Deciphering the Evolutionary History of Arowana Fishes (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes, Osteoglossidae): Insight from Comparative Cytogenomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
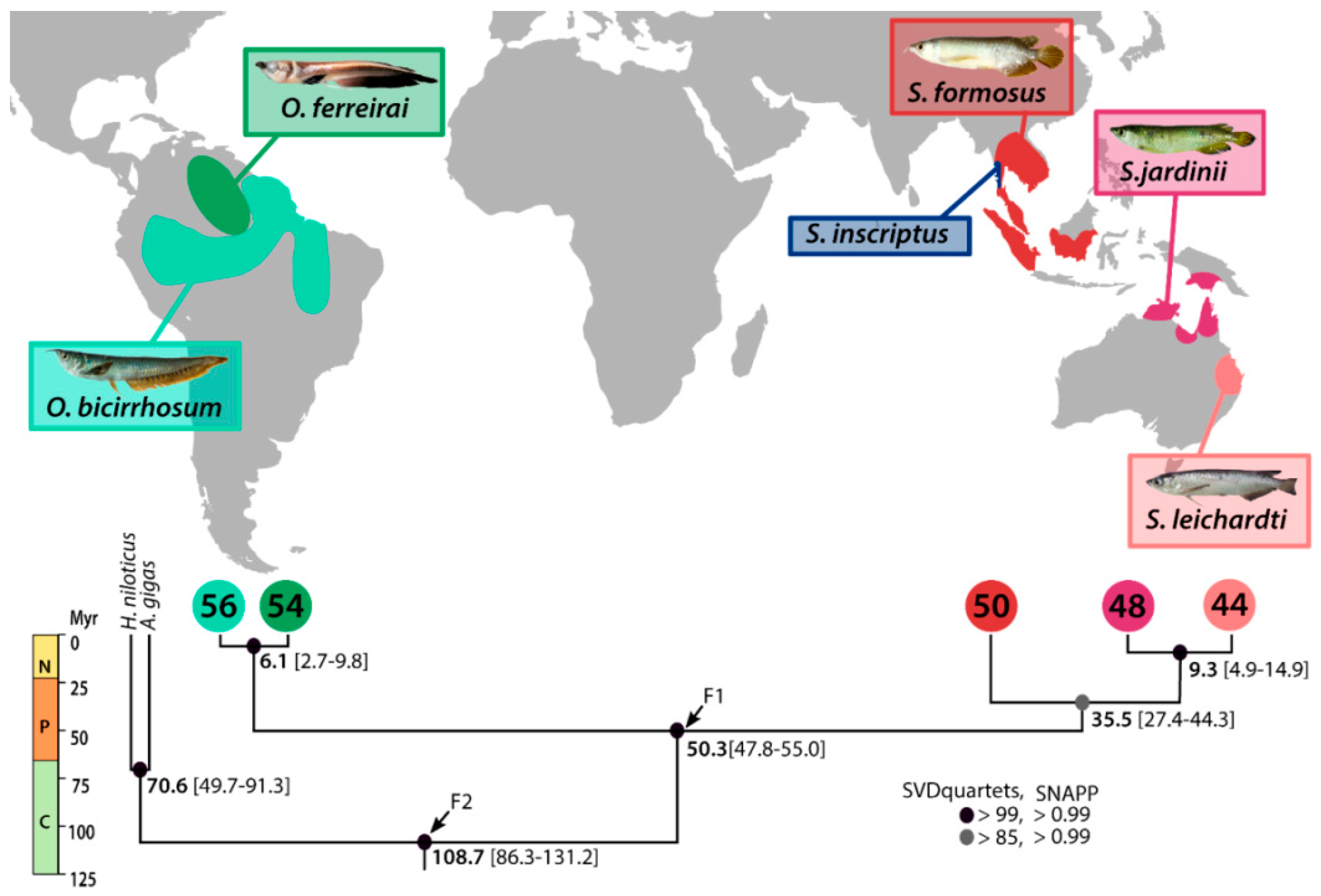
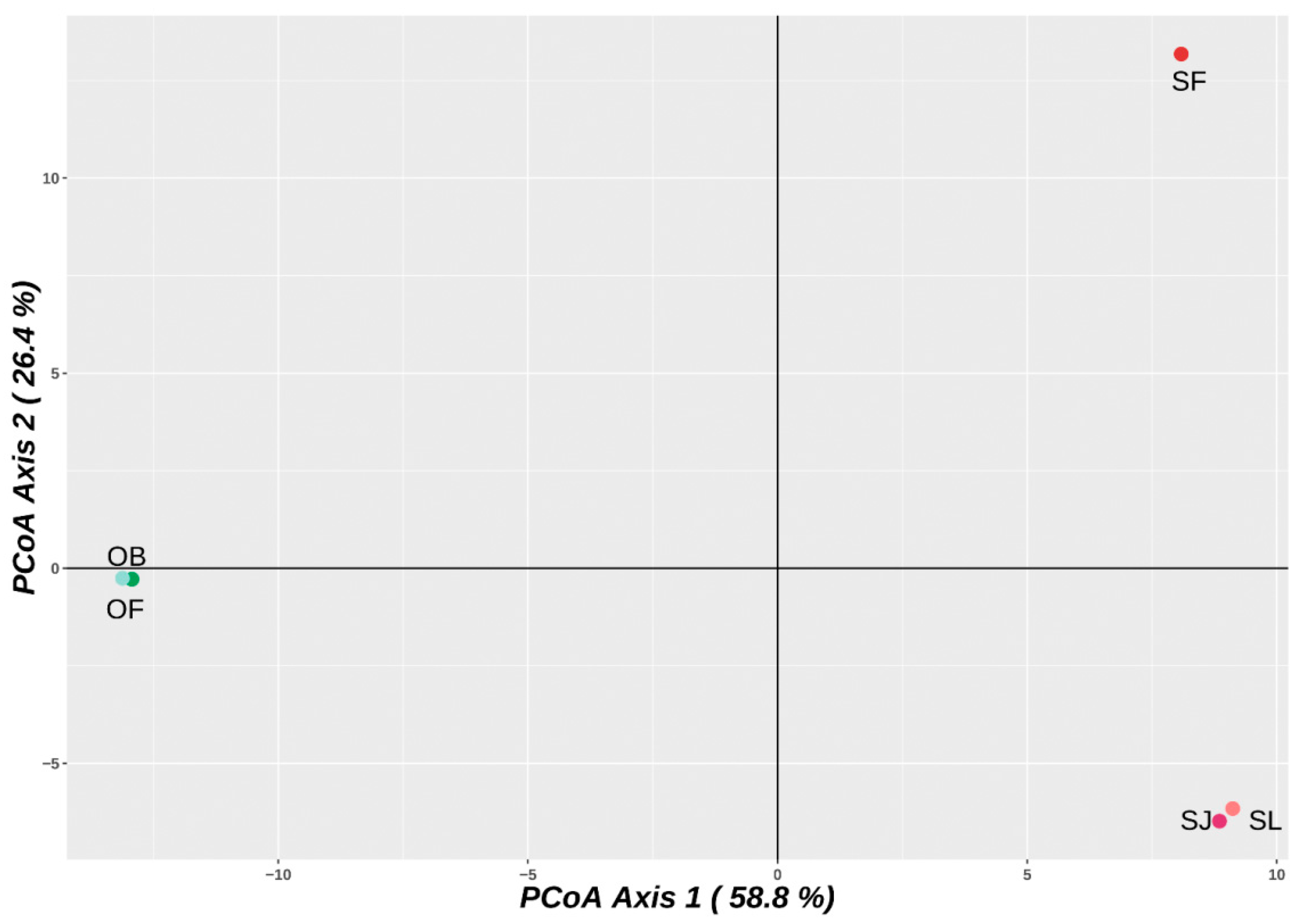
2.1. DArTseq Genotyping and Genetic Relationships
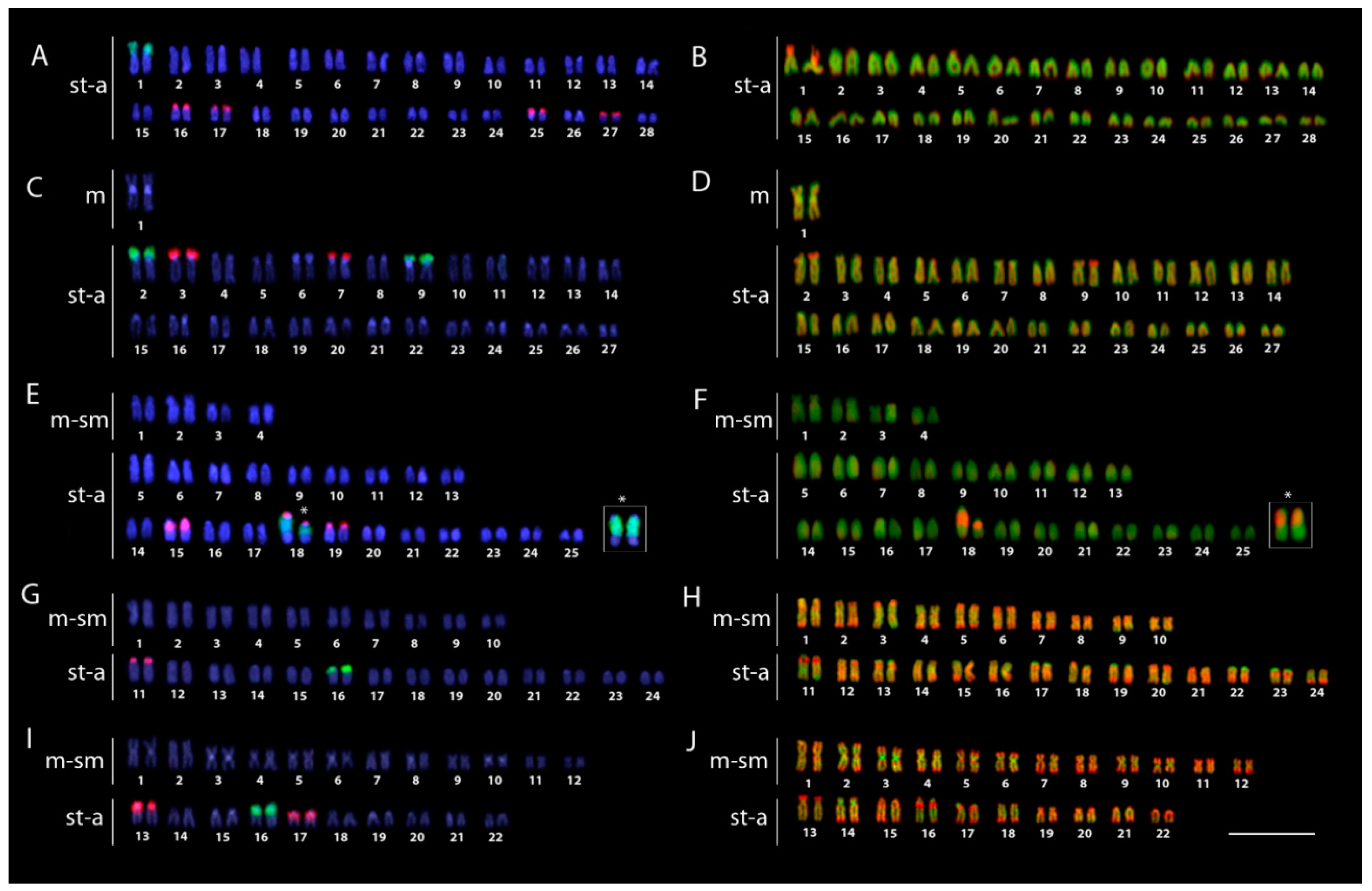
2.2. Karyotypes and C-Banding
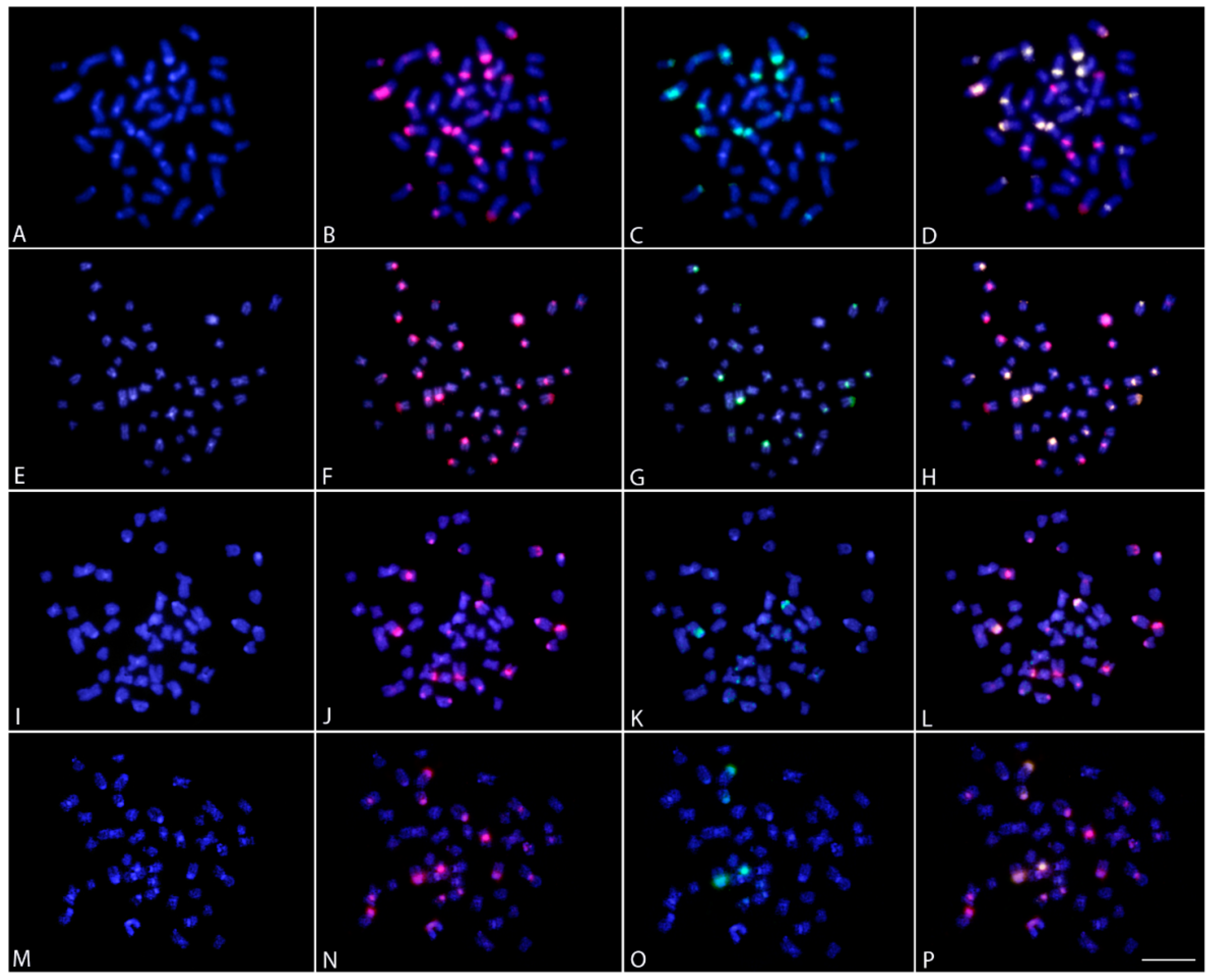
2.3. FISH Mapping and CMA3 Banding
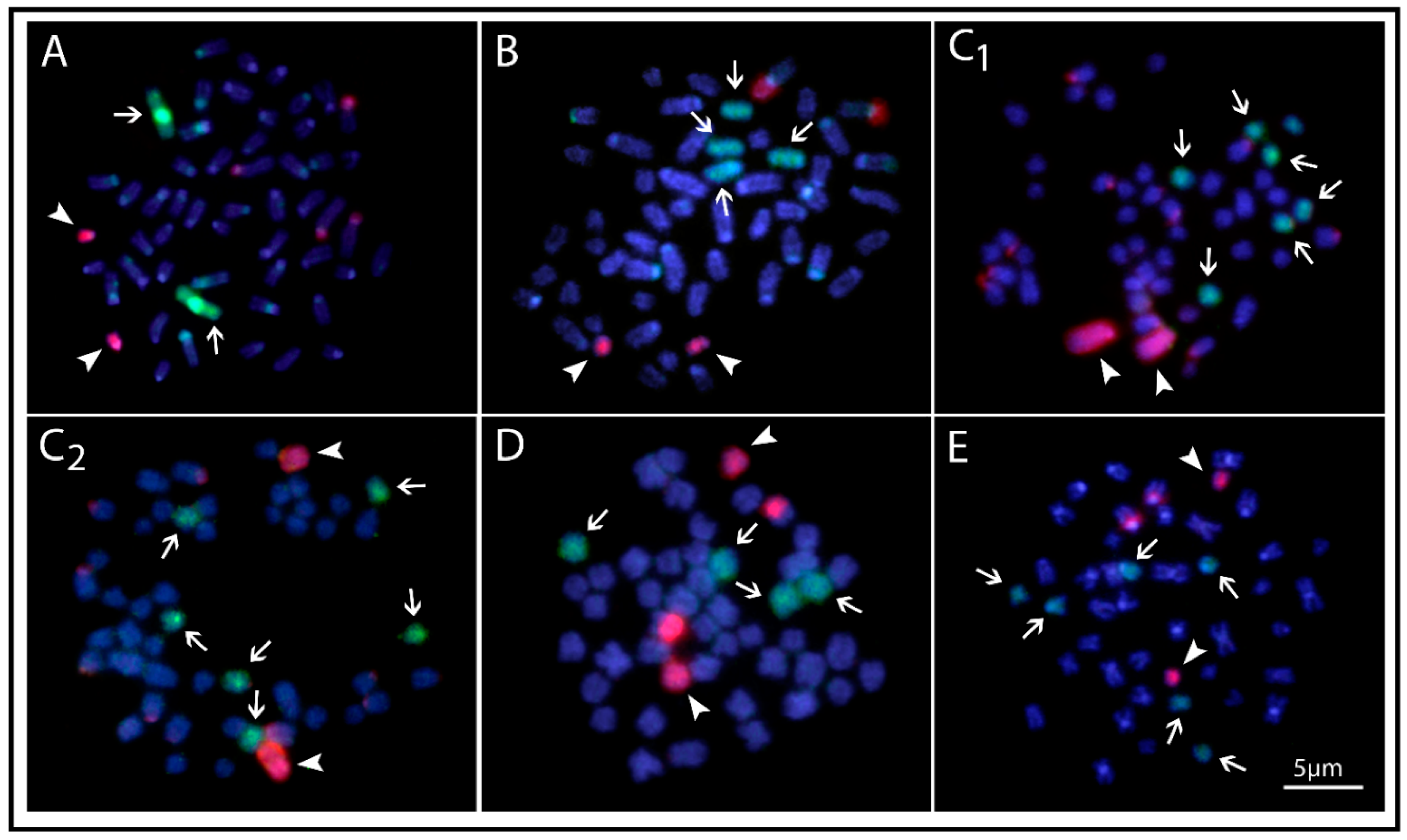
2.4. Comparative Genomic Hybridization
2.5. Whole Chromosome Painting of the OFE-1 Probe
3. Discussion
3.1. Cytogenetic Differentiation of Osteoglossum and Scleropages
3.2. Sex Chromosomes in Scleropages formosus?
3.3. Comparison of Cytogenetics of Arowana Species and Other Osteoglossiform Representatives
3.4. Biogeography of Osteoglossinae
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Individuals
4.2. DArTseq Genotyping and Genetic Relationships
4.3. Species Tree and Divergence Times
4.4. Chromosome Preparations, C- and CMA3 Banding
4.5. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) for Repetitive DNA Mapping
4.6. Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH)
4.7. Microdissection and the Preparation of Chromosome Painting Probes
4.8. Image Analysis and Processing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patterson, C.; Rosen, D.E. Review of ichthyodectiform and other Mesozoic teleost fishes, and the theory and practice of classifying fossils. Bull. AMNH 1977, 158, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Arratia, G. Basal Teleosts and teleostean phylogeny. Palaeo Ichthyol. 1997, 7, 5–168. [Google Scholar]
- Near, T.J.; Eytan, R.I.; Dornburg, A.; Kuhn, K.L.; Moore, J.A.; Davis, M.P.; Wainwright, P.C.; Friedman, M.; Smith, W.L. Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13698–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancur-R, R.; Wiley, E.O.; Arratia, G.; Acero, A.; Bailly, N.; Miya, M.; Lecointre, G.; Orti, G. Phylogenetic classification of bony fishes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 111834233X. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, E.J.; Lavoué, S. A review of the systematic biology of fossil and living bony-tongue fishes, Osteoglossomorpha (Actinopterygii: Teleostei). Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2018, 16, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.; van der Laan, R. Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species, References, California Academy of Sciences; California Academy of Sciences: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cavin, L.; Lionel. Freshwater Fishes: 250 Million Years of Evolutionary History; Press-Elsevier, I., Ed.; ISTE Press-Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780081011416. [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco, A.; Friedman, M. Vicariance and dispersal in southern hemisphere freshwater fish clades: a palaeontological perspective. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 662–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottelat, M. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, Version 2014. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/ (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Roberts, T.R. Scleropages inscriptus, a new fish species from the Tananthayi or Tenasserim River basin, Malay Peninsula of Myanmar (Osteoglossidae: Osteoglossiformes). Aqua. Int. J. Ichthyol. 