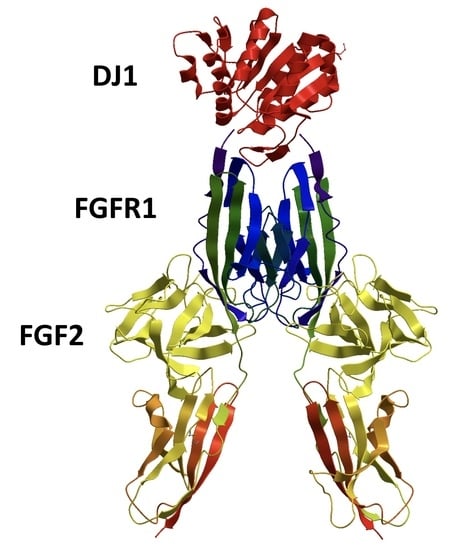
DJ-1 Can Replace FGF-2 for Long-Term Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Defined Media and Feeder-Free Condition
Abstract
1. Introduction
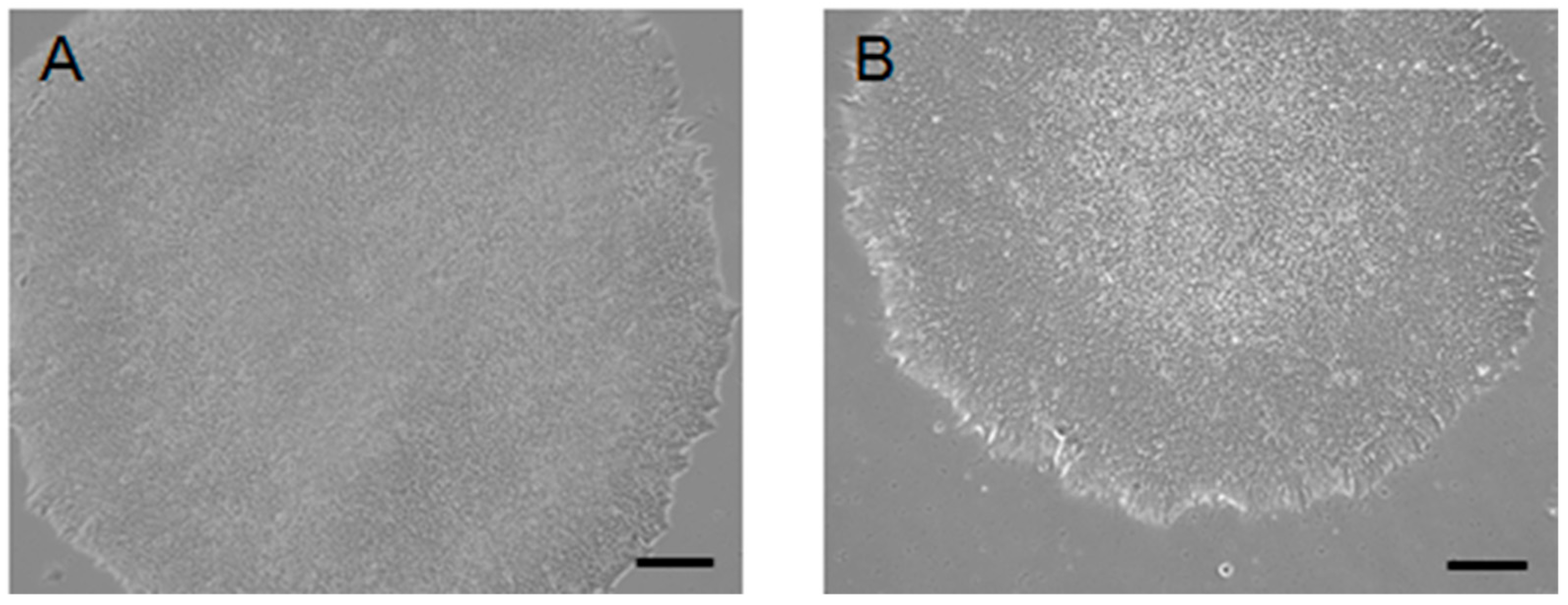
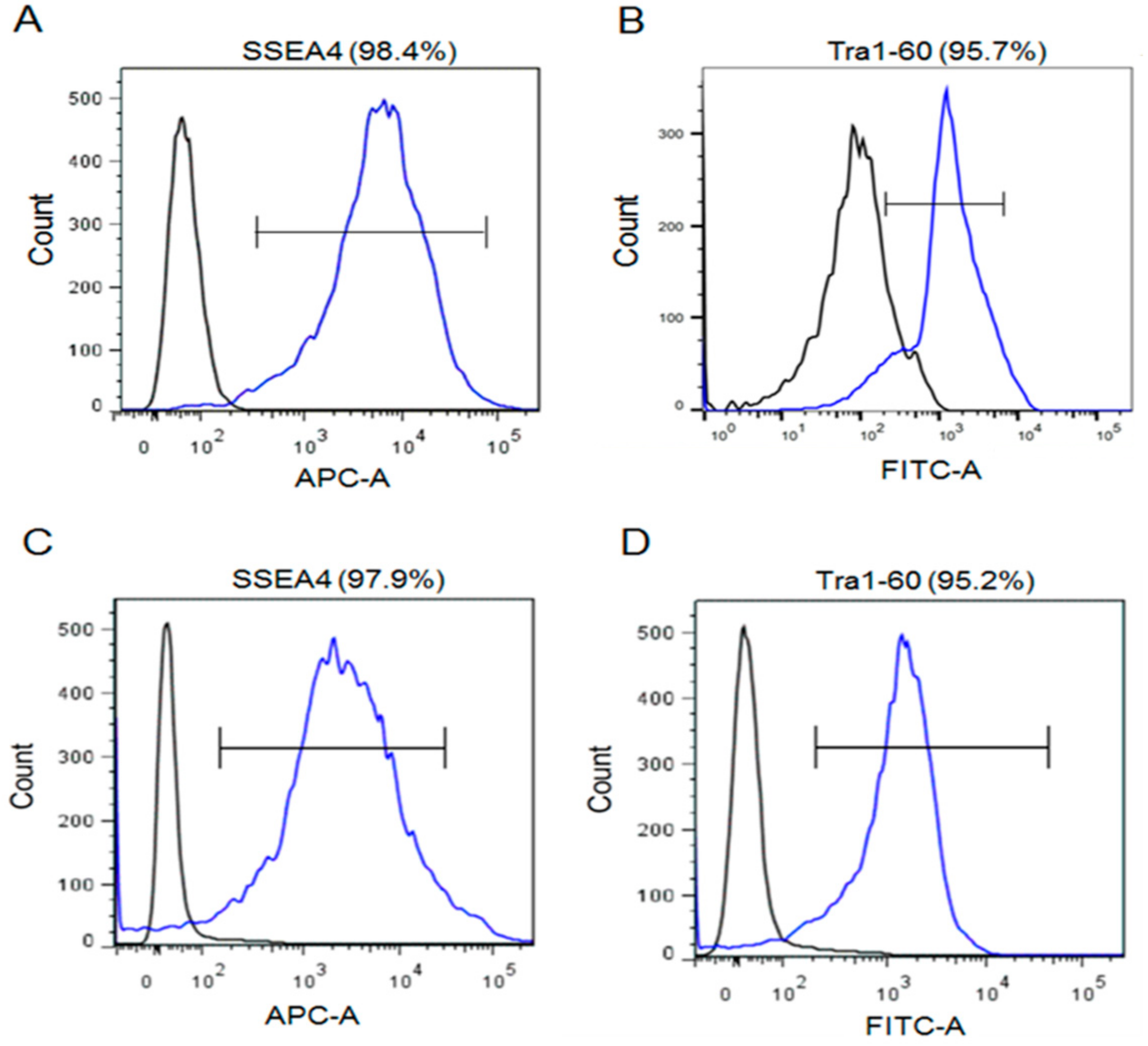
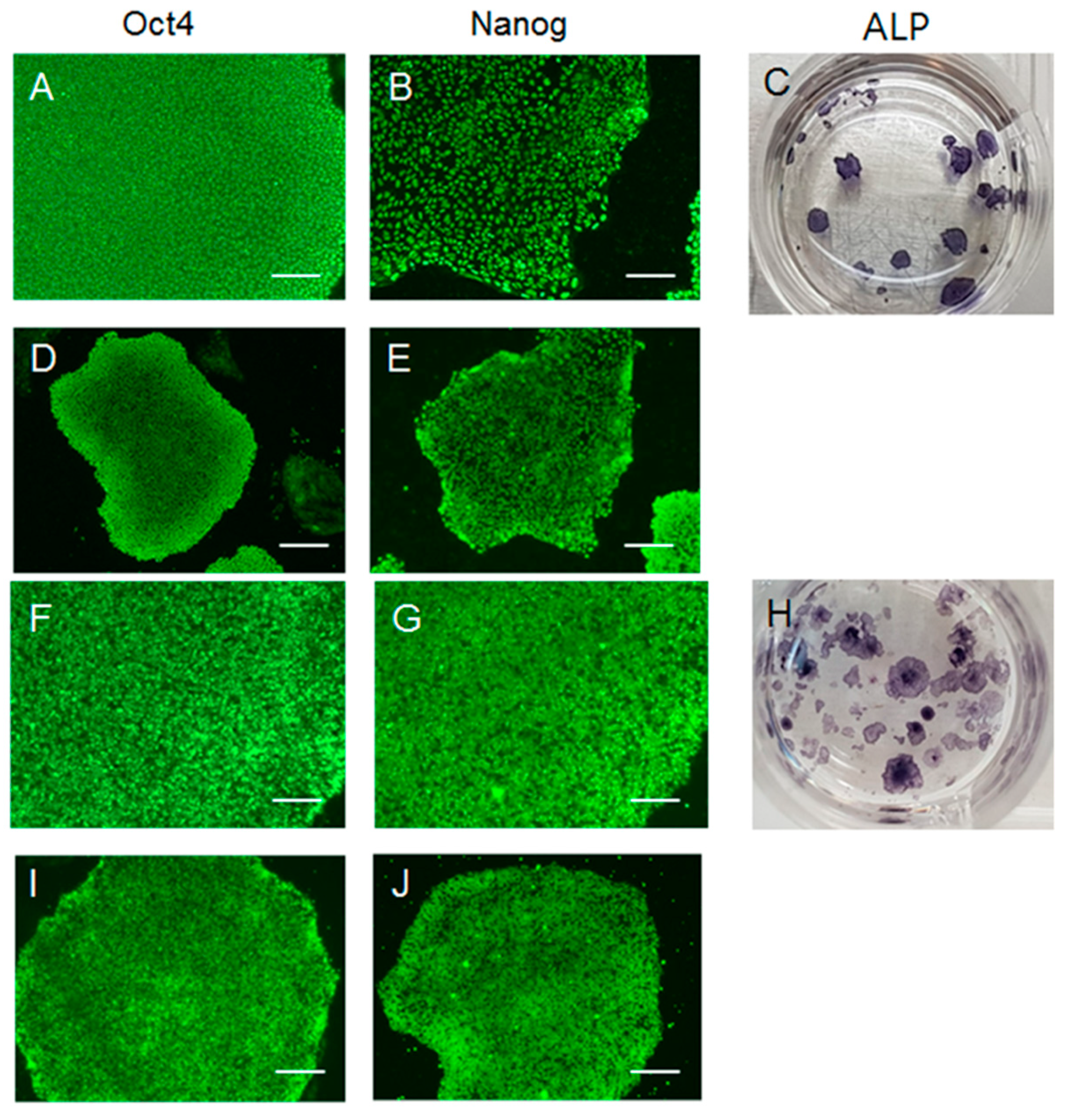
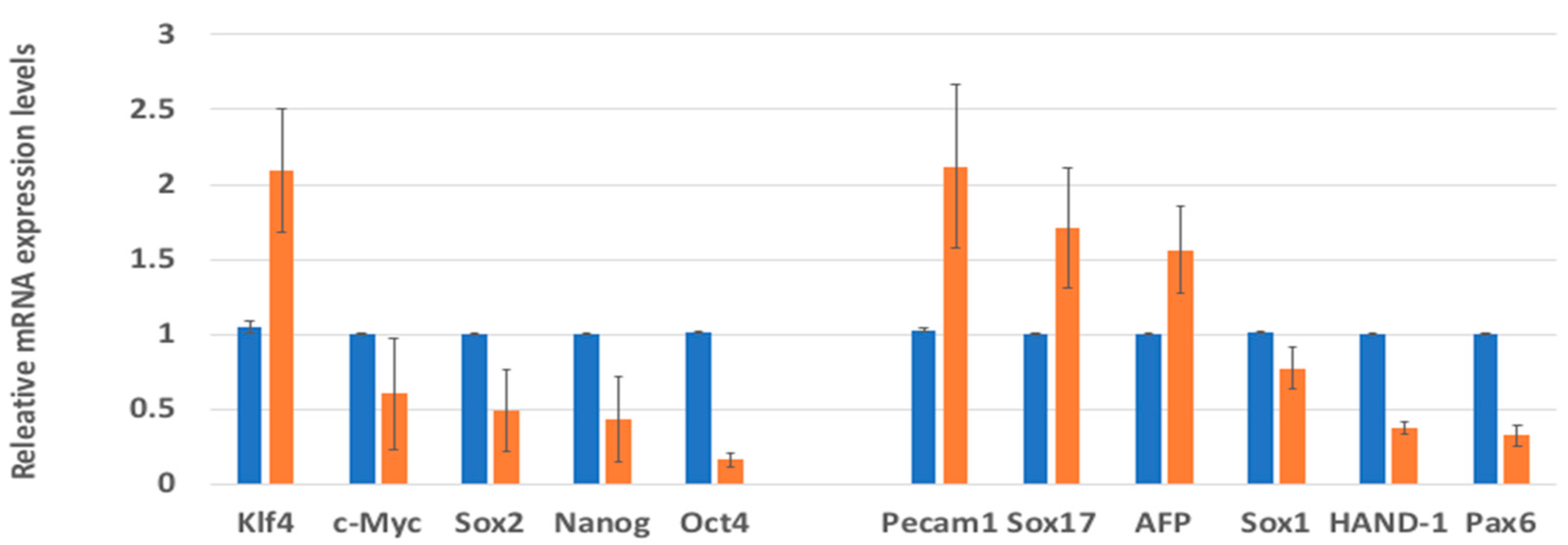
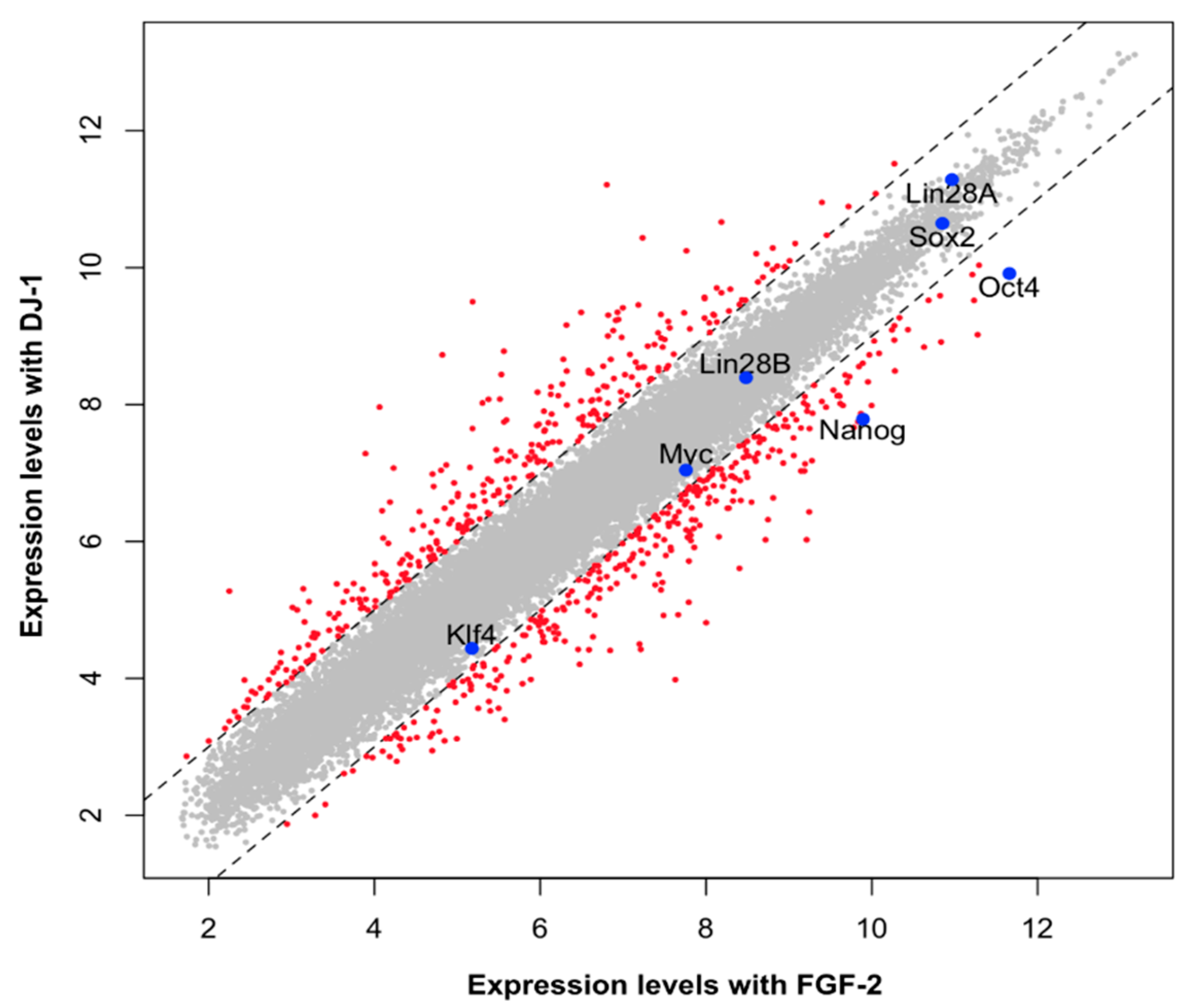
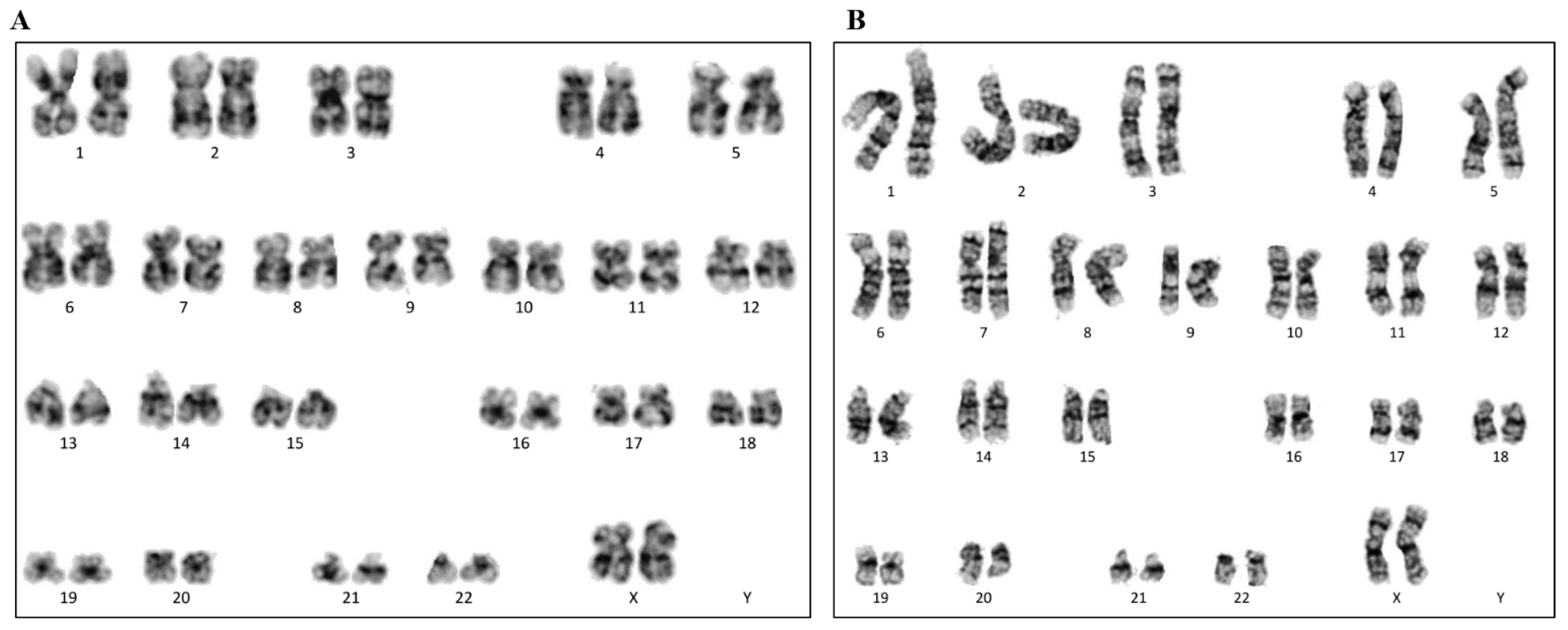
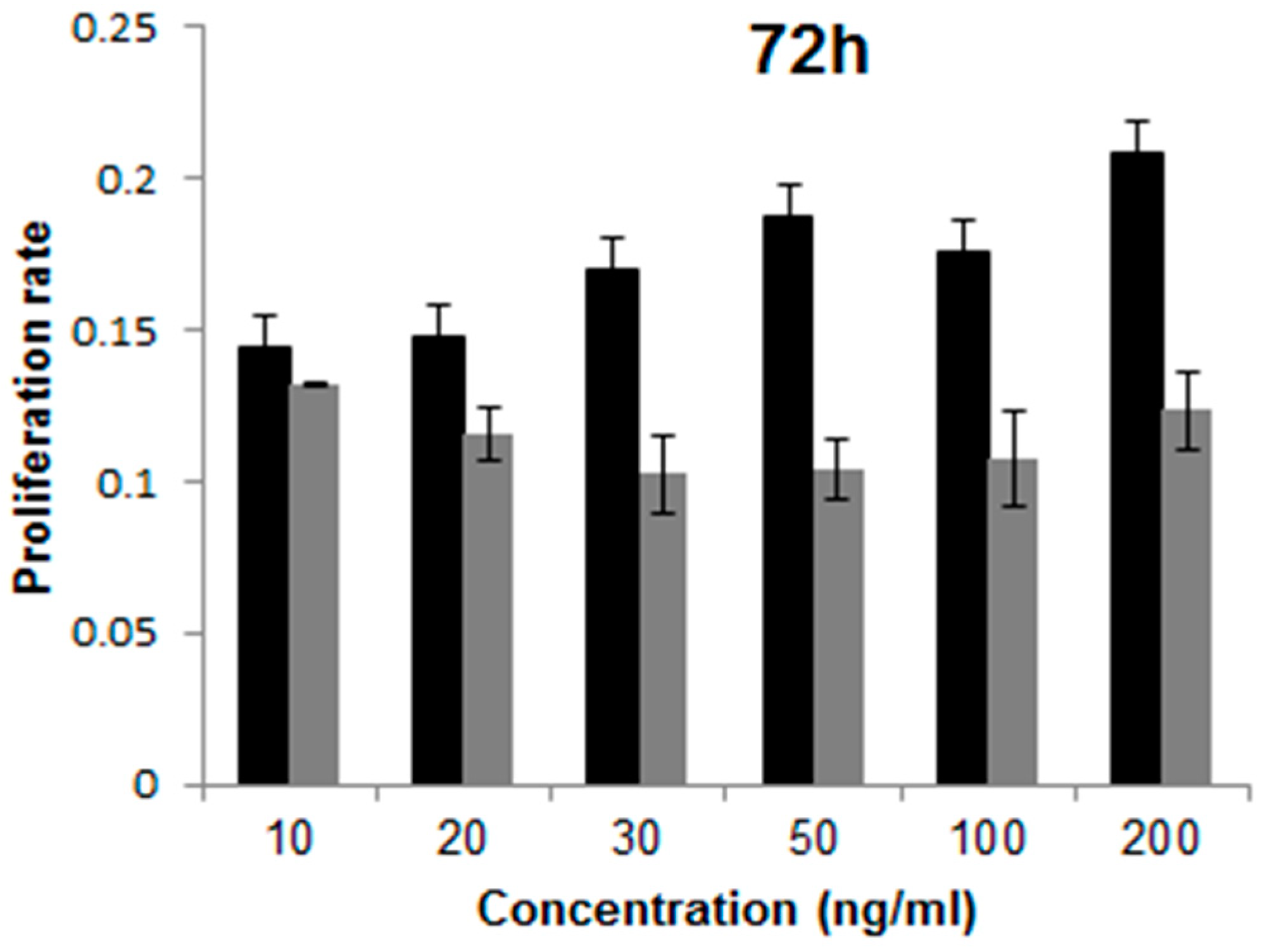
2. Result
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Optimization of Extracellular Factors
4.3. Alkaline Phosphatase Staining and Immunofluorescence
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Quantification
4.6. Karyotyping
4.7. Proliferation Assay
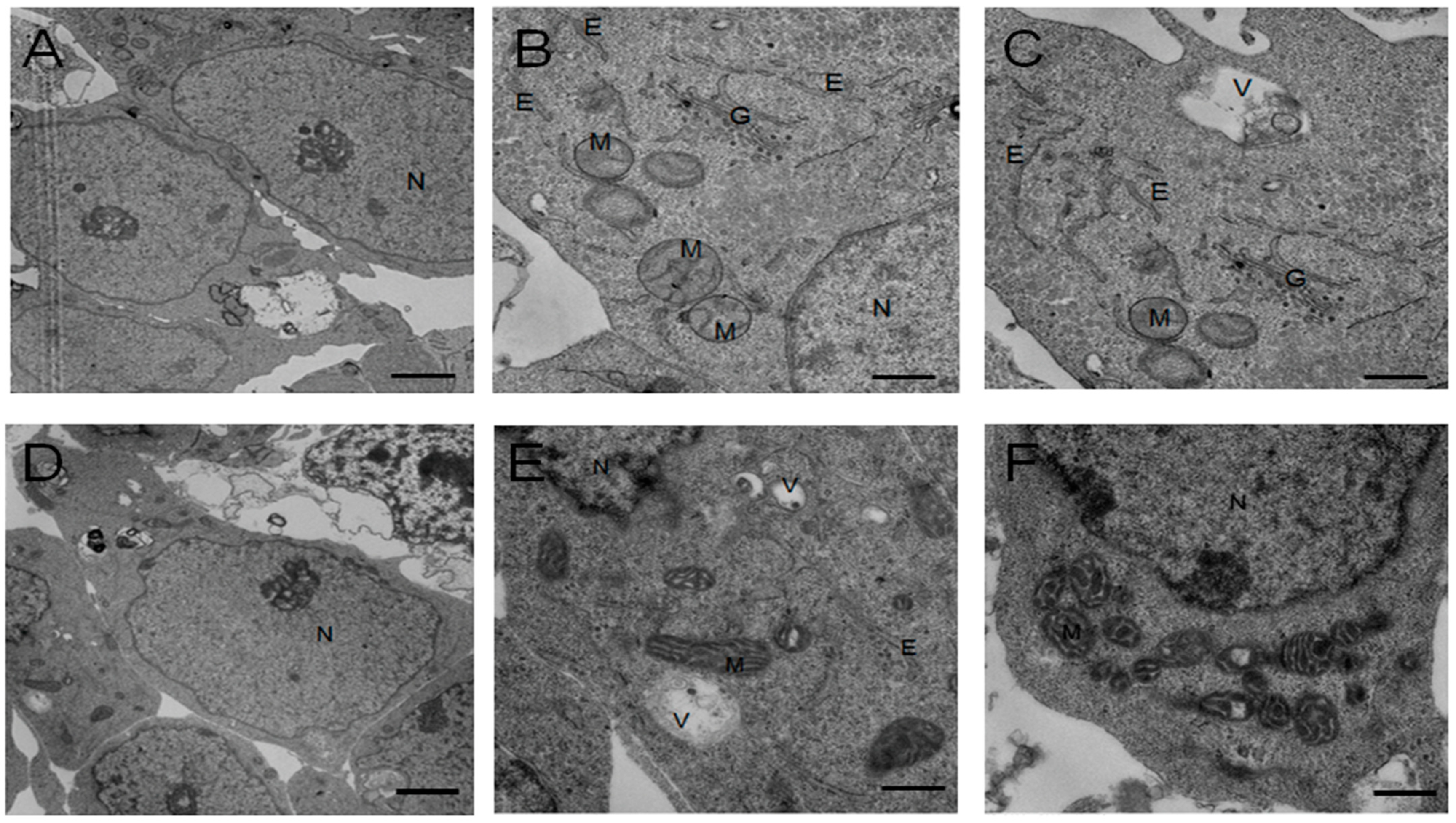
4.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.9. DNA Microarray
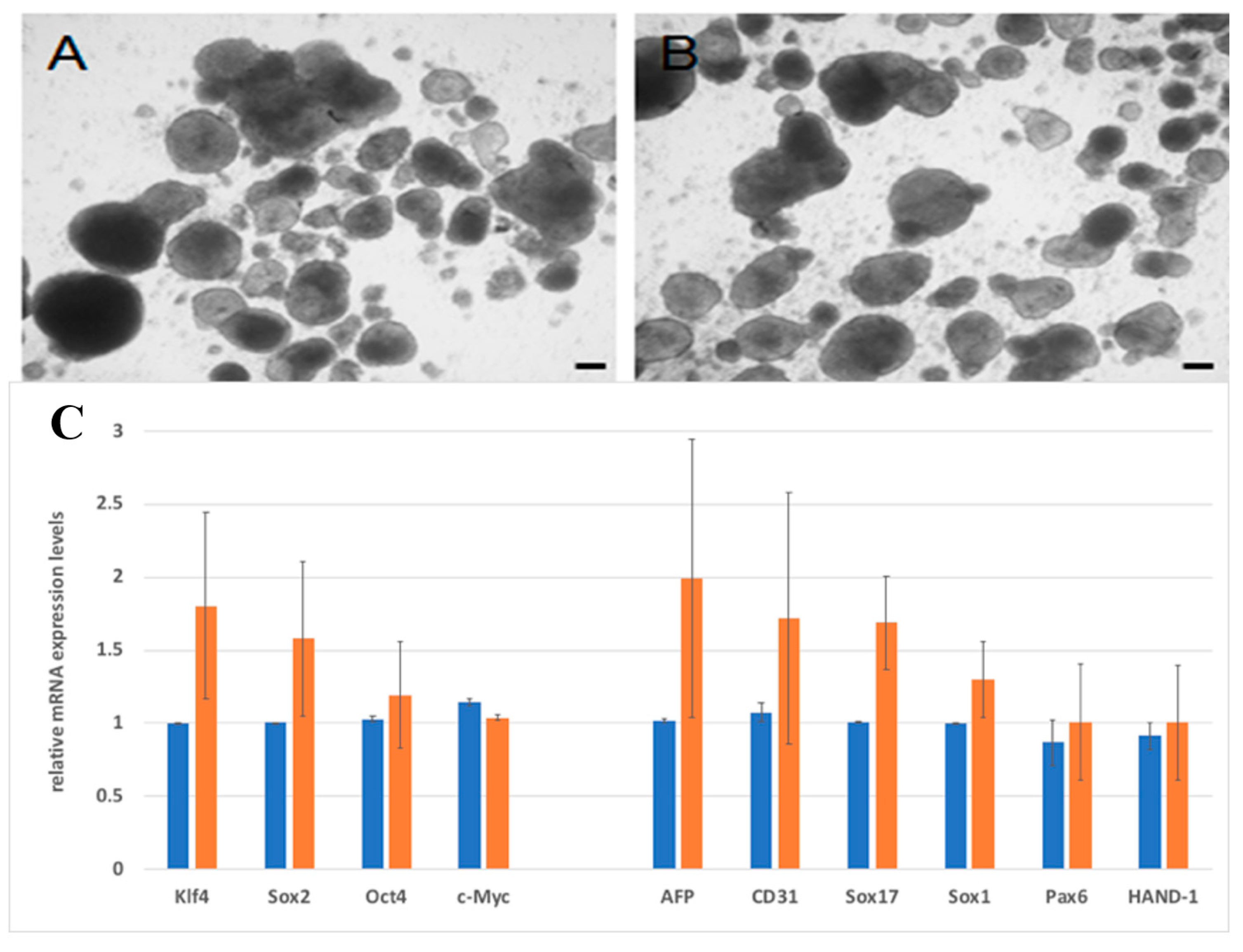
4.10. Differentiation Assay
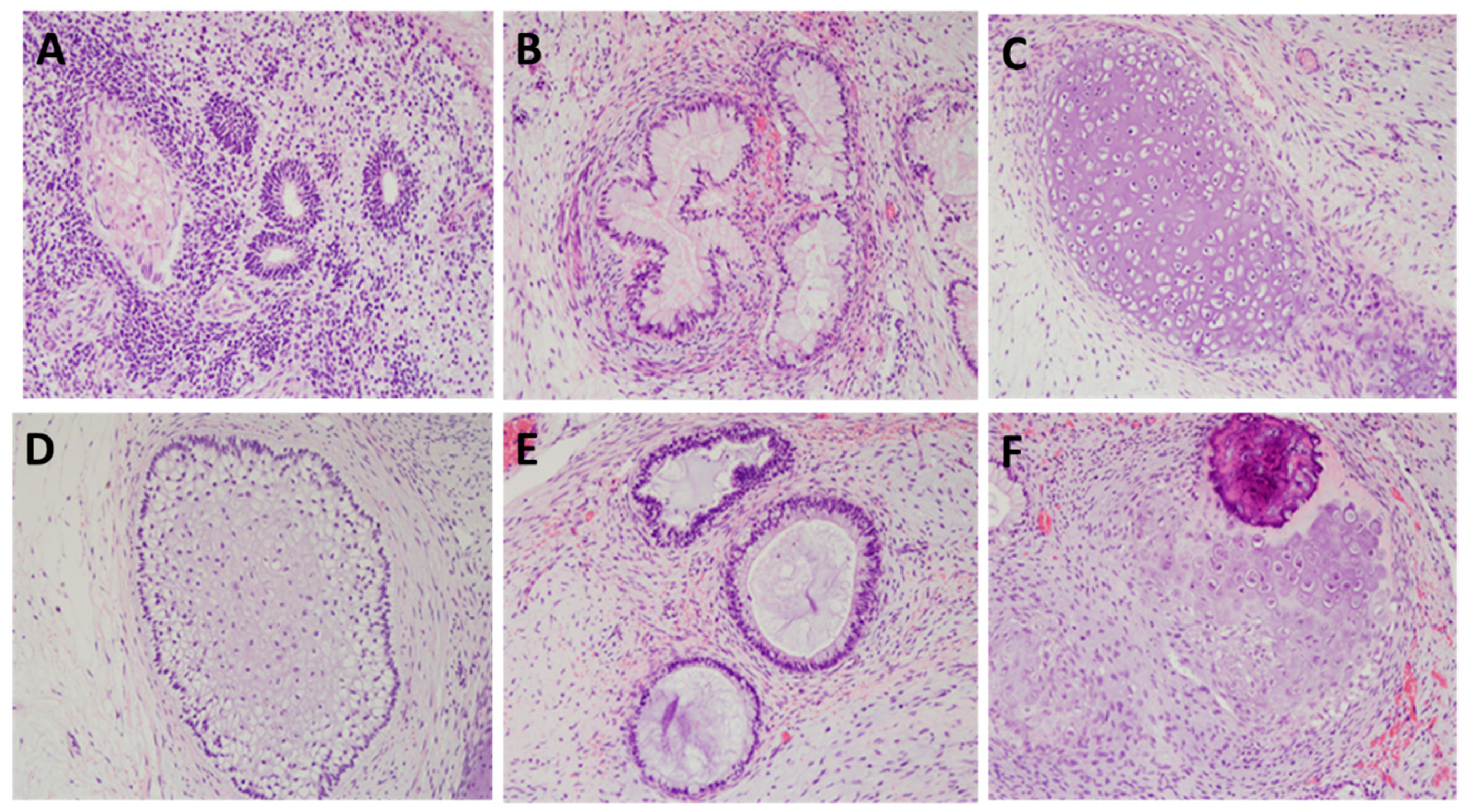
4.11. Teratoma Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Significance Statement
References
- Xu, C.; Rosler, E.; Jiang, J.; Lebkowski, J.S.; Gold, J.D.; O’Sullivan, C.; Delavan-Boorsma, K.; Mok, M.; Bronstein, A.; Carpenter, M.K. Basic fibroblast growth factor supports undifferentiated human embryonic stem cell growth without conditioned medium. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenstein, M.E.; Ludwig, T.E.; Xu, R.H.; Llanas, R.A.; VanDenHeuvel-Kramer, K.; Manning, D.; Thomson, J.A. Basic fibroblast growth factor support of human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Pan, G.; Yu, J.; Thomson, J.A. FGF2 sustains NANOG and