Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
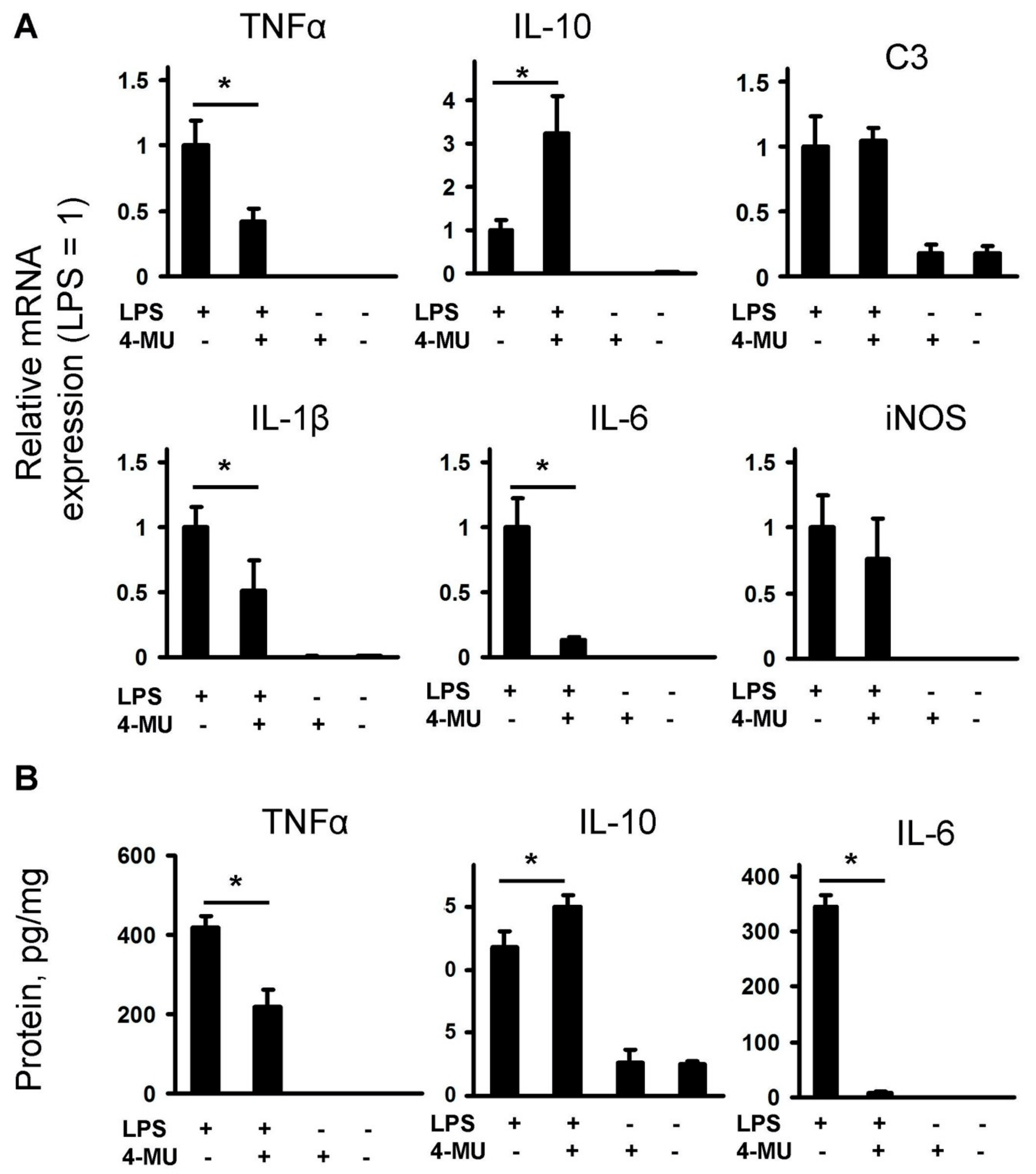
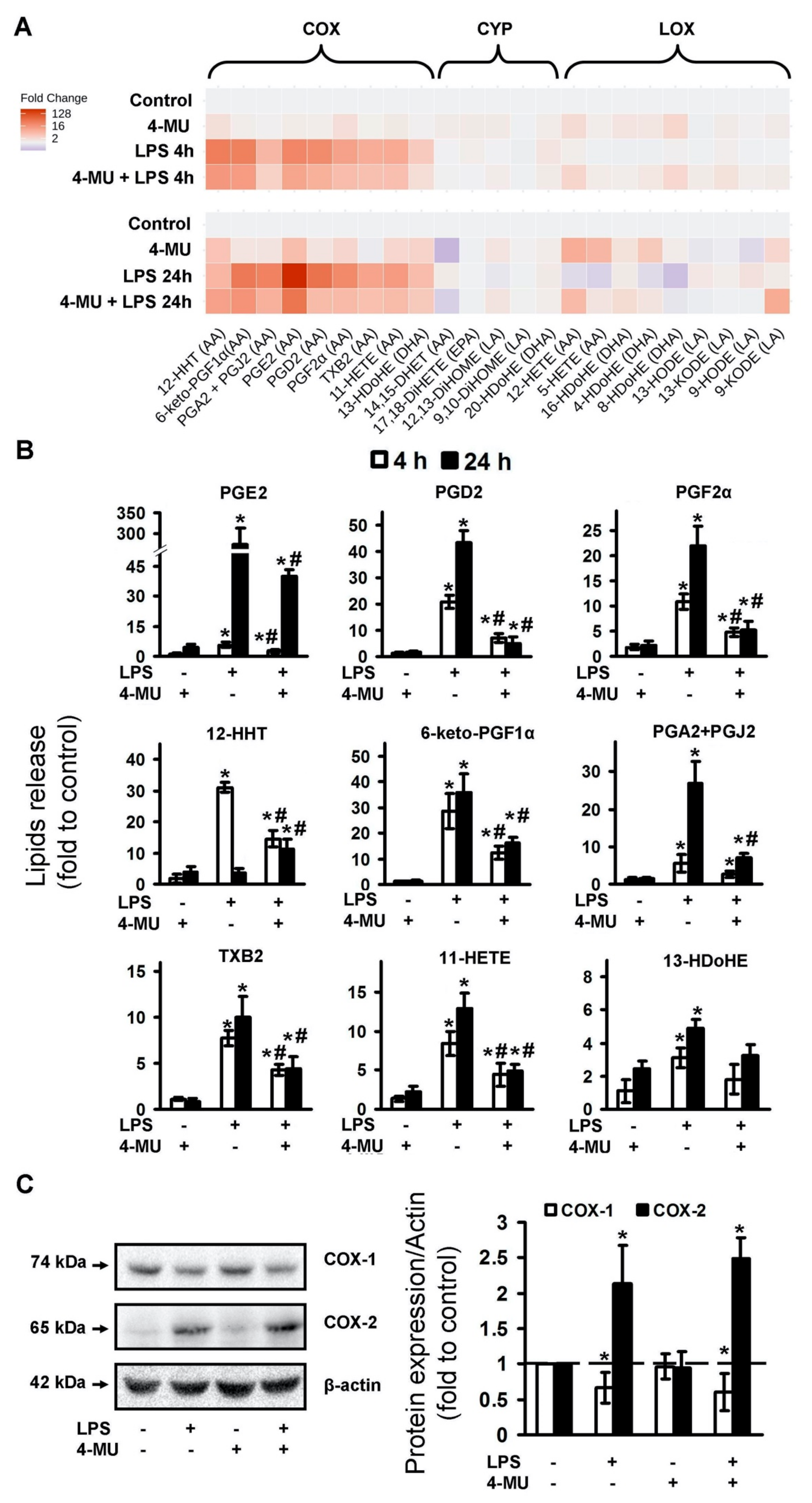
2.1. LPS-Induced Release of Cytokines and Oxylipins Modulates by 4-MU
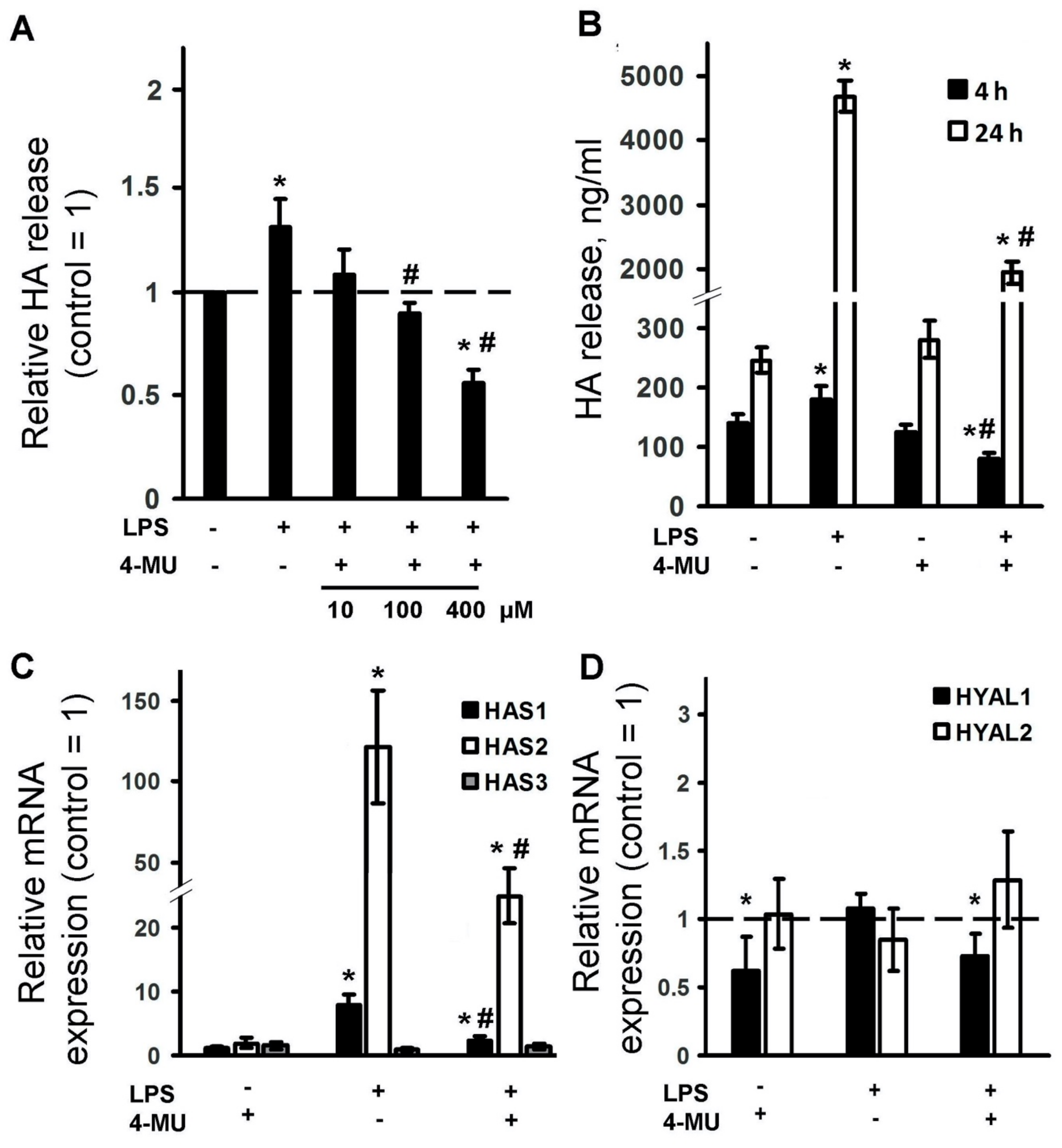
2.2. LPS Induces Expression of HA Synthase Enzymes and HA Release, Which Is Inhibited by 4-MU
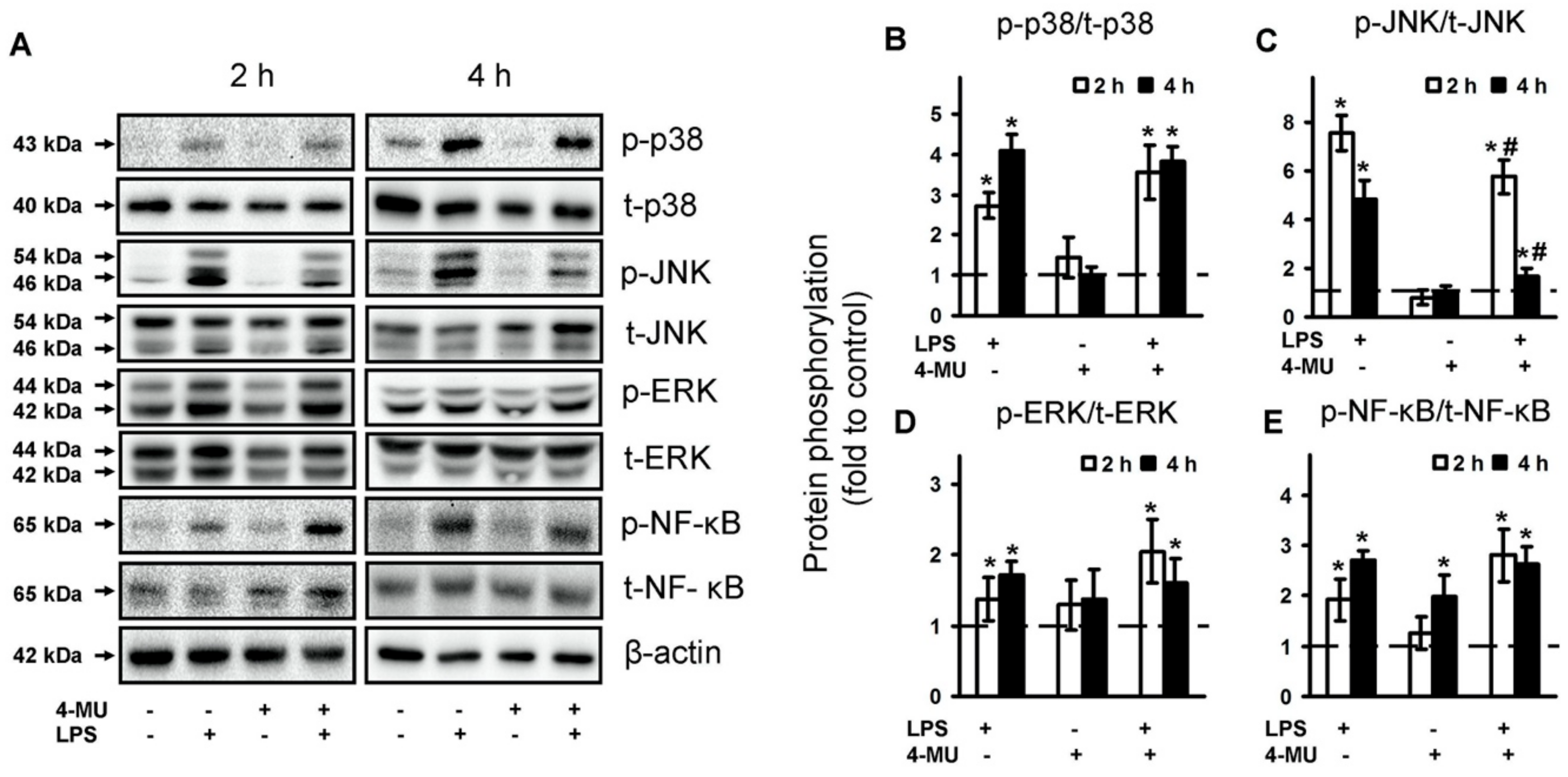
2.3. 4-MU Modulate TLR-Mediated JNK but Not p38, ERK MAPK and NF-kB Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Primary Cell Culture
4.3. Measurement of the Relative RNA Expression Level
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. UPLC-MS/MS Conditions and Sample Preparation
4.6. Determination of TNFα, IL-10, IL-6 and Hyaluronic Acid by Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay
4.7. Experimental Data Analysis and Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| COX | Cyclooxygenase |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| HA | hyaluronic acid |
| IL-10 | interleukin-10 |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LOX | Lipoxygenase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| PG | Prostaglandin |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| UPLC-MS/MS | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
References
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Schafer, D.; Vincent, A.; Blachère, N.E.; Bar-Or, A. Neuroinflammation: Ways in Which the Immune System Affects the Brain. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farina, C.; Aloisi, F.; Meinl, E. Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol 2007, 28, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohlfeld, R.; Kerschensteiner, M.; Meinl, E. Dual role of inflammation in CNS disease. Neurology 2007, 68, S58–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filous, A.R.; Silver, J. Targeting astrocytes in CNS injury and disease: A translational research approach. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 144, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graeber, M.B.; Li, W.; Rodriguez, M.L. Role of microglia in CNS inflammation. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3798–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rietdijk, C.D.; Van Wezel, R.J.A.