ANGPTL4 Induces TMZ Resistance of Glioblastoma by Promoting Cancer Stemness Enrichment via the EGFR/AKT/4E-BP1 Cascade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
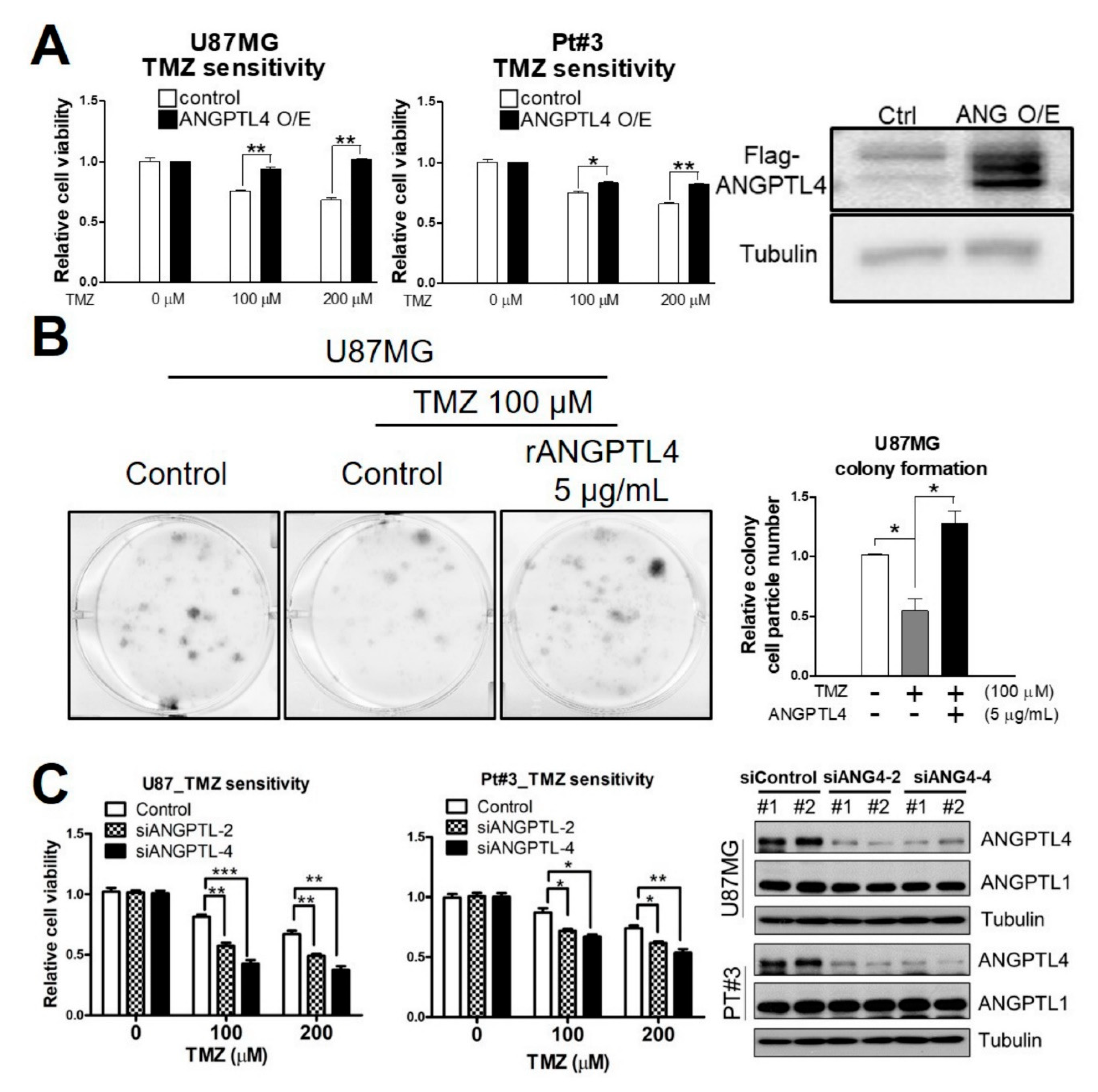
2.1. ANGPTL4 Induces TMZ Resistance in GBM Cells
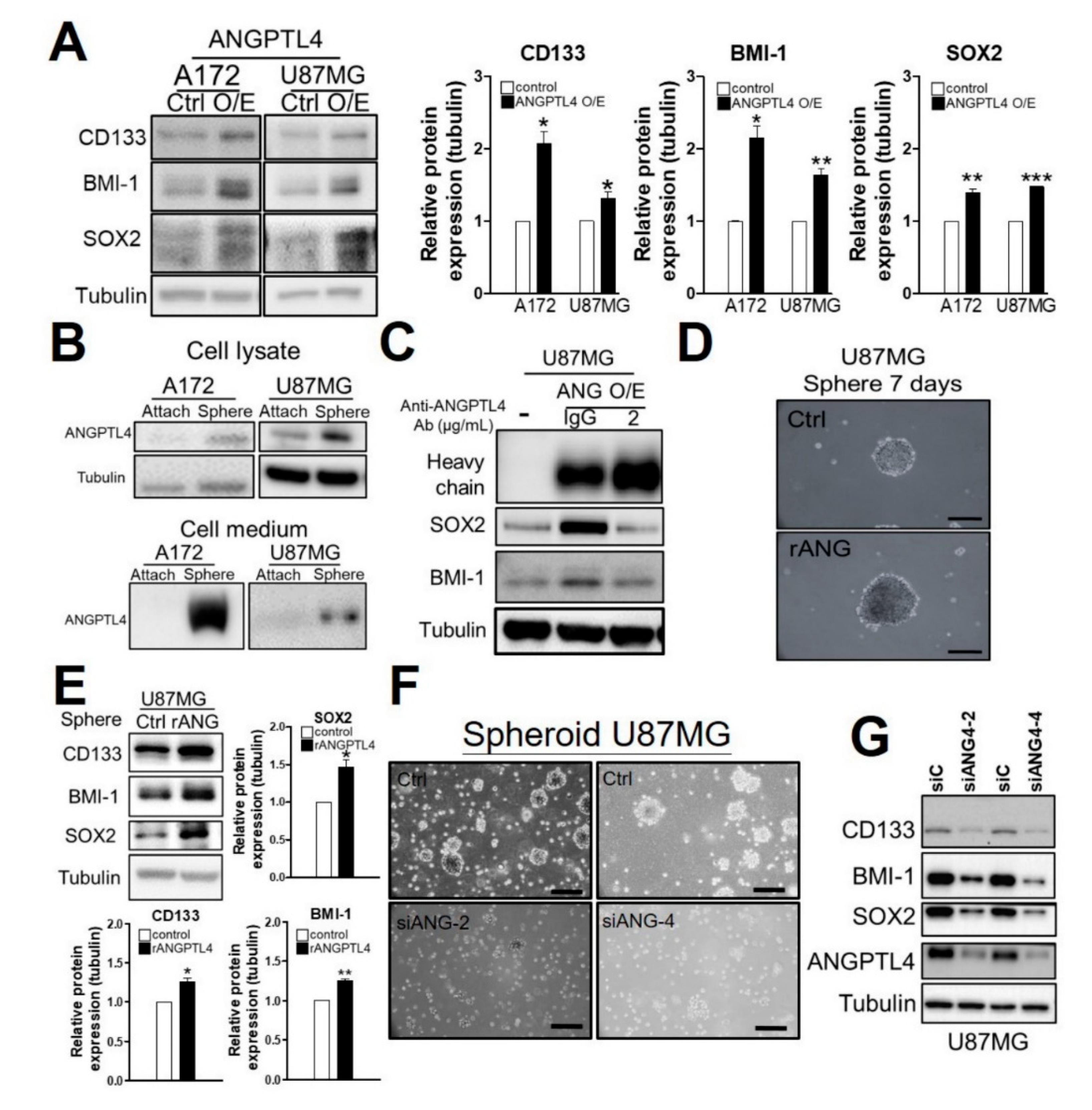
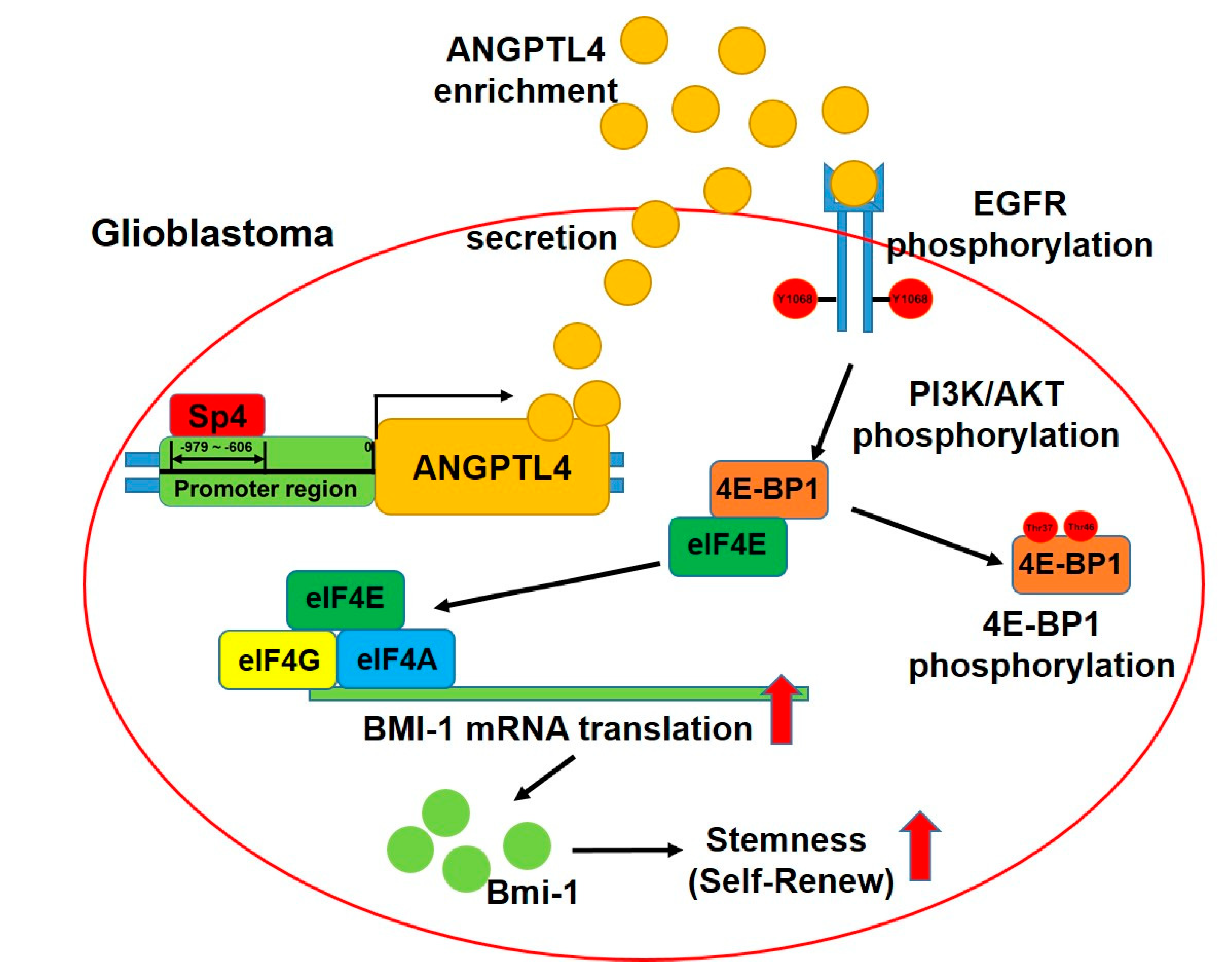
2.2. ANGPTL4 Secretion by GBM Cells Increases GSC Enrichment
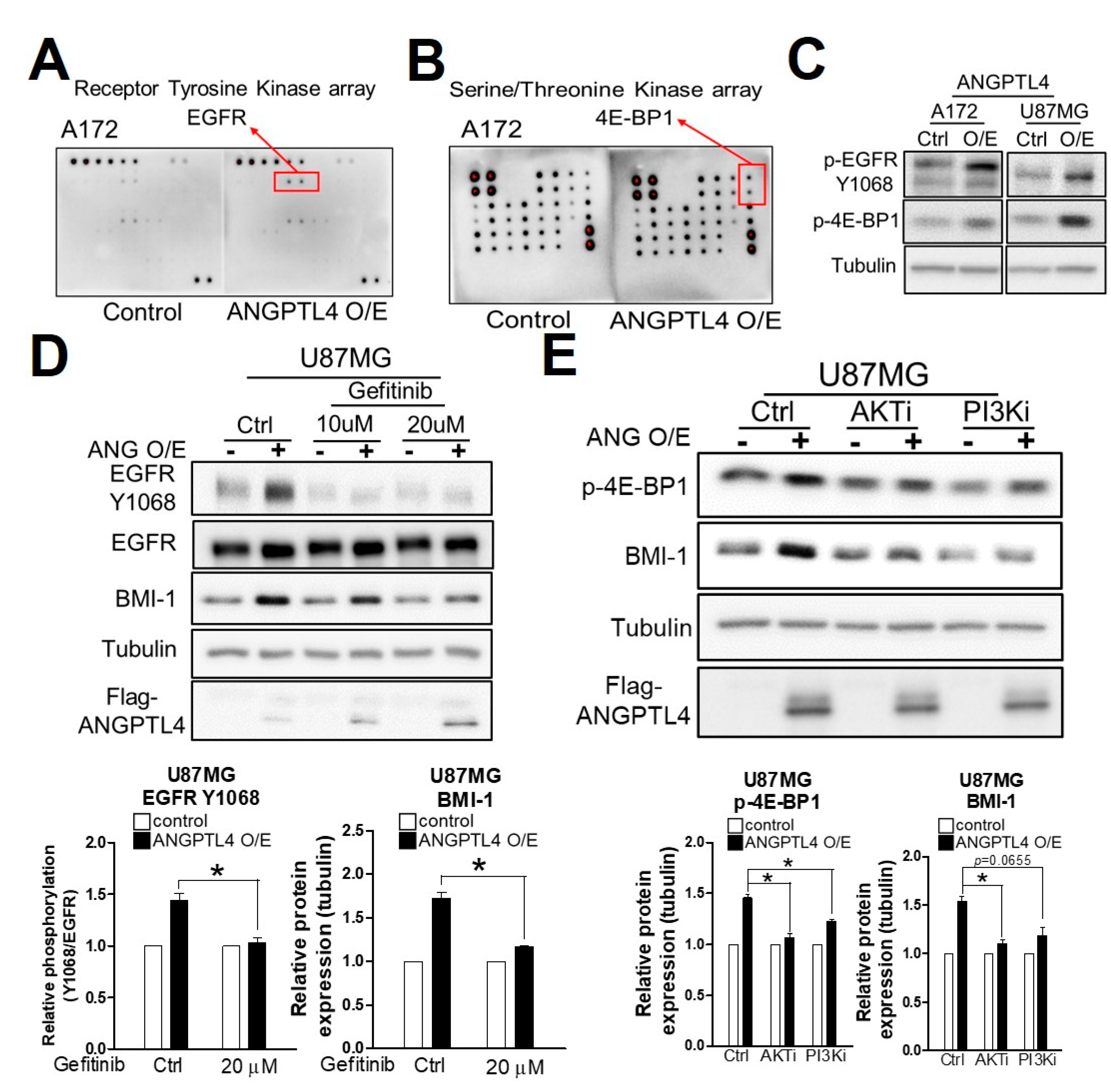
2.3. ANGPTL4 Regulates Stemness through the EGFR/AKT/4E-BP1 Cascade
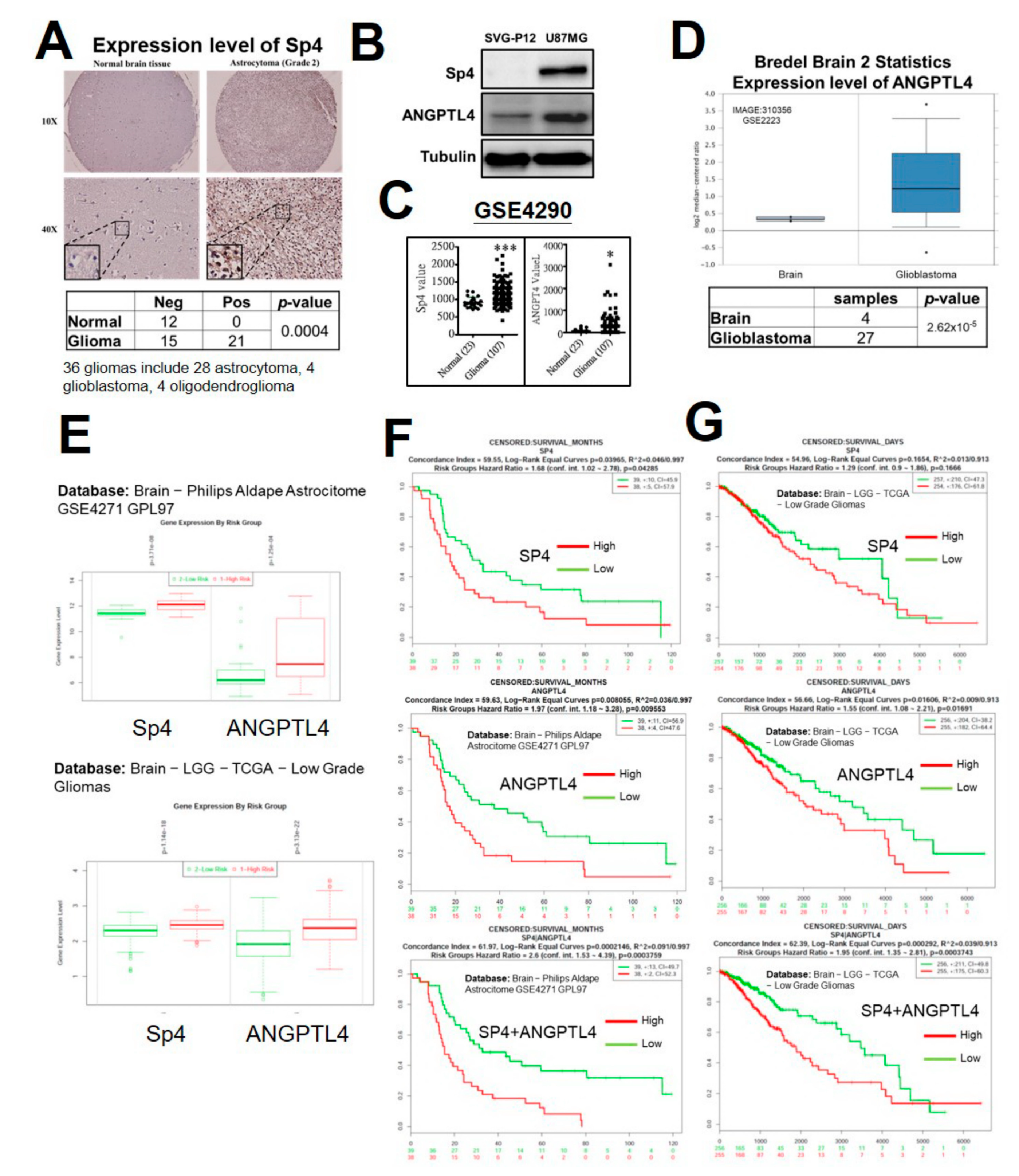
2.4. Sp4 Increases ANGPTL4 Expression Leading to Stemness Development
2.5. High Expression of Sp4 and ANGPTL4 Correlate with a Poor Prognosis of GBM
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Human Specimens and Primary Glioblastoma Cells Pt#3
4.3. Chemicals
4.4. Transfection and Plasmids
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Colony Formation
4.8. Phosphorylation Array
4.9. Reporter Assay
4.10. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Coupled with Sequencing (ChIP-seq) and Data Analysis
4.11. Microarray Analysis
4.12. Databases
4.13. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4E-BP1 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E)-binding protein 1 |
| AKAP12 | A-kinase anchoring protein 12 |
| ANGPTL4 | Angiopoietin-like 4 protein |
| CCN3 | Cellular communication network factor 3 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 |
| CEMIP | Cell migration-inducing hyaluronidase 1 |
