SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Background
2. Biogenesis, Distribution, and Function of LDs
2.1. LD Biogenesis
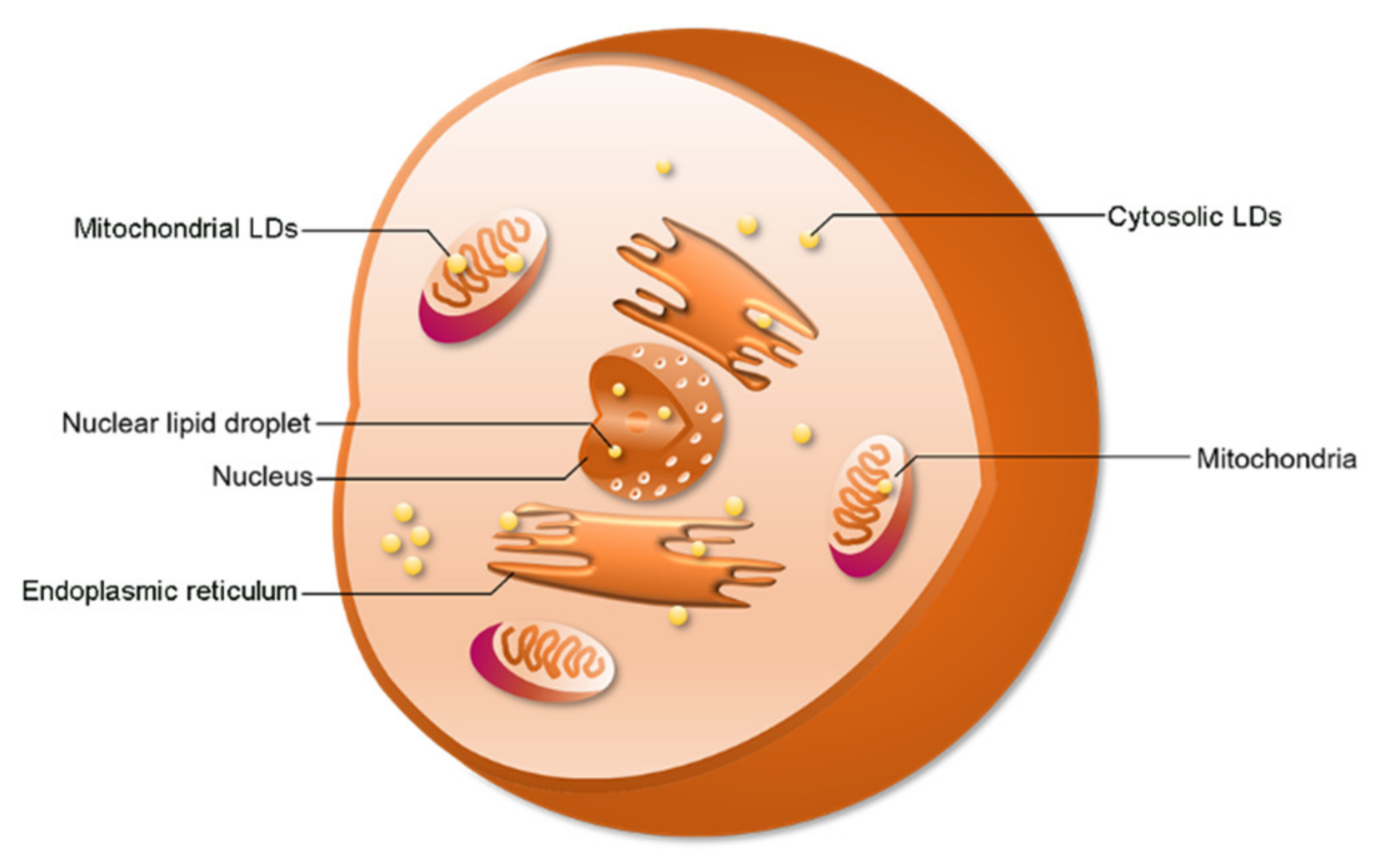
2.2. LD Distribution
2.3. Function of cLDs and nLDs
3. Structure and Function of SEIPIN
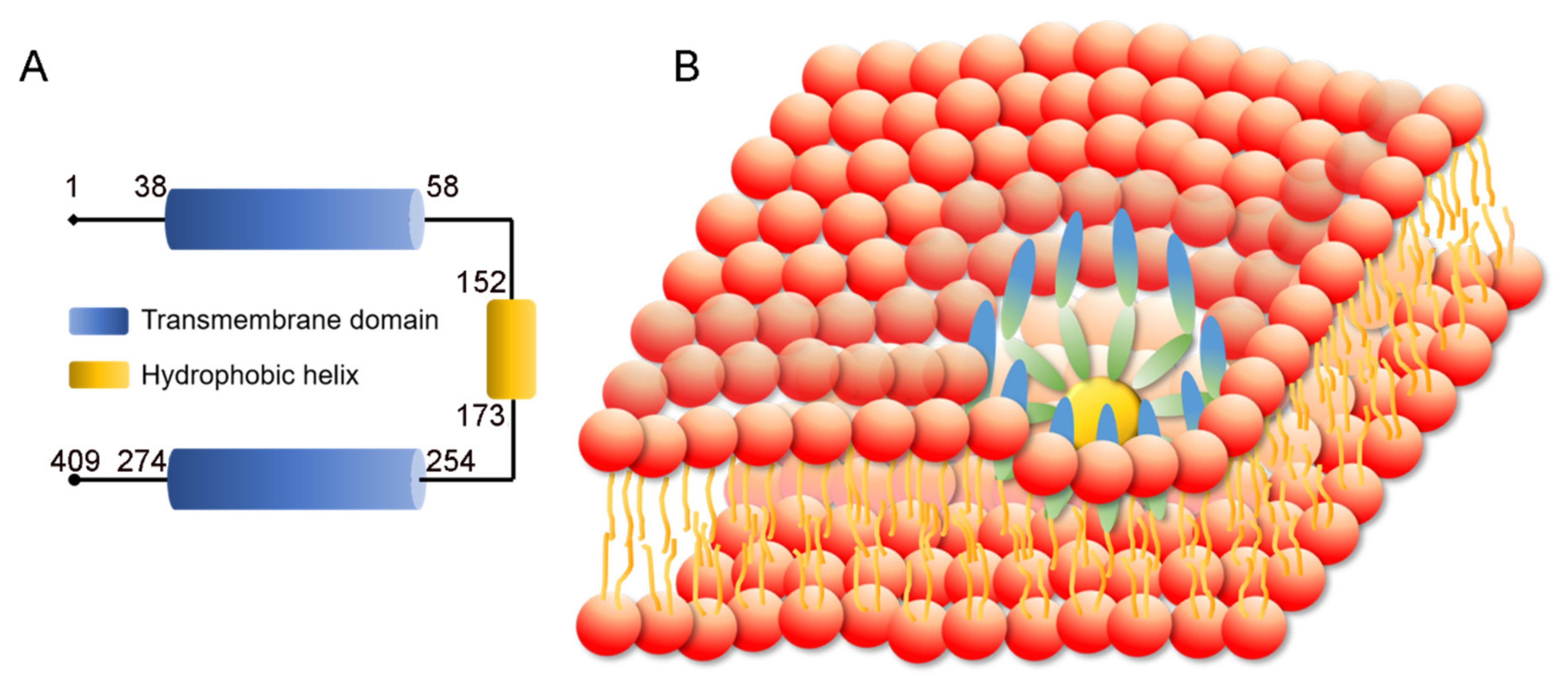
3.1. SEIPIN Structure
3.2. SEIPIN Function
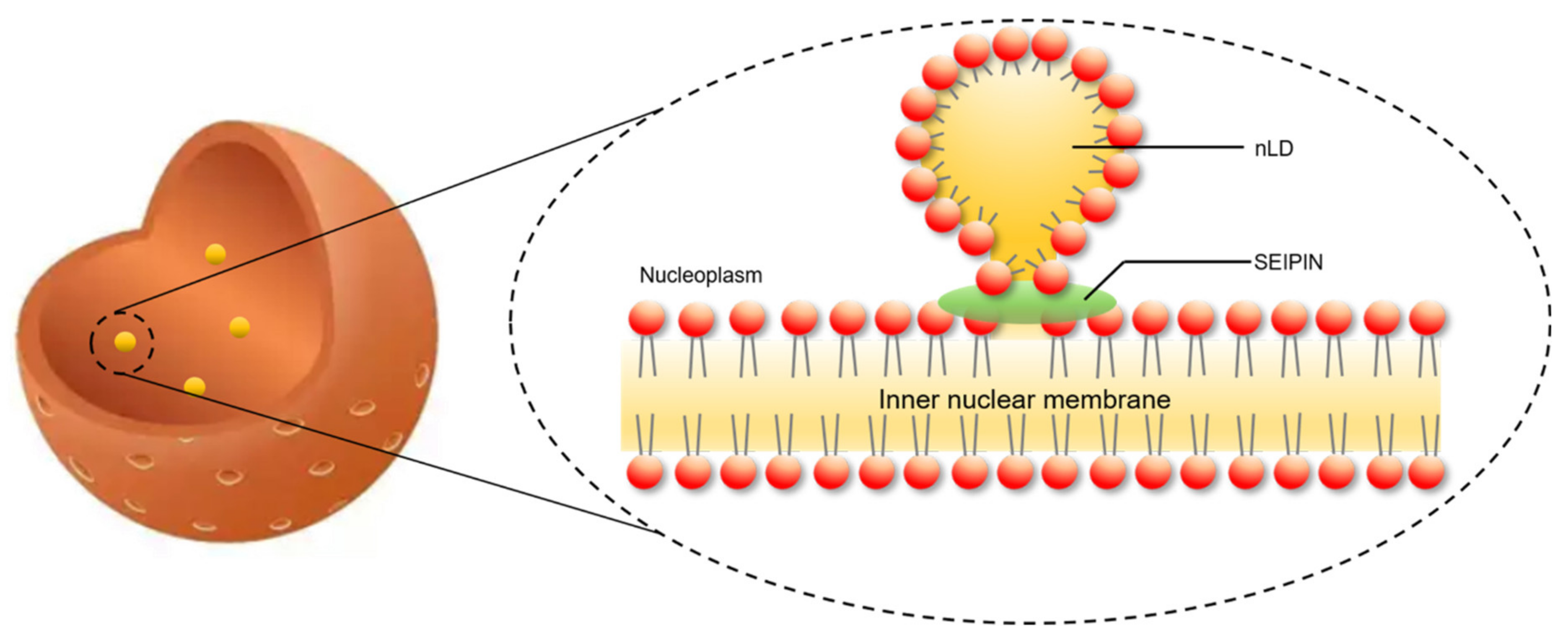
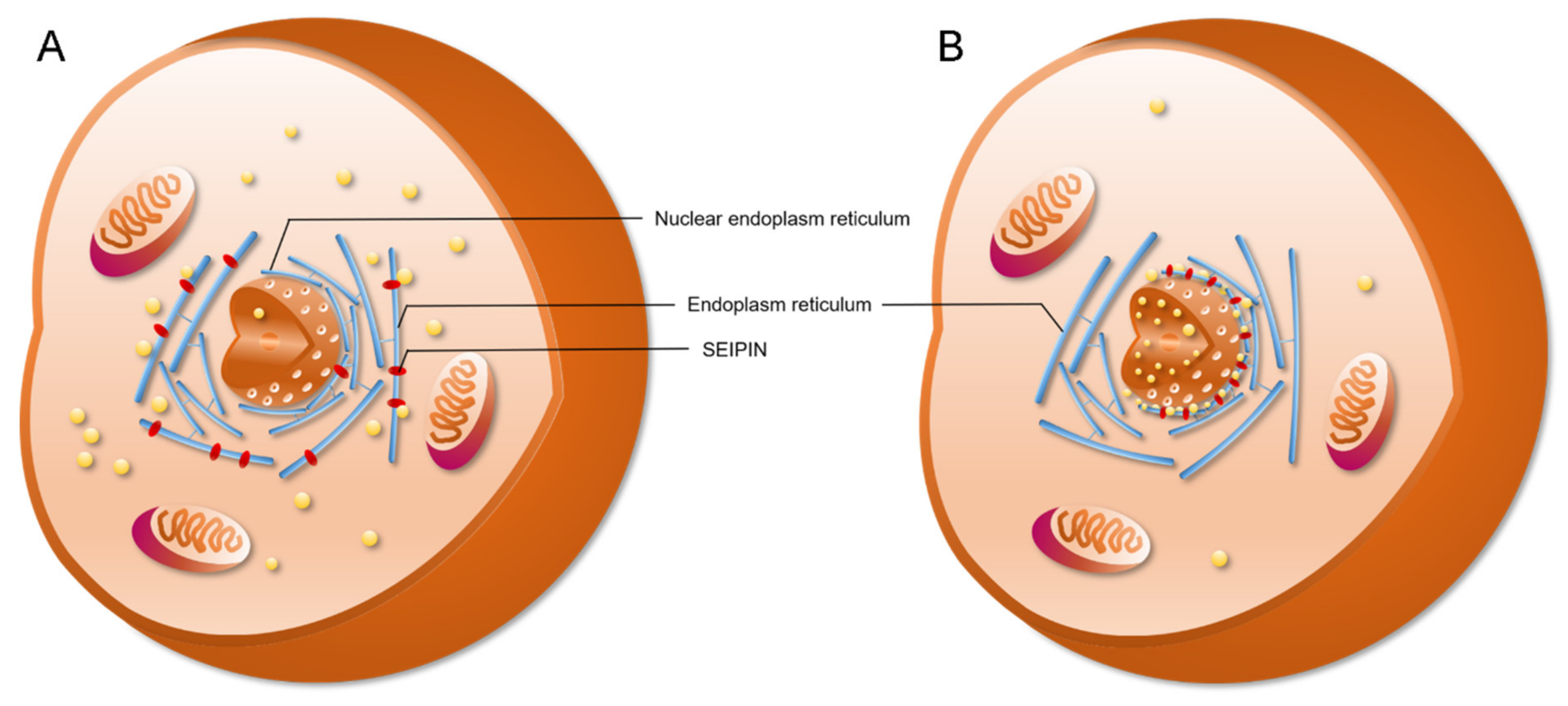
4. The Role of SEIPIN in cLD and nLD Biogenesis
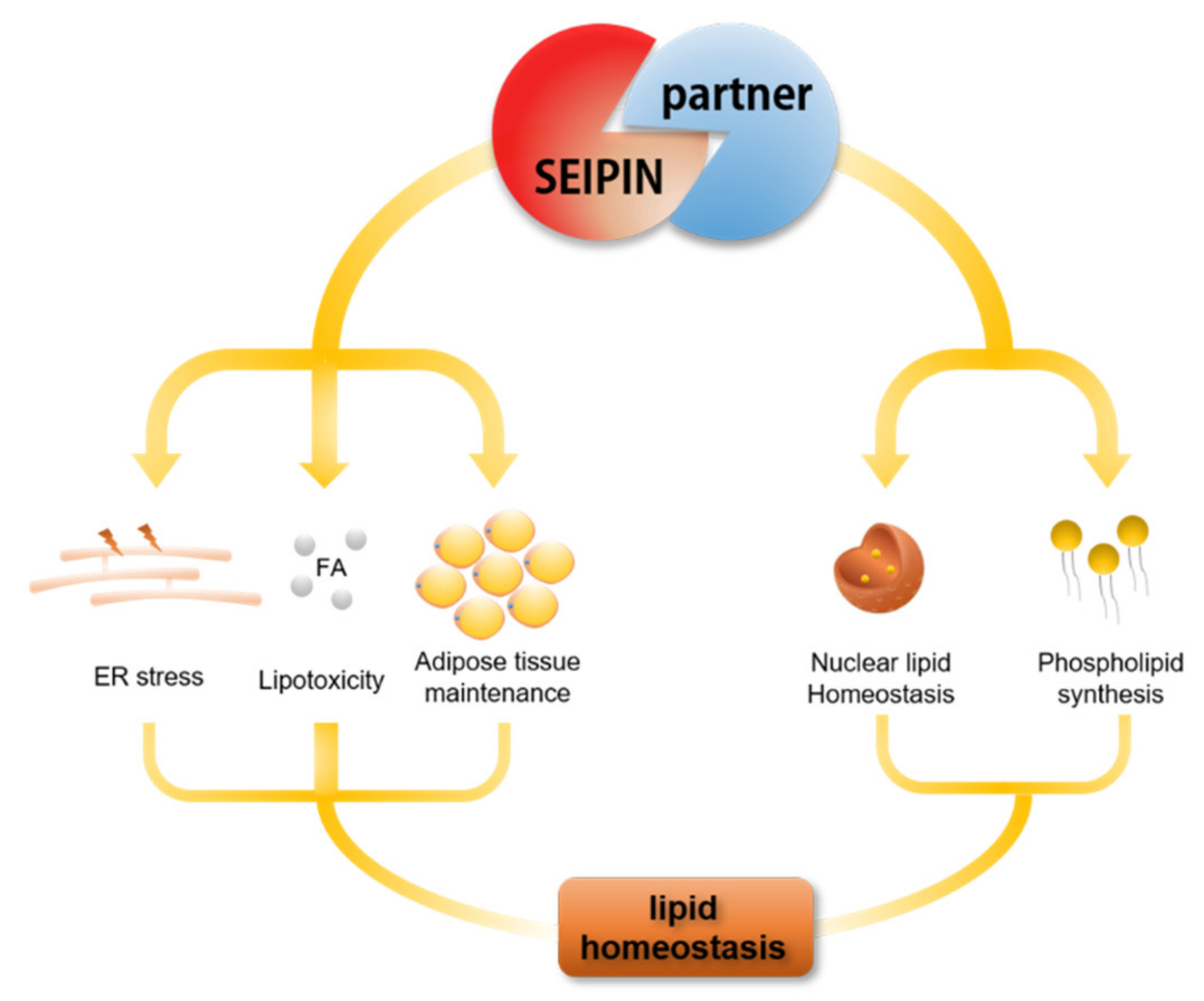
5. The Role of SEIPIN Partners in Maintaining Cell Lipid Homeostasis
6. The Potential Biological Significance of SEIPIN in Regulating nLD Generation
7. Relationship Between LDs and Human Diseases
8. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LD | LD |
| cLD | cytoplasmic LD |
| nLD | nuclear LD |
| TAG | triacylglycerols |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ACSL | acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member |
| SCD | stearoyl-CoA desaturase |
| GPAT | glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase |
| DGAT | diacylglycerol-O-acyltransferase |
| HNE | 4-hydroxynonenal |
| FA | fatty acid |
| PFOA | perfluorooctanoic acid |
| CCTα | CDP-choline diacylglycerol phosphotransferase α |
| FABP | fatty acid binding protein |
| SERCA | sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase |
| LIPIN | phosphatidic acid phosphatase |
| AGPAT | acylglycerol-phosphate acyltransferase |
| REEP | reticulon-like protein |
References
- Missaglia, S.; Coleman, R.A.; Mordente, A.; Tavian, D. Neutral Lipid Storage Diseases as Cellular Model to Study Lipid Droplet Function. Cells 2019, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welte, M.A. Expanding roles for lipid droplets. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R470–R481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, T.C.; Chung, J.; Farese, R.V. Lipid Droplet Biogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 33, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilfling, F.; Haas, J.T.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplet biogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welte, M.A.; Gould, A.P. Lipid droplet functions beyond energy storage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.J. The biogenesis and functions of lipid bodies in animals, plants and microorganisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 2001, 40, 325–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.J.; Vance, J. Mechanisms of lipid-body formation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olzmann, J.A.; Carvalho, P. Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanauska, A.; Köhler, A. The Inner Nuclear Membrane Is a Metabolically Active Territory that Generates Nuclear Lipid Droplets. Cell 2018, 174, 700–715.