Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Novel PIM Kinase Inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 Cells through the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of KMU-470 as A Novel PIM Kinase Inhibitor and Analysis of Inflammatory Kinase
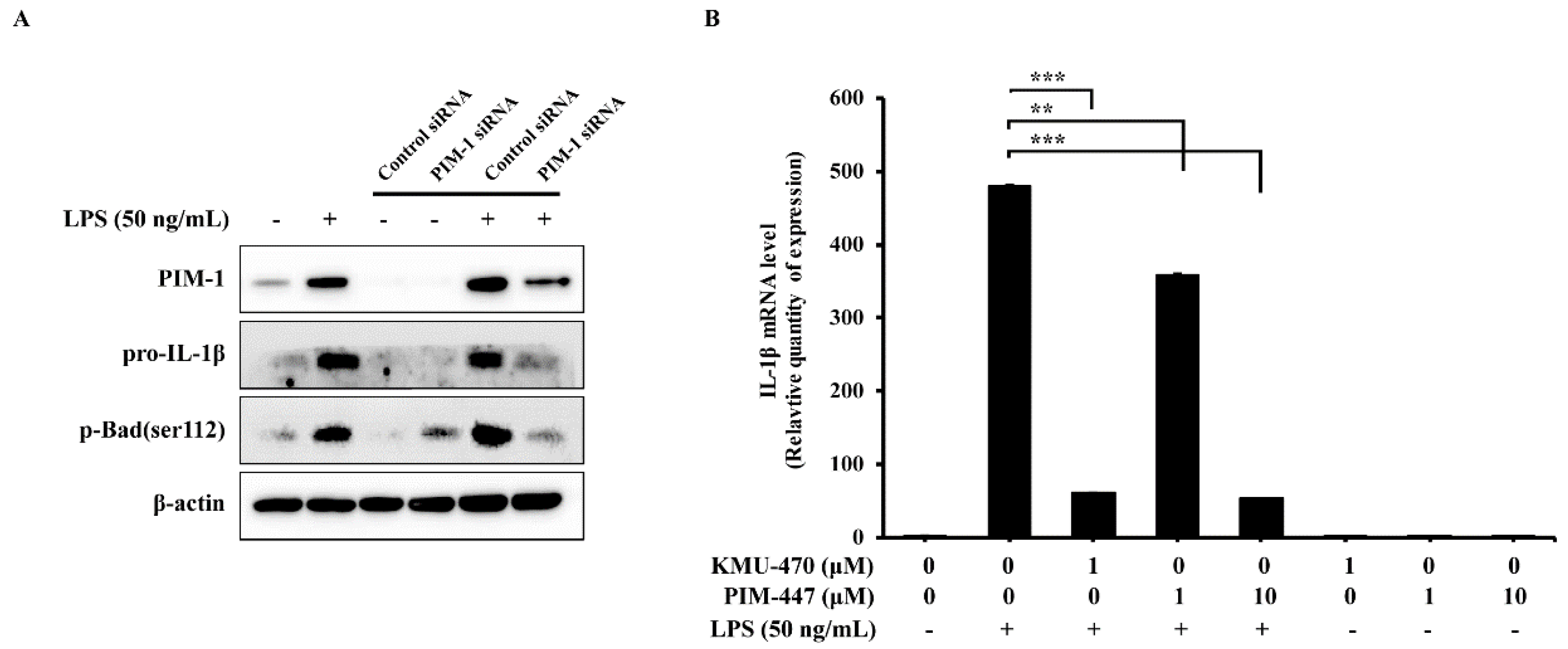
2.2. Inhibition of PIM-1 Suppresses LPS-Induced Pro-IL-1β in RAW 264.7 Cells
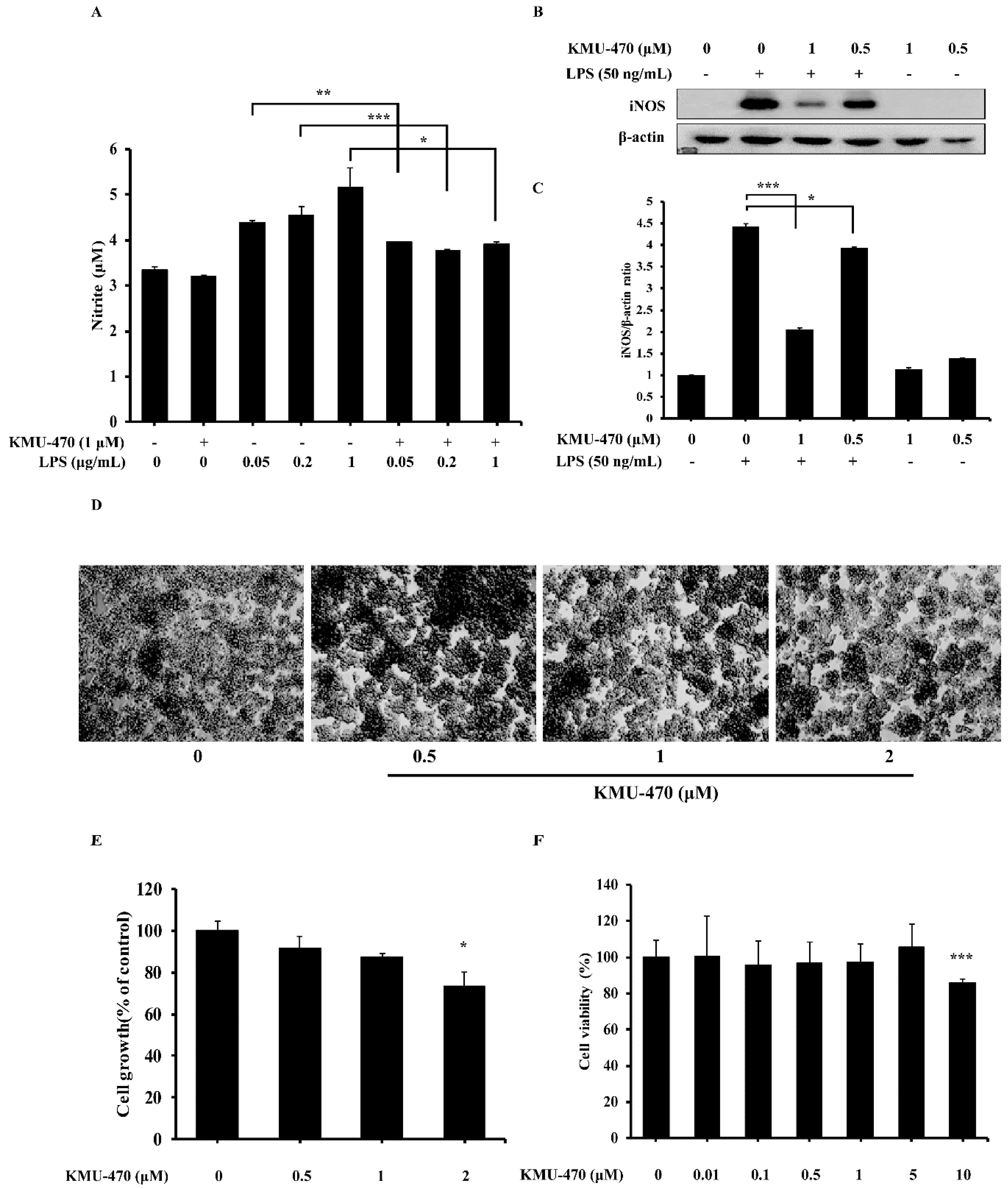
2.3. KMU-470 Inhibits LPS-Induced NO Production and iNOS Expression in RAW 264.7 Cells
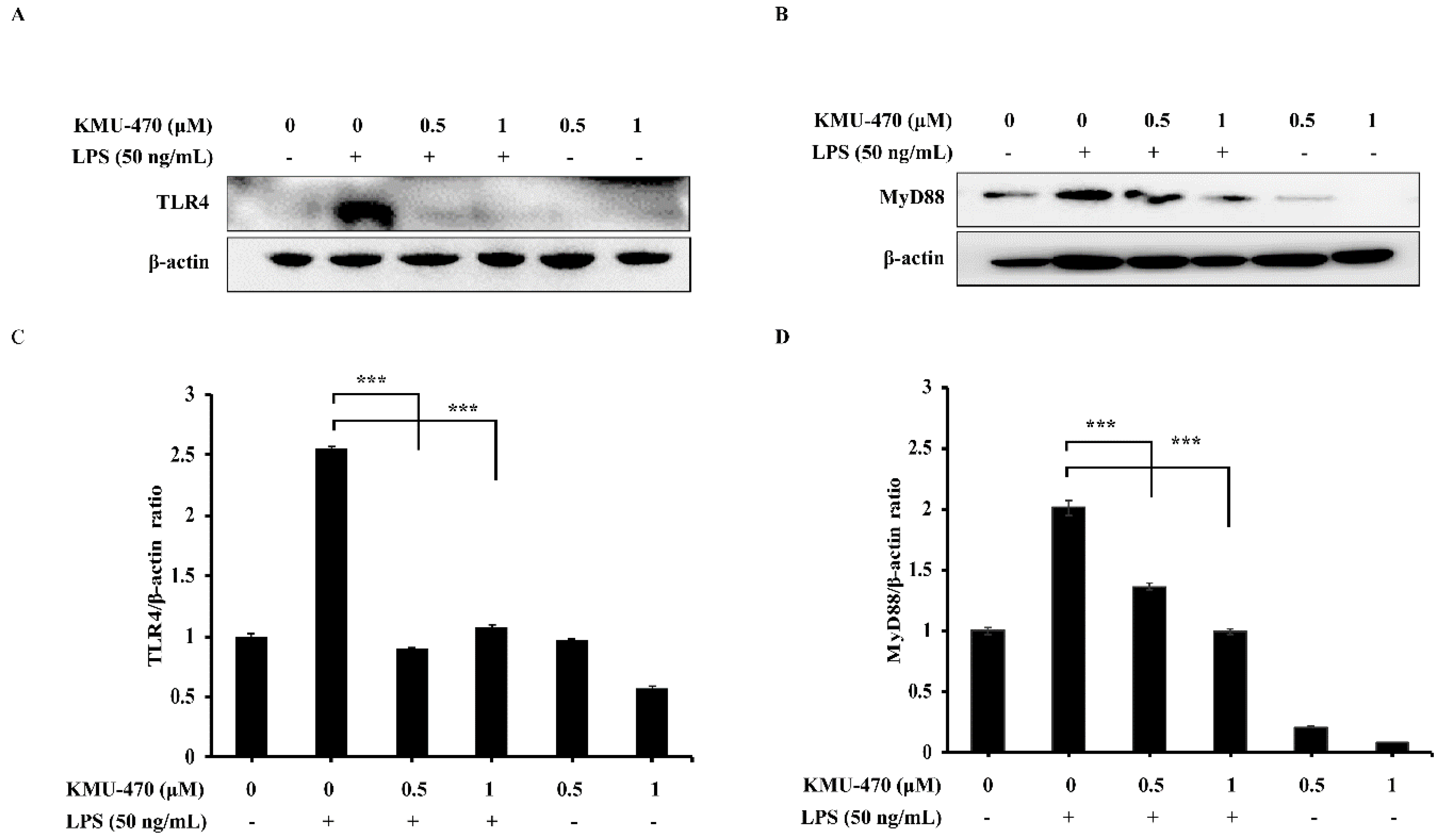
2.4. KMU-470 Suppressed LPS-Induced TLR4 and MyD88 Expression in RAW 264.7 Cells
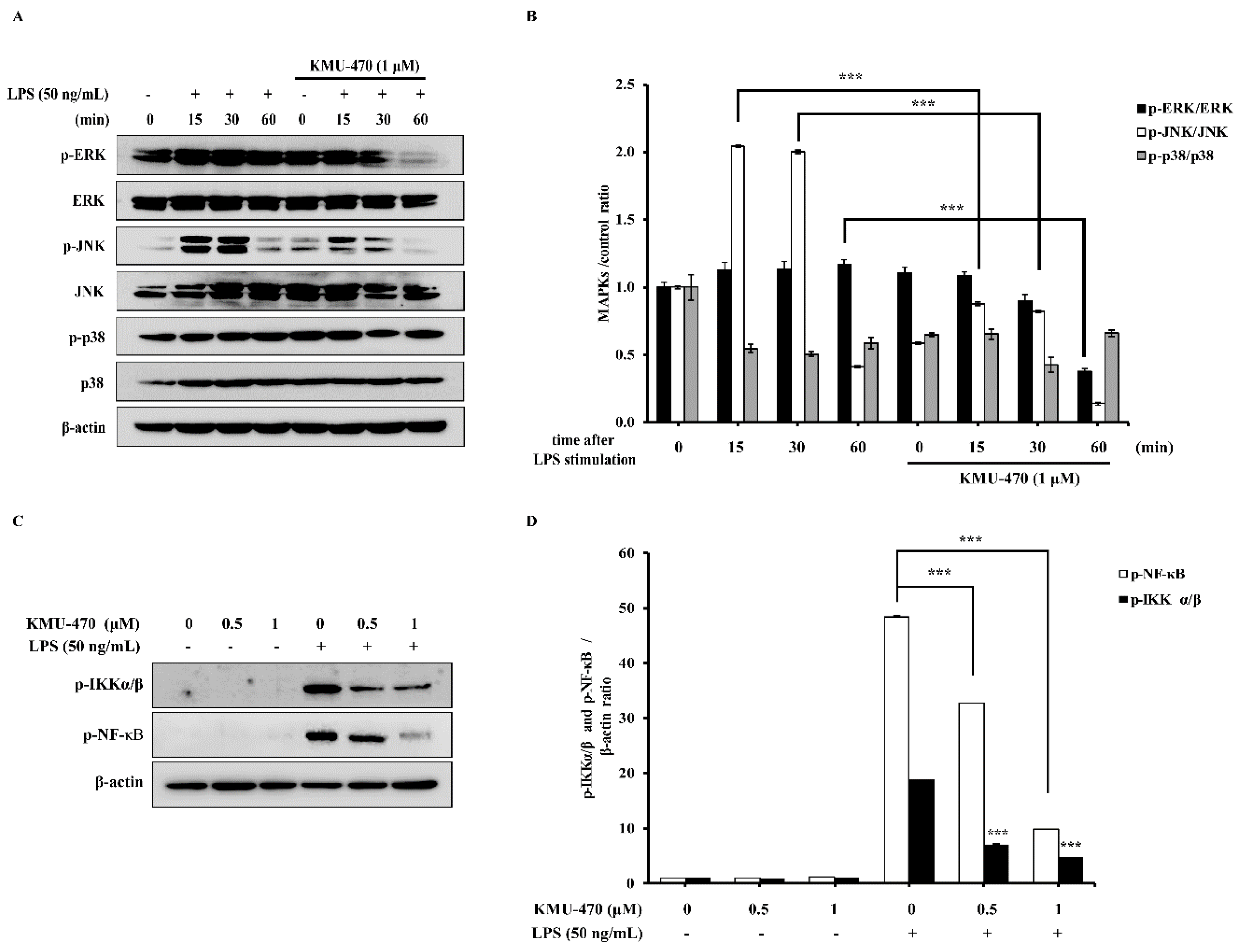
2.5. KMU-470 Inhibits LPS-Induced Phosphorylation of MAPKs and Activation of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 Cells
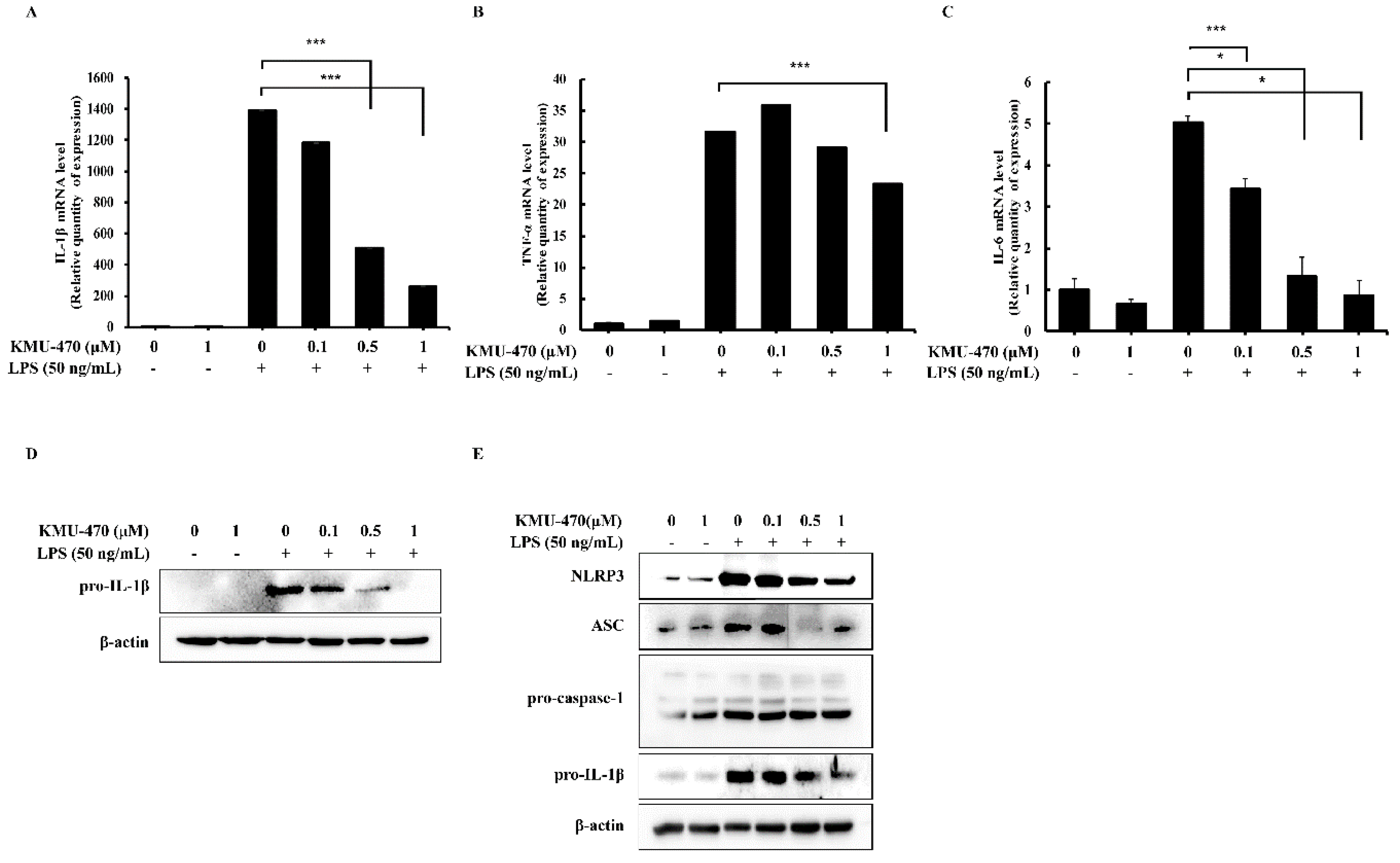
2.6. KMU-470 Inhibits LPS-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Up-Regulation of Pro-IL-1β
2.7. KMU-470 Decreased LPS-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in RAW 264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of KMU-470
4.1.1. General Information
4.1.2. 5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)indolin-2-one (1)
4.1.3. N-(6-Chloropyrazin-2-yl)-N’,N’-dimethylethane-1,2-diamine (2)
4.1.4. 5-(6-(2-Dimethylamino)ethylamino)pyrazin-2-yl)indolin-2-one (3)
4.1.5. (Z)-3-((1H-Imidazol-5-yl)methylene)-5-(6-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)amino)pyrazin-2-yl)indolin-2-one
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Biochemical IC50 Value Determination
4.4. Kinase Profiling
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Measurement of NO Production
4.8. RNA Extraction and Real Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Small Interfering RNA Transfection
