Discontinued Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease from 2016 to 2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discontinued Drugs
2.1. General Overview
2.2. Discontinued Drugs in Phase I
2.2.1. PF-06282999
2.2.2. OPC-108459
2.2.3. ONO-4232
2.3. Discontinued Drugs in Phase II
2.3.1. GSK-2798745
2.3.2. MDCO-216
2.3.3. TRV027
2.3.4. Ubenimex
2.3.5. LIK-066
2.3.6. Sodium Nitrite
2.4. Discontinued Drugs in Phase III
2.4.1. TAK-536TCH
2.4.2. Losmapimod
2.4.3. Bococizumab
3. Expert Opinion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Cardiovascular Diseases. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/ (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- Zhao, H.P.; Jiang, H.M.; Xiang, B.R. Discontinued drugs in 2011: Cardiovascular drugs. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.P.; Jiang, H.M.; Xiang, B.R. Discontinued drugs in 2012: Cardiovascular drugs. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.P.; Xiang, B.R. Discontinued cardiovascular drugs in 2013 and 2014. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2015, 24, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.P.; Dai, Y.; Xiang, B.R. Discontinued cardiovascular drugs in 2015. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 1039–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lièvre, M.; Ménard, J.; Bruckert, E.; Cogneau, J.; Delahaye, F.; Giral, P.; Leitersdorf, E.; Luc, G.; Masana, L.; Moulin, P.; et al. Premature discontinuation of clinical trial for reasons not related to efficacy, safety, or feasibility. BMJ 2001, 322, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integrity: Essential Knowledge to Empower Your Drug Discovery and Development. Available online: https://clarivate.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/Crv_LS_Integrity_SellSheetShort_A4_FA.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2019).
- Dong, J.Q.; Varma, M.V.; Wolford, A.; Ryder, T.; Di, L.; Feng, B.; Terra, S.G.; Sagawa, K.; Kalgutkar, A.S. Pharmacokinetics and Disposition of the Thiouracil Derivative PF-06282999, an Orally Bioavailable, Irreversible Inactivator of Myeloperoxidase Enzyme, Across Animals and Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevic-Pasti, T.; Leskovac, A.; Vasic, V. Myeloperoxidase Inhibitors as Potential Drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 2015, 16, 168–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, R.B.; Buckbinder, L.; Bagley, S.W.; Carpino, P.A.; Conn, E.L.; Dowling, M.S.; Fernando, D.P.; Jiao, W.; Kung, D.W.; Orr, S.T.; et al. Discovery of 2-(6-(5-Chloro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2-thioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)acetamide (PF-06282999): A Highly Selective Mechanism-Based Myeloperoxidase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8513–8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.Q.; Gosset, J.R.; Fahmi, O.A.; Lin, Z.; Chabot, J.R.; Terra, S.G.; Le, V.; Chidsey, K.; Nouri, P.; Kim, A.; et al. Examination of the Human Cytochrome P4503A4 Induction Potential of PF-06282999, an Irreversible Myeloperoxidase Inactivator: Integration of Preclinical, In Silico, and Biomarker Methodologies in the Prediction of the Clinical Outcome. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscovitz, J.E.; Lin, Z.; Johnson, N.; Tu, M.; Goosen, T.C.; Weng, Y.; Kalgutkar, A.S. Induction of human cytochrome P450 3A4 by the irreversible myeloperoxidase inactivator PF-06282999 is mediated by the pregnane X receptor. Xenobiotica 2018, 48, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. A Study to Test the Safety, Amount and Effects of PF-06282999 in Healthy Overweight Adults and a Study to Test the Effects of PF-06282999 on the Amount of the Approved Drug, Midazolam, in Healthy Adults. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01707082?term=PF-06282999&rank=2&view=record (accessed on 10 April 2019).
- Roth Flach, R.J.; Su, C.; Bollinger, E.; Cortes, C.; Robertson, A.W.; Opsahl, A.C.; Coskran, T.M.; Maresca, K.P.; Keliher, E.J.; Yates, P.D.; et al. Myeloperoxidase inhibition in mice alters atherosclerotic lesion composition. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. A Trial to Determine the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy of OPC-108459 Administered as a Single Intravenous Dose to Patients With Paroxysmal or Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (AF). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02069119?term=OPC-108459&rank=1 (accessed on 10 April 2019).
