Disordered Regions of Mixed Lineage Leukemia 4 (MLL4) Protein Are Capable of RNA Binding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Silico Analysis of the RNA Binding Capacity of MLL Proteins
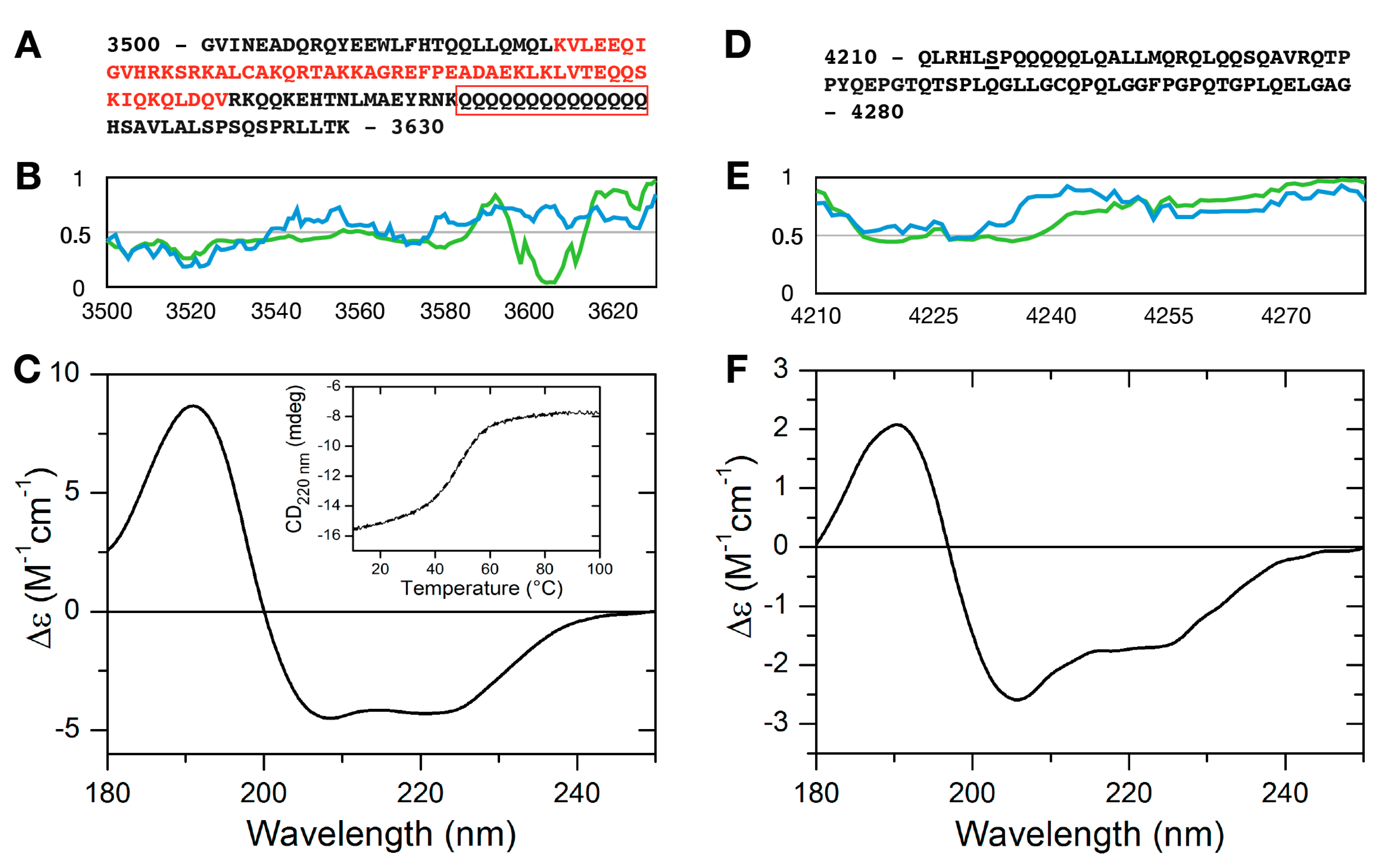
2.2. Secondary Structure of MLL43500–3630 and MLL44210–4280
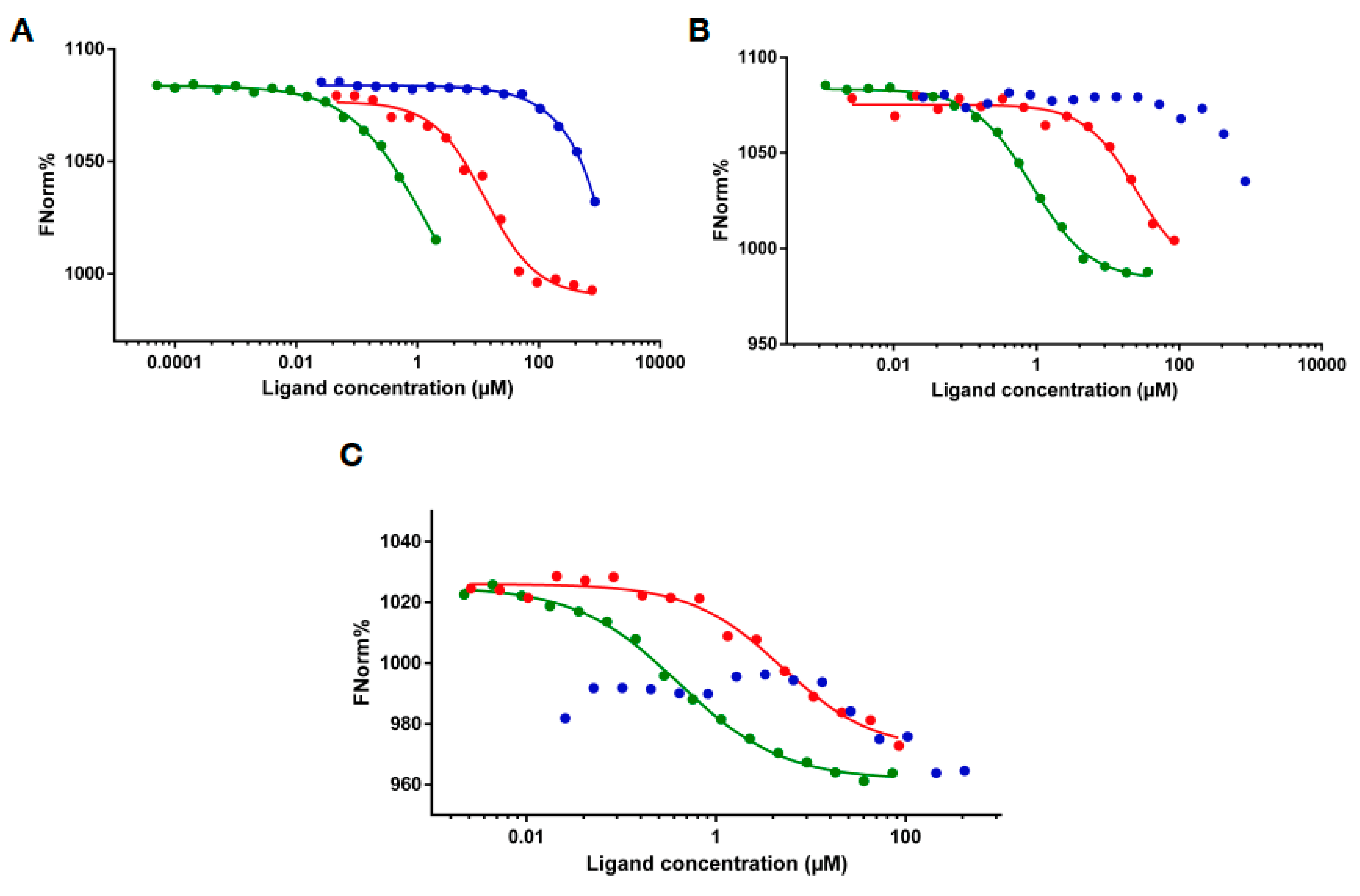
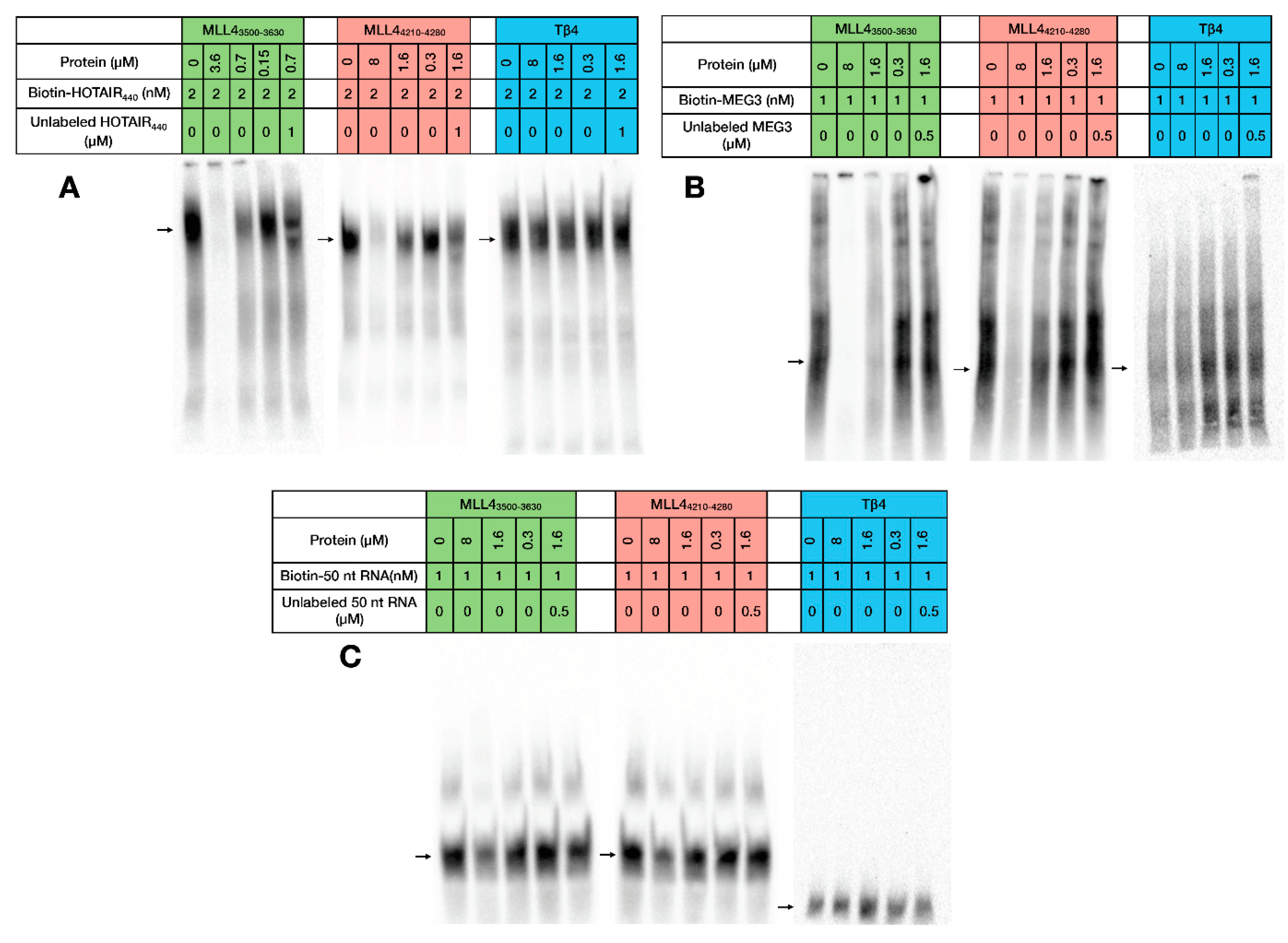
2.3. RNA Binding of MLL43500–3630 and MLL44210–4280
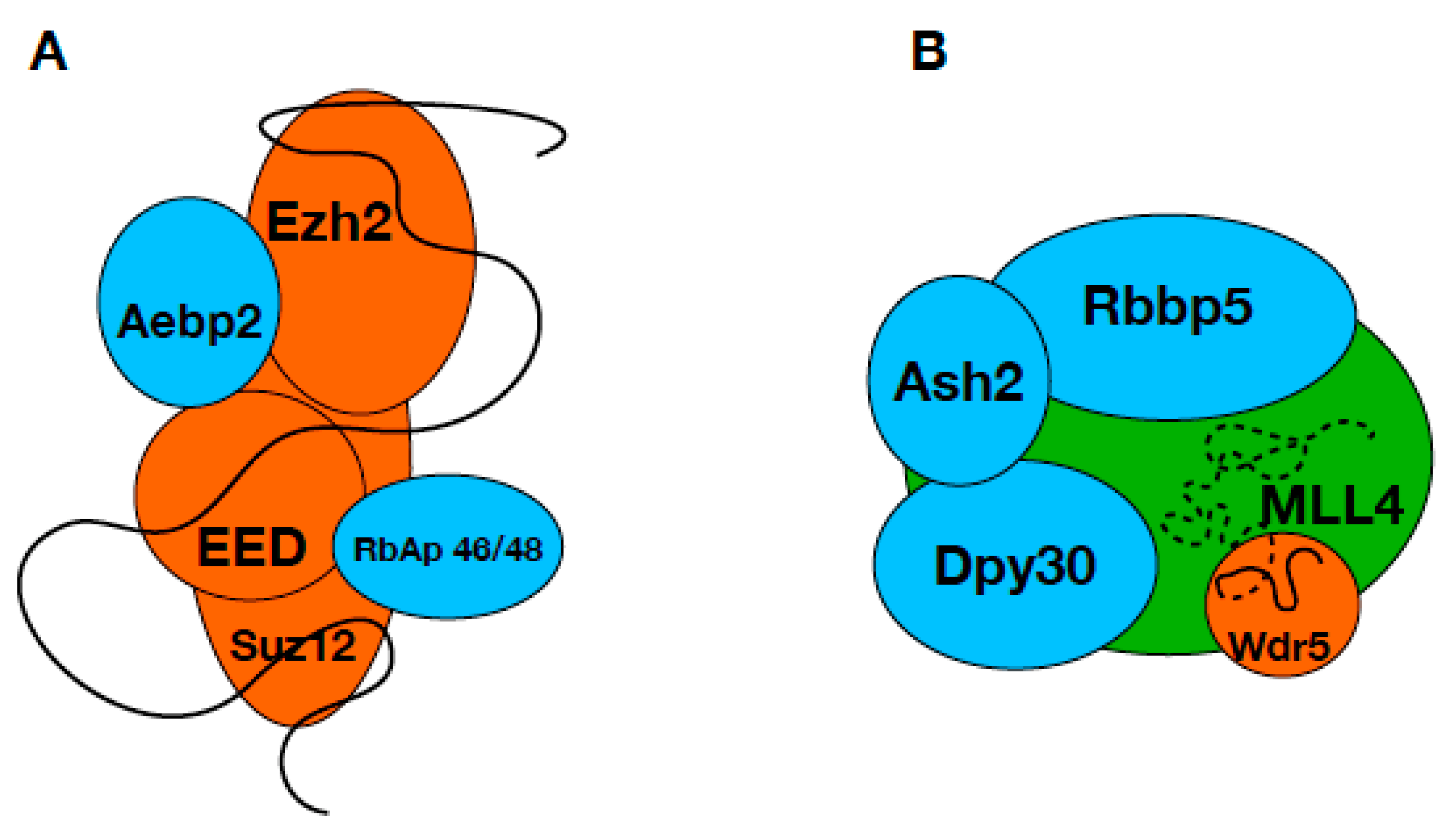
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.2. Accession Numbers
4.3. Overexpression and Purification of MLL4 Protein Regions
4.4. RNA Preparation
4.5. Far-UV CD Measurements
4.6. Microscale Thermophoresis
4.7. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EMSA | Electrophoretic mobility shift assay |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 |
| HKMT | Histone lysin methyltransferase |
| HOTAIR | HOX transcript antisense RNA |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| MEG3 | Maternally Expressed 3 |
| MLL | Mixed lineage leukemia |
| MST | Microscale thermophoresis |
| PRC2 | Polycomb repressive complex |
| WDR5 | WD repeat-containing protein 5 |
References
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S.; et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartonicek, N.; Maag, J.L.V.; Dinger, M.E. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer: Mechanisms of action and technological advancements. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Deng, X.; Ma, W.; Berletch, J.B.; Rabaia, N.; Wei, G.; Moore, J.M.; Filippova, G.N.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. The lncRNA Firre anchors the inactive X chromosome to the nucleolus by binding CTCF and maintains H3K27me3 methylation. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.M.; Guttman, M.; Huarte, M.; Garber, M.; Raj, A.; Morales, D.R.; Thomas, K.; Presser, A.; Bernstein, B.E.; Van Oudenaarden, A.; et al. Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heery, R.; Finn, S.P.; Cuffe, S.; Gray, S.G. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Key Regulators of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Tumour Drug Resistance and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Fan, R.; Jiang, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Nie, F.; Lu, K.; Sun, M. Over-expressed long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS promotes cell cycle progression and metastasis in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhan, A.; Deb, P.; Shihabeddin, N.; Ansari, K.I.; Brotto, M.; Mandal, S.S. Histone methylase MLL1 coordinates with HIF and regulate lncRNA HOTAIR expression under hypoxia. Gene 2017, 629, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liang, H.; Yang, H.; Zhou, K.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Lai, B.; Song, L.; Luo, H.; Peng, J.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: The novel diagnostic biomarkers for leukemia. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 55, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Kang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tan, H.; Chen, R.; et al. A long noncoding RNA critically regulates Bcr-Abl-mediated cellular transformation by acting as a competitive endogenous RNA. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ren, Z.; Sun, P. Overexpression of the long non-coding RNA MEG3 impairs in vitro glioma cell proliferation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, H.-G.; Lu, C. A novel long non-coding RNA T-ALL-R-LncR1 knockdown and Par-4 cooperate to induce cellular apoptosis in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yuan, P.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z. LncRNA MEG3 Regulates Imatinib Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia via Suppressing MicroRNA-21. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mer, A.S.; Lindberg, J.; Nilsson, C.; Klevebring, D.; Wang, M.; Grönberg, H.; Lehmann, S.; Rantalainen, M. Expression levels of long non-coding RNAs are prognostic for AML outcome. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidovich, C.; Cech, T.R. The recruitment of chromatin modifiers by long noncoding RNAs: Lessons from PRC2. RNA 2015, 21, 2007–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Hernandez, A.J.; Sarma, K.; Lee, J.T. Regulatory interactions between RNA and polycomb repressive complex 2. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovich, C.; Wang, X.; Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Goodrich, K.J.; Gooding, A.R.; Lee, J.T.; Cech, T.R. Toward a Consensus on the Binding Specificity and Promiscuity of PRC2 for RNA. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, S.; Li, G.; Son, J.; Xu, C.F.; Margueron, R.; Neubert, T.A.; Reinberg, D. Phosphorylation of the PRC2 component Ezh2 is cell cycle-regulated and up-regulates its binding to ncRNA. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.D.; Huang, G.W.; Xie, Y.H.; He, J.Z.; Guo, J.C.; Xu, X.E.; Liao, L.D.; Xie, Y.M.; Song, Y.M.; Li, E.M.; et al. The interaction of lncRNA EZR-AS1 with SMYD3 maintains overexpression of EZR in ESCC cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1793–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, V.B.; Ovsepian, S.V.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Buske, F.A.; Radulovic, V.; Niyazi, M.; Moertl, S.; Trau, M.; Atkinson, M.J.; Anastasov, N. PARTICLE, a Triplex-Forming Long ncRNA, Regulates Locus-Specific Methylation in Response to Low-Dose Irradiation. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Leary, V.B.; Hain, S.; Maugg, D.; Smida, J.; Azimzadeh, O.; Tapio, S.; Ovsepian, S.V.; Atkinson, M.J. Long non-coding RNA PARTICLE bridges histone and DNA methylation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, J.A.; Wapinski, O.L.; Yang, Y.W.; Bureau, J.F.; Gopinath, S.; Monack, D.M.; Chang, H.Y.; Brahic, M.; Kirkegaard, K. The NeST Long ncRNA Controls Microbial Susceptibility and Epigenetic Activation of the Interferon-γ Locus. Cell 2013, 152, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.W.; Flynn, R.A.; Chen, Y.; Qu, K.; Wan, B.; Wang, K.C.; Lei, M.; Chang, H.Y. Essential role of lncRNA binding for WDR5 maintenance of active chromatin and embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Elife 2014, 3, e02046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sze, C.C.; Shilatifard, A. MLL3/MLL4/COMPASS Family on Epigenetic Regulation of Enhancer Function and Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herz, H.M.; Mohan, M.; Garruss, A.S.; Liang, K.; Takahashi, Y.H.; Mickey, K.; Voets, O.; Verrijzer, C.P.; Shilatifard, A. Enhancer-associated H3K4 monomethylation by Trithorax-related, the Drosophila homolog of mammalian Mll3/Mll4. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2604–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henikoff, S.; Shilatifard, A. Histone modification: Cause or cog? Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, T.; Schad, E.; Szabo, B.; Horvath, T.; Meszaros, A.; Tompa, P.; Tantos, A. Intrinsic protein disorder in histone lysine methylation. Biol. Dir. 2016, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mészáros, B.; Simon, I.; Dosztányi, Z. Prediction of Protein Binding Regions in Disordered Proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Elbaum-Garfinkle, S.; Langdon, E.M.; Taylor, N.; Occhipinti, P.; Bridges, A.A.; Brangwynne, C.P.; Gladfelter, A.S. RNA Controls PolyQ Protein Phase Transitions. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Bulyáki, É.; Kun, J.; Moussong, É.; Lee, Y.H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. BeStSel: A web server for accurate protein secondary structure prediction and fold recognition from the circular dichroism spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W315–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Kernya, L.; Lee, Y.H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. Accurate secondary structure prediction and fold recognition for circular dichroism spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3095–E3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzer, A.; Emmrich, S.; Schmidt, F.; Beck, D.; Ng, M.; Reimer, C.; Adams, F.F.; Grasedieck, S.; Witte, D.; Käbler, S.; et al. The non-coding RNA landscape of human hematopoiesis and leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistelli, C.; Cicchini, C.; Santangelo, L.; Tramontano, A.; Grassi, L.; Gonzalez, F.J.; de Nonno, V.; Grassi, G.; Amicone, L.; Tripodi, M. The Snail repressor recruits EZH2 to specific genomic sites through the enrollment of the lncRNA HOTAIR in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2016, 36, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidovich, C.; Zheng, L.; Goodrich, K.J.; Cech, T.R. Promiscuous RNA binding by Polycomb repressive complex 2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banani, S.F.; Lee, H.O.; Hyman, A.A.; Rosen, M.K. Biomolecular condensates: Organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon, E.M.; Qiu, Y.; Niaki, A.G.; McLaughlin, G.A.; Weidmann, C.; Gerbich, T.M.; Smith, J.A.; Crutchley, J.M.; Termini, C.M.; Weeks, K.M.; et al. mRNA structure determines specificity of a polyQ-driven phase separation. Science 2018, 360, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.-J.; Wang, X.-Z.; Pan, Y.-X.; Luo, J.