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| TLR4 | toll-like receptor 4 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| MyD88 | myeloid differentiation factor 88 |
| MAPKs | mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| IKK | inhibitor kappa B kinase |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| NRLP3 | nod-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| ASC | adaptor apoptosis-associated speck-like protein |
| OD | optical density |
References
- Cuypers, H.T.; Selten, G.; Quint, W.; Zijlstra, M.; Maandag, E.R.; Boelens, W.; van Wezenbeek, P.; Melief, C.; Berns, A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: Integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell 1984, 37, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bhattacharya, N.; Weaver, M.; Petersen, K.; Meyer, M.; Gapter, L.; Magnuson, N.S. Pim-1: A serine/threonine kinase with a role in cell survival, proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J. Vet. Sci. 2001, 2, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daenthanasanmak, A.; Wu, Y.; Iamsawat, S.; Nguyen, H.D.; Bastian, D.; Zhang, M.; Sofi, M.H.; Chatterjee, S.; Hill, E.G.; Mehrotra, S.; et al. PIM-2 protein kinase negatively regulates T cell responses in transplantation and tumor immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2787–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaida, N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.Y. Roles of Pim-3, a novel survival kinase, in tumorigenesis. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, L.; Chen, B.L.; Leng, A.M.; Mu, Y.B.; Zhang, G.Y. Inhibition of Pim-1 kinase ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.S.; Takeda, K.; Shiraishi, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, M.; Jackson, L.; Wright, A.D.; Carter, L.; Robinson, J.; Hicken, E.; et