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D. Neuronal toll-like receptors and neuro-immunity in Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and stroke. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Gavrish, G.E.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Azbukina, N.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Oxylipin profiles as functional characteristics of acute inflammatory responses in astrocytes pre-treated with IL-4, IL-10, or LPS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Azbukina, N.V.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. High and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Differentially Influences Oxylipins Synthesis in Course of Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2015, 109, 14.12.1–14.12.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Aleshin, S.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Reiser, G. Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/δ expression and activity levels by toll-like receptor agonists and MAP kinase inhibitors in rat astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garantziotis, S.; Savani, R.C. Hyaluronan biology: A complex balancing act of structure, function, location and context. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theocharis, A.D.; Manou, D.; Karamanos, N.K. The extracellular matrix as a multitasking player in disease. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 2830–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan as an Immune Regulator in Human Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 221–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagy, N.; Kuipers, H.F.; Frymoyer, A.R.; Ishak, H.D.; Bollyky, J.B.; Wight, T.N.; Bollyky, P.L. 4-Methylumbelliferone treatment and hyaluronan inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, L.W.; Cua, R.; Keough, M.B.; Haylock-Jacobs, S.; Yong, V.W. Pathophysiology of the brain extracellular matrix: A new target for remyelination. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneh-Barkay, D.; Wiley, C.A. Brain extracellular matrix in neurodegeneration. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.S.; Franco, S.J.; Müller, U. Extracellular Matrix: Functions in the nervous system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toole, B.P. Hyaluronan: From extracellular glue to pericellular cue. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.M.; Yoon, B.H.; Sadiq, S.A. Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis protects against central nervous system (CNS) autoimmunity and increases CXCL12 expression in the inflamed CNS. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22888–22899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherman, L.S.; Matsumoto, S.; Su, W.; Srivastava, T.; Back, S.A. Hyaluronan Synthesis, Catabolism, and Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marret, S.; Delpech, B.; Delpech, A.; Asou, H.; Girard, N.; Courel, M.N.; Chauzy, C.; Maingonnat, C.; Fessard, C. Expression and Effects of Hyaluronan and of the Hyaluronan-Binding Protein Hyaluronectin in Newborn Rat Brain Glial Cell Cultures. J. Neurochem. 1994, 62, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, R.; Bignami, A. Localization of hyaluronate in primary glial cell cultures derived from newborn rat brain. Exp. Cell Res. 1991, 195, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Kozawa, E.; Urakawa, H.; Arai, E.; Futamura, N.; Zhuo, L.; Kimata, K.; Ishiguro, N.; Nishida, Y. Suppression of hyaluronan synthesis alleviates inflammatory responses in murine arthritis and in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Funahashi, M.; Takagaki, K.; Munakata, H.; Tanaka, K.; Saito, Y.; Endo, M. Effect of 4-methylumbelliferone on cell-free-synthesis of hyaluronic acid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1997, 43, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Hao, P.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Han, R.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X. Effects of 4-methylumbelliferone and high molecular weight hyaluronic acid on the inflammation of corneal stromal cells induced by LPS. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgoczi, E.; Jeney, F.; Katko, M.; Erdei, A.; Gazdag, A.; Sira, L.; Bodor, M.; Berta, E.; Ujhelyi, B.; Steiber, Z.; et al. Characteristics of hyaluronan synthesis inhibition by 4-methylumbelliferone in orbital fibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilla, K.; Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Rieppo, J.; Tammi, M.; Tammi, R. The hyaluronan synthesis inhibitor 4-methylumbelliferone prevents keratinocyte activation and epidermal hyperproliferation induced