Abstract
The hard tick Ixodes ricinus is a vector of Lyme disease and tick-borne encephalitis. Host blood protein digestion, essential for tick development and reproduction, occurs in tick midgut digestive cells driven by cathepsin proteases. Little is known about the regulation of the digestive proteolytic machinery of I. ricinus. Here we characterize a novel cystatin-type protease inhibitor, mialostatin, from the I. ricinus midgut. Blood feeding rapidly induced mialostatin expression in the gut, which continued after tick detachment. Recombinant mialostatin inhibited a number of I. ricinus digestive cysteine cathepsins, with the greatest potency observed against cathepsin L isoforms, with which it co-localized in midgut digestive cells. The crystal structure of mialostatin was determined at 1.55 Å to explain its unique inhibitory specificity. Finally, mialostatin effectively blocked in vitro proteolysis of blood proteins by midgut cysteine cathepsins. Mialostatin is likely to be involved in the regulation of gut-associated proteolytic pathways, making midgut cystatins promising targets for tick control strategies.
Keywords:
cathepsin; crystal structure; cysteine protease; digestion; Ixodes ricinus; midgut; parasite 1. Introduction
Ticks are globally distributed ectoparasitic arthropods that strictly feed on host blood. While soft ticks (family Argasidae) feed only for a few hours, hard ticks (family Ixodidae) usually attach to their hosts for several days to fully engorge and proceed to their next developmental stage. The hard tick Ixodes ricinus is found mainly in Europe but also in neighboring parts of Africa and the Middle East, where it is a major vector of pathogens such as Lyme disease spirochetes (Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato), tick-borne encephalitis virus [1] or Babesia spp. [2]. Adult I. ricinus females feed for 6–9 days on a vertebrate host to enlarge over 100 times in weight [3].
Since blood is a highly specific and sole source of nutrients for these ticks, they have adapted to efficiently process large amounts of host blood. Blood degrades in the acidic endolysosomes of digestive cells of the tick midgut. Gut lumen uptake of the two main blood constituents, albumin and hemoglobin, is facilitated by two different mechanisms [4]: albumin is taken up non-specifically by fluid-phase endocytosis, while hemoglobin is recognized by specific receptor-mediated endocytosis. Subsequently, albumin is directed to small acidic vesicles and hemoglobin to a population of large digestive vesicles [4]. Despite these differences, both albumin and hemoglobin are cleaved and processed to single amino acids and short peptides by the same proteolytic system [5,6]. The degradation pathway for hemoglobin is described in detail elsewhere [4]. Briefly, the initial phase is catalyzed by three I. ricinus digestive endopeptidases at low pH (3.5 to 4.5) including a cysteine protease legumain (IrAE) [7] and aspartic protease cathepsin D (IrCD1) [8]. Two cysteine protease cathepsin L isoforms, IrCL1 [9] (GenBank: EF428205) and IrCL3 (GenBank: QBK51063), complement the initial phase: IrCL1 expression in tick gut cells peaks at the end of tick feeding [9], while its ortholog, IrCL3, is present in the tick midgut predominantly after feeding, where it complements the activity of IrCL1 (D. Sojka, personal communication, December 2020). Cysteine proteases with exopeptidase activity, cathepsins B and C (IrCB and IrCC), continue hemoglobin degradation to dipeptides at an optimal pH of 5.5–6.0 in digestive cells [6,10,11]. Digestion to single amino acids is facilitated by carboxypeptidase and leucine aminopeptidase [6]. Blood processing by ticks and the roles of individual proteases are reviewed in detail elsewhere [12,13].
Under physiological conditions, cysteine protease activity is regulated by proteinaceous inhibitors, including those in the cystatin family [14,15]. Cystatins are tight binding, reversible inhibitors of legumain and papain-like cysteine proteases [16]. According to MEROPS nomenclature, cystatins are subdivided into three subfamilies: I25A (type 1, stefins), I25B (type 2 and type 3, kininogens), and I25C (type 4, fetuins) [17]. Only type 1 and 2 cystatins have so far been identified in ticks [18]. Cystatins are mostly associated with the regulation of proteases involved in blood digestion and heme detoxification in the tick midgut [18] and with the modulation of the host immune system as components of tick saliva [19,20], although they have also been detected in other tick tissues [21,22].
In soft ticks, only two midgut cystatins have been functionally characterized: Om-cystatins 1 and 2 from Ornithodoros moubata [23]. While Om-cystatin 1 is exclusively expressed in the midgut, Om-cystatin 2 can be found in all tissues and has immunomodulatory properties when secreted into the host [24,25]. Both inhibit cathepsins B, C, and H and are involved in blood processing [23]. Gut-associated cystatins from only two Ixodes species have been reported to date: a gut-secreted cystatin JpIocys2a from Ixodes ovatus was shown to inhibit cathepsins B, C, and L [26], while the expression of three Ixodes persulcatus cystatins, JpIpcys2a, b, and c, was demonstrated in almost all tissues and instars [27].
Despite the relatively good characterization of the digestive proteases present in the I. ricinus midgut [13], there has been little functional characterization of their inhibitors and regulatory mechanisms. Here we report a novel cystatin from the I. ricinus midgut, mialostatin, and present its crystal structure, inhibitory specificity, tissue localization, and role in the regulation of blood digestion.
2. Results
2.1. Mialostatin Transcript Predominantly Accumulates in the Tick Midgut
In order to clone mialostatin, we used primers based on available cystatin sequences identified in Ixodes scapularis tick genome. To obtain the longest possible reads, we also focused on the 5’ UTRs and 3’ UTRs regions. In the course of our study, an I. ricinus transcriptome was published with a transcript of an identical sequence to mialostatin (Genbank accession number GFVZ01041806.1) [28]. However, since this particular transcript was obtained from whole body tick sequencing, we used BLAST to search for highly similar sequences in other transcriptomic studies to specifically localize its expression (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 20 May 2021). As a result we found a highly similar transcript SigP-158801 upregulated mainly in the tick midgut [29]; similarly to another transcript GCJO01026918.1 identified in a study focusing on the tick gut [30]. To verify the localization of mialostatin, we examined its expression in different tick tissues and feeding stages and confirmed its predominantly midgut expression.
Increased transcription of mialostatin over the feeding course implies an important role in tick metabolism [18]. Figure 1 shows the expression of mialostatin in the tick midgut, ovaries, and salivary glands before, during, and after feeding. Mialostatin transcript was predominantly present in the tick midgut, where expression oscillated throughout feeding and after detachment but at consistently higher expression than the other examined tissues. The presence and upregulation of mialostatin transcript in tick salivary glands and ovaries were low, peaking in fully fed ticks and at the early phase of detachment at maximum levels of only 10–20% of midgut expression (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Mialostatin is predominantly produced in the tick midgut and its expression is upregulated by tick feeding. Expression maxima are prior to rapid engorgement, in fully fed females, and at two weeks post tick detachment from the host. Mialostatin expression was determined by quantitative PCR using cDNA templates prepared from a pool of three tissues from female ticks (MG—midgut, OVA—ovaries, SG—salivary glands). The qPCR output was normalized to the I. ricinus elongation factor 1 gene and compared across all values with the highest expression set to 100%. Data show an average of three biological replicates ± SEM. Categories: UF—unfed ticks; 1d, 3d, 5d—ticks after 1, 3, or 5 days of feeding; FF—fully fed ticks after 7–8 days of feeding; 3AD, 6AD, 12AD—ticks 3, 6, or 12 days after detachment.