2012, 18, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, P.K.L.; Tan, H.H. Freshwater fishes of Southeast Asia: potential for the aquarium fish trade and conservation issues. Aquarium Sci. Conserv. 1997, 1, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouyaud, L.; Sudarto;Teugels, G.G. The different colour varieties of the asian arowana Scleropages formosus (Osteoglossidae) are distinct species: Morphologic and genetic evidences. Cybium 2003, 27, 287–305. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M. The fishes of Danau Sentarum National Park and the Kapuas Lakes area, Kalimantan Barat, Indonesia. Raffles Bull Zool Suppl 2005, 13, 139–173. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, J.G.; Kumazawa, Y.; Miya, M.; Nishida, M. The historical biogeography of the freshwater knifefishes using mitogenomic approaches: A Mesozoic origin of the Asian notopterids (Actinopterygii: Osteoglossomorpha). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 51, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoué, S. Testing a time hypothesis in the biogeography of the arowana genus Scleropages (Osteoglossidae). J. Biogeogr. 2015, 42, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoué, S. Was Gondwanan breakup the cause of the intercontinental distribution of Osteoglossiformes? A time-calibrated phylogenetic test combining molecular, morphological, and paleontological evidence. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 99, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, E.J. Comparative osteology and phylogenetic systematics of fossil and living bony-tongue fishes (Actinopterygii, Teleostei, Osteoglossomorpha). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2003, 137, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, L.L.; Maddison, W.P. Statistical phylogeography. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2623–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R.; Beaumont, M.A. Statistical inferences in phylogeography. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S.V. Is a new and general theory of molecular systematics emerging? Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 2009, 63, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrick, R.C.; Bonatelli, I.A.S.; Hyseni, C.; Morales, A.; Pelletier, T.A.; Perez, M.F.; Rice, E.; Satler, J.D.; Symula, R.E.; Thomé, M.T.C.; et al. The evolution of phylogeographic data sets. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R. High-Throughput Genomic Data in Systematics and Phylogenetics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2013, 44, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, J.E.; Hird, S.M.; Zellmer, A.J.; Carstens, B.C.; Brumfield, R.T. Applications of next-generation sequencing to phylogeography and phylogenetics. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, J.; Haines, M.L.; Hale, J.; Chapple, S.; Ritchie, E.G. Concordance in phylogeography and ecological niche modelling identify dispersal corridors for reptiles in arid Australia. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, P.; Kjeldsen, S.R.; Meekan, M.G.; Mccormick, M.I.; Finn, J.K.; Huffard, C.L.; Zenger, K.R. Genome-wide comparisons reveal a clinal species pattern within a holobenthic octopod—the Australian Southern blue-ringed octopus, Hapalochlaena maculosa (Cephalopoda: Octopodidae). Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 2253–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges, A.; Gruber, B.; Pauly, G.B.; White, D.; Adams, M.; Young, M.J.; Kilian, A.; Zhang, X.; Shaffer, H.B.; Unmack, P.J. Genomewide SNP markers breathe new life into phylogeography and species delimitation for the problematic short-necked turtles (Chelidae: Emydura) of eastern Australia. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 5195–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unmack, P.J.; Young, M.J.; Gruber, B.; White, D.; Kilian, A.; Zhang, X.; Georges, A. Phylogeography and species delimitation of Cherax destructor (Decapoda: Parastacidae) using genome-wide SNPs. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unmack, P.J.; Adams, M.; Bylemans, J.; Hardy, C.M.; Hammer, M.P.; Georges, A. Perspectives on the clonal persistence of presumed ‘ghost’genomes in unisexual or allopolyploid taxa arising via hybridization. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.J. Infraorbital bones and their bearing on the phylogeny and geography of osteoglossomorph fishes. Am. Mus. Nov. 1969, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cracraft, J. Continental drift and vertebrate distribution. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1974, 5, 215–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonde, N. Osteoglossomorphs of the marine Lower Eocene of Denmark–with remarks on other Eocene taxa and their importance for palaeobiogeography. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2008, 295, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverne, L. On the presence of the osteoglossid genus Scleropages in the Paleocene of Niger, Africa (Teleostei, Osteoglossomorpha). Bull. R. des Sci. Nat. Belgique. Sci. la terre 2009, 79, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Amemiya, C.T.; Alfoldi, J.; Lee, A.P.; Fan, S.; Philippe, H.; MacCallum, I.; Braasch, I.; Manousaki, T.; Schneider, I.; Rohner, N.; et al. The African coelacanth genome provides insights into tetrapod evolution. Nature 2013, 496, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ráb, P.; Yano, C.F.; Lavoué, S.; Jegede, O.I.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Ezaz, T.; Majtánová, Z.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Cioffi, M.B. Karyotype and Mapping of Repetitive DNAs in the African Butterfly Fish Pantodon buchholzi, the Sole Species of the Family Pantodontidae. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2016, 149, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonová, R.; Majtánová, Z.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Mořkovský, L.; Kořínková, T.; Cavin, L.; Pokorná, M.J.; Doležálková, M.; Flajšhans, M.; Normandeau, E.; et al. Genome Compositional Organization in Gars Shows More Similarities to Mammals than to Other Ray-Finned Fish. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2017, 328, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majtánová, Z.; Symonová, R.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.; Sallan, L.; Ráb, P. “Holostei versus Halecostomi” Problem: Insight from Cytogenetics of Ancient Nonteleost Actinopterygian Fish, Bowfin Amia calva. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2017, 328, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alda, F.; Tagliacollo, V.A.; Bernt, M.J.; Waltz, B.T.; Ludt, W.B.; Faircloth, B.C.; Alfaro, M.E.; Albert, J.S.; Chakrabarty, P. Resolving Deep Nodes in an Ancient Radiation of Neotropical Fishes in the Presence of Conflicting Signals from Incomplete Lineage Sorting. Syst. Biol. 2018, 68, 573–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozouf-Costaz, C.; Coutanceau, J.