by epidermal growth. J. Investig. Derm. 2004, 123, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edward, M.; Quinn, J.A.; Pasonen-Seppänen, S.M.; McCann, B.A.; Tammi, R.H. 4-Methylumbelliferone inhibits tumour cell growth and the activation of stromal hyaluronan synthesis by melanoma cell-derived factors. Br. J. Derm. 2010, 162, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, H.; Yoshihara, S.; Kudo, D.; Morohashi, H.; Kakizaki, I.; Kon, A.; Takagaki, K.; Sasaki, M. 4-methylumbelliferone, a hyaluronan synthase suppressor, enhances the anticancer activity of gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2006, 57, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKallip, R.J.; Hagele, H.F.; Uchakina, O.N. Treatment with the hyaluronic acid synthesis inhibitor 4-methylumbelliferone suppresses SEB-induced lung inflammation. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKallip, R.J.; Ban, H.; Uchakina, O.N. Treatment with the Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis Inhibitor 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses LPS-Induced Lung Inflammation. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombaro, V.; Declèves, A.E.; Jadot, I.; Voisin, V.; Giordano, L.; Habsch, I.; Nonclercq, D.; Flamion, B.; Caron, N. Inhibition of hyaluronan is protective against renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013, 28, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagy, N.; Freudenberger, T.; Melchior-Becker, A.; Röck, K.; Ter Braak, M.; Jastrow, H.; Kinzig, M.; Lucke, S.; Suvorava, T.; Kojda, G.; et al. Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis accelerates murine atherosclerosis: Novel insights into the role of hyaluronan synthesis. Circulation 2010, 122, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sim, M.O.; Ham, J.R.; Lee, H.I.; Seo, K.I.; Lee, M.K. Long-term supplementation of umbelliferone and 4-methylumbelliferone alleviates high-fat diet induced hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycemia in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 216, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, A.R.; Marriott, I. The interleukin-10 family of cytokines and their role in the CNS. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serhan, C.N.; Brain, S.D.; Buckley, C.D.; Gilroy, D.W.; Haslett, C.; O’Neill, L.A.J.; Perretti, M.; Rossi, A.G.; Wallace, J.L. Resolution of inflammation: State of the art, definitions and terms. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabbs, M.; Leng, S.; Devassy, J.G.; Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Advances in Our Understanding of Oxylipins Derived from Dietary PUFAs. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Grabeklis, S.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Reiser, G. Astrocytes synthesize primary and cyclopentenone prostaglandins that are negative regulators of their proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhova, A.A.; Chistyakov, D.V.; Pankevich, E.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 expression by agonists of PPAR nuclear receptors in the model of endotoxin tolerance in astrocytes. Biochemistry 2015, 80, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hascall, V.C.; Wang, A.; Tammi, M.; Oikari, S.; Tammi, R.; Passi, A.; Vigetti, D.; Hanson, R.W.; Hart, G.W. The dynamic metabolism of hyaluronan regulates the cytosolic concentration of UDP-GlcNAc. Matrix Biol. 2014, 35, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Aleshin, S.E.; Astakhova, A.A.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Reiser, G. Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) α and -γ of rat brain astrocytes in the course of activation by toll-like receptor agonists. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincozes-Santos, A.; Bobermin, L.D.; de Assis, A.M.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Souza, D.O. Fluctuations in glucose levels induce glial toxicity with glutamatergic, oxidative and inflammatory implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Azbukina, N.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Polozhintsev, A.I.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Reiser, G. Toll-like receptors control p38 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways in rat astrocytes differently, when cultured in normal or high glucose concentrations. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131, 104513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Signaling to NF-κB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Azbukina, N.