Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
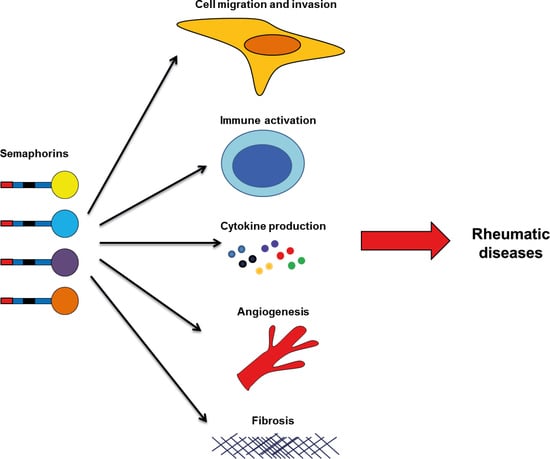
1. Introduction
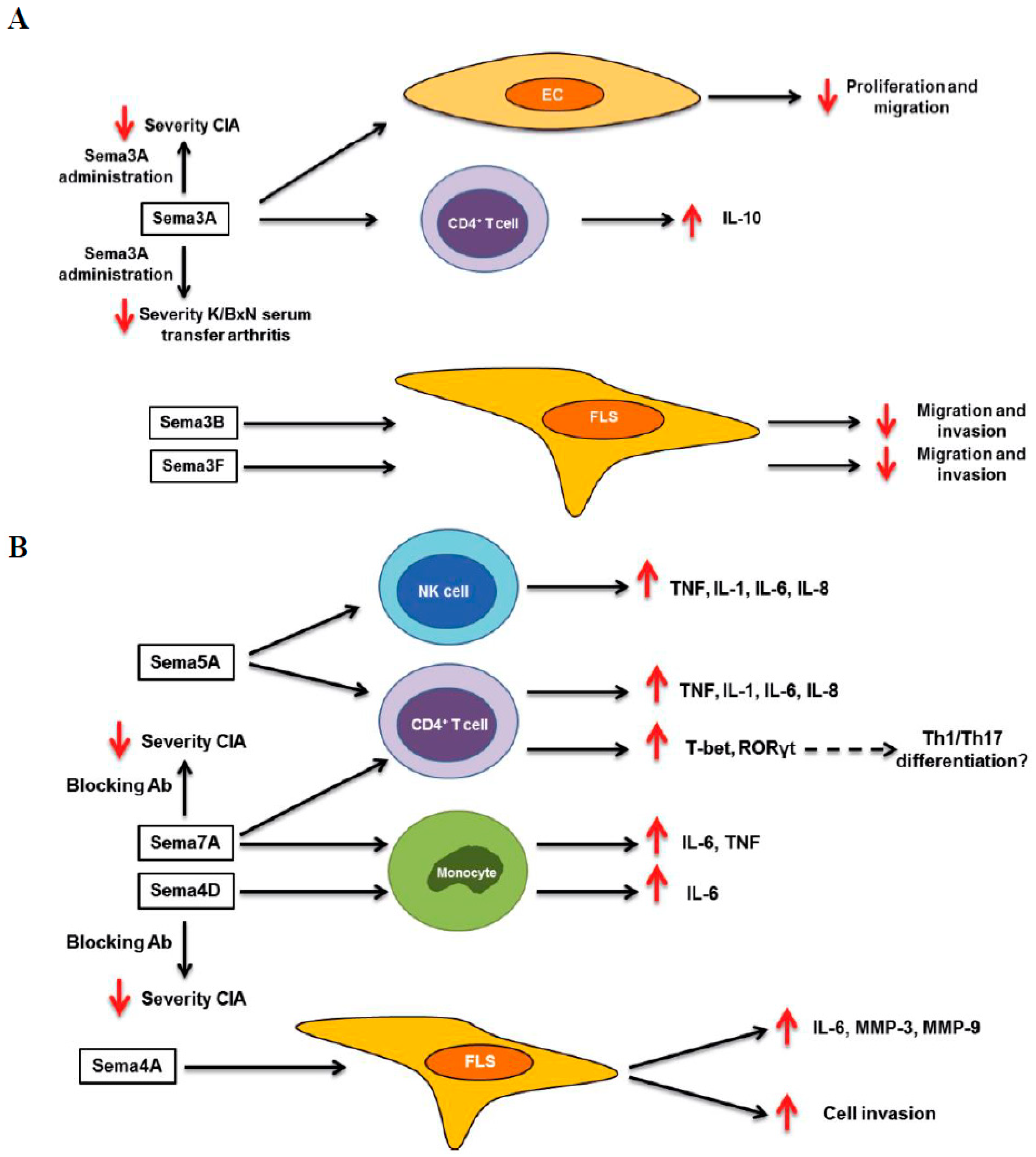
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
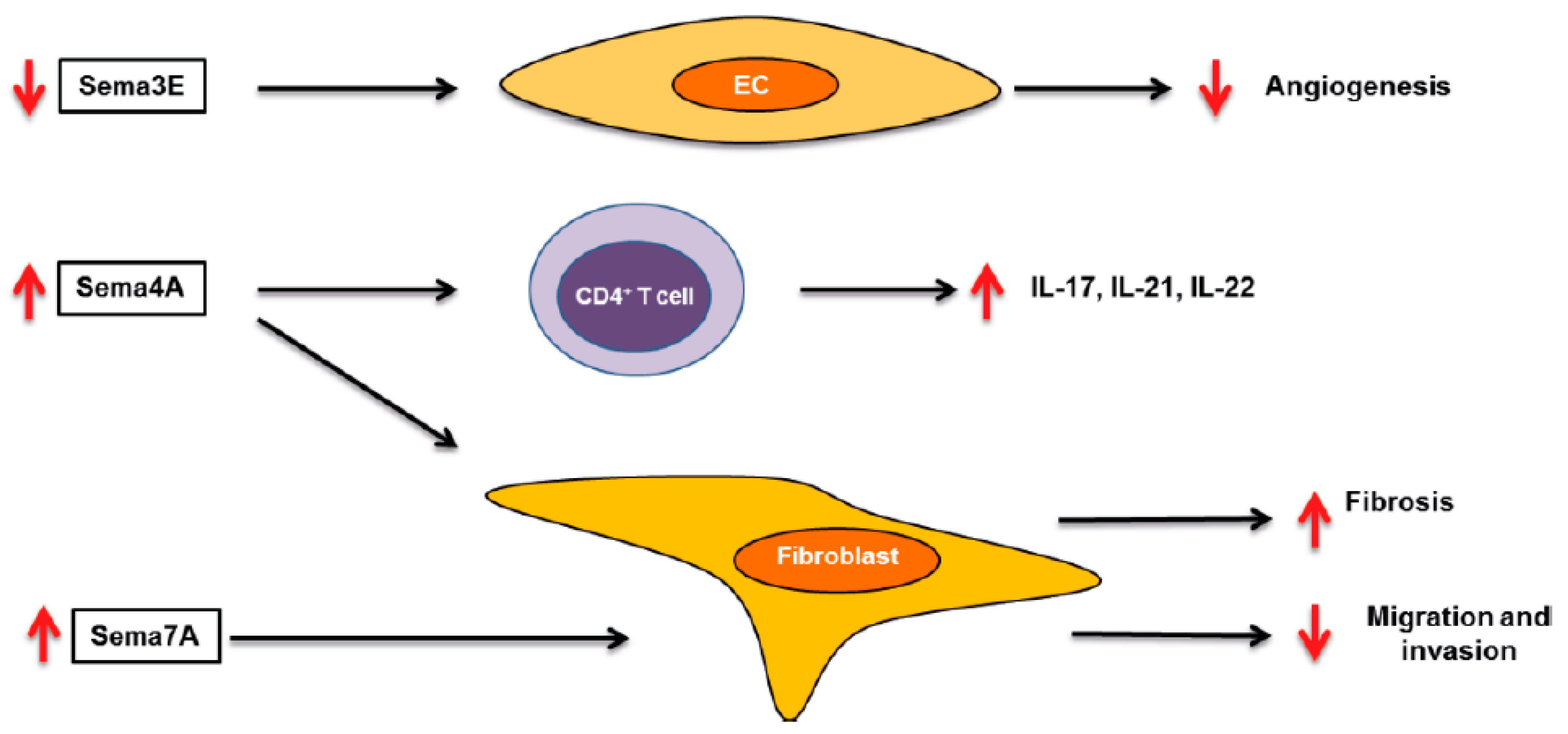
3. Systemic Sclerosis
4. Osteoarthritis
5. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
6. Spondyloarthritis
7. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gourley, M.; Miller, F.W. Mechanisms of disease: Environmental factors in the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblatt, F.; O’Neill, S.G. Clinical aspects of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2013, 382, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, H.; Kumanogoh, A. Diverse roles for semaphorin S plexin signaling in the immune system. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Immunological functions of the neuropilins and plexins as receptors for semaphorins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizui, M.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Immune semaphorins: Novel features of neural guidance molecules. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzfeld, T.; Offermanns, S. Semaphorins and plexins as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Semaphorins and their receptors in immune cell interactions. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishide, M.; Kumanogoh, A. The role of semaphorins in immune responses and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Verhaagen, J.; Harvey, A.R. Receptor complexes for each of the Class 3 Semaphorins. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhu, L. Semaphorins and their receptors: From axonal guidance to atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagnone, L. Emerging Role of Semaphorins as Major Regulatory Signals and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, G.; Kessler, O. The semaphorins: Versatile regulators of tumour progression and tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Giraudo, E. The role of semaphorins and their receptors in vascular development and cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, L.; Koncina, E.; Satkauskas, S.; Crémel, G.; Aunis, D.; Bagnard, D. The many faces of semaphorins: From development to pathology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, P.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Samuel, S.; Bose, D.; Zhou, Y.; Gray, M.J.; Dallas, N.A.; Fan, F.; Xia, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Role of class 3 semaphorins and their receptors in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6763–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, D.; Kumanogoh, A. The role of Sema4A in angiogenesis, immune responses, carcinogenesis, and retinal systems. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2016, 10, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.W.S.; Lee, A.Y.W. The Role of Semaphorins and Their Receptors in Gliomas. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 902854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Kumar, D.; Tomar, D.; Chakraborty, G.; Kumar, S.; Kundu, G.C. The potential of class 3 semaphorins as both targets and therapeutics in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, C.; Tamagnone, L. Semaphorin Signals Tweaking the Tumor Microenvironment, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Roles of semaphorins in the immune and hematopoietic system. Rheumatol. Int. 2009, 29, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kumanogoh, A. Semaphorins in bone development, homeostasis, and disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goshima, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Yamashita, N.; Nakamura, F. Class 3 semaphorins as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017, 389, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.E. Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: Future targets? Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Bresnihan, B. The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: Advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 2619–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Buckley, C.D.; Isaacs, J.D. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis—Shaping the immunological landscape. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Rheumatoid arthritis therapy reappraisal: Strategies, opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.E.; Weidler, C.; Falk, W.; Angele, P.; Schaumburger, J.; Schölmerich, J.; Straub, R.H. Increased Prevalence of Semaphorin 3C, a Repellent of Sympathetic Nerve Fibers, in the Synovial Tissue of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A. The neuroimmune semaphorin-3A reduces inflammation and progression of experimental autoimmune arthritis. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6373–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagawa, S.; Nakamura, F.; Kumagai, K.; Nagashima, Y.; Goshima, Y.; Saito, T. Decreased semaphorin3A expression correlates with disease activity and histological features of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of Sema3A alleviates rheumatoid arthritis in a serum-transfer induced mouse model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 66270–66280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.W.; Malvar Fernández, B.; Newsom, S.P.; van Buul, J.D.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Baeten, D.L.; Tak, P.P.; Reedquist, K.A.; García, S. Class 3 semaphorins modulate the invasive capacity of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Song, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, W.; Pan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, X. Expression of Semaphorin 4A and its potential role in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Ogata, A.; Kang, S.; Ebina, K.; Shi, K.; Nojima, S.; Kimura, T.; Ito, D.; Morimoto, K.; Nishide, M.; et al. Semaphorin 4D contributes to rheumatoid arthritis by inducing inflammatory cytokine production: Pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, W.; Xv, W.; Ye, L.; Wu, D.; Xue, J.; Sun, W.; Luo, J.; et al. Elevated semaphorin5A in systemic lupus erythematosus is in association with disease activity and lupus nephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 188, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, H. Semaphorin 7A as a potential immune regulator and promising therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, A.; Avvedimento, E.V.; Krieg, T. Scleroderma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1989–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, D.; Brown, M.; Postlethwaite, B.C.; Postlethwaite, A.E. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rhijn-Brouwer, F.C.; Gremmels, H.; Fledderus, J.O.; Radstake, T.R.; Verhaar, M.C.; van Laar, J.M. Cellular Therapies in Systemic Sclerosis: Recent Progress. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.; Praino, E.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Gabrielli, A.; Iannone, F.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Use of biologics and other novel therapies for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wu, W.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Fu, W.; Li, M. New insights into CD4+ T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.S.; Kong, J.; Cheema, G.S.; Keen, C.L.; Wick, G.; Gershwin, M.E. The Immunobiology of Systemic Sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 38, 132–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis with a focus on Th17 cells. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2012, 23, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lafyatis, R. Innate immunity and inflammation in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 21, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bon, L.; Cossu, M.; Radstake, T.R. An update on an immune system that goes awry in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabquer, B.J.; Koch, A.E. Angiogenesis and Vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis: Evolving Concepts. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wei, J.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Hinchcliff, M.; Gottardi, C.G.; Varga, J. Fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: Common and unique pathobiology. Fibrogenes Tissue Repair 2012, 5, S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizzolini, C.; Brembilla, N.C.; Montanari, E.; Truchetet, M.E. Fibrosis and immune dysregulation in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimar, D.; Nov, Y.; Rosner, I.; Slobodin, G.; Rozenbaum, M.; Halasz, K.; Haj, T.; Jiries, N.; Kaly, L.; Boulman, N.; et al. Semaphorin 3A: An immunoregulator in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, E.; Chora, I.; Manetti, M.; Mazzotta, C.; Rosa, I.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Blagojevic, J.; Soares, R.; Avouac, J.; Allanore, Y.; et al. Decreased expression of neuropilin-1 as a novel key factor contributing to peripheral microvasculopathy and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzotta, C.; Romano, E.; Bruni, C.; Manetti, M.; Lepri, G.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Blagojevic, J.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Guiducci, S. Plexin-D1/Semaphorin 3E pathway may contribute to dysregulation of vascular tone control and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besliu, A.; Banica, L.; Predeteanu, D.; Vlad, V.; Ionescu, R.; Pistol, G.; Opris, D.; Berghea, F.; Stefanescu, M.; Matache, C. Peripheral blood lymphocytes analysis detects CD100/SEMA4D alteration in systemic sclerosis patients. Autoimmunity 2011, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.Y.; Gao, W.; Chong, F.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, J. Semaphorin 4A enhances lung fibrosis through activation of Akt via PlexinD1 receptor. J. Biosci. 