Calcineurin B-Like Proteins CBL4 and CBL10 Mediate Two Independent Salt Tolerance Pathways in Arabidopsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
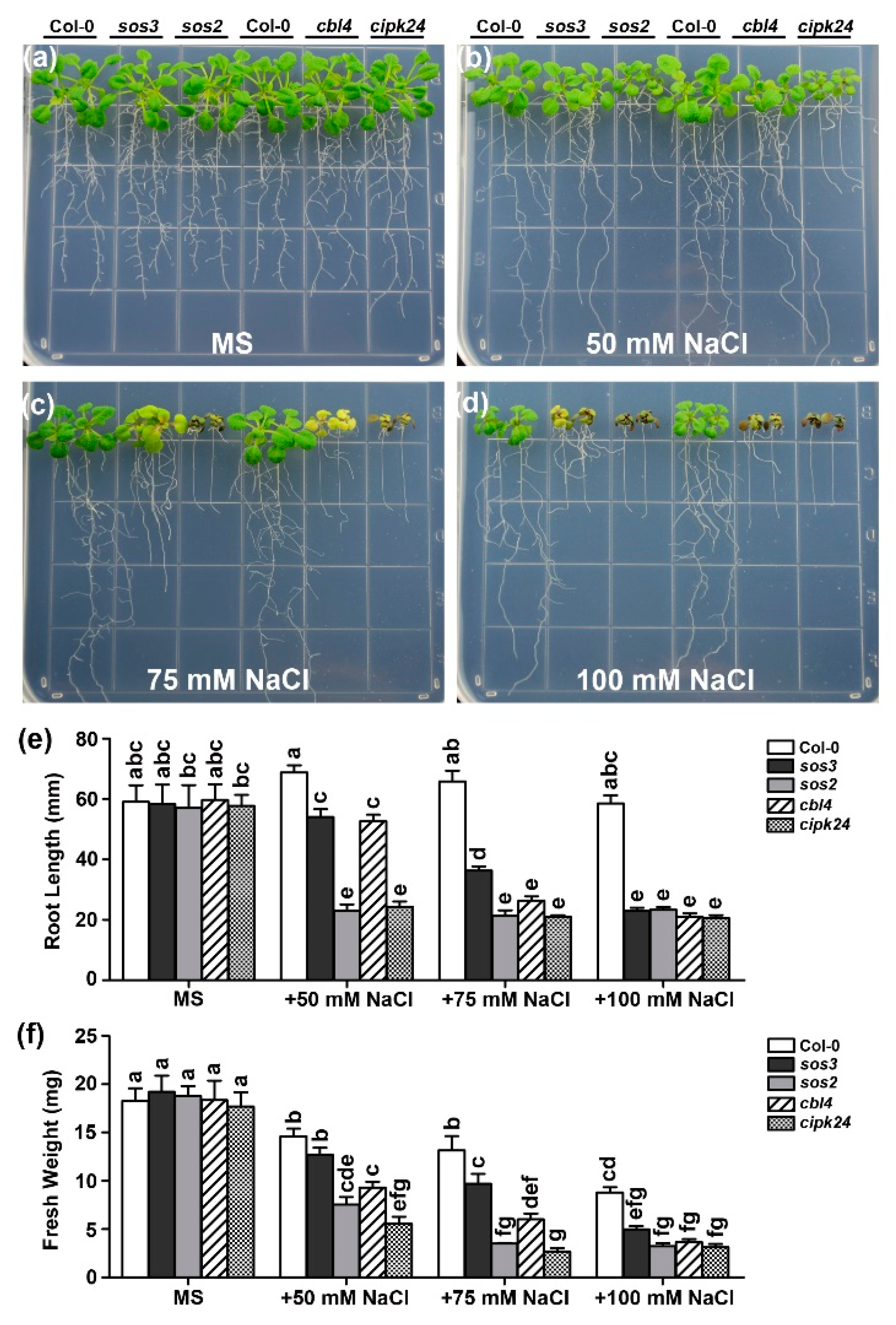
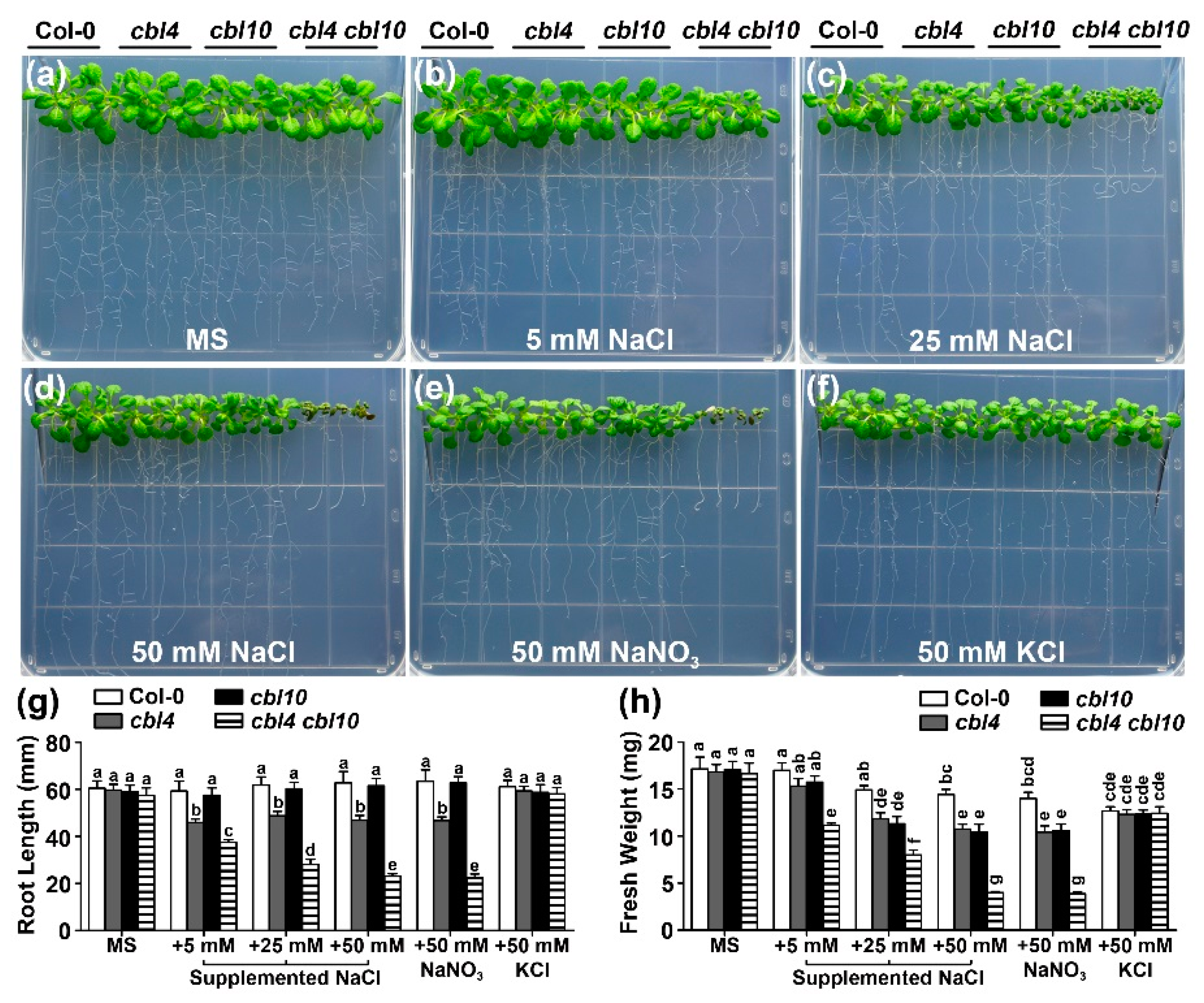
2.1. Functional Synergy of CBL4 and CBL10 in Arabidopsis
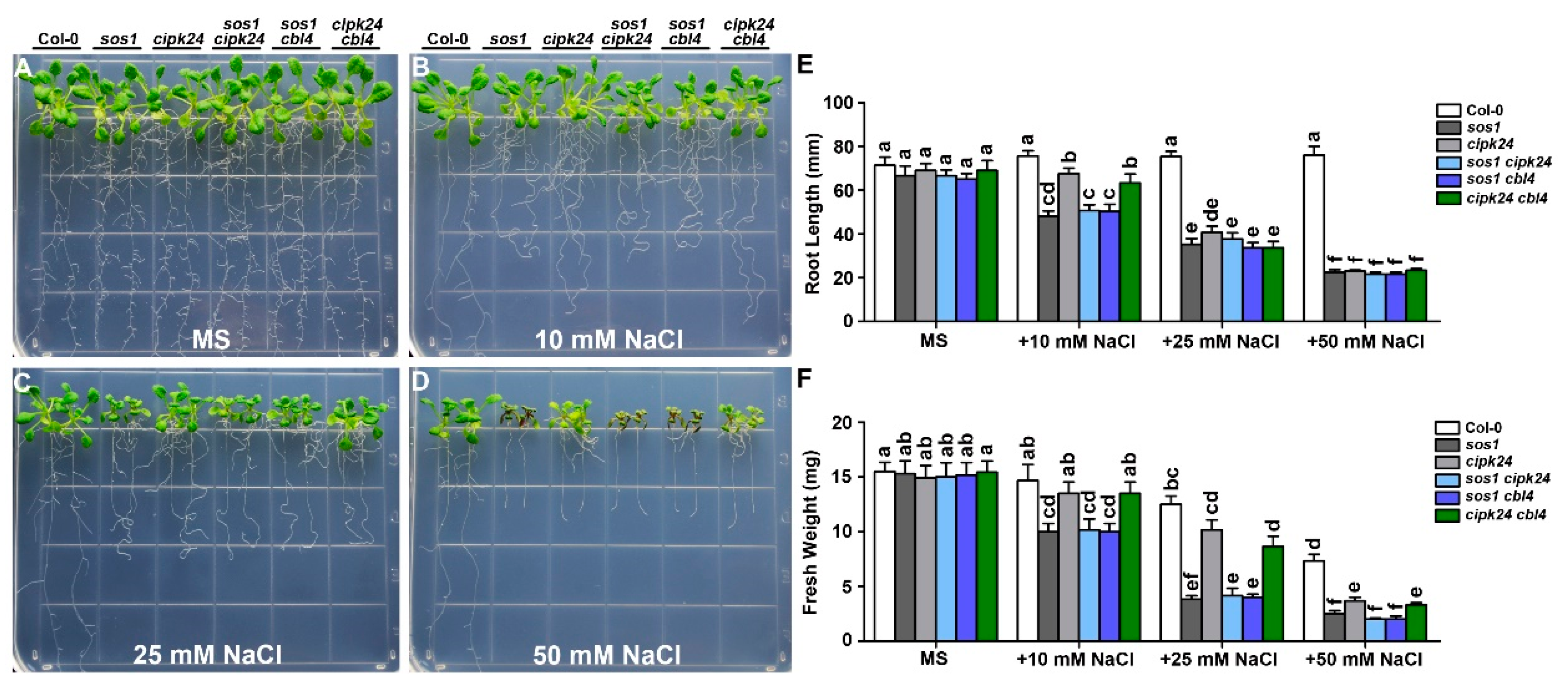
2.2. Genetic Interaction between CBL10 and CIPK24
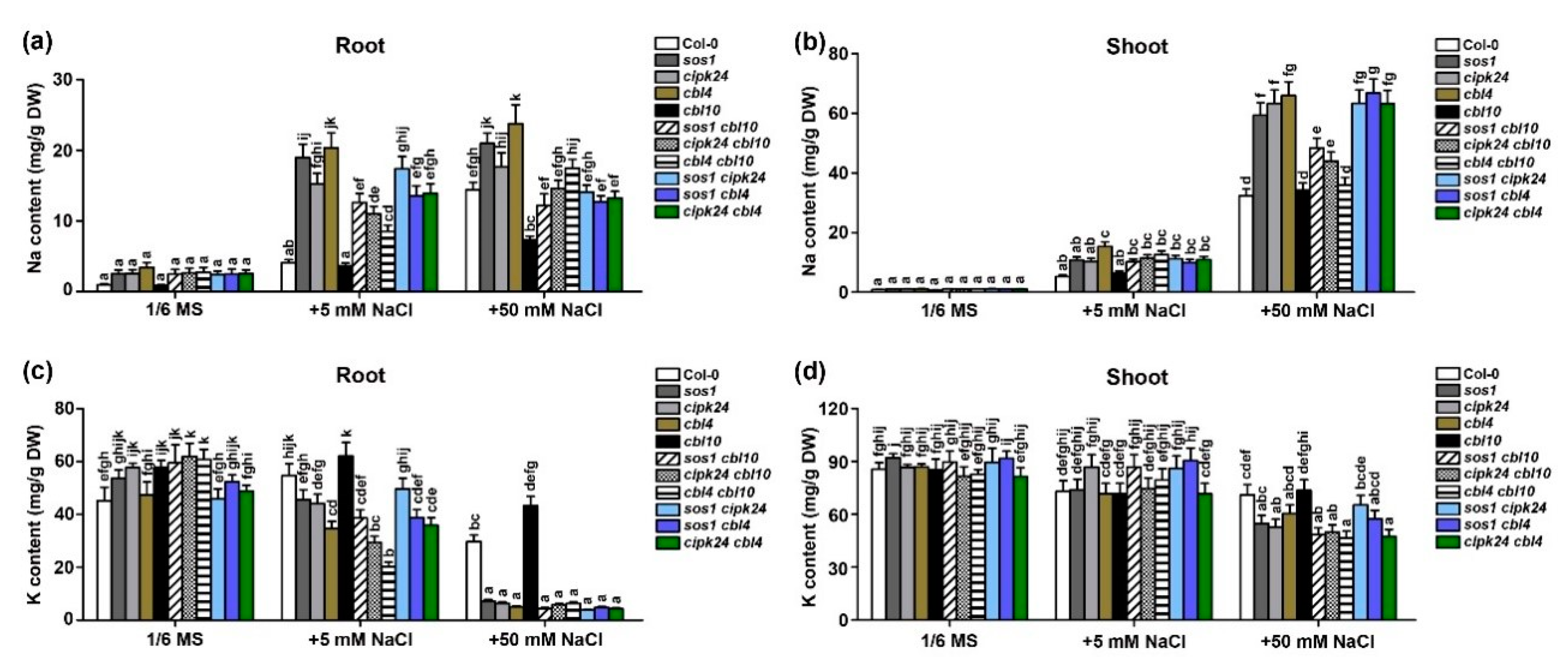
2.3. CBL10 and CBL4 Differentially Regulate Na+ and K+ Accumulation
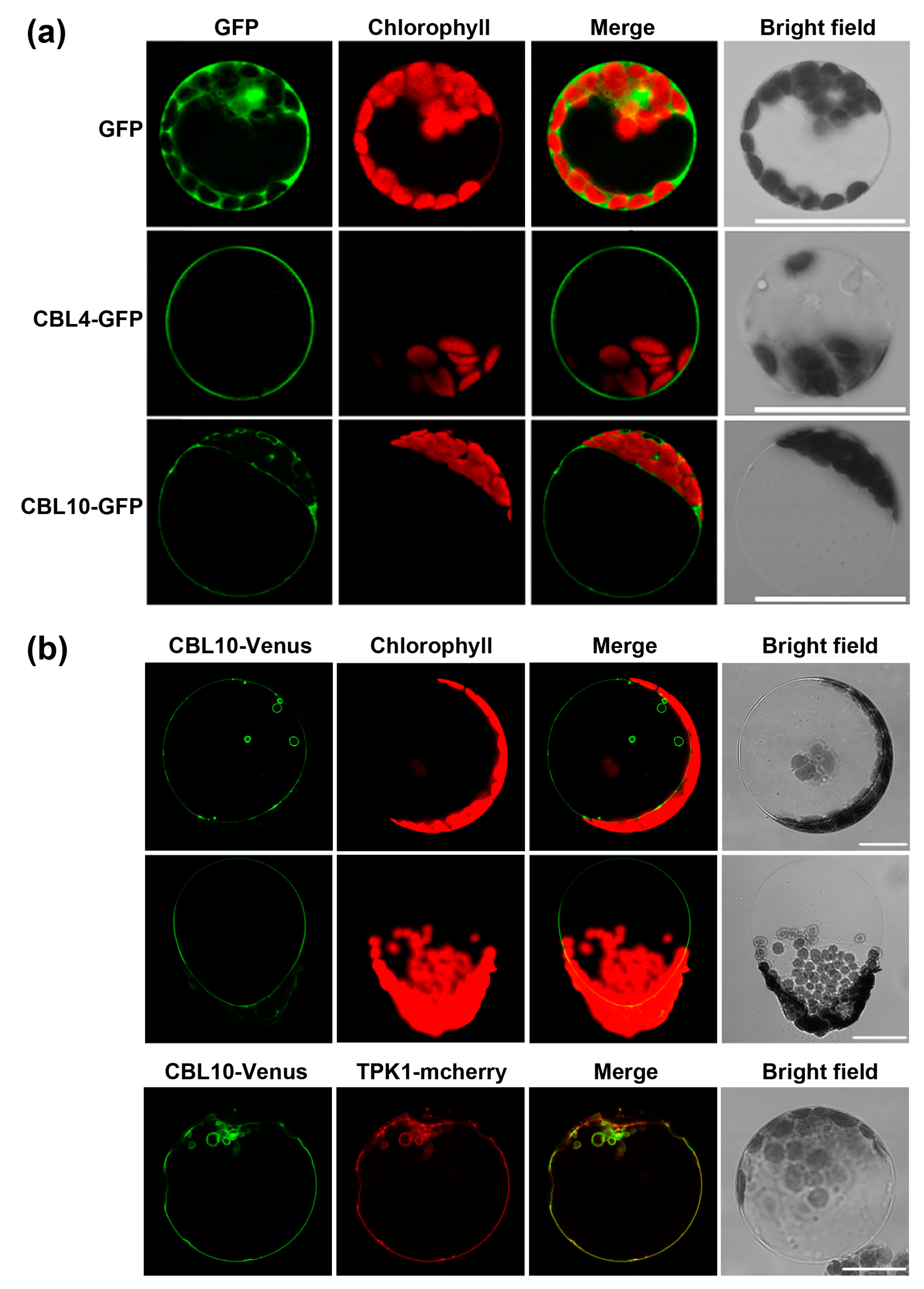
2.4. CBL10 and CBL4 Display Different Subcellular Localizations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Growth Conditions and Stress Rreatment
4.3. Measurements of Na+ and K+ Content
4.4. Subcellular Localization Studies
4.5. Statistical Analysis of the Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.K. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilleary, R.; Choi, W.G.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, S.D.; Gilroy, S. Sense and sensibility: The use of fluorescent protein-based genetically encoded biosensors in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 46, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.K. A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 1998, 280, 1943–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfter, U.; Ishitani, M.; Zhu, J.K. The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3735–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, F.J.; Ohta, M.