Connexin Signaling in the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) of Developing, Postnatal Healthy and Nephrotic Human Kidneys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
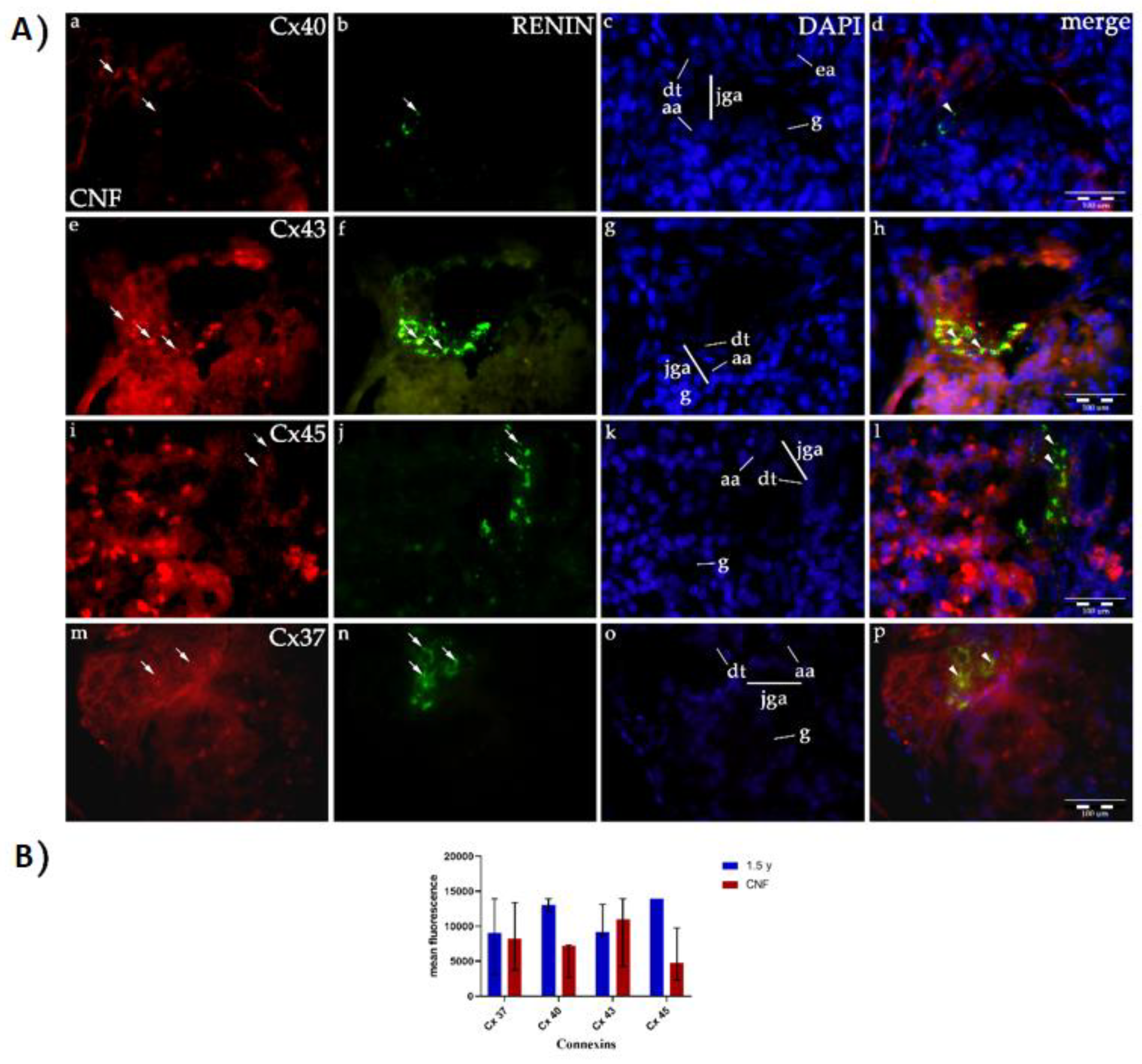
2.1. Double Immunofluorescence Staining of Renin and Different Cxs in Developing and Postnatal JGA of Human Kidneys
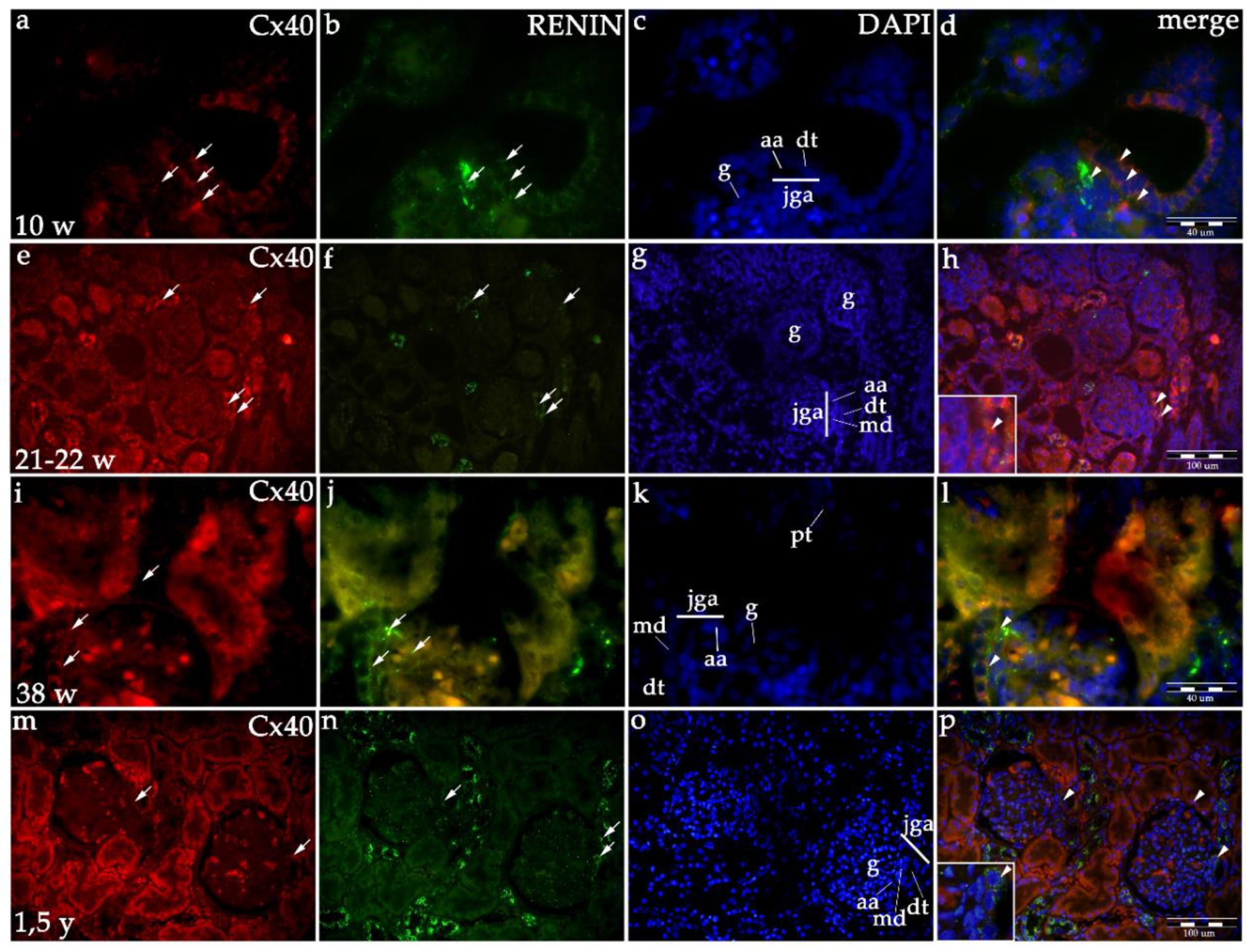
2.1.1. Cx40 Expression
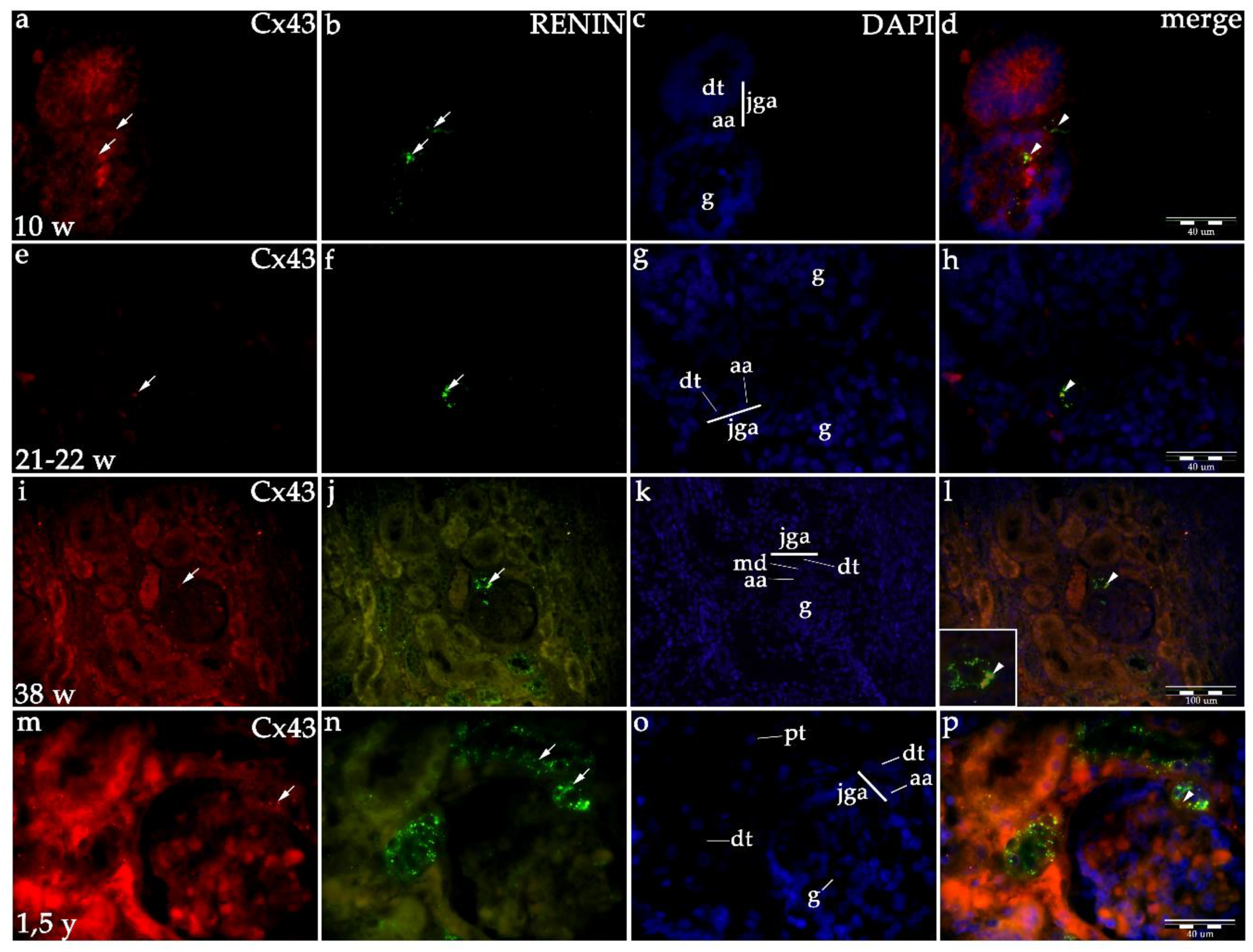
2.1.2. Cx43 Expression
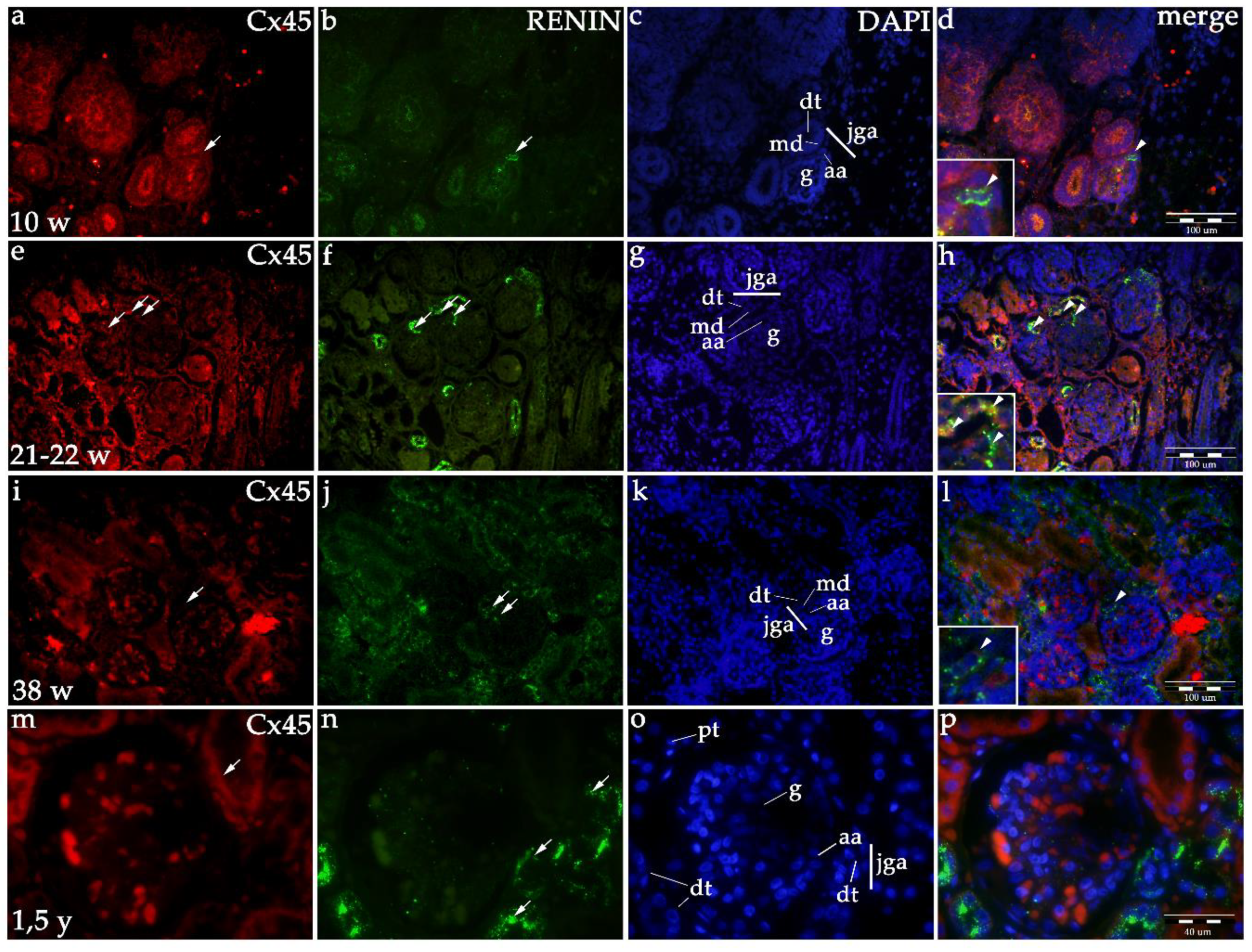
2.1.3. Cx45 Expression
2.1.4. Cx37 Expression
2.1.5. Co-Expression of Renin and Cxs
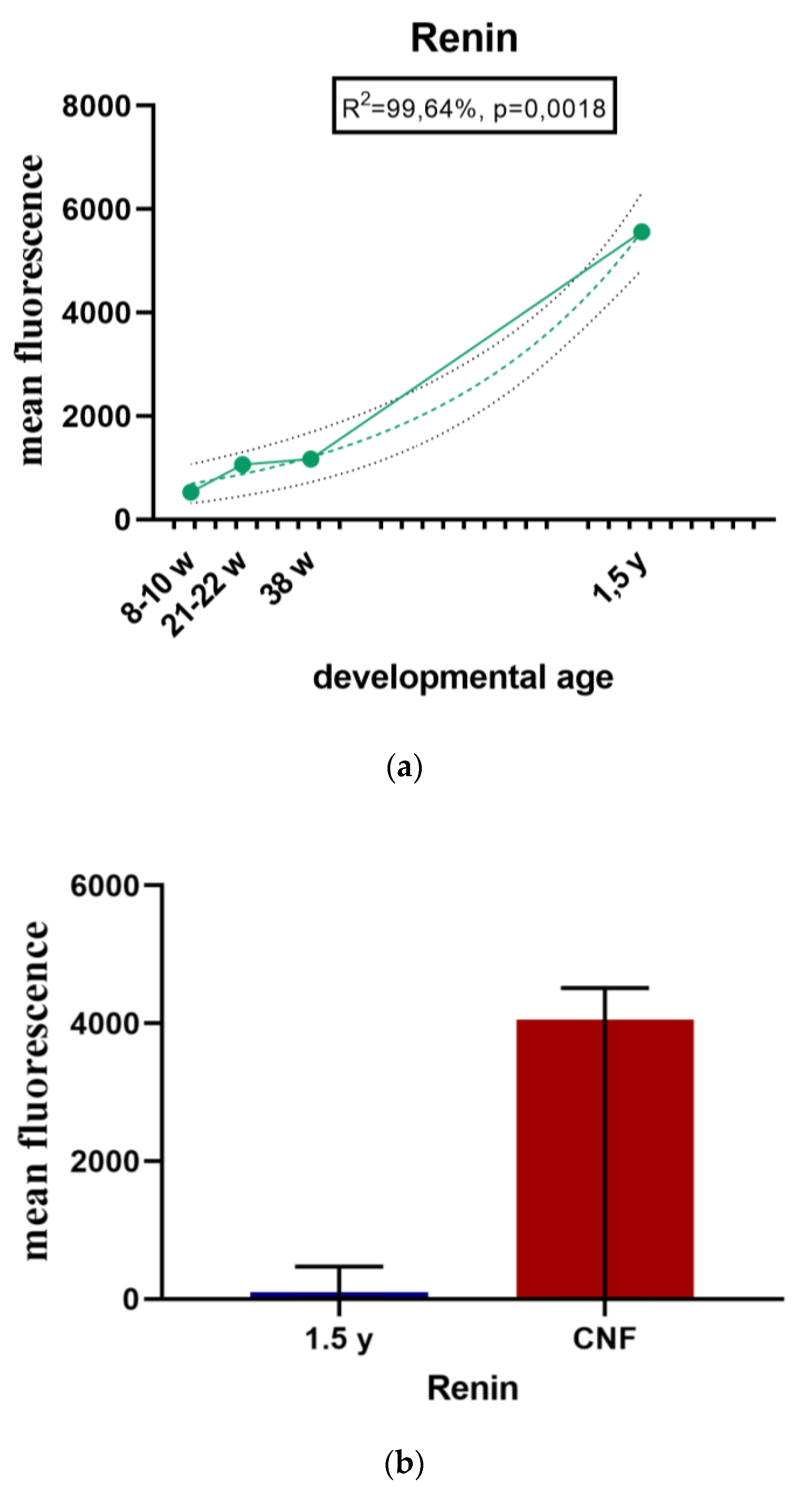
2.1.6. Renin Expression in Developing and Postnatal Human Kidneys
2.1.7. Renin Expression in CNF Kidneys
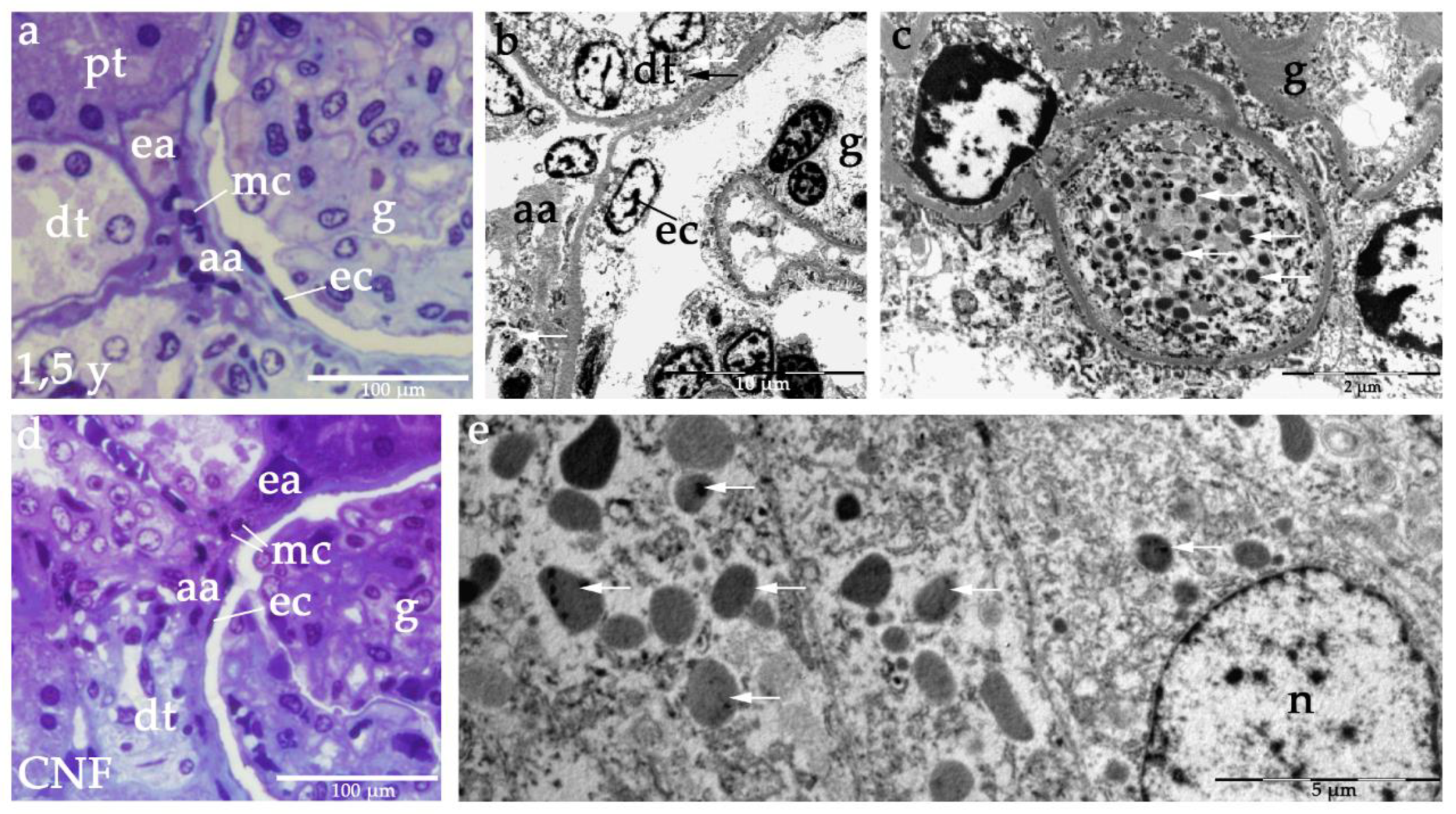
2.2. CNF
2.3. Semi-Thin Sections and Electron Microscopy of JGA in Healthy and CNF Postnatal Kidneys
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Material
4.2. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence Staining
4.3. Semi-Thin and Ultra-Thin Sections and Electron Microscopy
4.4. Semi-Quantification
4.5. Statistics and Microphotograph Quantification
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MET | Mesenchymal to epithelial transition |
| JC | Juxtaglomerular cells |
| JGA | Juxtaglomerular apparatus |
| EM | Extraglomerular mesangium |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
| RAS | Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
| AKI-CKD | Acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition |
| Cxs | Connexins |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CNF | Nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type |
References
- Filipovic, N.; Vukojevic, K.; Bocina, I.; Saraga, M.; Durdov, M.G.; Kablar, B.; Saraga-Babic, M. Immunohistochemical and electronmicroscopic features of mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in human developing, postnatal and nephrotic podocytes. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 147, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racetin, A.; Raguz, F.; Durdov, M.G.; Kunac, N.; Saraga, M.