Therapeutic Effect of Ecdysterone Combine Paeonol Oral Cavity Direct Administered on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Rats
Abstract
Significance Statement
1. Introduction
2. Results
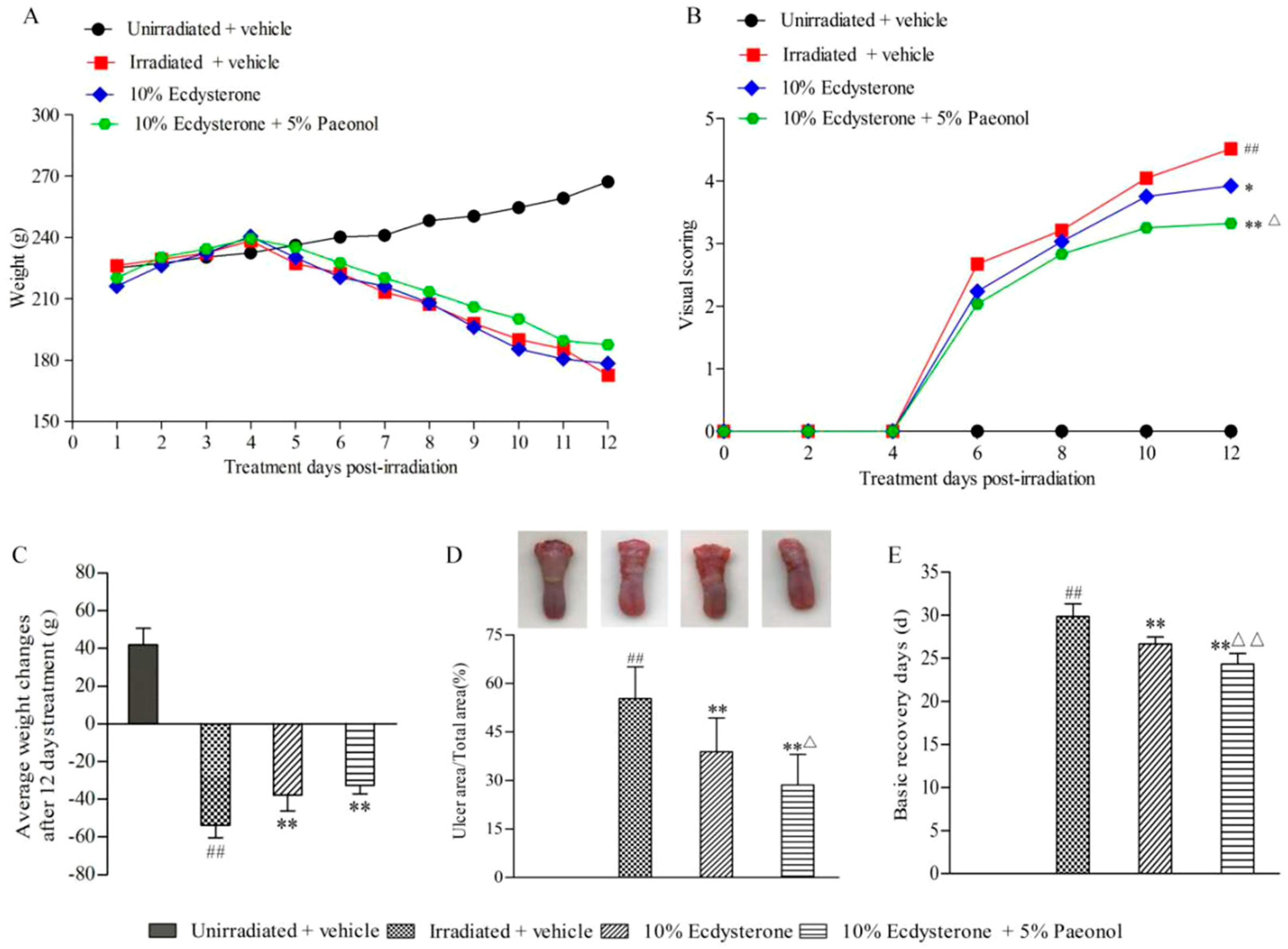
2.1. Ecdysterone-Paeonol Alleviates the Development of Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis, and the Treatment Effect is Better than Ecdysterone Treatment Alone
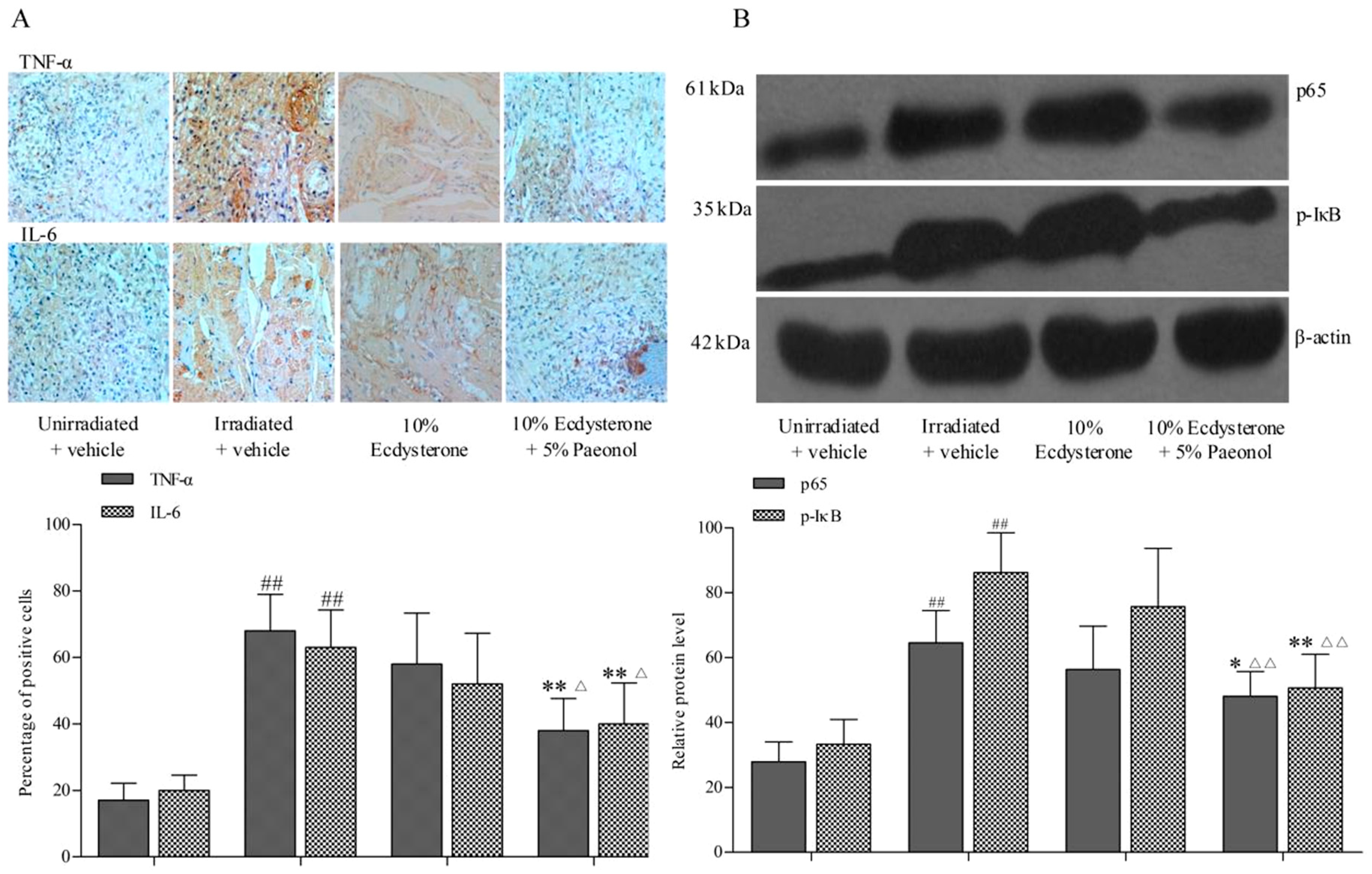
2.2. Ecdysterone-Paeonol Alleviates Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion by Inhibiting the NF-κB Pathway
2.3. Drug Targeting and Network Construction
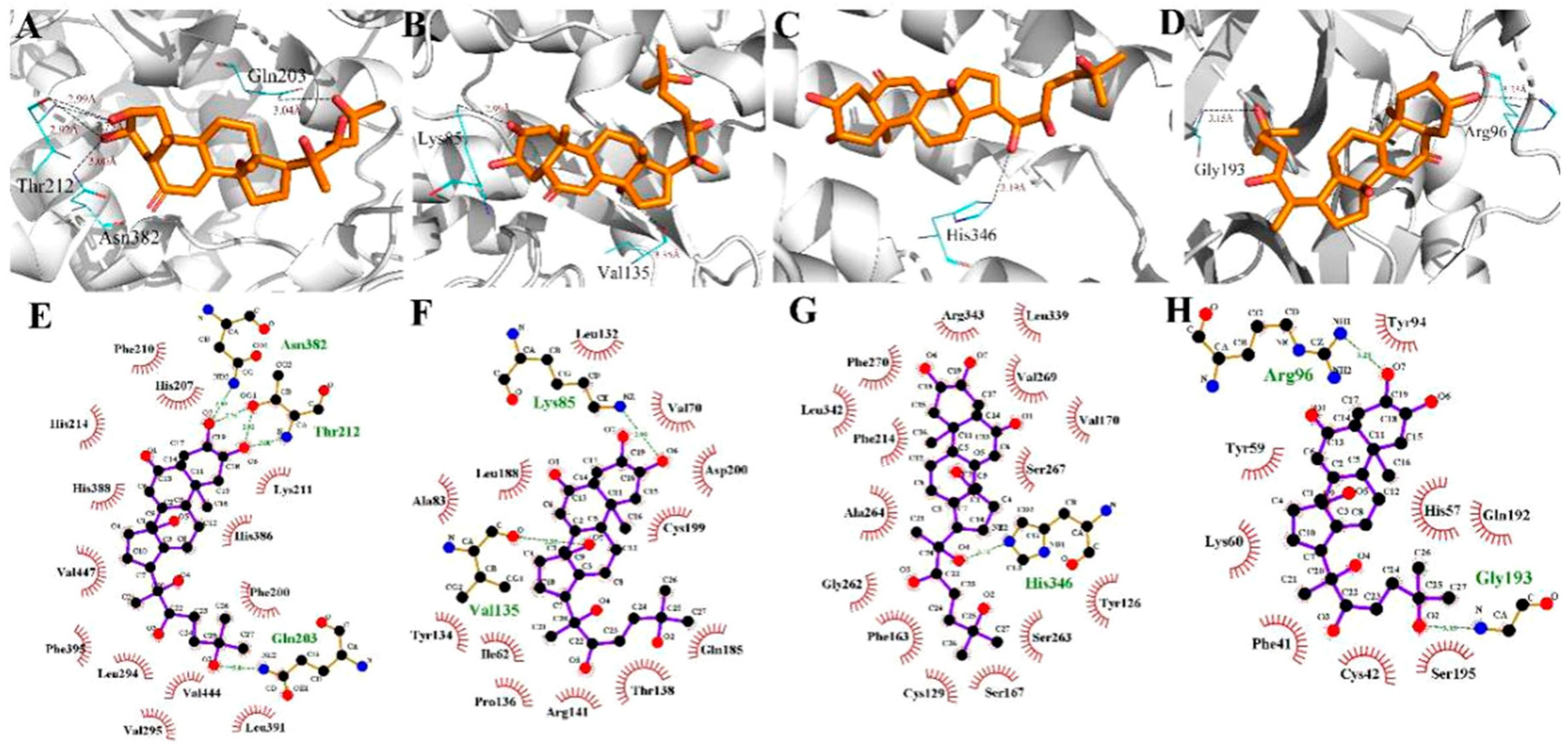
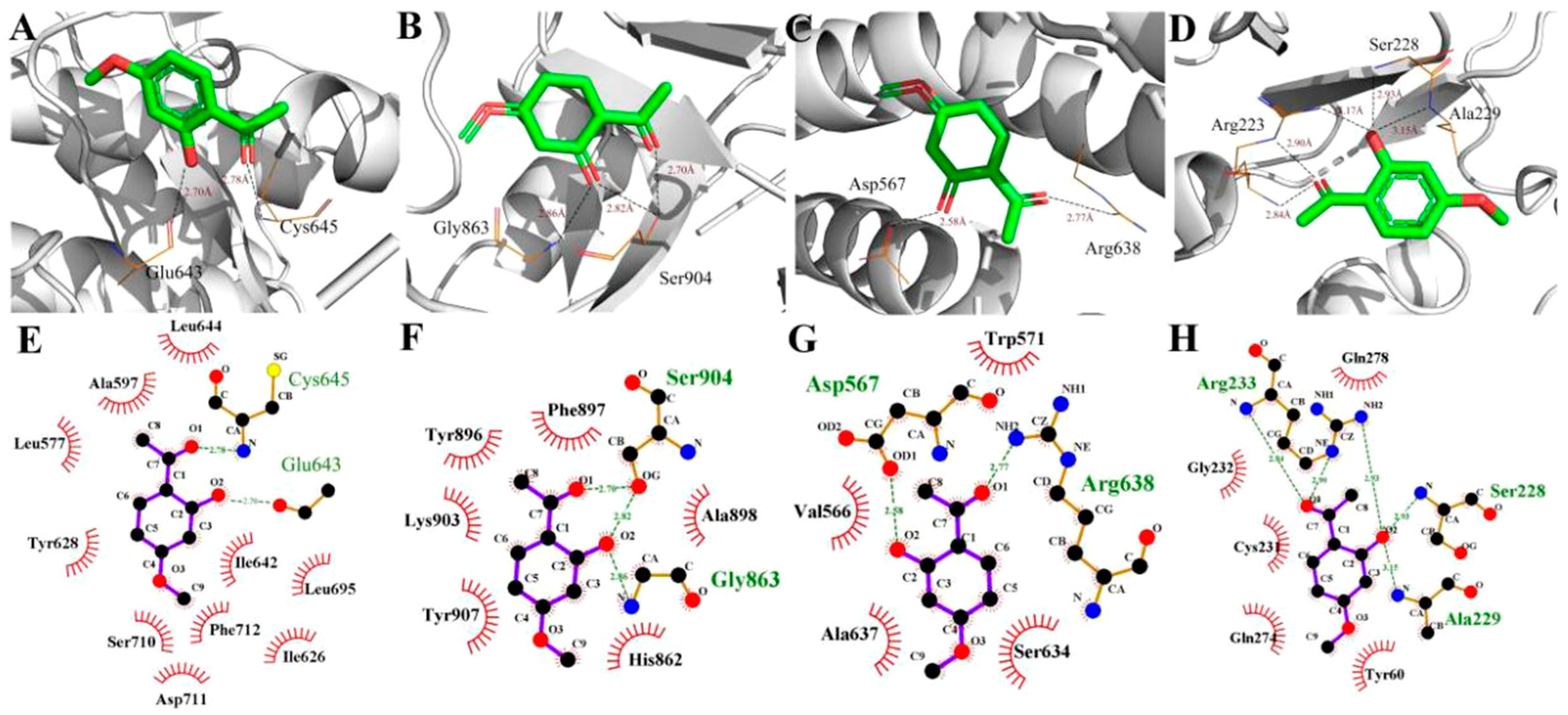
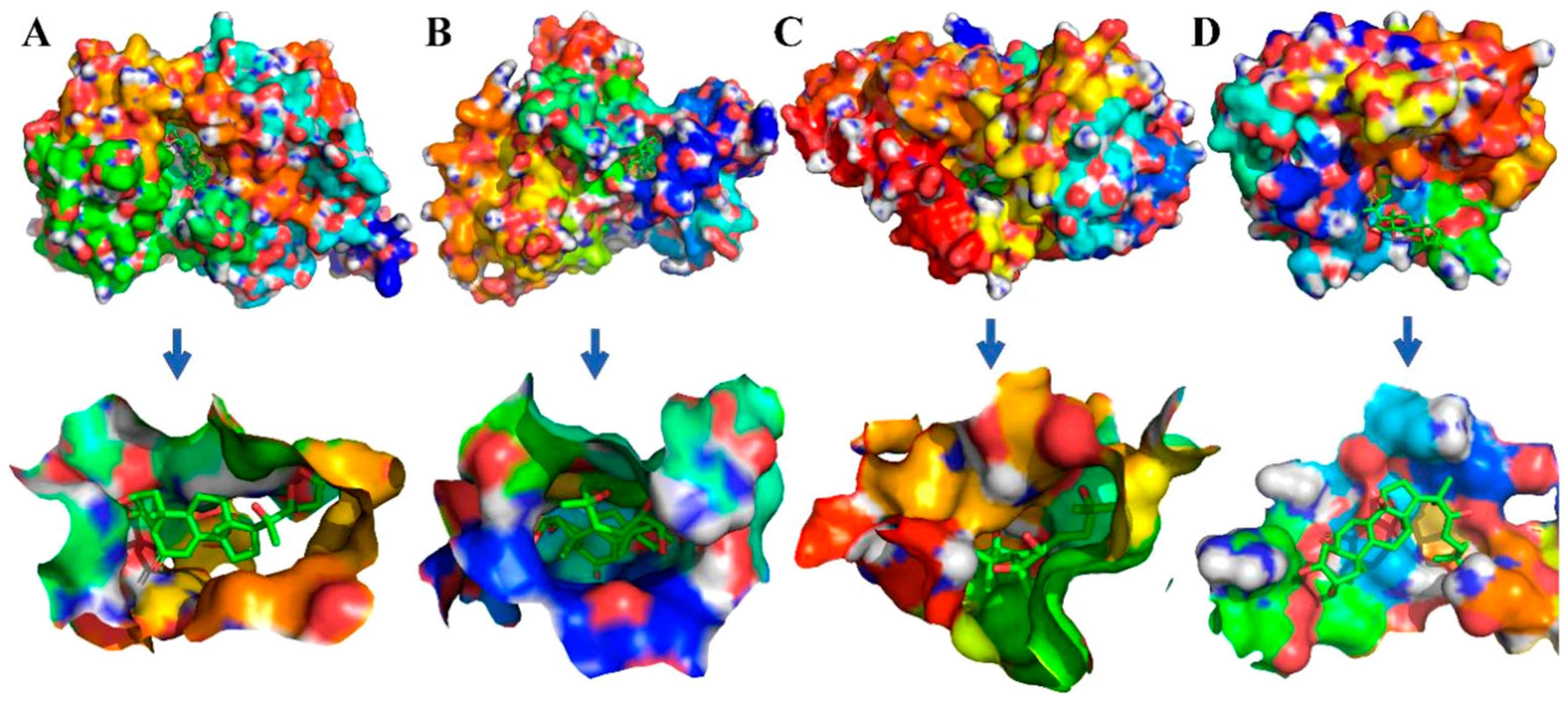
2.4. Molecular Docking Simulations
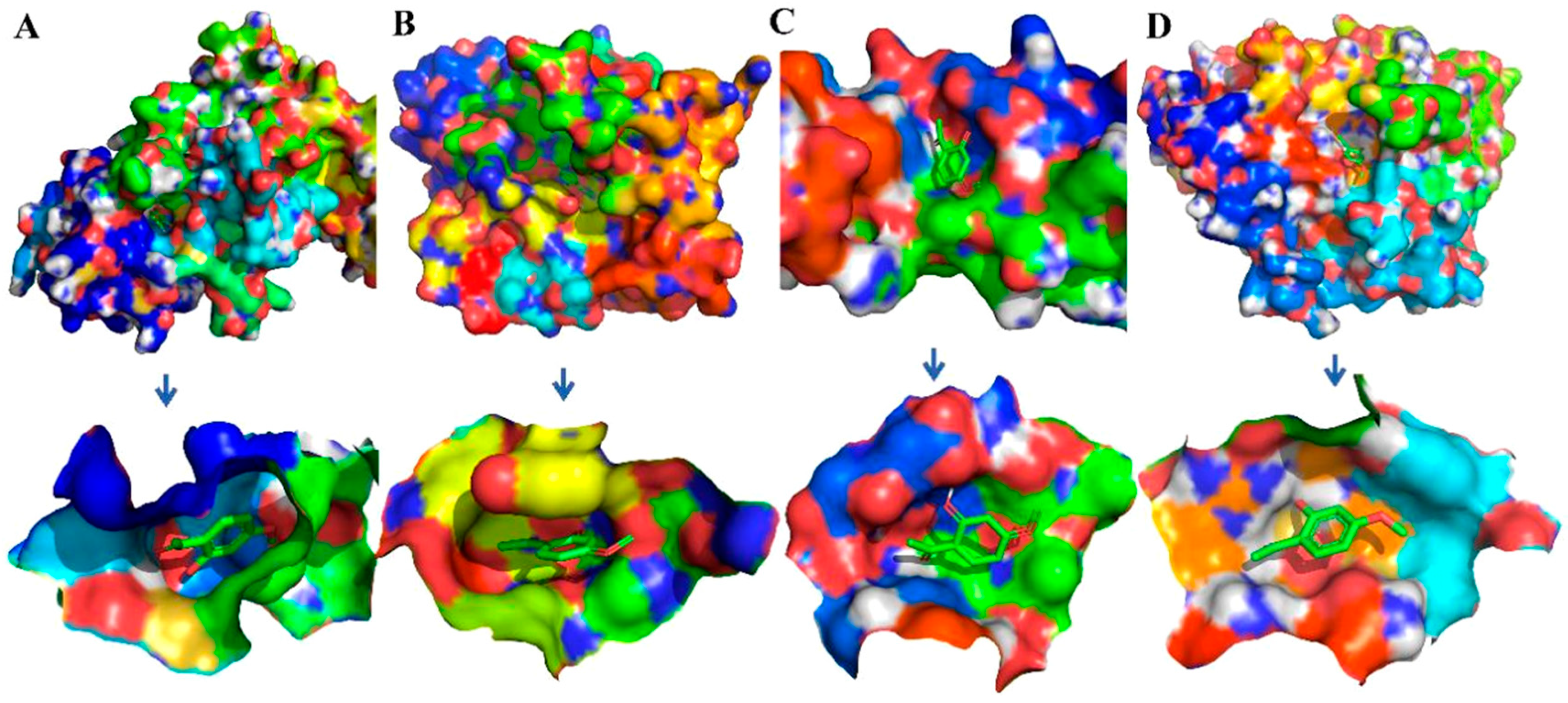
2.5. Binding Free Energy Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Rats’ Living and Feeding Conditions
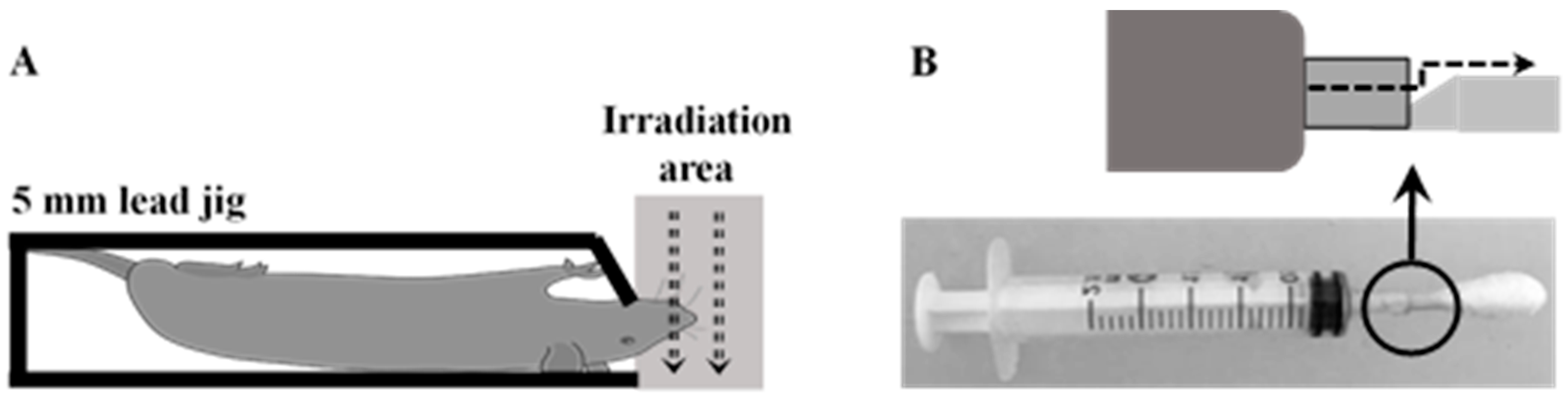
4.3. Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis Rat Model
4.4. Treatment Administration
4.5. Immunohistochemistry Assay
4.6. Western Blotting Assay for NF-κB Pathway
4.7. Target Fishing and Network Construction
4.8. Molecular Docking
