In Vitro Inhibitory Mechanism Effect of TRAIP on the Function of TRAF2 Revealed by Characterization of Interaction Domains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
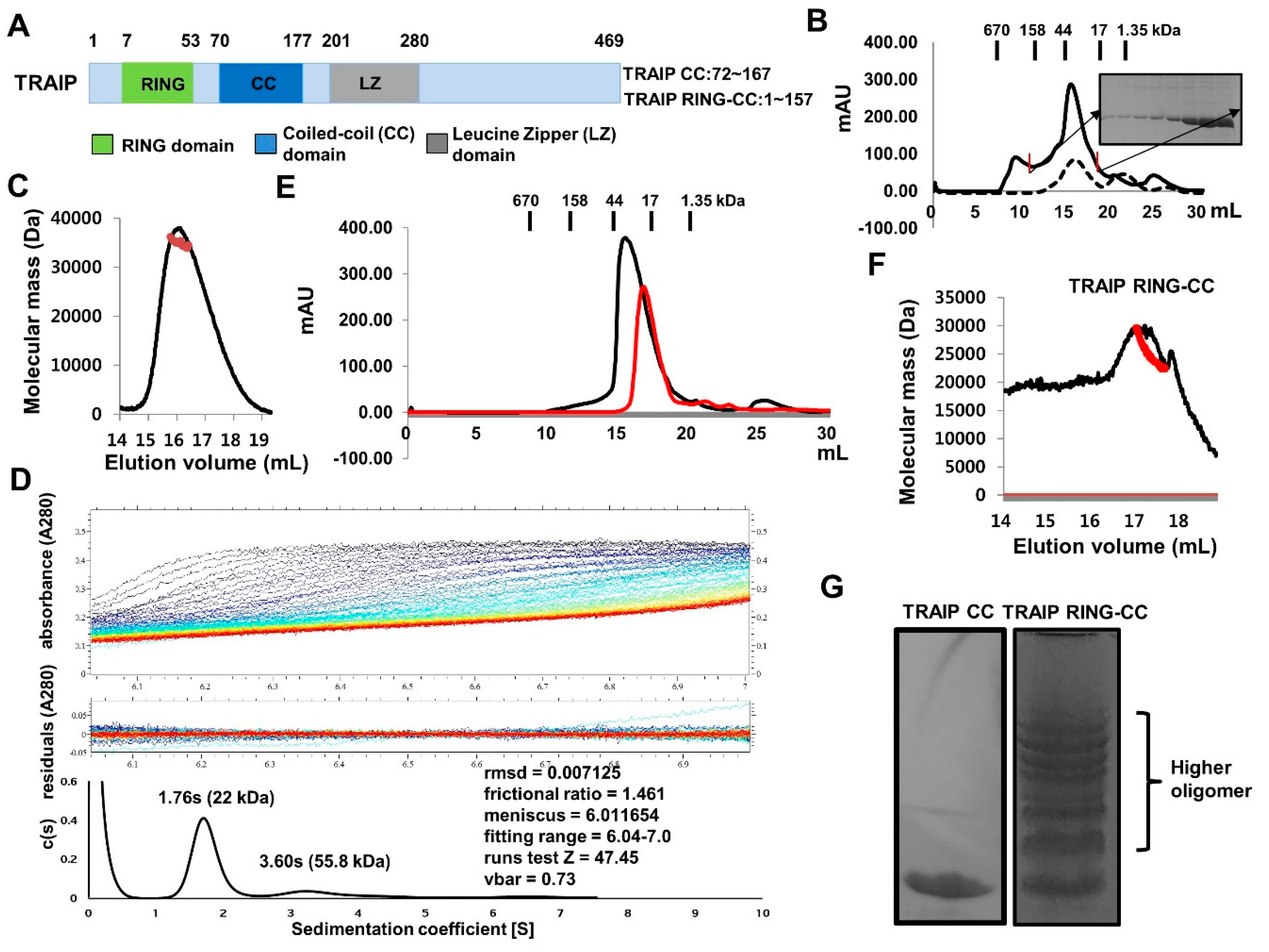
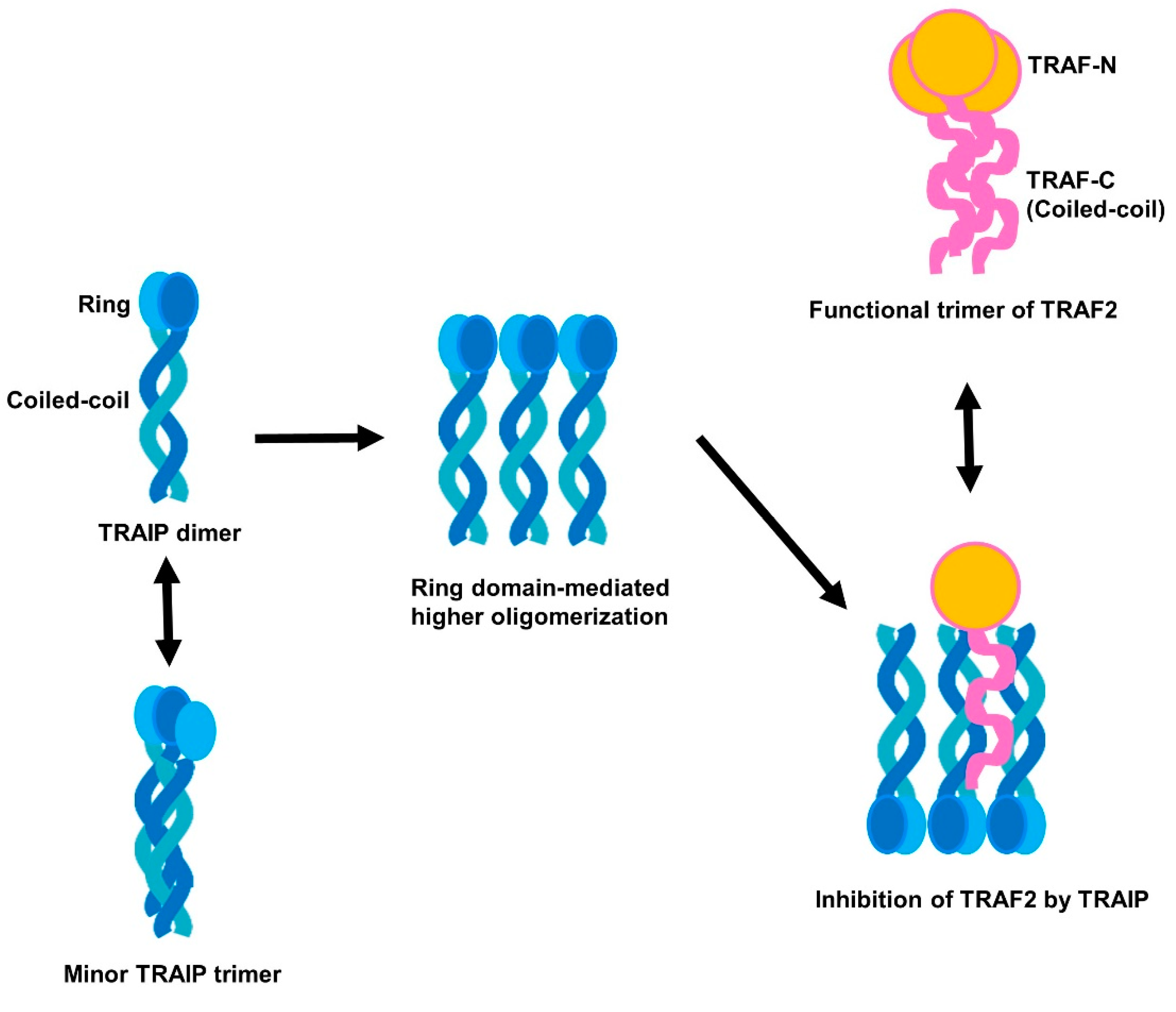
2.1. TRAF-Interacting Protein (TRAIP) RING Domain Mediates Higher-Order Oligomerization of TRAIP
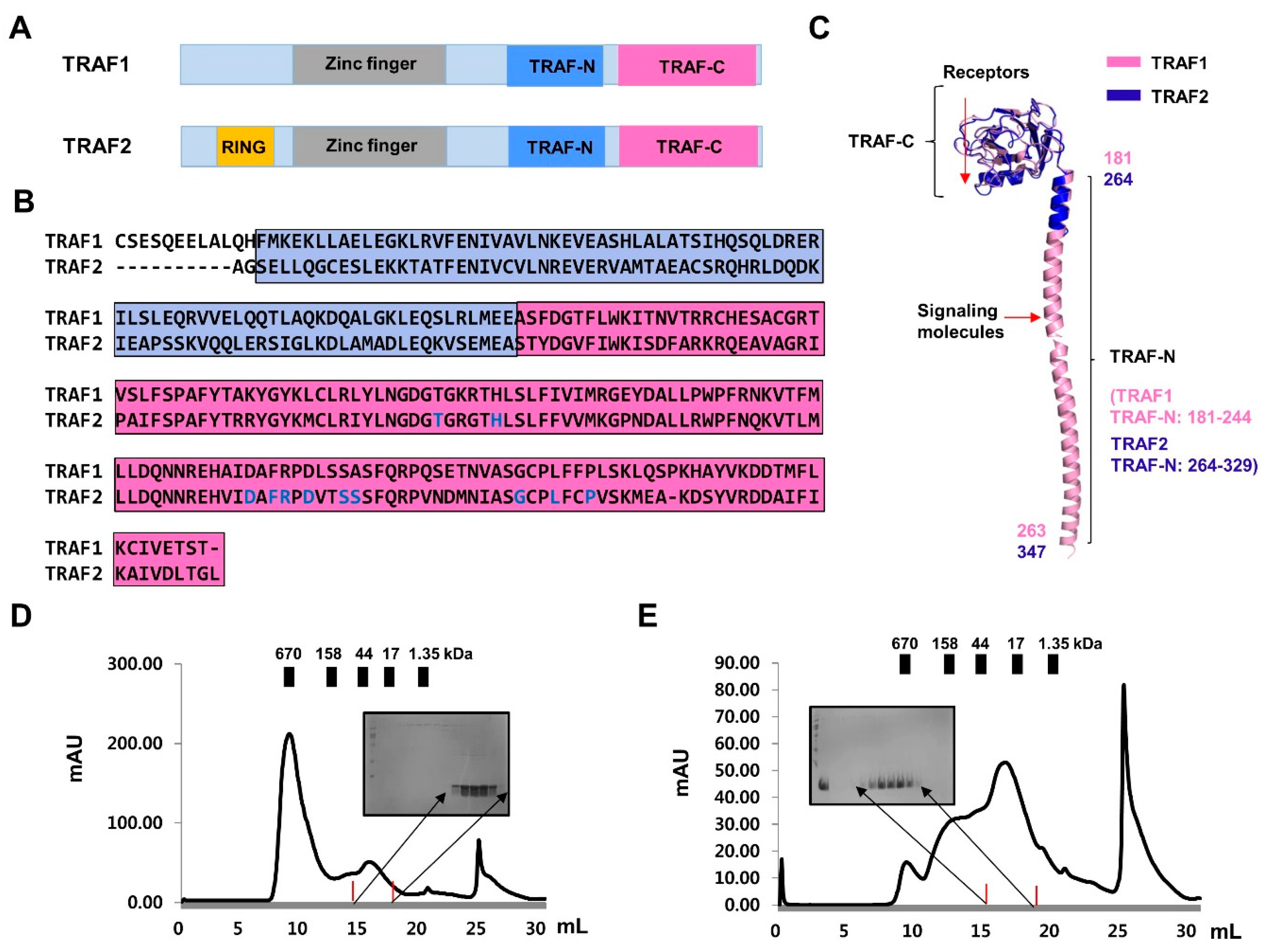
2.2. Purification and Characterization of TRAF-N Domains of TRAF1 and TRAF2
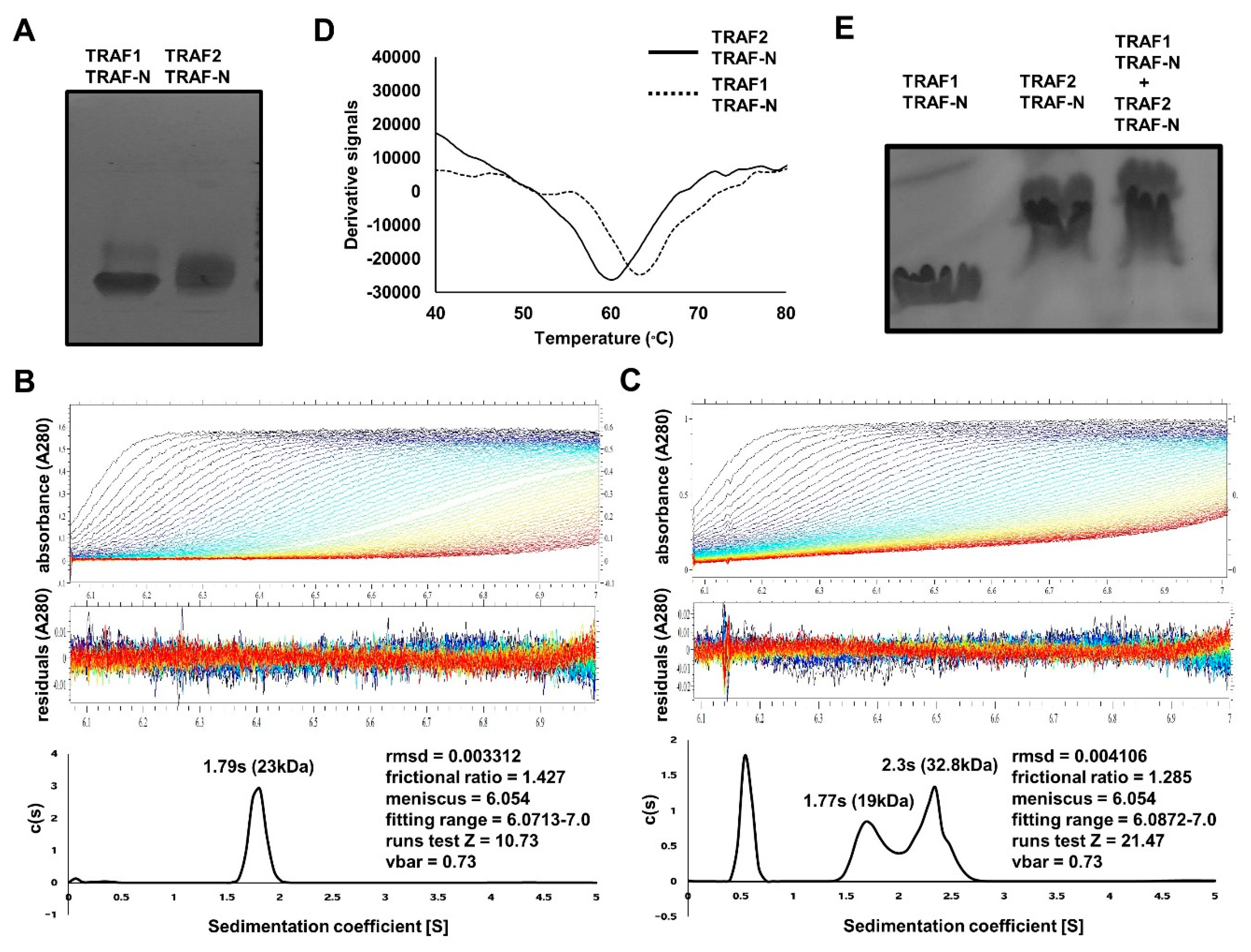
2.3. TRAF-N Is Critical for Functional Trimer Formation and Maintaining the Stability of the TRAF Domain
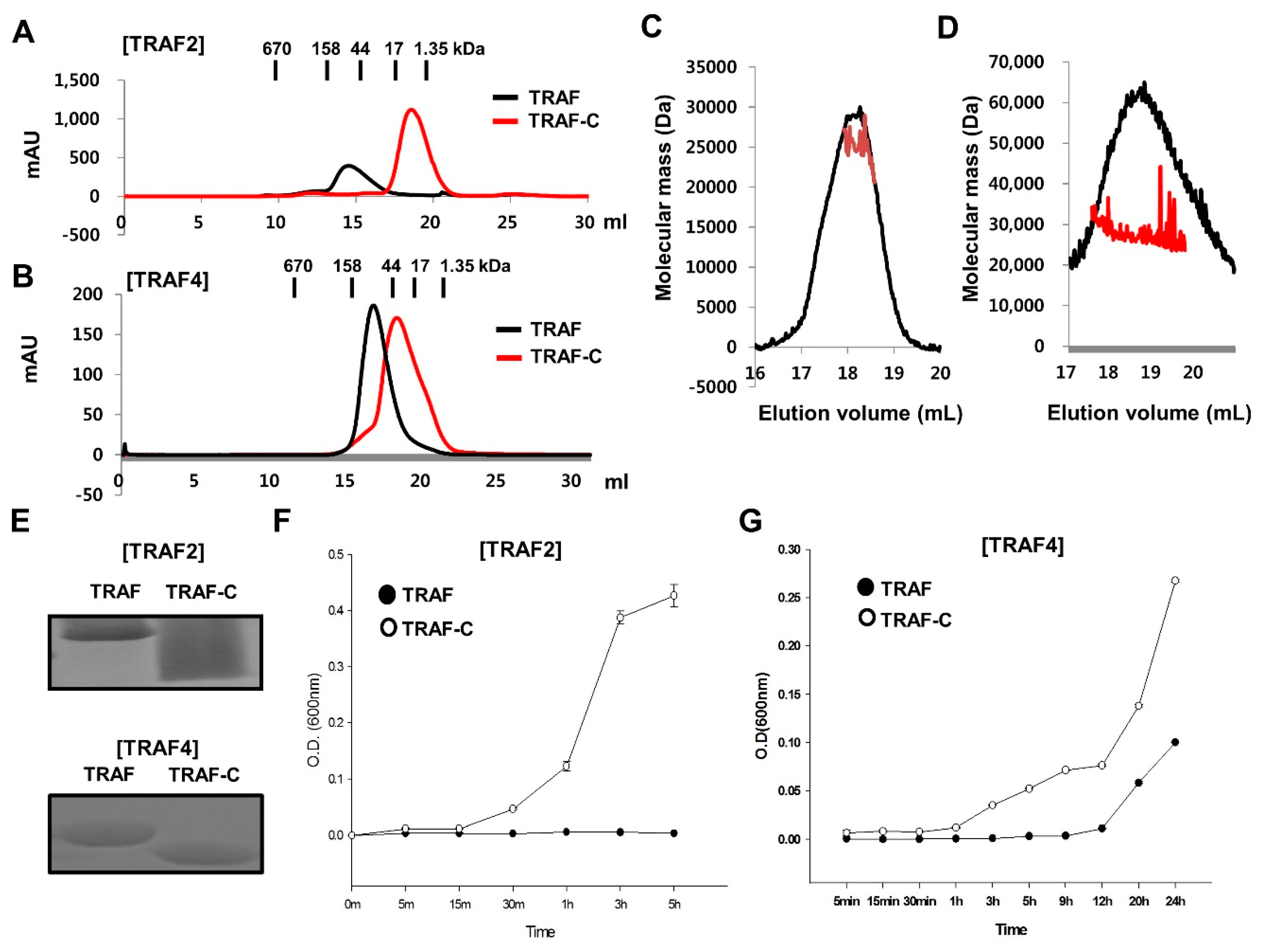
2.4. RING Domain-Mediated Oligomerization of TRAIP Is Critical for the Specific Interaction with TRAF2
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Protein Expression and Purification
3.2. Multi-Angle Light Scattering (MALS)
3.3. Analytical Ultra-Centrifugation (AUC)
3.4. Native-PAGE Shift Assay
3.5. Sequence Alignment
3.6. Solubility Assay
3.7. Thermostability Assay
3.8. Complex Association Assay by Size-Exclusion Chromatography
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, J.; Ishida, T.; Tsukamoto, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Naito, A.; Azuma, S.; Yamamoto, T. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family: Adapter proteins that mediate cytokine signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 254, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.Y.; Park, Y.C.; Ye, H.; Wu, H. All trafs are not created equal: Common and distinct molecular mechanisms of TRAF-mediated signal transduction. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradley, J.R.; Pober, J.S. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFS). Oncogene 2001, 20, 6482–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arch, R.H.; Gedrich, R.W.; Thompson, C.B. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFS)—A family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2821–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.; Huang, J.; Shu, H.B.; Baichwal, V.; Goeddel, D.V. TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase rip to the tnf receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity 1996, 4, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Regnier, C.H.; Kirschning, C.J.; Goeddel, D.V.; Rothe, M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated kinase cascades: Bifurcation of nuclear factor-κB and c-Jun N-Terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways at TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9792–9796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeflich, K.P.; Yeh, W.C.; Yao, Z.; Mak, T.W.; Woodgett, J.R. Mediation of tnf receptor-associated factor effector functions by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1). Oncogene 1999, 18, 5814–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshaies, R.J.; Joazeiro, C.A. Ring domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, H.; Tseng, P.H.; Karin, M. Expanding TRAF function: TRAF3 as a tri-faced immune regulator. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, J.M.; Lefebvre, S.; Reed, J.C. Targeting trafs for therapeutic intervention. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 597, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Son, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.H. Molecular basis for unique specificity of human TRAF4 for platelets GPIbβ and GPVI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11422–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Choi, Y. TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP): A novel component of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)- and CD30-TRAF signaling complexes that inhibits TRAF2-mediated NF-κB activation. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.; Ryser, S.; Obarzanek-Fojt, M.; Hohl, D.; Huber, M. The TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP) is a regulator of keratinocyte proliferation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapard, C.; Meraldi, P.; Gleich, T.; Bachmann, D.; Hohl, D.; Huber, M. TRAIP is a regulator of the spindle assembly checkpoint. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 5149–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, M.E.; Murina, O.; Leitch, A.; Higgs, M.R.; Bicknell, L.S.; Yigit, G.; Blackford, A.N.; Zlatanou, A.; Mackenzie, K.J.; Reddy, K.; et al. TRAIP promotes DNA damage response during genome replication and is mutated in primordial dwarfism. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, K.; Meng, H.; Zhao, W.; Gao, C. TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP) negatively regulates IFN-β production and antiviral response by promoting proteasomal degradation of tank-binding kinase 1. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regamey, A.; Hohl, D.; Liu, J.W.; Roger, T.; Kogerman, P.; Toftgard, R.; Huber, M. The tumor suppressor CYLD interacts with TRIP and regulates negatively nuclear factor κB activation by tumor necrosis factor. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothe, M.; Wong, S.C.; Henzel, W.J.; Goeddel, D.V. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 1994, 78, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Bhat, E.A.; Jeong, J.H.; Son, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Park, H.H. Crystal structure of TRAF1 TRAF domain and its implications in the TRAF1-mediated intracellular signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Jeong, J.H.; Son, Y.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.; Park, H.H. Molecular basis for tank recognition by traf1 revealed by the crystal structure of TRAF1/tank complex. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Kabaleeswaran, V.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Wu, H. Crystal structures of the TRAF2: cIAP2 and the TRAF1: TRAF2: cIAP2 complexes: Affinity, specificity, and regulation. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.C.; Burkitt, V.; Villa, A.R.; Tong, L.; Wu, H. Structural basis for self-association and receptor recognition of human TRAF2. Nature 1999, 398, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Cho, Y.J.; Park, H.H. Structure of the TRAF4 TRAF domain with a coiled-coil domain and its implications for the TRAF4 signalling pathway. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuck, P. Size-distribution analysis of macromolecules by sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation and lamm equation modeling. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 1606–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondos, S.E.; Bicknell, A. Detection and prevention of protein aggregation before, during, and after purification. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 316, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhat, E.A.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, S.; Park, H.H. In Vitro Inhibitory Mechanism Effect of TRAIP on the Function of TRAF2 Revealed by Characterization of Interaction Domains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082457
Bhat EA, Kim CM, Kim S, Park HH. In Vitro Inhibitory Mechanism Effect of TRAIP on the Function of TRAF2 Revealed by Characterization of Interaction Domains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082457
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhat, Eijaz Ahmed, Chang Min Kim, Sunghwan Kim, and Hyun Ho Park. 2018. "In Vitro Inhibitory Mechanism Effect of TRAIP on the Function of TRAF2 Revealed by Characterization of Interaction Domains" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082457
APA StyleBhat, E. A., Kim, C. M., Kim, S., & Park, H. H. (2018). In Vitro Inhibitory Mechanism Effect of TRAIP on the Function of TRAF2 Revealed by Characterization of Interaction Domains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082457






