Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
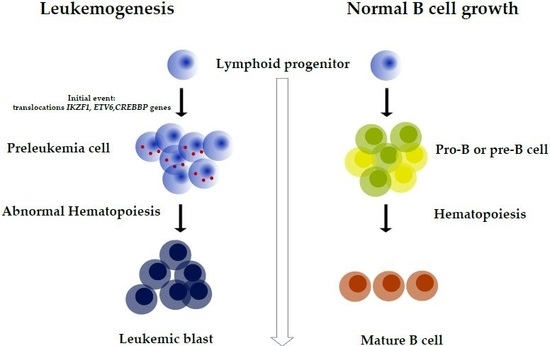
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Features of Patients
2.2. Novel Fusion Transcripts
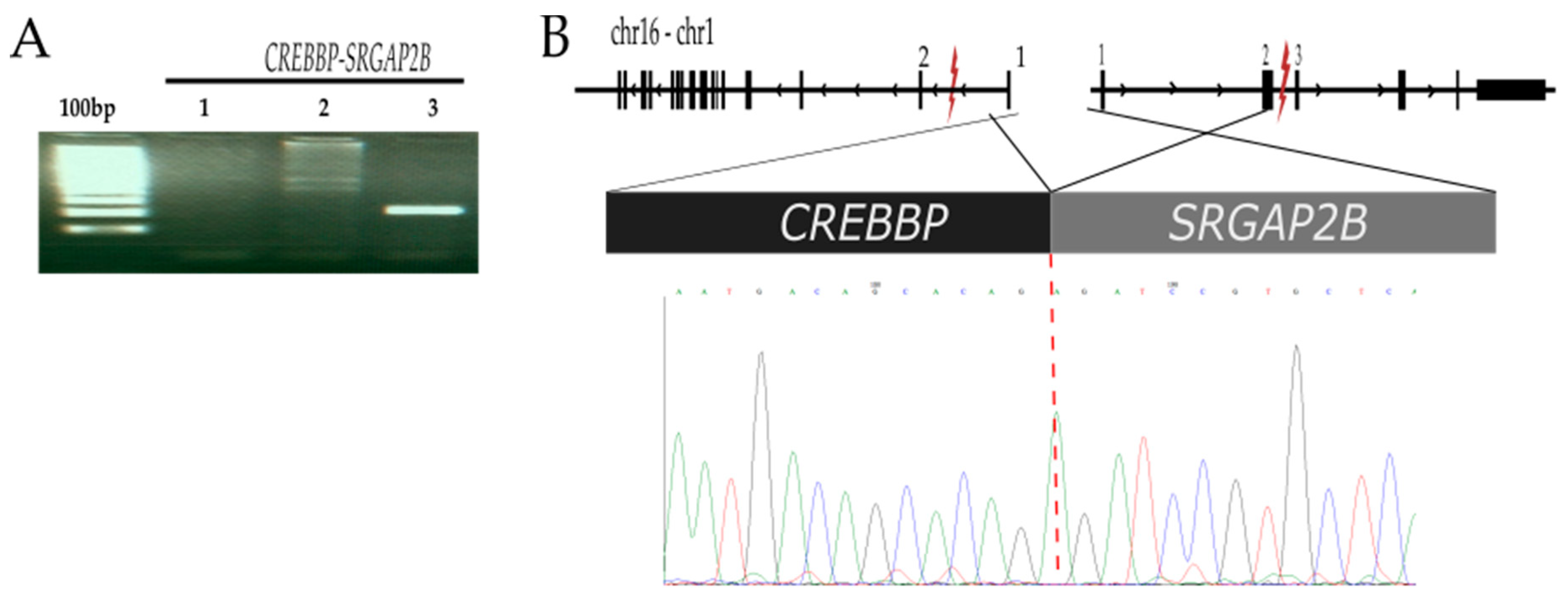
2.2.1. CREBBP-SRGAP2B t (16;1) (p13.3;q21.1)
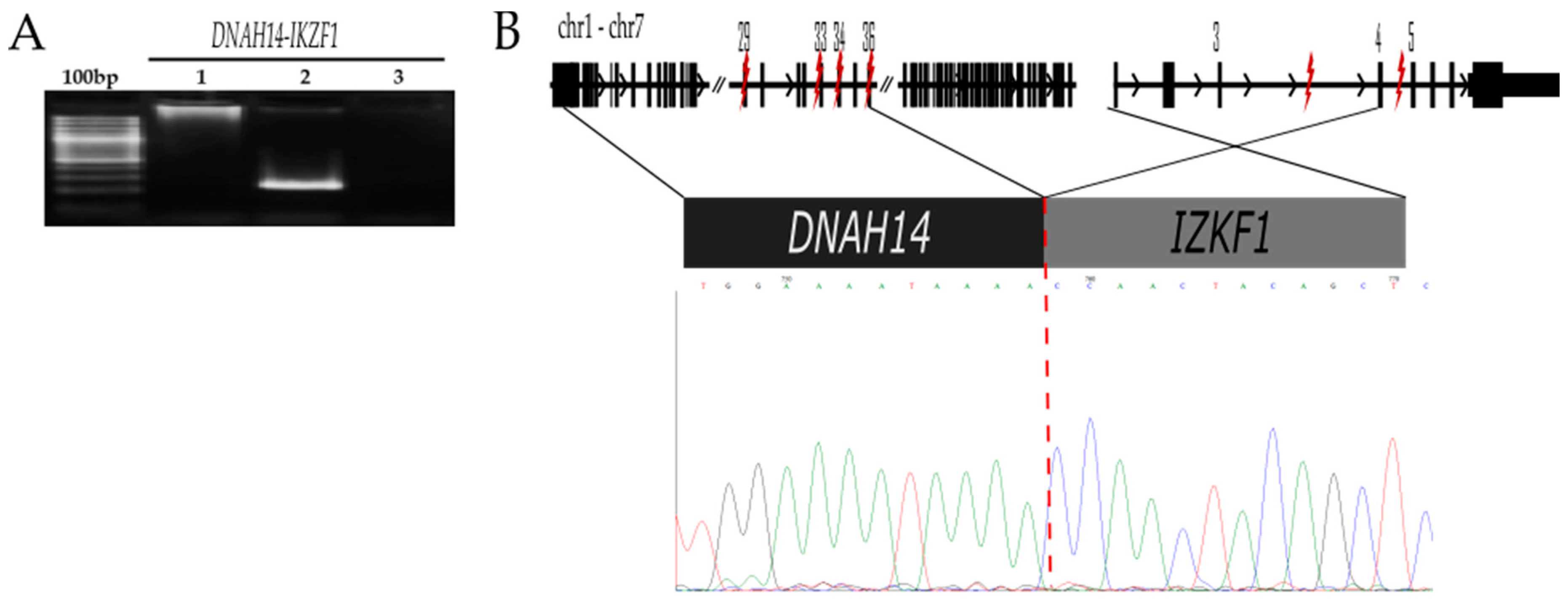
2.2.2. DNAH14-IKZF1 t (1;7) (q42.12;7p12.2)
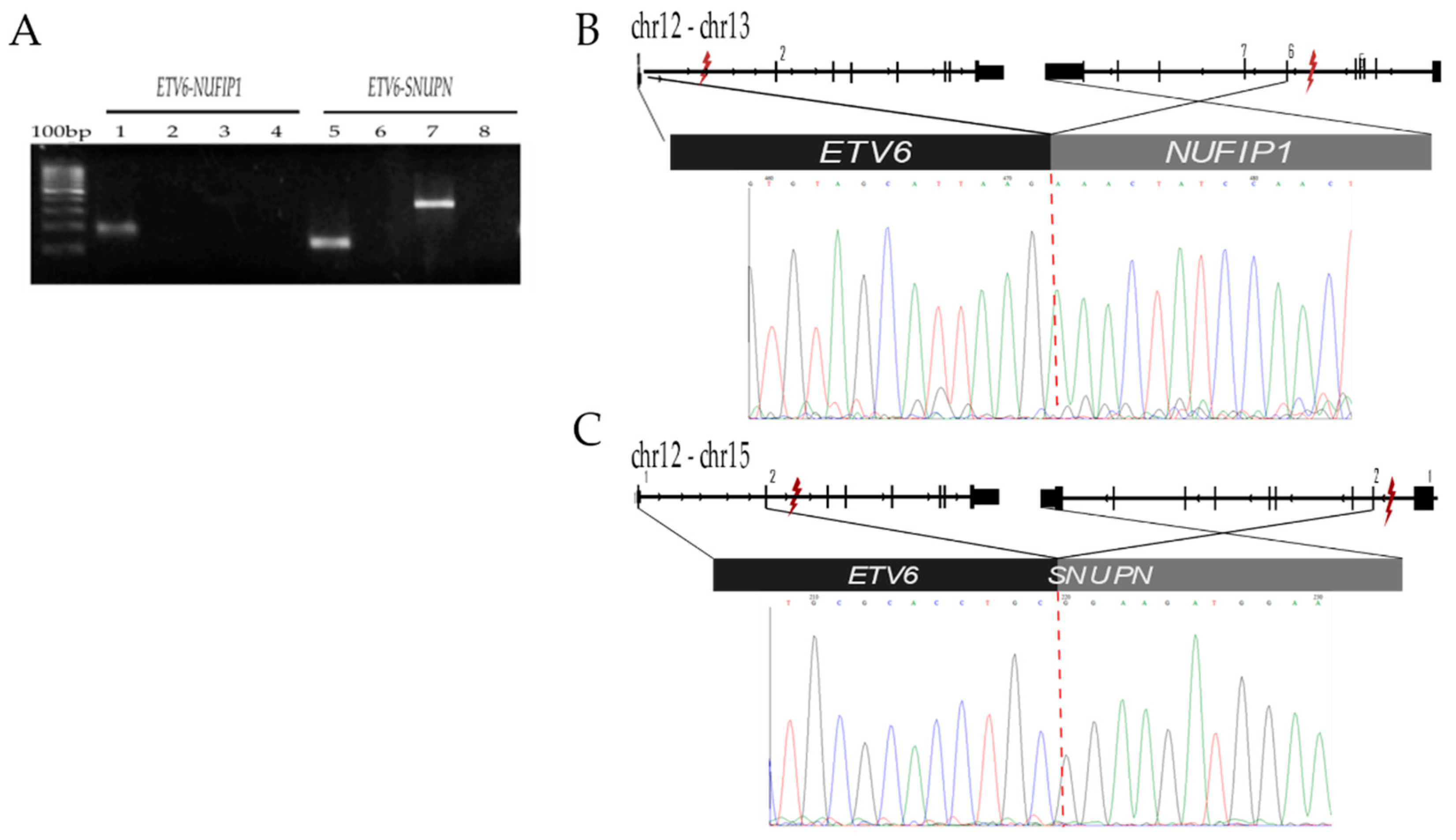
2.2.3. ETV6-SNUPN t (12;15) (p13.2;q24.2) and ETV6-NUFIP1 t (12;13) (p13.2;q14.12)
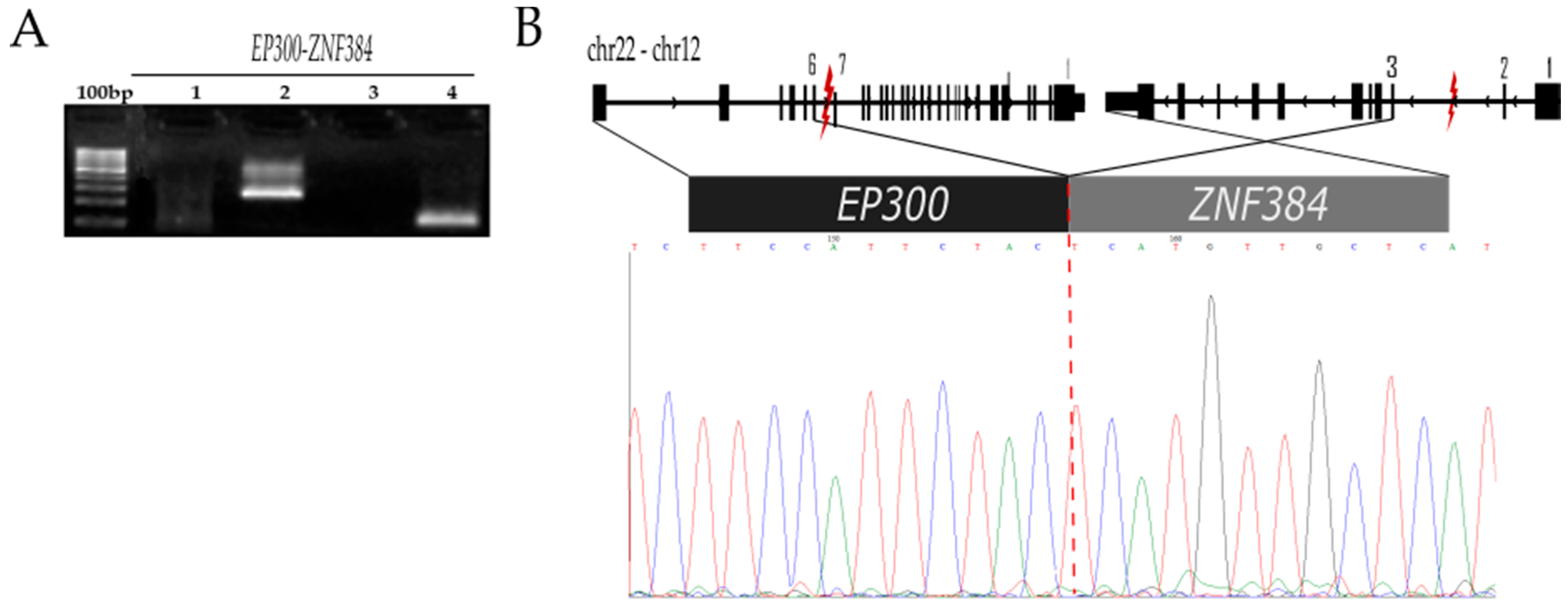
2.2.4. EP300-ZNF384 t (22;12) (q13.2;p13.31;)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. RNA-Seq Libraries and Sequencing
4.3. Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) for Fusion Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| RNA-seq | RNA-sequencing |
| IP | Immunophenotype |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| BCP | Bicytopenia |
| SS | Septic shock |
| HLH | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
| MOF | Multiple organ failure |
| TC | Toxicity |
| PN | Pneumonia |
| CR | Complete remission central nervous system relapse |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CDS | Coding sequence |
| ETS | E-twenty-six |
References
- Pérez-Saldivar, M.L.; Fajardo-Gutiérrez, A.; Bernáldez-Ríos, R.; Martínez-Avalos, A.; Medina-Sanson, A.; Espinosa-Hernández, L.; de Diego Flores-Chapa, J.; Amador-Sánchez, R.; Peñaloza-González, J.G.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, F.J.; et al. Childhood acute leukemias are frequent in Mexico City: Descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swords, R.; Sznol, J.; Elias, R.; Watts, J.; Zelent, A.; Martin, E.; Vargas, F.; Bethel-Ellison, S.; Kobetz, E. Acute leukemia in adult Hispanic Americans: A large-population study. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Luna, R.; Correa-González, C.; Altamirano-Alvarez, E.; Sánchez-Zubieta, F.; Cárdenas-Cardós, R.; Escamilla-Asian, G.; Olaya-Vargas, A.; Bautista-Marquez, A.; Aguilar-Romo, M. Incidence of childhood cancer among Mexican children registered under a public medical insurance program. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G. The molecular genetic makeup of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2012, 2012, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, T.; Kanakura, Y. Genetic abnormalities associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, M.F.; Wiemels, J. Origins of chromosome translocations in childhood leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aplan, P.D. Causes of oncogenic chromosomal translocation. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasty, P.; Montagna, C. Chromosomal Rearrangements in Cancer: Detection and potential causal mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 1, e29904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, A.K.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Gedman, A.L.; Dang, J.; Nakitandwe, J.; Holmfeldt, L.; Parker, M.; Easton, J.; et al. The landscape of somatic mutations in infant MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurtleff, S.A.; Buijs, A.; Behm, F.G.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hancock, M.L.; Chan, G.C.; Pui, C.H.; Grosveld, G.; Downing, J.R. TEL/AML1 fusion resulting from a cryptic t(12;21) is the most common genetic lesion in pediatric ALL and defines a subgroup of patients with an excellent prognosis. Leukemia 1995, 9, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shurtleff, S.A.; Buijs, A.; Behm, F.G.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hancock, M.L.; Chan, G.C.; Pui, C.H.; Grosveld, G.; Downing, J.R. Prevalence of gene rearrangements in Mexican children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A population study-report from the Mexican Interinstitutional Group for the identification of the causes of childhood leukemia. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 210560. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Razzaq, S.K.; Vo, A.D.; Gautam, M.; Li, H. Identifying fusion transcripts using next generation sequencing. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 7, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talkowski, M.E.; Ernst, C.; Heilbut, A.; Chiang, C.; Hanscom, C.; Lindgren, A.; Kirby, A.; Liu, S.; Muddukrishna, B.; Ohsumi, T.K.; et al. Next-generation sequencing strategies enable routine detection of balanced chromosome rearrangements for clinical diagnostics and genetic research. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gocho, Y.; Kiyokawa, N.; Ichikawa, H.; Nakabayashi, K.; Osumi, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Ueno, H.; Terada, K.; Oboki, K.; Sakamoto, H.; et al. A novel recurrent EP300–ZNF384 gene fusion in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2445–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Zhang, J.; Kasper, L.H.; Lerach, S.; Payne-Turner, D.; Phillips, L.A.; Heatley, S.L.; Holmfeldt, L.; Collins-Underwood, J.R.; Ma, J.; et al. CREBBP mutations in relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 471, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobitzsch, B.; Gökbuget, N.; Schwartz, S.; Reinhardt, R.; Brüggemann, M.; Viardot, A.; Wäsch, R.; Starck, M.; Thiel, E.; Hoelzer, D.; et al. Loss-of-function but not dominant-negative intragenic IKZF1 deletions are associated with an adverse prognosis in adult BCR-ABL-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Miller, C.B.; Radtke, I.; Phillips, L.A.; Dalton, J.; Ma, J.; White, D.; Hughes, T.P.; Le Beau, M.M.; Pui, C.H.; et al. BCR-ABL1 lymphoblastic leukaemia is characterized by the deletion of Ikaros. Nature 2008, 453, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchman, M.L.; Low, J.; Qu, C.; Paietta, E.M.; Kasper, L.H.; Chang, Y.; Payne-Turner, D.; Althoff, M.J.; Song, G.; Chen, S.C.; et al. Efficacy of Retinoids in IKZF1-Mutated BCR-ABL1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Braekeleer, E.; Douet-Guilbert, N.; Morel, F.; Le Bris, M.J.; Basinko, A.; De Braekeleer, M. ETV6 fusion genes in hematological malignancies: A review. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.H.; Smolik, S. CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia, J.C.; Kwok, R.P.; Lamb, N.; Hagiwara, M.; Montminy, M.R.; Goodman, R.H. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature 1993, 365, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M.Y.; Nuttle, X.; Sudmant, P.H.; Antonacci, F.; Graves, T.A.; Nefedov, M.