al. Inhibition of Pim1 kinase activation attenuates allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. Am. J. Respir. cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, M.; Heijink, I.H.; Gras, R.; den Boef, L.E.; Reinders-Luinge, M.; Pouwels, S.D.; Hylkema, M.N.; van der Toorn, M.; Brouwer, U.; van Oosterhout, A.J.; et al. Pim1 kinase protects airway epithelial cells from cigarette smoke-induced damage and airway inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L240–L251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerkies, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. Toll-Like Receptors and their Contribution to Innate Immunity: Focus on TLR4 Activation by Lipopolysaccharide. Adv. Cell Biology 2014, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zoete, M.R.; Palm, N.W.; Zhu, S.; Flavell, R.A. Inflammasomes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2014, 6, a016287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, Q. Toll-like receptor 4: A promising therapeutic target for pneumonia caused by Gram-negative bacteria. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5868–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Kundu, J.K.; Lee, M.H.; Liu, Z.Z. PIM Kinase as an Executional Target in Cancer. J. Cancer. Prev. 2018, 23, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, A.; Locatelli, A.; Morigi, R.; Rambaldi, M. 2-Indolinone a versatile scaffold for treatment of cancer: A patent review (2008-2014). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblish, H.; Li, Y.L.; Shin, N.; Hall, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Covington, M.; Marando, C.; Bowman, K.; Boer, J.; et al. Preclinical characterization of INCB053914, a novel pan-PIM kinase inhibitor, alone and in combination with anticancer agents, in models of hematologic malignancies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, M.T.; Nishiguchi, G.; Han, W.; Lan, J.; Simmons, R.; Atallah, G.; Ding, Y.; Tamez, V.; Zhang, Y.; Mathur, M.; et al. Identification of N-(4-((1R,3S,5S)-3-Amino-5-methylcyclohexyl)pyridin-3-yl)-6-(2,6-difluorophenyl)- 5-fluoropicolinamide (PIM447), a Potent and Selective Proviral Insertion Site of Moloney Murine Leukemia (PIM) 1, 2, and 3 Kinase Inhibitor in Clinical Trials for Hematological Malignancies. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8373–8386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dakin, L.A.; Block, M.H.; Chen, H.; Code, E.; Dowling, J.E.; Feng, X.; Ferguson, A.D.; Green, I.; Hird, A.W.; Howard, T.; et al. Discovery of novel benzylidene-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-diones as potent and selective inhibitors of the PIM-1, PIM-2, and PIM-3 protein kinases. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4599–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Hong, V.S.; Lee, J. Synthesis of (Z)-3-((1H-imidazol-5-yl) methylene) indolin-2-one Derivatives as Pim Kinase Inhibitors. Quant. Bio-Sci. 2018, 37, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, K.N.; Jang, H.W.; Hong, V.S.; Lee, J. Pim kinase inhibitory and antiproliferative activity of a novel series of meridianin C derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Hong, V.S. Synthesis and evaluation of 5-(3-(pyrazin-2-yl)benzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives as pan-pim kinases inhibitors. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2014, 62, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tripathi, P.; Tripathi, P.; Kashyap, L.; Singh, V. The role of nitric oxide in inflammatory reactions. FEMS Immunol Med. Microbiol 2007, 51, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.Y.