-P.; Bonillo, C.; Belkadi, L.; Fermon, Y.; Agnèse, J.-F.; Guidi-Rontani, C.; Paugy, D.; Agnese, J.F.; Guidi-Rontani, C.; et al. First insights into karyotype evolution within the family Mormyridae. Cybium 2015, 39, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, C.; Hu, Y.; Ravi, V.; Kuznetsova, I.S.; Shen, X.; Mu, X.; Sun, Y.; You, X.; Li, J.; Li, X.; et al. The Asian arowana (Scleropages formosus) genome provides new insights into the evolution of an early lineage of teleosts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, T.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Ráb, P.; Yano, C.F.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Ezaz, T.; Jegede, O.O.I.; Liehr, T.; Olaleye, V.F.; de Bello Cioffi, M. First chromosomal analysis in Gymnarchus niloticus (Gymnarchidae: Osteoglossiformes): insights into the karyotype evolution of this ancient fish order. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 125, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barby, F.; Rab, P.; Lavoue, S.; Ezaz, T.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Kilian, A.; Maruyama, S.R.; Oliveira, E.A.; Artoni, R.F.; Santos, M.H.; et al. From chromosomes to genome: insights into the evolutionary relationships and biogeography of Old World knifefishes (Notopteridae; Osteoglossiformes). Genes 2018, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barby, F.F.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Yano, C.F.; Hatanaka, T.; Ráb, P.; Sember, A.; Ezaz, T.; Artoni, R.F.; Liehr, T.; et al. Emerging patterns of genome organization in Notopteridae species (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes) as revealed by Zoo-FISH and Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushido, T. Karyotype of three species of fishes in the order Osteoglossiformes. Chromosom. Inform. Serv. 1975, 18, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Magtoon, W.; Donsakul, T. Morphology and cytogenetics of Arowana fishes in subfamily Osteoglossinae from Asia, Australia and South America. In Proceedings of the 30th Congress on Science and Technology of Thailand, Bangkok, Thailand, 26–30 January 2004; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.Y.; Kwan, H.Y.; Thevasagayam, N.M.; Prakki, S.R.S.; Kuznetsova, I.S.; Ngoh, S.Y.; Lim, Z.; Feng, F.; Chang, A.; Orbán, L. The first transcriptome and genetic linkage map for Asian arowana. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, J.; Urushido, T. Karyotypes and DNA content in the Osteoglossiformes. Sci Rep Res Inst Evol Biol 2000, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A.; Taki, Y.; Urushido, T. Karyotypes of two species of arowana, Osteoglossum bicirrhosum and O. ferreirai. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1982, 29, 220–222. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, K.Y.; Kovarik, A.; Matyasek, R.; Chase, M.W.; Clarkson, J.J.; Grandbastien, M.A.; Leitch, A.R. Sequence of events leading to near-complete genome turnover in allopolyploid Nicotiana within five million years. New Phytol. 2007, 175, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majka, J.; Majka, M.; Kwiatek, M.; Wiśniewska, H. Similarities and differences in the nuclear genome organization within Pooideae species revealed by comparative genomic in situ hybridization (GISH). J. Appl. Genet. 