NtRNF217, Encoding a Putative RBR E3 Ligase Protein of Nicotiana tabacum, Plays an Important Role in the Regulation of Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
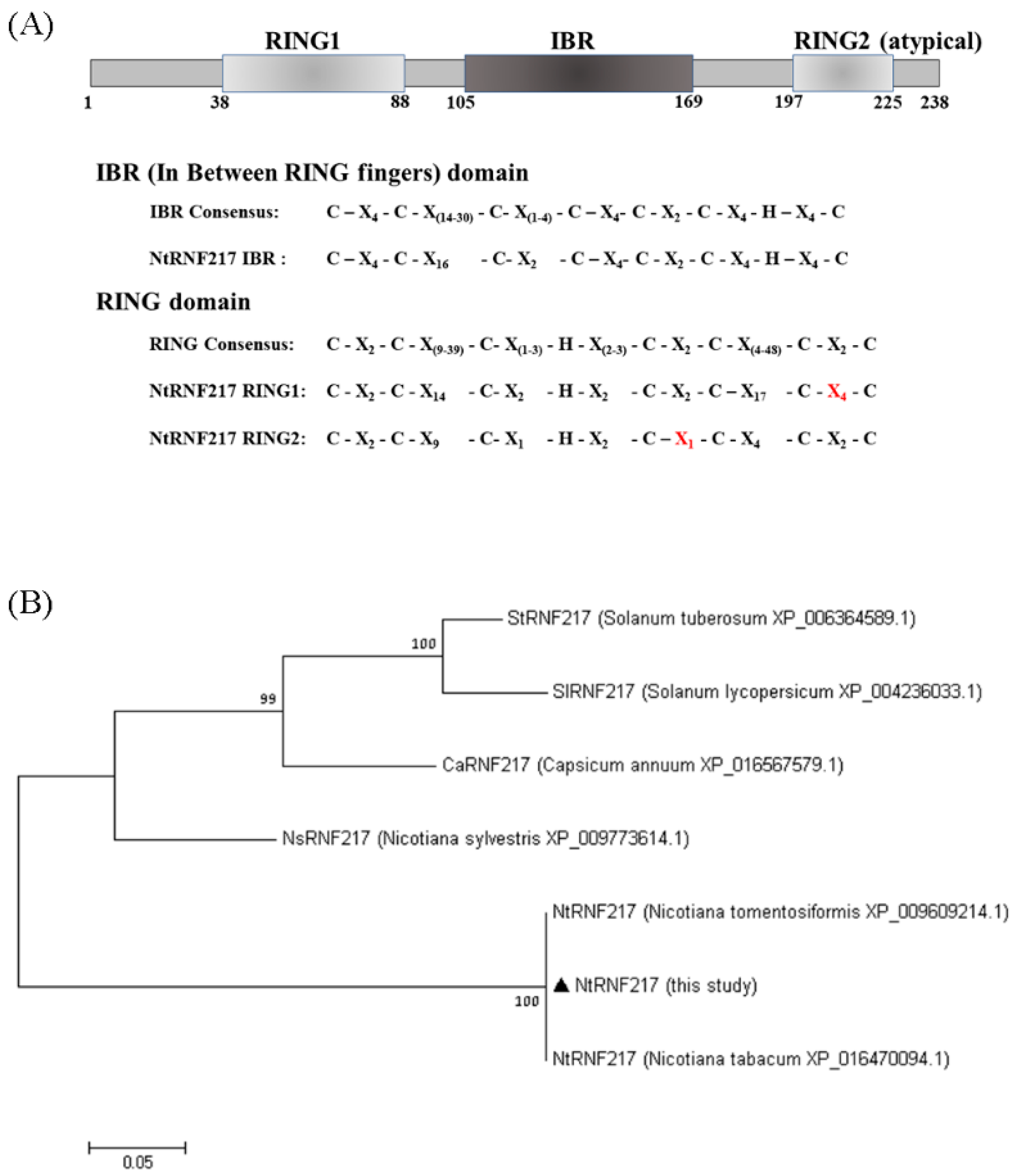
2.1. Amino Acids Sequence Analyses of NtRNF217
2.2. Response of NtRNF217 Transcript Levels to R. solanacearum and Exogenous Hormones
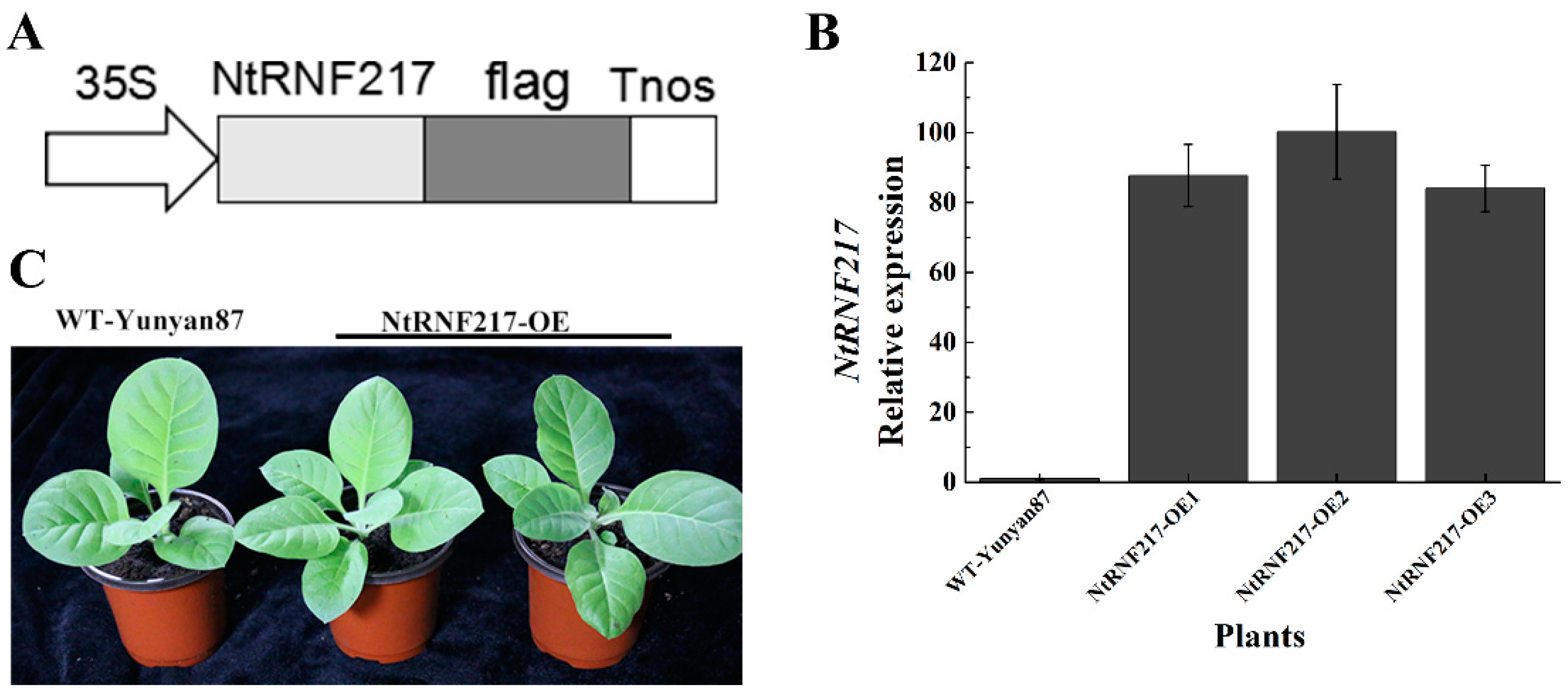
2.3. Overexpression of NtRNF217 Enhances Resistance of Tobacco to R. solanacearum
2.4. Overexpression of NtRNF217 Increases the Accumulation of H2O2 and O2− Production
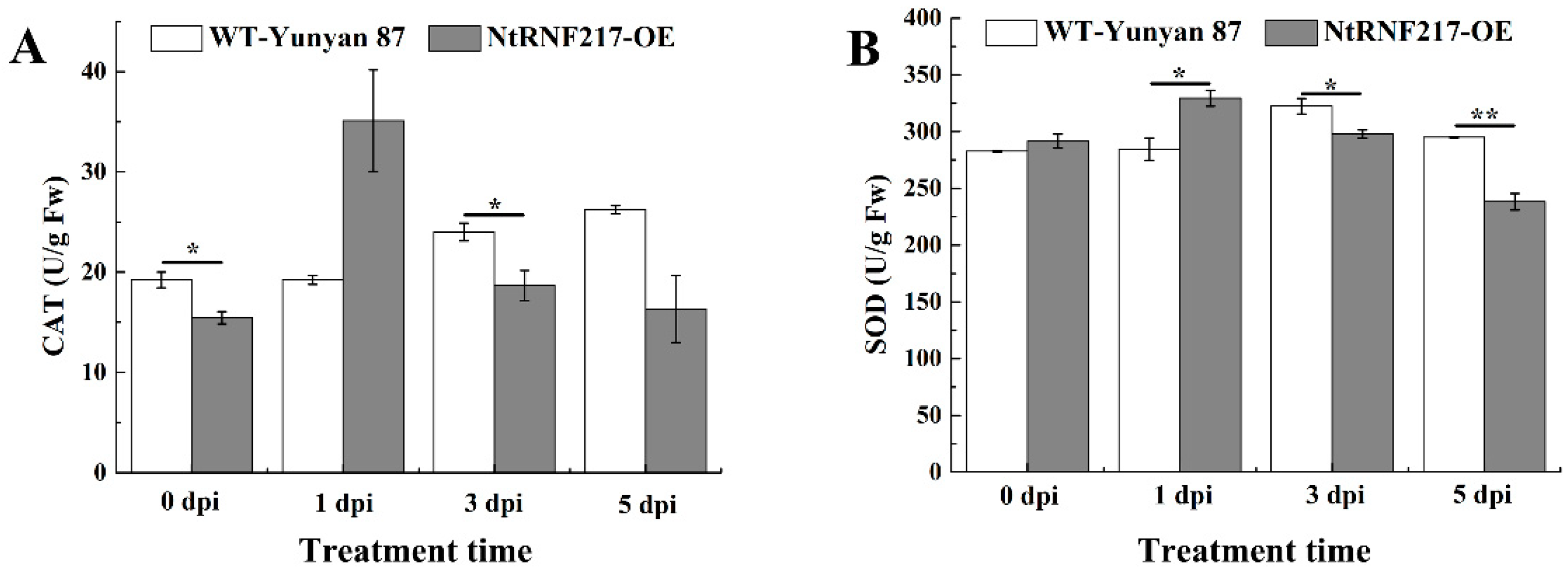
2.5. Overexpression of NtRNF217 Enhances the Antioxidant System of Tobacco
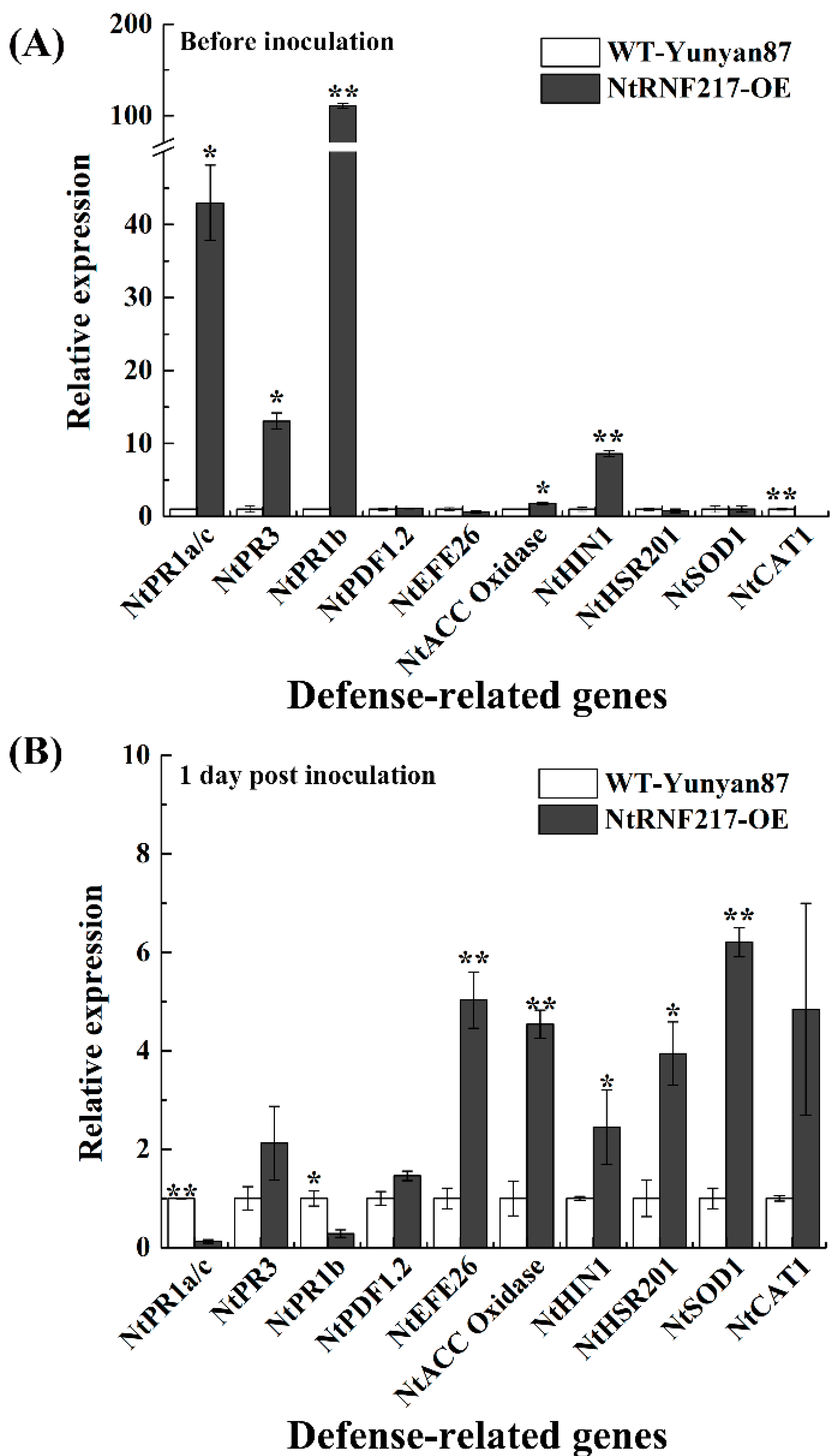
2.6. Overexpression of NtRNF217 Activates the Expression of Defense-Related Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Characterization of the NtRNF217 Gene and Construction of Over-Expressing Plants
4.3. Application of Plant Hormones and Exogenous Inducers
4.4. Pathogens and Inoculation Procedures
4.5. Histochemical Staining and SOD, CAT Activities
4.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smalle, J.; Vierstra, R.D. The ubiquitin 26S proteasome proteolytic pathway. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 555–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadanandom, A.; Bailey, M.; Ewan, R.; Lee, J.; Nelis, S. The ubiquitin-proteasome system: Central modifier of plant signalling. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.R.; Estelle, M. Ubiquitin-mediated control of plant hormone signaling. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, L.; Su, Z. plantsUPS: A database of plants’ Ubiquitin Proteasome System. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucotelli, E.; Belloni, S.; Marone, D.; De Leonardis, A.M.; Guerra, D.; Fonzo, N.; Cattivelli, L.; Mastrangelo, A.M. The E3 ubiquitin ligase gene family in plants: Regulation by degradation. Curr. Genom. 2006, 7, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndsen, C.E.; Wolberger, C. New insights into ubiquitin E3 ligase mechanism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshaies, R.J.; Joazeiro, C.A.P. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.B.; Hristova, V.A.; Weissman, A.M. HECT and RING finger families of E3 ubiquitin ligases at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, Y.; Huibregtse, J.M. Regulation of catalytic activities of HECT ubiquitin ligases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhaber, B.; Chumak, N.; Eisenhaber, F.; Hauser, M.T. The ring between ring fingers (RBR) protein family. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratt, D.E.; Walden, H.; Shaw, G.S. RBR E3 ubiquitin ligases: New structures, new insights, new questions. Biochem. J. 2014, 458, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Ferrus, A. Comparative Genomics of the RBR family, including the Parkinson’s disease-related gene Parkin and the genes of the Ariadne subfamily. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, D.; Peeters, N.; Rivas, S. Ubiquitination during plant immune signaling. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, I.; Campos, L.; Rivas, S. Roles of E3 ubiquitin-ligases in nuclear protein homeostasis during plant stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.J.; Zeng, L.R. Conventional and unconventional ubiquitination in plant immunity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 1313–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genin, S.; Denny, T.P. Pathogenomics of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2012, 50, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.F.; Wei, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.L.; Zhang, Y.; She, X.M.; Macho, A.P.; Ding, W.; Liao, B.S. Bacterial wilt in China: History, current Status, and future perspectives. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.R.; Uknes, S.J.; Williams, S.C.; Dincher, S.S.; Wiederhold, D.L.; Alexander, D.C.; Ahlgoy, P.; Metraux, J.P.; Ryals, J.A. Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.-W.; Li, G.-L.; Cheng, Z.-P.; Hu, M.; Liu, W.