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J.K.; Pardo, J.M. Reconstitution in yeast of the Arabidopsis SOS signaling pathway for Na+ homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9061–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Ishitani, M.; Wu, S.J.; Kim, C.S.; Zhu, J.K. The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6896–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.H.; Pittman, J.K.; Zhu, J.K.; Hirschi, K.D. The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2922–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batelli, G.; Verslues, P.E.; Agius, F.; Qiu, Q.; Fujii, H.; Pan, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; Grillo, S.; Zhu, J.K. SOS2 promotes salt tolerance in part by interacting with the vacuolar H+-ATPase and upregulating its transport activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7781–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huertas, R.; Olías, R.; Eljakaoui, Z.; Gálvez, F.J.; Li, J.; De Morales, P.A.; Belver, A.; Rodríguez-Rosales, M.P. Overexpression of SlSOS2 (SlCIPK24) confers salt tolerance to transgenic tomato. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1467–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.S.; Guo, Y.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Regulation of vacuolar Na+/H+ exchange in Arabidopsis thaliana by the SOS pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Ali, Z.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Cha, J.Y.; Perez-Hormaeche, J.; Quintero, F.J.; Shin, G.; Kim, M.R.; Qiang, Z.; et al. Release of SOS2 kinase from sequestration with GIGANTEA determines salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. SOS3 mediates