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Neurobiology of nitric oxide. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 1996, 10, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMicking, J.; Xie, Q.W.; Nathan, C. Nitric oxide and macrophage function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 323–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharm. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.H.; Park, H.C.; Choi, S.; Kim, S.; Bao, C.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, H.K.; Lee, H.J.; Auh, J.H. Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Cyanidins in Black Raspberry as Candidates for Suppression of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Murine Macrophages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5449–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasare, C.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptors: Linking innate and adaptive immunity. Microbes. Infect. 2004, 6, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Bowie, A.G.; Jefferies, C.A.; Mansell, A.S.; Brady, G.; Brint, E.; Dunne, A.; Gray, P.; Harte, M.T.; et al. Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction. Nature 2001, 413, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.D.; Riches, D.W. IFN-gamma + LPS induction of iNOS is modulated by ERK, JNK/SAPK, and p38(mapk) in a mouse macrophage cell line. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C441–C450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, M.; Watters, J.J.; Pfeiffer, Z.A.; Wiepz, G.J.; Sommer, J.A.; Bertics, P.J. Evidence for nucleotide receptor modulation of cross talk between MAP kinase and NF-kappa B signaling pathways in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 286, C923–C930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFranco, A.L.; Hambleton, J.; McMahon, M.; Weinstein, S.L. Examination of the role of MAP kinase in the response of macrophages to lipopolysaccharide. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1995, 392, 407–420. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminska, B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy--from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1754, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Xu, L.H.; Ouyang, D.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zha, Q.B.; Hou, X.F.; He, X.H. The second-generation mTOR kinase inhibitor INK128 exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflammation 2014, 37, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Yuan, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Li, Q.; Tai, G. Escherichia coli maltose-binding protein activates mouse peritoneal macrophages and induces M1 polarization via TLR2/4 in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol 2014, 21, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Lo, C.P.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, N.S.; Kuo, Y.H.; Shyur, L.F. Ethyl caffeate suppresses NF-kappaB activation and its downstream inflammatory mediators, iNOS, COX-2, and PGE2 in vitro or in mouse skin. Br. J. Pharm. 2005, 146, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Brough, D. Understanding the mechanism of IL-1beta secretion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling in macrophages. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, M.R.; Reyes, J.L.; Iannuzzi, J.; Leung, G.; McKay, D.M. The pro-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-6, enhances the polarization of alternatively activated macrophages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, P.; Chen, T.; Mou, Y.; Wu, H.; Xie, P.; Lu, G.; Gong, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H. NZ suppresses TLR4/NF-kappaB signalings and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. 2015, 64, 799–808. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.P.; Jiang, L.; Kang, K.; Fei, D.S.; Meng, X.L.; Nan, C.C.; Pan, S.H.; Zhao, M.R.; Zhao, M.Y. Hemin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury, involving heme oxygenase-1. Int. Immunopharmacol 2014, 20, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.E.; Jeong, J.J.; Hyam, S.R.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Ursolic acid isolated from the seed of Cornus officinalis ameliorates colitis in mice by inhibiting the binding of lipopolysaccharide to Toll-like receptor 4 on macrophages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9711–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Tamura, K.; DeAngelo, D.J.; de Bono, J.; Lorente, D.; Minden, M.; Uy, G.L.; Kantarjian, H.; Chen, L.S.; Gandhi, V.; et al. Phase I studies of AZD1208, a proviral integration Moloney virus kinase inhibitor in solid and haematological cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | Inhibitory Activity IC50 (nM) * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PIM-1 | PIM-2 | PIM-3 | |
| KMU-470 | 5.6 | 220 | 6.9 |
| AZD-1208 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 |
| PIM-447 | 2.1 | 12 | 0.9 |
| KMU-470 10 (μM) | KMU-470 1 (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase | Activity (% Control) | Kinase | Activity (% Control) |
| MAPK1 (h) | −18 | MAPK1 (h) | 6 |
| Yes (h) | −3 | Yes (h) | 22 |
| Blk (h) | 5 | Blk (h) | 53 |
| Fgr (h) | 8 | Fgr (h) | 42 |
