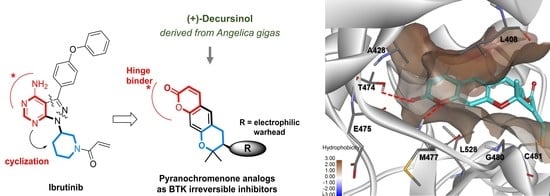
Discovery of Tricyclic Pyranochromenone as Novel Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with In Vivo Antirheumatic Activity
Abstract
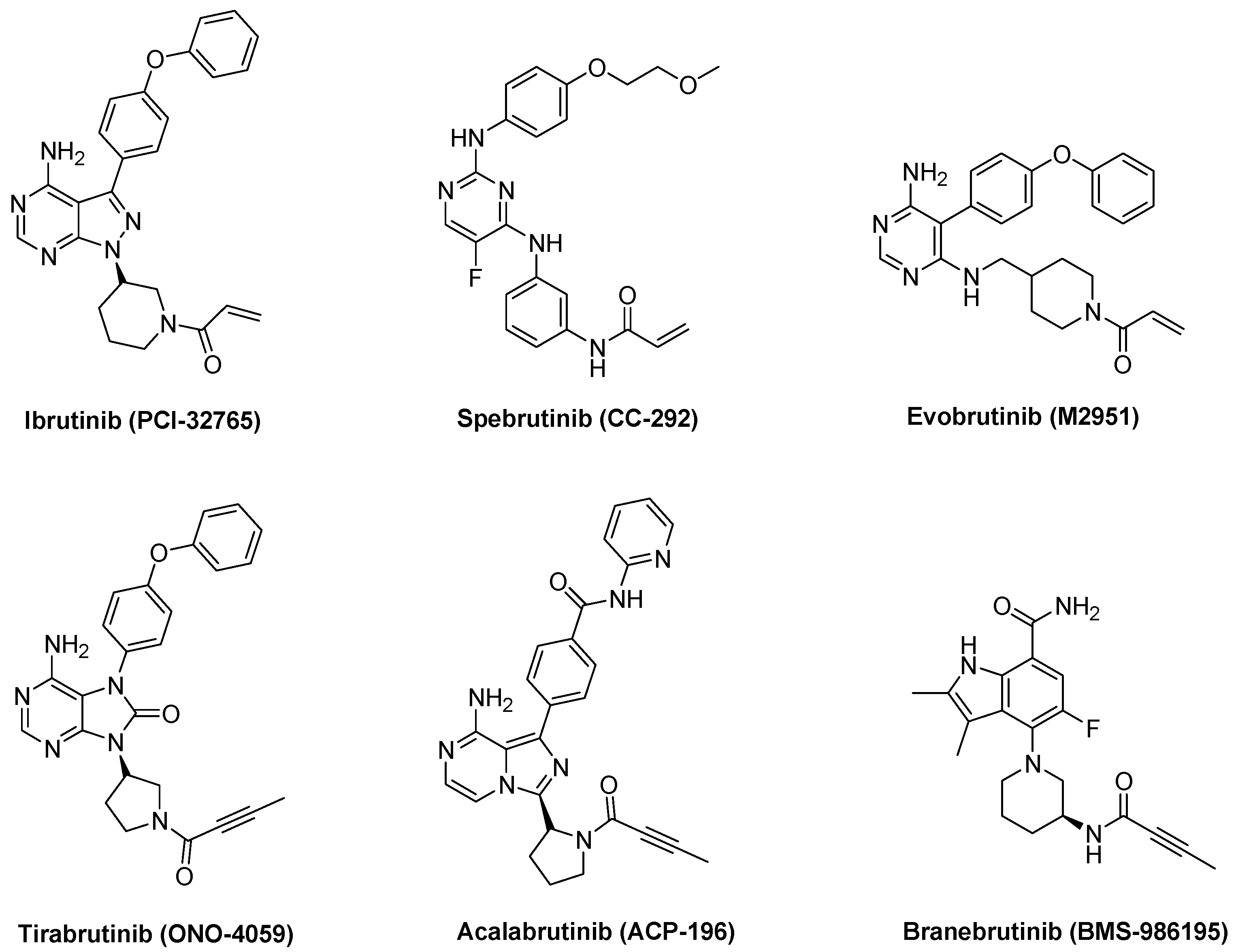
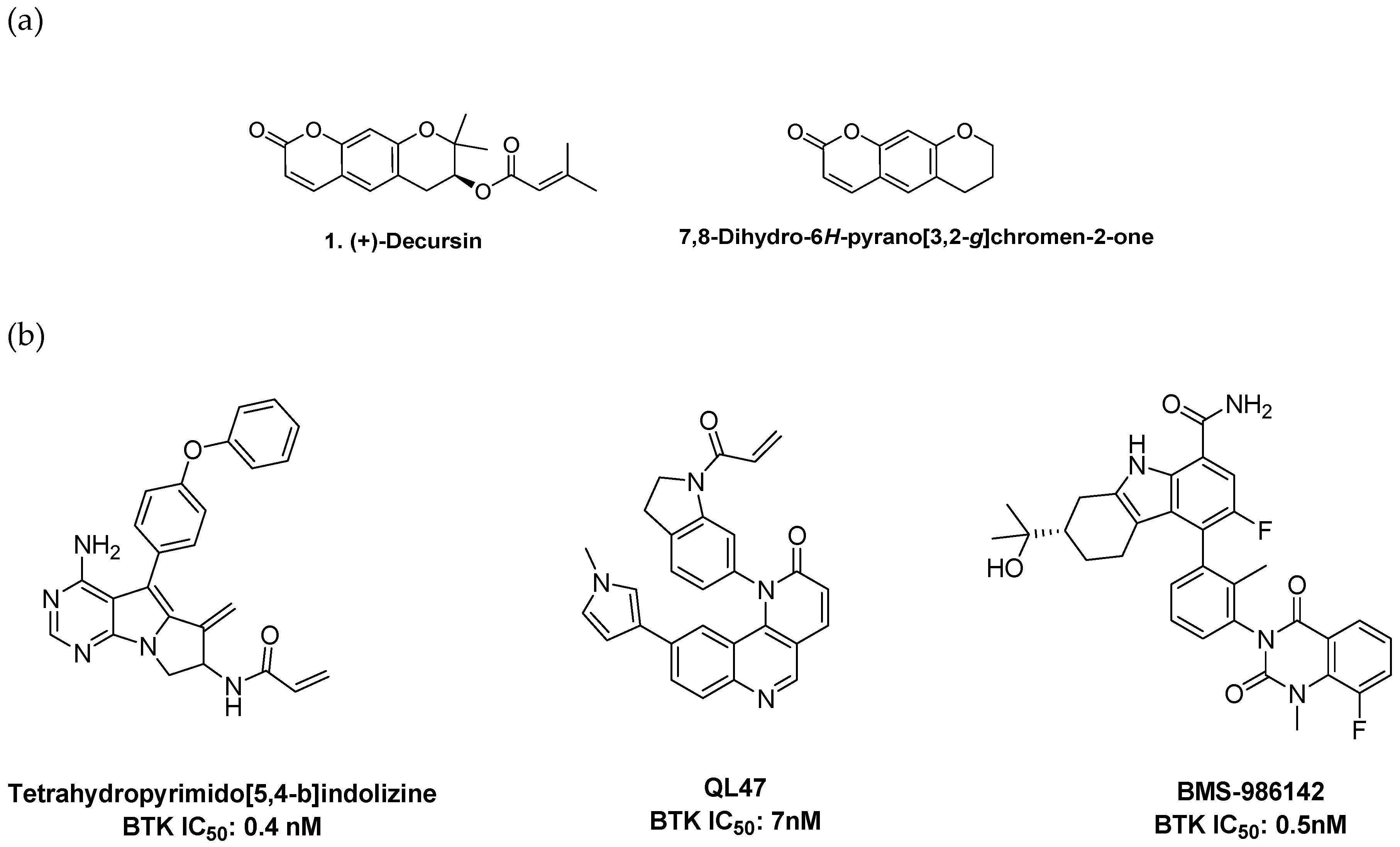
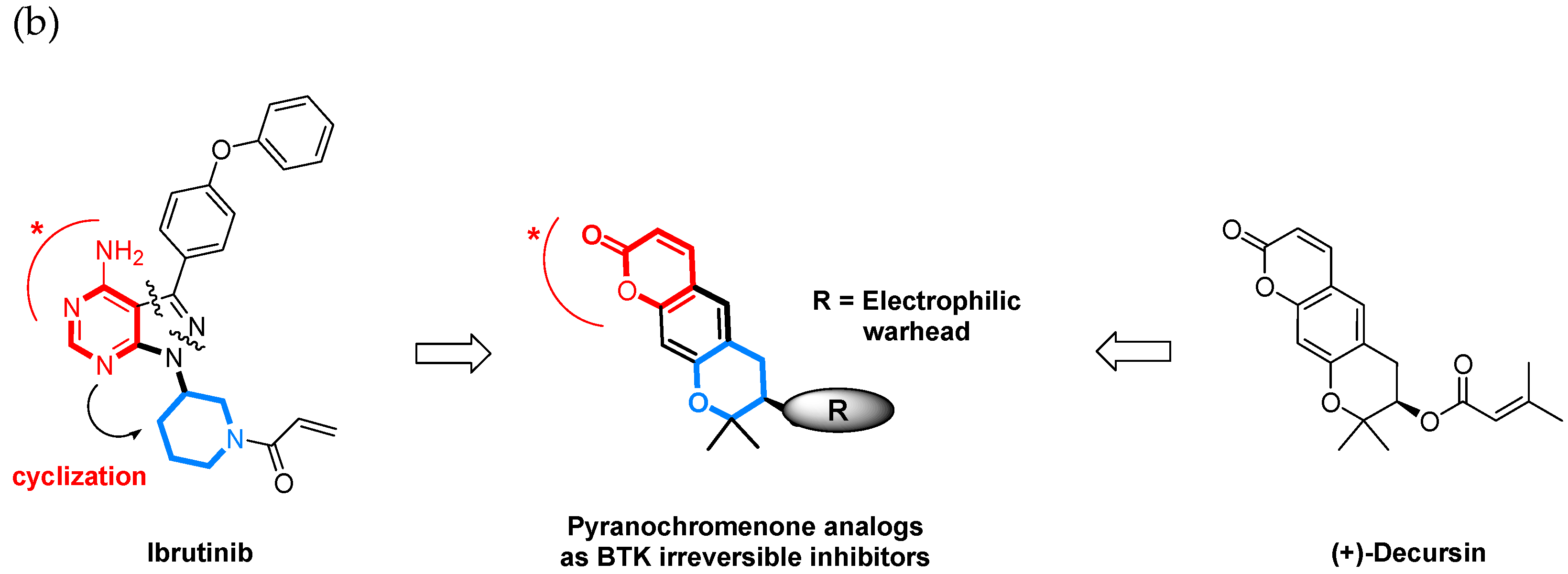
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
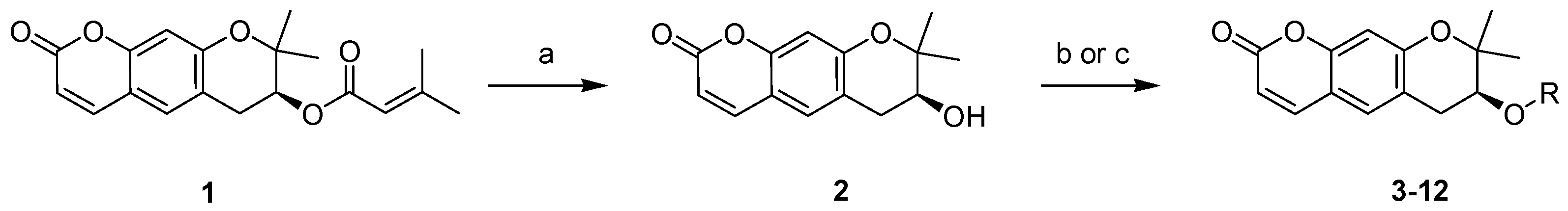
2.1. Synthesis of Pyranochromenone Analogs
2.2. Structure–Activity Relationship Analysis
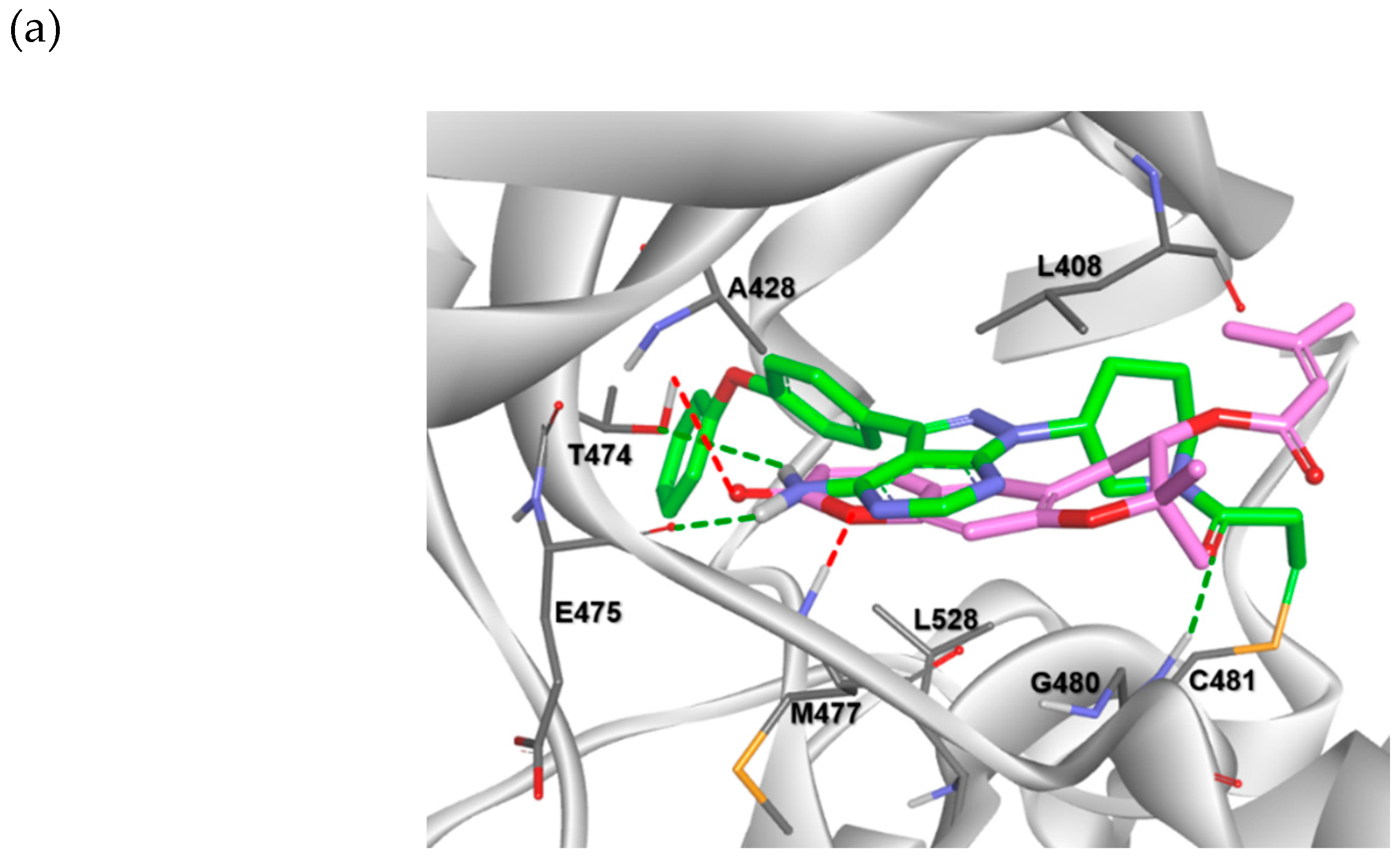
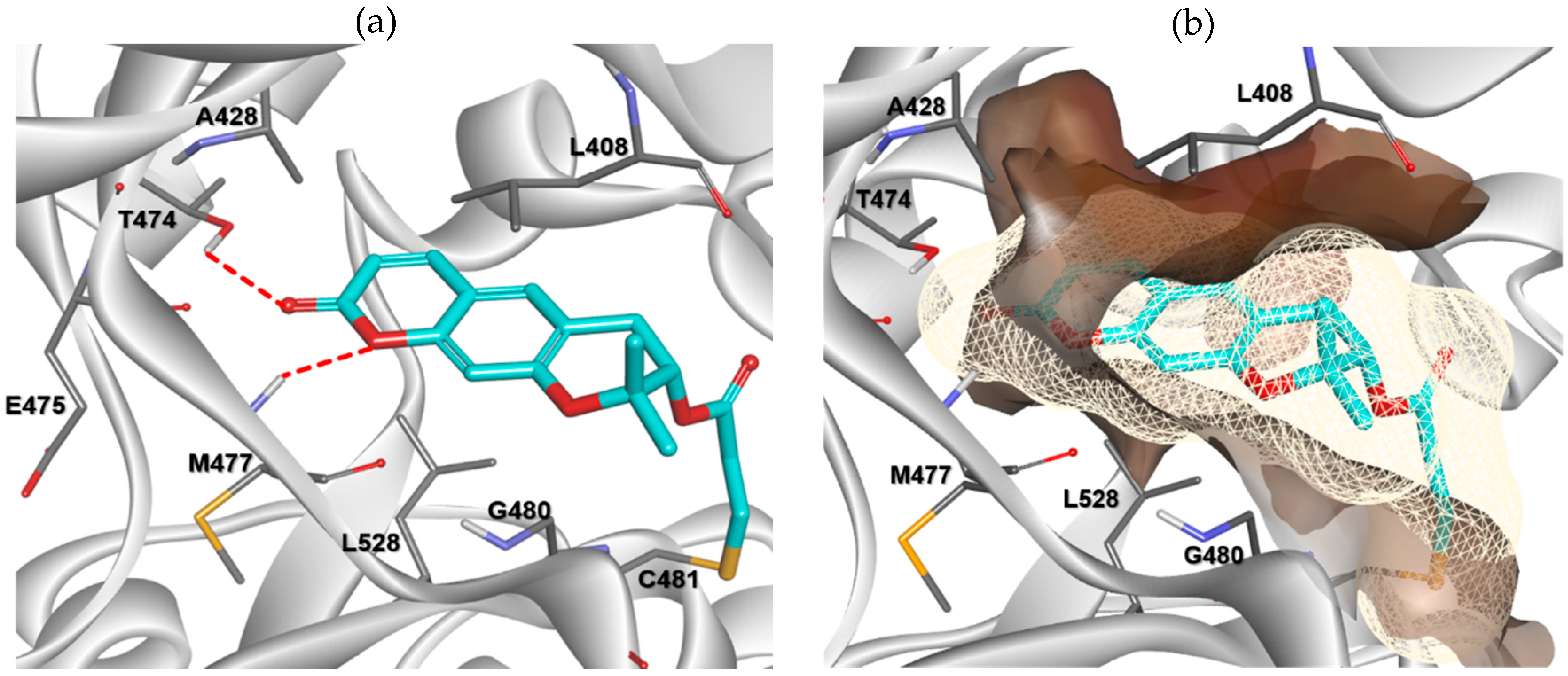
2.3. Molecular Docking Analysis
2.4. Permeability and CYP Inhibitory Activity
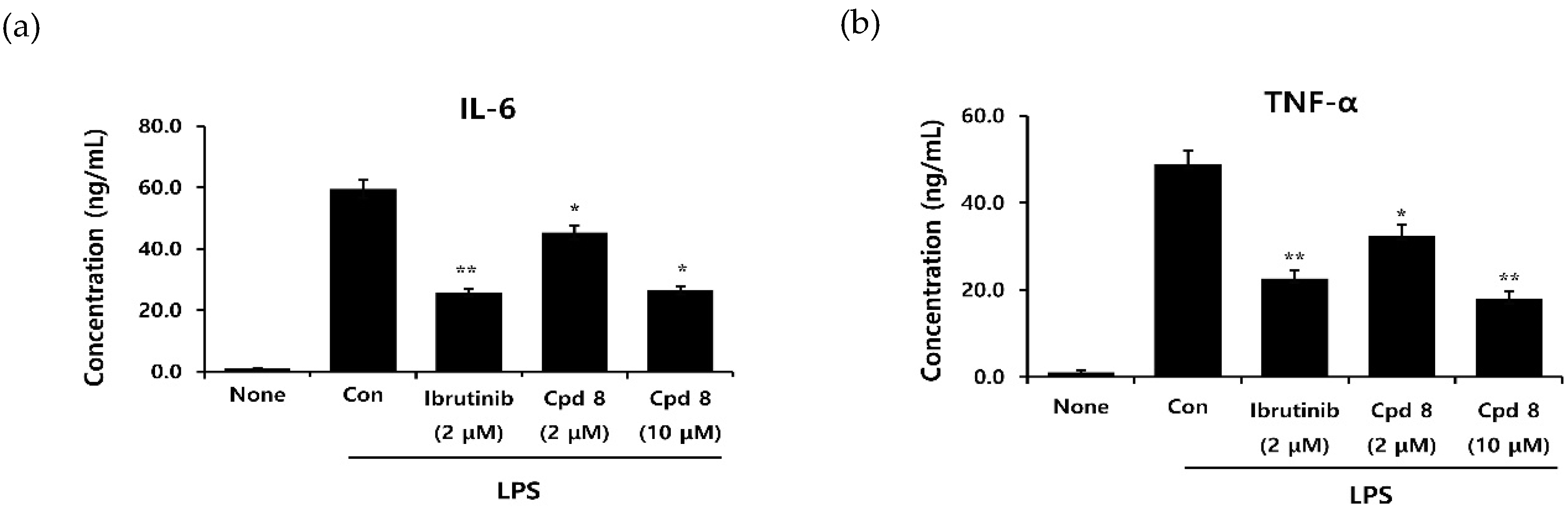
2.5. In Vitro Inhibitory Activity on Cytokine Production
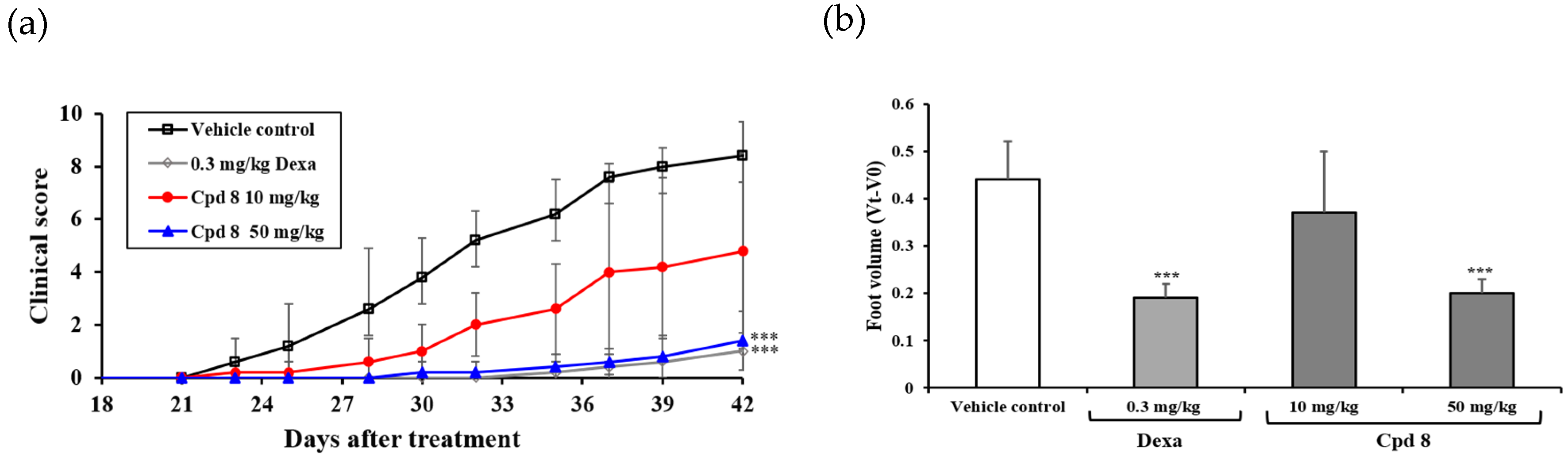
2.6. Antirheumatic Activity in a Murine Model of Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Preparation of Decursin (1)
3.1.2. S-(+)-Decursinol (2)
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 3–7, 11, and 12
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 8–10