switches the outcome of BMP4-induced human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Gulbranson, D.R.; Hou, Z.; Bolin, J.M.; Ruotti, V.; Probasco, M.D.; Smuga-Otto, K.; Howden, S.E.; Diol, N.R.; Propson, N.E.; et al. Chemically defined conditions for human iPSC derivation and culture. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, J.; Gulbranson, D.R.; George, N.; Siniscalchi, L.I.; Jones, J.; Thomson, J.A.; Chen, G. Passaging and colony expansion of human pluripotent stem cells by enzyme-free dissociation in chemically defined culture conditions. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Gulbranson, D.R.; Yu, P.; Hou, Z.; Thomson, J.A. Thermal stability of fibroblast growth factor protein is a determinant factor in regulating self-renewal, differentiation, and reprogramming in human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.C.; Nagamori, E.; Horie, M.; Kino-Oka, M. Culture medium refinement by dialysis for the expansion of human induced pluripotent stem cells in suspension culture. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakubo, D.; Taira, T.; Kitaura, H.; Ikeda, M.; Tamai, K.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.; Ariga, H. DJ-1, a novel oncogene which transforms mouse NIH3T3 cells in cooperation with ras. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 231, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifati, V.; Rizzu, P.; van Baren, M.J.; Schaap, O.; Breedveld, G.J.; Krieger, E.; Dekker, M.C.; Squitieri, F.; Ibanez, P.; Joosse, M.; et al. Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 2003, 299, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Chin, L.S. Parkinson disease protein DJ-1 converts from a zymogen to a protease by carboxyl-terminal cleavage. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 2395–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Song, J.; Kwon, K.; Jang, S.; Kim, C.; Baek, K.; Kim, J.; Park, C. Human DJ-1 and its homologs are novel glyoxalases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3215–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihoub, M.; Abdallah, J.; Gontero, B.; Dairou, J.; Richarme, G. The DJ-1 superfamily member Hsp31 repairs proteins from glycation by methylglyoxal and glyoxal. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Mayorga, E.; Diaz-Sanchez, A.G.; Dagda, R.K.; Dominguez-Solis, C.A.; Dagda, R.Y.; Coronado-Ramirez, C.K.; Martinez-Martinez, A. Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, I.K.; Ko, J.; Jeong, C.S.; Kim, G.H.; Park, C.; Kang, S.O.; Suh, P.G.; Lee, H.S.; et al. Crystal structures of human DJ-1 and Escherichia coli Hsp31, which share an evolutionarily conserved domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44552–44559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shendelman, S.; Jonason, A.; Martinat, C.; Leete, T.; Abeliovich, A. DJ-1 is a redox-dependent molecular chaperone that inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregate formation. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junn, E.; Jang, W.H.; Zhao, X.; Jeong, B.S.; Mouradian, M.M. Mitochondrial localization of DJ-1 leads to enhanced neuroprotection. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Shin, H.I.; Cha, S.S.; Lee, C.S.; Hong, B.S.; Lim, S.