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Soljic, V.; Martinovic, V.; Petricevic, J.; Kostic, S.; et al. Immunohistochemical expression pattern of RIP5, FGFR1, FGFR2 and HIP2 in the normal human kidney development. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequeira Lopez, M.L.; Gomez, R.A. Development of the renal arterioles. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2011, 22, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanska, A.; Kenyon, C.; Christian, H.C.; Buckley, C.; Shaw, I.; Mullins, J.J.; Peault, B. Human kidney pericytes produce renin. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, I.; Rider, S.; Mullins, J.; Hughes, J.; Peault, B. Pericytes in the renal vasculature: Roles in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, R.A. Fate of renin cells during development and disease. Hypertension 2017, 69, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosypiv, I.V.; Sequeira-Lopez, M.L.S.; Song, R.; De Goes Martini, A. Stromal prorenin receptor is critical for normal kidney development. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 316, R640–R650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira-Lopez, M.L.; Nagalakshmi, V.K.; Li, M.; Sigmund, C.D.; Gomez, R.A. Vascular versus tubular renin: Role in kidney development. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R650–R657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, A.; Machura, K.; Neubauer, B.; Kurtz, A.; Wagner, C. Development of renin expression in the mouse kidney. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira Lopez, M.L.; Pentz, E.S.; Nomasa, T.; Smithies, O.; Gomez, R.A. Renin cells are precursors for multiple cell types that switch to the renin phenotype when homeostasis is threatened. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Oite, T.; Kitamura, M. Gap junctional intercellular communication in the juxtaglomerular apparatus. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, F939–F946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peti-Peterdi, J.; Harris, R.C. Macula densa sensing and signaling mechanisms of renin release. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2010, 21, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubler, M.C.; Antignac, C. Renin-angiotensin system in kidney development: Renal tubular dysgenesis. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J. The (pro)renin receptor and its interaction partners. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2017, 469, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Urushihara, M.; Saijo, T.; Nakagawa, R.; Kagami, S. (Pro)renin and (pro)renin receptor expression during kidney development in neonates. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, M.K.; Atkins, C.E.; Pitt, B. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its suppression. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Poyan Mehr, A.; Kreutz, R. Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 747–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, A.; Kobori, H. Independent regulation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the kidney. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, S.S.; Culver, S.A.; Li, C.; Siragy, H.M. Interaction of the renin angiotensin and cox systems in the kidney. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2016, 8, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, S.; Le Moullec, J.M.; Corvol, P.; Gasc, J.M. Early expression of all the components of the renin-angiotensin-system in human development. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Urushihara, M.; Kagami, S. Role of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in the progression of renal disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.; Delarue, F.; Burckle, C.; Bouzhir, L.; Giller, T.; Sraer, J.D. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, P.; Remuzzi, G.; Glassock, R.; Levin, A.; Jager, K.J.; Tonelli, M.; Massy, Z.; Wanner, C.; Anders, H.J. Chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.H.; Chu, T.S.; Lin, S.L. Role of renin-angiotensin system in acute kidney injury-chronic kidney disease transition. Nephrology (Carlton) 2018, 23 (Suppl. 4), 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C. Function of connexins in the renal circulation. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyz, J. The stage-specific function of gap junctions during tumourigenesis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2008, 13, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, M.; Decrock, E.; Leybaert, L.; Bultynck, G.; Himpens, B.