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Sajjadian, S.; Malig, M.; Kotkiewicz, H.; et al. Evolution of human-specific neural SRGAP2 genes by incomplete segmental duplication. Cell 2012, 149, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boija, A.; Mahat, D.B.; Zare, A.; Holmqvist, P.H.; Philip, P.; Meyers, D.J.; Cole, P.A.; Lis, J.T.; Stenberg, P.; Mannervik, M. CBP Regulates Recruitment and Release of Promoter-Proximal RNA Polymerase II. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 491–503.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovic, T.; Marston, E. Molecular mechanisms involved in chemoresistance in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Srp. Arh. Celok. Lek. 2008, 136, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrock, A.B.; Zhu, V.W.; Hsieh, W.S.; Madison, R.; Creelan, B.; Silberberg, J.; Costin, D.; Bharne, A.; Bonta, I.; Bosemani, T.; et al. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Fusions and BRAF Kinase Fusions are Rare but Actionable Resistance Mechanisms to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, W.; Teng, W.; Ma, X.; Guo, L.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Retrospective analysis of 36 fusion genes in 2479 Chinese patients of de novo acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2018, 72, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, K.; Bigby, M.; Wang, J.H.; Molnar, A.; Wu, P.; Winandy, S.; Sharpe, A. The Ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell 1994, 79, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, B.J.; Mackay, J.P.; Gell, D. Ikaros: A key regulator of haematopoiesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.; Cronshagen, U.; Kadokura, M.; Marshallsay, C.; Wada, T.; Sekine, M.; Lührmann, R. Snurportin1, an m3G-cap-specific nuclear import receptor with a novel domain structure. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4114–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shago, M.; Abla, O.; Hitzler, J.; Weitzman, S.; Abdelhaleem, M. Frequency and outcome of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia with ZNF384 gene rearrangements including a novel translocation resulting in an ARID1B/ZNF384 gene fusion. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Nijveen, H.; Rao, X.; Bisseling, T.; Geurts, R.; Leunissen, J.A.M. Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W71–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case | Age (Years) | Sex | Fusion Transcripts by NGS | Relapse | Death | Adherence | Diagnosis/Year | Initial WBC Count × 106 Cell/L | BM Blast % at Diagnosis | IP | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 74MO | 10.8 | M | BCR-ABL minor SRGAP2B-CREBBP | Yes | SS | Yes | ALL/2013 | 15,630 | 100 | Pre-B | Progressed quickly; expired in 2 weeks |
| 77MO | 17.4 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2014 | 12,570 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 197MO | 9.4 | F | EP300-ZNF384 | No | No | Yes | ALL/2014 | 2430 | 95 | Pre-B | CR |
| 199MO | 3.9 | M | NF | No | SS | Yes | ALL/2014 | 440 | 100 | Pre-B | Died after remission |
| 63MO | 2.0 | M | TCF3-PBX1 | No | SS | Yes | ALL/2015 | 7500 | 97 | T cell | Died after remission |
| 123MO | 4.7 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 42,100 | 25 | Pre-B | CR |
| 269MO | 4.0 | F | ETV6-RUNX1 | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 9200 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 273MO | 14.8 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 12,460 | 96 | Pre-B | CR |
| 289MO | 0.6 | F | MLL-AF4, GLYR1-SLC9A8a | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 371,000 | 80 | Pre-B | CR |
| 374MO | 4.4 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 20,220 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 385MO | 5.5 | M | NF | ND | ND | A | ALL/2015 | 7200 | 85 | Pre-B | ND |
| 405MO | 4.6 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 2700 | 25 | Pre-B | CR |
| 420MO | 6.0 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 2360 | 90 | Pre-B | CR |
| 545MO | 7.2 | F | WDR74-RCC1a | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 8600 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 549MO | 4.9 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 13,300 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 99MO | 9.8 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 9000 | 90 | Pre-B | CR |