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elting, L.S.; Cooksley, C.D.; Chambers, M.S.; Garden, A.S. Risk, outcomes, and costs of radiation-induced oral mucositis among patients with head-and-neck malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, A.; Akintoye, S.O. Dental Management of Patients Who Have Undergone Oral Cancer Therapy. Dent Clin. North. Am. 2018, 62, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, O.M.; Eliopoulos, N.; Muanza, T. Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis. Front Oncol. 2017, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, C.; Sonis, S.; Diz, P.D. Oral mucositis. Oral Dis. 2006, 12, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ansari, S.; Zecha, J.A.; Barasch, A.; de Lange, J.; Rozema, F.R.; Raber-Durlacher, J.E. Oral Mucositis Induced By Anticancer Therapies. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2015, 2, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonis, S.T. Pathobiology of oral mucositis: Novel insights and opportunities. J. Support Oncol. 2007, 5, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.K.; Wu, C.L.; Tsai, T.H.; Hsieh, C.L. Anti-inflammatory and anticoagulative effects of paeonol on LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. Evid Based Complement. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med 2012, 2012, 837513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of paeonol in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Shen, Q.; Chen, J. Transdermal delivery of paeonol using cubic gel and microemulsion gel. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Jia, W. Paeonol attenuates high-fat-diet-induced atherosclerosis in rabbits by anti-inflammatory activity. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Paeonol prevents IL-1beta-induced inflammatory response and degradation of type II collagen in human primary chondrocytes. Artif Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Fang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. A systematic prediction of multiple drug-target interactions from chemical, genomic, and pharmacological data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Huang, S.; Baltzis, D.; Rivas-Estilla, A.M.; Pluquet, O.; Hatzoglou, M.; Koumenis, C.; Taya, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Koromilas, A.E. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces p53 cytoplasmic localization and prevents p53-dependent apoptosis by a pathway involving glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Genes. Dev. 2004, 18, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papareddy, P.; Rydengard, V.; Pasupuleti, M.; Walse, B.; Morgelin, M.; Chalupka, A.; Malmsten, M.; Schmidtchen, A. Proteolysis of human thrombin generates novel host defense peptides. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, K.C.; Frost, G.H.; Bergmann, J.S.; Carney, D.H. Synthetic peptides bind to high-affinity thrombin receptors and modulate thrombin mitogenesis. Pept. Res. 1988, 1, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spalinger, M.R.; Lang, S.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fried, M.; Rogler, G.; Scharl, M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 modulates NOD2-induced cytokine release and autophagy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, P.; Livstone, M.S.; Lewis, S.E.; Thomas, P.D. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 2011, 12, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, M.; Lin, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B. Systems Pharmacology Dissection of Multiscale Mechanisms of Action for Herbal Medicines in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3201–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Computational Study Exploring the Interaction Mechanism of Benzimidazole Derivatives as Potent Cattle Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5941–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Tao, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Systematic Investigation of Ginkgo Biloba Leaves for Treating Cardio-cerebrovascular Diseases in an Animal Model. Acs Chem. Biol. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; D’Souza, W.D. A Treatment Planning Method for Better Management of Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. J. Med. Phys. 2018, 43, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sonis, S.T. Mucositis: The impact, biology and therapeutic opportunities of oral mucositis. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, D.M. Mucositis guidelines: What have they achieved, and where to from here? Support Care Cancer. 2006, 14, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostler, W.J.; Hejna, M.; Wenzel, C.; Zielinski, C.C. Oral mucositis complicating chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy: Options for prevention and treatment. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2001, 51, 290–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, G.; Fox, J.; Ashton, B.; Middleton, J. Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells: Their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007, 25, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Yao, L.P.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.J. Paeonol alleviated acute alcohol-induced liver injury via SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 60, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.A.; Park, M.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.D.; Na, H.J.; Kim, H.M.; Shin, M.K.; Ahn, K.S. Paeonol inhibits anaphylactic reaction by regulating histamine and TNF-alpha. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, L.; Wu, H.; Dai, M. Paeonol Inhibits Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Vascular Endothelial Cells Autophagy by Upregulating the Expression of miRNA-30a. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L. Exploring the structural determinants of novel xanthine derivatives as A2B adenosine receptor antagonists: A computational study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Du, J.; Zheng, Q.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y. A New Strategy for Deleting Animal drugs from Traditional Chinese Medicines based on Modified Yimusake Formula. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.Y.; Dai, S.M. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of paeonia lactiflora pall., a traditional chinese herbal medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ailing, H.; Jian, P. Ecdysterone Accelerates Healing of Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Rats by Increasing Matrix Cell Proliferation. Radiat. Res. 2019, 191, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome. Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Olson, A.J. Using AutoDock for ligand-receptor docking. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2008, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, P.A.; Chaires, J.B.; Trent, J.O. Molecular docking of intercalators and groove-binders to nucleic acids using Autodock and Surflex. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 1602–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
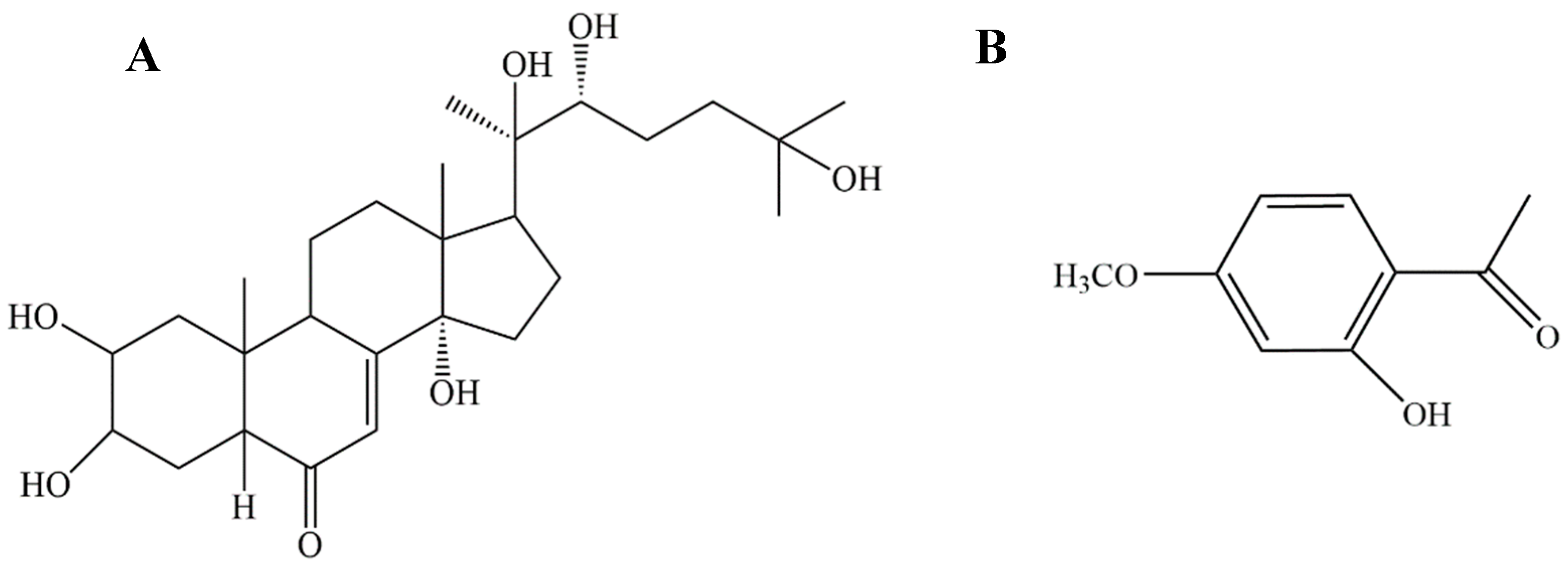
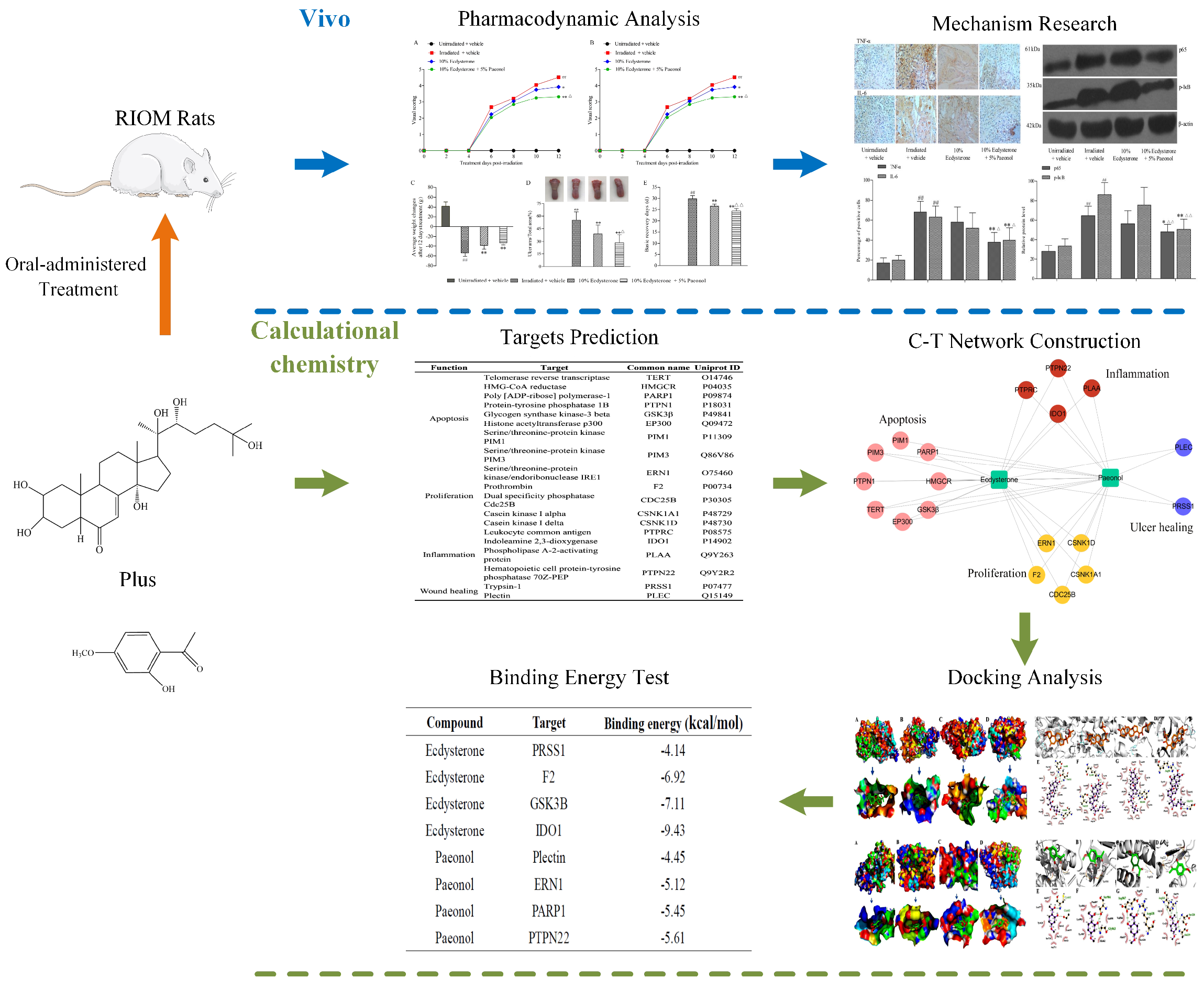
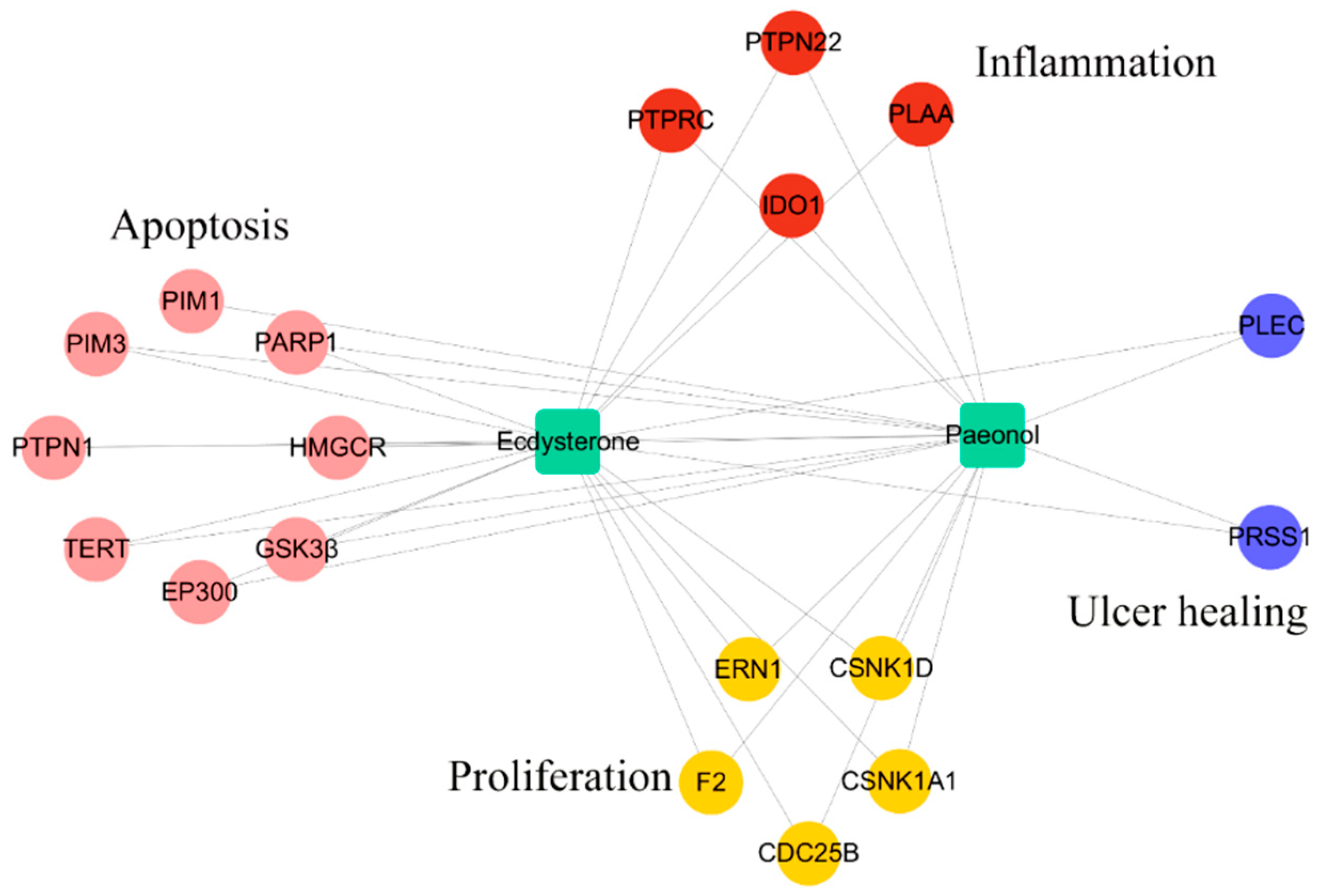
| Function | Target | Common Name | Uniprot ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apoptosis | Telomerase reverse transcriptase | TERT | O14746 |
| HMG-CoA reductase | HMGCR | P04035 | |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase-1 | PARP1 | P09874 | |
| Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B | PTPN1 | P18031 | |
| Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | GSK3β | P49841 | |
| Histone acetyltransferase p300 | EP300 | Q09472 | |
| Serine/threonine-protein kinase PIM1 | PIM1 | P11309 | |
| Serine/threonine-protein kinase PIM3 | PIM3 | Q86V86 | |
| Proliferation | Serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease IRE1 | ERN1 | O75460 |
| Prothrombin | F2 | P00734 | |
| Dual specificity phosphatase Cdc25B | CDC25B | P30305 | |
| Casein kinase I alpha | CSNK1A1 | P48729 | |
| Casein kinase I delta | CSNK1D | P48730 | |
| Inflammation | Leukocyte common antigen | PTPRC | P08575 |
| Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase | IDO1 | P14902 | |
| Phospholipase A-2-activating protein | PLAA | Q9Y263 | |
| Hematopoietic cell protein-tyrosine phosphatase 70Z-PEP | PTPN22 | Q9Y2R2 | |
| Wound healing | Trypsin-1 | PRSS1 | P07477 |
| Plectin | PLEC | Q15149 |
| Compound | Target | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Ecdysterone | PRSS1 | −4.14 |
| Ecdysterone | F2 | −6.92 |
| Ecdysterone | GSK3B | −7.11 |
| Ecdysterone | IDO1 | −9.43 |
| Paeonol | Plectin | −4.45 |
| Paeonol | ERN1 | −5.12 |
| Paeonol | PARP1 | −5.45 |
| Paeonol | PTPN22 | −5.61 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Pan, J. Therapeutic Effect of Ecdysterone Combine Paeonol Oral Cavity Direct Administered on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153800
Yang L, Pan J. Therapeutic Effect of Ecdysterone Combine Paeonol Oral Cavity Direct Administered on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153800
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Li, and Jian Pan. 2019. "Therapeutic Effect of Ecdysterone Combine Paeonol Oral Cavity Direct Administered on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153800
APA StyleYang, L., & Pan, J. (2019). Therapeutic Effect of Ecdysterone Combine Paeonol Oral Cavity Direct Administered on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153800