- Kanaji, T.; Fuchibe, K.; Takahashi, M.; Shiroya, T. ONO-4232, an EP4-selective Agonist, Improves Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction and Ameliorates Acute and Chronic Heart Failure in Animal Models. Circulation 2012, 126, A15345. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, C.L.; Jamieson, V.; Nabata, T.; Sharpe, J.; Dozono, K.; Suto, F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Gussak, I. First Clinical Experience with ONO-4232: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Healthy Volunteer Study of a Novel Lusitropic Agent for Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ONO. Consolidated Financial Statements (Marc 2016). 11 May 2017. Available online: http://www.ono.co.jp/jpnw/ir/pdf/k_tanshin/2934r/03.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2018).
- Goyal, N.; Skrdla, P.; Schroyer, R.; Kumar, S.; Fernando, D.; Oughton, A.; Norton, N.; Sprecher, D.L.; Cheriyan, J. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of a Novel, First-in-Class TRPV4 Ion Channel inhibitor, GSK27987445, in Healthy and Heart Failure Subjects. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2019, 19, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. A Phase I Study to Assess the Pharmacokinetics of GSK2798745 Tablets. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02925546 (accessed on 21 April 2018).
- ClinicalTrials. A First Time in Human Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of GSK2798745 in Healthy Subjects and Stable Heart Failure Patients. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02925546 (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- ClinicalTrials. A Study to Evaluate the Effect of the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) Channel Blocker, GSK2798745, on Pulmonary Gas Transfer and Respiration in Patients With Congestive Heart Failure. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02497937 (accessed on 21 November 2017).
- GSK. 2018 Full Year Results. Available online: https://www.gsk.com/media/5293/fy-2018-results-slides.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Caparon, M.H.; Rust, K.J.; Hunter, A.K.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Thomas, K.E.; Herberg, J.T.; Shell, R.E.; Lanter, P.B.; Bishop, B.F.; Dufield, R.L.; et al. Integrated solution to purification challenges in the manufacture of a soluble recombinant protein in E. coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 105, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempen, H.J.; Gomaraschi, M.; Bellibas, S.E.; Plassmann, S.; Zerler, B.; Collins, H.L.; Adelman, S.J.; Calabresi, L.; Wijngaard, P.L. Effect of repeated apoA-IMilano/POPC infusion on lipids, (apo)lipoproteins, and serum cholesterol efflux capacity in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Lipid. Res. 2013, 54, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempen, H.J.; Asztalos, B.F.; Moerland, M.; Jeyarajah, E.; Otvos, J.; Kallend, D.G.; Bellibas, S.E.; Wijngaard, P.L. High-Density Lipoprotein Subfractions and Cholesterol Efflux Capacities After Infusion of MDCO-216 (Apolipoprotein A-IMilano/Palmitoyl-Oleoyl-Phosphatidylcholine) in Healthy Volunteers and Stable Coronary Artery Disease Patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallend, D.G.; Reijers, J.A.; Bellibas, S.E.; Bobillier, A.; Kempen, H.; Burggraaf, J.; Moerland, M.; Wijngaard, P.L. A single infusion of MDCO-216 (ApoA-1 Milano/POPC) increases ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux and pre-beta 1 HDL in healthy volunteers and patients with stable coronary artery disease. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovas. Pharmacother. 2016, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempen, H.J.; Gomaraschi, M.; Simonelli, S.; Calabresi, L.; Moerland, M.; Otvos, J.; Jeyarajah, E.; Kallend, D.; Wijngaard, P.L.J. Persistent changes in lipoprotein lipids after a single infusion of ascending doses of MDCO-216 (apoA-IMilano/POPC) in healthy volunteers and stable coronary artery disease patients. Atherosclerosis 2016, 255, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. MDCO-216 Infusions Leading to Changes in Atherosclerosis: A Novel Therapy in Development to Improve Cardiovascular Outcomes—Proof of Concept Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS), Lipids, and Other Surrogate Biomarkers Trial (PILOT). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02678923?term=MDCO-216&rank=1 (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- The Medicines Company. The Medicines Company Discontinues Development of MDCO-216, its Investigational Cholesterol Efflux Promoter. Available online: http://www.themedicinescompany.com/investors/news/medicines-company-discontinues-development-mdco-216-its-investigational-cholesterol (accessed on 3 April 2018).