2015, 40, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Reilkoff, R.; Peng, X.; Russell, T.; Chen, Q.; Mathai, S.K.; Homer, R.; Gulati, M.; Siner, J.; Elias, J.; et al. Role of semaphorin 7a signaling in transforming growth factor beta1-induced lung fibrosis and scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Minicis, S.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; Saccomanno, S.; Trozzi, L.; Candelaresi, C.; Bataller, R.; Millán, C.; Brenner, D.A.; Vivarelli, M.; et al. Semaphorin 7A Contributes to TGF-β—Mediated Liver Fibrogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Lee, C.G.; Homer, R.J.; Elias, J.A. Semaphorin 7A plays a critical role in TGF-β 1–induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynard, L.N.; Loughlin, J. Maturitas Genetics and epigenetics of osteoarthritis. Maturitas 2012, 71, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, R.; Villalvilla, A.; Largo, R.; Gualillo, O.; Herrero-beaumont, G. TLR4 signalling in osteoarthritis—Finding targets for candidate DMOADs. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. Changes in the osteochondral unit. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, S.; FitzGerald, U.; Murphy, J.M. Interplay of Inflammatory Mediators with Epigenetics and Cartilage Modifications in Osteoarthritis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, M.; Kimura, T.; Fujita, Y.; Mochizuki, S.; Niki, Y.; Enomoto, H.; Suda, Y.; Toyama, Y.; Okada, Y. Semaphorin 3A is expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage and antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor 165-promoted chondrocyte migration: An implication for chondrocyte cloning. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Lu, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Inflammatory milieu cultivated Sema3A signaling promotes chondrocyte apoptosis in knee osteoarthritis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, C.; Hirose, N.; Yanoshita, M.; Takano, M.; Nishiyama, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Asakawa, Y.; Tanimoto, K. Semaphorin 3A inhibits inflammation in chondrocytes under excessive mechanical stress. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 5703651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Nakashima, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Kodama, T.; Kumanogoh, A.; Takayanagi, H. Osteoprotection by semaphorin 3A. Nature 2012, 485, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokos, G.C. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2110–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadasz, Z.; Toubi, E. Semaphorin 3A-a marker for disease activity and a potential putative disease-modifying treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2012, 21, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadasz, Z.; Ben-Izhak, O.; Bejar, J.; Sabo, E.; Kessel, A.; Storch, S.; Toubi, E. The involvement of immune semaphorins and neuropilin-1 in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2011, 20, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadasz, Z.; Peri, R.; Eiza, N.; Slobodin, G.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Toubi, E. The Expansion of CD25 high IL-10 high FoxP3 high B Regulatory Cells Is in Association with SLE Disease Activity. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 254245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejar, J.; Kessler, O.; Sabag, A.D.; Sabo, E.; Itzhak, O.B.; Neufeld, G.; Vadasz, Z. Semaphorin3A: A Potential Therapeutic Tool for Lupus Nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moz, S.; Aita, A.; Basso, D.; Ramonda, R.; Plebani, M.; Punzi, L. Spondyloarthritis: Matrix metalloproteinasesas biomarkers of pathogenesis and response to tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieper, J.; Poddubnyy, D. Axial spondyloarthritis. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2017, 390, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambarus, C.; Yeremenko, N.; Tak, P.P.; Baeten, D. Pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis: Autoimmune or autoinflammatory? Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruithof, E.; Baeten, D.; De Rycke, L.; Vandooren, B.; Foell, D.; Roth, J.; Cañete, J.D.; Boots, A.M.; Veys, E.M.; De Keyser, F. Synovial histopathology of psoriatic arthritis, both oligo- and polyarticular, resembles spondyloarthropathy more than it does rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R569–R580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeten, D.; Demetter, P.; Cuvelier, C.; Van den Bosch, F.; Kruithof, E.; Van Damme, N.; Verbruggen, G.; Mielants, H.; Veys, E.M.; De Keyser, F. Comparative study of the synovial histology in rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, and osteoarthritis: Influence of disease duration and activity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, F.M.; Ceccarelli, F.; Barbati, C.; Colasanti, T.; Montepaone, M.; Alessandri, C.; Valesini, G.; Lubrano, E. Assessment of semaphorin 3A and its role in bone remodelling in a group of ankylosing spondylitis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.T.; Lin, Y.F.; Chou, C.T.; Tsai, C.Y. Semaphorin 3A in Ankylosing Spondylitis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moots, R.J.; Naisbett-Groet, B. The efficacy of biologic agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: A systematic review. Rheumatol. (Oxf.) 2012, 51, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, J.E.; Fisher, T.L.; Winter, L.A.; Cornelius, C.A.; Reilly, C.; Smith, E.S.; Zauderer, M. Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of VX15/2503, a Humanized IgG4 Anti-SEMA4D Antibody. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, A.; Weiss, G.J.; Leonard, J.E.; Rasco, D.W.; Sachdev, J.C.; Fisher, T.L.; Winter, L.A.; Reilly, C.; Parker, R.B.; Mutz, D.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of a Humanized Anti-Semaphorin 4D Antibody, in a First-In-Human Study of Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaGanke, C.; Samkoff, L.; Edwards, K.; Henson, L.J.; Repovic, P.; Lynch, S.; Stone, L.; Mattson, D.; Galluzzi, A.; Fisher, T.L.; et al. Safety/tolerability of the anti-semaphorin 4D antibody VX15/2503 in a randomized phase 1 trial. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. NeuroInflamm. 2017, 4, e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, S. Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374
Garcia S. Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Samuel. 2019. "Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374
APA StyleGarcia, S. (2019). Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374