3.2. In Vitro Kinase Enzymatic Assays
3.3. Molecular Modeling
3.4. Cytokine Assay
3.5. In Vitro Permeability Assay
3.6. In Vitro CYP Inhibition Assay
3.7. In Vivo Antirheumatic Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DMAC | Dimethylacetamide |
| DW | Distilled water |
| PAMPA | Parallel artificial membrane permeability assay |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
References
- Smith, C.I.; Islam, T.C.; Mattsson, P.T.; Mohamed, A.J.; Nore, B.F.; Vihinen, M. The Tec family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases: Mammalian Btk, Bmx, Itk, Tec, Txk and homologs in other species. BioEssays 2001, 23, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, J.M. The Src, Syk, and Tec family kinases: Distinct types of molecular switches. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppers, R. Mechanisms of B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakken, B.; Munthe, L.A.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Sandberg, A.K.; Szekanecz, Z.; Alex, P.; Szodoray, P. B-cells and their targeting in rheumatoid arthritis--current concepts and future perspectives. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 11, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, A.M.; Rivera, J. The tyrosine kinase network regulating mast cell activation. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satterthwaite, A.B.; Li, Z.; Witte, O.N. BTK function in B cell development and response. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, U.; Boucheron, N.; Unger, B.; Ellmeier, W. The role of Tec family kinases in myeloid cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 134, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, C.; Muller, B.; Wirth, T. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase is involved in innate and adaptive immunity. Histol Histopathol. 2005, 20, 945–955. [Google Scholar]
- Pal Singh, S.; Dammeijer, F.; Hendriks, R.W. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, R.W.; Yuvaraj, S.; Kil, L.P. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cell malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwood, N.J.; Urbaniak, A.M.; Danks, L. Tec family kinases in inflammation and disease. Int Rev. Immunol. 