2017, 58, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sember, A.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Ráb, P.; Yano, C.F.; Hatanaka, T.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Cioffi, M.d.B. Sex Chromosome Evolution and Genomic Divergence in the Fish Hoplias malabaricus (Characiformes, Erythrinidae). Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bian, C.; Hu, Y.; Mu, X.; Shen, X.; Ravi, V.; Kuznetsova, I.S.; Sun, Y.; You, X.; Qiu, Y.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the Asian arowana, Scleropages formosus. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callan, H.G.; Lloyd, L. Lampbrush chromosomes of crested newts Triturus cristatus (Laurenti). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 1960, 243, 135–219. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, S.H.; Macgregor, H.C.; Pellatt, P.S.; Horner, H.A. Chromosome 1 in crested and marbled newts (Triturus). Chromosoma 1984, 89, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetti, P.M.; Foresti, F.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Moreira Filho, O. Heteromorphic sex chromosomes in three species of the genus Leporinus (Pisces, Anostomidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 1981, 29, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestriner, C.A.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Galetti, P.M. Chromosome banding and synaptonemal complexes in Leporinus lacustris (Pisces, Anostomidae): analysis of a sex system. Chromosom. Res. 1995, 3, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, K.M.; Phillips, R.B. Polymorphism of the nucleolus organizer region (NOR) on the putative sex chromosomes of Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) is not sex related. Chromosom. Res 1997, 5, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, W.F.; Schmid, M.; Galetti, P.M. Heterochromatin and sex chromosomes in the Neotropical fish genus Leporinus (Characiformes, Anostomidae). Cytobios 1998, 94, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth, D.; Charlesworth, B.; Marais, G. Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity 2005, 95, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, M.B.; Moreira-Filho, O.; Almeida-Toledo, L.F.; Bertollo, L.A.C. The contrasting role of heterochromatin in the differentiation of sex chromosomes: an overview from Neotropical fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 80, 2125–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornung, E. Twenty years of physical mapping of major ribosomal RNA genes across the teleosts: a review of research. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sember, A.; Bohlen, J.; Šlechtová, V.; Altmanová, M.; Symonová, R.; Ráb, P. Karyotype differentiation in 19 species of river loach fishes (Nemacheilidae, Teleostei): Extensive variability associated with rDNA and heterochromatin distribution and its phylogenetic and ecological interpretation. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonová, R.; Howell, W. Vertebrate Genome Evolution in the Light of Fish Cytogenomics and rDNAomics. Genes 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, W.F.; Galetti, P.M. Robertsonian rearrangements in the reef fish Chromis (Perciformes, Pomacentridae) involving chromosomes bearing 5S rRNA genes. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2002, 25, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getlekha, N.; Molina, W.F.; de Bello Cioffi, M.; Yano, C.F.; Maneechot, N.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Supiwong, W.; Tanomtong, A. Repetitive DNAs highlight the role of chromosomal fusions in the karyotype evolution of Dascyllus species (Pomacentridae, Perciformes). Genetica 2016, 144, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Ende, C.; White, L.T.; van Welzen, P.C. The existence and break-up of the Antarctic land bridge as indicated by both amphi-Pacific distributions and tectonics. Gondwana Res. 2017, 44, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.R.; Krause, D.W. Late Cretaceous bioconnections between Indo-Madagascar and Antarctica: refutation of the Gunnerus Ridge causeway hypothesis. J. Biogeogr. 2011, 38, 1855–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.V.H.; Murray, A.M. Osteoglossomorpha: phylogeny, biogeography, and fossil record and the significance of key African and Chinese fossil taxa. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2008, 295, 185–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, Y.; Nishida, M. Molecular phylogeny of osteoglossoids: A new model for Gondwanian origin and plate tectonic transportation of the Asian arowana. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, C.; Karlstrom, K.E.; Shuster, D.L.; Kelley, S.; Fox, M. 6 Ma age of carving Westernmost Grand Canyon: Reconciling geologic data with combined AFT,(U–Th)/He, and 4He/3He thermochronologic data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 474, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.S.; Val, P.; Hoorn, C. The changing course of the Amazon River in the Neogene: center stage for Neotropical diversification. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2018, 16, e180033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kilian, A.; Wenzl, P.; Huttner, E.; Carling, J.; Xia, L.; Blois, H.; Caig, V.; Heller-Uszynska, K.; Jaccoud, D.; Hopper, C. Diversity arrays technology: a generic genome profiling technology on open platforms. In Data Production and Analysis in Population Genomics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 67–89. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, B.; Unmack, P.J.; Berry, O.F.; Georges, A. dartr: An r package to facilitate analysis of SNP data generated from reduced representation genome sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, T. RADseq Data Exploration, Manipulation and Visualization Using R. 2016. Available online: https://thierrygosselin.github.io/radiator/ (accessed on 10 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Chifman, J.; Kubatko, L. Quartet Inference from SNP Data Under the Coalescent Model. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony and Other Methods; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A Software Platform for Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, M.; Sánchez-Villagra, M.R.; Salzburger, W.; Matschiner, M. Bayesian Divergence-Time Estimation with Genome-Wide Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Data of Sea Catfishes (Ariidae) Supports Miocene Closure of the Panamanian Isthmus. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Wilson, M.V.H. First complete fossil Scleropages (Osteoglossomorpha). Vertebr. Palasiat. 