Combination of HIV-1 and Diabetes Enhances Blood Brain Barrier Injury via Effects on Brain Endothelium and Pericytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
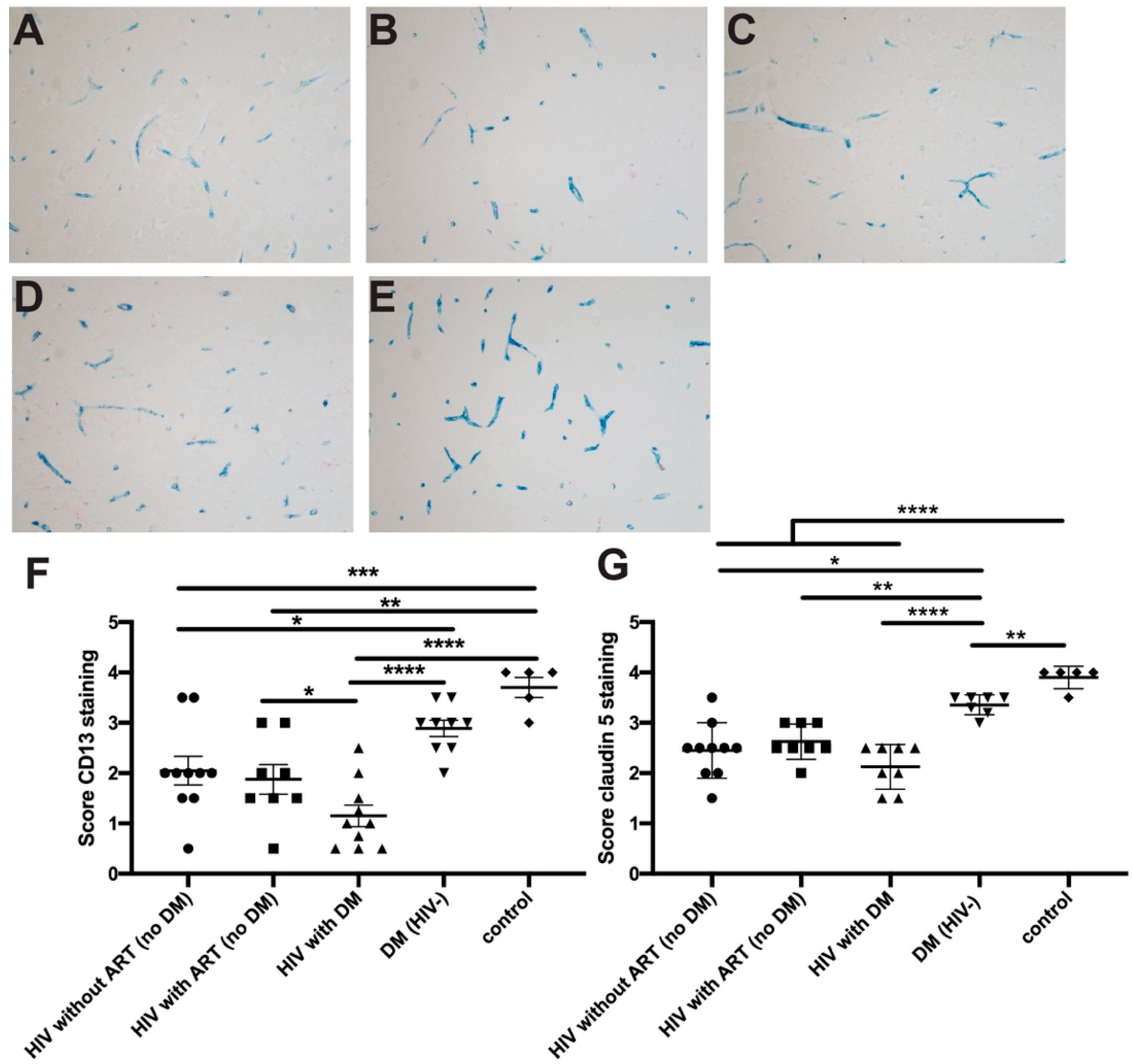
2.1. HIV Infection and Hyperglycemia Result in Decreased Claudin-5, TJ Protein, and CD13 Expression in Cerebral Microvessels of DM Patients with HIV
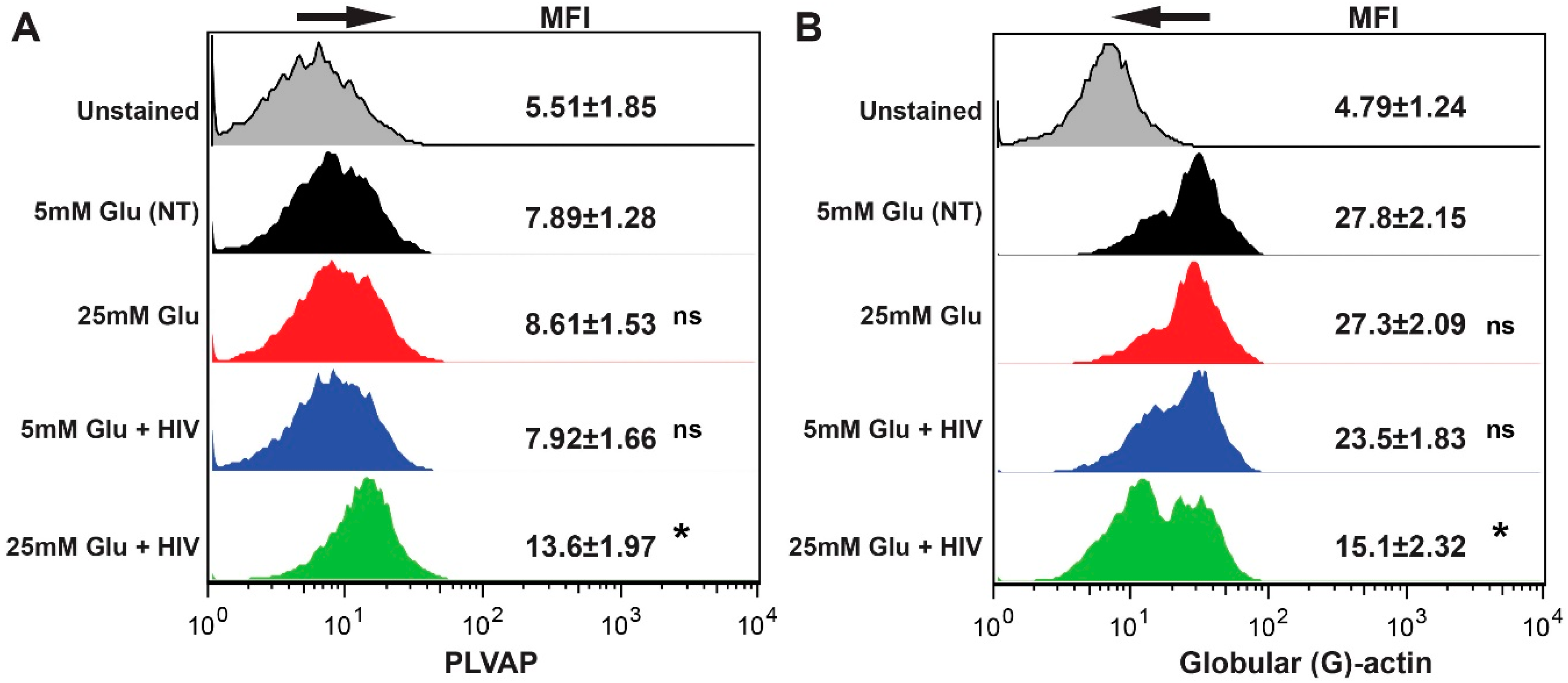
2.2. Hyperglycemia and HIV Exposure Diminish BBB Tightness and Intensify Primary Human Monocyte Adhesion to BMVEC
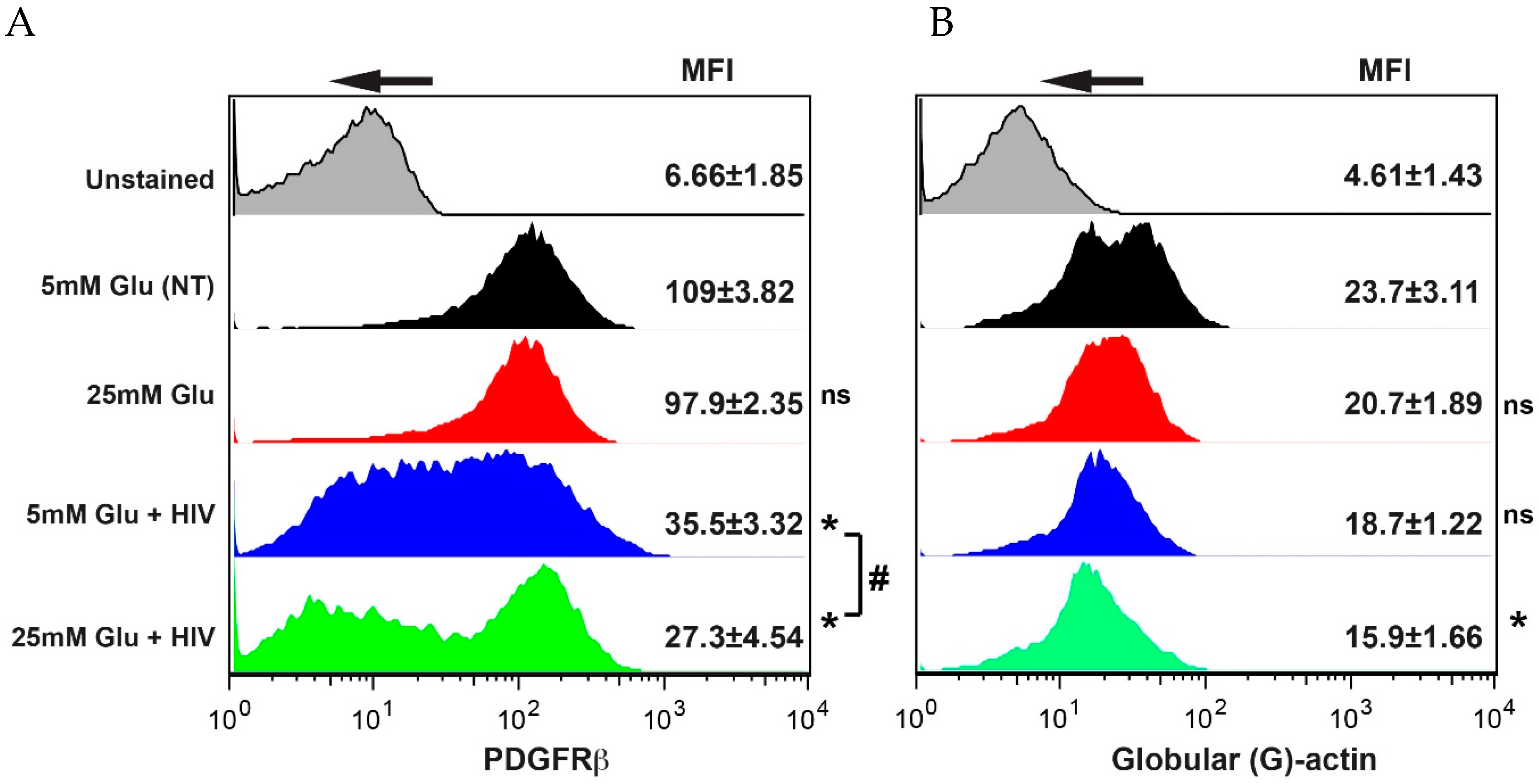
2.3. Hyperglycemia and HIV Exposure Reduce PDGF-Rβ Expression and Stimulate Actin Cytoskeletal Rearrangements in Primary Human Pericytes
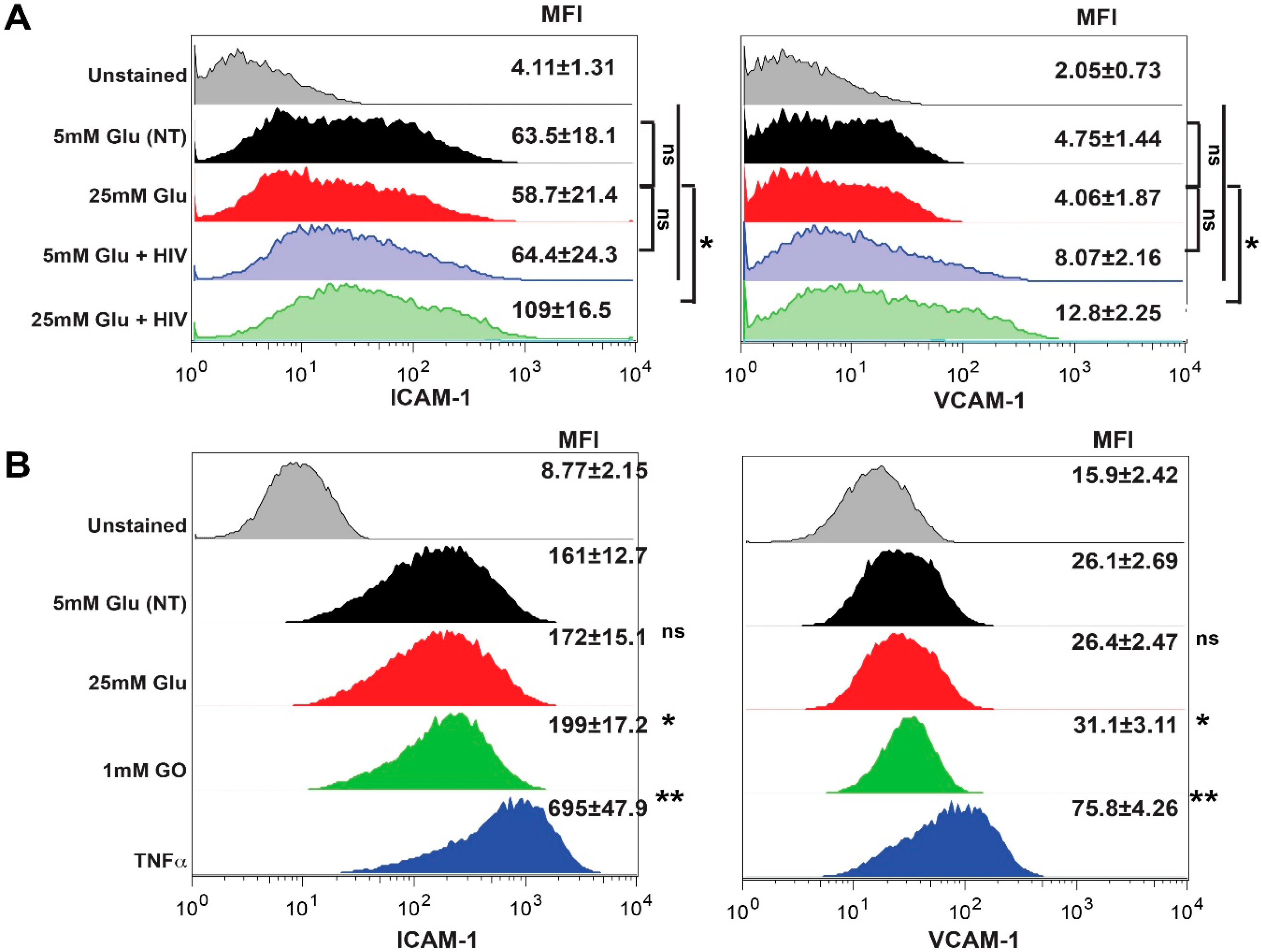
2.4. Exposure to HIV and Hyperglycemia Stimulates Expression of Adhesion Molecules on Both Primary Endothelial Cells and Pericytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. Determination of HIV-1 p24 Concentration
4.3. Monocyte Adhesion Assays
4.4. Transendothelial Electrical Resistance (TEER)
4.5. ICAM-1, VCAM-1, PLVAP, PDGF-Rβ Expression and G-actin Quantification by Flow Cytometry
4.6. Human Brain Tissues
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snyder, E.L.; Stramer, S.L.; Benjamin, R.J. The Safety of the Blood Supply--Time to Raise the Bar. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisler, K.; Nelson, A.R.; Rege, S.V.; Ramanathan, A.; Wang, Y.; Ahuja, A.; Lazic, D.; Tsai, P.S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Pericyte degeneration leads to neurovascular uncoupling and limits oxygen supply to brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, S.; Heldt, N.A.; Gajghate, S.; Seliga, A.; Reichenbach, N.; Persidsky, Y. Hyperglycemia and advanced glycation end products disrupt BBB and promote occludin and claudin-5 protein secretion on extracellular microvesicles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, S.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Gajghate, S.; Seliga, A.; Winfield, M.; Heldt, N.A.; Kolpakov, M.A.; Bashkirova, Y.V.; Sabri, A.K.; Persidsky, Y. Hyperglycemia-Driven Neuroinflammation Compromises BBB Leading to Memory Loss in Both Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Type 1 and Type 2 Mouse Models. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1883–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J.; Badiee, J.; Vaida, F.; Letendre, S.; Heaton, R.K.; Clifford, D.; Collier, A.C.; Gelman, B.; McArthur, J.; Morgello, S.; et al. CD4 nadir is a predictor of HIV neurocognitive impairment in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2011, 25, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft-Terry, S.D.; Stothert, A.R.; Buch, S.; Gendelman, H.E. HIV-1 neuroimmunity in the era of antiretroviral therapy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.A.; Cherry, C.L.; Bell, J.E.; McLean, C.A. Brain Cell Reservoirs of Latent Virus in Presymptomatic HIV-Infected Individuals. Am. J. Pathol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, C.; Tapp, R.J.; Hughes, A.D.; Magnussen, C.G.; Blizzard, L.; Phan, T.G.; Beare, R.; Witt, N.; Venn, A.; Munch, G.; et al. The Association of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Cerebral Gray Matter Volume Is