2012, 31, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Scheerens, H.; Li, S.J.; Schultz, B.E.; Sprengeler, P.A.; Burrill, L.C.; Mendonca, R.V.; Sweeney, M.D.; Scott, K.C.; Grothaus, P.G.; et al. Discovery of selective irreversible inhibitors for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Chem. Med. Chem. 2007, 2, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.K.; Tester, R.; Aslanian, S.; Karp, R.; Sheets, M.; Labenski, M.T.; Witowski, S.R.; Lounsbury, H.; Chaturvedi, P.; Mazdiyasni, H.; et al. Inhibition of BTK with CC-292 provides early pharmacodynamic assessment of activity in mice and humans. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walter, H.S.; Rule, S.A.; Dyer, M.J.; Karlin, L.; Jones, C.; Cazin, B.; Quittet, P.; Shah, N.; Hutchinson, C.V.; Honda, H.; et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of the selective BTK inhibitor ONO/GS-4059 in relapsed and refractory mature B-cell malignancies. Blood 2016, 127, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, Y.; O’Brien, S. Acalabrutinib and its use in treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowndhararajan, K.; Kim, S. Neuroprotective and Cognitive Enhancement Potentials of Angelica gigas Nakai Root: A Review. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 85, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.H.; Kwon, J.E.; Cho, Y.; Kim, I.; Kang, S.C. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Angelica gigas via Heme Oxygenase (HO)-1 Expression. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4862–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahat, B.; Chae, J.W.; Baek, I.H.; Song, G.Y.; Song, J.S.; Ma, J.Y.; Kwon, K.I. Biopharmaceutical characterization of decursin and their derivatives for drug discovery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Deacon, S.; Horiuchi, K. The challenge of selecting protein kinase assays for lead discovery optimization. Expert Opin. Drug. Discov. 2008, 3, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; O’Brien, S.; James, D.F. Ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1278–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, P.H.; Kivitz, A.J.; Ma, J.; Korish, S.; Sutherland, D.; Li, L.; Azaryan, A.; Kosek, J.; Adams, M.; Capone, L.; et al. Spebrutinib (CC-292) Affects Markers of B Cell Activation, Chemotaxis, and Osteoclasts in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a Mechanistic Study. Rheum. Ther. 2020, 7, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotla, S.; Singh, N.K.; Rao, G.N. ROS via BTK-p300-STAT1-PPARgamma signaling activation mediates cholesterol crystals-induced CD36 expression and foam cell formation. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
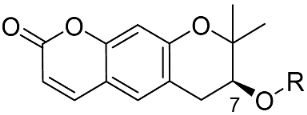
| Compound No. | R | % Inhibition (10 µM) a | IC50 (µM) b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTK-wt | BTK-C481S | |||
| 1 | 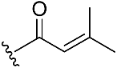 | 32.0 | >10 µM | |
| 2 | H | 7.7 | >10 µM | |
| 3 | 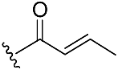 | 11.3 | >10 µM | |
| 4 |  | 20.3 | >10 µM | |
| 5 | 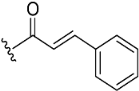 | NA c | >10 µM | |
| 6 |  | NA | >10 µM | |
| 7 | 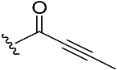 | 34.5 | 7.0 | |
| 8 | 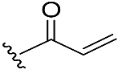 | 98.2 | 9.7 | 0.8 |
| 9 | 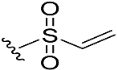 | 95.8 | 15.8 | 0.9 |
| 10 |  | 99.2 | 18.6 | 0.5 |
| 11 | 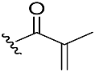 | NA | >10 µM | |
| 12 | 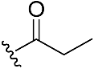 | NA | >10 µM | |
| Ibrutinib d | - | 99.6 | 0.00018 | |
| Kinase | % Inhibition at 10 µM a |
|---|---|
| BTK | 98.2 |
| BMX | 95.4 |
| TXK | 88.5 |
| TEC | 54.5 |
| ITK | 17.3 |
| EGFR | 32.9 |
| ERBB2 | 59.2 |
| ERBB4 | NA b |
| JAK3 | 13.2 |
| Permeability a | −4.06 ± 0.064 | |
| CYP inhibition b | 1A2 | <1 |
| 2C9 | 66.1 | |
| 2C19 | 48.2 | |
| 2D6 | 18.9 | |
| 3A4 | <1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.; Lee, E.; Kwon, H.A.; Seul, L.; Jeon, H.-J.; Yu, J.H.; Ryu, J.-H.; Jeon, R. Discovery of Tricyclic Pyranochromenone as Novel Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with In Vivo Antirheumatic Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217919
Cho H, Lee E, Kwon HA, Seul L, Jeon H-J, Yu JH, Ryu J-H, Jeon R. Discovery of Tricyclic Pyranochromenone as Novel Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with In Vivo Antirheumatic Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):7919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217919
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hyewon, Eun Lee, Hye Ah Kwon, Lee Seul, Hui-Jeon Jeon, Ji Hoon Yu, Jae-Ha Ryu, and Raok Jeon. 2020. "Discovery of Tricyclic Pyranochromenone as Novel Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with In Vivo Antirheumatic Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 7919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217919
APA StyleCho, H., Lee, E., Kwon, H. A., Seul, L., Jeon, H.-J., Yu, J. H., Ryu, J.-H., & Jeon, R. (2020). Discovery of Tricyclic Pyranochromenone as Novel Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with In Vivo Antirheumatic Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 7919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217919