lateral root development under low salt stress through regulation of auxin redistribution and maxima in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.T.; Pardo, J.M.; Batelli, G.; Oosten, M.J.V.; Bressan, R.A.; Li, X. The salt overly sensitive (SOS) pathway: Established and emerging roles. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.G.; Waadt, R.; Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Dominguez-Solis, J.R.; Schültke, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 52, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, R.; Lin, H.; Mendoza, I.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Yang, Y.; Shang, M.; Chen, S.; Pardo, J.M.; Guo, Y. SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waadt, R.; Schmidt, L.K.; Lohse, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Bock, R.; Kudla, J. Multicolor bimolecular fluorescence complementation reveals simultaneous formation of alternative CBL/CIPK complexes in planta. Plant J. 2008, 56, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monihan, S.M.; Magness, C.A.; Yadegari, R.; Smith, S.E.; Schumaker, K.S. Arabidopsis CALCINEURIN B-LIKE10 functions independently of the SOS pathway during reproductive development in saline conditions. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.T.; Yu, M.M.; Gao, X.S.; Zhang, H.X. Poplar calcineurin B-like proteins PtCBL10A and PtCBL10B regulate shoot salt tolerance through interaction with PtSOS2 in the vacuolar membrane. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, I.; Pineda, B.; Ortíz-Atienza, A.; Plasencia, F.A.; Drevensek, S.; García-Sogo, B.; Yuste-Lisbona, F.J.; Barrero-Gil, J.; Atarés, A.; Flores, F.B.; et al. The SlCBL10 Calcineurin B-Like Protein ensures plant growth under salt stress by regulating Na+ and Ca2+ homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1676–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, F.; Gutiérrez-Beltrán, E.; Pareja-Jaime, Y.; Chakravarthy, S.; Martin, G.B.; del Pozo, O. The tomato calcium sensor Cbl10 and its interacting protein kinase Cipk6 define a signaling pathway in plant immunity. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2748–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S. The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.J.; Luan, S. Regulation of calcium and magnesium homeostasis in plants: From transporters to signaling network. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 39, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, V.; Weinl, S.; Blazevic, D.; D’Angelo, C.; Batistic, O.; Kolukisaoglu, U.; Bock, R.; Schulz, B.; Harter, K.; Kudla, J. The calcium sensor CBL1 integrates plant responses to abiotic stresses. Plant J. 2003, 36, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, K.N.; Pandey, G.K.; Gupta, R.; Grant, J.J.; Luan, S. CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.K.; Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, K.N.; Grant, J.J.; Li, L.; Hung, W.; D’Angelo, C.; Weinl, S.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1912–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Kanwar, P.; Singh, A.; Steinhorst, L.; Pandey, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Tokas, I.; Sanyal, S.K.