c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Is Regulated Downstream of the Cytoskeletal Protein Synemin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Radioresistance and DNA Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
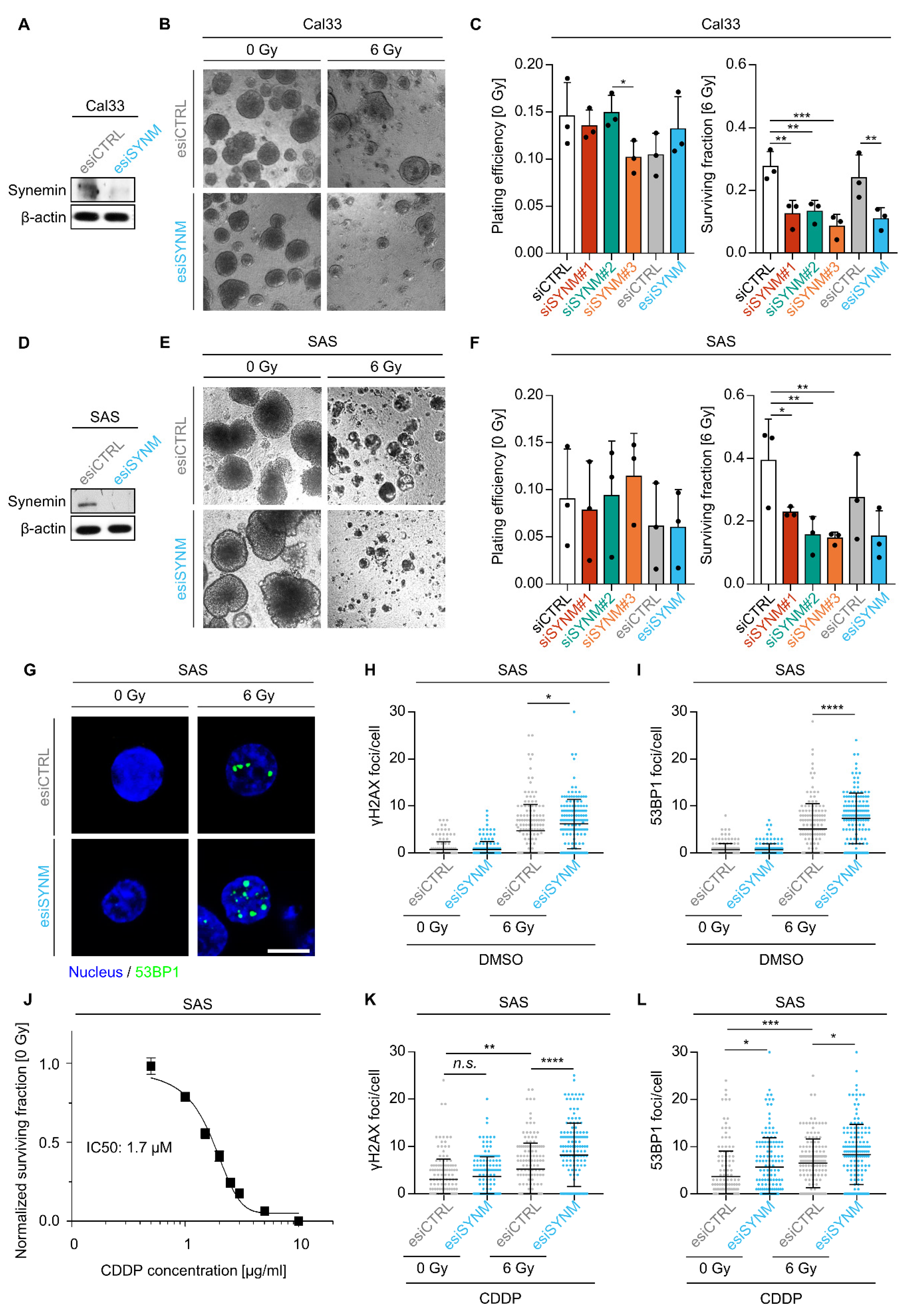
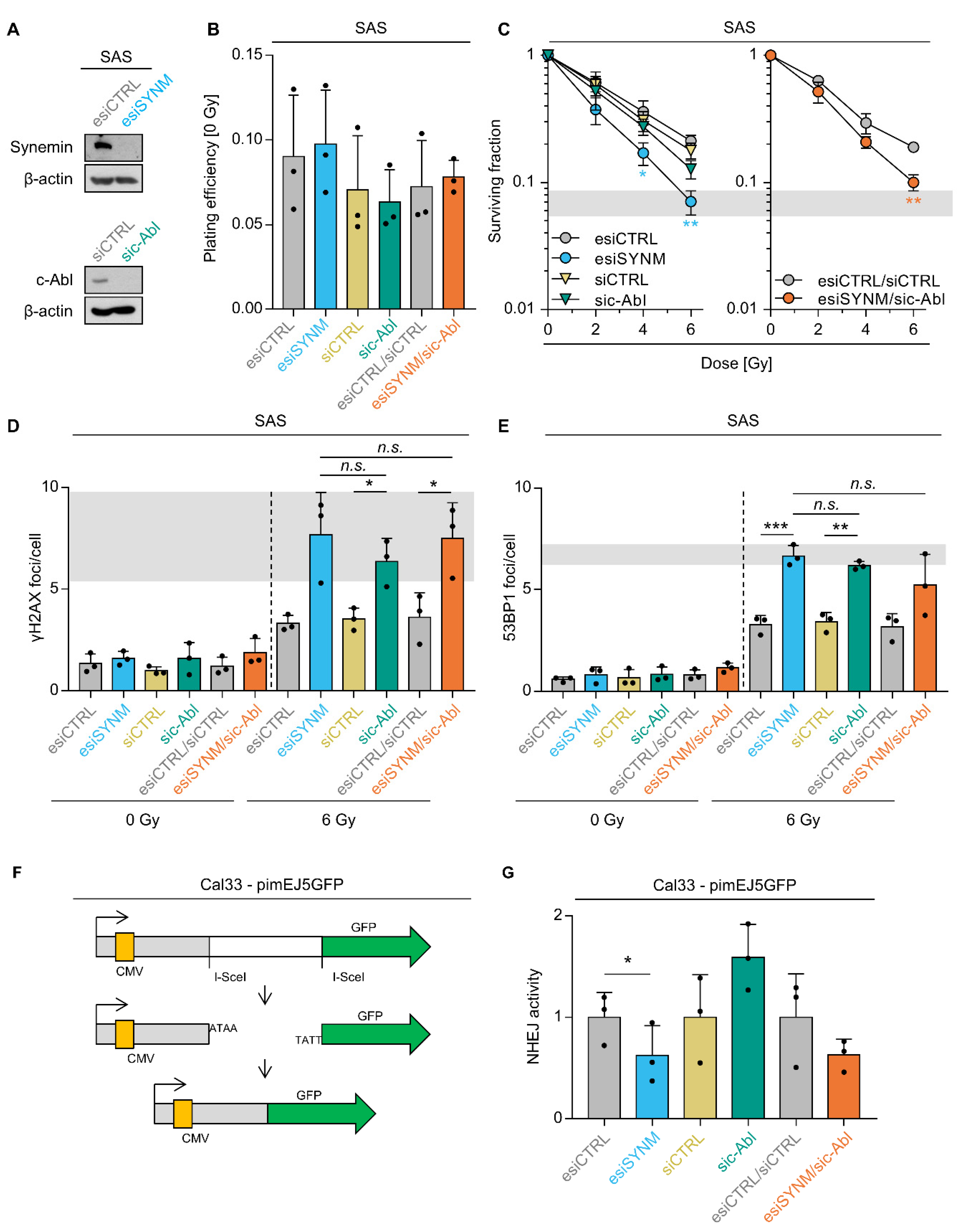
2.1. Synemin Regulates Radiochemosensitivity and DNA Double Strand Break Repair in HNSCC Cells
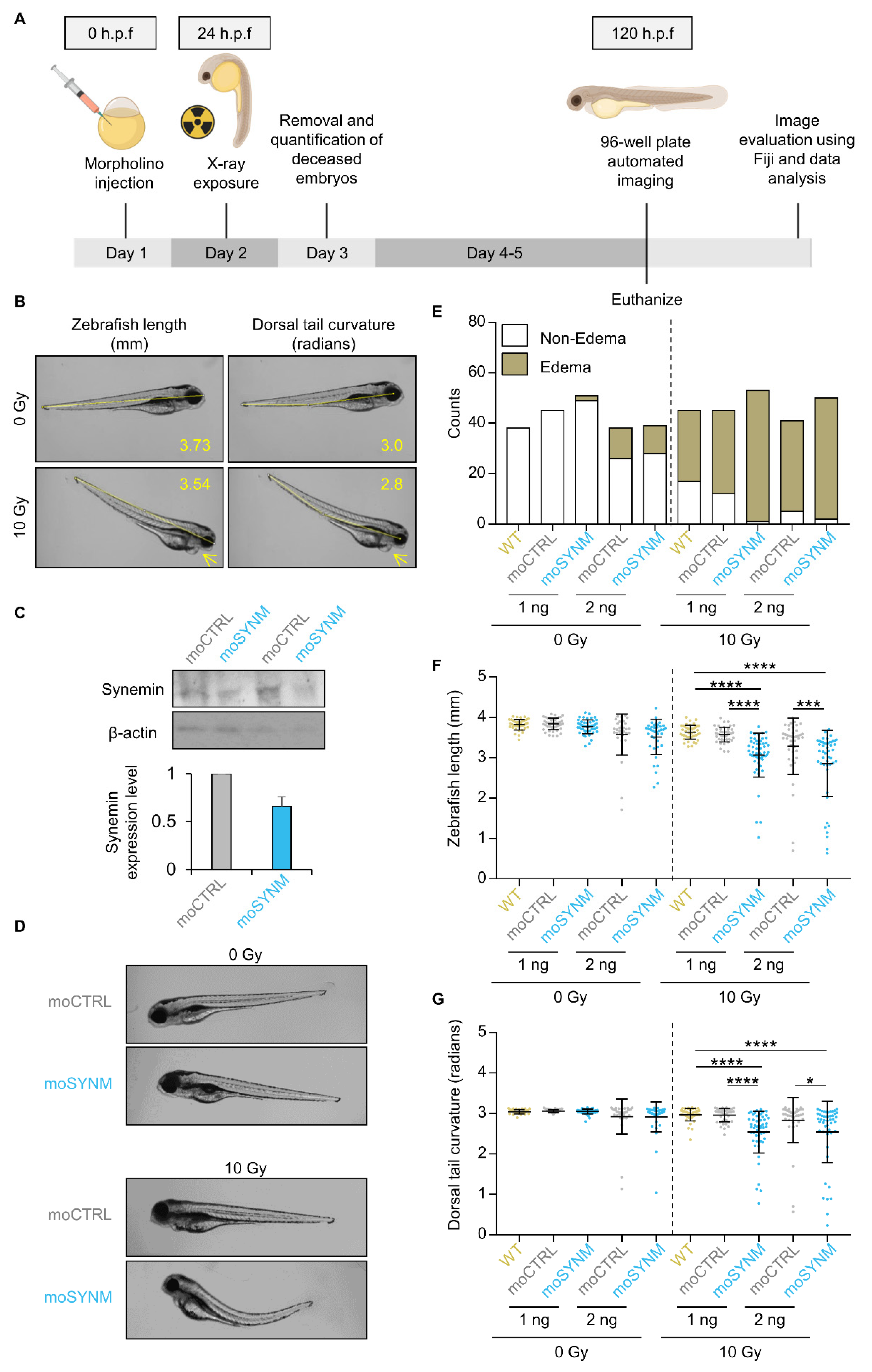
2.2. Synemin Modulates Radiation Sensitivity in Zebrafish
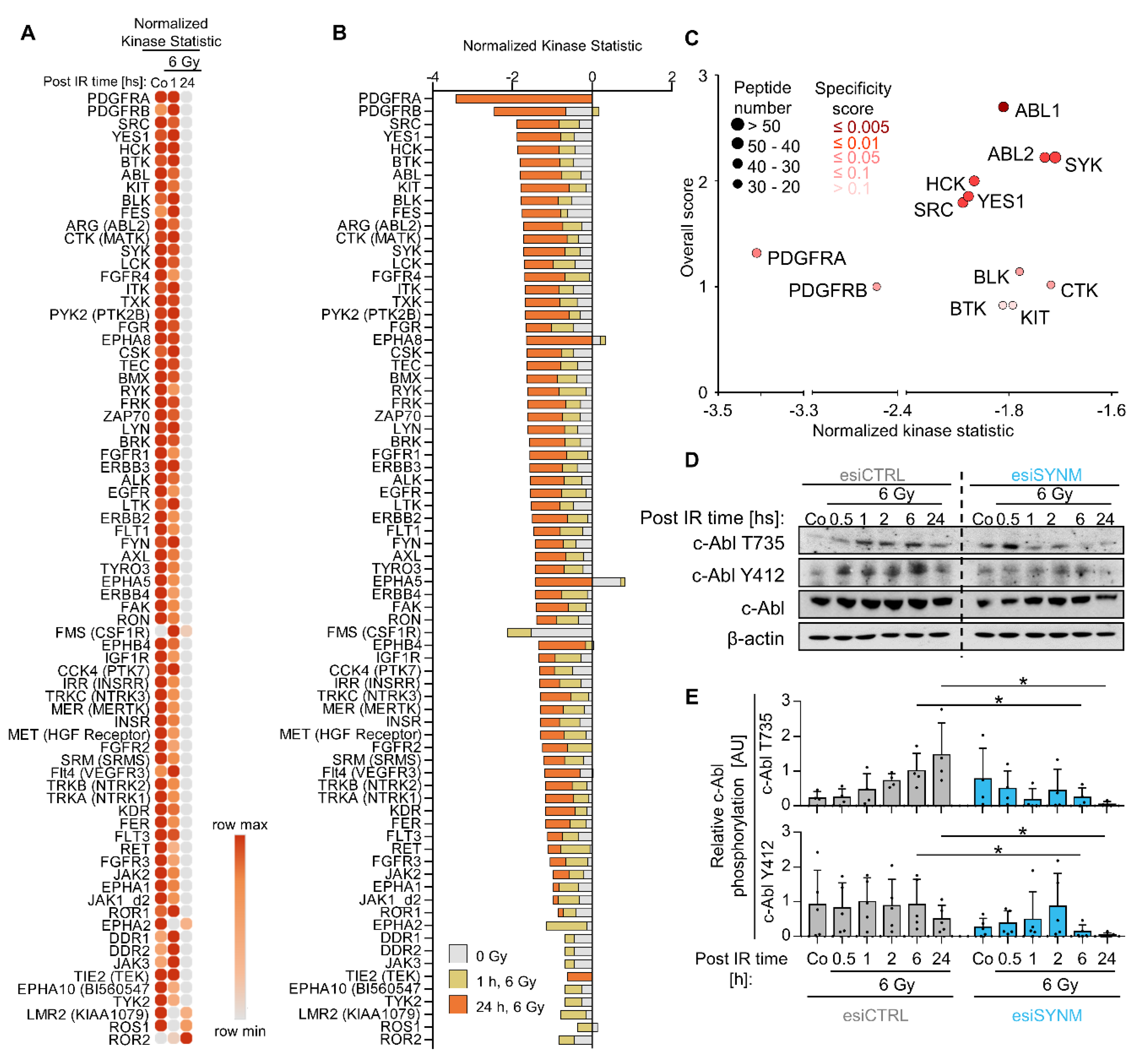
2.3. Activity of c-Abl and Src Family Members Depends on Synemin
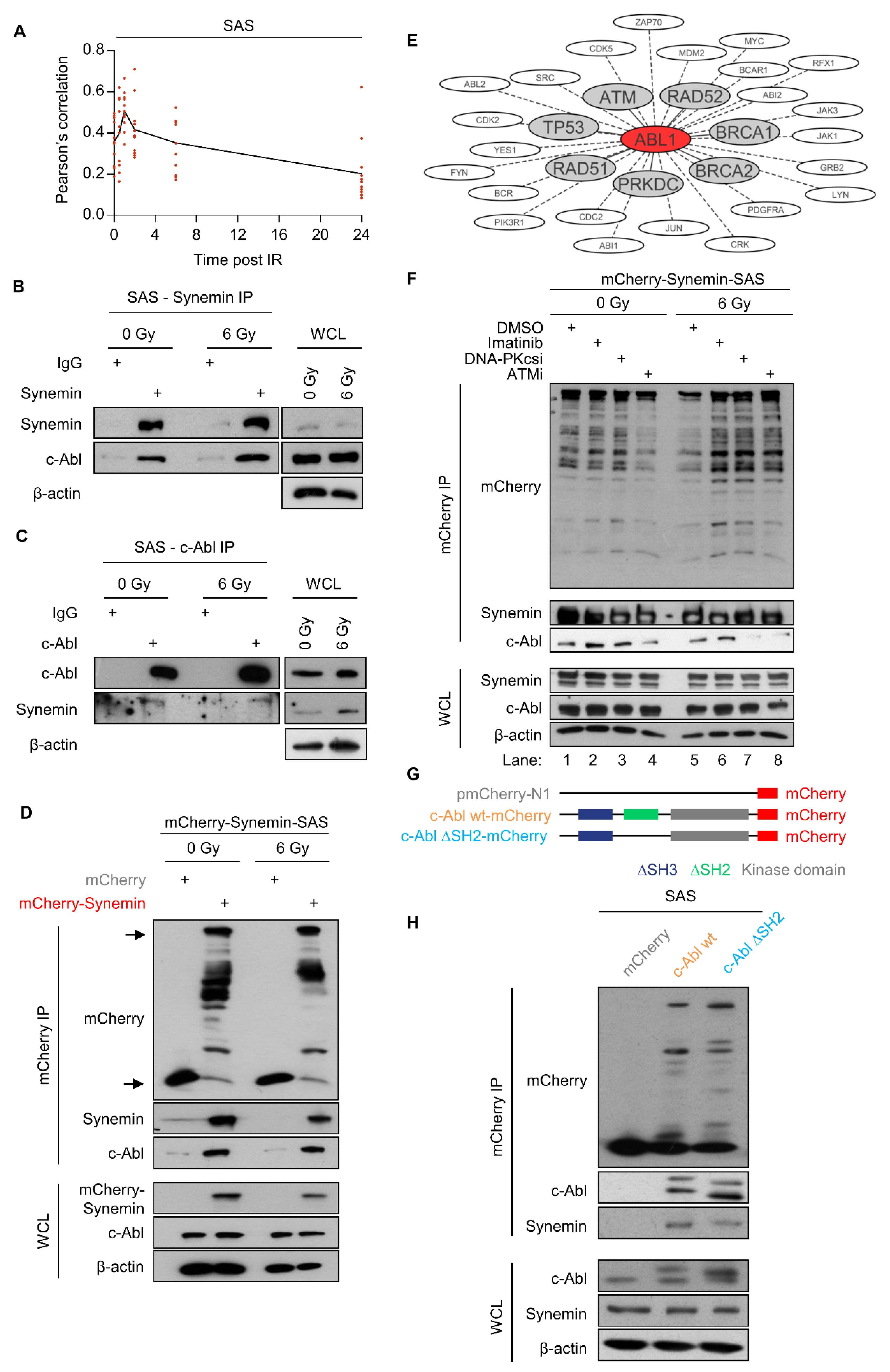
2.4. Synemin Functionally Interacts with c-Abl
2.5. Synemin Influences DSB Repair and Radiation Survival Responses by Regulating c-Abl
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and 3D Cell Culture
4.2. X-ray Irradiation
4.3. Antibodies
4.4. esiRNA and siRNA Transfection
4.5. Total Protein Extraction, Western Blotting
4.6. 3D Colony Formation Assay
4.7. Foci Assay
4.8. Synenim Constructs and Stable Transfection
4.9. Zebrafish Lines and Maintenance
4.10. Analysis of Zebrafish Embryos
4.11. pimEJ5GFP-Based Chromosomal Break Reporter Assay
4.12. Kinome Analysis
4.13. Immunoprecipitation
4.14. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eke, I.; Cordes, N. Focal adhesion signaling and therapy resistance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, I.; Zscheppang, K.; Dickreuter, E.; Hickmann, L.; Mazzeo, E.; Unger, K.; Krause, M.; Cordes, N. Simultaneous β1 integrin-EGFR Targeting and Radiosensitization of Human Head and Neck Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deville, S.S.; Cordes, N. The Extracellular, Cellular, and Nuclear Stiffness, a Trinity in the Cancer Resistome—A Review. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringer, P.; Colo, G.; Fässler, R.; Grashoff, C. Sensing the mechano-chemical properties of the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 2017, 64, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizzi, M.F.; Tarone, G.; Defilippi, P. Extracellular matrix, integrins, and growth factors as tailors of the stem cell niche. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickreuter, E.; Eke, I.; Krause, M.; Borgmann, K.; Van Vugt, M.A.; Cordes, N. Targeting of β1 integrins impairs DNA repair for radiosensitization of head and neck cancer cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotula, E.; Faigle, W.; Berthault, N.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Sun, J.-S.; Dutreix, M.; Quanz, M. DNA-PK Target Identification Reveals Novel Links between DNA Repair Signaling and Cytoskeletal Regulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Osterman, C.J.; Ozmadenci, D.; Kleinschmidt, E.G.; Taylor, K.N.; Barrie, A.M.; Jiang, S.; Bean, L.M.; Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Tancioni, I.; et al. FAK activity sustains intrinsic and acquired ovarian cancer resistance to platinum chemotherapy. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.M.; Pandita, R.K.; Singh, D.K.; Hunt, C.R.; Pandita, T.K. β1-Integrin Impacts Rad51 Stability and DNA Double-Strand Break Repair by Homologous Recombination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, M.; Diesler, K.; Majhen, D.; Steigerwald, C.; Berte, N.; Freund, H.; Stojanovic, N.; Kaina, B.; Osmak, M.; Ambriovic-Ristov, A.; et al. Integrin αVβ3 silencing sensitizes malignant glioma cells to temozolomide by suppression of homologous recombination repair. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27754–27771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Kharbanda, S.; Mayer, B.; Kufe, D.; Weaver, D.T. Binding of Ku and c-Abl at the kinase homology region of DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24763–24766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, K.; Mahajan, N.P. Cross talk of tyrosine kinases with the DNA damage signaling pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 10588–10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, W.D.; Koleske, A.J. Regulation of cell migration and morphogenesis by Abl-family kinases: Emerging mechanisms and physiological contexts. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3441–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, B.; Hantschel, O.; Young, M.A.; Scheffzek, K.; Veach, D.; Bornmann, W.; Clarkson, B.; Superti-Furga, G.; Kuriyan, J. Structural basis for the autoinhibition of c-Abl tyrosine kinase. Cell 2003, 112, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.S.; Plattner, R. Activation of abl family kinases in solid tumors. Genes Cancer 2012, 3, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puil, L.; Liu, J.; Gish, G.; Mbamalu, G.; Bowtell, D.; Pelicci, P.G.; Arlinghaus, R.; Pawson, T. Bcr-Abl oncoproteins bind directly to activators of the Ras signalling pathway. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehler, T.; Von Wichert, G.; Schimanski, C.; Kanzler, S.; Moehler, M.H.; Hinke, A.; Seufferlein, T.; Siebler, J.; Hochhaus, A.; Arnold, D.; et al. Phase I/II trial of capecitabine and oxaliplatin in combination with bevacizumab and imatinib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: AIO KRK 0205. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maass, N.; Schem, C.; Bauerschlag, D.O.; Tiemann, K.; Schaefer, F.W.; Hanson, S.; Muth, M.; Baier, M.; Weigel, M.T.; Wenners, A.S.; et al. Final Safety and Efficacy Analysis of a Phase I/II Trial with Imatinib and Vinorelbine for Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncology 2014, 87, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; Corless, C.L.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Fletcher, J.A.; Zhu, M.; Marino-Enriquez, A.; Friedlander, P.; Gonzalez, R.; Weber, J.S.; Gajewski, T.F.; et al. Imatinib for Melanomas Harboring Mutationally Activated or Amplified KIT Arising on Mucosal, Acral, and Chronically Sun-Damaged Skin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3182–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greuber, E.K.; Smith-Pearson, P.; Wang, J.; Pendergast, A.M. Role of ABL family kinases in cancer: From leukaemia to solid tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.R.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Boulton, S.J. Playing the End Game: DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Pathway Choice. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackford, A.N.; Jackson, S.P. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: The Trinity at the Heart of the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deville, S.S.; Vehlow, A.; Förster, S.; Dickreuter, E.; Borgmann, K.; Cordes, N. The Intermediate Filament Synemin Regulates Non-Homologous End Joining in an ATM-Dependent Manner. Cancers 2020, 12, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, G.A.; Parker, S.E.; Beothy, A.P.; Tucker, J.A.; Mullins, M.C.; Kao, G.D. Zebrafish as a “biosensor”? Effects of ionizing radiation and amifostine on embryonic viability and development. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8172–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software Environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ren, J.; Gao, X.; Jin, C.; Wen, L.; Yao, X. GPS 2.0, a tool to predict kinase-specific phosphorylation sites in hierarchy. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, H.; Gae, D.; Taccioli, G.E. Novel localization of the DNA-PK complex in lipid rafts. A putative role in the signal transduction pathway of the ionizing radiation response. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22136–22143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monferran, S.; Paupert, J.; Dauvillier, S.; Salles, B.; Muller, C. The membrane form of the DNA repair protein Ku interacts at the cell surface with metalloproteinase 9. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3758–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, S.E.; Rosenberg, E.; Valerie, N.; Hussaini, I.; Frigerio, M.; Cockcroft, X.F.; Wei, Y.C.; Hummersone, M.; Rigoreau, L.; Menear, K.A.; et al. Improved ATM kinase inhibitor KU-60019 radiosensitizes glioma cells, compromises insulin, AKT and ERK prosurvival signaling, and inhibits migration and invasion. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2894–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, J.F.; Kothari, V.; Drake, J.M.; Zhao, S.; Dylgjeri, E.; Dean, J.L.; Schiewer, M.J.; McNair, C.; Jones, J.K.; Aytes, A.; et al. DNA-PKcs-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation Drives Prostate Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, D.; Kaetzel, D.M.; Plattner, R. Reciprocal regulation of Abl and receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Furlan, A.; Stagni, V.; Hussain, A.; Richelme, S.; Conti, F.; Prodosmo, A.; Destro, A.; Roncalli, M.; Barilà, D.; Mainá, F. Abl interconnects oncogenic Met and p53 core pathways in cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Parker, L.L. Detection of Early Abl Kinase Activation after Ionizing Radiation by Using a Peptide Biosensor. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihira, K.; Taira, N.; Miki, Y.; Yoshida, K. TTK/Mps1 controls nuclear targeting of c-Abl by 14-3-3-coupled phosphorylation in response to oxidative stress. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7285–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Natsume, T.; Kufe, D.; Miki, Y. JNK phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins regulates nuclear targeting of c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, S.E.; Krishnaswami, M.; Miller, A.L.; Koleske, A.J. How do Abl family kinases regulate cell shape and movement? Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennardo, N.; Cheng, A.; Huang, N.; Stark, J.M. Alternative-NHEJ Is a Mechanistically Distinct Pathway of Mammalian Chromosome Break Repair. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, M.; Heijink, A.M.; Bisselink, Y.J.W.M.; Seinstra, R.I.; Silljé, H.H.W.; De Vries, E.G.E.; Van Vugt, M.A.T.M. Forced activation of Cdk1 via wee1 inhibition impairs homologous recombination. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3001–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deville, S.S.; Delgadillo Silva, L.F.; Vehlow, A.; Cordes, N. c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Is Regulated Downstream of the Cytoskeletal Protein Synemin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Radioresistance and DNA Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197277
Deville SS, Delgadillo Silva LF, Vehlow A, Cordes N. c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Is Regulated Downstream of the Cytoskeletal Protein Synemin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Radioresistance and DNA Repair. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(19):7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197277
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeville, Sara Sofia, Luis Fernando Delgadillo Silva, Anne Vehlow, and Nils Cordes. 2020. "c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Is Regulated Downstream of the Cytoskeletal Protein Synemin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Radioresistance and DNA Repair" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 19: 7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197277
APA StyleDeville, S. S., Delgadillo Silva, L. F., Vehlow, A., & Cordes, N. (2020). c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Is Regulated Downstream of the Cytoskeletal Protein Synemin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Radioresistance and DNA Repair. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(19), 7277. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197277






