissue Damage. Nature 2001, 414, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskó, G.; Csóka, B.; Németh, Z.H.; Vizi, E.S.; Pacher, P. A2B Adenosine Receptors in Immunity and Inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscsó, B.; Csóka, B.; Kókai, E.; Németh, Z.H.; Pacher, P.; Virág, L.; Leibovich, S.J.; Haskó, G. Adenosine Augments IL-10-Induced STAT3 Signaling in M2c Macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, Z.H.; Lutz, C.S.; Csóka, B.; Deitch, E.A.; Leibovich, S.J.; Gause, W.C.; Tone, M.; Pacher, P.; Vizi, E.S.; Haskó, G. Adenosine Augments IL-10 Production by Macrophages through an A2B Receptor-Mediated Posttranscriptional Mechanism. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 8260–8270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joós, G.; Jákim, J.; Kiss, B.; Szamosi, R.; Papp, T.; Felszeghy, S.; Sághy, T.; Nagy, G.; Szondy, Z. Involvement of Adenosine A3 Receptors in the Chemotactic Navigation of Macrophages towards Apoptotic Cells. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 183, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislat, G.; Lawrence, T. Autophagy in Dendritic Cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurr, M.; Toy, T.; Shin, A.; Hartmann, G.; Rothenfusser, S.; Soellner, J.; Davis, I.D.; Cebon, J.; Maraskovsky, E. Role of Adenosine Receptors in Regulating Chemotaxis and Cytokine Production of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. Blood 2004, 103, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Zuo, A.; Shao, H.; Chen, M.; Kaplan, H.J.; Sun, D. A2B Adenosine Receptor Activation Switches Differentiation of Bone Marrow Cells to a CD11c+Gr-1+ Dendritic Cell Subset That Promotes the Th17 Response. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2015, 3, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Kuchroo, V.K. Th17 Cells: From Precursors to Players in Inflammation and Infection. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, R.; Martinez-Navio, J.M.; Lejeune, M.; Climent, N.; Oliva, H.; Gatell, J.M.; Gallart, T.; Mallol, J.; Lluis, C.; Franco, R. CD26, Adenosine Deaminase, and Adenosine Receptors Mediate Costimulatory Signals in the Immunological Synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9583–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novitskiy, S.V.; Ryzhov, S.; Zaynagetdinov, R.; Goldstein, A.E.; Huang, Y.; Tikhomirov, O.Y.; Blackburn, M.R.; Biaggioni, I.; Carbone, D.P.; Feoktistov, I.; et al. Adenosine Receptors in Regulation of Dendritic Cell Differentiation and Function. Blood 2008, 112, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, L.; Olle, L.; Martin, M.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Muñoz-Cano, R. Adenosine Signaling in Mast Cells and Allergic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystel-Whittemore, M.; Dileepan, K.N.; Wood, J.G. Mast Cell: A Multi-Functional Master Cell. Front. Immunol. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.-G.; Jacobson, K.A. Purinergic Signaling in Mast Cell Degranulation and Asthma. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudich, N.; Dekel, O.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. Down-Regulation of the A3 Adenosine Receptor in Human Mast Cells Upregulates Mediators of Angiogenesis and Remodeling. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 65, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudich, N.; Ravid, K.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. Mast Cell Adenosine Receptors Function: A Focus on the A3 Adenosine Receptor and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, C. Neutrophil: A Cell with Many Roles in Inflammation or Several Cell Types? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, K.E.; Ley, K.; Mehrad, B. Regulation of Neutrophil Function by Adenosine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, D. Purinergic Regulation of Neutrophil Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riff, R.; Naamani, O.; Mazar, J.; Haviv, Y.S.; Chaimovitz, C.; Douvdevani, A. A1 and A2A Adenosine Receptors Play a Protective Role to Reduce Prevalence of Autoimmunity Following Tissue Damage. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yago, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Thompson, L.F.; McEver, R.P. Multi-Inhibitory Effects of A2A Adenosine Receptor Signaling on Neutrophil Adhesion Under Flow. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3880–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambelluca, M.S.; Pouliot, M. Early Tyrosine Phosphorylation Events Following Adenosine A2A Receptor in Human Neutrophils: Identification of Regulated Pathways. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasson, A.P.; Menezes, C.B.; Goelzer, G.K.; Gnoatto, S.C.B.; Garcia, S.C.; Tasca, T. Adenosine Reduces Reactive Oxygen Species and Interleukin-8 Production by Trichomonas Vaginalis-Stimulated Neutrophils. Purinergic Signal. 2017, 13, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriden, R.; Self, T.; Akong-Moore, K.; Nizet, V.; Kellam, B.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. Adenosine-A3 Receptors in Neutrophil Microdomains Promote the Formation of Bacteria-Tethering Cytonemes. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hoeven, D.; Wan, T.C.; Gizewski, E.T.; Kreckler, L.M.; Maas, J.E.; Van Orman, J.; Ravid, K.; Auchampach, J.A. A Role for the Low-Affinity A2B Adenosine Receptor in Regulating Superoxide Generation by Murine Neutrophils. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, J.; Cekic, C. Regulation of Lymphocyte Function by Adenosine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.K.; Silva, M.; Labuda, J.; Thayer, M.; Cain, D.W.; Philbrook, P.; Sethumadhavan, S.; Hatfield, S.; Ohta, A.; Sitkovsky, M. The GS Protein-Coupled A2a Adenosine Receptor Controls T Cell Help in the Germinal Center. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheta, M.; Painter, C.A.; Moore, F.E.; Lobbardi, R.; Bryll, A.; Freiman, E.; Stachura, D.; Rogers, A.B.; Houvras, Y.; Langenau, D.M.; et al. Identification and Characterization of T Reg–like Cells in Zebrafish. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 3519–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romio, M.; Reinbeck, B.; Bongardt, S.; Hüls, S.; Burghoff, S.; Schrader, J. Extracellular Purine Metabolism and Signaling of CD73-Derived Adenosine in Murine Treg and Teff Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C530–C539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, A.; Kini, R.; Ohta, A.; Subramanian, M.; Madasu, M.; Sitkovsky, M. The Development and Immunosuppressive Functions of CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells Are under Influence of the Adenosine-A2A Adenosine Receptor Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakowicz-Burkiewicz, M.; Kocbuch, K.; Grden, M.; Maciejewska, I.; Szutowicz, A.; Pawelczyk, T. Impact of adenosine receptors on immunoglobulin production by human peripheral blood b lymphocytes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Przybyła, T.; Sakowicz-Burkiewicz, M.; Pawełczyk, T. Purinergic Signalling in B Cells. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saze, Z.; Schuler, P.J.; Hong, C.