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. Non-channel functions of connexins in cell growth and cell death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanner, F.; Sorensen, C.M.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Peti-Peterdi, J. Connexins and the kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R1143–R1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoessel, A.; Himmerkus, N.; Bleich, M.; Bachmann, S.; Theilig, F. Connexin 37 is localized in renal epithelia and responds to changes in dietary salt intake. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F216–F223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, A. Renal connexins and blood pressure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haefliger, J.A.; Nicod, P.; Meda, P. Contribution of connexins to the function of the vascular wall. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 62, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arensbak, B.; Mikkelsen, H.B.; Gustafsson, F.; Christensen, T.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H. Expression of connexin 37, 40, and 43 mRNA and protein in renal preglomerular arterioles. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 115, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seul, K.H.; Beyer, E.C. Mouse connexin37: Gene structure and promoter analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1492, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, L.; Schweda, F.; de Wit, C.; Kriz, W.; Witzgall, R.; Warth, R.; Sauter, A.; Kurtz, A.; Wagner, C. Lack of connexin 40 causes displacement of renin-producing cells from afferent arterioles to the extraglomerular mesangium. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2007, 18, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, T.; Inoue, T.; Kanno, Y.; Okada, H.; Meaney, K.R.; Hill, C.E.; Suzuki, H. Expression and role of connexins in the rat renal vasculature. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamelin, R.; Allagnat, F.; Haefliger, J.A.; Meda, P. Connexins, diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2009, 10, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefliger, J.A.; Demotz, S.; Braissant, O.; Suter, E.; Waeber, B.; Nicod, P.; Meda, P. Connexins 40 and 43 are differentially regulated within the kidneys of rats with renovascular hypertension. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubas, J.; Beck, S.; Pageaud, A.L.; Huby, A.C.; Mael-Ainin, M.; Dussaule, J.C.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Chadjichristos, C.E. Alteration of connexin expression is an early signal for chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 301, F24–F32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, A.; Toubas, J.; Kavvadas, P.; Authier, F.; Cathelin, D.; Alfieri, C.; Boffa, J.J.; Dussaule, J.C.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Chadjichristos, C.E. Targeting connexin 43 protects against the progression of experimental chronic kidney disease in mice. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillis, G.S.; Duthie, L.A.; Mlynski, R.; McKay, N.G.; Mistry, S.; MacLeod, A.M.; Simpson, J.G.; Haites, N.E. The expression of connexin 43 in human kidney and cultured renal cells. Nephron 1997, 75, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, K.; Mukoyama, M.; Mori, K.; Yokoi, H.; Koshikawa, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Takeda, R.; Sugawara, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Saleem, M.A.; et al. Redistribution of connexin43 expression in glomerular podocytes predicts poor renal prognosis in patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 2472–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Kurtz, L.; Schweda, F.; Simon, A.M.; Kurtz, A. Connexin 37 is dispensable for the control of the renin system and for positioning of renin-producing cells in the kidney. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 459, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, L.; Janssen-Bienhold, U.; Kurtz, A.; Wagner, C. Connexin expression in renin-producing cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2009, 20, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krattinger, N.; Capponi, A.; Mazzolai, L.; Aubert, J.F.; Caille, D.; Nicod, P.; Waeber, G.; Meda, P.; Haefliger, J.A. Connexin40 regulates renin production and blood pressure. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweda, F.; Kurtz, L.; de Wit, C.; Janssen-Bienhold, U.; Kurtz, A.; Wagner, C. Substitution of connexin40 with connexin45 prevents hyperreninemia and attenuates hypertension. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanner, F.; von Maltzahn, J.; Maxeiner, S.; Toma, I.; Sipos, A.; Kruger, O.; Willecke, K.; Peti-Peterdi, J. Connexin45 is expressed in the juxtaglomerular apparatus and is involved in the regulation of renin secretion and blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R371–R380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vinken, M.; Decrock, E.; De Vuyst, E.; Ponsaerts, R.; D’Hondt, C.; Bultynck, G.; Ceelen, L.; Vanhaecke, T.; Leybaert, L.; Rogiers, V. Connexins: Sensors and regulators of cell cycling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1815, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, T.; Johnstone, S.; Vidal-Brime, L.; Lynn, K.S.; Koval, M. Connexins: Synthesis, post-translational modifications, and trafficking in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosovic, I.; Filipovic, N.; Benzon, B.; Vukojevic, K.; Saraga, M.; Glavina Durdov, M.; Bocina, I.; Saraga-Babic, M. Spatio-temporal patterning of different connexins in developing and postnatal human kidneys and in nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type (CNF). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, R.A.; Lynch, K.R.; Sturgill, B.C.; Elwood, J.P.; Chevalier, R.L.; Carey, R.M.; Peach, M.J. Distribution of renin mRNA and its protein in the developing kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 257, F850–F858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minuth, M.; Hackenthal, E.; Poulsen, K.; Rix, E.; Taugner, R. Renin immunocytochemistry of the differentiating juxtaglomerular apparatus. Anat. Embryol. 1981, 162, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrop, H.; Hocherl, K.; Kurtz, A.; Schweda, F.; Todorov, V.; Wagner, C. Physiology of kidney renin. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 607–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, L.; Madsen, K.; Kurt, B.; Jensen, B.L.; Walter, S.; Banas, B.; Wagner, C.; Kurtz, A. High-level connexin expression in the human juxtaglomerular apparatus. Nephron Physiol. 