-M. The Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 and its Target miR-147 Regulate JAK/STAT Pathway in Advanced Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. EBioMedicine 2018, 34, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Huang, S.-H.; Zhou, H.-R.; Chen, C.-J.; Tian, L.-H.; Shen, J.-Z. Role of HOTAIR in the diagnosis and prognosis of acute leukemia. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 3113–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mészáros, B.; Erdos, G.; Dosztányi, Z. IUPred2A: Context-dependent prediction of protein disorder as a function of redox state and protein binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W329–W337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Kurgan, L. High-throughput prediction of RNA, DNA and protein binding regions mediated by intrinsic disorder. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.J.; Shamsaddini, A.; Pan, Y.; Smith, K.; Crichton, D.J.; Simonyan, V.; Mazumder, R. A framework for organizing cancer-related variations from existing databases, publications and NGS data using a High-performance Integrated Virtual Environment (HIVE). Database 2014, 2014, bau022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, S.A.; Beare, D.; Gunasekaran, P.; Leung, K.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Ding, M.; Bamford, S.; Cole, C.; Ward, S.; et al. COSMIC: Exploring the world’s knowledge of somatic mutations in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, D805–D811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Batista, D.L.; Gejman, R.; Ansell, P.J.; Zhao, J.; Weng, C.; Klibanski, A. Activation of p53 by MEG3 non-coding RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24731–24742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, P.; Holland, D.R.; Kirsch, J.F. Thermal stability determinants of chicken egg-white lysozyme core mutants: Hydrophobicity, packing volume, and conserved buried water molecules. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| MLL1 | MLL2 | MLL3 | MLL4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 296–327 | 84–107 | 1068–1079 | 1559–1567 |