| ChIP-seq | Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with sequencing |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EGR1 | Early growth response protein 1 |
| EGR2 | Early growth response protein 2 |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| FGF1 | Fibroblast growth factor 1 |
| ERK | Extracellular signal–regulated kinase |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| GSCs | Glioma stem-like cells |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| LD | linear dichroism |
| LY96 | Lymphocyte antigen 96 |
| MEME-ChIP | Motif analysis of large DNA datasets |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| Poly-HEMA | Poly-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| rANGPTL4 | Human recombinant ANGPTL4 protein |
| RTK | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| Sp | Specificity protein |
| SOX2 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| TMZ | Temozolomide |
| TYROBP | TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein |
| WNT5b | Wnt family member 5B |
References
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.M.; Simjee Sh, U. Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of its Epidemiology and Pathogenesis through Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiapaer, S.; Furuta, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kitabayashi, T.; Nakada, M. Potential Strategies Overcoming the Temozolomide Resistance for Glioblastoma. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2018, 58, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.A.; Karajannis, M.A.; Harter, D.H. Glioblastoma multiforme: State of the art and future therapeutics. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2014, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffinger, B.; Tobias, A.L.; Han, Y.; Lee, G.; Guo, D.; Dey, M.; Lesniak, M.S.; Ahmed, A.U. Conversion of differentiated cancer cells into cancer stem-like cells in a glioblastoma model after primary chemotherapy. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, M.; Bharali, D.J.; Sudha, T.; Khedr, M.; Guest, I.; Sell, S.; Glinsky, G.V.; Mousa, S.A. Downregulation of Bmi1 in breast cancer stem cells suppresses tumor growth and proliferation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38731–38742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, P.; Seyfrid, M.; Venugopal, C.; Qazi, M.A.; Salim, S.; Isserlin, R.; Subapanditha, M.; O’Farrell, E.; Mahendram, S.; Singh, M.; et al. Bmi1 regulates human glioblastoma stem cells through activation of differential gene networks in CD133+ brain tumor initiating cells. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 143, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ye, Q.; She, Q.B. New insights into 4E-BP1-regulated translation in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Cell Microenviron 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Molinolo, A.A.; Martin, D.; Vitale-Cross, L.; Nohata, N.; Ando, M.; Wahba, A.; Amornphimoltham, P.; Wu, X.; et al. 4E-BP1 Is a Tumor Suppressor Protein Reactivated by mTOR Inhibition in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Paglia, L.; Listi, A.; Caruso, S.; Amodeo, V.; Passiglia, F.; Bazan, V.; Fanale, D. Potential