2010, 116, p1–p8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; de Wit, C.; Kurtz, L.; Grunberger, C.; Kurtz, A.; Schweda, F. Connexin40 is essential for the pressure control of renin synthesis and secretion. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wit, C.; Roos, F.; Bolz, S.S.; Kirchhoff, S.; Kruger, O.; Willecke, K.; Pohl, U. Impaired conduction of vasodilation along arterioles in connexin40-deficient mice. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerl, M.; Kurt, B.; Kurtz, A.; Wagner, C. Connexin 43 is not essential for the control of renin synthesis and secretion. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 466, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefliger, J.A.; Krattinger, N.; Martin, D.; Pedrazzini, T.; Capponi, A.; Doring, B.; Plum, A.; Charollais, A.; Willecke, K.; Meda, P. Connexin43-dependent mechanism modulates renin secretion and hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carev, D.; Saraga, M.; Saraga-Babic, M. Expression of intermediate filaments, EGF and TGF-alpha in early human kidney development. J. Mol. Histol. 2008, 39, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racetin, A.; Juric, M.; Filipovic, N.; Solic, I.; Kosovic, I.; Glavina Durdov, M.; Kunac, N.; Zekic Tomas, S.; Saraga, M.; Soljic, V.; et al. Expression and localization of DAB1 and Reelin during normal human kidney development. Croat. Med. J. 2019, 60, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojevic, K.; Kero, D.; Novakovic, J.; Kalibovic Govorko, D.; Saraga-Babic, M. Cell proliferation and apoptosis in the fusion of human primary and secondary palates. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2012, 120, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Weeks/Years | Cx40 | Cx43 | Cx45 | Cx37 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8–10 weeks | ++/+++ | +/++ | +/++ | +/++ |
| 21–22 weeks | ++/+++ | +/++ | +/++ | +/++ |
| 38 weeks | ++ | +/++ | +/++ | +/++ |
| 1.5 year | +/++ | ++/+++ | ++ | ++ |
| CNF—cca 1.5 year | + | +++ | ++/+++ | ++/+++ |