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, J.; Yang, Y.R.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. DJ-1 promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis by activating FGF receptor-1 signaling. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Taniguchi, Y.; Senda, S.; Takizawa, N.; Ichisaka, T.; Asano, K.; Morizane, A.; Doi, D.; Takahashi, J.; Nishizawa, M.; et al. A novel efficient feeder-free culture system for the derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M.; Quan, M.; Zhang, J.S.; Li, X. FGF Signaling Pathway: A Key Regulator of Stem Cell Pluripotency. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, S.Y.; Ikeda, T.; Shahsavarani, H.; Yoshida, N.; Nayer, B.; Hino, M.; Vartak-Sharma, N.; Suemori, H.; Hasegawa, K. Chemically defined and growth-factor-free culture system for the expansion and derivation of human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, N.C.; Caperna, T.J. Proteome array identification of bioactive soluble proteins/peptides in Matrigel: Relevance to stem cell responses. Cytotechnology 2015, 67, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hong, A.; Ren, J.S.; Sun, F.Y.; Shi, Y.J.; Liu, K.; Xie, Q.L.; Dai, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, Y. Biochemical properties of C78SC96S rhFGF-2: A double point-mutated rhFGF-2 increases obviously its activity. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 121, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, K.; Hagiwara, A.; Komi-Kuramochi, A.; Hanyu, Y.; Honda, E.; Suzuki, M.; Kimura, M.; Oki, J.; Asada, M.; Sakaguchi, N.; et al. An FGF1:FGF2 chimeric growth factor