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Sex-mediated differences in lps induced alterations of TNFα, IL-10 expression, and prostaglandin synthesis in primary astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astakhova, A.A.; Chistyakov, D.V.; Sergeeva, M.G.; Reiser, G. Regulation of the ARE-binding proteins, TTP (tristetraprolin) and HuR (human antigen R), in inflammatory response in astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 118, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.W.; Schrör, K. Regulation of hyaluronan synthesis by vasodilatory prostaglandins: Implications for atherosclerosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, I.; Kojima, K.; Takagaki, K.; Endo, M.; Kannagi, R.; Ito, M.; Maruo, Y.; Sato, H.; Yasuda, T.; Mita, S.; et al. A novel mechanism for the inhibition of hyaluronan biosynthesis by 4-methylumbelliferone. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33281–33289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kultti, A.; Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Jauhiainen, M.; Rilla, K.J.; Kärnä, R.; Pyöriä, E.; Tammi, R.H.; Tammi, M.I. 4-Methylumbelliferone inhibits hyaluronan synthesis by depletion of cellular UDP-glucuronic acid and downregulation of hyaluronan synthase 2 and 3. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, N.; Sawai, T.; Yoshida, M.; Lenas, P.; Yamada, Y.; Imagawa, M.; Shinomura, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Ohnuki, Y.; et al. Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25085–25092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishizuka, S.; Askew, E.B.; Ishizuka, N.; Knudson, C.B.; Knudson, W. 4-Methylumbelliferone diminishes catabolically activated articular chondrocytes and cartilage explants via a mechanism independent of hyaluronan inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12087–12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Fujita, Y.; Kuroda, A.; Menju, T.; Sonobe, M.; Kondo, N.; Torii, I.; Nakano, T.; Lara, P.N.; et al. Trametinib plus 4-Methylumbelliferone Exhibits Antitumor Effects by ERK Blockade and CD44 Downregulation and Affects PD-1 and PD-L1 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kretschmer, I.; Freudenberger, T.; Twarock, S.; Fischer, J.W. Synergistic effect of targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor and hyaluronan synthesis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Br. J. Pharm. 