| 348–408 | 184–234 | 1678–1695 | 3526–3581 |
| 415–418 | 241–244 | 1701–1709 | 3899–3983 |
| 1155–1194 | 536–560 | 1715–1737 | 4960–5014 |
| 1977–1992 | 783–806 | 2406–2409 | 5147–5165 |
| 3854–3861 | 820–828 | 3052–3073 | 5227–5251 |
| 1753–1778 | 3246–3250 | ||
| 2600–2616 | 3394–3427 | ||
| 2685–2709 | 4330–4356 | ||
| 4514–4524 | |||
| 4586–4625 |
| Title | LED Power (%) | MST Power (%) | Before MST (s) | MST on (s) | After MST (s) | Delay (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Round 1 | 10 or 40 | 20 | 5 | 30 | 5 | 25 |
| Round 2 | 10 or 40 | 40 | 5 | 30 | 5 | 25 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, B.; Murvai, N.; Abukhairan, R.; Schád, É.; Kardos, J.; Szeder, B.; Buday, L.; Tantos, Á. Disordered Regions of Mixed Lineage Leukemia 4 (MLL4) Protein Are Capable of RNA Binding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113478
Szabó B, Murvai N, Abukhairan R, Schád É, Kardos J, Szeder B, Buday L, Tantos Á. Disordered Regions of Mixed Lineage Leukemia 4 (MLL4) Protein Are Capable of RNA Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113478
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, Beáta, Nikoletta Murvai, Rawan Abukhairan, Éva Schád, József Kardos, Bálint Szeder, László Buday, and Ágnes Tantos. 2018. "Disordered Regions of Mixed Lineage Leukemia 4 (MLL4) Protein Are Capable of RNA Binding" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113478
APA StyleSzabó, B., Murvai, N., Abukhairan, R., Schád, É., Kardos, J., Szeder, B., Buday, L., & Tantos, Á. (2018). Disordered Regions of Mixed Lineage Leukemia 4 (MLL4) Protein Are Capable of RNA Binding. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113478