- Singh, A.; Laribi, S.; Teerlink, J.R.; Mebazaa, A. Agents with vasodilator properties in acute heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violin, J.D.; DeWire, S.M.; Yamashita, D.; Rominger, D.H.; Nguyen, L.; Schiller, K.; Whalen, E.J.; Gowen, M.; Lark, M.W. Selectively engaging beta-arrestins at the angiotensin II type 1 receptor reduces blood pressure and increases cardiac performance. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerrigter, G.; Lark, M.W.; Whalen, E.J.; Soergel, D.G.; Violin, J.D.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Cardiorenal actions of TRV120027, a novel ss-arrestin-biased ligand at the angiotensin II type I receptor, in healthy and heart failure canines: A novel therapeutic strategy for acute heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerrigter, G.; Soergel, D.G.; Violin, J.D.; Lark, M.W.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. TRV120027, a novel beta-arrestin biased ligand at the angiotensin II type I receptor, unloads the heart and maintains renal function when added to furosemide in experimental heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soergel, D.G.; Subach, R.A.; Cowan, C.L.; Violin, J.D.; Lark, M.W. First clinical experience with TRV027: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 53, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soergel, D.G.; Subach, R.A.; James, I.E.; Conrad, L.C.; Maxine, G.; Michael, L. TRV027, a β-arrestin biased ligand at the angiotensin 2 type 1 receptor, produces rapid, reversible changes in hemodynamics in patients with stable systolic heart failure. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1221–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. A Study to Explore the Efficacy of TRV027 in Patients Hospitalized for Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (BLAST-AHF). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01966601?term=NCT01966601&rank=1 (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Trevena. TRV027. Available online: http://www.trevena.com/TRV027.php (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Felker, G.M.; Butler, J.; Collins, S.P.; Cotter, G.; Davison, B.A.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Filippatos, G.; Levy, P.D.; Metra, M.; Ponikowski, P.; et al. Heart failure therapeutics on the basis of a biased ligand of the angiotensin-2 type 1 receptor. Rationale and design of the BLAST-AHF study (Biased Ligand of the Angiotensin Receptor Study in Acute Heart Failure). JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.S.; Butler, J.; Collins, S.P.; Cotter, G.; Davison, B.A.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Filippatos, G.; Levy, P.D.; Metra, M.; Ponikowski, P.; et al. Biased ligand of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in patients with acute heart failure: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIB, dose ranging trial (BLAST-AHF). Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Heron, D.; Davenport, I.; Huckaba, T.; Graves, R.; Mandal, T.; Muniruzzaman, S.; Wang, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.S. Protective effects of bestatin in the retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 149, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzoljić, E.; Varagić, V.M. Effects of bestatin and phosphoramidon on the hypertensive response to physostigmine in the rat. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1987, 1, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Jiang, X.; Tamosiuniene, R.; Sung, Y.K.; Qian, J.; Dhillon, G.; Gera, L.; Farkas, L.; Rabinovitch, M.; Zamanian, R.T.; et al. Blocking macrophage leukotriene b4 prevents endothelial injury and reverses pulmonary hypertension. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 200ra117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. A Study of Ubenimex in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (WHO Group 1) (LIBERTY). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT02664558?cond=Ubenimex&rank=2 (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Qian, J.; Tian, W.; Jiang, X.; Tamosiuniene, R.; Sung, Y.K.; Shuffle, E.M.; Tu, A.B.; Valenzuela, A.; Jiang, S.; Zamanian, R.T.; et al. Leukotriene B4 Activates Pulmonary Artery Adventitial Fibroblasts in Pulmonary Hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 66, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. Open-Label Extension Study of Ubenimex in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (WHO Group 1) (LIBERTY2). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02736149?cond=Ubenimex&rank=3 (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- ClinicalTrials. A Dose Finding Study to Assess the Effect of LIK066 Compared to Placebo or Empagliflozin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03152552?cond=LIK-066&draw=2&rank=10 (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Shiva, S.; Ifedigbo, E.; Mathier, M.A.; Mollen, K.P.; Rao, J.; Bauer, P.M.; Choi, J.J.; Curtis, E.; Choi, A.M.; et al. Nitrite potently inhibits hypoxic and inflammatory pulmonary arterial hypertension and smooth muscle proliferation via xanthine oxidoreductase-dependent nitric oxide generation. Circulation 2010, 121, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, C.J.; Dejam, A.; Blood, A.B.; Shields, H.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B.; Machado, R.F.; Tarekegn, S.; Mulla, N.; Hopper, A.O.; Schechter, A.N.; et al. Inhaled nebulized nitrite is a hypoxia-sensitive NO-dependent selective pulmonary vasodilator. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rix, P.J.; Vick, A.; Attkins, N.J.; Barker, G.E.; Bott, A.W.; Alcorn, H., Jr.; Gladwin, M.T.; Shiva, S.; Bradley, S.; Hussaini, A.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and tolerability of nebulized sodium nitrite (AIR001) following repeat-dose inhalation in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 54, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- ClinicalTrials. Dose-Finding, Safety, Pharmacodynamic Effect Study of Sodium Nitrite Inhalation Solution in Normal, Healthy Volunteers (AIR001-CS02). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00814645?cond=sodium+nitrite&draw=5&rank=15 (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- ClinicalTrials. Safety, Tolerability, and PK Parameters of Sodium Nitrite Inhalation Solution in Healthy Subjects. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01409122?cond=sodium+nitrite&draw=4&rank=8&view=record (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- ClinicalTrials. Pilot Study of Sodium Nitrite in Resuscitated Cardiac Arrest Patients. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01178359 (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Dezfulian, C.; Olsufka, M.; Fly, D.; Scruggs, S.; Do, R.; Maynard, C.; Nichol, G.; Kim, F. Hemodynamic effects of IV sodium nitrite in hospitalized comatose survivors of out of hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2018, 122, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION. Form-10Q, 30 Sep 2014; p. 20. Available online: http://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1160308/000156459014004815/mstx-10q_20140930.htm (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- ClinicalTrials. A Phase 2 Study to Determine the Safety and Efficacy of AIR001 in Subjects with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01725256?cond=sodium+nitrite&draw=3&rank=24 (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- ClinicalTrials. Long-Term Study of AIR001 in Subjects with WHO Group 1 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Who Completed AIR001-CS05. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01725269?cond=sodium+nitrite&draw=6&rank=23 (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- ClinicalTrials. Inhaled Sodium Nitrite on Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT02262078?cond=Sodium+Nitrite+on+Heart+Failure&rank=1 (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Borlaug, B.A.; Melenovsky, V.; Koepp, K.E. Inhaled Sodium Nitrite Improves Rest and Exercise Hemodynamics in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Anstrom, K.J.; Lewis, G.D.; Shah, S.J.; Levine, J.A.; Koepp, G.A.; Givertz, M.M.; Felker, G.M.; LeWinter, M.M.; Mann, D.L.; et al. Effect of Inorganic Nitrite vs Placebo on Exercise Capacity Among Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: The INDIE-HFpEF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. Inorganic Nitrite Delivery to Improve Exercise Capacity in HFpEF (INDIE-HFpEF). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02742129 (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Savara Pharmaceuticals. Press Release. 11 March 2019. Available online: https://savarapharma.com/investors/press-releases/release/?id=2337400 (accessed on 19 April 2019).
- Takeda. Takeda FY2016 Q4 Results Data Book. Available online: https://www.takeda.com/siteassets/system/investors/report/quarterlyannouncements/fy2016/fy-2016-q4-announcements-released-on-may-10-2017/qr2016_q4_d1_en.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- ClinicalTrials. A Phase I Food Effect Study of TAK-536TCH Final Formulation Tablet. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02348658?term=TAK-536TCH&rank=1 (accessed on 19 November 2018).