-Q. Introns identification and transient expression analysis of NtNAC-R1 gene in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2013, 42, 27–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, S.-I.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, B.-R.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lim, C.K.; Hur, J.H.; Lee, J.-Y. Transgenic tobacco expressing the hrpNEP gene from Erwinia pyrifoliae triggers defense responses against Botrytis cinerea. Mol. Cells 2007, 24, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Goodwin, P.H.; Hsiang, T. The role of ethylene during the infection of Nicotiana tabacum by Colletotrichum destructivum. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghannam, A.; Jacques, A.; de Ruffray, P.; Kauffmann, S. NtRING1, putative RING-finger E3 ligase protein, is a positive regulator of the early stages of elicitin-induced HR in tobacco. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Chen, Z.X.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.D.; Klessig, D.F. Development of necrosis and activation of disease resistance in transgenic tobacco plants with severely reduced catalase levels. Plant J. 1997, 11, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Choi, H.W.; Hwang, B.K. The pepper E3 ubiquitin ligase RING1 Gene, CaRING1, is required for cell death and the salicylic acid-dependent defense response. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 2011–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Xia, Z.L.; Wang, M.P.; Zhang, X.Q.; Yang, T.Z.; Wu, J.Y. Overexpression of a maize E3 ubiquitin ligase gene enhances drought tolerance through regulating stomatal aperture and antioxidant system in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 73, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, C.; Kitagawa, M. RING-, HECT-, and RBR-type E3 ubiquitin ligases: Involvement in human cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2016, 16, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Dai, X.M.; Jiang, W.