2017, 55, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertollo, L.A.C.; Cioffi, M.B.; Moreira-Filho, O. Direct chromosome preparation from Freshwater Teleost Fishes. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques (Chondrichthyans and Teleosts); Ozouf-Costaz, C., Pisano, E., Foresti, F., Almeida Toledo, L.F., Eds.; CRC Press: Enfield, CT, USA, 2015; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M. Chromosome banding in Amphibia. IV. Differentiation of GC-and AT-rich chromosome regions in Anura. Chromosoma 1980, 77, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, A.T. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 1972, 75, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendás, A.M.; Móran, P.; Freije, J.P.; Garcia-Vásquez, E. Chromosomal location and nucleotide sequence of two tandem repeats of the Atlantic salmon 5S rDNA. Cytogenet Cell Genet 1994, 67, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, M.B.; Martins, C.; Centofante, L.; Jacobina, U.; Bertollo, L.A.C. Chromosomal Variability among Allopatric Populations of Erythrinidae Fish Hoplias malabaricus: Mapping of Three Classes of Repetitive DNAs. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2009, 125, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, C.F.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Cioffi, M.B. Fish-FISH: molecular cytogenetics in fish species. In Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)- Application Guide; Liehr, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 429–444. [Google Scholar]
- Zwick, M.S.; Hanson, R.E.; Mcknight, T.D.; Islam-Faridi, M.H.; Stelly, D.M.; Wing, R.A.; Price, H.J. A rapid procedure for the isolation of C 0 t-1 DNA from plants. Genome 1997, 40, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonová, R.; Majtánová, Z.; Sember, A.; Staaks, G.B.O.; Bohlen, J.; Freyhof, J. Genome differentiation in a species pair of coregonine fishes: an extremely rapid speciation driven by stress - activated retrotransposons mediating extensive ribosomal DNA multiplications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonová, R.; Flajšhans, M.; Sember, A.; Havelka, M.; Gela, D.; Kořínková, T.; Rodina, M.; Rábová, M.; Ráb, P. Molecular cytogenetics in artificial hybrid and highly polyploid sturgeons: an evolutionary story narrated by repetitive sequences. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.C.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Yano, C.F.; Oliveira, C.; Decru, E.; Jegede, O.I.; Hatanaka, T.; Liehr, T.; Al-Rikabi, A.B.H.; et al. First Chromosomal Analysis in Hepsetidae (Actinopterygii, Characiformes): Insights into Relationship between African and Neotropical Fish Groups. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, N.L.; Al-Rikabi, A.B.H.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Ezaz, T.; Yano, C.F.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Hatanaka, T.; de Bello Cioffi, M. Early Stages of XY Sex Chromosomes Differentiation in the Fish Hoplias malabaricus (Characiformes, Erythrinidae) Revealed by DNA Repeats Accumulation. Curr. Genom. 2018, 19, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moraes, R.L.R.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Marinho, M.M.F.; Yano, C.F.; Hatanaka, T.; Barby, F.F.; Troy, W.P.; Cioffi, M.d.B. Evolutionary Relationships and Cytotaxonomy Considerations in the Genus Pyrrhulina (Characiformes, Lebiasinidae). Zebrafish 2017, 14, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, E.A.; Sember, A.