- Rakugi, H.; Shimizu, K.; Sano, Y.; Nishiyama, Y.; Kinugawa, Y.; Terashio, S. Effects of triple combination therapy with azilsartan/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide on office/home blood pressure: A randomized-controlled trial in Japanese essential hypertensive patients. Blood Press. Monit. 2018, 23, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Combined Administration of TAK-536CCB and Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients with Grade I or II Essential Hypertension. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02072330?term=Takeda&cond=Essential+Hypertension&rank=5 (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Rakugi, H.; Shimizu, K.; Nishiyama, Y.; Sano, Y.; Umeda, Y. A phase III, open-label, multicenter study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of long-term triple combination therapy with azilsartan, amlodipine, and hydrochlorothiazide in patients with essential hypertension. Blood Press. 2018, 27, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. A Phase III Long-term Study of TAK-536TCH in Participants with Essential Hypertension. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02277691?term=Takeda&cond=Essential+Hypertension&rank=1 (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Kragholm, K.; Newby, L.K.; Melloni, C. Emerging treatment options to improve cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome: Focus on losmapimod. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar]
- Willette, R.N.; Eybye, M.E.; Olzinski, A.R.; Behm, D.J.; Aiyar, N.; Maniscalco, K.; Bentley, R.G.; Coatney, R.W.; Zhao, S.; Westfall, T.D.; et al. Differential effects of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors in a model of cardiovascular disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Niu, W.; He, Z.; Ding, L.; Jia, J. Suppression of mitochondrial fission in experimental cerebral ischemia: The potential neuroprotective target of p38 MAPK inhibition. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ino, H.; Takahashi, N.; Terao, T.; Igarashi, H.; Sarai, N. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of losmapimod in healthy Japanese volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2015, 4, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. Phase I Study of GW856553 (Losmapimod). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01648192?term=Losmapimod&rank=6 (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- Barbour, A.M.; Sarov-Blat, L.; Cai, G.; Fossler, M.J.; Sprecher, D.L.; Graggaber, J.; McGeoch, A.T.; Maison, J.; Cheriyan, J. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of losmapimod following a single intravenous or oral dose in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. PK Study of IV Formulation of GW856553. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01039961?term=Losmapimod&rank=8 (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- Yang, S.; Beerahee, M. Losmapimod concentration-QT relationship in healthy volunteers: Meta-analysis of data from six clinical trials. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newby, L.K.; Marber, M.S.; Melloni, C.; Sarov-Blat, L.; Aberle, L.H.; Aylward, P.E.; Cai, G.; de Winter, R.J.; Hamm, C.W.; Heitner, J.F.; et al. Losmapimod, a novel p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, in non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: A randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloni, C.; Sprecher, D.L.; Sarov-Blat, L.; Patel, M.R.; Heitner, J.F.; Hamm, C.W.; Aylward, P.; Tanguay, J.F.; DeWinter, R.J.; Marber, M.S.; et al. The study of LoSmapimod treatment on inflammation and InfarCtSizE (SOLSTICE): Design and rationale. Am. Heart J. 2012, 164, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronow, W.S.; Kaple, R.K. Losmapimod does not reduce cardiovascular events in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 2328–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Glaser, R.; Cavender, M.A.; Aylward, P.E.; Bonaca, M.P.; Budaj, A.; Davies, R.Y.; Dellborg, M.; Fox, K.A.; Gutierrez, J.A.; et al. Effect of Losmapimod on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Glaser, R.; Aylward, P.E.; Cavender, M.A.; Crisp, A.; Fox, K.A.; Laws, I.; Lopez-Sendon, J.L.; Steg, P.G.; Theroux, P.; et al. Rationale and design of the LosmApimod To Inhibit p38 MAP kinase as a TherapeUtic target and moDify outcomes after an acute coronary syndromE trial. Am. Heart J. 2015, 169, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. A Phase 3 Clinical Outcomes Study to Compare the Incidence of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Subjects Presenting With Acute Coronary Syndrome Treated with Losmapimod Compared to Placebo (LATITUDE-TIMI 60) (LATITUDE). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02145468?term=GlaxoSmithKline++Losmapimod&cond=Myocardial+Infarction&rank=1 (accessed on 23 April 2018).
- Udata, C.; Garzone, P.D.; Gumbiner, B.; Joh, T.; Liang, H.; Liao, K.H.; Williams, J.H.; Meng, X. A Mechanism-Based Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Model for Bococizumab, a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Against Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type9, and Its Application in Early Clinical Development. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 57, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjiphilippou, S.; Ray, K.K. PCSK9 inhibition and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention: Does reality match the hype? Heart 2017, 103, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. A Study to Access the Safety And Tolerability of RN316 (PF-04950615) When Administered to Healthy Adult Subjects. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00991159?term=NCT00991159&rank=1 (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- ClinicalTrials. A Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of PF-04950615 in Subjects with Hypercholesterolemia. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01435382?term=NCT01435382&rank=1 (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- ClinicalTrials. Safety and Tolerability of Multiple Doses of PF-04950615 (RN316) in Subjects with Hypercholesterolemia. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01243151?term=NCT01243151&rank=1 (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- Wan, H.; Gumbiner, B.; Joh, T.; Riel, T.; Udata, C.; Forgues, P.; Garzone, P.D. Effects of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Inhibition with Bococizumab on Lipoprotein Particles in Hypercholesterolemic Subjects. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 2243–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, C.M.; Neutel, J.; Cropp, A.; Duggan, W.; Wang, E.Q.; Plowchalk, D.; Sweeney, K.; Kaila, N.; Vincent, J.; Bays, H. Results of bococizumab, a monoclonal antibody against proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, from a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study in statin-treated subjects with hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro-Riggers, J.; Liang, H.; DeVay, R.M.; Bai, L.F.; Sutton, J.E.; Chen, W.; Geng, T.; Lindquist, K.; Casas, M.G.; Boustany, L.M.; et al. Increasing serum half-life and extending cholesterol lowering in vivo by engineering antibody with pH-sensitive binding to PCS-K9. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11090–11097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer. Pfizer Discontinues Global Development of Bococizumab, Its Investigational PCSK9 Inhibitor. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release detail/pfizer_discontinues_global_development_of_bococizumab_its_investigational_pcsk9_inhibitor (accessed on 24 November 2018).