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Wei, W.Y. RBR E3 ubiquitin ligases in tumorigenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 67, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devoto, A.; Muskett, P.R.; Shirasu, K. Role of ubiquitination in the regulation of plant defence against pathogens. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genin, S. Molecular traits controlling host range and adaptation to plants in Ralstonia solanacearum. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camejo, D.; Guzman-Cedeno, A.; Moreno, A. Reactive oxygen species, essential molecules, during plant-pathogen interactions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Mishra, R.K.; Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, V.P.; Chauhan, D.K.; Prasad, S.M. Reactive oxygen species (ROS): Beneficial companions of plants’ developmental processes. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breusegem, F.; Dat, J.F. Reactive oxygen species in plant cell death. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.; Pennell, R.I.; Alvarez, M.E.; Palmer, R.; Lamb, C. Calcium-mediated apoptosis in a plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, L.F.; Tenhaken, R.; Lamb, C. Function of oxidative cross-linking of cell wall structural proteins in plant disease resistance. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foyer, C.H.; Lopez-Delgado, H.; Dat, J.F.; Scott, I.M. Hydrogen peroxide- and glutathione-associated mechanisms of acclimatory stress tolerance and signalling. Physiol. Plant. 1997, 100, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.; Dixon, R.A. The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annu. Rev. Plant Phys. 1997, 48, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Ravindran, P.; Kumar, P.P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chico, J.M.; Lechner, E.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Canibano, E.; Garcia-Casado, G.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Hammann, P.; Zamarreno, A.M.; Garcia-Mina, J.M.; Rubioa, V.; et al. CUL3(BPM) E3 ubiquitin ligases regulate MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 stability and JA responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6205–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.Q.; Dong, X.N. Systemic acquired resistance: Turning local infection into global defense. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 839–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.M.; Zhu, S.F.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Signal regulators of systemic acquired resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer-Michalski, E.M.; Conrath, U. Innate immune memory in plants. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, F.; Wang, Y.; She, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Eulgem, T.; Lai, Y.; Lin, J.; Yu, L.; Lei, D.; et al. Overexpression of CaWRKY27, a subgroup IIe WRKY transcription factor of Capsicum annuum, positively regulates tobacco resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 150, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, W. Overexpression of NtPR-Q up-regulates multiple defense-related genes in Nicotiana tabacum and enhances plant resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.K.; Park, J.M.; Joung, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Chung, E.; Kim, S.Y.; Yu, S.H.; Choi, D. A plant EPF-type zinc-finger protein, CaPIF1, involved in defence against pathogens. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Li, S.; Ding, W. The sequevar distribution of Ralstonia solanacearum in tobacco-growing zones of China is structured by elevation. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 147, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, C.A.; Barberis, P.A.; Demery, D.A. Transposon mutagenesis of Pseudomonas solanacearum: Isolation of Tn5-induced avirulent mutants. Microbiology 1985, 131, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, F.F.; Wang, Y.N.; Yu, L.; Eulgem, T.; Lai, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, X.; Qiu, A.L.; Zhang, T.X.; Lin, J.; et al. CaWRKY40, a WRKY protein of pepper, plays an important role in the regulation of tolerance to heat stress and resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doke, N. Generation of superoxide anion by potato tuber protoplasts during the hypersensitive response to hyphal wall components of Phytophthora infestans and specific inhibition of the reaction by suppressors of hypersensitivity. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1983, 23, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thordal-Christensen, H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Wei, Y.D.; Collinge, D.B. Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants: H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley-powdery mildew interaction. Plant J. 1997, 11, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Qin, L.N.; Liu, Y.J.; Fan, H.C.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.F. The comparison of two methods of testing superoxide dismutase activity. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2014, 5, 3318–3323. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.X.; Liu, J.M.; Song, Y.X. Detection of APX and CAT activity in AtDREB1A transgenic Yinxin poplar. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2007, 19, 89–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tan, X.; Ding, W. NtRNF217, Encoding a Putative RBR E3 Ligase Protein of Nicotiana tabacum, Plays an Important Role in the Regulation of Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115507
Liu Y, Tang Y, Tan X, Ding W. NtRNF217, Encoding a Putative RBR E3 Ligase Protein of Nicotiana tabacum, Plays an Important Role in the Regulation of Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115507
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ying, Yuanman Tang, Xi Tan, and Wei Ding. 2021. "NtRNF217, Encoding a Putative RBR E3 Ligase Protein of Nicotiana tabacum, Plays an Important Role in the Regulation of Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115507
APA StyleLiu, Y., Tang, Y., Tan, X., & Ding, W. (2021). NtRNF217, Encoding a Putative RBR E3 Ligase Protein of Nicotiana tabacum, Plays an Important Role in the Regulation of Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115507