Independent of Retinal Vascular Architecture and Retinopathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 6328953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Sajja, R.K.; Naik, P.; Cucullo, L. Diabetes Mellitus and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction: An Overview. J. Pharmacovigil 2014, 2, 125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, G.T.; Lim, J.; Srikanth, V.; Bruce, D.G. Epidemiological Approaches to Understanding the Link Between Type 2 Diabetes and Dementia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2017, 59, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, E.; Jha, J.C.; Sharma, A.; Wilkinson-Berka, J.L.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A.; de Haan, J.B. Are reactive oxygen species still the basis for diabetic complications? Clin. Sci. (London, England: 1979) 2015, 129, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bussel, F.C.G.; Backes, W.H.; Hofman, P.A.M.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; van Boxtel, M.P.J.; Verhey, F.R.J.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Schram, M.T.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Wildberger, J.E.; et al. Cerebral Pathology and Cognition in Diabetes: The Merits of Multiparametric Neuroimaging. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamine, R.; Kawamura, T.; Umemura, T.; Umegaki, H.; Kawano, N.; Hotta, M.; Kouchi, Y.; Hatsuda, S.; Watarai, A.; Kanai, A.; et al. Does cerebral small vessel disease predict future decline of cognitive function in elderly people with type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 94, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Hertze, J.; Nagga, K.; Nilsson, K.; Nilsson, C.; Wennstrom, M.; van Westen, D.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Increased blood-brain barrier permeability is associated with dementia and diabetes but not amyloid pathology or APOE genotype. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 51, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Singh, N. Pitavastatin and 4’-hydroxy-3’-methoxyacetophenone (HMAP) reduce cognitive dysfunction in vascular dementia during experimental diabetes. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2010, 7, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranahan, A.M.; Hao, S.; Dey, A.; Yu, X.; Baban, B. Blood-brain barrier breakdown promotes macrophage infiltration and cognitive impairment in leptin receptor-deficient mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacktor, N. Changing clinical phenotypes of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. J. Neurovirol 2018, 24, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, A.N.; Rubin, L.H.; Neigh, G.N. Untangling the Gordian knot of HIV, stress, and cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 4, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, P.M.; Rubin, L.H.; Valcour, V.; Martin, E.; Crystal, H.; Young, M.; Weber, K.M.; Manly, J.; Richardson, J.; Alden, C.; et al. Cognitive function in women with HIV: Findings from the Women’s Interagency HIV Study. Neurology 2015, 84, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persidsky, Y.; Hill, J.; Zhang, M.; Dykstra, H.; Winfield, M.