Role of ANGPTL4 in the Cross Talk between Metabolism and Cancer through PPAR Signaling Pathway. Ppar Res. 2017, 2017, 8187235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Miyamoto, H. Androgen Receptor Signaling in Bladder Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.H.; Chiang, K.H.; Shieh, J.M.; Huang, C.R.; Shen, C.J.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, B.K. Epidermal growth factor-induced ANGPTL4 enhances anoikis resistance and tumour metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2228–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Babapoor-Farrokhran, S.; Rodrigues, M.; Deshpande, M.; Puchner, B.; Kashiwabuchi, F.; Hassan, S.J.; Asnaghi, L.; Handa, J.T.; Merbs, S.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 upregulation of both VEGF and ANGPTL4 is required to promote the angiogenic phenotype in uveal melanoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7816–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okochi-Takada, E.; Hattori, N.; Tsukamoto, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Ando, T.; Ito, S.; Yamamura, Y.; Wakabayashi, M.; Nobeyama, Y.; Ushijima, T. ANGPTL4 is a secreted tumor suppressor that inhibits angiogenesis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2273–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.J.; Teo, Z.; Sng, M.K.; Zhu, P.; Tan, N.S. Emerging roles of angiopoietin-like 4 in human cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, J.M.; Ellison, D.W.; Finkelstein, D.; Ganguly, D.; Du, Z.; Sims, M.; Yang, C.H.; Interiano, R.B.; Davidoff, A.M.; Pfeffer, L.M. Molecular