-S.; Cheng, D.; Jackson, E.K.; Whiteside, T.L. Adenosine Production by Human B Cells and B Cell–Mediated Suppression of Activated T Cells. Blood 2013, 122, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronstein, B.N.; Sitkovsky, M. Adenosine and Adenosine Receptors in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; McCarey, D.W.; Capell, H.; McInnes, I.B. Explaining How “High-Grade” Systemic Inflammation Accelerates Vascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Circulation 2003, 108, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Padovan, M.; Govoni, M.; Vincenzi, F.; Trotta, F.; Borea, P.A. The Role of Adenosine Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 10, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borea, P.A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S. The A3 Adenosine Receptor: History and Perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 74–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, B.; Cronstein, B. Methotrexate Mechanism in Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 2019, 86, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovan, M.; Vincenzi, F.; Govoni, M.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Adenosine and Adenosine Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Massara, A.; Vincenzi, F.; Tosi, A.; Padovan, M.; Trotta, F.; Borea, P.A. Normalization of A2A and A3 Adenosine Receptor Up-Regulation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients by Treatment with Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha but Not Methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2880–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravani, A.; Vincenzi, F.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Padovan, M.; Pasquini, S.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Govoni, M.; Varani, K. Role and Function of A2A and A₃ Adenosine Receptors in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, K.; Padovan, M.; Vincenzi, F.; Targa, M.; Trotta, F.; Govoni, M.; Borea, P.A. A2A and A3 Adenosine Receptor Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Upregulation, Inverse Correlation with Disease Activity Score and Suppression of Inflammatory Cytokine and Metalloproteinase Release. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, J.L.G.; Passos, D.F.; Bernardes, V.M.; Leal, D.B.R. ATP and Adenosine: Role in the Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 214, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, F.; Padovan, M.; Targa, M.; Corciulo, C.; Giacuzzo, S.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Govoni, M.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. A(2A) Adenosine Receptors Are Differentially Modulated by Pharmacological Treatments in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Their Stimulation Ameliorates Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzon, E.; Esposito, E.; Impellizzeri, D.; DI Paola, R.; Melani, A.; Bramanti, P.; Pedata, F.; Cuzzocrea, S. CGS 21680, an Agonist of the Adenosine (A2A) Receptor, Reduces Progression of Murine Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flögel, U.; Burghoff, S.; van Lent, P.L.E.M.; Temme, S.; Galbarz, L.; Ding, Z.; El-Tayeb, A.; Huels, S.; Bönner, F.; Borg, N.; et al. Selective Activation of Adenosine A2A Receptors on Immune Cells by a CD73-Dependent Prodrug Suppresses Joint Inflammation in Experimental Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 146ra108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobak, P.; Charlebois, R.; Rejtar, P.; El Bikai, R.; Allard, B.; Stagg, J. CD73 Plays a Protective Role in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, C.; Ma, L.; Jiang, Y. High Frequencies of Activated B Cells and T Follicular Helper Cells Are Correlated with Disease Activity in Patients with New-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 174, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, C.; Ma, B.; Tian, J.; Baidoo, S.E.; Mao, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Tong, J.; Yang, M.; et al. Increased Frequency of Circulating Follicular Helper T Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 827480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiel, S.E.; Kalekar, L.A.; Zhang, N.; Blankespoor, T.W.; Robinson, L.J.; Mueller, D.L. Adenosine 2a Receptor Signals Block Autoimmune Arthritis by Inhibiting Pathogenic Germinal Center T Follicular Helper Cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharav, E.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Madi, L.; Silberman, D.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Halpren, M.; Ochaion, A.; Weinberger, A.; Fishman, P. Antiinflammatory Effect of A3 Adenosine Receptor Agonists in Murine Autoimmune Arthritis Models. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Barer, F.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Fishman, P. A₃ Adenosine Receptor Allosteric Modulator Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Effect: In Vivo Studies and Molecular Mechanism of Action. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 708746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochaion, A.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Cohen, S.; Amital, H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Joshi, B.V.; Gao, Z.G.; Barer, F.; Patoka, R.; Del Valle, L.; et al. The A3 Adenosine Receptor Agonist CF502 Inhibits the PI3K, PKB/Akt and NF-KappaB Signaling Pathway in Synoviocytes from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, M.H.; Strand, V.; Markovits, D.; Nahir, M.; Reitblat, T.; Molad, Y.; Rosner, I.; Rozenbaum, M.; Mader, R.; Adawi, M.; et al. Clinical Evidence for Utilization of the A3 Adenosine Receptor as a Target to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis: Data from a Phase II Clinical Trial. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fishman, P.; Cohen, S. The A3 Adenosine Receptor (A3AR): Therapeutic Target and Predictive Biological Marker in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2359–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, D.F.; Bernardes, V.M.; da Silva, J.L.G.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Leal, D.B.R. Adenosine Signaling and Adenosine Deaminase Regulation of Immune Responses: Impact on the Immunopathogenesis of HIV Infection. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine A1 Receptor Regulates Osteoclast Formation by Altering TRAF6/TAK1 Signaling. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramachi, J.; Kukita, A.; Li, Y.-J.; Ushijima, Y.; Ohkuma, H.; Wada, N.; Watanabe, T.; Nakamura, S.; Kukita, T. Adenosine Abolishes MTX-Induced Suppression of Osteoclastogenesis and Inflammatory Bone Destruction in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2011, 91, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, F.M.; Chitu, V.; Sloane, J.; Axelrod, M.; Fredholm, B.B.; Stanley, E.R.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine A1 Receptors (A1Rs) Play a Critical Role in Osteoclast Formation and Function. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.K.; El-Said, T.O.; Askar, H.Y.; ElKady, B.A. Performance of Serum Adenosine Deaminase in Measuring Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2019, 41, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinapamula, K.S.; Pemmaraju, S.V.L.N.; Bhattaram, S.K.; Bitla, A.R.; Manohar, S.M. Serum Adenosine Deaminase as Inflammatory Marker in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2015, 9, BC08–BC10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadbeigi, S.; Saghiri, R.; Ebrahimi-Rad, M.; Khatami, S.; Akhbari, H. Adenosine Deaminase Activity and HLA-DRB as Diagnostic Markers for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2019, 15, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Haskó, G. The Purinergic System as a Pharmacological Target for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 345–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Colucci, R.; La Motta, C.; Tuccori, M.; Awwad, O.; Da Settimo, F.; Blandizzi, C.; Fornai, M. Adenosine Deaminase in the Modulation of Immune System and Its Potential as a Novel Target for Treatment of Inflammatory Disorders. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corciulo, C.; Lendhey, M.; Wilder, T.; Schoen, H.; Cornelissen, A.S.; Chang, G.; Kennedy, O.D.; Cronstein, B.N. Endogenous Adenosine Maintains Cartilage Homeostasis and Exogenous Adenosine Inhibits Osteoarthritis Progression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Corciulo, C.; Arabagian, S.; Ulman, A.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine-Functionalized Biodegradable PLA-b-PEG Nanoparticles Ameliorate Osteoarthritis in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, B.; Corciulo, C.; Castro, C.M.; Cronstein, B.N. Adenosine A2A Receptor Signaling Promotes FoxO Associated Autophagy in Chondrocytes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Yehuda, S.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Del Valle, L.; Ochaion, A.; Cohen, S.; Patoka, R.; Zozulya, G.; Barer, F.; Atar, E.; Piña-Oviedo, S.; et al. Induction of an Antiinflammatory Effect and Prevention of Cartilage Damage in Rat Knee Osteoarthritis by CF101 Treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Liang, B.T.; Jacobson, K.A. Pharmacological and Therapeutic Effects of A3 Adenosine Receptor Agonists. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, M.; Pagani, S.; Giavaresi, G.; De Mattei, M.; Ongaro, A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Massari, L.; Cadossi, M. Functional Tissue Engineering in Articular Cartilage Repair: Is There a Role for Electromagnetic Biophysical Stimulation? Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; De Mattei, M.; Vincenzi, F.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Pellati, A.; Ongaro, A.; Caruso, A.; Cadossi, R.; Borea, P.A. Characterization of Adenosine Receptors in Bovine Chondrocytes and Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Exposed to Low Frequency Low Energy Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields. Osteoarth. Cartil. 2008, 16, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattei, M.; Varani, K.; Masieri, F.F.; Pellati, A.; Ongaro, A.; Fini, M.; Cadossi, R.; Vincenzi, F.; Borea, P.A.; Caruso, A. Adenosine Analogs and Electromagnetic Fields Inhibit Prostaglandin E2 Release in Bovine Synovial Fibroblasts. Osteoarth. Cartil. 2009, 17, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzi, F.; Targa, M.; Corciulo, C.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Setti, S.; Cadossi, R.; Goldring, M.B.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Increased the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of A₂A and A₃ Adenosine Receptors in Human T/C-28a2 Chondrocytes and HFOB 1.19 Osteoblasts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Schneider, D.J.; Blackburn, M.R. Adenosine Signaling and the Regulation of Chronic Lung Disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Asthma and COPD. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-T.T.; Berg, N.K.; Harting, M.T.; Li, X.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Yuan, X. Purinergic Signaling in Pulmonary Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver, A.G.; Kukoly, C.A.; Ali, S.; Mustafa, S.J. Adenosine in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid in Asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huszár, E.; Vass, G.; Vizi, E.; Csoma, Z.; Barát, E.; Molnár Világos, G.; Herjavecz, I.; Horváth, I. Adenosine in Exhaled Breath Condensate in Healthy Volunteers and in Patients with Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esther, C.R.; Lazaar, A.L.; Bordonali, E.; Qaqish, B.; Boucher, R.C. Elevated Airway Purines in COPD. Chest 2011, 140, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh Patidar, B.; Meena, A.; Kumar, M.; Menon, B.; Rohil, V.; Kumar Bansal, S. Adenosine Metabolism in COPD: A Study on Adenosine Levels, 5’-Nucleotidase, Adenosine Deaminase and Its Isoenzymes Activity in Serum, Lymphocytes and Erythrocytes. COPD 2018, 15, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, M.R. Too Much of a Good Thing: Adenosine Overload in Adenosine-Deaminase-Deficient Mice. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 24, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Blackburn, M.R.; Lee, C.G.; Homer, R.J.; Liu, W.; Flavell, R.A.; Boyden, L.; Lifton, R.P.; Sun, C.-X.; Young, H.W.; et al. Adenosine Metabolism and Murine Strain-Specific IL-4-Induced Inflammation, Emphysema, and Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polosa, R.; Blackburn, M.R. Adenosine Receptors as Targets for Therapeutic Intervention in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polosa, R. Adenosine-Receptor Subtypes: Their Relevance to Adenosine-Mediated Responses in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.J.; Lindsay, J.C.; Zhou, Y.; Molina, J.G.; Blackburn, M.R. Adenosine and Osteopontin Contribute to the Development of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Zhong, H.; Acero, L.; Weng, T.; Melicoff, E.; West, J.D.; Hemnes, A.; Grenz, A.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Blackwell, T.S.; et al. The A2B Adenosine Receptor Modulates Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2012, 26, 2546–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaynagetdinov, R.; Ryzhov, S.; Goldstein, A.E.; Yin, H.; Novitskiy, S.V.; Goleniewska, K.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Newcomb, D.C.; Mitchell, D.; Morschl, E.; et al. Attenuation of Chronic Pulmonary Inflammation in A2B Adenosine Receptor Knockout Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 42, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Philip, K.; Acero, L.F.; Chen, N.-Y.; Weng, T.; Molina, J.G.; Luo, F.; Davies, J.; Le, N.-B.; Bunge, I.; et al. Deletion of ADORA2B from Myeloid Cells Dampens Lung Fibrosis and Pulmonary Hypertension. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2015, 29, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Chunn, J.L.; Volmer, J.B.; Fozard, J.R.; Blackburn, M.R. Adenosine-Mediated Mast Cell Degranulation in Adenosine Deaminase-Deficient Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 298, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Chunn, J.L.; Young, H.W.; Banerjee, S.K.; Colasurdo, G.N.; Blackburn, M.R. Adenosine-Dependent Airway Inflammation and Hyperresponsiveness in Partially Adenosine Deaminase-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4676–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-X.; Zhong, H.; Mohsenin, A.; Morschl, E.; Chunn, J.L.; Molina, J.G.; Belardinelli, L.; Zeng, D.; Blackburn, M.R. Role of A2B Adenosine Receptor Signaling in Adenosine-Dependent Pulmonary Inflammation and Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.W.J.; Molina, J.G.; Dimina, D.; Zhong, H.; Jacobson, M.; Chan, L.