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, S.C.; et al. Calcineurin B-Like Protein-Interacting Protein Kinase CIPK21 Regulates Osmotic and Salt Stress Responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.K. An Arabidopsis mutant that requires increased calcium for potassium nutrition and salt tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14960–14964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitani, M.; Liu, J.; Halfter, U.; Kim, C.S.; Wei, M.; Zhu, J.K. SOS3 function in plant salt tolerance requires N-myristoylation and calcium binding. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M.; Zhu, J.K. The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Gilliham, M. Salinity tolerance of crops—What is the cost? New Phytol. 2015, 208, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apse, M.P.; Blumwald, E. Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, E.; Zhang, S.; Gong, H.; Tajima, H.; Blumwald, E. Cation specificity of vacuolar NHX-type cation/H+ antiporters. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.; Beyhl, D.; Gorlich, E.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Marten, I.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Hedrich, R.; Schumacher, K. Arabidopsis V-ATPase activity at the tonoplast is required for efficient nutrient storage but not for sodium accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, E.; Ohto, M.A.; Esumi, T.; Tajima, H.; Zhu, Z.; Cagnac, O.; Belmonte, M.; Peleg, Z.; Yamaguchi, T.; Blumwald, E. The Arabidopsis intracellular Na+/H+ antiporters NHX5 and NHX6 are endosome associated and necessary for plant growth and development. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julkowska, M.M.; Testerink, C. Tuning plant signaling and growth to survive salt. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.K.; Choi, M.N.; Kim, K.N. Calcineurin B-like Protein CBL10 directly interacts with TOC34 (Translocon of the Outer Membrane of the Chloroplasts) and decreases its GTPase activity in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.D.; Cho, Y.H.; Sheen, J. Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: A versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, R.-J.; Xu, H.-X.; Lan, W.-Z.; Zhao, F.; Luan, S. Calcineurin B-Like Proteins CBL4 and CBL10 Mediate Two Independent Salt Tolerance Pathways in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102421
Yang Y, Zhang C, Tang R-J, Xu H-X, Lan W-Z, Zhao F, Luan S. Calcineurin B-Like Proteins CBL4 and CBL10 Mediate Two Independent Salt Tolerance Pathways in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102421
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Chi Zhang, Ren-Jie Tang, Hai-Xia Xu, Wen-Zhi Lan, Fugeng Zhao, and Sheng Luan. 2019. "Calcineurin B-Like Proteins CBL4 and CBL10 Mediate Two Independent Salt Tolerance Pathways in Arabidopsis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102421
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhang, C., Tang, R.-J., Xu, H.-X., Lan, W.-Z., Zhao, F., & Luan, S. (2019). Calcineurin B-Like Proteins CBL4 and CBL10 Mediate Two Independent Salt Tolerance Pathways in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102421