| Lyn (h) | 10 | Lyn (h) | 30 |
| Lck (h) | 14 | Lck (h) | 41 |
| TYK2 (h) | 14 | TYK2 (h) | 54 |
| JAK3 (h) | 15 | JAK3 (h) | 38 |
| Fyn (h) | 16 | Fyn (h) | 97 |
| JAK1 (h) | 20 | JAK1 (h) | 61 |
| Itk (h) | 21 | Itk (h) | 75 |
| Syk (h) | 21 | Syk (h) | 82 |
| JAK2 (h) | 23 | JAK2 (h) | 107 |
| JNK1α1 (h) | 34 | ||
| Hck (h) | 37 | ||
| Pyk2 (h) | 41 | ||
| Csrc (h) | 43 | ||
| Bmx (h) | 47 | ||
| Txk (h) | 50 | ||
| Tec (h) activated | 71 | ||
| SAPK2a (h) | 77 | ||
| BTK (h) | 80 | ||
| ZAP-70 (h) | 100 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, H.S.; Min, H.J.; Hong, V.S.; Kwon, T.K.; Park, J.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Novel PIM Kinase Inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 Cells through the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145138
Baek HS, Min HJ, Hong VS, Kwon TK, Park JW, Lee J, Kim S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Novel PIM Kinase Inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 Cells through the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145138
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Hye Suk, Hyeon Ji Min, Victor Sukbong Hong, Taeg Kyu Kwon, Jong Wook Park, Jinho Lee, and Shin Kim. 2020. "Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Novel PIM Kinase Inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 Cells through the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145138
APA StyleBaek, H. S., Min, H. J., Hong, V. S., Kwon, T. K., Park, J. W., Lee, J., & Kim, S. (2020). Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Novel PIM Kinase Inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 Cells through the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 5138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145138