heterogeneity in a patient-derived glioblastoma xenoline is regulated by different cancer stem cell populations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katanasaka, Y.; Kodera, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Tamura, T.; Koizumi, F. Epidermal growth factor receptor variant type III markedly accelerates angiogenesis and tumor growth via inducing c-myc mediated angiopoietin-like 4 expression in malignant glioma. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, Y.Y.; Pal, M.; Chong, H.C.; Zhu, P.; Tan, M.J.; Punugu, L.; Lam, C.R.; Yau, Y.H.; Tan, C.K.; Huang, R.L.; et al. Angiopoietin-like 4 interacts with integrins beta1 and beta5 to modulate keratinocyte migration. Am. J. Pathol 2010, 177, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez Perdiguero, E.; Liabotis-Fontugne, A.; Durand, M.; Faye, C.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Simonutti, M.; Augustin, S.; Robb, B.M.; Paques, M.; Valenzuela, D.M.; et al. ANGPTL4-alphavbeta3 interaction counteracts hypoxia-induced vascular permeability by modulating Src signalling downstream of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. J. Pathol. 2016, 240, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Tan, M.J.; Huang, R.L.; Tan, C.K.; Chong, H.C.; Pal, M.; Lam, C.R.; Boukamp, P.; Pan, J.Y.; Tan, S.H.; et al. Angiopoietin-like 4 protein elevates the prosurvival intracellular O2(-):H2O2 ratio and confers anoikis resistance to tumors. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.W.; Nicolaides, T.P.; Weiss, W.A. Inhibiting 4EBP1 in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, L.; Magagnin, M.G.; Cleven, A.H.; Weppler, S.A.; Grenacher, B.; Landuyt, W.; Lieuwes, N.; Lambin, P.; Gorr, T.A.; Koritzinsky, M.; et al. Inhibition of 4E-BP1 sensitizes U87 glioblastoma xenograft tumors to irradiation by decreasing hypoxia tolerance. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 73, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekir, K.; Dubois-Pot-Schneider, H.; Desert, R.; Daniel, Y.; Glaise, D.; Rauch, C.; Morel, F.; Fromenty, B.; Musso, O.; Cabillic, F.; et al. Retrodifferentiation of Human Tumor Hepatocytes to Stem Cells Leads to Metabolic Reprogramming and Chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, B.; Johar, K.; Priya, A.; Wong-Riley, M.T. Specificity protein 4 (Sp4) transcriptionally regulates inhibitory GABAergic receptors in neurons. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1863, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.B.; Chuang, J.Y.; Ko, C.Y.; Chang, W.C.; Hsu, T.I. Dehydroepiandrosterone Induces Temozolomide Resistance Through Modulating Phosphorylation and Acetylation of Sp1 in Glioblastoma. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Ko, C.Y.; Kao, T.J.; Yang, W.B.; Tsai, Y.T.; Chuang, J.Y.; Hu, S.L.; Yang, P.Y.; Lo, W.L.; Hsu, T.I. CYP17A1 Maintains the Survival of Glioblastomas by Regulating SAR1-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Health and Redox Homeostasis. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.Y.; Hsu, T.I.; Hsu, C.C.; Tsai, S.