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltysik, K.; Ohsaki, Y.; Tatematsu, T.; Cheng, J.L.; Fujimoto, T. Nuclear lipid droplets derive from a lipoprotein precursor and regulate phosphatidylcholine synthesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windpassinger, C.; Auer-Grumbach, M.; Irobi, J.; Patel, H.; Petek, E.; Hörl, G.; Malli, R.; A Reed, J.; Dierick, I.; Verpoorten, N.; et al. Heterozygous missense mutations in BSCL2 are associated with distal hereditary motor neuropathy and Silver syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magré, J.; Delépine, M.; Khallouf, E.; Gedde-Dahl, T.; Van Maldergem, L.; Sobel, E.; Papp, J.; Meier, M.; Mégarbané, A.; Bachy, A.; et al. Identification of the gene altered in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy on chromosome 11q13. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Yang, X.; Tian, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ding, M.; Shui, G.; Huang, X. Seipin regulates lipid homeostasis by ensuring calcium-dependent mitochondrial metabolism. EMBO J. 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, V.T.; Li, S.; Vihinen, H.; Hölttä-Vuori, M.; Szkalisity, A.; Horvath, P.; Belevich, I.; Peränen, J.; Thiele, C.; Somerharju, P.; et al. Seipin Facilitates Triglyceride Flow to Lipid Droplet and Counteracts Droplet Ripening via Endoplasmic Reticulum Contact. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 478–493.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Idrissi, F.-Z.; Hermansson, M.; Grippa, A.; Ejsing, C.S.; Carvalho, P. Seipin and the membrane-shaping protein Pex30 cooperate in organelle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, R.C.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G.; Zhou, L.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Adipose-Specific Knockout of Seipin/BSCL2 Results in Progressive Lipodystrophy. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2320–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, V.T.; Belevich, I.; Li, S.; Karhinen, L.; Vihinen, H.; Vigouroux, C.; Magré, J.; Thiele, C.; Hölttä-Vuori, M.; Jokitalo, E.; et al. Seipin regulates ER –lipid droplet contacts and cargo delivery. Embo J. 2016, 35, 2699–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, W.H.; Shui, G.H.; Gaeta, B.; Du, X.M.; Kuerschner, L.; Li, P.; Brown, A.J.; Wenk, M.R.; Parton, R.G.; Yang, H.Y. Fld1p, a functional homologue of human seipin, regulates the size of lipid droplets in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Huang, L.-J.; Chen, S.-W.; Nebenfuhr, B.; Wysolmerski, B.; Wu, J.-C.; Olson, S.K.; Golden, A.; Wang, C.-W. Loss of the seipin gene perturbs eggshell formation in C. elegans. Development 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Goodman, J.M.; Pyc, M.; Mullen, R.T.; Dyer, J.M.; Chapman, K.D. Arabidopsis SEIPIN Proteins Modulate Triacylglycerol Accumulation and Influence Lipid Droplet Proliferation. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2616–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettebrock, N.T.; Bohnert, M. Born this way—Biogenesis of lipid droplets from specialized ER subdomains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Goodman, J.M. The collaborative work of droplet assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquier, N.; Choudhary, V.; Mari, M.; Toulmay, A.; Reggiori, F.; Schneiter, R. Lipid droplets are functionally connected to the endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassan, A.; Herms, A.; Fernández-Vidal, A.; Bosch, M.; Schieber, N.L.; Reddy, B.J.N.; Fajardo, A.; Gelabert-Baldrich, M.; Tebar, F.; Enrich, C.; et al. Acyl-CoA synthetase 3 promotes lipid droplet biogenesis in ER microdomains. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 203, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuldiner, M.; Bohnert, M. A different kind of love—Lipid droplet contact sites. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, V.T.; Ikonen, E. Moving out but keeping in touch: Contacts between endoplasmic reticulum and lipid droplets. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 57, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfling, F.; Thiam, A.R.; Olarte, M.J.; Wang, J.; Beck, R.; Gould, T.J.; Allgeyer, E.S.; Pincet, F.; Bewersdorf, J.; Farese, R.V.; et al. Arf1/COPI machinery acts directly on lipid droplets and enables their connection to the ER for protein targeting. eLife 2014, 3, e01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Becuwe, M.; E Housden, B.; Chitraju, C.; Porras, A.J.; Graham, M.M.; Liu, X.N.; Thiam, A.R.; Savage, D.B.; Agarwal, A.K.; et al. Seipin is required for converting nascent to mature lipid droplets. eLife 2016, 5, e16582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maté, S.M.; Brenner, R.R.; Ves-Losada, A. Endonuclear lipids in liver cells. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 84, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layerenza, J.P.; González, P.; García de Bravo, M.M.; Polo, M.P.; Sisti, M.S.; Ves-Losada, A. Nuclear lipid droplets: A novel nuclear domain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Tham, D.K.L.; Liang, F.-X.; Chang, J.; Wei, Y.; Sudhir, P.-R.; Sall, J.; Ren, S.J.; Chicote, J.U.; Arnold, L.L.; et al. Mitochondrial lipid droplet formation as a detoxification mechanism to sequester and degrade excessive urothelial membranes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 2969–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Andre, C.; Xu, C. A chloroplast pathway for the de novo biosynthesis of triacylglycerol inChlamydomonas reinhardtii. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarc, E.; Petan, T. Lipid Droplets and the Management of Cellular Stress. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2019, 92, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, D.J.; Dos Santos, M.S.; Huang, S.; Russell, M.R.G.; Collinson, L.M.; Macrae, J.I.; West, A.; Jiang, H.; Gutierrez, M.G. Subcellular antibiotic visualization reveals a dynamic drug reservoir in infected macrophages. Science 2019, 364, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Cermelli, S.; Li, Z.; Kassan, A.; Bosch, M.; Sigua, R.; Huang, L.; Ouellette, A.; Pol, A.; Welte, M.; et al. A novel role for lipid droplets in the organismal antibacterial response. eLife 2012, 1, e00003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, G. Lipid Droplet Metabolism during Dengue Virus Infection. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanari, Y.; Atsuzawa, K.; Usuda, N.; Watashi, K.; Hishiki, T.; Zayas, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Wakita, T.; Hijikata, M.; Shimotohno, K. The lipid droplet is an important organelle for hepatitis C virus production. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, F.; Masouleh, S.K.; Wunderling, K.; Surendar, J.; Schmitt, V.; Kazakov, A.; Michla, M.; Hölzel, M.; Thiele, C.; Wilhelm, C. Lipid-Droplet Formation Drives Pathogenic Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Airway Inflammation. Immunity 2020, 52, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.R.; Stephenson, R.A.; Ghaemmaghami, S.; Welte, M.A. Developmentally regulated H2Av buffering via dynamic sequestration to lipid droplets in Drosophila embryos. eLife 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.A.; Olzmann, J.A. Protein Quality Control and Lipid Droplet Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 36, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.P.; Koster, G.; Guillermier, C.; Hirst, E.M.; Macrae, J.I.; Lechene, C.P.; Postle, A.D.; Gould, A.P. Antioxidant Role for Lipid Droplets in a Stem Cell Niche of Drosophila. Cell 2015, 163, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welte, M.A. How Brain Fat Conquers Stress. Cell 2015, 163, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, J.E. Lipotoxicity: When tissues overeat. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petan, T.; Jarc, E.; Jusović, M. Lipid Droplets in Cancer: Guardians of Fat in a Stressful World. Molecules 2018, 23, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accioly, M.T.; Pacheco, P.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Carrossini, N.; Robbs, B.K.; Oliveira, S.S.; Kaufmann, C.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A.; Bozza, P.T.; Viola, J.P. Lipid Bodies Are Reservoirs of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Sites of Prostaglandin-E2 Synthesis in Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, S.; Cable, C.; Penrose, H.; Makboul, R.; Biswas, D.; Cabe, M.; Crawford, S.E.; Savkovic, S.D. Intestinal inflammation requires FOXO3 and prostaglandin E2-dependent lipogenesis and elevated lipid droplets. Am. J. Physiol. Gastr. Liver 2016, 310, G844–G854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, P.T.; Viola, J.P. Lipid droplets in inflammation and cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2010, 82, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.C.N.; Weller, P.F. Lipid droplets in leukocytes: Organelles linked to inflammatory responses. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 340, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzbekov, R.; Roingeard, P. Nuclear lipid droplets identified by electron microscopy of serial sections. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, A.; Fu, J.; Jiang, G. Specific Accumulation of Lipid Droplets in Hepatocyte Nuclei of PFOA-exposed BALB/c Mice. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, srep02174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Ding, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Lan, L.; Ma, Q.; Chi, X.; Wei, P.; Zhao, Y.F.; Steinbuchel, A.; et al. Bacterial lipid droplets bind to DNA via an intermediary protein that enhances survival under stress. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huo, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, P.; Na, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. The proteomics of lipid droplets: Structure, dynamics, and functions of the organelle conserved from bacteria to humans. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, A.S.C.; Medeiros, L.B.D.A.; Agnez-Lima, L.F.; Lima, J.G.; Campos, J.T.A.D.M. Exploring Seipin: From Biochemistry to Bioinformatics Predictions. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binns, D.; Lee, S.; Hilton, C.L.; Jiang, Q.-X.; Goodman, J.M. Seipin Is a Discrete Homooligomer. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 10747–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Qian, H.; Lukmantara, I.; Gao, M.; Du, X.; Yan, N.; Yang, H. Human SEIPIN Binds Anionic Phospholipids. Dev. Cell 2018, 47, 248–256.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, M. New friends for seipin—Implications of seipin partner proteins in the life cycle of lipid droplets. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Deng, J.; Xu, G.; Peng, X.; Ju, S.; Liu, G.; et al. Seipin ablation in mice results in severe generalized lipodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3022–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chang, B.; Saha, P.; Hartig, S.M.; Li, L.; Reddy, V.T.; Yang, Y.; Yechoor, V.; Mancini, M.A.; Chan, L. Berardinelli-seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/seipin is a cell-autonomous regulator of lipolysis essential for adipocyte differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieur, X.; Dollet, L.; Takahashi, M.; Nemani, M.; Pillot, B.; Le May, C.; Mounier, C.; Takigawa-Imamura, H.; Zelenika, D.; Matsuda, F.; et al. Thiazolidinediones partially reverse the metabolic disturbances observed in BSCL2/seipin-deficient mice. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, V.A.; Grimsey, N.; Tuthill, A.; Virtue, S.; Gray, S.L.; Dalla Nora, E.; Semple, R.K.; O’Rahilly, S.; Rochford, J.J. The human lipodystrophy gene BSCL2/seipin may be essential for normal adipocyte differentiation. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, M. Wrapping up the fats—A structure of the lipid droplet biogenesis protein seipin. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 4053–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolinski, H.; Kolb, D.; Hermann, S.; Koning, R.I.; Kohlwein, S.D. A role for seipin in lipid droplet dynamics and inheritance in yeast. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3894–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grippa, A.; Buxó, L.; Mora, G.; Funaya, C.; Idrissi, F.Z.; Mancuso, F.; Gomez, R.; Muntanyà, J.; Sabidó, E.; Carvalho, P. The seipin complex Fld1/Ldb16 stabilizes ER-lipid droplet contact sites. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 211, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Wu, X.; Lambert, T.J.; Lai, Z.W.; Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V. LDAF1 and Seipin Form a Lipid Droplet Assembly Complex. Dev. Cell 2019, 51, 551–563.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Seipin promotes adipose tissue fat storage through the ER Ca2+-ATPase SERCA. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.G.; Eisenberg-Bord, M.; Persiani, E.; Rochford, J.J.; Schuldiner, M.; Bohnert, M. Promethin Is a Conserved Seipin Partner Protein. Cells 2019, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Arlt, H.; Brock, K.P.; Lai, Z.W.; DiMaio, F.; Marks, D.S.; Liao, M.; Farese, R.V.; Walther, T.C. Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the lipid droplet-formation protein seipin. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 4080–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, K.M.; Binns, D.; Bartz, R.; Grishin, N.V.; Li, W.-P.; Agarwal, A.K.; Garg, A.; Anderson, R.G.W.; Goodman, J.M. The lipodystrophy protein seipin is found at endoplasmic reticulum lipid droplet junctions and is important for droplet morphology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20890–20895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, M.M.; Dennis, R.J.; Aubry, E.M.; Ramanathan, N.; Sembongi, H.; Saudek, V.; Ito, D.; O’Rahilly, S.; Siniossoglou, S.; Rochford, J.J. The human lipodystrophy protein seipin is an ER membrane adaptor for the adipogenic PA phosphatase lipin 1. Mol. Metab. 2013, 2, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.U.; Sim, M.M.; O’Rahilly, S.; Edwardson, J.M.; Rochford, J.J. Seipin oligomers can interact directly with AGPAT2 and lipin 1, physically scaffolding critical regulators of adipogenesis. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagac, M.; Cooper, D.E.; Qi, Y.; Lukmantara, I.E.; Mak, H.Y.; Wu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lei, M.; Du, X.; et al. SEIPIN Regulates Lipid Droplet Expansion and Adipocyte Development by Modulating the Activity of Glycerol-3-phosphate Acyltransferase. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1546–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounis, M.A.; LaLonde, S.; Rial, S.A.; Bergeron, K.-F.; Ralston, J.C.; Mutch, D.M.; Mounier, C. Hepatic BSCL2 (Seipin) Deficiency Disrupts Lipid Droplet Homeostasis and Increases Lipid Metabolism via SCD1 Activity. Lipids 2016, 52, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renvoisé, B.; Malone, B.; Falgairolle, M.; Munasinghe, J.; Stadler, J.; Sibilla, C.; Park, S.H.; Blackstone, C. Reep1 null mice reveal a converging role for hereditary spastic paraplegia proteins in lipid droplet regulation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 5111–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Thein, S.; Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Ericksen, R.E.; Xu, F.; Han, W. BSCL2/seipin regulates adipogenesis through actin cytoskeleton remodelling. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahmer, N.; Jr, R.V.F.; Walther, T.C. Balancing the fat: Lipid droplets and human disease. Embo Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Agarwal, A.K. Lipodystrophies: Disorders of adipose tissue biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2009, 1791, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang-Doran, I.; Sleigh, A.; Rochford, J.J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Savage, D.B. Lipodystrophy: Metabolic insights from a rare disorder. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 207, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigouroux, C.; Caron-Debarle, M.; Le Dour, C.; Magré, J.; Capeau, J. Molecular mechanisms of human lipodystrophies: From adipocyte lipid droplet to oxidative stress and lipotoxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oral, E.A.; Simha, V.; Ruiz, E.; Andewelt, A.; Premkumar, A.; Snell, P.; Wagner, A.J.; DePaoli, A.M.; Reitman, M.L.; Taylor, S.I.; et al. Leptin-Replacement Therapy for Lipodystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, I.; Hammer, R.E.; Ikemoto, S.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Leptin reverses insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in mice with congenital lipodystrophy. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 401, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, C.; Trayhurn, P. New insights into adipose tissue atrophy in cancer cachexia. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2009, 68, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Eder, S.; Schauer, S.; Diwoky, C.; Temmel, H.; Guertl, B.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Tamilarasan, K.P.; Kumari, P.; Trauner, M.; et al. Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Contributes to Cancer-Associated Cachexia. Science 2011, 333, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, M.; Lass, A.; Zimmermann, R.; Eichmann, T.O.; Zechner, R. Neutral lipid storage disease: Genetic disorders caused by mutations in adipose triglyceride lipase/PNPLA2orCGI-58/ABHD5. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2009, 297, E289–E296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, C.; Jobard, F.; Caux, F.; Bouadjar, B.; Karaduman, A.; Heilig, R.; Lakhdar, H.; Wollenberg, A.; Verret, J.-L.; Weissenbach, J.; et al. Mutations in CGI-58, the Gene Encoding a New Protein of the Esterase/Lipase/Thioesterase Subfamily, in Chanarin-Dorfman Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haemmerle, G.; Moustafa, T.; Woelkart, G.; Büttner, S.; Schmidt, A.; van de Weijer, T.; Hesselink, M.; Jaeger, D.; Kienesberger, P.; Zierler, K.; et al. ATGL-mediated fat catabolism regulates cardiac mitochondrial function via PPAR-α and PGC-1. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, W.; Inoue, M.; Ohtake, T.; Takahashi, N.; Nagamine, M.; Tanno, S.; Kohgo, Y.; Okumura, T. Up-regulation of ADRP in fatty liver in human and liver steatosis in mice fed with high fat diet. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Sentinelli, F.; Dash, S.; Yeo, G.S.H.; Savage, D.B.; Leonetti, F.; Capoccia, D.; Incani, M.; Maglio, C.; Iacovino, M.; et al. Morbid obesity exposes the association between PNPLA3 I148M (rs738409) and indices of hepatic injury in individuals of European descent. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 34, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Wolfe, D.; Han, G.; French, S.W.; Ross, M.G.; Desai, M. Early onset of fatty liver in growth-restricted rat fetuses and newborns. Congenit. Anom. 2011, 51, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Wu, J.; Hernaez, R.; Kim, L.J.; Palmer, C.D.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Garcia, M.E.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Variants Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease That Have Distinct Effects on Metabolic Traits. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantartzis, K.; Machicao, F.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Stefan, N. The DGAT2 gene is a candidate for the dissociation between fatty liver and insulin resistance in humans. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Lazar, M.A. Dissociating fatty liver and diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Tabas, I. Macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell 2011, 145, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner-Weibel, G.; Jerome, W.G.; Small, D.M.; Warner, G.J.; Stoltenborg, J.K.; A Kearney, M.; Corjay, M.H.; Phillips, M.C.; Rothblat, G.H. Effects of intracellular free cholesterol accumulation on macrophage viability: A model for foam cell death. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornfeldt, K.; Tabas, I. Insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maté, S.; Layerenza, J.; Ves-Losada, A. Arachidonic acid pools of rat kidney cell nuclei. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 345, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsaki, Y.; Kawai, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jokitalo, E.; Fujimoto, T. PML isoform II plays a critical role in nuclear lipid droplet formation. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 212, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maté, S.; Layerenza, J.; Ves-Losada, A. Incorporation of arachidonic and stearic acids bound to L-FABP into nuclear and endonuclear lipids from rat liver cells. Lipids 2007, 42, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.D.; Siniossoglou, S. New kid on the block: Lipid droplets in the nucleus. FEBS J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, P.; Ren, Z. SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218208
Jin Y, Tan Y, Zhao P, Ren Z. SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218208
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yi, Yanjie Tan, Pengxiang Zhao, and Zhuqing Ren. 2020. "SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218208
APA StyleJin, Y., Tan, Y., Zhao, P., & Ren, Z. (2020). SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218208