-N.L.; Chan, T.-S.; Lee, J.J.; Blackburn, M.R. A3 Adenosine Receptor Signaling Contributes to Airway Inflammation and Mucus Production in Adenosine Deaminase-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.-X.; Young, H.W.; Molina, J.G.; Volmer, J.B.; Schnermann, J.; Blackburn, M.R. A Protective Role for the A1 Adenosine Receptor in Adenosine-Dependent Pulmonary Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsenin, A.; Mi, T.; Xia, Y.; Kellems, R.E.; Chen, J.-F.; Blackburn, M.R. Genetic Removal of the A2A Adenosine Receptor Enhances Pulmonary Inflammation, Mucin Production, and Angiogenesis in Adenosine Deaminase-Deficient Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L753–L761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varani, K.; Caramori, G.; Vincenzi, F.; Adcock, I.; Casolari, P.; Leung, E.; MacLennan, S.; Gessi, S.; Morello, S.; Barnes, P.J.; et al. Alteration of Adenosine Receptors in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Caramori, G.; Vincenzi, F.; Tosi, A.; Barczyk, A.; Contoli, M.; Casolari, P.; Triggiani, M.; Hansel, T.; Leung, E.; et al. Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress Selectively Altered A(2B) Adenosine Receptors in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckle, T.; Grenz, A.; Laucher, S.; Eltzschig, H.K. A2B Adenosine Receptor Signaling Attenuates Acute Lung Injury by Enhancing Alveolar Fluid Clearance in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3301–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckle, T.; Hughes, K.; Ehrentraut, H.; Brodsky, K.S.; Rosenberger, P.; Choi, D.-S.; Ravid, K.; Weng, T.; Xia, Y.; Blackburn, M.R.; et al. Crosstalk between the Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter ENT2 and Alveolar Adora2b Adenosine Receptors Dampens Acute Lung Injury. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2013, 27, 3078–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konrad, F.M.; Neudeck, G.; Vollmer, I.; Ngamsri, K.C.; Thiel, M.; Reutershan, J. Protective Effects of Pentoxifylline in Pulmonary Inflammation Are Adenosine Receptor A2A Dependent. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2013, 27, 3524–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkesson, H.G.; Kuzenko, S.R.; Lipson, D.A.; Matthay, M.A.; Simmons, M.A. The Adenosine 2A Receptor Agonist GW328267C Improves Lung Function after Acute Lung Injury in Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L259–L271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegl, S.; Brodsky, K.S.; Blackburn, M.R.; Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Zwissler, B.; Eltzschig, H.K. Alveolar Epithelial A2B Adenosine Receptors in Pulmonary Protection during Acute Lung Injury. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konrad, F.M.; Meichssner, N.; Bury, A.; Ngamsri, K.-C.; Reutershan, J. Inhibition of SDF-1 Receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 Attenuates Acute Pulmonary Inflammation via the Adenosine A2B-Receptor on Blood Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, J.N.; Gorshkov, B.; Varn, M.N.; Zemskova, M.A.; Zemskov, E.A.; Sridhar, S.; Lucas, R.; Verin, A.D. Protective Effect of Adenosine Receptors against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L497–L507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, F.M.; Zwergel, C.; Ngamsri, K.-C.; Reutershan, J. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Heme Oxygenase-1 Depend on Adenosine A2A- and A2B-Receptor Signaling in Acute Pulmonary Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Di Paola, R.; Esposito, E.; Mazzon, E.; Paterniti, I.; Melani, A.; Bramanti, P.; Pedata, F.; Cuzzocrea, S. CGS 21680, an Agonist of the Adenosine (A2A) Receptor, Decreases Acute Lung Inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamsri, K.-C.; Wagner, R.; Vollmer, I.; Stark, S.; Reutershan, J. Adenosine Receptor A1 Regulates Polymorphonuclear Cell Trafficking and Microvascular Permeability in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lung Injury. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4374–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulloy, D.P.; Sharma, A.K.; Fernandez, L.G.; Zhao, Y.; Lau, C.L.; Kron, I.L.; Laubach, V.E. Adenosine A3 Receptor Activation Attenuates Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 95, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschl, E.; Molina, J.G.; Volmer, J.B.; Mohsenin, A.; Pero, R.S.; Hong, J.-S.; Kheradmand, F.; Lee, J.J.; Blackburn, M.R. A3 Adenosine Receptor Signaling Influences Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, C.; Caracciolo, M.; Correale, P.; Macheda, S.; Vadalà, E.G.; La Scala, S.; Tescione, M.; Danieli, R.; Ferrarelli, A.; Tarsitano, M.G.; et al. Can Adenosine Fight COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Ben, D.; Antonioli, L.; Lambertucci, C.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Volpini, R. Purinergic Ligands as Potential Therapeutic Tools for the Treatment of Inflammation-Related Intestinal Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, M.S.; Moss, A.; Jiang, Z.G.; Robson, S.C. Purinergic Signaling during Intestinal Inflammation. J. Mol. Med. Berl. Ger. 2017, 95, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odashima, M.; Bamias, G.; Rivera-Nieves, J.; Linden, J.; Nast, C.C.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Marini, M.; Sugawara, K.; Kozaiwa, K.; Otaka, M.; et al. Activation of A2A Adenosine Receptor Attenuates Intestinal Inflammation in Animal Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Ghisu, N.; Blandizzi, C.; Del Tacca, M. A2a Receptors Mediate Inhibitory Effects of Adenosine on Colonic Motility in the Presence of Experimental Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Awwad, O.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Del Tacca, M.; Blandizzi, C. Differential Recruitment of High Affinity A1 and A2A Adenosine Receptors in the Control of Colonic Neuromuscular Function in Experimental Colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; El-Tayeb, A.; Pellegrini, C.; Fornai, M.; Awwad, O.; Giustarini, G.; Natale, G.; Ryskalin, L.; Németh, Z.H.; Müller, C.E.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Novel Locally Acting A2A Receptor Agonist in a Rat Model of Oxazolone-Induced Colitis. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, M.; Wiznerowicz, E.B.; Lappas, C.M.; Linden, J.; Worthington, M.T.; Ernst, P.B. Cutting Edge: Critical Role for A2A Adenosine Receptors in the T Cell-Mediated Regulation of Colitis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2765–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimian, R.; Fakhfouri, G.; Daneshmand, A.; Mohammadi, H.; Bahremand, A.; Rasouli, M.R.; Mousavizadeh, K.; Dehpour, A.R. Adenosine A2A Receptors and Uric Acid Mediate Protective Effects of Inosine against TNBS-Induced Colitis in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, I.C.; Castro, M.V.; Barreto, A.R.F.; Sullivan, G.W.; Vale, M.; Almeida, P.R.C.; Linden, J.; Rieger, J.