2.2. Mialostatin Is a Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor of Cysteine Cathepsins and Is Highly Effective against Cathepsin L
Purified recombinant mialostatin was screened in vitro for its inhibitory potential against major endogenous digestive proteases present in the I. ricinus gut [6]. These proteases were tested in the form of recombinant enzymes or proteolytic activities in the gut tissue extract (Table 1, left and middle panels). The strongest inhibition was found for recombinant I. ricinus cathepsins L1 and L3 (IC50s of 0.071 and 0.39 nM, respectively), which are papain-type cysteine proteases and consistent with sub-nanomolar inhibition of cathepsin L-like activity by the extract (IC50 of 0.18 nM). The cathepsin B-like and cathepsin C-like activities of the extract were inhibited with lower potency, with IC50 values in the double-digit nanomolar range (12.1 and 91.7 nM, respectively). Mialostatin did not inhibit I. ricinus digestive proteases out of the papain family, including the aspartic protease cathepsin D1 and the clan CD cysteine protease legumain (asparaginyl endopeptidase).

Table 1.
Inhibitory effect of mialostatin on the activity of tick and human proteases. The inhibitory potency of mialostatin was determined against: (i) native cysteine cathepsins present in I. ricinus gut tissue extract using protease-specific assays (left panel); (ii) selected digestive proteases of I. ricinus prepared as recombinant proteins (middle panel); and (iii) a representative set of human cysteine cathepsins (right panel). The IC50 values (mean values ± SE) were measured by kinetic activity assays using specific fluorogenic peptide substrates (for details, see Methods).
We next expanded a spectrum of papain-type cysteine proteases and screened mialostatin against a representative panel of human cathepsins selected to cover a wide range of endo- and exopeptidase activities (Table 1, right panel) including endopeptidases cathepsins L, K, and S and exopeptidases cathepsin B (a peptidyl dipeptidase and endopeptidase), cathepsin C (a dipeptidyl peptidase), and cathepsin H (an aminopeptidase). Human cathepsin L was inhibited at subnanomolar concentrations (IC50 0.38 nM), similar to its I. ricinus homologs, and all other human cysteine cathepsins were inhibited with IC50 values in a narrow range from 2.2 to 24 nM.
In conclusion, mialostatin displays an unusually broad inhibitory specificity against cysteine cathepsins, with a particularly strong interaction with cathepsin L isoforms. The high affinity for cysteine cathepsins with endopeptidase and exopeptidase activities clearly distinguishes mialostatin from other described Ixodes cystatins, which display weak or no inhibition of these exopeptidases (see below).
2.3. Mialostatin Is Present in the Tick Gut Wall and Lumen
We further investigated mialostatin’s distribution within the tick midgut. Gut epithelia and lumina were collected from fully fed I. ricinus adult females and subjected to proteomic analysis to directly determine the presence or absence of mialostatin. The LC-MS/MS strategy was based on the enzymatic digestion of a complex protein mixture and MS/MS peptide sequencing. This analysis provided 11–71% peptide coverage of the mialostatin sequence and a mass accuracy of <5 p.p.m. (Table S1), allowing us to conclude that mialostatin is present in both the gut tissue and luminal contents of I. ricinus ticks.
Immunolabeling was used to evaluate the potential biological selectivity of mialostatin towards different papain-like enzymes present in tick gut tissue. Localization of mialostatin with IrCB, IrCL1, and IrCL3 was examined using multicolor immunohistochemistry (Figure 2), with the sample collection and section preparation time points selected based on qPCR-determined dynamic expression profiles of individual proteases (sixth day of feeding for IrCLB and IrCL1; eleventh day post feeding for IrCL3) to establish the availability of these proteases for co-localization with mialostatin at these timepoints. IrCL3 was the most probable target protease for mialostatin, as co-localization signals at the surface of large vesicles in tick gut cells (specific ring patterns) was nearly complete. However, there was also some co-localization of mialostatin with IrCL1 but not the cysteine protease cathepsin B (IrCB).
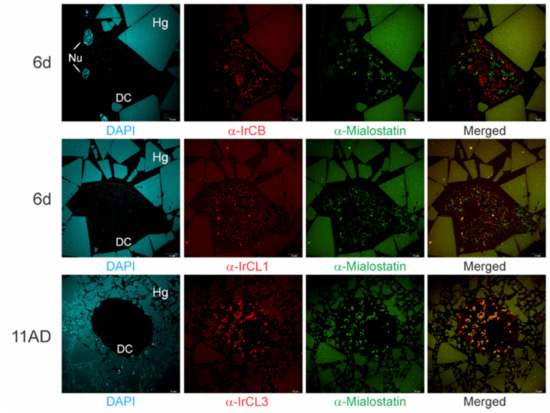
Figure 2.
Mialostatin co-localizes with IrCL3 inside gut digestive cells of female I. ricinus ticks. Multicolored confocal immunofluorescence indicates variable colocalization of mialostatin (green signal) with the cathepsin-type proteases IrCB, IrCL1, and IrCL3 (red signal) in female tick gut sections at the sixth day of feeding (6d) and eleventh day post detachment from the host (11AD). Mialostatin and IrCL3 show the greatest co-localization (yellow signal in merged images), thus IrCL3 represents the most probable target protease. DAPI counterstaining is shown in cyan. DC—digestive cells; Nu—nucleus; Hg—hemoglobin crystals in gut lumen, scale bar-10 µm.
Immunoblot analyses of tick gut tissue were performed to (i) confirm mialostatin selectivity for IrCL3 and further evaluate potential interactions with IrCL1; and (ii) evaluate potential secretion of mialostatin and the cathepsin-L-like tick proteases into the gut lumen. The latter could not be observed by immunohistochemical labeling due to the rapid dilution of gut epithelial cell secretions with the large amount of imbibed host blood in the lumen. However, mialostatin was detected in the gut wall (Figure 3A) at all collected time-points during feeding. Gut tissue originating from ticks membrane-fed on pure bovine blood serum (without erythrocytes) [31] was used to avoid interference between mialostatin-specific signals and host hemoglobin proteins of identical molecular weight. IrCL1 and IrCL3 signals were also detected in both the gut epithelium (cell wall) and the gut lumen (Figure 3B). The multiple IrCL1 bands corresponded to the proenzyme and mature enzyme forms [9].
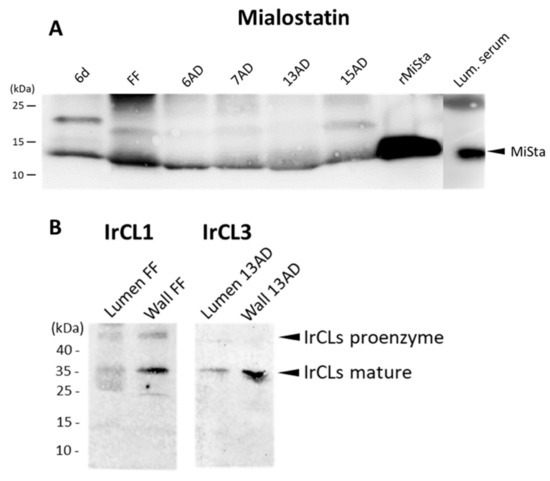
Figure 3.
Western blot analysis of mialostatin, IrCL1, and IrCL3 in the tick midgut. (A) Tick midgut wall tissue extracts from various stages of tick feeding and midgut lumina from fully fed ticks were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Mialostatin was labeled with a mouse monoclonal antibody and its signal detected using a fluorescently labeled secondary antibody. (B) Tick midgut wall and midgut lumen homogenates from fully fed ticks were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with α-IrCL1 and α-IrCL3 rabbit polyclonal antibodies. Goat α-rabbit IgG Alexa 488 fluorescent secondary antibody was used to visualize protein bands using ChemiDoc MP imager. 6d—sixth day of feeding; FF—fully fed; 6, 7, 13, 15 AD—days post detachment from the host. Lum. serum—luminal fluid from ticks fed on erythrocyte-free serum; rMista—recombinant mialostatin. Full view of presented Western blots can be found in the Supplementary Materials, Figures S2–S4.