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Potula, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Ramirez, S.H.; Rom, S. Dysfunction of brain pericytes in chronic neuroinflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, D.E.; Fazeli, P.L.; Dodson, J.E.; Ackerman, M.; Talley, M.; Appel, S.J. The synergistic effects of HIV, diabetes, and aging on cognition: Implications for practice and research. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2014, 46, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylor, D.; Dickens, A.M.; Sacktor, N.; Haughey, N.; Slusher, B.; Pletnikov, M.; Mankowski, J.L.; Brown, A.; Volsky, D.J.; McArthur, J.C. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder - pathogenesis and prospects for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2016, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIMH NeuroHIV in the ART era. Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/news/events/2017/neurohiv-in-the-art-era.shtml (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Liebner, S.; Corada, M.; Bangsow, T.; Babbage, J.; Taddei, A.; Czupalla, C.J.; Reis, M.; Felici, A.; Wolburg, H.; Fruttiger, M. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling controls development of the blood-brain barrier. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, E.K.; van Noorden, C.J.F.; Schlingemann, R.O.; Klaassen, I. The role of plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein in pathological breakdown of blood-brain and blood-retinal barriers: Potential novel therapeutic target for cerebral edema and diabetic macular edema. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Hou, Y.; Wei, T.; Liu, J. Plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein: A crucial component of vascular homeostasis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Rom, S.; Ramirez, S.H.; Persidsky, Y. Emerging Roles of Pericytes in the Regulation of the Neurovascular Unit in Health and Disease. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persidsky, Y.; Heilman, D.; Haorah, J.; Zelivyanskaya, M.; Persidsky, R.; Weber, G.A.; Shimokawa, H.; Kaibuchi, K.; Ikezu, T. Rho-mediated regulation of tight junctions during monocyte migration across the blood-brain barrier in HIV-1 encephalitis (HIVE). Blood 2006, 107, 4770–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanmogne, G.D.; Schall, K.; Leibhart, J.; Knipe, B.; Gendelman, H.E.; Persidsky, Y. HIV-1 gp120 compromises blood-brain barrier integrity and enhance monocyte migration across blood-brain barrier: Implication for viral neuropathogenesis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, S.H.; Fan, S.; Dykstra, H.; Rom, S.; Mercer, A.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Gofman, L.; Persidsky, Y. Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3beta Promotes Tight Junction Stability in Brain Endothelial Cells by Half-Life Extension of Occludin and Claudin-5. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, S.; Dykstra, H.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Persidsky, Y. miR-98 and let-7g* protect the blood-brain barrier under neuroinflammatory conditions. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, S.; Fan, S.; Reichenbach, N.; Dykstra, H.; Ramirez, S.H.; Persidsky, Y. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibition prevents monocyte migration across brain endothelial cells via Rac1-GTPase suppression and down-regulation of active integrin conformation. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, S.; Persidsky, Y. Cannabinoid receptor 2: Potential role in immunomodulation and neuroinflammation. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, S.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Dykstra, H.; Reichenbach, N.; Ramirez, S.H.; Persidsky, Y. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition in brain endothelium protects the blood–brain barrier under physiologic and neuroinflammatory conditions. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, S.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Dykstra, H.; Persidsky, Y. The dual action of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase -1 (PARP-1) inhibition in HIV-1 infection: HIV-1 LTR inhibition and diminution in Rho GTPase activity. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadian, S.; Patel, P.; Spudich, S. Neurological Complications of HIV Infection. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorpade, A.; Nukuna, A.; Che, M.; Haggerty, S.; Persidsky, Y.; Carter, E.; Carhart, L.; Shafer, L.; Gendelman, H.E. Human immunodeficiency virus neurotropism: An analysis of viral replication and cytopathicity for divergent strains in monocytes and microglia. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 3340–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendelman, H.E.; Orenstein, J.M.; Martin, M.A.; Ferrua, C.; Mitra, R.; Phipps, T.; Wahl, L.A.; Lane, H.C.; Fauci, A.S.; Burke, D.S.; et al. Efficient isolation and propagation of human immunodeficiency virus on recombinant colony-stimulating factor 1-treated monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, S.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Dykstra, H.; Gajghate, S.; Pacher, P.; Persidsky, Y. PARP inhibition in leukocytes diminishes inflammation via effects on integrins/cytoskeleton and protects the blood-brain barrier. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, B.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K.; Wolburg, H. Involvement of the choroid plexus in central nervous system inflammation. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 52, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.B. The adhesion molecule ICAM-1 and its regulation in relation with the blood-brain barrier. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 128, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, E.; Delachanal, E.; Duperray, A. Analysis of the roles of ICAM-1 in neutrophil transmigration using a reconstituted mammalian cell expression model: Implication of ICAM-1 cytoplasmic domain and Rho-dependent signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Froio, R.M.; Sciuto, T.E.; Dvorak, A.M.; Alon, R.; Luscinskas, F.W. ICAM-1 regulates neutrophil adhesion and transcellular migration of TNF-alpha-activated vascular endothelium under flow. Blood 2005, 106, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, S.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Dykstra, H.