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; Guerrant, R.L.; et al. Effect of Novel A2A Adenosine Receptor Agonist ATL 313 on Clostridium Difficile Toxin A-Induced Murine Ileal Enteritis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallio, G.; Bitto, A.; Pizzino, G.; Galfo, F.; Irrera, N.; Squadrito, F.; Squadrito, G.; Pallio, S.; Anastasi, G.P.; Cutroneo, G.; et al. Adenosine Receptor Stimulation by Polydeoxyribonucleotide Improves Tissue Repair and Symptomology in Experimental Colitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.; Abdel-Aziz, H.; Weiser, D.; Müller, C.E.; Kelber, O.; Nieber, K. Adenosine A2A Receptor Contributes to the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of the Fixed Herbal Combination STW 5 (Iberogast®) in Rat Small Intestinal Preparations. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolachala, V.; Ruble, B.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Wang, L.; Mwangi, S.; Figler, H.; Figler, R.; Srinivasan, S.; Gewirtz, A.; Linden, J.; et al. Blockade of Adenosine A2B Receptors Ameliorates Murine Colitis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolachala, V.L.; Vijay–Kumar, M.; Dalmasso, G.; Yang, D.; Linden, J.; Wang, L.; Gewirtz, A.; Ravid, K.; Merlin, D.; Sitaraman, S.V. A2B Adenosine Receptor Gene Deletion Attenuates Murine Colitis. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Fan, J.; Chen, Y.-X.; Wang, J.-H. Inhibition of A2B Adenosine Receptor Attenuates Intestinal Injury in a Rat Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 1562973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, J.-S.; MacManus, C.F.; Scully, M.; Glover, L.E.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Colgan, S.P. Contribution of Adenosine A2B Receptors to Inflammatory Parameters of Experimental Colitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4957–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Del Tacca, M.; Blandizzi, C. Pharmacological Modulation of Adenosine System: Novel Options for Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabley, J.; Soriano, F.; Pacher, P.; Haskó, G.; Marton, A.; Wallace, R.; Salzman, A.; Szabó, C. The Adenosine A3 Receptor Agonist, N6-(3-Iodobenzyl)-Adenosine-5′-N-Methyluronamide, Is Protective in Two Murine Models of Colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 466, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.; Yu, J.G.; Suntres, Z.; Bozarov, A.; Cooke, H.; Javed, N.; Auer, H.; Palatini, J.; Hassanain, H.H.; Cardounel, A.J.; et al. ADOA3R as a Therapeutic Target in Experimental Colitis: Proof by Validated High-Density Oligonucleotide Microarray Analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 766–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Tian, T.; Feng, X.; Ye, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, W.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Zeng, J.; et al. An Adenosine A3 Receptor Agonist Inhibits DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice through Modulation of the NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.H.; Lv, M.M.; An, X.M.; Leung, W.K.; Seto, W.-K. Activation of Adenosine A3 Receptor Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Colonic Mucosa of Patients with Ulcerative Colitis by Down-Regulating the Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Signaling. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.B.; Lee, G.; Grimm, G.R.; Barrett, T.A. Therapeutic Benefit of Pentostatin in Severe IL-10−/− Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, B.; Rieder, F.; Albrich, S.; Firestein, G.S.; Boyle, D.; Hartmann, G.; Endres, S.; Eigler, A. Adenosine Kinase Inhibitor GP515 Improves Experimental Colitis in Mice by Inhibition of TH1 Cytokine Synthesis. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, A578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Ghisu, N.; Da Settimo, F.; Natale, G.; Kastsiuchenka, O.; Duranti, E.; Virdis, A.; Vassalle, C.; et al. Inhibition of Adenosine Deaminase Attenuates Inflammation in Experimental Colitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Awwad, O.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Da Settimo, F.; La Motta, C.; Natale, G.; Duranti, E.; et al. The Blockade of Adenosine Deaminase Ameliorates Chronic Experimental Colitis through the Recruitment of Adenosine A2A and A3 Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Motta, C.; Sartini, S.; Mugnaini, L.; Salerno, S.; Simorini, F.; Taliani, S.; Marini, A.M.; Da Settimo, F.; Lavecchia, A.; Novellino, E.; et al. Exploiting the Pyrazolo[3,4-d]Pyrimidin-4-One Ring System as a Useful Template To Obtain Potent Adenosine Deaminase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Brown, M.A. Innate Immunity in the Central Nervous System. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiSabato, D.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The Devil Is in the Details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derecki, N.C.; Cardani, A.N.; Yang, C.H.; Quinnies, K.M.; Crihfield, A.; Lynch, K.R.; Kipnis, J. Regulation of Learning and Memory by Meningeal Immunity: A Key Role for IL-4. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, D.P.; Stevens, B. Phagocytic Glial Cells: Sculpting Synaptic Circuits in the Developing Nervous System. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.-H. Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders: The Roles of Microglia and Astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. An Introduction to the Roles of Purinergic Signalling in Neurodegeneration, Neuroprotection and Neuroregeneration. Neuropharmacology 2016, 104, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troubat, R.; Barone, P.; Leman, S.; Desmidt, T.; Cressant, A.; Atanasova, B.; Brizard, B.; El Hage, W.; Surget, A.; Belzung, C.; et al. Neuroinflammation and Depression: A Review. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, S.; Pearlman, D.M.; Alper, K.; Najjar, A.; Devinsky, O. Neuroinflammation and Psychiatric Illness. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí Navia, A.; Dal Ben, D.; Lambertucci, C.; Spinaci, A.; Volpini, R.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Coelho, J.E.; Lopes, L.V.; Marucci, G.; Buccioni, M. Adenosine Receptors as Neuroinflammation Modulators: Role of A1 Agonists and A2A Antagonists. Cells 2020, 9, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedata, F.; Pugliese, A.M.; Coppi, E.; Dettori, I.; Maraula, G.; Cellai, L.; Melani, A. Adenosine A 2A Receptors Modulate Acute Injury and Neuroinflammation in Brain Ischemia. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppi, E.; Dettori, I.; Cherchi, F.; Bulli, I.; Venturini, M.; Lana, D.; Giovannini, M.G.; Pedata, F.; Pugliese, A.M. A2B Adenosine Receptors: When Outsiders May Become an Attractive Target to Treat Brain Ischemia or Demyelination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, S.A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E.; Campolo, M.; Niehoff, M.L.; Doyle, T.M.; Salvemini, D. Adenosine A3 Receptor as a Novel Therapeutic Target to Reduce Secondary Events and Improve Neurocognitive Functions Following Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boison, D.; Chen, J.-F.; Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine Signalling and Function in Glial Cells. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, A.G.; Orr, A.L.; Li, X.-J.; Gross, R.E.; Traynelis, S.F. Adenosine A(2A) Receptor Mediates Microglial Process Retraction. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghetti, L.; Greco, A.; Potenza, R.L.; Pezzola, A.; Blum, D.; Bantubungi, K.; Popoli, P. Effects of the Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonist SCH 58621 on Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression, Glial Activation, and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Availability in a Rat Model of Striatal Neurodegeneration. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 66, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Aguinaga, D.; Lillo, A.; Jiménez, J.; Raïch, I.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Canela, E.I.; Sánchez de Medina, V.; et al. Potentiation of Cannabinoid Signaling in Microglia by Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists. Glia 2019, 67, 2410–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, M.; Zinni, M.; Pansiot, J.; Cassanello, M.; Mairesse, J.; Ramenghi, L.; Baud, O. Modulation of Microglial Activation by Adenosine A2a Receptor in Animal Models of Perinatal Brain Injury. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebola, N.; Simões, A.P.; Canas, P.M.; Tomé, A.R.; Andrade, G.M.; Barry, C.E.; Agostinho, P.M.; Lynch, M.A.; Cunha, R.A. Adenosine A2A Receptors Control Neuroinflammation and Consequent Hippocampal Neuronal Dysfunction. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, L.; Guida, F.; Imperatore, R.; Napolitano, F.; Gatta, L.; Cristino, L.; Giordano, C.; Siniscalco, D.; Di Marzo, V.; Bellini, G.; et al. The A1 Adenosine Receptor as a New Player in Microglia Physiology. Glia 2014, 62, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marucci, G.; Ben, D.D.; Lambertucci, C.; Navia, A.M.; Spinaci, A.; Volpini, R.; Buccioni, M. Combined Therapy of A1AR Agonists and A2AAR Antagonists in Neuroinflammation. Molecules 2021, 26, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselkorn, M.L.; Shellington, D.K.; Jackson, E.K.; Vagni, V.A.; Janesko-Feldman, K.; Dubey, R.K.; Gillespie, D.G.; Cheng, D.; Bell, M.J.; Jenkins, L.W.; et al. Adenosine A1 Receptor Activation as a Brake on the Microglial Response after Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, R.; Tabata, M.; Maruhama, K.; Iida, S. A3 Adenosine Receptor Agonist Attenuates Neuropathic Pain by Suppressing Activation of Microglia and Convergence of Nociceptive Inputs in the Spinal Dorsal Horn. Exp. Brain Res. 2018, 236, 3203–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Silva, J.; Aires, I.D.; Boia, R.; Ambrósio, A.F.; Santiago, A.R. Activation of Adenosine A3 Receptor Inhibits Microglia Reactivity Elicited by Elevated Pressure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, X.; Deng, P.; Wang, D.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Belguise, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; et al. Activation of Adenosine A3 Receptor Reduces Early Brain Injury by Alleviating Neuroinflammation after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Elderly Rats. Aging 2020, 13, 694–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Bencivenni, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K.; Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S. A2B Adenosine Receptors Stimulate IL-6 Production in Primary Murine Microglia through P38 MAPK Kinase Pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, S.; Poloni, T.E.; Terrazzan, A.; Moretti, E.; Gessi, S.; Ferrari, D. Alzheimer and Purinergic Signaling: Just a Matter of Inflammation? Cells 2021, 10, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, S.; Poloni, T.E.; Pelloni, L.; Pasquini, S.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S. An Open Question: Is the A2A Adenosine Receptor a Novel Target for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment? Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 652455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A.M.; Fathalla, A.M.; Moustafa, A.A. Adenosine Role in Brain Functions: Pathophysiological Influence on Parkinson’s Disease and Other Brain Disorders. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazario, L.R.; da Silva, R.S.; Bonan, C.D. Targeting Adenosine Signaling in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pharmacological to Non-Pharmacological Approaches. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarzadeh, E.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Motallebnezhad, M.; Yousefi, M. The Role of Adenosine and Adenosine Receptors in the Immunopathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. Al 2016, 65, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślak, M.; Kukulski, F.; Komoszyński, M. Emerging Role of Extracellular Nucleotides and Adenosine in Multiple Sclerosis. Purinergic Signal. 2011, 7, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Blum, D.; Chern, Y.; Domenici, M.R.; Buée, L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Rea, W.; Ferré, S.; Popoli, P. The Role of Adenosine Tone and Adenosine Receptors in Huntington’s Disease. J. Caffeine Adenosine Res. 2018, 8, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, F.; Corciulo, C.; Targa, M.; Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Casetta, I.; Gentile, M.; Granieri, E.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Multiple Sclerosis Lymphocytes Upregulate A2A Adenosine Receptors That Are Antiinflammatory When Stimulated. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merighi, S.; Battistello, E.; Casetta, I.; Gragnaniello, D.; Poloni, T.E.; Medici, V.; Cirrincione, A.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Borea, P.A.; et al. Upregulation of Cortical A2A Adenosine Receptors Is Reflected in Platelets of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. JAD 2021, 80, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casetta, I.; Vincenzi, F.; Bencivelli, D.; Corciulo, C.; Gentile, M.; Granieri, E.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. A(2A) Adenosine Receptors and Parkinson’s Disease Severity. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Tosi, A.; Gessi, S.; Casetta, I.; Granieri, G.; Fazio, P.; Leung, E.; MacLennan, S.; Granieri, E.; et al. A2A Adenosine Receptor Overexpression and Functionality, as Well as TNF-Alpha Levels, Correlate with Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Bachoud-Lévi, A.-C.; Mariotti, C.; Tarditi, A.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Gasperi, V.; Borea, P.A.; Dolbeau, G.; Gellera, C.; Solari, A.; et al. Biological Abnormalities of Peripheral A(2A) Receptors in a Large Representation of Polyglutamine Disorders and Huntington’s Disease Stages. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 27, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Cannella, M.; Cislaghi, G.; Giallonardo, P.; Mariotti, C.; Cattabriga, E.; Cattabeni, F.; Borea, P.A.; Squitieri, F.; et al. Aberrant A2A Receptor Function in Peripheral Blood Cells in Huntington’s Disease. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2003, 17, 2148–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, C.S.; Farooqi, N.; O’Brien, K.; Gran, B. Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a Model for Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsui, S.; Schnermann, J.