Calmodulin Supports TRPA1 Channel Association with Opioid Receptors and Glutamate NMDA Receptors in the Nervous Tissue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
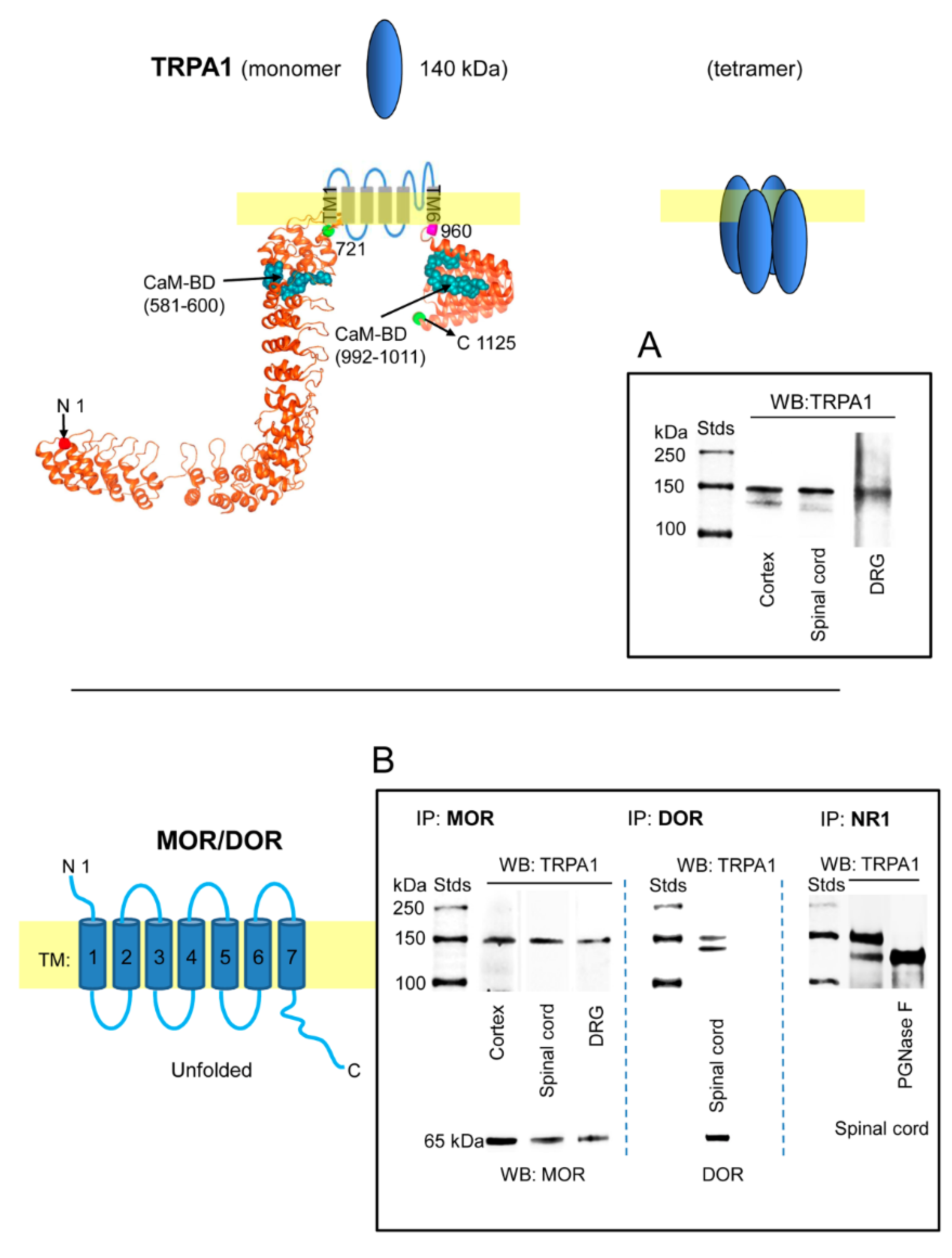
2.1. TRPA1 Channel Association with MORs, DORs and NR1 Subunits, in the Cerebral Cortex, Spinal Cord and DRGs. Effect of Pharmacological Interventions
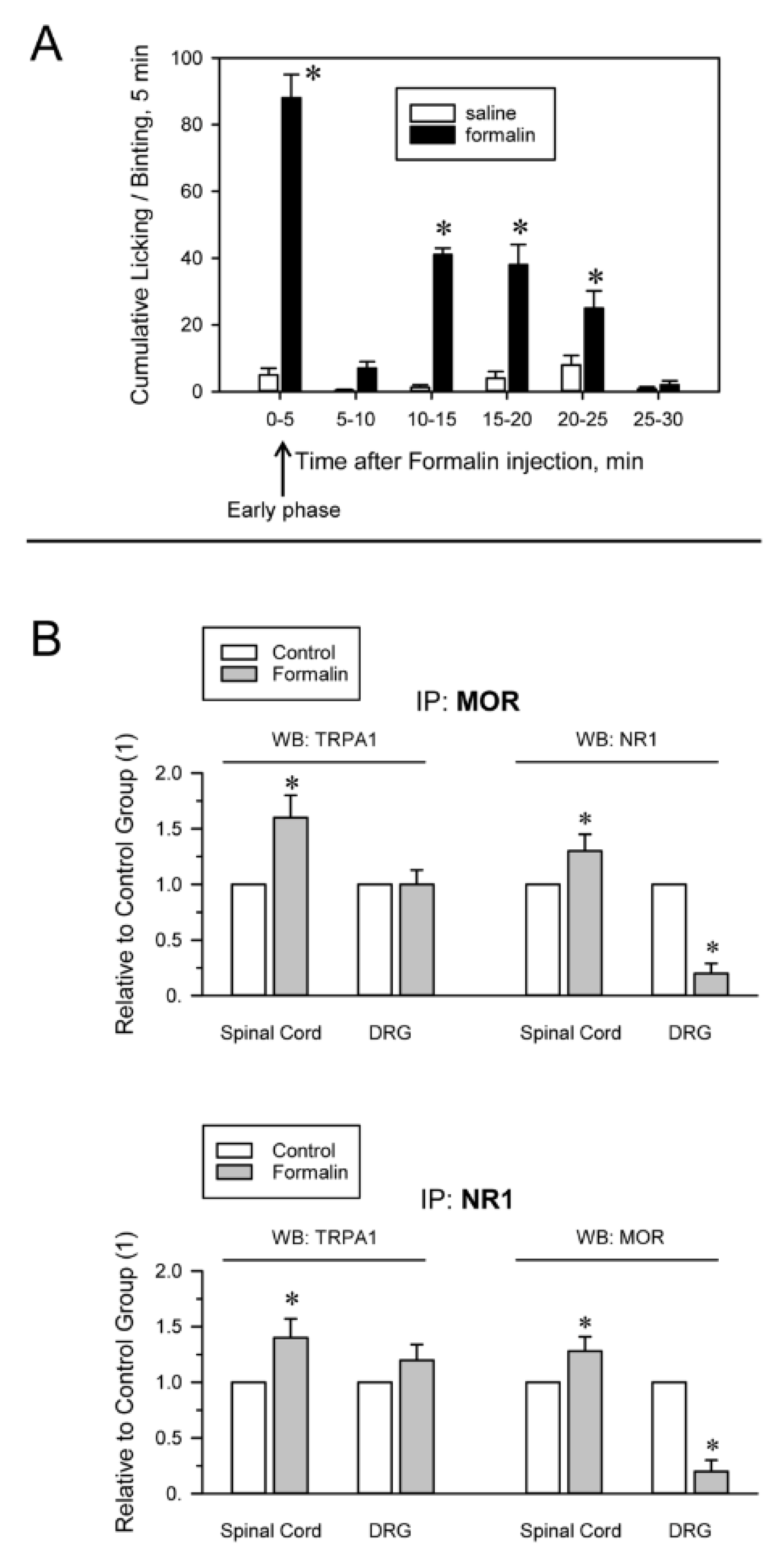
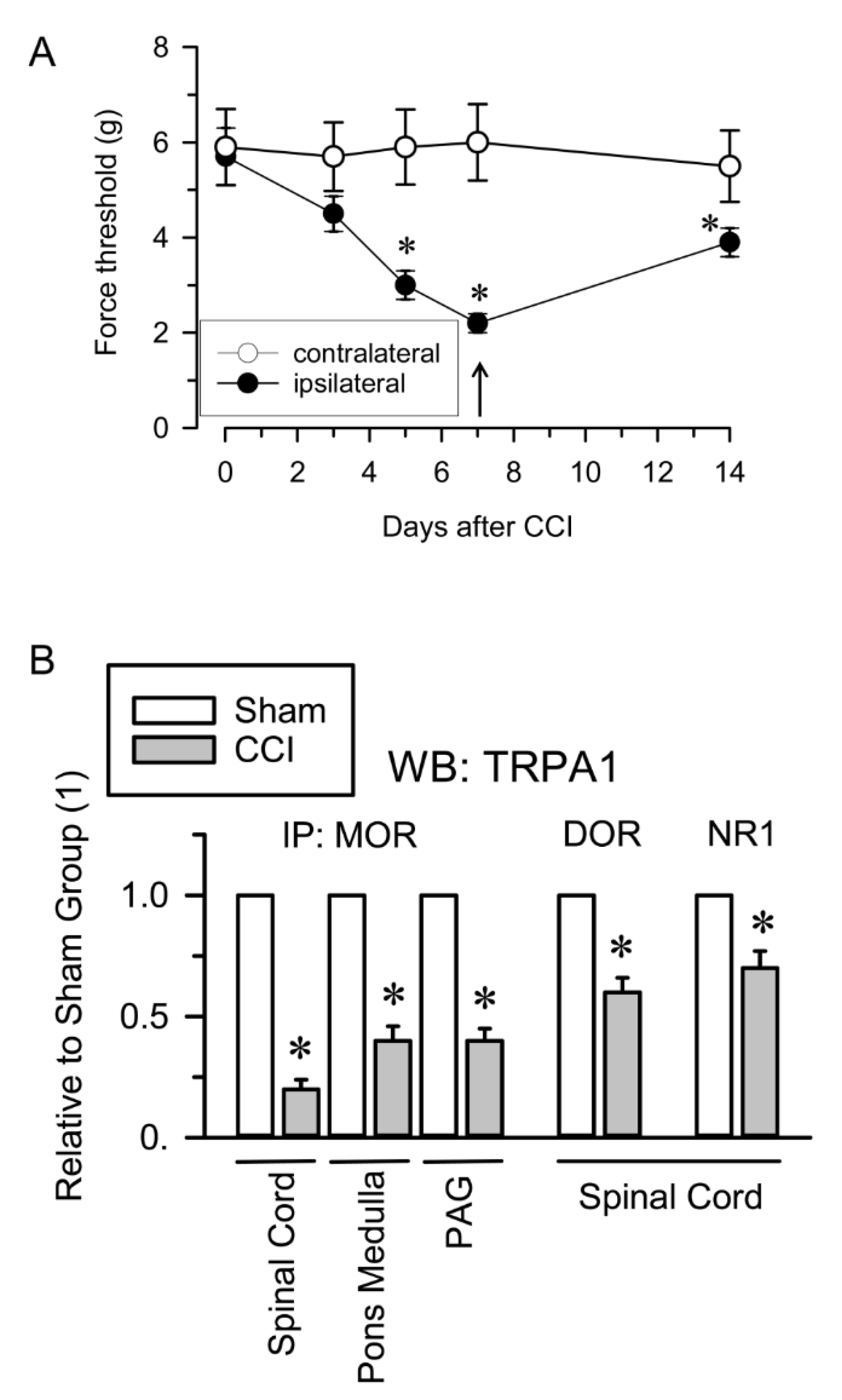
2.2. Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain Alters TRPA1 Channel Association with MORs and NMDARs
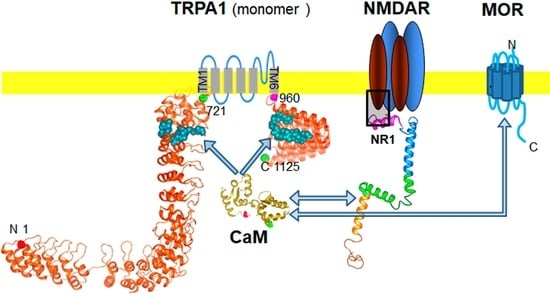
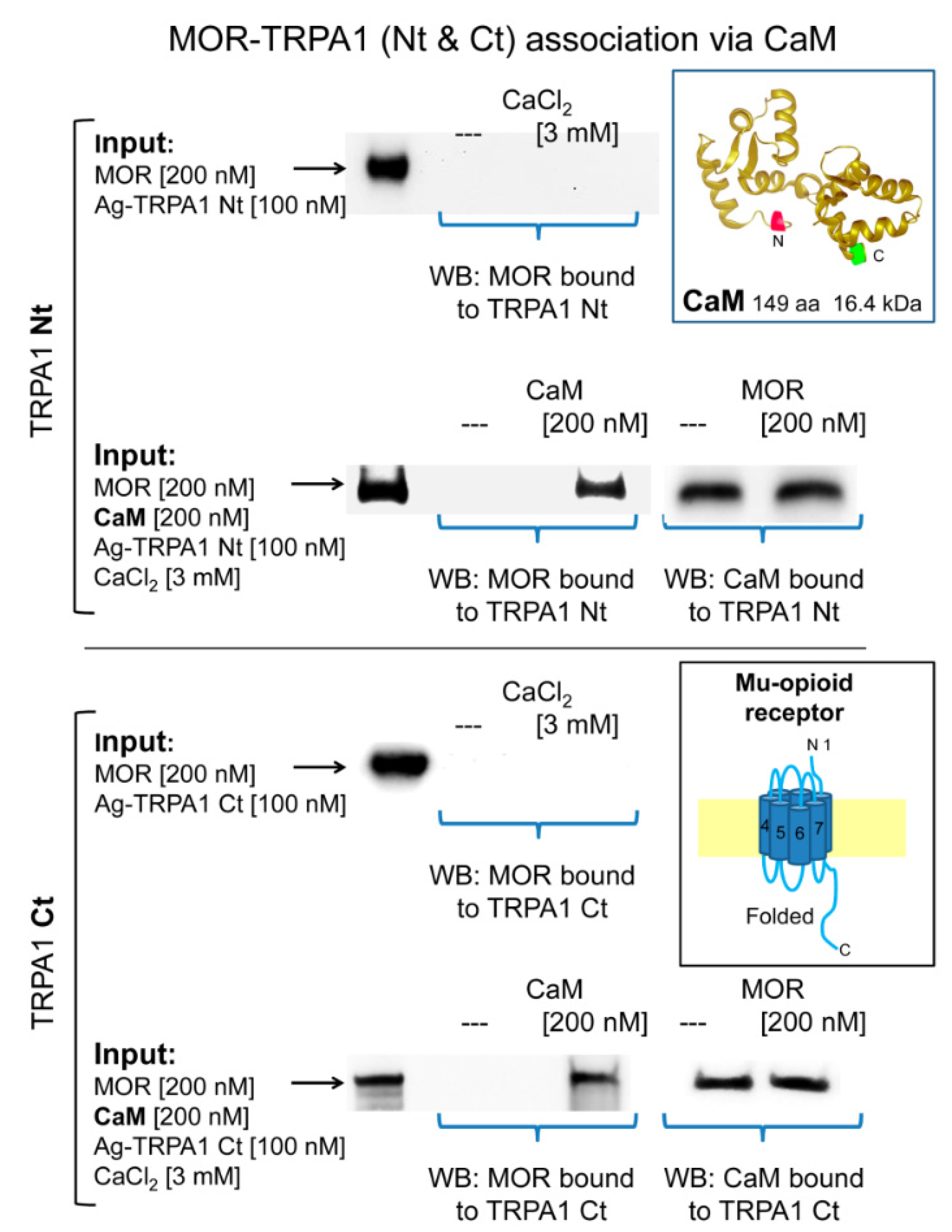
2.3. Calmodulin Mediates TRPA1 Channel Association with MORs and NR1 Subunits of Glutamate NMDARs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal and Drugs
4.2. Formalin-Induced Pain
4.3. Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI)
4.4. Immunoprecipitation and Western Blotting
4.5. PNGase F Digestion of Immunoprecipitated Proteins
4.6. Recombinant Proteins and In Vitro Interactions between Recombinant Proteins
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CaM | calmodulin |
| CCI | chronic contrition injury |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| DOR | delta-opioid receptor |
| DRG | dorsal root ganglia |
| HINT1 | histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 1 |
| MOR | mu-opioid receptor |
| NMDAR | N-methyl-d-aspartate acid glutamate receptor |
| σ1R | type 1 sigma receptor |
| TRP | transient receptor potential calcium channel |
| TRPA1 | transient receptor potential ankyrin member 1 |
| WT | wild type |
References
- Montell, C.; Birnbaumer, L.; Flockerzi, V. The TRP channels, a remarkably functional family. Cell 2002, 108, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature 2003, 426, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilius, B.; Flockerzi, V. Mammalian transient receptor potential (TRP) cation channels. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 223, pp. v–vi. [Google Scholar]
- Story, G.M.; Peier, A.M.; Reeve, A.J.; Eid, S.R.; Mosbacher, J.; Hricik, T.R.; Earley, T.J.; Hergarden, A.C.; Andersson, D.A.; Hwang, S.W.; et al. ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures. Cell 2003, 112, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, C.E.; Armache, J.P.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Julius, D. Structure of the TRPA1 ion channel suggests regulatory mechanisms. Nature 2015, 520, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, R.; Brauchi, S.; Orta, G.; Zaelzer, C.; Vargas, G. ThermoTRP channels as modular proteins with allosteric gating. Cell Calcium 2007, 42, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspani, O.; Heppenstall, P.A. TRPA1 and cold transduction: An unresolved issue? J. Gen. Physiol. 2009, 133, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basbaum, A.I.; Bautista, D.M.; Scherrer, G.; Julius, D. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 2009, 139, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.L.; Meotti, F.C.; Calixto, J.B. TRPA1 antagonists as potential analgesic drugs. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, D.M.; Pellegrino, M.; Tsunozaki, M. TRPA1: A gatekeeper for inflammation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julius, D. TRP channels and pain. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 355–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordt, S.E.; Bautista, D.M.; Chuang, H.H.; McKemy, D.D.; Zygmunt, P.M.; Hogestatt, E.D.; Meng, I.D.; Julius, D. Mustard oils and cannabinoids excite sensory nerve fibres through the TRP channel ANKTM1. Nature 2004, 427, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karashima, Y.; Damann, N.; Prenen, J.; Talavera, K.; Segal, A.; Voets, T.; Nilius, B. Bimodal action of menthol on the transient receptor potential channel TRPA1. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9874–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, K.Y.; Glazer, J.M.; Corey, D.P.; Rice, F.L.; Stucky, C.L. TRPA1 modulates mechanotransduction in cutaneous sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4808–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Fukuoka, T.; Obata, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Dai, Y.; Tokunaga, A.; Noguchi, K. Distinct expression of TRPM8, TRPA1, and TRPV1 mRNAs in rat primary afferent neurons with adelta/c-fibers and colocalization with trk receptors. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 493, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Duggan, A.; Kumar, G.; Garcia-Anoveros, J. Nociceptor and hair cell transducer properties of TRPA1, a channel for pain and hearing. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 4052–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, M.; Nakatsuka, T.; Fujita, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Kumamoto, E. Activation of TRPA1 channel facilitates excitatory synaptic transmission in substantia gelatinosa neurons of the adult rat spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, P.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Vaughan, C.W. Primary afferents with TRPM8 and TRPA1 profiles target distinct subpopulations of rat superficial dorsal horn neurones. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.R.; Crown, E.D.; Moore, E.L.; Liang, H.A.; Choong, K.C.; Dima, S.; Henze, D.A.; Kane, S.A.; Urban, M.O. HC-030031, a TRPA1 selective antagonist, attenuates inflammatory- and neuropathy-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. Mol. Pain 2008, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, D.S.; Meotti, F.C.; Andrade, E.L.; Leal, P.C.; Motta, E.M.; Calixto, J.B. The involvement of the transient receptor potential A1 (TRPA1) in the maintenance of mechanical and cold hyperalgesia in persistent inflammation. Pain 2010, 148, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, C.R.; Mandel-Brehm, J.; Bautista, D.M.; Siemens, J.; Deranian, K.L.; Zhao, M.; Hayward, N.J.; Chong, J.A.; Julius, D.; Moran, M.M.; et al. TRPA1 mediates formalin-induced pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13525–13530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Bian, D.; Jiang, B.; Zhai, Q.; Gao, N.; Wang, R. TRPA1 contributed to the neuropathic pain induced by docetaxel treatment. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisan, G.; Benemei, S.; Materazzi, S.; De, L.F.; De, S.G.; Fusi, C.; Fortes, R.M.; Coppi, E.; Marone, I.M.; Ferreira, J.; et al. TRPA1 mediates trigeminal neuropathic pain in mice downstream of monocytes/macrophages and oxidative stress. Brain 2016, 139, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Katsura, H.; Mizushima, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Dai, Y.; Fukuoka, T.; Tokunaga, A.; Tominaga, M.; Noguchi, K. TRPA1 induced in sensory neurons contributes to cold hyperalgesia after inflammation and nerve injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqboul, A.; Elsadek, B. A Novel Model of Cancer-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy and the Role of TRPA1 in Pain Transduction. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 3517207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Backonja, M.; Rowbotham, M.C.; Allen, R.R.; Argoff, C.R.; Bennett, G.J.; Bushnell, M.C.; Farrar, J.T.; Galer, B.S.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; et al. Advances in neuropathic pain: Diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staud, R.; Smitherman, M.L. Peripheral and central sensitization in fibromyalgia: Pathogenetic role. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2002, 6, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, H.; Watanabe, C.; Yonezawa, A.; Sakurada, S. New therapy for neuropathic pain. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2009, 85, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Thompson, S.W. The induction and maintenance of central sensitization is dependent on N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor activation; implications for the treatment of post-injury pain hypersensitivity states. Pain 1991, 44, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Sheng, M.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N.; Basbaum, A.I. Evidence for presynaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate autoreceptors in the spinal cord dorsal horn. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8383–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvizon, J.C.; McRoberts, J.A.; Ennes, H.S.; Song, B.; Wang, X.; Jinton, L.; Corneliussen, B.; Mayer, E.A. Two N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in rat dorsal root ganglia with different subunit composition and localization. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 446, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcangio, M.; Fernandes, K.; Tomlinson, D.R. NMDA receptor activation modulates evoked release of substance P from rat spinal cord. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaksh, T.L.; Jessell, T.M.; Gamse, R.; Mudge, A.W.; Leeman, S.E. Intrathecal morphine inhibits substance P release from mammalian spinal cord in vivo. Nature 1980, 286, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, I.; Marvizon, J.C.; Song, B.; Salgado, F.; Codeluppi, S.; Hua, X.Y.; Yaksh, T.L. Inhibition by spinal mu- and delta-opioid agonists of afferent-evoked substance P release. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3651–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariou, V.; Goldstein, B.D. Delta-Opioid receptor modulation of the release of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the dorsal horn of the rat following mechanical or thermal noxious stimulation. Brain Res. 1996, 736, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laulin, J.P.; Maurette, P.; Corcuff, J.B.; Rivat, C.; Chauvin, M.; Simonnet, G. The role of ketamine in preventing fentanyl-induced hyperalgesia and subsequent acute morphine tolerance. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walwyn, W.M.; Chen, W.; Kim, H.; Minasyan, A.; Ennes, H.S.; McRoberts, J.A.; Marvizon, J.C. Sustained Suppression of Hyperalgesia during Latent Sensitization by mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors and alpha2A Adrenergic Receptors: Role of Constitutive Activity. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, G.W.; Kolesnikov, Y.A.; Babey, A.M. Perspectives on the N-methyl-d-aspartate/nitric oxide cascade and opioid tolerance. Neuropsychopharmacology 1995, 13, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, K.A. The neurobiology of opiate tolerance, dependence and sensitization: Mechanisms of NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity. Neurotox. Res. 2002, 4, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przewlocki, R.; Przewlocka, B. Opioids in neuropathic pain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 3013–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Berrocoso, E.; Garzón, J. The plasticity of the association between mu-opioid receptor and glutamate ionotropic receptor N in opioid analgesic tolerance and neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 716, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wu, H.Y.; Fan, H.; Li, T.F.; Ma, A.N.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Pertovaara, A. Potential role of spinal TRPA1 channels in antinociceptive tolerance to spinally administered morphine. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Vicente-Sánchez, A.; Berrocoso, E.; Garzón, J. The mu-opioid receptor and the NMDA receptor associate in PAG neurons: Implications in pain control. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Cortés-Montero, E.; Pozo-Rodrigalvarez, A.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Garzón-Niño, J. The ON:OFF switch, sigma1R-HINT1 protein, controls GPCR-NMDA receptor cross-regulation: Implications in neurological disorders. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35458–35477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huang, L.Y. Sustained potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated glutamate responses through activation of protein kinase C by a mu opioid. Neuron 1991, 7, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Herrero-Labrador, R.; Martínez-Murillo, R.; Merlos, M.; Vela, J.M.; Garzón, J. The sigma1 receptor engages the redox-regulated HINT1 protein to bring opioid analgesia under NMDA receptor negative control. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 799–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.D.; Zhang, S.; Bernhadt, J.P.; Huganir, R.L. Inactivation of NMDA receptors by direct interaction of calmodulin with the NR1 subunit. Cell 1996, 84, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P. Direct association of Mu-opioid and NMDA glutamate receptors supports their cross-regulation: Molecular implications for opioid tolerance. Curr. Drug Abuse Rev. 2012, 5, 199–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Garzón, J. Nitric oxide and zinc-mediated protein assemblies involved in mu opioid receptor signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Montero, E.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Onetti, Y.; Merlos, M.; Garzón, J. Ligands Exert Biased Activity to Regulate Sigma 1 Receptor Interactions With Cationic TRPA1, TRPV1, and TRPM8 Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, S.; Tominaga, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Fukuoka, T.; Higashi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Obata, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Noguchi, K. Sensitization of TRPA1 by PAR2 contributes to the sensation of inflammatory pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Son, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Paik, S.K.; Dai, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Ahn, D.K.; Bae, Y.C. Expression of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) in the rat trigeminal sensory afferents and spinal dorsal horn. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunert-Keil, C.; Bisping, F.; Kruger, J.; Brinkmeier, H. Tissue-specific expression of TRP channel genes in the mouse and its variation in three different mouse strains. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggeshall, R.E.; Zhou, S.; Carlton, S.M. Opioid receptors on peripheral sensory axons. Brain Res. 1997, 764, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, W.; Cheng, C.; Xu, Q.G.; Li, X.Q.; Zochodne, D.W. Mu opioid receptors and analgesia at the site of a peripheral nerve injury. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, T.J.; Acuna, M.A.; Zenobi-Wong, M.; Zeilhofer, H.U.; Urech, D. Effects of N-Glycosylation of the human cation channel TRPA1 on agonist-sensitivity. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherzadeh, G.; Dehzangi, A.; Golchin, M.; Zhou, Y.; Campbell, M.P. SPRINT-Gly: Predicting N- and O-linked glycosylation sites of human and mouse proteins by using sequence and predicted structural properties. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4140–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Cano, R.; Montilla-García, A.; Ruiz-Cantero, M.C.; Bravo-Caparros, I.; Tejada, M.A.; Nieto, F.R.; Cobos, E.J. The search for translational pain outcomes to refine analgesic development: Where did we come from and where are we going? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 113, 238–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Cortés-Montero, E.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Merlos, M.; Garzón-Niño, J. The Sigma 2 receptor promotes and the Sigma 1 receptor inhibits mu-opioid receptor-mediated antinociception. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Vicente-Sánchez, A.; Bailon, C.; Martín-Aznar, B.; Garzón, J. The histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 supports mu-opioid receptor-glutamate NMDA receptor cross-regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2933–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Chen, S.R.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.D.; Sirrieh, R.E.; MacLean, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.H.; Jayaraman, V.; et al. The alpha2delta-1-NMDA Receptor Complex Is Critically Involved in Neuropathic Pain Development and Gabapentin Therapeutic Actions. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2307–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickle, A.D.; Shepherd, A.J.; Mohapatra, D.P. Sensory TRP channels: The key transducers of nociception and pain. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2015, 131, 73–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, O.; L’Herondelle, K.; Lebonvallet, N.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Sakka, M.; Buhe, V.; Plee-Gautier, E.; Carre, J.L.; Lefeuvre, L.; Misery, L.; et al. TRPV1 and TRPA1 in cutaneous neurogenic and chronic inflammation: Pro-inflammatory response induced by their activation and their sensitization. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilius, B.; Appendino, G.; Owsianik, G. The transient receptor potential channel TRPA1: From gene to pathophysiology. Pflug. Arch. 2012, 464, 425–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, M.; Yazawa, I.; Ikeda, K.; Kawakami, K.; Onimaru, H. Long-lasting facilitation of respiratory rhythm by treatment with TRPA1 agonist, cinnamaldehyde. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 114, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheradpezhouh, E.; Choy, J.M.C.; Daria, V.R.; Arabzadeh, E. TRPA1 expression and its functional activation in rodent cortex. Open Biol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Garzón, J. HINT1 protein cooperates with cannabinoid 1 receptor to negatively regulate glutamate NMDA receptor activity. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, R.; Leeson-Payne, A.T.; Jaggar, J.H.; Zhang, X. Calmodulin is responsible for Ca(2+)-dependent regulation of TRPA1 Channels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Morales, J.F.; Gracheva, E.O.; Julius, D. Cytoplasmic ankyrin repeats of transient receptor potential A1 (TRPA1) dictate sensitivity to thermal and chemical stimuli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2011, 108, E1184–E1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLander, G.E.; Portoghese, P.S.; Takemori, A.E. Role of spinal mu opioid receptors in the development of morphine tolerance and dependence. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1984, 231, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Brackley, A.D.; Gomez, R.; Guerrero, K.A.; Akopian, A.N.; Glucksman, M.J.; Du, J.; Carlton, S.M.; Jeske, N.A. A-Kinase Anchoring Protein 79/150 Scaffolds Transient Receptor Potential A 1 Phosphorylation and Sensitization by Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, S.A.; Dubuis, E.D.; Belvisi, M.G. G-protein coupled receptors regulating cough. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meents, J.E.; Fischer, M.J.; McNaughton, P.A. Sensitization of TRPA1 by Protein Kinase A. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulak, M.A.; Ghosh, M.; Sinharoy, P.; Andrei, S.R.; Damron, D.S. Modulation of TRPA1 channel activity by Cdk5 in sensory neurons. Channels 2018, 12, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Lang, L.J. Peripheral mechanisms of opioid analgesia. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Bandell, M.; Petrus, M.J.; Zhu, M.X.; Patapoutian, A. Zinc activates damage-sensing TRPA1 ion channels. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, S.M.; Hargett, G.L.; Coggeshall, R.E. Localization and activation of glutamate receptors in unmyelinated axons of rat glabrous skin. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 197, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggeshall, R.E.; Carlton, S.M. Ultrastructural analysis of NMDA, AMPA, and kainate receptors on unmyelinated and myelinated axons in the periphery. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 391, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinkelin, I.; Brocker, E.B.; Koltzenburg, M.; Carlton, S.M. Localization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in peripheral axons of human skin. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 283, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ro, J.Y. Differential regulation of glutamate receptors in trigeminal ganglia following masseter inflammation. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 421, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, G.; Randic, M. Excitatory amino acid-mediated components of synaptically evoked input from dorsal roots to deep dorsal horn neurons in the rat spinal cord slice. Neurosci. Lett. 1989, 106, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momiyama, A. Distinct synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors identified in dorsal horn neurones of the adult rat spinal cord. J. Physiol. 2000, 523, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRoberts, J.A.; Coutinho, S.V.; Marvizon, J.C.; Grady, E.F.; Tognetto, M.; Sengupta, J.N.; Ennes, H.S.; Chaban, V.V.; Amadesi, S.; Creminon, C.; et al. Role of peripheral N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in visceral nociception in rats. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, J.D.; Karlsten, R.; Gordh, T.; Berge, O.G. The NMDA antagonist 3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid (CPP) has antinociceptive effect after intrathecal injection in the rat. Pain 1994, 56, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; López-Fando, A.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P. The RGSZ2 protein exists in a complex with mu-opioid receptors and regulates the desensitizing capacity of Gz proteins. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, T.J.; Mccormick, W.G. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1957, 12, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.A.; Montilla-García, A.; Cronin, S.J.; Cikes, D.; Sánchez-Fernández, C.; González-Cano, R.; Ruiz-Cantero, M.C.; Penninger, J.M.; Vela, J.M.; Baeyens, J.M.; et al. Sigma-1 receptors control immune-driven peripheral opioid analgesia during inflammation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8396–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, J.M.; Basbaum, A.I. Differential ATF3 expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons reveals the profile of primary afferents engaged by diverse noxious chemical stimuli. Pain 2010, 150, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J.; Herrero-Labrador, R.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Shah, R.; Vicente-Sánchez, A.; Wagner, C.R.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P. HINT1 protein: A new therapeutic target to enhance opioid antinociception and block mechanical allodynia. Neuropharmacology 2015, 89, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.J.; Xie, Y.K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 1988, 33, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; López-Fando, A.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P. Activation of mu-opioid receptors transfers control of Galpha subunits to the regulator of G-protein signaling RGS9-2: Role in receptor desensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8951–8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Torre-Madrid, E.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Garzón, J. Morphine induces endocytosis of neuronal mu-opioid receptors through the sustained transfer of Galpha subunits to RGSZ2 proteins. Mol. Pain 2007, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzón, J.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P. Morphine alters the selective association between mu-opioid receptors and specific RGS proteins in mouse periaqueductal gray matter. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortés-Montero, E.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Ruiz-Cantero, M.C.; Cobos, E.J.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P.; Garzón-Niño, J. Calmodulin Supports TRPA1 Channel Association with Opioid Receptors and Glutamate NMDA Receptors in the Nervous Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010229
Cortés-Montero E, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, Ruiz-Cantero MC, Cobos EJ, Sánchez-Blázquez P, Garzón-Niño J. Calmodulin Supports TRPA1 Channel Association with Opioid Receptors and Glutamate NMDA Receptors in the Nervous Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010229
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortés-Montero, Elsa, María Rodríguez-Muñoz, M. Carmen Ruiz-Cantero, Enrique J. Cobos, Pilar Sánchez-Blázquez, and Javier Garzón-Niño. 2021. "Calmodulin Supports TRPA1 Channel Association with Opioid Receptors and Glutamate NMDA Receptors in the Nervous Tissue" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010229
APA StyleCortés-Montero, E., Rodríguez-Muñoz, M., Ruiz-Cantero, M. C., Cobos, E. J., Sánchez-Blázquez, P., & Garzón-Niño, J. (2021). Calmodulin Supports TRPA1 Channel Association with Opioid Receptors and Glutamate NMDA Receptors in the Nervous Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010229