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Pacher, P.; Persidsky, Y. Selective activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 in leukocytes suppresses their engagement of the brain endothelium and protects the blood-brain barrier. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hyun, Y.M.; Chung, H.L.; McGrath, J.L.; Waugh, R.E.; Kim, M. Activated integrin VLA-4 localizes to the lamellipodia and mediates T cell migration on VCAM-1. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Wakelin, M.W.; Henault, L.; Goetz, D.J.; Yednock, T.; Cabanas, C.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Lichtman, A.H.; Luscinskas, F.W. Alpha4beta1-integrin activation is necessary for high-efficiency T-cell subset interactions with VCAM-1 under flow. Microcirculation 2000, 7, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, A.; Misra, V.; Cassol, E.; Ancuta, P.; Yan, Z.; Li, C.; Morgello, S.; Gabuzda, D. A plasma biomarker signature of immune activation in HIV patients on antiretroviral therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, P.J.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Bolo, N.R. Diabetes and the link between neuroplasticity and glutamate in the aging human motor cortex. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, X.; Gu, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, X.Y.; Qian, C.; Yang, Y.; Teng, G.J. Cerebral perfusion alterations in type 2 diabetes and its relation to insulin resistance and cognitive dysfunction. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 11, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umegaki, H. Type 2 diabetes as a risk factor for cognitive impairment: Current insights. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boven, L.A.; Gomes, L.; Hery, C.; Gray, F.; Verhoef, J.; Portegies, P.; Tardieu, M.; Nottet, H.S. Increased peroxynitrite activity in AIDS dementia complex: Implications for the neuropathogenesis of HIV-1 infection. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4319–4327. [Google Scholar]
- Persidsky, Y.; Zheng, J.; Miller, D.; Gendelman, H.E. Mononuclear phagocytes mediate blood-brain barrier compromise and neuronal injury during HIV-1-associated dementia. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 68, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Persidsky, Y.; Limoges, J.; Rasmussen, J.; Zheng, J.; Gearing, A.; Gendelman, H.E. Reduction in glial immunity and neuropathology by a PAF antagonist and an MMP and TNFalpha inhibitor in SCID mice with HIV-1 encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 114, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, J.; Marripudi, K.; Staub, L.P.; Rae, C.D.; Gates, T.M.; Moffat, K.J.; Brew, B.J. Imaging correlates of the blood-brain barrier disruption in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder and therapeutic implications. AIDS 2019, 33, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehade, J.M.; Haas, M.J.; Mooradian, A.D. Diabetes-related changes in rat cerebral occludin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) expression. Neurochem. Res. 2002, 27, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, J.D.; VanGilder, R.L.; Houser, K.A. Streptozotocin-induced diabetes progressively increases blood-brain barrier permeability in specific brain regions in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 2006, 291, H2660–H2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, B.T.; Lundeen, T.F.; Norwood, K.M.; Brooks, H.L.; Egleton, R.D. Increased blood-brain barrier permeability and altered tight junctions in experimental diabetes in the rat: Contribution of hyperglycaemia and matrix metalloproteinases. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, M.; Horiuchi, M. Neurovascular coupling in cognitive impairment associated with diabetes mellitus. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2011, 75, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Maratha, A.; Siednienko, J.; Natarajan, A.; Gajanayake, T.; Hoashi, S.; Miggin, S. Analysis of inflammatory cytokine and TLR expression levels in Type 2 Diabetes with complications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Cai, L.; Chakrabarti, S.; Li, X. Cytokines and diabetes research. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 920613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuji, F.N.; Onyenekwe, C.C.; Ahaneku, J.E.; Ukibe, N.R. The effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy on the serum levels of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in HIV infected subjects. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatovic, S.M.; Keep, R.F.; Kunkel, S.L.; Andjelkovic, A.V. Potential role of MCP-1 in endothelial cell tight junction ‘opening’: Signaling via Rho and Rho kinase. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 4615–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, H.; Ishii, K.; Horiuchi, H.; Arai, H.; Kawamoto, T.; Okawa, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; Kita, T. Cutting edge: Combined treatment of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma causes redistribution of junctional adhesion molecule in human endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, W.; Hargrove, J.L.; Greenspan, P.; Dean, R.G.; Taylor, E.W.; Hartle, D.K. Inhibition of TNF-alpha induced ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression by selenium. Atherosclerosis 2002, 161, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliaro, L.; Piconi, L.; Assaloni, R.; Da Ros, R.; Maier, A.; Zuodar, G.; Ceriello, A. Intermittent high glucose enhances ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture: The distinct role of protein kinase C and mitochondrial superoxide production. Atherosclerosis 2005, 183, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wetering, S.; Van Den Berk, N.; Van Buul, J.D.; Mul, F.P.; Lommerse, I.; Mous, R.; Ten Klooster, J.P.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Hordijk, P.L. VCAM-1-mediated Rac signaling controls endothelial cell-cell contacts and leukocyte transmigration. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2003, 285, C343–C352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.R.; Rachel, G.; Parthasarathy, D. HIV Proteins and Endothelial Dysfunction: Implications in Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aversa, T.G.; Eugenin, E.A.; Berman, J.W. NeuroAIDS: Contributions of the human immunodeficiency virus-1 proteins Tat and gp120 as well as CD40 to microglial activation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 81, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, S.; Pacifici, M.; Passiatore, G.; Aprea, S.; Waligorska, A.; Del Valle, L.; Peruzzi, F. HIV-1 Tat binds to SH3 domains: Cellular and viral outcome of Tat/Grb2 interaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Marle, G.; Henry, S.; Todoruk, T.; Sullivan, A.; Silva, C.; Rourke, S.B.; Holden, J.; McArthur, J.C.; Gill, M.J.; Power, C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein mediates neural cell death: A neurotoxic role for IP-10. Virology 2004, 329, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Duan, F.; Morsey, B.; Persidsky, Y.; Kanmogne, G.D. HIV-1 activates proinflammatory and interferon-inducible genes in human brain microvascular endothelial cells: Putative mechanisms of blood-brain barrier dysfunction. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner, C.M.; Luers, A.J.; Calderon, T.M.; Eugenin, E.A.; Berman, J.W. Neuroimmunity and the blood-brain barrier: Molecular regulation of leukocyte transmigration and viral entry into the nervous system with a focus on neuroAIDS. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006, 1, 160–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avison, M.J.; Nath, A.; Greene-Avison, R.; Schmitt, F.A.; Greenberg, R.N.; Berger, J.R. Neuroimaging correlates of HIV-associated BBB compromise. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 157, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.R.; Avison, M. The blood brain barrier in HIV infection. Front. Biosci 2004, 9, 2680–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ramirez, S.H.; Fan, S.; Dykstra, H.; Reichenbach, N.; Del Valle, L.; Potula, R.; Phipps, R.P.; Maggirwar, S.B.; Persidsky, Y. Dyad of CD40/CD40 ligand fosters neuroinflammation at the blood-brain barrier and is regulated via JNK signaling: Implications for HIV-1 encephalitis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9454–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, B.; Eum, S.Y.; Toborek, M. HIV-1 Tat triggers nuclear localization of ZO-1 via Rho signaling and cAMP response element-binding protein activation. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Yao, H.; Zhang, W.; Sutliff, R.L.; Buch, S. Tat 101-mediated enhancement of brain pericyte migration involves platelet-derived growth factor subunit B homodimer: Implications for human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurocognitive disorders. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11812–11825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengillo, J.D.; Winkler, E.A.; Walker, C.T.; Sullivan, J.S.; Johnson, M.; Zlokovic, B.V. Deficiency in mural vascular cells coincides with blood-brain barrier disruption in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2012, 23, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.A.; Sengillo, J.D.; Sullivan, J.S.; Henkel, J.S.; Appel, S.H.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown and pericyte reductions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M. Signaling required for blood vessel maintenance: Molecular basis and pathological manifestations. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2012, 2012, 293641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vates, G.E.; Takano, T.; Zlokovic, B.; Nedergaard, M. Pericyte constriction after stroke: The jury is still out. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, I.H.; Griffiths, H.R. Oxidative stress in diabetes - circulating advanced glycation end products, lipid oxidation and vascular disease. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 51, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, X. Involvement of RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway in hyperglycemia-induced microvascular endothelial dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7268–7277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vermeire, J.; Naessens, E.; Vanderstraeten, H.; Landi, A.; Iannucci, V.; Van Nuffel, A.; Taghon, T.; Pizzato, M.; Verhasselt, B. Quantification of reverse transcriptase activity by real-time PCR as a fast and accurate method for titration of HIV, lenti- and retroviral vectors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| HIV with ART (11) | HIV without ART (10) | HIV with Diabetes (8, ART - 6, without ART - 2) | HIV Naive with Diabetes (11) | HIV Naïve (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||||
| <35 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 36–64 | 10 | 0 | 6 | 8 | 3 |
| >64 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 5 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 3 |
| Female | 5 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| Ethnicity | |||||
| Caucasian | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 1 |
| African | |||||
| American | 6 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Hispanic | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Comorbidity | |||||
| Hepatitis C | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Hepatitis B | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hepatitis B and C | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rom, S.; Gajghate, S.; Winfield, M.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Persidsky, Y. Combination of HIV-1 and Diabetes Enhances Blood Brain Barrier Injury via Effects on Brain Endothelium and Pericytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134663
Rom S, Gajghate S, Winfield M, Reichenbach NL, Persidsky Y. Combination of HIV-1 and Diabetes Enhances Blood Brain Barrier Injury via Effects on Brain Endothelium and Pericytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(13):4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134663
Chicago/Turabian StyleRom, Slava, Sachin Gajghate, Malika Winfield, Nancy L. Reichenbach, and Yuri Persidsky. 2020. "Combination of HIV-1 and Diabetes Enhances Blood Brain Barrier Injury via Effects on Brain Endothelium and Pericytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 13: 4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134663
APA StyleRom, S., Gajghate, S., Winfield, M., Reichenbach, N. L., & Persidsky, Y. (2020). Combination of HIV-1 and Diabetes Enhances Blood Brain Barrier Injury via Effects on Brain Endothelium and Pericytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(13), 4663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134663