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; Yano, C.F.; Ezaz, T.; Moreira-Filho, O.; Hatanaka, T.; Trifonov, V.; Liehr, T.; Al-Rikabi, A.B.H.; et al. Tracking the evolutionary pathway of sex chromosomes among fishes: characterizing the unique XX/XY1Y2 system in Hoplias malabaricus (Teleostei, Characiformes). Chromosoma 2018, 127, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonová, R.; Sember, A.; Majtánová, Z.; Ráb, P. Characterization of fish genomes by GISH and CGH. In Fish Cytogenetic Techniques. Ray-Fin Fishes and Chondrichthyans; CCR Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Trifonov, V.; Ng, B.L.; Kosyakova, N.; Carter, N.P. Generation of paint probes by flow-sorted and microdissected chromosomes. In Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)—Application Guide; Liehr, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Levan, A.; Fredga, K.; Sandberg, A.A. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 1964, 52, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Sampling Site | N |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoglossum bicirrhosum | Confusão Lake, Araguaia River. | (12♀ 11♂) |
| Osteoglossum bicirrhosum | Catalão Lake, Solimões River | (12♀ 11♂) |
| Osteoglossum ferreirai | Negro River (Amazon River Basin) | (15♀ 19♂) |
| Scleropages formosus (Super Red variety) | Origin unknown, Aquarium trade | (03♀ 02♂) |
| Scleropages jardinii | Corroboree Billabong, Mary River | (05♀ 03♂) |
| Scleropages leichardti | Fitzroy River via aquarium trade | (03♀ 04♂) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Bello Cioffi, M.; Ráb, P.; Ezaz, T.; Antonio Carlos Bertollo, L.; Lavoué, S.; Aguiar de Oliveira, E.; Sember, A.; Franco Molina, W.; Henrique Santos de Souza, F.; Majtánová, Z.; et al. Deciphering the Evolutionary History of Arowana Fishes (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes, Osteoglossidae): Insight from Comparative Cytogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174296
de Bello Cioffi M, Ráb P, Ezaz T, Antonio Carlos Bertollo L, Lavoué S, Aguiar de Oliveira E, Sember A, Franco Molina W, Henrique Santos de Souza F, Majtánová Z, et al. Deciphering the Evolutionary History of Arowana Fishes (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes, Osteoglossidae): Insight from Comparative Cytogenomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174296
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Bello Cioffi, Marcelo, Petr Ráb, Tariq Ezaz, Luiz Antonio Carlos Bertollo, Sebastien Lavoué, Ezequiel Aguiar de Oliveira, Alexandr Sember, Wagner Franco Molina, Fernando Henrique Santos de Souza, Zuzana Majtánová, and et al. 2019. "Deciphering the Evolutionary History of Arowana Fishes (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes, Osteoglossidae): Insight from Comparative Cytogenomics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174296
APA Stylede Bello Cioffi, M., Ráb, P., Ezaz, T., Antonio Carlos Bertollo, L., Lavoué, S., Aguiar de Oliveira, E., Sember, A., Franco Molina, W., Henrique Santos de Souza, F., Majtánová, Z., Liehr, T., Basheer Hamid Al-Rikabi, A., Fernanda Yano, C., Viana, P., Feldberg, E., Unmack, P., Hatanaka, T., Tanomtong, A., & Fernandez Perez, M. (2019). Deciphering the Evolutionary History of Arowana Fishes (Teleostei, Osteoglossiformes, Osteoglossidae): Insight from Comparative Cytogenomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174296