2.4. Mialostatin Inhibits Blood-Protein Digestion Catalyzed by Tick Gut Cysteine Cathepsins
In tick gut tissue, cysteine cathepsins play a critical role in the acidic degradation of the two most abundant host blood proteins, hemoglobin and serum albumin. In particular, cathepsin L is involved in the initial phase of the degradation pathway, which is continued by the action of cathepsins B and C [5,6]. We evaluated the effect of mialostatin on the in vitro degradation of hemoglobin and serum albumin by the proteolytically active extract of I. ricinus gut tissue (limited to cysteine proteases by treatment with inhibitors of other protease classes). Both blood proteins were digested at optimal acidic pH, and SDS-PAGE analysis demonstrated highly efficient degradation of these substrates (Figure 4A,B). These processes were effectively blocked by mialostatin in a dose-dependent manner, with complete inhibition at a low nanomolar concentration of mialostatin. A similar effect was achieved by adding E-64, a small molecule general inhibitor of cysteine cathepsins. Further, we tested the stability of mialostatin exposed to the complex proteolytic environment of the gut tissue extract (Figure 4C), which revealed that mialostatin was generally stable and showed only partial degradation over long-term treatment. In summary, the blood protein digestion catalyzed by cysteine cathepsins of I. ricinus can be effectively controlled by mialostatin under native-like conditions.
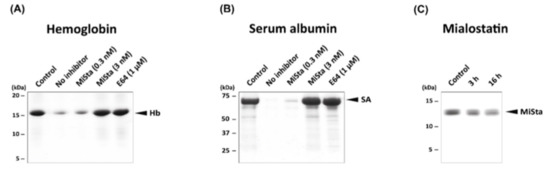
Figure 4.
Blood protein digestion with tick gut proteases is inhibited by mialostatin. Hemoglobin (A) and serum albumin (B) were digested in vitro with I. ricinus gut tissue extracts in the presence and absence of mialostatin. Blood protein substrate (5 µg of hemoglobin or 10 µg of serum albumin) was incubated with 0.4 µg gut tissue extract of cysteine proteases at pH 3.6 for 16 h. The extract was pre-incubated with mialostatin (MiSta) or the general cysteine protease inhibitor E-64 at the indicated concentrations prior to initiation of digestion. The digests were subjected to Tricine-SDS-PAGE (A) or Laemmli-SDS-PAGE (B) and visualized by protein staining. The hemoglobin (Hb) and serum albumin (SA) substrates are marked; the non-digested control is indicated. (C) Proteolytic stability of mialostatin in the gut tissue extract. Mialostatin (5 µg) was incubated with 0.4 µg gut extract protein under the same conditions as in (A,B), subjected to Tricine-SDS-PAGE, and visualized by protein staining. Mialostatin (MiSta) is marked; the non-digested control is indicated.
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis and Three-Dimensional Structure of Mialostatin and Its Reactive Site
Phylogenetic analysis clearly demonstrated that mialostatin belongs to the cystatin superfamily. According to the maximum likelihood method, the tick cystatin phylogenetic tree contained three separate prostriate clades (Figure 5A and Figure S1). As shown in the simplified tree in Figure 5A, mialostatin fell into a strongly supported group with four other cystatins from the genus Ixodes. This clade was distant from other clades, including the recently described iristatin [32] and previously characterized sialostatins L and L2 [33,34]. In general, tick cystatins cluster into several clades specific for either prostriate, metastriate, or argasid tick species, suggesting fast evolution of cystatin genes in ticks. The full phylogenetic tree presented in Figure S1 shows strong bootstrap support for smaller clades, but the topology is less clear closer to the root of the tree. The analysis shows mialostatin as a new distinct Ixodes cystatin consistent with its presumed major role in the midgut, as most previously characterized cystatins from Ixodes spp. are of salivary origin.
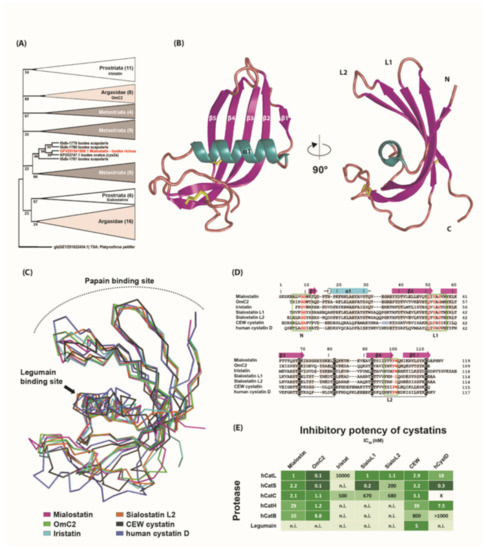
Figure 5.
Crystal structure of mialostatin and its comparison with other family 2 cystatins. (A) Molecular phylogenetic analysis (maximum likelihood model) of secreted tick cystatins. Simplified consensus tree based on the maximum likelihood method with 1000-repeat bootstrap support. All clades except the one with mialostatin (highlighted in red) are condensed. Cystatin from the mite Platynothrus peltifer was used as an outgroup. The tree with the highest log-likelihood (−4870, 9711) is shown. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 20% bootstrap replicates are collapsed. Numbers next to branches represent percentage of trees, in which the associated taxa clustered together during bootstrap analysis. For full tree see Figure S1. (B) The three-dimensional structure of mialostatin (PDB code 6ZTK) is shown as a cartoon representation colored by secondary structural elements (α1—cyan; β1-5—magenta). The N- and C-termini and two disulfide bridges, Cys69–Cys82 and Cys93–Cys113 (yellow sticks), are indicated. The hairpin loops L1 and L2 and the N-terminus of cystatins are involved in the binding of papain-type cysteine proteases. (C) Superposition of Cα traces of the mialostatin structure with five other cystatin structures including OmC2 from the soft tick O. moubata (PDB code 3L0R), iristatin from the hard tick I. ricinus (5O46), sialostatin L2 from the hard tick I. scapularis (3LH4), and representative vertebrate members of family 2 cystatins: chicken egg white (CEW) cystatin (1CEW) and human cystatin D (1RN7). The orientation of mialostatin is as in (B). Color coding of the structures and positions of the binding sites for papain-type cysteine proteases and legumains are indicated. (D) Structure-based sequence alignment of mialostatin with OmC2, iristatin, sialostatins L1 and L2, CEW cystatin, and human cystatin D. Residues identical to those of mialostatin are shaded grey. The secondary structural elements of mialostatin are depicted in magenta for β-strands and cyan for α-helices. The conserved disulfide bridges are indicated by the connecting black lines. Three regions involved in the interaction between cystatins and papain-type cysteine proteases are boxed in green and labeled (the region size was selected based on the predominant binding residues in the available complex structures); the consensus core residues are highlighted in red. The legumain binding site in CEW cystatin is highlighted in blue. Mature protein sequences were used in the alignment; residue numbering is according to mialostatin. (E) A comparison of the inhibitory potency of mialostatin with the other family 2 cystatins (shown in D) against various cysteine proteases including human papain-type cathepsins L to B (hCatL to hCatB) and mammalian legumains. IC50 values are presented [23,32,33,35,36,37] and displayed as a heat map (green scale); n.i.—not inhibited; x—no literature data are available.
The crystal structure of mialostatin was determined by molecular replacement using the structure of the tick cystatin OmC2 as a search model and refined using data to 1.55 Å resolution (Table S2). The hexagonal prism crystal form contained two molecules in the asymmetric unit with a solvent content of about 57%. All protein residues could be modeled into a well-defined electron density map with the exception of the first nine residues, which formed a flexible N-terminus (Ser1 to Gly9), and the last two C-terminal residues (Asn118, Val119) of chain A. The final model consisted of two mialostatin molecules, chains A and B, containing 108 and 110 residues, respectively. The root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) for superposition of the Cα atoms of the two chains was 0.14 Å, a low value within the range observed for different crystal structures of identical proteins.