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Henry, S.; Yong, V.W.; Winston, B.W.; Warren, K.; Power, C. A1 Adenosine Receptor Upregulation and Activation Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Demyelination in a Model of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.-Q.; Li, Z.-Z.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.-W.; Augusto, E.; He, J.-C.; Wang, X.-T.; Chen, J.-F.; Zheng, R.-Y. Genetic Inactivation of the Adenosine A(2A) Receptor Exacerbates Brain Damage in Mice with Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingwersen, J.; Wingerath, B.; Graf, J.; Lepka, K.; Hofrichter, M.; Schröter, F.; Wedekind, F.; Bauer, A.; Schrader, J.; Hartung, H.-P.; et al. Dual Roles of the Adenosine A2a Receptor in Autoimmune Neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.H.; Thompson, L.F.; Mueller, C.; Waickman, A.T.; Jalkanen, S.; Niemela, J.; Airas, L.; Bynoe, M.S. CD73 Is Required for Efficient Entry of Lymphocytes into the Central Nervous System during Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9325–9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.H.; Kim, D.-G.; Krenz, A.; Chen, J.-F.; Bynoe, M.S. A2A Adenosine Receptor Signaling in Lymphocytes and the Central Nervous System Regulates Inflammation during Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5713–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Zheng, L.-P.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Yin, W.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-S.; Hou, S.-T.; Chen, J.-F.; et al. The Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonist SCH58261 Reduces Macrophage/Microglia Activation and Protects against Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Mice. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 129, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Alahiri, M.; Ulloa, B.; Xie, B.; Sadiq, S.A. Adenosine A2A Receptor Agonist Ameliorates EAE and Correlates with Th1 Cytokine-Induced Blood Brain Barrier Dysfunction via Suppression of MLCK Signaling Pathway. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2018, 6, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loram, L.C.; Strand, K.A.; Taylor, F.R.; Sloane, E.; Van Dam, A.-M.; Rieger, J.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Adenosine 2A Receptor Agonism: A Single Intrathecal Administration Attenuates Motor Paralysis in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalopathy in Rats. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2015, 46, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strakhova, R.; Cadassou, O.; Cros-Perrial, E.; Jordheim, L.P. Regulation of Tumor Infiltrated Innate Immune Cells by Adenosine. Purinergic Signal. 2020, 16, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.A.; Amir, E. HYPE or HOPE: The Prognostic Value of Infiltrating Immune Cells in Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. Adenosine as an Endogenous Immunoregulator in Cancer Pathogenesis: Where to Go? Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliagas, E.; Vidal, A.; Texidó, L.; Ponce, J.; Condom, E.; Martín-Satué, M. High Expression of Ecto-Nucleotidases CD39 and CD73 in Human Endometrial Tumors. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 509027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastid, J.; Regairaz, A.; Bonnefoy, N.; Déjou, C.; Giustiniani, J.; Laheurte, C.; Cochaud, S.; Laprevotte, E.; Funck-Brentano, E.; Hemon, P.; et al. Inhibition of CD39 Enzymatic Function at the Surface of Tumor Cells Alleviates Their Immunosuppressive Activity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.-Y.; Ni, X.-C.; Yi, Y.; He, H.-W.; Wang, J.-X.; Fu, Y.-P.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Jin, J.-J.; et al. Overexpression of CD39 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is an Independent Indicator of Poor Outcome after Radical Resection. Medicine 2016, 95, e4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, I.; Vigano, S.; Faouzi, M.; Treilleux, I.; Michielin, O.; Ménétrier-Caux, C.; Caux, C.; Romero, P.; de Leval, L. CD73 Expression and Clinical Significance in Human Metastatic Melanoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26659–26669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengler, V.L.; Galbraith, M.; Espinosa, J.M. Transcriptional Regulation by Hypoxia Inducible Factors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizume, S.; Miyagi, Y. Diverse Mechanisms of Sp1-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation Potentially Involved in the Adaptive Response of Cancer Cells to Oxygen-Deficient Conditions. Cancers 2015, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, E.; Jung, D.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, G.-C.; Jun, D.Y.; Lee, J.; Jung, B.; Kirchner, V.A.; Hwang, S.; Song, G.-W.; et al. Protective Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α-Dependent CD39 and CD73 in Fulminant Acute Liver Failure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 314, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poth, J.M.; Brodsky, K.; Ehrentraut, H.; Grenz, A.; Eltzschig, H.K. Transcriptional Control of Adenosine Signaling by Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factors during Ischemic or Inflammatory Disease. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, F.P.; Ramello, M.C.; Núñez, N.; Furlan, C.L.A.; Bossio, S.N.; Serrán, M.G.; Boari, J.T.; del Castillo, A.; Ledesma, M.; Sedlik, C.; et al. CD39 Expression Defines Cell Exhaustion in Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnotta, S.M.; Laudanna, C.; Pancione, M.; Sabatino, L.; Votino, C.; Remo, A.; Cerulo, L.; Zoppoli, P.; Manfrin, E.; Colantuoni, V.; et al. Ensemble of Gene Signatures Identifies Novel Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer Activated through PPARγ and TNFα Signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhov, S.V.; Pickup, M.W.; Chytil, A.; Gorska, A.E.; Zhang, Q.; Owens, P.; Feoktistov, I.; Moses, H.L.; Novitskiy, S.V. Role of TGFβ Signaling in Generation of CD39+CD73+ Myeloid Cells in Tumors. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3155–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigano, S.; Alatzoglou, D.; Irving, M.; Ménétrier-Caux, C.; Caux, C.; Romero, P.; Coukos, G. Targeting Adenosine in Cancer Immunotherapy to Enhance T-Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroumov, D.; Fekete-Drimusz, N.; Saborowski, M.; Kühnel, F.; Woller, N. CD4 and CD8 T Lymphocyte Interplay in Controlling Tumor Growth. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 689–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskó, G.; Pacher, P. Regulation of Macrophage Function by Adenosine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, C.J.; Pinhal-Enfield, G.; Elson, G.; Cronstein, B.N.; Hasko, G.; Outram, S.; Leibovich, S.J. The Adenosine-Dependent Angiogenic Switch of Macrophages to an M2-like Phenotype Is Independent of Interleukin-4 Receptor Alpha (IL4Rα) Signaling. Inflammation 2013, 36, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velot, E.; Haas, B.; Léonard, F.; Ernens, I.; Rolland-Turner, M.; Schwartz, C.; Longrois, D.; Devaux, Y.; Wagner, D.R. Activation of the Adenosine-A3 Receptor Stimulates Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Secretion by Macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 80, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csóka, B.; Selmeczy, Z.; Koscsó, B.; Németh, Z.H.; Pacher, P.; Murray, P.J.; Kepka-Lenhart, D.; Morris, S.M.; Gause, W.C.; Leibovich, S.J.; et al. Adenosine Promotes Alternative Macrophage Activation via A2A and A2B Receptors. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Saxena, S.; Awaji, M.; Singh, R.K. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in Cancer: Going Pro. Cancers 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenich, D.S.; de Souza, P.O.; Omizzollo, N.; Lenz, G.S.; Sevigny, J.; Braganhol, E. Neutrophils: Fast and Furious—The Nucleotide Pathway. Purinergic Signal. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColl, S.R.; St-Onge, M.; Dussault, A.-A.; Laflamme, C.; Bouchard, L.; Boulanger, J.; Pouliot, M. Immunomodulatory Impact of the A2A Adenosine Receptor on the Profile of Chemokines Produced by Neutrophils. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2006, 20, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S.; Cattabriga, E.; Iannotta, V.; Leung, E.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A. A3 Adenosine Receptors in Human Neutrophils and Promyelocytic HL60 Cells: A Pharmacological and Biochemical Study. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Ngiow, S.F.; Gao, Y.; Patch, A.-M.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Messaoudene, M.; Lin, G.; Coudert, J.D.; Stannard, K.A.; Zitvogel, L.; et al. A2AR Adenosine Signaling Suppresses Natural Killer Cell Maturation in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, S.Y.; Yang, Y.; Record, J.; Ma, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Tobin, N.P.; Blake, E.; Seitz, C.; Thomas, R.; et al. CD73 Immune Checkpoint Defines Regulatory NK Cells within the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzalczany, Y.; Akiva, E.; Klein, O.; Merimsky, O.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. Mast Cells Are Directly Activated by Contact with Cancer Cells by a Mechanism Involving Autocrine Formation of Adenosine and Autocrine/Paracrine Signaling of the Adenosine A3 Receptor. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzalczany, Y.; Merimsky, O.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. Mast Cells Are Directly Activated by Cancer Cell–Derived Extracellular Vesicles by a CD73- and Adenosine-Dependent Mechanism. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coillard, A.; Segura, E. In Vivo Differentiation of Human Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, B.; Allard, D.; Buisseret, L.; Stagg, J. The Adenosine Pathway in Immuno-Oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediavilla-Varela, M.; Luddy, K.; Noyes, D.; Khalil, F.K.; Neuger, A.M.; Soliman, H.; Antonia, S.J. Antagonism of Adenosine A2A Receptor Expressed by Lung Adenocarcinoma Tumor Cells and Cancer Associated Fibroblasts Inhibits Their Growth. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavis, P.A.; Divisekera, U.; Paget, C.; Chow, M.T.; John, L.B.; Devaud, C.; Dwyer, K.; Stagg, J.; Smyth, M.J.; Darcy, P.K. Blockade of A2A Receptors Potently Suppresses the Metastasis of CD73+ Tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14711–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, D.; Sinha, D.; Barkauskas, D.; Young, A.; Kalimutho, M.; Stannard, K.; Caramia, F.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Stagg, J.; Khanna, K.K.; et al. Adenosine 2B Receptor Expression on Cancer Cells Promotes Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4372–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannone, R.; Miele, L.; Maiolino, P.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. Blockade of A2b Adenosine Receptor Reduces Tumor Growth and Immune Suppression Mediated by Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in a Mouse Model of Melanoma. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekic, C.; Sag, D.; Li, Y.; Theodorescu, D.; Strieter, R.M.; Linden, J. Adenosine A2B Receptor Blockade Slows Growth of Bladder and Breast Tumors. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, C.; Miele, L.; Porta, A.; Pinto, A.; Morello, S. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Contribute to A2B Adenosine Receptor-Induced VEGF Production and Angiogenesis in a Mouse Melanoma Model. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27478–27489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | Pharmacological Behavior | Condition | Phase | Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regadenoson | A2AAR agonist | Lung Transplantation | 1 | NCT03072589 |
| Regadenoson | A2AAR agonist | Lung Transplantation | 1 | NCT04521569 |
| Regadenoson | A2AAR agonist | Gliomas | 1 | NCT03971734 |
| Regadenoson | A2AAR agonist | COVID-19 | 1/2 | NCT04606069 |
| Regadenoson | A2AAR agonist | Heart Transplant | 4 | NCT03102125 |
| Ciforadenant | A2AAR antagonist | Incurable Cancers | 1 | NCT02655822 |
| Ciforadenant | A2AAR antagonist | Multiple Myeloma | 1 | NCT04280328 |
| Ciforadenant | A2AAR antagonist | Advanced Cancers | 1 | NCT03454451 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Metastatic Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer | 1b/2 | NCT04381832 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Head and Neck Cancers | 1 | NCT04892875 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | 2 | NCT04791839 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | 2 | NCT04262856 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Advanced Cancers | 1 | NCT03629756 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Lung Cancer | 1 | NCT03846310 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer or Gynecologic Malignancies | 1 | NCT03719326 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Colorectal Cancer | 1/2 | NCT04660812 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Prostate Cancer | 2 | NCT03821246 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma | 1/2 | NCT03193190 |
| Etrumadenant (AB928) | A2A and A2B AR antagonist | Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | 1/2 | NCT03555149 |
| PBF-1129 | A2BAR antagonist | Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | 1 | NCT03274479 |
| Namodenoson (CF102) | A3AR agonist | Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis | 2 | NCT04697810 |
| Piclidenoson (IB-MECA) | A3AR agonist | COVID-19 | 2 | NCT04333472 |
| CF101 (IB-MECA) | A3AR agonist | Plaque Psoriasis | 3 | NCT03168256 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasquini, S.; Contri, C.; Borea, P.A.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Adenosine and Inflammation: Here, There and Everywhere. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147685
Pasquini S, Contri C, Borea PA, Vincenzi F, Varani K. Adenosine and Inflammation: Here, There and Everywhere. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(14):7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147685
Chicago/Turabian StylePasquini, Silvia, Chiara Contri, Pier Andrea Borea, Fabrizio Vincenzi, and Katia Varani. 2021. "Adenosine and Inflammation: Here, There and Everywhere" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 14: 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147685
APA StylePasquini, S., Contri, C., Borea, P. A., Vincenzi, F., & Varani, K. (2021). Adenosine and Inflammation: Here, There and Everywhere. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147685