| Antibodies | Host | Dilution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Anti-Cx37/GJA4 ab181701 | Rabbit | 1:500 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) |
| Anti-Cx40/GJA5 ab213688 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Anti-Cx43&GJA1 ab87645 | Goat | 1:200 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Anti-Cx45/GJA7 ab135474 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Anti-Renin [7D3-E3] (ab134783) | Mouse | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Secondary | Anti-Goat IgG, Rhodamine Red™-X (RRX) 705-295-003 | Donkey | 1:400 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc., Baltimore, PA, USA |
| Anti-Rabbit IgG, Rhodamine (TRITC) 711-025-152 | Donkey | 1:400 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc., Baltimore, PA, USA | |
| Anti-Mouse IgG, Alexa Fluor® 488 ab150105 | Donkey | 1:400 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosovic, I.; Filipovic, N.; Benzon, B.; Bocina, I.; Glavina Durdov, M.; Vukojevic, K.; Saraga, M.; Saraga-Babic, M. Connexin Signaling in the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) of Developing, Postnatal Healthy and Nephrotic Human Kidneys. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218349
Kosovic I, Filipovic N, Benzon B, Bocina I, Glavina Durdov M, Vukojevic K, Saraga M, Saraga-Babic M. Connexin Signaling in the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) of Developing, Postnatal Healthy and Nephrotic Human Kidneys. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218349
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosovic, Ivona, Natalija Filipovic, Benjamin Benzon, Ivana Bocina, Merica Glavina Durdov, Katarina Vukojevic, Marijan Saraga, and Mirna Saraga-Babic. 2020. "Connexin Signaling in the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) of Developing, Postnatal Healthy and Nephrotic Human Kidneys" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218349
APA StyleKosovic, I., Filipovic, N., Benzon, B., Bocina, I., Glavina Durdov, M., Vukojevic, K., Saraga, M., & Saraga-Babic, M. (2020). Connexin Signaling in the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) of Developing, Postnatal Healthy and Nephrotic Human Kidneys. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218349