Figure 5B shows the overall structure of mialostatin. The molecule adopts a typical cystatin fold (so called ‘hot dog’ fold [38]) characterized by a five-stranded twisted antiparallel β-sheet wrapped around a central α-helix. Mialostatin contains two conserved disulfide bridges connecting Cys69 with Cys82 and Cys93 with Cys113. Structural comparison and sequence alignment with other known cystatin structures clearly demonstrated that mialostatin belongs to family 2 of the cystatin superfamily (Figure 5C,D). The closest structural homolog of mialostatin was the salivary/gut cystatin OmC2 from the soft tick O. moubata [24] with the highest sequence identity (53%) and lowest RMSD for Cα (0.86 Å), followed by salivary homologs iristatin (41% identity, 1.56 Å RMSD) from the hard tick I. ricinus and sialostatins L1 (42%, 2.09 Å) and L2 (40%, 2.50 Å) from the hard tick I. scapularis [32,33]. Lower structural similarity was found with vertebrate members, namely human cystatin D (35%, 4.80 Å) and chicken egg white (CEW) cystatin (23%, 3.80 Å) (Figure 5D) [39,40].
The interaction between family 2 cystatins and papain-type cysteine proteases is mediated by three regions, the N-terminal segment and two hairpin loops L1 and L2, which form a tripartite wedge-shaped edge that binds to the enzyme active site cleft (Figure 5B,C) [40,41,42]. In mialostatin, the first part of the binding site is formed by the N-terminal segment around Gly10, which is the first visible residue in the electron density map. The conserved pair of glycines (Gly9, Gly10) provide conformational flexibility to the N-terminal segment to adopt an optimal conformation for target binding. The L1 loop (between β1 and β2) of mialostatin exposes the segment Gln51-Ile52-Val53-Ala54-Gly55 corresponding to the critical binding motif Gln-Xaa-Val-Xaa-Gly conserved in cystatins (Figure 5B). The L2 loop (between β3 and β4) is characterized in mialostatin and other cystatins, except sialostatins, by the presence of a conservative Pro101-Trp102 segment. To conclude, the structural analysis of mialostatin demonstrated a functionally competent reactive site against papain-type cysteine proteases. The binding motif for legumain-type cysteine proteases, which has been characterized in several cystatins (e.g., CEW cystatin), was absent in mialostatin (Figure 5C,D), consistent with the fact that mialostatin and other tick cystatins do not suppress legumain activity (Table 1, Figure 5E).
The inhibitory selectivity of the structurally analyzed cystatins is illustrated in Figure 5E. Mialostatin and OmC2 represent broad-spectrum inhibitors of papain-type cathepsins and are the most versatile in terms of their interactions of the analyzed tick cystatins. However, the other tick homologs displayed a distinct selectivity profile limited to effective inhibition of only some cathepsins. This may reflect structural changes in the conserved motifs on the L1 and L2 loops of iristatin and sialostatins, respectively, and in their N-terminal sequence potentially clashing with the partially occluded active sites of exopeptidases such as cathepsins B or H. Conversely, binding events to, for example, cathepsins B and C, can be supported by the electrostatic interactions formed by a positively charged basic patch (residues 12, 20, 106, 107) located at the reactive site of mialostatin and OmC2.
3. Discussion
Ixodes ricinus has previously been used as a model tick species to investigate and describe the complex intestinal digestive proteolytic mechanisms occurring in hematophagous arthropods. Blood proteins have been shown to be processed intracellularly by a multienzyme network of cysteine and aspartic proteases, with major involvement of cysteine cathepsin-type proteases from the CA clan [6]. However, previous studies have not investigated the regulation of digestive proteolysis, including the control mechanisms that protect the gut epithelium from excessive proteolysis and potential cell damage. Cystatins, naturally occurring cysteine protease inhibitors, are among the primary molecules of interest in the I. ricinus anti-proteolytic system, as they have been previously proposed to interact with digestive proteases in several other tick species [26,43,44].
In this study, we identified mialostatin as the first gut-associated cystatin to be identified in I. ricinus and present its comprehensive functional and structural characterization. Mialostatin was a potent inhibitor of I. ricinus digestive cysteine proteases of clan CA, covering both exopeptidases cathepsins B and C and endopeptidases cathepsins L1 and L3 (named IrCB, IrCC, IrCL1, and IrCL3, respectively). Its broad inhibitory selectivity is in clear contrast with Ixodes salivary cystatins such as sialostatins L1, L2, and iristatin, which have much narrower selectivity and mainly target endopeptidases [32,33,34]. On the other hand, similar broad anti-protease activity has been reported for OmC2 and partially also for OmC1 [23], cystatins present in the midgut of O. moubata soft ticks, or rBrBmcys2b from Rhipicephalus microplus [26] hard ticks. The 3D structural analysis identified mialostatin as a close homolog of OmC2 and provided a structural explanation for its binding selectivity through comparison of the architecture of the reactive site of mialostatin with other publicly available tick cystatin structures. Specifically, we highlight a combination of structural changes in three segments forming a tripartite wedge on mialostatin and OmC2 that slots into the cathepsin active site cleft. Based on structure-activity relationships and phylogenetic data, we propose that well-characterized mialostatin and OmC2 represent a new evolutionary subgroup of tick gut-associated cystatins that differ from salivary cystatins modulating host immune responses. Functional diversification of the cystatin superfamily is described in vertebrates [45]. It is likely that similar process occurs in ticks due to fast evolution of secreted proteins, therefore the phylogenetic tree reflects both localization and function of the cystatins. It is interesting to note that OmC2 also exhibits immunomodulatory properties, which correlate with its dual expression pattern in both the salivary glands and gut of O. moubata ticks, while OmC1 and mialostatin are expressed predominantly in tick midguts [23].
The biological role(s) of mialostatin in the tick gut can be inferred in the context of tick feeding behavior and associated physiological processes. Adult I. ricinus females engorge an enormous amount of host blood that exceeds the weight of the unfed tick more than a hundred-fold. The current model of the multienzyme digestive protease network responsible for blood protein processing is based mainly on investigations of the well-developed digestive midgut cells occurring in partially engorged I. ricinus females at the end of the slow feeding period at day 6–7 [13]. This period is followed by a rapid engorgement phase lasting 12–24 h, which accounts for about two-thirds of the total blood volume ingested before detachment from the host. Most blood proteins are used for vitellogenesis and massive egg production during several weeks off-host [5,46]. The molecular mechanisms underlying the associated protein turnover and long-term blood meal storage in the tick gut lumen remain unexplored, mainly due to technical limitations in studying fully fed females. Nevertheless, advances in the field and initial results led to the hypothesis that off-host digestion may include extracellular proteolysis of blood proteins in the gut lumen, which supports or replaces intracellular digestive proteolysis in the gut epithelium [47]. Despite the broad biochemical selectivity of mialostatin, its biological selectivity is limited due to compartmentalization in tick midgut cells. Our immunohistochemistry results demonstrated that mialostatin is localized to the same population of intracellular vesicles as IrCL3 on the 11th day post detachment, suggesting that mialostatin predominantly targets IrCL3. Mialostatin is stored in these vesicles in some cells even during tick feeding. Forming an inhibitory complex between mialostatin and IrCL3 might be relevant for intracellular trafficking of enzymatically inactive IrCL3 in tick gut cells. The localization of the mialostatin-IrCL3 complex to the surface of the large dense granules two weeks post detachment is probably associated with an excretion/secretion mechanism allowing translocation of the complex to the gut lumen. We hypothesize that IrCL3 might partially restore its proteolytic activity in the diluted contents of the gut lumen, where mialostatin can competitively interact with other secreted cysteine cathepsins including IrCL1 as the strongest mialostatin binder. This would enable cathepsin-mediated luminal proteolysis of blood proteins or the generation of antimicrobial peptides under general mialostatin control [48]. Luminal IrCL3 might also act as an anti-coagulation factor, as recently reported for a related R. microplus cathepsin L [49].