exhibits universal FGF receptor specificity, enhanced stability and augmented activity useful for epithelial proliferation and radioprotection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuma, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Aiki, Y.; Shu, Y.; Asada, M.; Asashima, M.; Suzuki, M.; Imamura, T.; Ito, Y. A stable chimeric fibroblast growth factor (FGF) can successfully replace basic FGF in human pluripotent stem cell culture. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ye, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Feng, W.; et al. Solid-phase N-terminus PEGylation of recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 2 on heparin-sepharose column. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M.K.; Na, J.; Jackson, J.P.; Okamoto, T.; Jones, M.; Baker, D.; Hata, R.; Moore, H.D.; Sato, J.D.; Andrews, P.W. Heparin promotes the growth of human embryonic stem cells in a defined serum-free medium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13409–13414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, S.; Goderie, S.; Tokas, N.; Hirsch, S.E.; Ahmad, F.; Corneo, B.; Le, S.; Banerjee, A.; Kane, R.S.; Stern, J.H.; et al. Sustained levels of FGF2 maintain undifferentiated stem cell cultures with biweekly feeding. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.; Levine, A.J.; Besser, D.; Hemmati-Brivanlou, A. TGFbeta/activin/nodal signaling is necessary for the maintenance of pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Development 2005, 132, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego Romero, I.; Pavlovic, B.J.; Hernando-Herraez, I.; Zhou, X.; Ward, M.C.; Banovich, N.E.; Kagan, C.L.; Burnett, J.E.; Huang, C.H.; Mitrano, A.; et al. A panel of induced pluripotent stem cells from chimpanzees: A resource for comparative functional genomics. eLife 2015, 4, e07103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.S.; Zimmerlin, L.; Evans-Moses, R.; Zambidis, E.T. Chemical Reversion of Conventional Human Pluripotent Stem Cells to a Naive-like State with Improved Multilineage Differentiation Potency. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 57921. [Google Scholar]
- Skiniotis, G.; Lupardus, P.J.; Martick, M.; Walz, T.; Garcia, K.C. Structural organization of a full-length gp130/LIF-R cytokine receptor transmembrane complex. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Yasuda, S.Y.; Teo, J.L.; Nguyen, C.; McMillan, M.; Hsieh, C.L.; Suemori, H.; Nakatsuji, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Miyabayashi, T.; et al. Wnt signaling orchestration with a small molecule DYRK inhibitor provides long-term xeno-free human pluripotent cell expansion. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Meijer, L.; Skaltsounis, L.; Greengard, P.; Brivanlou, A.H. Maintenance of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling by a pharmacological GSK-3-specific inhibitor. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Ye, Z.; Zhou, B.Y.; Mali, P.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, L. Promoting human embryonic stem cell renewal or differentiation by modulating Wnt signal and culture conditions. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, K.; Weiss, J.; Zaehres, H.; Kim, Y.M.; Lutzko, C.; Roosta, N.; Hescheler, J.; Muschen, M. The WNT receptor FZD7 contributes to self-renewal signaling of human embryonic stem cells. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, T.; Tsuneyoshi, N.; Nakatsuji, N.; Suemori, H. Defining early lineage specification of human embryonic stem cells by the orchestrated balance of canonical Wnt/beta-catenin, Activin/Nodal and BMP signaling. Development 2008, 135, 2969–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, J.J.; Fu, W.; Kan, L.; Cuadra, A.E.; Kessler, J.A. Beta-catenin signaling is required for neural differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Development 2004, 131, 3545–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemitsu, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Itoh, H.; Okazaki, J.; Uchiyama, M.; Yoshida, K.; Onimaru, M.; Onohara, T.; Inoguchi, H.; Kyuragi, R.; et al. DVC1-0101 to treat peripheral arterial disease: A Phase I/IIa open-label dose-escalation clinical trial. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.A.; Davis-Dusenbery, B.N.; Eggan, K.C. SnapShot: Directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. Cell 2012, 149, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Liu, X.M.; Sun, J.G.; Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Dong, M.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.Q.; Ding, J.Q.; Li, D.H.; et al. DJ-1 maintains energy and glucose homeostasis by regulating the function of brown adipose tissue. Cell Discov. 2017, 3, 16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookson, M.R. Parkinsonism due to mutations in PINK1, parkin, and DJ-1 and oxidative stress and mitochondrial pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.A.; Koo, B.K.; Chong, S.H.; Kwak, J.; Ryu, H.B.; Nguyen, M.T.; Vu, T.T.; Jeong, B.; Kim, S.W.; Choe, H. Expression and purification of biologically active human FGF2 containing the b’a’ domains of human PDI in Escherichia coli. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Baek, S.; Hong, Y.J.; de Paula, M.N.; Jahan Prima, M.; Oh, Y.-M.; Cha, S.-S.; Do, J.T.; Jang, Y.J.; Choe, H. DJ-1 Can Replace FGF-2 for Long-Term Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Defined Media and Feeder-Free Condition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115954
Kim J, Baek S, Hong YJ, de Paula MN, Jahan Prima M, Oh Y-M, Cha S-S, Do JT, Jang YJ, Choe H. DJ-1 Can Replace FGF-2 for Long-Term Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Defined Media and Feeder-Free Condition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115954
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Julee, Sangki Baek, Yean Ju Hong, Michelle Novais de Paula, Musharrat Jahan Prima, Yeon-Mok Oh, Sun-Shin Cha, Jeong Tae Do, Yeon Jin Jang, and Han Choe. 2021. "DJ-1 Can Replace FGF-2 for Long-Term Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Defined Media and Feeder-Free Condition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115954
APA StyleKim, J., Baek, S., Hong, Y. J., de Paula, M. N., Jahan Prima, M., Oh, Y.-M., Cha, S.-S., Do, J. T., Jang, Y. J., & Choe, H. (2021). DJ-1 Can Replace FGF-2 for Long-Term Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in Defined Media and Feeder-Free Condition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115954