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Chou, S.W.; Liu, M.S.; Liou, J.P.; Ko, C.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; et al. Specificity protein 1-modulated superoxide dismutase 2 enhances temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma, which is independent of O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. Redox. Biol. 2017, 13, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2009, 37, W202-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovelson, D.H.; McDaniel, A.S.; Cani, A.K.; Johnson, B.; Rhodes, K.; Williams, P.D.; Bandla, S.; Bien, G.; Choppa, P.; Hyland, F.; et al. Development and validation of a scalable next-generation sequencing system for assessing relevant somatic variants in solid tumors. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredel, M.; Bredel, C.; Juric, D.; Harsh, G.R.; Vogel, H.; Recht, L.D.; Sikic, B.I. Functional network analysis reveals extended gliomagenesis pathway maps and three novel MYC-interacting genes in human gliomas. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8679–8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Gamboa, R.; Gomez-Rueda, H.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Martinez-Torteya, A.; Chacolla-Huaringa, R.; Rodriguez-Barrientos, A.; Tamez-Pena, J.G.; Trevino, V. SurvExpress: An online biomarker validation tool and database for cancer gene expression data using survival analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravendeel, L.A.; Kouwenhoven, M.C.; Gevaert, O.; de Rooi, J.J.; Stubbs, A.P.; Duijm, J.E.; Daemen, A.; Bleeker, F.E.; Bralten, L.B.; Kloosterhof, N.K.; et al. Intrinsic gene expression profiles of gliomas are a better predictor of survival than histology. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 9065–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, H.S.; Kharbanda, S.; Chen, R.; Forrest, W.F.; Soriano, R.H.; Wu, T.D.; Misra, A.; Nigro, J.M.; Colman, H.; Soroceanu, L.; et al. Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, Y.-T.; Wu, A.-C.; Yang, W.-B.; Kao, T.-J.; Chuang, J.-Y.; Chang, W.-C.; Hsu, T.-I. ANGPTL4 Induces TMZ Resistance of Glioblastoma by Promoting Cancer Stemness Enrichment via the EGFR/AKT/4E-BP1 Cascade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225625
Tsai Y-T, Wu A-C, Yang W-B, Kao T-J, Chuang J-Y, Chang W-C, Hsu T-I. ANGPTL4 Induces TMZ Resistance of Glioblastoma by Promoting Cancer Stemness Enrichment via the EGFR/AKT/4E-BP1 Cascade. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225625
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Yu-Ting, An-Chih Wu, Wen-Bin Yang, Tzu-Jen Kao, Jian-Ying Chuang, Wen-Chang Chang, and Tsung-I. Hsu. 2019. "ANGPTL4 Induces TMZ Resistance of Glioblastoma by Promoting Cancer Stemness Enrichment via the EGFR/AKT/4E-BP1 Cascade" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225625
APA StyleTsai, Y.-T., Wu, A.-C., Yang, W.-B., Kao, T.-J., Chuang, J.-Y., Chang, W.-C., & Hsu, T.-I. (2019). ANGPTL4 Induces TMZ Resistance of Glioblastoma by Promoting Cancer Stemness Enrichment via the EGFR/AKT/4E-BP1 Cascade. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225625