In conclusion, mialostatin is the first gut-associated cystatin characterized from I. ricinus at the functional and structural levels. Mialostatin localized to both digestive cells and the gut lumen, where it targets cathepsin L isoforms and regulates their activity during trafficking and processing of host blood proteins. As components of gut-associated proteolytic pathways, mialostatin and homologous cystatins in other tick species represent potential vaccination antigens for novel anti-tick interventions targeting tick reproduction. The vaccination efficacy of proteins derived from the tick gut (“concealed” antigens) in controlling tick infestations has already been successfully demonstrated [50], and new candidate antigens are increasingly in demand to combat tick infestations and to limit the global spread of tick-borne diseases.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ticks and Laboratory Animals
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the Animal Protection Law of the Czech Republic No. 246/1992 Sb., ethics approval No. 34/2018, and protocols approved by the responsible committee of the Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre of the Czech Academy of Sciences. Male and female adult I. ricinus ticks were collected by flagging in a forest near České Budějovice in the Czech Republic and then kept in 95% humidity chambers under a 12 h light/dark cycle at room temperature. Female BALB/c mice were purchased from Velaz (Prague, Czech Republic). Mice were housed in individually ventilated cages maintained under a 12 h light/dark cycle. Mice were used at 8–12 weeks of age. Laboratory rabbits were purchased from RABBIT CZ a. s. (Trhový Štěpánov, Czech Republic) and housed individually in cages in the animal facility of the Institute of Parasitology. Guinea pigs were bred and housed in cages in the animal facility of the Institute of Parasitology. All mammals were fed a standard pellet diet and provided with water ad libitum.
4.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Female I. ricinus ticks were fed on rabbits and allowed to mate with male ticks. Salivary glands, midguts, and ovaries from five ticks per time point were dissected on a petri dish under a drop of ice-cold DEPC-treated PBS. Total RNA was isolated from dissected tissue using the NucleoSpin RNA kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) and its quality checked by agarose gel electrophoresis before storing the RNA at −80 °C. cDNA was prepared from 500 ng of total RNA from independent biological triplicates using the Transcriptor High-Fidelity cDNA Synthesis Kit (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany). The cDNAs served as templates for subsequent quantitative expression analyses of mialostatin transcription by qRT-PCR. Samples were analysed with a LightCycler 480 (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany) using FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master Mix (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany). Reaction conditions over 50 cycles were as follows: denaturation, 95 °C/10 s; annealing, 60 °C/10 s; extension, 72 °C/10 s. Relative expression values were standardized to a reference gene, I. ricinus elongation factor 1 (ef1; GenBank: GU074828) [51,52,53], and normalized to the sample with the highest level of expression. The primers sequences for mialostatin and ef1 RT-PCR are shown in Table S3.
4.3. Mialostatin Cloning, Expression, Refolding, and Purification and Antibody Production
The full cDNA sequence of the gene encoding mialostatin was amplified using primers designed based on the GFVZ01041806.1 [28] transcript from NCBI GenBank. The primer sequences used for the final cloning of mialostatin are presented in Table S3. A pool of I. ricinus cDNA prepared from the salivary glands of female ticks fed for three and six days on rabbits was used as a template. The 372 base pair DNA fragment encoding mialostatin without a signal peptide and with an inserted ATG codon was cloned into a pET-17b vector (Novagen, Darmstadt, Germany) and transformed into Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3)pLysS (Novagen) for expression. Bacterial cultures were grown in LB medium with 100 µg/mL ampicillin and 34 µg/mL chloramphenicol to an OD600 of 0.8, when protein expression was induced by the addition of isopropyl 1-thio-β-D-galactopyranoside to a final concentration of 1 mM. Cultures were harvested after 2 h of incubation at 37 °C at 200 rpm shaking speed. Isolated inclusion bodies were dissolved in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride, 20 mM Tris, and 10 mM DTT, pH 8 for 1 h followed by centrifugation (10 min, 10,000× g) to remove undissolved impurities. Refolding was performed by rapid dilution in 160 × excess of 20 mM Tris and 300 mM NaCl, pH 8.5. The resulting refolded protein was purified by HiLoad Superdex 200 26/60 gel filtration chromatography and HiPrep Q FF 16/10 ion exchange chromatography. Endotoxin was removed using a detergent-based method. Purified recombinant mialostatin was used to raise antibodies in a mouse and rabbit as described previously [54,55]. The immunoglobulin (Ig) fraction of rabbit serum was obtained by caprylic acid precipitation of serum proteins as described previously [56]. Hybridoma cells were raised by fusing splenocytes from immunized mice and mouse myeloma SP 2/0-Ag14 cells. Monoclonal antibodies were produced in cell culture following the previously described protocol [55].
4.4. Preparation of Tick Gut Samples
I. ricinus midguts were dissected from female I. ricinus fed on laboratory guinea pigs (samples for proteolysis analysis and Western blotting) or from females’ membrane fed on erythrocyte-depleted blood serum (samples for mass spectrometry analysis) [5]. The gut contents were carefully removed without disrupting the epithelium, and the gut tissue was washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). For mass spectrometry analysis, the gut contents were processed as described previously [6]. Gut tissue extract (150 mg protein/mL) was prepared by homogenization of the pooled gut tissue in 0.1 M Na acetate pH 4.5, 1% CHAPS on ice. The extract was cleared by centrifugation (16,000× g, 10 min, 4 °C), filtered through Ultrafree MC 0.22 µm (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA), and stored at −80 °C.
4.5. Protease Inhibition Assays
Inhibition measurements were performed in triplicate in 96-well microplates (100 µL assay volume) at 37 °C. Recombinant mialostatin was preincubated with protease for 10 min followed by the addition of specific fluorogenic substrate (see Section 4.5.1, Section 4.5.2 and Section 4.5.3). The kinetics of product release were continuously monitored using an Infinite M1000 (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland) microplate fluorescence reader at 360 nm excitation and 465 nm emission wavelengths (for AMC-containing substrates) or at 320 nm excitation and 420 nm emission wavelengths (for Abz-containing substrate). IC50 values were determined from residual velocities using dose-response plots; nonlinear regression was fitted using GraFit software (Erithacus, East Grinstead, UK).
4.5.1. Inhibition of Proteases in Tick Gut Homogenates
To prevent interference of non-target proteases, homogenates (80 ng) were treated with specific low molecular weight inhibitors (final assay concentrations are indicated) including 1 µM pepstatin and 1 mM EDTA (against aspartic proteases and metalloproteases; all assays), 1 µM E-64 (against cathepsins L/B; cathepsin C assay), 1 µM CA-074 (against cathepsin B; cathepsin L assay), and 1 µM Z–Phe–Phe–DMK (against cathepsin L; cathepsin B assay) [6]. The assay substrates and buffers were as follows: 20 µM Z–Phe–Arg–AMC substrate and 0.1 M Na acetate pH 4.5 or 5.0 in the cathepsin L and L/B assays, respectively; 20 µM Z–Arg–Arg–AMC substrate and 0.1 M MES pH 6.5 in the cathepsin B assay; 20 µM Gly–Arg–AMC substrate in 0.1 M Na acetate pH 5.5, 25 mM NaCl in the cathepsin C assay; all assay buffers contained 2.5 mM DTT and 0.1% PEG 1500.
4.5.2. Inhibition Assays of Recombinant Tick Proteases
The assay conditions for individual proteases were as follows: 1.2 nM IrCD1 and 20 μM Abz–Lys–Pro–Ala–Glu–Phe–Nph–Ala–Leu substrate in 0.1 M Na acetate pH 4.0; 1.25 nM IrAE and 20 µM Z–Ala–Ala–Asn–AMC substrate in 0.1 M MES pH 5.0, 2.5 mM DTT, 1 µM E-64; 0.1 nM IrCL1 or 20 pM IrCL3 and 20 µM Z–Phe–Arg–AMC substrate in 0.1 M Na acetate pH 4.5, 2.5 mM DTT; all assay buffers contained 0.1% PEG 1500. The tick proteases were prepared as described elsewhere [7,9,10,57,58].