| 109MO | 4.7 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 19,900 | 96 | Pre-B | CR |
| 122MO | 12.3 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 4700 | 96 | Pre-B | CR |
| 179MO | 1.8 | F | DNAH14-IKZF1 | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 32,780 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 196MO | 4.1 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 2780 | 25 | Pre-B | CR |
| 369MO | 2.3 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 2710 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 546MO | 13.0 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 8000 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 28MO | 10.3 | F | ETV6-SNUPN, ETV6-NUFIP1 | No | MOF TC, PN, TC. | Yes | ALL/2016 | 46,300 | 99.5 | Pre-B | Progressed quickly; poorly responded to therapy, died after 2 weeks |
| 73MO * | 37.3 | F | NF | ND | ND | ND | HLH/2014 | 2200 | - | NA | NA |
| 159MO * | 5.8 | M | NF | ND | ND | ND | EBV/2015 | 3620 | 15 | NA | NA |
| 165MO * | 2.2 | M | NF | ND | ND | ND | EBV/2015 | 29,740 | - | NA | NA |
| 83MO * | 5.8 | F | NF | ND | ND | ND | BCP/2017 | 2390 | - | NA | NA |
| Fusion | Gene Symbol (Chromosome Band) | Nucleotides (hg19) | Gene Description | Sample | Gene Previously Reported as Potential Prognostic Indicator | In-Frame | Fusion Validated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREBBP-SRGAP2B | SRGAP2B (1q21.1) | 144013900 | SLIT-ROBO Rho GTPase-activating protein 2B | 74MO | No reported | Yes | Yes |
| CREBBP (16p13.3) | 3929832 | CREB-binding protein (CBP) | Mutations may confer to chemotherapy resistance and possibility of relapse [15] | ||||
| DNAH14-IKZF1 | DNAH14 (1q41.12) | 225333860, 225333863, 225347499, 225354984, 225374260, 225346497 | Dynein Axonemal Heavy Chain 14 | 179MO | No reported | Yes | Yes |
| IKZF1 (7p12.2) | 50444490, 50367352, 50435762, 50444490, 50448363, 50444230 | IKAROS Family Zinc Finger 1 | Deletions and mutation were related to adverse prognosis, treatment failure, and risk of relapse [16,17,18] | ||||