- ClinicalTrials. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of Bococizumab Alone and When Combined with Recombinant Human Hyaluronidase. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02667223?term=Pfizer+Bococizumab&cond=Hypercholesterolaemia&rank=2 (accessed on 24 November 2018).
- Ridker, P.M.; Tardif, J.C.; Amarenco, P.; Duggan, W.; Glynn, R.J.; Jukema, J.W.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Kim, A.M.; Koenig, W.; Nissen, S.; et al. Lipid-Reduction Variability and Antidrug-Antibody Formation with Bococizumab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Rose, L.M.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Santos, R.D.; Wei, C.; Revkin, J.; Yunis, C.; Tardif, J.C.; Shear, C.L. Cardiovascular event reduction with PCSK9 inhibition among 1578 patients with familial hypercholesterolemia: Results from the SPIRE randomized trials of bococizumab. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. A 52 Week Study to Assess the Use of Bococizumab (PF-04950615; RN316) in Subjects with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (SPIRE-FH). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01968980?term=Pfizer+Bococizumab&rank=8 (accessed on 24 November 2018).
- Ridker, P.M.; Revkin, J.; Amarenco, P.; Brunell, R.; Curto, M.; Civeira, F.; Flather, M.; Glynn, R.J.; Gregoire, J.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Cardiovascular Efficacy and Safety of Bococizumab in High-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. The Evaluation of Bococizumab (PF-04950615; RN316) in Reducing the Occurrence of Major Cardiovascular Events in High Risk Subjects. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01975389?term=NCT01975389&rank=1 (accessed on 29 June 2019).
- FDA. FDA Approves Praluent to Treat Certain Patients with High Cholesterol. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm455883.htm (accessed on 23 April 2018).
- Amgen. FDA Approves Amgen’s Repatha (evolocumab) To Prevent Heart Attack and Stroke. Available online: http://www.amgen.com/media/news-releases/2017/12/fda-approves-amgens-repatha-evolocumab-to-prevent-heart-attack-and-stroke/ (accessed on 24 January 2019).
- Kola, I.; Landis, J. Can the pharmaceutical industry reduce attrition rates? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIO, Biomedtracker, Amplion. Clinical Development Success Rates 2006–2015. 25 May 2016. Available online: https://www.bio.org/sites/default/files/Clinical%20Development%20Success%20Rates%202006-2015%20-%20BIO,%20Biomedtracker,%20Amplion%202016.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2019).