4.5.3. Inhibition Assays of Human Proteases
Inhibition assays were performed following the same protocol used in our previous publications [24,32]. The assay conditions for individual proteases were as follows: 35 pM cathepsin B or 33 pM cathepsin L or 5 nM cathepsin K and 250 µM Z–Leu–Arg–AMC substrate in 0.1 M Na acetate pH 5.5, 0.1 M NaCl; 350 pM cathepsin S and 250 µM Z–Val–Val–Arg–AMC substrate in the same buffer; 0.5 nM cathepsin C and 250 µM Gly-Arg-AMC substrate in the same buffer; 20 nM cathepsin H and 40 µM Z–Leu–Arg–AMC substrate in 0.1 M Na/K phosphate pH 6.8; all assay buffers contained 1 mM EDTA, 2.5 mM DTT, and 0.01% Triton X-100. The human proteases were purchased from Merck (Kenilworth, NJ, USA) and Biomol (Hamburg, Germany).
4.6. Protein Digestion Assay
Digestion of 10 µg human serum albumin (Sigma Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), 5 µg bovine hemoglobin (Sigma Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), and 5 µg of mialostatin was performed with the tick gut tissue homogenate (0.4 µg protein) in 50 mM Na citrate pH 3.6, 2.5 mM DTT, in a total volume of 100 µL for 16 h at 26 °C. In the albumin and hemoglobin digestion assays, the homogenate was preincubated (15 min) in the same buffer with non-cysteine protease inhibitors: 1 µM pepstatin, 100 µM Pefablock, and 1 mM EDTA. The albumin digest was resolved with Laemmli SDS-PAGE gels (15%) and the hemoglobin and mialostatin digests by Tricine-SDS-PAGE gels (16% T/6% C) containing 6 M urea [59]. Electrophoresis was performed under reducing conditions, and protein was stained with Coomassie Blue G250.
4.7. Reducing SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
Tick tissue homogenates were separated by reducing SDS-PAGE using 4–20% Mini-PROTEAN® TGX™ Precast Protein Gels (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). Separated protein loads were visualized using TGX stain-free chemistry in the ChemiDoc MP imager (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). After protein load documentation, separated proteins were electro-transferred from the gel onto an Immun-Blot® LF PVDF membrane using the Trans-Blot Turbo system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Prior to Western blot analyses, membranes were blocked with 3% non-fat milk in PBS with 0.05% Tween 20 (PBS-Tween) for 1 h at room temperature. Blocked membranes were incubated with the rabbit Ig fraction of α-IrCL1 or α-IrCL3 polyclonal sera diluted 1:1000 in PBS-Tween containing 1% milk. Goat anti-rabbit IgG Alexa 488-labeled antibody (1:1000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used as a secondary antibody. For mialostatin detection, α-mialostatin monoclonal antibody (1:30) diluted in in PBS-Tween containing 1% milk and the goat anti-mouse Alexa 546-labeled antibody (1:1000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were used. In between individual steps of the whole procedure, membranes were washed 3 × 5 min in PBS-Tween on a rotating shaker platform at room temperature. Labeling with primary antibodies was performed on a rotating shaker platform at 4 °C overnight. Labeling with secondary antibodies was performed on a rotating shaker platform at room temperature for 1 h. Fluorescent signals were again visualized using the ChemiDoc MP imager and analyzed using Image Lab Software (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
Samples of I. ricinus gut tissues were prepared as described previously [11]. Briefly, the gut was dissected from adult females at specific days of feeding on the host and days post-attachment and fixed in 4% formaldehyde and 0.1% glutaraldehyde solution, washed with PBS, dehydrated using ascending ethanol dilutions, then infiltrated with LR White resin (London Resin Company, Stansted, UK) and polymerized. Semi-thin sections (0.5 µm) were blocked with 1% BSA and 1% milk in PBS-Tween (0.3% (v/v) Tween 20) for 45 min. Immunohistochemical double-staining was performed gradually, with the initial antibody labeling of the respective intestinal protease (I. ricinus cathepsin L1 IrCL1 [9]; cathepsin L3 IrCL3; cathepsin B IrCB [11]) subsequently followed with immunolabeling of mialostatin. First, semi-thin tick gut tissue sections were blocked with blocking solution (1% BSA, 1% milk solution in PBS-Tween) for 45 min at room temperature. For protease immunostaining, sections were first labeled (4 °C overnight) with primary antibodies: (i) rabbit α-IrCL1 affinity-purified polyclonal serum diluted 1:5 in PBS-Tween; (ii) rabbit α-IrCB affinity-purified polyclonal serum diluted 1:5 in PBS-Tween; (iii) isolated Ig fraction of α-IrCL3 polyclonal serum diluted 1:5 (IrCL1) in PBS-Tween. After washing 3 × 5 min in PBS-Tween, sections were subsequently labeled with Alexa Fluor® 647 goat α-rabbit secondary antibody (diluted 1:500 in PBS-Tween; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Sections were subsequently used for mialostatin immunolabeling: sections were once again washed 3 × 5 min in PBS-Tween and incubated with mouse α-mialostatin monoclonal antibody diluted 1:50 in PBS-Tween. Incubation was performed in a humid chamber at room temperature for 90 min. Sections were once again washed (3 × 5 min in PBS-Tween) and incubated with secondary goat α-mouse Alexa Fluor® 488 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) diluted 1:500 in PBS-Tween for 1 h at room temperature. Finally, all sections were washed in PBS-Tween and counterstained with DAPI (4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole; 2.5 μg/mL; Sigma Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) for 7 min, washed again with PBS-Tween, mounted in Fluoromount medium (Sigma Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), and examined with the IX83 confocal microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Images were processed with FluoView FV3000 software (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
4.9. Evolutionary Analysis by the Maximum Likelihood Method
The evolutionary history was inferred using the maximum likelihood method and JTT matrix-based model [60]. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1000 replicates was taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed [61]. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 20% bootstrap replicates were collapsed. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches [61]. Initial tree(s) for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying Neighbor-Join and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the JTT model and then selecting the topology with the superior log-likelihood value. This analysis involved 71 amino acid sequences. There were 108 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X [62].
4.10. Crystallization and Data Collection
Screening for crystallization conditions was performed using the JCSG-plus kit (Molecular Dimensions, Sheffield, UK) by the sitting drop vapor diffusion technique. Preliminary crystals of mialostatin were obtained in 0.1 M citric acid pH 3.5, 0.8 M ammonium sulfate. Optimal crystals were prepared at 18 °C using the hanging drop vapor diffusion technique in 15-well NeXtal plates (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The crystallization drop consisted of 2 μL of the mialostatin protein solution (12.5 mg/mL in 10 mM Tris buffer, pH 8.0) and 1 μL of the precipitant solution equilibrated over a reservoir containing 300 µL precipitant solution (0.1 M citric acid pH 4.0, 0.8 M ammonium sulfate). Crystals shaped as hexagonal prisms reached their final size of 0.6 × 0.3 × 0.3 mm within 1 month. For data collection, crystals were soaked in reservoir solution supplemented with 20% glycerol and flash cooled in liquid nitrogen. Diffraction data at 100 K were collected using a BL14.1 beamline operated by the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) at the BESSY II electron storage ring (Berlin-Adlershof, Germany) [63] and processed using the XDS suite of programs [64]. Crystals exhibited the symmetry of space group P6222 and contained two molecules in the asymmetric unit. Crystal parameters and data collection statistics are shown in Table S2.