| ETV6-SNUPN | ETV6 (12p13.2) | 11905512 | ETS family transcription factor, Variant 6 | 28MO | In fusion with RUNX1, the most common genetic aberration in pediatric ALL and is related to favorable prognosis [19] | Yes | Yes |
| SNUPN (15q24.2) | 75913396 | Snurportin 1 | No reported | ||||
| ETV6-NUFIP1 | ETV6 (12p13.2) | 11803093 | ETS family transcription factor, Variant 6 | 28MO | Yes | Yes | |
| NUFIP1 (13q14.12) | 45540070 | Nuclear Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein Interacting Protein 1 | No reported | ||||
| EP300-ZNF384 | ZNF384 (12p13.31) | 6788687 | Zinc finger protein 384 | 197MO | EP300-ZNF384 fusion is associated with a B-cell precursor ALL in childhood (3–4%) with better favorable response to chemotherapy than patients with MLL translocations [14] | Yes | Yes |
| EP300 (22q13.2) | 41527639 | E1A binding protein p300 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mata-Rocha, M.; Rangel-López, A.; Jiménez-Hernández, E.; Morales-Castillo, B.A.; González-Torres, C.; Gaytan-Cervantes, J.; Álvarez-Olmos, E.; Núñez-Enríquez, J.C.; Fajardo-Gutiérrez, A.; Martín-Trejo, J.A.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394
Mata-Rocha M, Rangel-López A, Jiménez-Hernández E, Morales-Castillo BA, González-Torres C, Gaytan-Cervantes J, Álvarez-Olmos E, Núñez-Enríquez JC, Fajardo-Gutiérrez A, Martín-Trejo JA, et al. Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394
Chicago/Turabian StyleMata-Rocha, Minerva, Angelica Rangel-López, Elva Jiménez-Hernández, Blanca Angélica Morales-Castillo, Carolina González-Torres, Javier Gaytan-Cervantes, Enrique Álvarez-Olmos, Juan Carlos Núñez-Enríquez, Arturo Fajardo-Gutiérrez, Jorge Alfonso Martín-Trejo, and et al. 2019. "Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394
APA StyleMata-Rocha, M., Rangel-López, A., Jiménez-Hernández, E., Morales-Castillo, B. A., González-Torres, C., Gaytan-Cervantes, J., Álvarez-Olmos, E., Núñez-Enríquez, J. C., Fajardo-Gutiérrez, A., Martín-Trejo, J. A., Solís-Labastida, K. A., Medina-Sansón, A., Flores-Lujano, J., Sepúlveda-Robles, O. A., Peñaloza-González, J. G., Espinoza-Hernández, L. E., Núñez-Villegas, N. N., Espinosa-Elizondo, R. M., Cortés-Herrera, B., ... Mejía-Aranguré, J. M. (2019). Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394