2015, 172, 4560–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twarock, S.; Tammi, M.I.; Savani, R.C.; Fischer, J.W. Hyaluronan stabilizes focal adhesions, filopodia, and the proliferative phenotype in esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23276–23284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lokeshwar, V.B.; Lopez, L.E.; Munoz, D.; Chi, A.; Shirodkar, S.P.; Lokeshwar, S.D.; Escudero, D.O.; Dhir, N.; Altman, N. Antitumor activity of hyaluronic acid synthesis inhibitor 4-methylumbelliferone in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchakina, O.N.; Ban, H.; McKallip, R.J. Targeting hyaluronic acid production for the treatment of leukemia: Treatment with 4-methylumbelliferone leads to induction of MAPK-mediated apoptosis in K562 leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigetti, D.; Viola, M.; Karousou, E.; De Luca, G.; Passi, A. Metabolic control of hyaluronan synthases. Matrix Biol. 2014, 35, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigetti, D.; Ori, M.; Viola, M.; Genasetti, A.; Karousou, E.; Rizzi, M.; Pallotti, F.; Nardi, I.; Hascall, V.C.; De Luca, G.; et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase from the amphibian Xenopus laevis and its involvement in hyaluronan synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8254–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigetti, D.; Rizzi, M.; Viola, M.; Karousou, E.; Genasetti, A.; Clerici, M.; Bartolini, B.; Hascall, V.C.; De Luca, G.; Passi, A. The effects of 4-methylumbelliferone on hyaluronan synthesis, MMP2 activity, proliferation, and motility of human aortic smooth muscle cells. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heurtaux, T.; Benani, A.; Moulin, D.; Muller, N.; Netter, P.; Minn, A. Induction of UGT1A6 isoform by inflammatory conditions in rat astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 2006, 50, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulson-Thomas, V.J.; Lauer, M.E.; Soleman, S.; Zhao, C.; Hascall, V.C.; Day, A.J.; Fawcett, J.W. Tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6 (tsg-6) is constitutively expressed in adult central nervous system (cns) and associated with astrocyte-mediated glial scar formation following spinal cord injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 19939–19952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, A.J.; Milner, C.M. TSG-6: A multifunctional protein with anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective properties. Matrix Biol. 2019, 78, 60–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, S.R.; Barrow, K.A.; Rich, L.M.; White, M.P.; Shubin, N.J.; Chan, C.K.; Kang, I.; Ziegler, S.F.; Piliponsky, A.M.; Wight, T.N.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection of Human Lung Fibroblasts Induces a Hyaluronan-Enriched Extracellular Matrix That Binds Mast Cells and Enhances Expression of Mast Cell Proteases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha TNFα | CAAGGAGGAGAAGTTCCCAA | TGATCTGAGTGTGAGGGTCTG |
| Interleukin 10 IL-10 | CCCAGAAATCAAGGAGCATTTG | TCATTCTTCACCTGCTCCAC |
| Complement component 3 C3 | AAGCCCAACACCAGCTACATC | ACTTCTGATCCTGGCATTCTTCT |
| Interleukin 1 beta IL-1β | CACCTCTCAAGCAGAGCACAG | GGGTTCCATGGTGAAGTCAAC |
| Interleukin 6 IL-6 | CTGGTCTTCTGGAGTTCCGT | TGGTCTTGGTCCTTAGCCAC |
| Inducible nitric oxide synthase iNOS | CCACAATAGTACAATACTACTTGG | ACGAGGTGTTCAGCGTGCTCCACG |
| Hyaluronan synthase 1 has1 | AGGTGCTGTTGGAGGAGATGTGA | AAGCTCGCTCCACATTGAAGGCTA |
| Hyaluronan synthase 2 has2 | CCAATGCAGTTTCGGTGATG | ACTTGGACCGAGCCGTGTAT |
| Hyaluronan synthase 3 has3 | CCTCATCGCCACAGTCATACAA | CCACCAGCTGCACCGTTAGT |
| Hyaluronidase-1 hyal1 | TCGGACCCTTTATCCTGAAC | TTCTTACACCACTCTCCACTC |
| Hyaluronidase-2 hyal2 | TCAGTGTACGCTTCAAGTATGGA | GACTGAGGTGCAAGAAGGTACTG |
| β-actin | AGATGACCCAGATCATGTTTGAG | GGCATACAGGGACAACACAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chistyakov, D.V.; Nikolskaya, A.I.; Goriainov, S.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Sergeeva, M.G. Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218203
Chistyakov DV, Nikolskaya AI, Goriainov SV, Astakhova AA, Sergeeva MG. Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218203
Chicago/Turabian StyleChistyakov, Dmitry V., Arina I. Nikolskaya, Sergei V. Goriainov, Alina A. Astakhova, and Marina G. Sergeeva. 2020. "Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218203
APA StyleChistyakov, D. V., Nikolskaya, A. I., Goriainov, S. V., Astakhova, A. A., & Sergeeva, M. G. (2020). Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218203