4.11. Structure Determination
The phase problem was solved by molecular replacement using Molrep [65] from the CCP4 package [66]. The search model was derived from the structure of cystatin OmC2 (PDB code 3L0R) [24] sharing 53% sequence identity with mialostatin. Model refinement was carried out using REFMAC 5.8 [66] from the CCP4 package with 5% of the reflections reserved for cross-validation. Manual building and addition of water molecules was performed using Coot [67]. The quality of the final model was validated with Molprobity [68]. Final refinement statistics are given in Supporting Information Table S2. Figures showing structural representations were prepared with the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (Schrödinger, New York, NY, USA). Atomic coordinates and structure factors were deposited in the PDB under accession code 6ZTK.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were performed in biological triplicate. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) in all graphs. Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA were used to calculate statistical differences between two or more groups, respectively. Statistically significant results are marked: * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; **** p ≤ 0.0001.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms22105371/s1, Figure S1: The phylogenetic tree of 71 cystatins from both Ixodidae and Argasidae tick species, Figure S2: Detection of mialostatin in midgut of blood fed ticks, Figure S3: Detection of mialostatin in midgut of serum fed ticks, Figure S4: Detection of I. ricinus cathepsins L in midgut of blood fed ticks, Table S1: Identification of mialostatin by mass spectrometry, Table S2: X-ray data collection and refinement statistics, Table S3: Primer sequences.
Author Contributions
J.K., M.B., J.C., D.S., M.M. and M.K. designed and performed the experiments, performed the analyses, and wrote the manuscript; V.U., P.Ř. and H.L. designed and performed the experiments and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (No. 19-382 07247S to M.K.), the project CePaViP OPVVV (No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000759 to M.K.) from the European Regional Development Fund and institutional project RVO 60077344 to M.K., M.B., P.Ř., and M.M. were supported by project ChemBioDrug CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000729 from the European Regional Development Fund (OP RDE) and the institutional project RVO 61388963. M.M., D.S. and V.U. were supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (No. 21-08826S). J.C. was supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (No. 19-14704Y).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the Animal Protection Law of the Czech Republic No. 246/1992 Sb., ethics approval No. 34/2018, and protocols approved by the responsible committee of the Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre of the Czech Academy of Sciences.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are either contained within the manuscript and supporting information or available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jiří Brynda and Martin Hubálek for technical assistance with crystallography and mass spectrometry analysis, respectively. Diffraction data were collected on BL14.1 at the BESSY II electron storage ring operated by the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin. The funders had no role in the design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lindgren, E.; Talleklint, L.; Polfeldt, T. Impact of climatic change on the northern latitude limit and population density of the disease-transmitting European tick Ixodes ricinus. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Christie, J.; Köster, L.; Du, A.; Yao, C. Emerging Human Babesiosis with “Ground Zero” in North America. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M. Biology of Ticks, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, F.A.; Lins, U.; Bechara, G.H.; Oliveira, P.L. Tracing heme in a living cell: Hemoglobin degradation and heme traffic in digest cells of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojka, D.; Pytelková, J.; Perner, J.; Horn, M.; Konvičková, J.; Schrenková, J.; Mareš, M.; Kopáček, P. Multienzyme degradation of host serum albumin in ticks. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, M.; Nussbaumerová, M.; Šanda, M.; Kovářová, Z.; Srba, J.; Franta, Z.; Sojka, D.; Bogyo, M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Kopáček, P.; et al. Hemoglobin Digestion in Blood-Feeding Ticks: Mapping a Multipeptidase Pathway by Functional Proteomics. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojka, D.; Hajdušek, O.; Dvořák, J.; Sajid, M.; Franta, Z.; Schneider, E.L.; Craik, C.S.; Vancová, M.; Burešová, V.; Bogyo, M.; et al. IrAE—An asparaginyl endopeptidase (legumain) in the gut of the hard tick Ixodes ricinus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Frantová, H.; Bartošová, P.; Horn, M.; Váchová, J.; O’Donoghue, A.J.; Eroy-Reveles, A.A.; Craik, C.S.; Knudsen, G.M.; et al. Characterization of Gut-associated Cathepsin D Hemoglobinase from Tick Ixodes ricinus (IrCD1). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21152–21163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franta, Z.; Sojka, D.; Frantova, H.; Dvorak, J.; Horn, M.; Srba, J.; Talacko, P.; Mares, M.; Schneider, E.; Craik, C.S.; et al. IrCL1—The haemoglobinolytic cathepsin L of the hard tick, Ixodes ricinus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Horn, M.; Hajdušek, O.; Caffrey, C.R.; Mares, M.; Kopáček, P. Profiling of proteolytic enzymes in the gut of the tick Ixodes ricinus reveals an evolutionarily conserved network of aspartic and cysteine peptidases. Parasites Vectors 2008, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franta, Z.; Frantová, H.; Konvičková, J.; Horn, M.; Sojka, D.; Mareš, M.; Kopáček, P. Dynamics of digestive proteolytic system during blood feeding of the hard tick Ixodes ricinus. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, D.; Francischetti, I.M.B.; Calvo, E.; Kotsyfakis, M. Cysteine Proteases from Bloodfeeding Arthropod Ectoparasites. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 712, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Horn, M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Mareš, M.; Kopáček, P. New insights into the machinery of blood digestion by ticks. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffrey, C.R.; Goupil, L.; Rebello, K.M.; Dalton, J.P.; Smith, D. Cysteine proteases as digestive enzymes in parasitic helminths. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0005840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novinec, M.; Lenarčič, B.; Turk, B. Cysteine Cathepsin Activity Regulation by Glycosaminoglycans. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, V.; Bode, W. The cystatins: Protein inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1991, 285, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Waller, M.; Barrett, A.J.; Bateman, A. MEROPS: The database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D503–D509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Valdés, J.J.; Kotsyfakis, M. The role of cystatins in tick physiology and blood feeding. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmelař, J.; Kotál, J.; Langhansová, H.; Kotsyfakis, M. Protease Inhibitors in Tick Saliva: The Role of Serpins and Cystatins in Tick-host-Pathogen Interaction. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, L.A.; Kotál, J.; Bensaoud, C.; Chmelař, J.; Kotsyfakis, M. Small protease inhibitors in tick saliva and salivary glands and their role in tick-host-pathogen interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.A.; Sasaki, S.D.; Tanaka, A.S. Bmcystatin, a cysteine proteinase inhibitor characterized from the tick Boophilus microplus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parizi, L.F.; Githaka, N.W.; Acevedo, C.; Benavides, U.; Seixas, A.; Logullo, C.; Konnai, S.; Ohashi, K.; Masuda, A.; Vaz, I.D.S. Sequence characterization and immunogenicity of cystatins from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunclová, L.; Horn, M.; Vancová, M.; Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Mares, M.; Kopáček, P. Two secreted cystatins of the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata: Differential expression pattern and inhibitory specificity. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salát, J.; Paesen, G.C.; Řezáčová, P.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Kovářová, Z.; Šanda, M.; Majtán, J.; Grunclová, L.; Horká, H.; Andersen, J.F.; et al. Crystal structure and functional characterization of an immunomodulatory salivary cystatin from the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavašnik-Bergant, T.; Vidmar, R.; Sekirnik, A.; Fonović, M.; Salát, J.; Grunclová, L.; Kopáček, P.; Turk, B. Salivary Tick Cystatin OmC2 Targets Lysosomal Cathepsins S and C in Human Dendritic Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parizi, L.F.; Sabadin, G.A.; Alzugaray, M.F.; Seixas, A.; Logullo, C.; Konnai, S.; Ohashi, K.; Masuda, A.; da Sliva Vaz, I., Jr. Rhipicephalus microplus and Ixodes ovatus cystatins in tick blood digestion and evasion of host immune response. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, C.K.; Parizi, L.F.; Sabadin, G.A.; Costa, E.P.; Romeiro, N.C.; Isezaki, M.; Githaka, N.W.; Seixas, A.; Logullo, C.; Konnai, S.; et al. Molecular and structural characterization of novel cystatins from the taiga tick Ixodes persulcatus. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrier, N.P.; Couton, M.; Voordouw, M.J.; Rais, O.; Durand-Hermouet, A.; Hervet, C.; Plantard, O.; Rispe, C. Whole body transcriptomes and new insights into the biology of the tick Ixodes ricinus. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsyfakis, M.; Schwarz, A.; Erhart, J.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Tissue- and time-dependent transcription in Ixodes ricinus salivary glands and midguts when blood feeding on the vertebrate host. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep09103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramaro, W.J.; Revets, D.; Hunewald, O.E.; Sinner, R.; Reye, A.L.; Muller, C.P. Integration of Ixodes ricinus genome sequencing with transcriptome and proteome annotation of the naïve midgut. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, J.; Provazník, J.; Schrenková, J.; Urbanová, V.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Kopáček, P. RNA-seq analyses of the midgut from blood- and serum-fed Ixodes ricinus ticks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotál, J.; Stergiou, N.; Buša, M.; Chlastáková, A.; Beránková, Z.; Řezáčová, P.; Langhansová, H.; Schwarz, A.; Calvo, E.; Kopecký, J.; et al. The structure and function of Iristatin, a novel immunosuppressive tick salivary cystatin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsyfakis, M.; Horka, H.; Salat, J.; Andersen, J.F. The crystal structures of two salivary cystatins from the tick Ixodes scapularis and the effect of these inhibitors on the establishment of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in a murine model. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsyfakis, M.; Sá-Nunes, A.; Francischetti, I.M.B.; Mather, T.N.; Andersen, J.F.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Antiinflammatory and Immunosuppressive Activity of Sialostatin L, a Salivary Cystatin from the Tick Ixodes scapularis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26298–26307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbin, M.; Hall, A.; Grubb, A.; Mason, R.W.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Abrahamson, M. Structural and functional characterization of two allelic variants of human cystatin D sharing a characteristic inhibition spectrum against mammalian cysteine proteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23156–23162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, A.; Brown, M.A.; Kembhavi, A.A.; Nicklin, M.J.H.; Sayers, C.A.; Sunter, D.C.; Barrett, A.J. Cystatin, a protein inhibitor of cysteine proteinases. Improved purification from egg white, characterization, and detection in chicken serum. Biochem. J. 1983, 211, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiljeva, O.; Dolinar, M.; Turk, V.; Turk, B. Recombinant Human Cathepsin H Lacking the Mini Chain Is an Endopeptidase. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 13522–13528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidugu, L.S.; Maity, K.; Ramaswamy, K.; Surolia, N.; Suguna, K. Analysis of proteins with the ’Hot dog’ fold: Prediction of function and identification of catalytic residues of hypothetical proteins. BMC Struct. Biol. 2009, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Fernandez, M.; Liang, Y.-H.; Abrahamson, M.; Su, X.-D. Crystal Structure of Human Cystatin D, a Cysteine Peptidase Inhibitor with Restricted Inhibition Profile. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18221–18228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, W.; Engh, R.; Musil, D.; Thiele, U.; Huber, R.; Karshikov, A.; Brzin, J.; Kos, J.; Turk, V. The 2.0 A X-ray crystal structure of chicken egg white cystatin and its possible mode of interaction with cysteine proteinases. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, V.; Stoka, V.; Vasiljeva, O.; Renko, M.; Sun, T.; Turk, B.; Turk, D. Cysteine cathepsins: From structure, function and regulation to new frontiers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, S.K.; Seal, A. Structural Dynamics Investigation of Human Family 1 & 2 Cystatin-Cathepsin L1 Interaction: A Comparison of Binding Modes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, J. Characterization of a secreted cystatin from the tick Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 67, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; da Rocha, L.A.; Torquato, R.J.; Junior, I.D.S.V.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Tanaka, A.S. A novel type 1 cystatin involved in the regulation of Rhipicephalus microplus midgut cysteine proteases. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordiš, D.; Turk, V. Phylogenomic analysis of the cystatin superfamily in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopáček, P.; Perner, J.; Sojka, D.; Šíma, R.; Hajdušek, O. Molecular Targets to Impair Blood Meal Processing in Ticks. In Ectoparasites; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 8, pp. 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, J.; Ayala-Chavez, C.; Sharma, A.; Pham, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Gulia-Nuss, M. Blood Digestion by Trypsin-Like Serine Proteases in the Replete Lyme Disease Vector Tick, Ixodes scapularis. Insects 2020, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, C.E.; Fogaça, A.C.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Angeli, C.B.; Belmonte, R.; Almeida, I.C.; Miranda, A.; Miranda, M.T.M.; Tanaka, A.S.; Braz, G.R.; et al. Characterization of proteinases from the midgut of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus involved in the generation of antimicrobial peptides. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.A.; Tirloni, L.; Torquato, R.; Tanaka, A.; Pinto, A.F.M.; Diedrich, J.K.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Seixas, A.; Termignoni, C. Blood anticlotting activity of a Rhipicephalus microplus cathepsin L-like enzyme. Biochimie 2019, 163, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Mallon, A. Developing Anti-tick Vaccines. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1404, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhof, A.M.; Balk, J.A.; Postigo, M.; Jongejan, F. Selection of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR studies in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Rhipicephalus appendiculatus ticks and determination of the expression profile of Bm86. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanová, V.; Hartmann, D.; Grunclová, L.; Šíma, R.; Flemming, T.; Hajdušek, O.; Kopáček, P. IrFC—An Ixodes ricinus injury-responsive molecule related to Limulus Factor C. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vechtova, P.; Fussy, Z.; Cegan, R.; Sterba, J.; Erhart, J.; Benes, V.; Grubhoffer, L. Catalogue of stage-specific transcripts in Ixodes ricinus and their potential functions during the tick life-cycle. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopácek, P.; Zdychová, J.; Yoshiga, T.; Weise, C.; Rudenko, N.; Law, J.H. Molecular cloning, expression and isolation of ferritins from two tick species--Ornithodoros moubata and Ixodes ricinus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, J.G.R. Monoclonal Hybridoma Antibodies: Techniques and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 239. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, C.; Callegaro, L.; Lanza, E.; Ferrone, S. Purification of IgG monoclonal antibody by caprylic acid precipitation. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Šíma, R.; Konvičková, J.; Perner, J.; Kopáček, P.; Sojka, D. Multiple legumain isoenzymes in ticks. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hánová, I.; Brynda, J.; Houštecká, R.; Alam, N.; Sojka, D.; Kopáček, P.; Marešová, L.; Vondrášek, J.; Horn, M.; Schueler-Furman, O.; et al. Novel Structural Mechanism of Allosteric Regulation of Aspartic Peptidases via an Evolutionarily Conserved Exosite. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 318–329.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schagger, H. Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.T.; Taylor, W.R.; Thornton, J.M. The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Bioinformatics 1992, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, U.; Darowski, N.; Fuchs, M.R.; Förster, R.; Hellmig, M.; Paithankar, K.S.; Pühringer, S.; Steffien, M.; Zocher, G.; Weiss, M.S. Facilities for macromolecular crystallography at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2012, 19, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabsch, W. Integration, scaling, space-group assignment and post-refinement. Acta Cryst. Sect. D Biol. Cryst. 2010, 66, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagin, A.; Teplyakov, A. Molecular replacement with MOLREP. Int. Tables Crystallogr. 2012, 66, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, M.D.; Ballard, C.C.; Cowtan, K.D.; Dodson, E.J.; Emsley, P.; Evans, P.R.; Keegan, R.M.; Krissinel, E.B.; Leslie, A.G.W.; McCoy, A.; et al. Overview of theCCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Cryst. Sect. D Biol. Cryst. 2011, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development ofCoot. Acta Cryst. Sect. D Biol. Cryst. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., 3rd; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).