| Drug Name(s), Structure | Organization | Mechanism of Action | Therapeutic Group | Development Phase Reached | Reason for Discontinuation | Discontinued Indications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PF-06282999 | Pfizer (Originator) | Myeloperoxidase Inhibitors | Treatment of Disorders of the Coronary Arteries and Atherosclerosis | I | Unspecified | Acute coronary syndrome |
| OPC-108459 * | Otsuka Pharmaceutical (Originator) | Unknown | Antiarrhythmic Drugs | I | Miscellaneous | Atrial Fibrillation, atrial |
| ONO-4232 * | Ono (Originator) | Signal Transduction Modulators; Prostanoid EP4 Receptor Agonists | Heart Failure Therapy | I | Strategic | Heart failure |
| GSK-2798745; 2798745 * | GlaxoSmithKline (Originator) | TRPV4 Antagonists | Edema, Treatment of; Heart Failure Therapy | II | Unspecified | Heart failure, congestive |
| MDCO-216 *; AIM; ApoA-1 Milano; ESP-24217; ETC-216; Recombinant ApoA-I Milano/phospholipid complex | The Medicines Co.; Esperion Therapeutics, Pfizer (Originator) | HDL-Cholesterol Increasing Agents | Restenosis Treatment of; Atherosclerosis Therapy; Treatment of Disorders of the Coronary Arteries and Atherosclerosis; Lipoprotein Disorders, Treatment of; Cardiovascular Diseases (Not Specified) | II | Efficacy | Atherosclerosis |
TRV027; TRV120027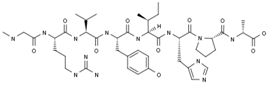 | Trevena (Originator) | Signal Transduction Modulators; Angiotensin AT1 Receptor Ligands | Heart Failure Therapy | II | Efficacy | Heart failure, acute decompensated |
Ubenimex; bestatin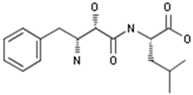 | Nippon Kayaku | Immunostimulant; Peptidase inhibitor; Leucotriene B4 antagonist; Hit substrate-selective leucotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitor | Lung Cancer Therapy; Leukemia Therapy; Immunostimulants; Cardiovascular Diseases (Not Specified); Pulmonary Hypertension, Treatment of | II | Efficacy | Hypertension, pulmonary arterial |
LIK-066 | Novartis | SGLT-1 Inhibitors; SGLT-2 Inhibitors | Treatment of Female Sexual Dysfunction; Antiobesity Drugs; Metabolic Disorders (Not Specified); Heart Failure Therapy; Type 2 Diabetes, Agents for | II | Strategic (slow enrollment) | Heart failure |
| Sodium nitrite; AIR-001; S-2252; TV-1001; TV-1001-SR 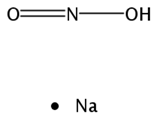 | TheraVasc | Nitric oxide stimulant | Septic Shock, Hemorrhagic Stroke, Non-Opioid Analgesics, Neuropathic Pain, Poisoning, Acute Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular Diseases, Ischemia, Peripheral Arterial Disease; Pulmonary Hypertension, Treatment of; Ulcers of the Extremities, Scleroderma Agents for; Cardioprotective Agents; Heart Failure Therapy; Antibacterial Drugs | II | Efficacy | Heart failure |
| TAK-536TCH #; Azilsartan/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide; TAK-536/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide | Takeda (Originator) | Signal Transduction Modulators; Insulin Sensitizers; Calcium Channel Blockers; Angiotensin AT2 Receptor Antagonists; Angiotensin AT1 Receptor Antagonists | Hypertension, Treatment of | III | Strategic | Hypertension, essential |
| Bococizumab *; L1L3; PF-04950615; RN-316 | Pfizer (Originator) | Anti-PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin-Type 9) | Atherosclerosis Therapy; Disorders of the Coronary Arteries and Atherosclerosis; Lipoprotein Disorders, Treatment of | III | Efficacy | Hyperlipidemia, Hypercholesterolemia, familial |
Losmapimod; 856553; GSK-AHAB; GW-856553; GW-856553X; SB-856553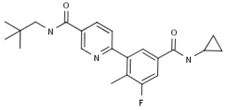 | GlaxoSmithKline (Originator) | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14(MAPK14; MAPK p38 alpha) Inhibitors; Signal Transduction Modulators | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD), Treatment of; Treatment of Renal Diseases; Neuropathic Pain, Treatment of; Atherosclerosis Therapy; Treatment of Disorders of the Coronary Arteries and Atherosclerosis; Antidepressants; Rheumatoid Arthritis; Lipoprotein Disorders, Treatment of; Antipsoriatics | III | Efficacy | Acute coronary syndrome |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Jiang, S.; Ni, B.; Cui, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, H. Discontinued Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease from 2016 to 2018. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184513
Li T, Jiang S, Ni B, Cui Q, Liu Q, Zhao H. Discontinued Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease from 2016 to 2018. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(18):4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tingting, Sida Jiang, Bingwei Ni, Qiuji Cui, Qinan Liu, and Hongping Zhao. 2019. "Discontinued Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease from 2016 to 2018" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 18: 4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184513
APA StyleLi, T., Jiang, S., Ni, B., Cui, Q., Liu, Q., & Zhao, H. (2019). Discontinued Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease from 2016 to 2018. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(18), 4513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184513




